Grade 12 Bio Exam
1/270
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
271 Terms
What are the structures of atoms?
Protons (+)
Neutrons (0)
Electrons (-)
Isotopes are:
Element that has the same number of protons but different number of neutrons
The type of electron that is involved in chemical bonds are:
Valence / outer electrons
Ionic bonds VS Covalent bonds:
Ionic bonds are between 2 opposite atoms while covalent bonds are between atoms that share electrons
Hydrogen bonding is
a type of intermolecular force where there is a attraction between slightly + & slightly - atoms in another molecule
Dehydration synthesis is
a biological reaction where 2 molecules join together when water is removed
Hydrolysis is
a reaction where a large molecule is split by adding a water molecule
Neutralization is
a reaction where an acid & a base are combined to create a salt & water
A redox reaction is
a type of reaction when electrons transfer
LEO the Lion Says GER means
Lose Electrons = Oxidization
Gain Electrons = Reduction
What are the properties of water?
Cohesion
Adhesion
High specific heat capacity
High specific heat of evaporation
Solid water is less dense than liquid water
Cohesion VS Adhesion
Cohesion is a type of attraction between the same kind of molecules while adhesion is a type of attraction between different molecules
High specific heat capacity is
When water absorbs large amounts of thermal energy when it is heated & releases it as it cools
High specific heat capacity relates to water because
it helps keep organisms at a constant temperature
Ice floats because
as water cools down the water molecules form a lattice structure that spreads the molecules apart when water cools down which means that solid water is less dense than liquid water
Ice floating has an impact on aquatic organisms
impacts aquatic animals in a positive way because the ice prevents them from dying or getting killed
Hydrophobic VS Hydrophillic
Hydrophobic substances do not like water & avoid it while hydrophilic substances like water & stick to it
A pH is important to living organisms because
Helps living organisms know what to eat or use
A pH scale is
a scale that measures how acidic or basic a substance is
A pH level below 7 means
the substance is acidic
A pH level above 7 means
the substance is basic
A pH level at 7 means
the substance is neutral
Carbon can form that many bonds
Carbon can form 4 bonds
Functional groups are
A group of atoms that affects the function of another molecule by getting involved in chemical reactions
Draw hydroxyl
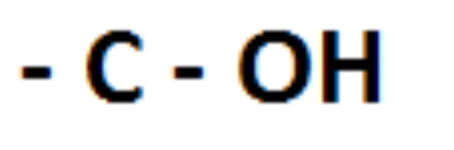
Draw carbonyl
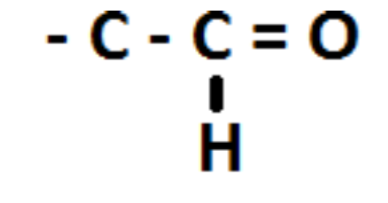
Draw carboxyl
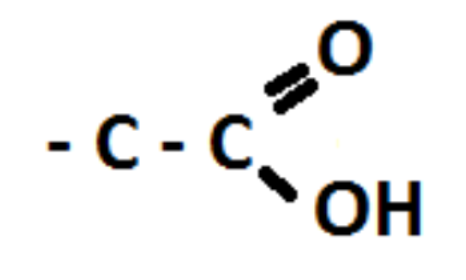
Draw amino

Draw phosphate

Draw dehydration synthesis & hydrolysis
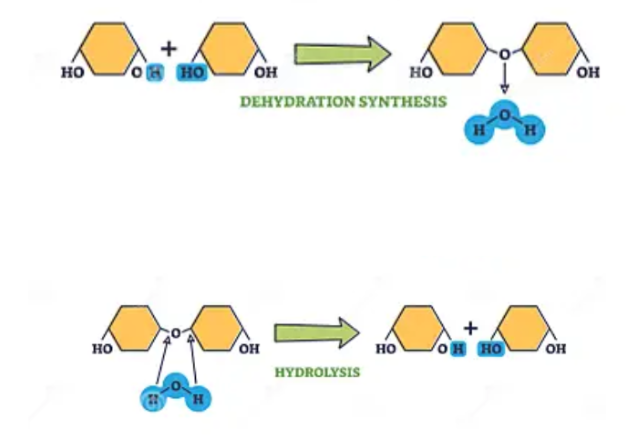
What is the difference between dehydration synthesis & hydrolysis
In dehydration an H & OH is removed & in hydrolysis an H & OH is added
Carbohydrates are made up of
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Monosaccharides are
Simplest type of carbohydrate that has 1 single sugar molecule, they can be linear or in a ring-like structure
An example of monosaccharides are
glucose
Disaccharides are
Carbohydrate molecules are made up of 2 monosaccharides and are joined by dehydration synthesis which causes glycosidic bonds to be formed
An example of disaccharides would be
Sucrose
Polysaccharides are
Hydrophilic carbohydrate molecules that have more than 2
Some examples of polysaccharides are
Starch, cellulose, & glycogen
Glycosidic bonds
are bonds that connect with sugar molecules
Monosaccharides are
the monomers of polysaccharides
Cellulose is
a polysaccharide that can be found in plants & gives structural support in the cell wall
Starch is
a polysaccharide that can be found in plants and it helps store sugar
Chitin is
a polysaccharide that can be found in the exoskeleton in bugs & give them structural support
Glycogen is
a polysaccharide that can be found in animals & it helps store sugar
A lipid is
a type of hydrophobic fat with hydrogen & carbon & it forms cell membranes, is a type of energy source, helps with waterproofing, insulation & is a type of cushioning
Fatty acids are
A molecule that had a carboxyl & hydrocarbon chain
Saturated fats are
Sold, Single bonded, & straight lipids
Unsaturated fats are
Liquid, double bonded, kinky, & healthy lipids
Fats are
a combination of fatty acids & glycerol molecules
Steroids are
Lipids with 4 carbon rings such as cholesterol & can be used to make hormones or vitamins
Waxes are
Lipids thats formed when fatty acid chains are joined with alcohol or carbon rings
Phospholipids are
Lipid that has 2 fatty acids & a phosphate group with a glycerol which creates a phospholipid bilayer
Triglycerides are
Fat that has 3 fatty acids that are linked to a glycerol
Proteins are
Polymers made up of amino acids that carry important structural & functional roles
The monomers of proteins are
Amino acids which makes up proteins that are made up of a carboxyl group & amino group
Essential VS Non-Essential Amino Acid
Essential amino acids are acids that need to be taken through eating while non-essential ones are made in the body
A peptide bond
connect amino acids together
R-groups are
molecules that give each amino acid different properties
A structural protein
is a protein that gives support
A defensive protein
is a protein that fights bacteria & infections
A signal protein
is a protein that carries messages
A recognition & receptor protein
is a protein that are cellular markers
Enzyme proteins are
proteins that are catalysts that speed up chemical reactions, break down & build molecules
Motile proteins are
proteins that help with movement
The 4 levels of protein structure are
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Quaternary
Primary protein structures
have a chain of amino acids
Secondary protein structures
are amino acid chains in a spiral or zigzag pattern
Tertiary protein structures
are folded because of R-group reactions
Quaternary protein structures
are many peptide chains that are linked together
Substrates are
substances that react with an enzyme
Active sites are
a place where the bonding process of a enzyme & substrate happens
The cell membrane
are found in animal cells & goes around the cell & controls what goes in & out of the cell
The cell wall
is a hard outer layer that surrounds plant cells
The cytosol
is the fluid inside cells
The nucleus
Has DNA & it controls the cell’s activities in both plant & animal cells
The nucleolus
Makes ribosomes in both plant & animal cells
The nuclear envelope
The outer layer that contains the nucleus & nucleolus in both plant & animal cells
Ribosomes
Builds proteins & reads RNA in both plant & animal cells
The Smooth ER
Makes lipids, steroids, breaks down toxins, & releases calcium in both plant & animal cells
The Rough ER
is covered with ribosomes & stores protein for later transport in both plant & animal cells
The Golgi Body
Moves & modifies substances in both plant & animal cells
Vacuoles in Plants
Are large membrane bound structures that acts as a storage compartment, keeps cells firm, removes harmful chemicals, & has defensive chemicals
Vacuoles in Animals
Are small transport sacs
Lysosomes are
organelles that have enzymes that digest other molecules, fights diseases, & recycles old cell parts in animal cells
The mitochondria
Place for cellular respiration which produces energy in both plant & animal cells
The cristae are the
folds of inner membrane which increases surface area in both plant & animal cells
The Matrix is
a type of fluid where reactions happen in animal cells
Chloroplasts are
photosynthetic organelles that makes sugar using sunlight in plant cells
The cytoskeleton
provides cell structure & helps with cell division in both plant & animal cells
Microtubules is a
support tube made of tubulin proteins that helps with support in both plant & animal cells
Microfilaments are
small threads made of actin proteins that help move muscles in both plant & animal cells
Cilium is
microtubes used for moving substances with small tails called paramecium in animal cells
Flagellum are
Long-tail like microtubes used for movement in both plant & animal cells
Pseudopods are
Limb like structures that are formed by amoeba in animal cells
The structure that is found within a cell membrane is
the phospholipid bilayer
The phospholipid bilayer is
made up of phospholipids which makes up most of the cell membrane & it had a hydrophilic head & hydrophobic tail
Passive transport is
a type of movement where a substance is moved across the membrane without energy
Facilitated diffusion is
a type of passive transport where proteins are used to transport substances across the membrane
Exocytosis vs Endocytosis
Exocytosis moves substances out of the cell while endocytosis moves things in & out using vesicles
Osmosis VS Diffusion
Osmosis is a type of passive transport where substances move for low to high concentration while diffusion is a type of passive transport where proteins are used to move substances