AP biology review 8-11 (copy)
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
What are the different forms of energy
kinetic energy potential energy and chemical energy
biological exapmle of kinetic energy
an animal running towards his next meal,
kinetic energy
the energy an object has because of its motion.
potential energy
the amount of energy something posseses due to location
chemical energy
energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules
biological example of potential energy
energy stored in chemical bonds, food molecules, and glycogen.
biological example of chemical energy
biomass, batteries, natural gas, petroleum, and coa
1st law of thermodynamics
energy can be transformed or transfered byt it cannot be created or destroyed
2nd law of thermodynamics
Every energy transfer or transformation increses entropy
how does photosynthesis relate to the laws of thermodynamics
energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed. This can be demonstrated within a classic food web where light energy from the sun is harnessed as radiant energy by plants, converted into chemical energy, and stored as complex carbohydrates.
how does cellular respiration relate to the laws of thermodynamics
during cellular respiration, some energy is lost as heat, which increases the entropy of the universe. Therefore, cellular respiration follows the laws of thermodynamics.
How do cells offset or temporarily postpone the effects of the 2nd law of thermodynamics?
Use anabolic reactions to use more energy that is being created by catabolic processes in order to move away from the tendecy of disorder
what is metabolism
the process used to store or release energy for use in the cell.
what is a reactant in a chemical reaction
the starting materials in a reaction that undergo a chemical change to form a product.
what is a product in a chemical reaction
a substance that is present at the end of a chemical reaction.
What is Gibbs free energy
the available energy of a substance that can be used in a chemical transformation or reaction.
What does it mean when Gibbs free energy is negative
the reaction will occur spontaneously.
What does it mean when Gibbs free energy is positive
the reaction is nonspontaneous
What is an exergonic reaction
When energy is lost to an enviorment
what is an endogenic reaction
Whe energy is gained during a reaction
How are endogenic and exogonic reaction related
A coupled reactions is a reaction that uses energy from an exergonic reaction to fuel an endergonic reaction.
What does ATP stand for
Adenosine triphosphate
What is the structure of ATP
an adenine nucleoside 'base', a five-carbon sugar (ribose), and triphosphate
What are the subunits from which ATP is made
a nitrogen base (adenine) and a sugar molecule (ribose),
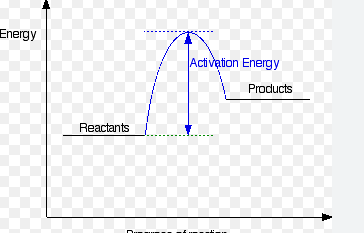
Is this and endo or exogonic profile diagram
endogonic
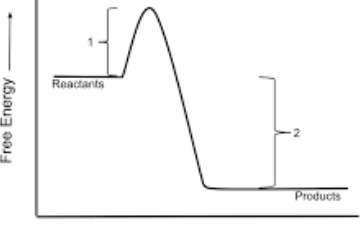
Is this and endo or exogonic profile diagram
exogonic
What is a coupled reaction
Two (or more) reactions may be combined such that a spontaneous reaction may be made 'drive' an nonspontaneous one
What is a biological example of a coupled reaction
a transmembrane ion pump
What is a metabolic pathway
transforms matter and energy. Its direction is driven by reactions that are displaced far from equilibrium.
What is an enzyme
a biological catalyst that is usually a protein but could be RNA. The point is to increase the speed with which a reaction happens.
what is a substrate
the substance on which an enzyme acts.
What is a functuion of an enzyme
to increase the speed of a reaction
What happens to an enzyme during a chemical reaction
increase the rate of chemical reactions without themselves being consumed or permanently altered by the reaction.
What factors can affect enzyme catalyzed reactions
temperature, pH, and concentration.
what is phosphorlation
the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion.
why would it be important to control enzyme catalyzed reactions
it allows each reaction to be controlled by the cell. an the speed at which each reaction is hapining
How do cells go about controlling the enzyme catalyzed reactions
through enzymes
What is catabolism
the breakdown of complex molecules in living organisms to form simpler ones, together with the release of energy; destructive metabolism.
What is anabolism
the synthesis of complex molecules in living organisms from simpler ones together with the storage of energy; constructive metabolism.
- receptor binds inactive G-protein and causes GTP to replace GDP on protein thereby activating G-protein
- activated G-protein binds another protein (usually an enzyme) and alters the activity of the enzyme
- get cell response
- G-protein is activated
- Phospholipase C enzyme converts a membrane lipid into DAG (diacylglycerol) and IP3 (inositol triphosphate)
- IP3 binds to ion-gated protein in ER membrane, which allows release of Calcium ions from the ER.
- Calcium ions interact with proteins to activate them
- signal proteins
- relay proteins
- proteins needed to carry out the response
What is step 1 of the signal transduction pathway
Recive
What happens in the first step of the signal transduction pathway
signaling molecule binds to recptor protein on target cell
Receptor protein must be complementary to
ligand
What is the signal transduction pathway doing
mechinism linking a mechanical or chemical stimuls to a specific cellular response
Is cellular respiration catabolic or anabolic
catabolic
what allows an organic molecules to posses potential energy
chemical energy through bonds
Where is the potential energy stored in organic molecules
the bonds
How is energy stored in chemical bonds released
hydrolisis
What molecule helps with the the breaking of chemical bonds?
H2O
What part of cellular respiration is anaerobic
glycolisis
What part of cellula respiration is aerobic
the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
What is the principle of redox reactions
the transfer of electrons between chemical species
How is cellular respiration a series of redox reactions
glucose molecules are oxidized and oxygen molecules are reduced to generate water molecules.
What is being oxidized in cellular respiration
glucose
What is being reduced in celllar respiration
oxygen
what is the importance of NAD+ in cellular respiration
is the electron acceptor
What is gylcolisis
a series of reactions that extract energy from glucose by splitting it into two three-carbon molecules called pyruvates.
Where does glycolisis occur in the cell
in the cytosol
What type of process is glycolysis
catabolic
Explain oxidation of pyruvate to actyl Coa
each pyruvate molecule loses one carbon atom with the release of carbon dioxide
What must be present in order for the oxidation of pyruvate to occur
oxygen
Where does the Calvin cycle occur
the stroma of the chloroplast.
What is the citric acidcycle
he mitochondrial hub for the final steps in carbon skeleton oxidative catabolism for carbohydrates, amino acids, and fatty acids.
How does the citric acid cycle work
serves as the mitochondrial hub for the final steps in carbon skeleton oxidative catabolism for carbohydrates, amino acids, and fatty acids.
what molecules link glycolysis and citric acid cycle to oxidative phosphorylation
pyruvate
What is oxidative phosphorlation
a cellular process that harnesses the reduction of oxygen to generate high-energy phosphate bonds in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).