Nucleotides and nucleic acids: Foundations in Biology: Biology OCR A Level
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Draw the structure of a nucleotide.
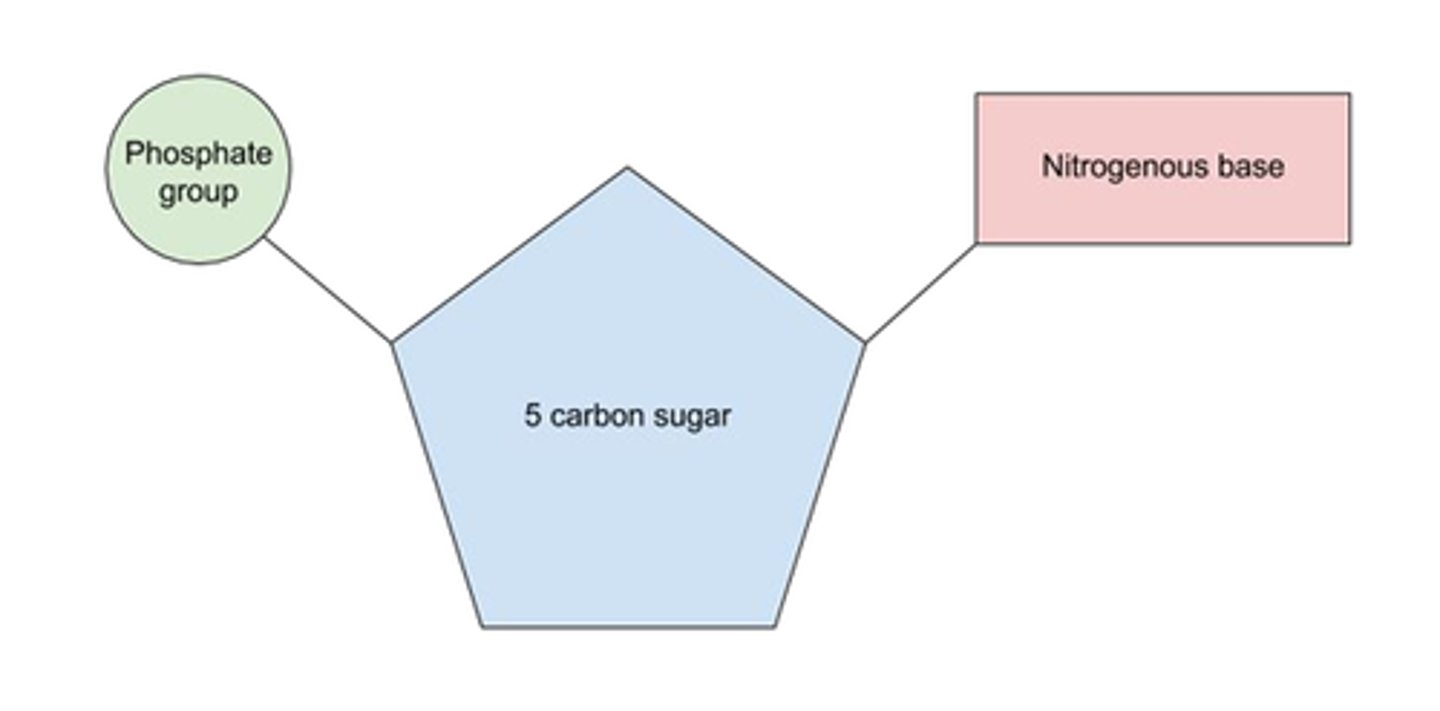
Name the pentose sugars in DNA & RNA.
DNA: deoxyribose
RNA: ribose
Describe how polynucleotide strands are formed and broken down.
Condensation reactions between nucleotides form strong phosphodiester bonds (sugar-phosphate backbone).
Hydrolysis reactions use a molecule of water to break these bonds.
Enzymes catalyse these reactions.
Describe the structure of DNA.
Molecule twists to form double helix of 2 deoxyribose polynucleotide strands (so there are 2 sugar-phosphate backbones).
H-bonds form between complementary base pairs (AT & GC) on strands that run antiparallel.
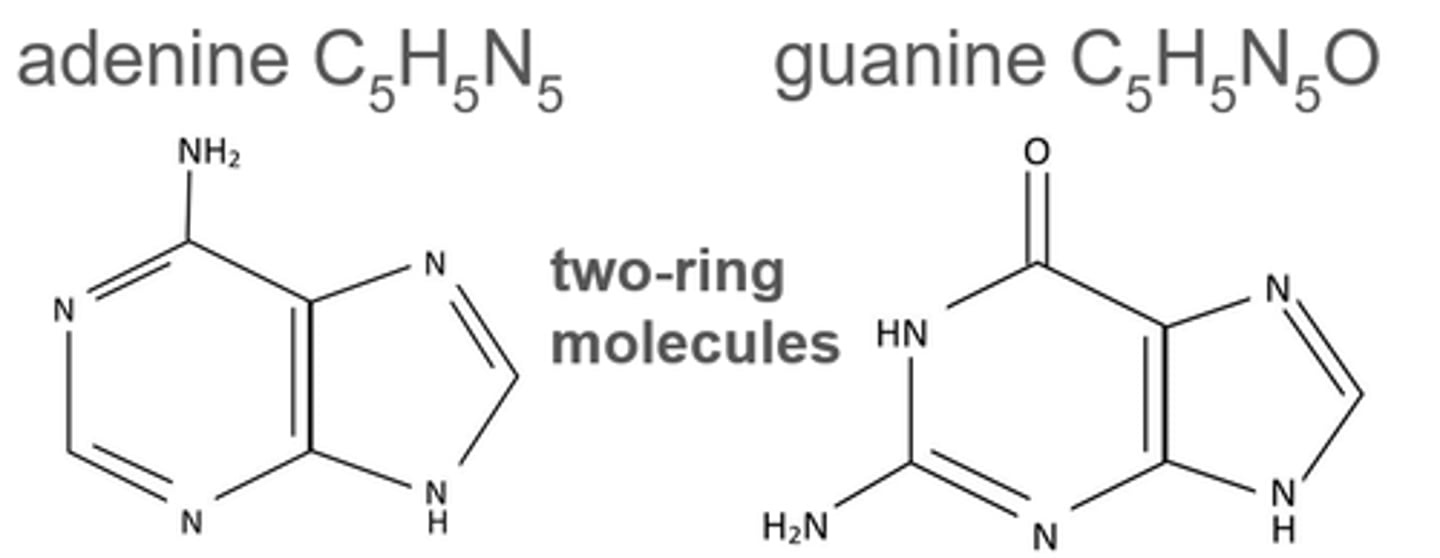
Name the purine bases and describe their structure.
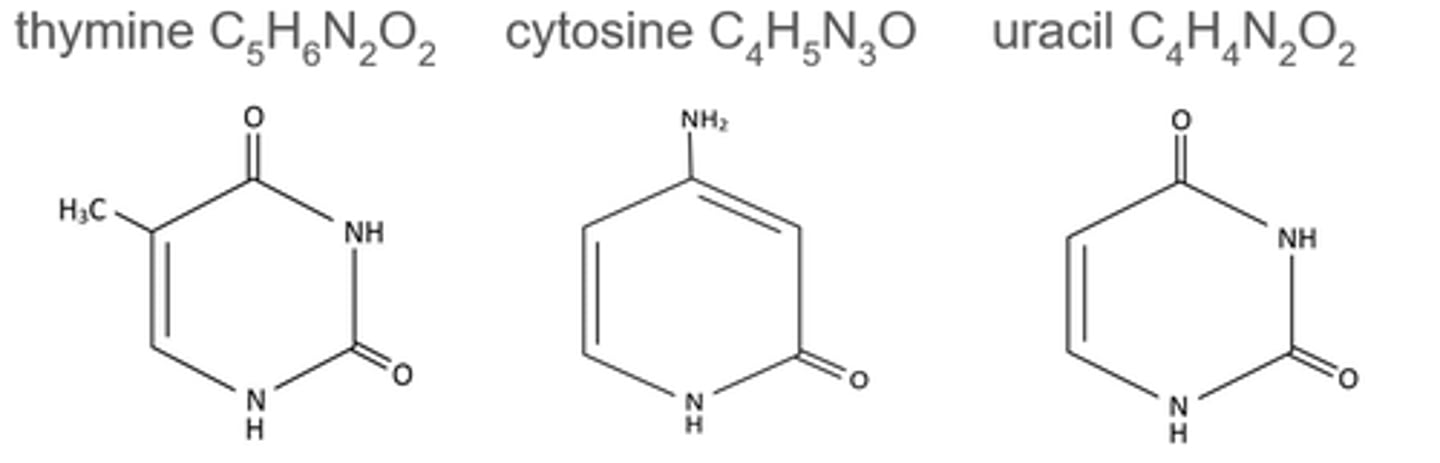
Name the pyrimidine bases and describe their
structure.
Name the complementary base pairs in DNA and RNA.
DNA: 2 H-bonds between adenine (A) + thymine (T)
RNA: 2 H-bonds between adenine (A) + uracil (U)
Both have 3 H-bonds between guanine (G) + cytosine (C)
Why is DNA replication described as semiconservative?
Strands from original DNA molecule act as templates.
New DNA molecule contains 1 old strand & 1 new strand (specific base pairing enables genetic material to be conserved accurately).
Explain the role of DNA helicase in semiconservative replication.
Breaks H-bonds between base pairs to form 2 single strands, each of which can act as a template.
How is a new strand formed during semiconservative replication?
1. Free nucleotides from nuclear sap attach to exposed bases by complementary base pairing.
2. DNA polymerase joins adjacent nucleotides on new strand in a 5’ → 3’ direction via condensation reactions to form phosphodiester bonds.
3. H-bonds reform.
Identify features of the genetic code.
● Non-overlapping: each triplet is only read once.
● Degenerate: more than one triplet codes for the same amino acid (64 possible triplets for 20 amino acids).
● Universal: same bases and sequences used by all species.
How does a gene determine the sequence of amino acids in a protein?
Consists of base triplets that code for a specific amino acids.
Describe how DNA can be purified by precipitation.
Add ethanol & a salt to aqueous solution.
Nucleic acids precipitate out of solution.
Centrifuge to obtain pellet of nucleic acid.
Wash pellet with ethanol & centrifuge again.
What does transcription produce and where does it occur?
produces mRNA.
occurs in nucleus.
Outline the process of transcription.
1. RNA polymerase binds to promoter region on a gene.
2. Section of DNA uncoils into 2 strands with exposed bases. Antisense strand acts as template.
3. Free nucleotides are attracted to their complementary bases.
4. RNA polymerase joins adjacent nucleotides to form
phosphodiester bonds.
What happens after a strand of mRNA is transcribed?
● RNA polymerase detaches at terminator region.
● H-bonds reform & DNA rewinds.
● splicing removes introns from pre-mRNA in eukaryotic cells.
● mRNA moves out of nucleus via nuclear pore & attaches to ribosome.
What does translation produce and where does it occur?
Produces proteins.
Occurs in cytoplasm on ribosomes (which are made of protein + rRNA).
Outline the process of translation.
1. Ribosome moves along mRNA until ‘start’ codon.
2. tRNA anticodon attaches to complementary bases on mRNA.
3. Condensation reactions between amino acids on tRNA form peptide bonds. Requires energy from ATP hydrolysis.
4. Process continues to form polypeptide chain until ‘stop’ codon is reached.
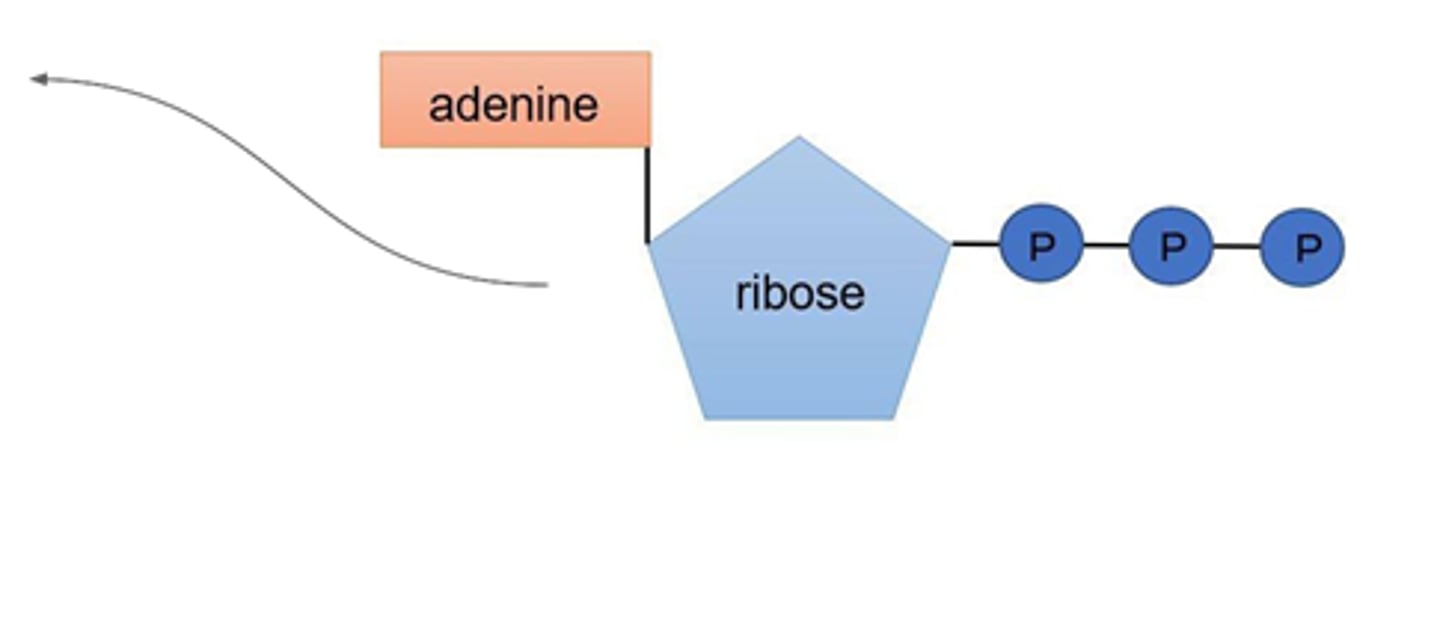
Describe the structure of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP).
nucleotide derivative of adenine.
ATP has 3 inorganic phosphate groups.
ADP has 2.
What is a mutation?
An alteration to the DNA base sequence. Mutations often arise spontaneously during DNA replication.