nutrients
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
how is nitrogen allocated within a leaf?
in C3 plants more is allocated to rubisco than C4 plants
this means in C4 plants there is more available for other uses such as soluble or ligh harvesting proteins, bioenergetics or others (more productive)
macronutrients
essential nutrients in plants required in large quantities
K, N, Ca, Mg, P, S
micronutrients
essential nutrients in plants required in small quantities
Cl, B, Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu, Ni, Mo
beneficial elements in plants
enhance performance in many plants but not necessarily essential
Si, Na, Co
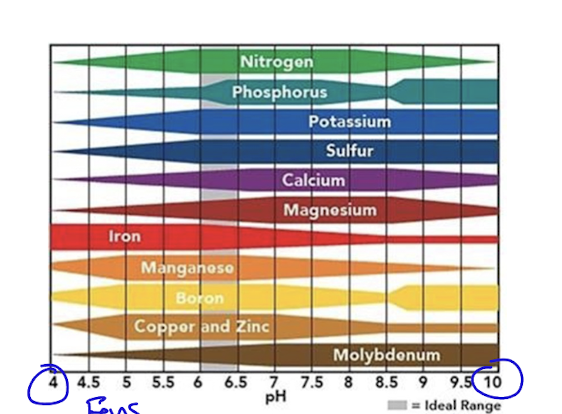
soil pH and element availability
as pH changes so does available nutrients
ideal zone is between 6-7 pH
often in agriculture they lime the soil to increase pH in acidic zones, increasing natural nutrient availability and boosting the effect of fertilizer
nutrient limitation
slowing or stopping of metabolic processes due to insufficient availability of essential nutrients
major includes nitrogen and phosphorus
nitrogen availability
limiting in water
readily available in atmosphere - 78% but not available for plant uptake due to strong triple bond
lightning and symbiotic organisms create available
forms include ammonium and nitrate (inorganic) and the available/organic form is only 2%
how do plants uptake nutrients?
via roots or atmosphere
symbiotic relationships - mychorrhizal fungi, rhizbium bacteria, frankia, cyanobacteria
carnivory, parasitic
phosphorus functions
major limiting in water, not easily dissolvable in soils
used fr DNA and RNA formation, energy storage and transportation (ATP)
mycorrhizae and root exudates facilitate uptake
nitrogen function
amino acids - proteins like rubisco, DNA, pigments like cholorphyll
often limiting factor for plant growth
limiting in soil
ammonium
NH4+
free living n fixing bacteria in soil, decomposition of biomass by fungi and bacteria
can be toxic to plants, therefore immediately transferred to amino acids after uptake - cant tolerate large amounts
nitrate
NO3-
free living n fixing bacteria in soil, decomposition of biomass by fungi and bacteria, lightning
not toxic and can be stored in roots/shoots, but immediate transformation to amino acids post uptake
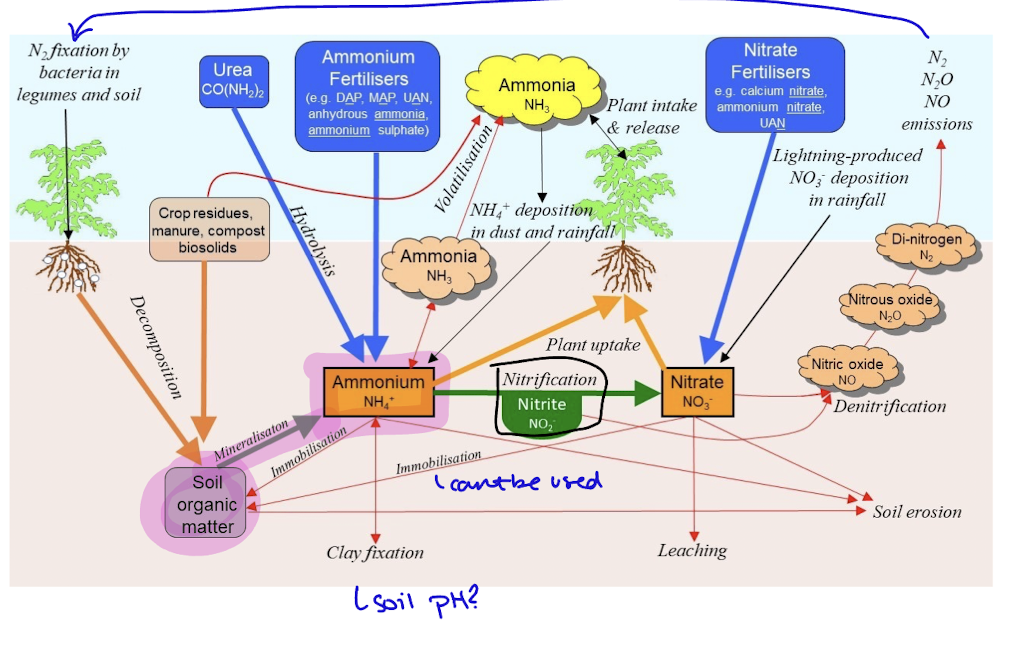
nitrogen cycle
nitrogen in the air is fixed by bacteria or lightning, or supplied by fertilizers
undergoes decomposition to soil organic matter then mineralization to become ammonium, from here it can either under nitrification to become nitrite and then nitrate, it can be released as ammonia, uptook by plants or it can be fixed/eroded to the soil
nitrate can also contribute to leaching, plant uptake, soil erosion, orimmobilization. denitrification converts back to N gas and then it is released as emissions in the air and the cycle continues
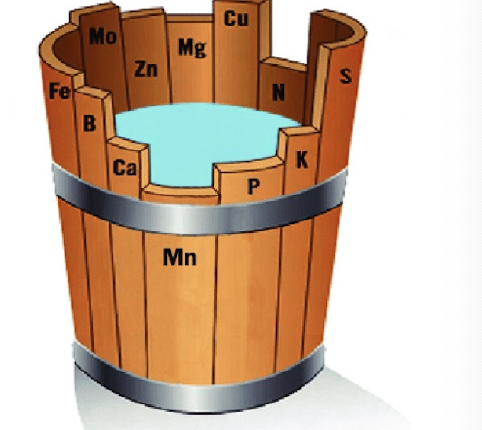
liebigs law of the minimum
one limiting nutrient will inhibit all others even if they have higher supply
the barrel represents plant growth or crop yield
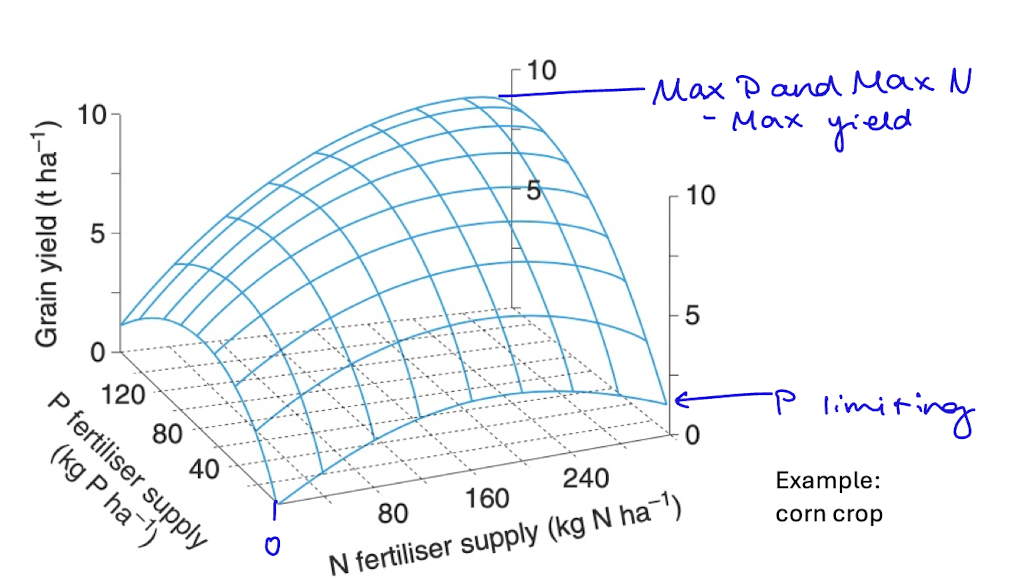
fertilizer effects
how P and N fertilizers work together
max yield is when max P and max N is used
adaptations to limitations
symbiosis with microorganisms, resorption of nutrients from senescing leaves, investment into root biomass or branching
but can be energetically costly and therefore these environments are usually adapted to by stress tolerant species with low productivity
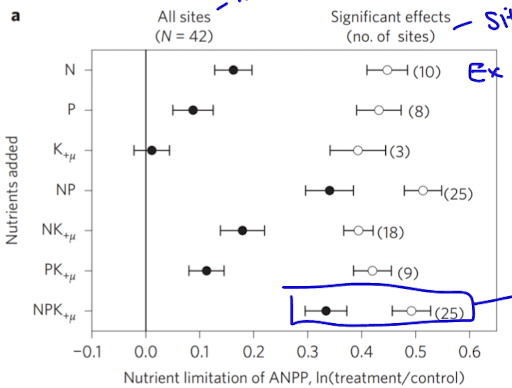
aboveground net primary productivity and limitations
observing how combinations of different nutrients effects global grasslands
NPK has very limiting effects together
additionally temperature effects as colder environments have slower rates of decomp
deficiency
not enough nutrients available of a specific kind
changes depending on the nutrient
toxicity
when there is too much of a nutrient
higher amounts may cause growth restrictions
easier among micronutrients where only small amounts are needed in the first place
saline habitats
unique habitats with salt deposition, adapted vegetation etc
electrical conductivity, fluctuates throughout the year
salinity gradient
freshwater → brackish → saline
impacts species composition
why is freshwater fresh?
always replenished by rain
where does salt come from?
on the coast could be due to runoff accumulation, seafloor openings, evaporation
inland could be from bedrock weathering, high evap/low leaching in arid climates, discharge of groundwater - irrigation in ag, road salting
glycophytes
salt sensitive species
halophytes
salt tolerant species
for example sea blite or foxtail barley
recretohalophytes
expel salt through specialized structures
salt glands in the epidermis may pump out salt, or salt bladders under leafs may accumulate salt excreted in an external vacuole
aluminium toxicity
issue in acidic soils, caused by bedrock, leaching in rainy areas (boreal or tropics), acid rain, root exudation in the rhizosphere
as pH decreases the solubility will increase
excluding Al
proposed research suggesting that root excretion of organic acids in roots across the plasma membrane to the apoplast (cell wall) then results in chelation (bonding/sequestration) of Al in the rhizosphere to the cell walls
aspen excluding al
may increase concentrations of citrate, malate and oxalate when Al concentrations increase
common in boreal and tropical forests
Al tolerance
chelation in cytosol (pulls into symplast), sequestration to vacuoles and then activation of tolerant metabolic pathways
triggers stress in cells
stressful environments
provide unique areas that result in biodiversity hotspots
ex in the cerrado ecoregion in brazil there are grasslands and savannas that are nutrient poor and al rich
high diversity and endemism - new niches, natural selections
ex bedrock meadows
nutrient poor soils, high al concentrations due to bedrock
biodiversity hot spots but have low productivity