Nervous System Cells and Resting Membrane Potential
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is the burden of mental health disease in Australia?
One in five (20%) Australians aged 16-85 experience a mental illness in any year, and almost half (45%) will experience a mental illness in their lifetime.
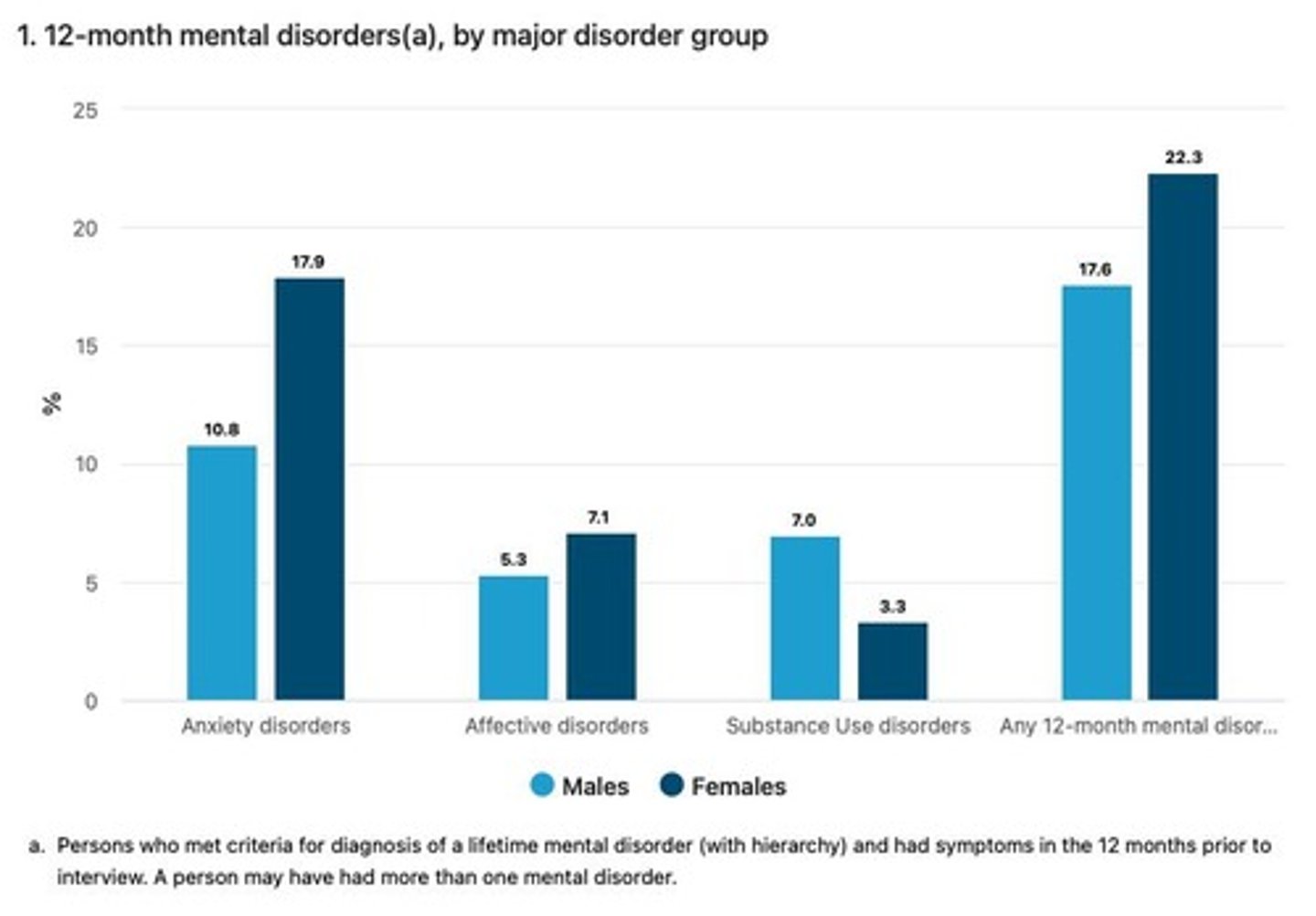
What is the leading cause of death for Australians aged 25-44?
Suicide is the leading cause of death for this age group.
What are some recommendations to reduce the risk of mental illness?
Be physically active, maintain a healthy weight, avoid smoking, eat a balanced diet, reduce alcohol intake, engage in cognitive training, and be socially active.
What are the main components of the nervous system?
The nervous system consists of neurons, glia, and the wiring that connects them (nerves).
What are the main structures of a neuron?
The main structures of a neuron include the cell body, dendrites, and axon.
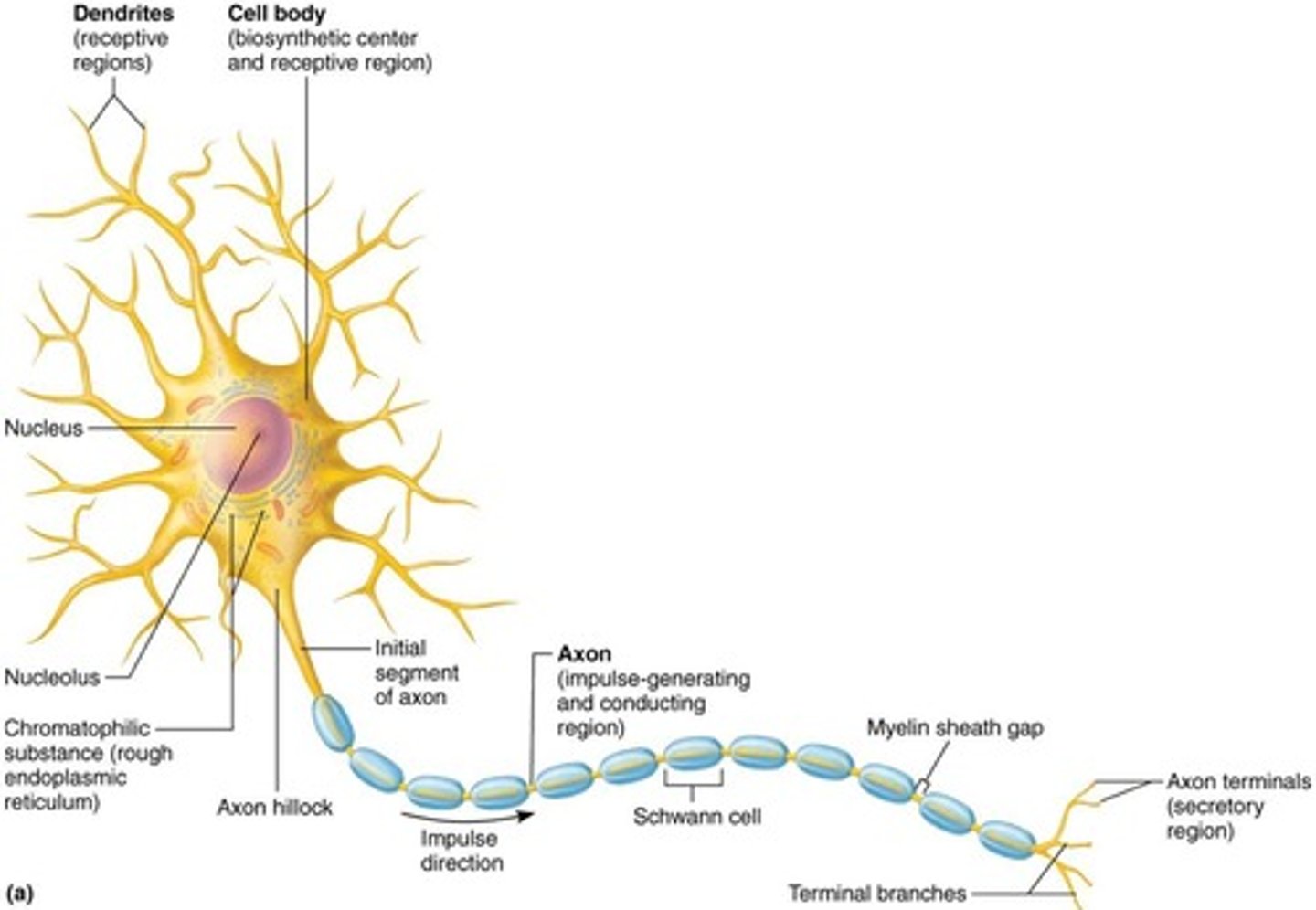
What is the function of dendrites in a neuron?
Dendrites receive inputs from other neurons.
What is the role of the axon in a neuron?
The axon sends output signals to the next neuron.
What are glial cells and their function?
Glial cells, or glia, provide connective and support functions in the nervous system.
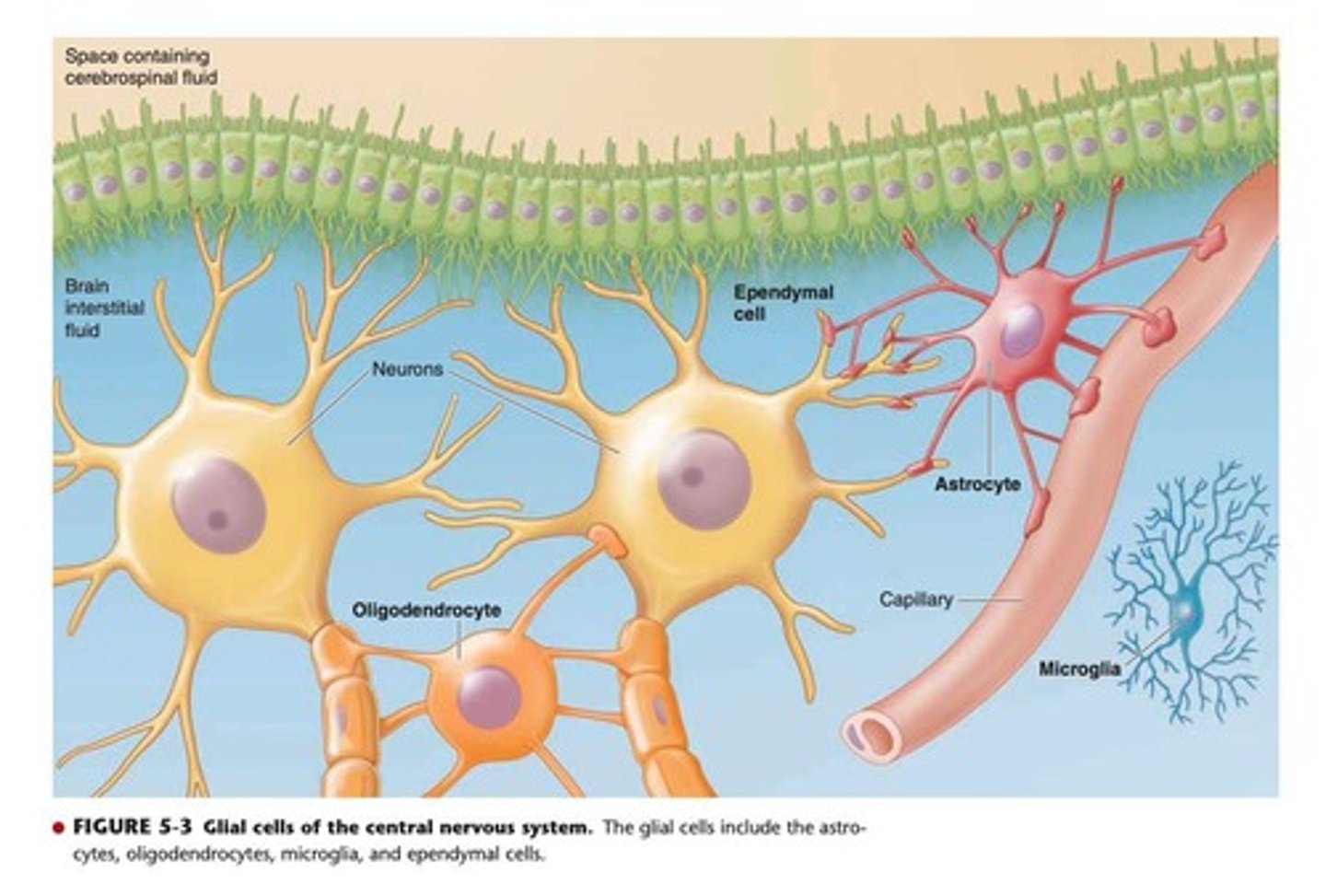
What are the four types of glial cells in the central nervous system (CNS)?
Astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and ependymal cells.
What is the function of astrocytes?
Astrocytes regulate ion and neurotransmitter levels, provide structural support, and form the blood-brain barrier.
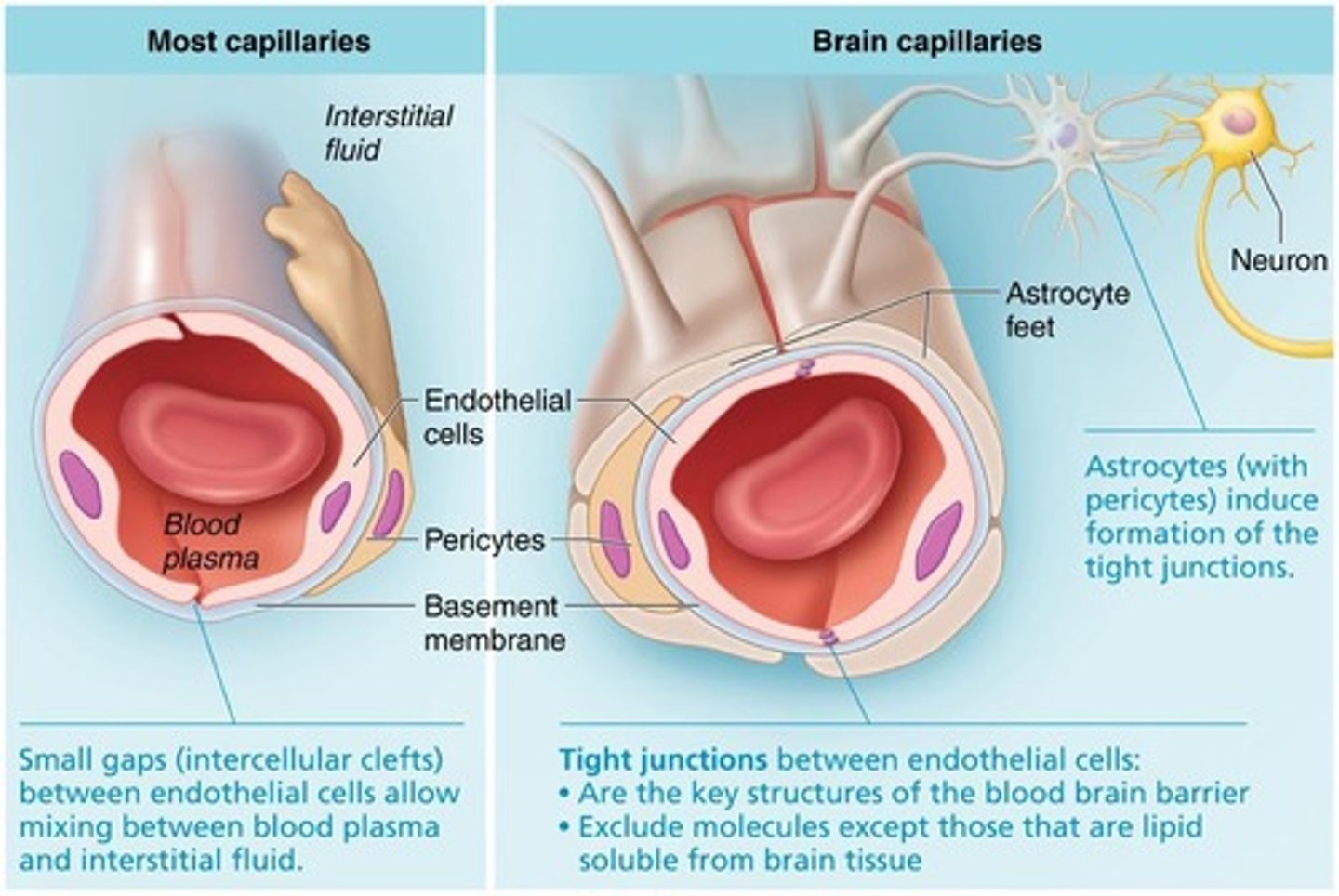
What is the blood-brain barrier?
A highly selective permeability barrier formed by astrocyte foot processes that protects the brain from toxic compounds and pathogens.
What is the role of oligodendrocytes?
Oligodendrocytes myelinate axons in the CNS.
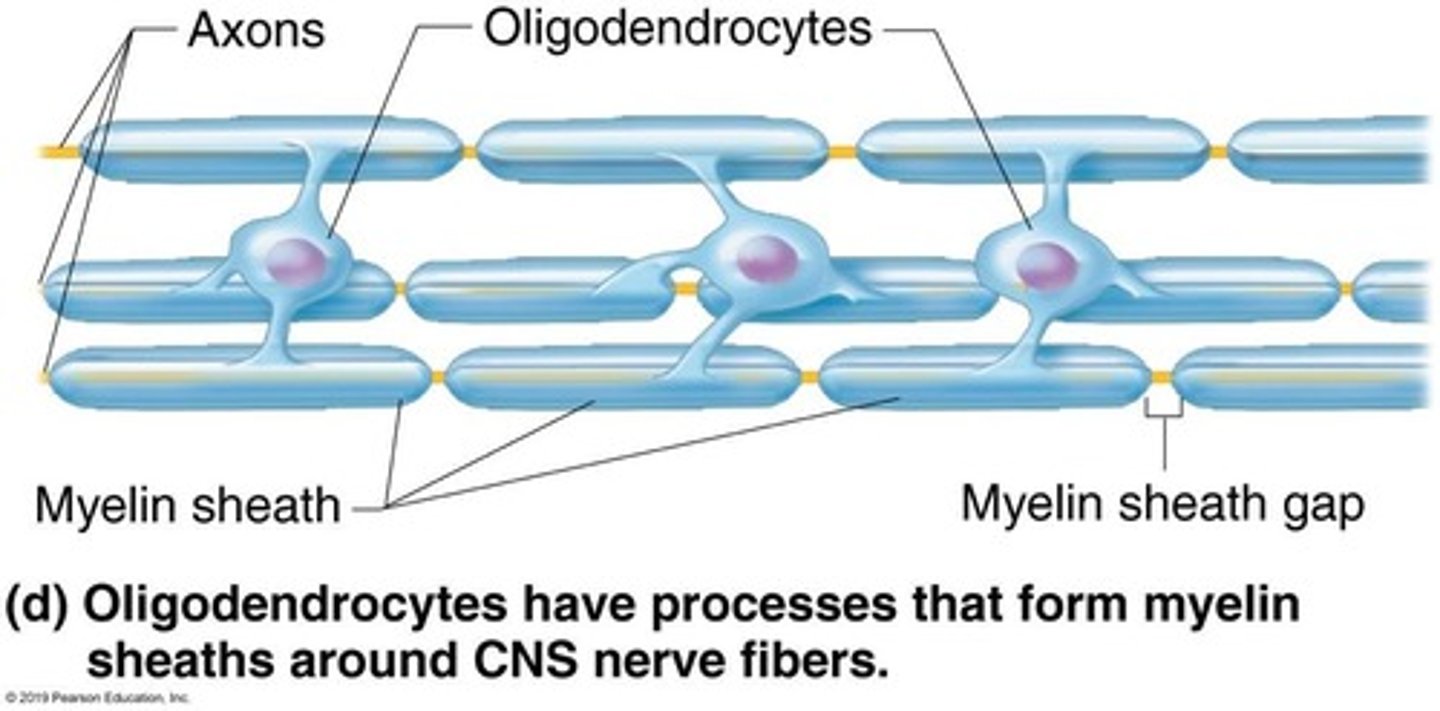
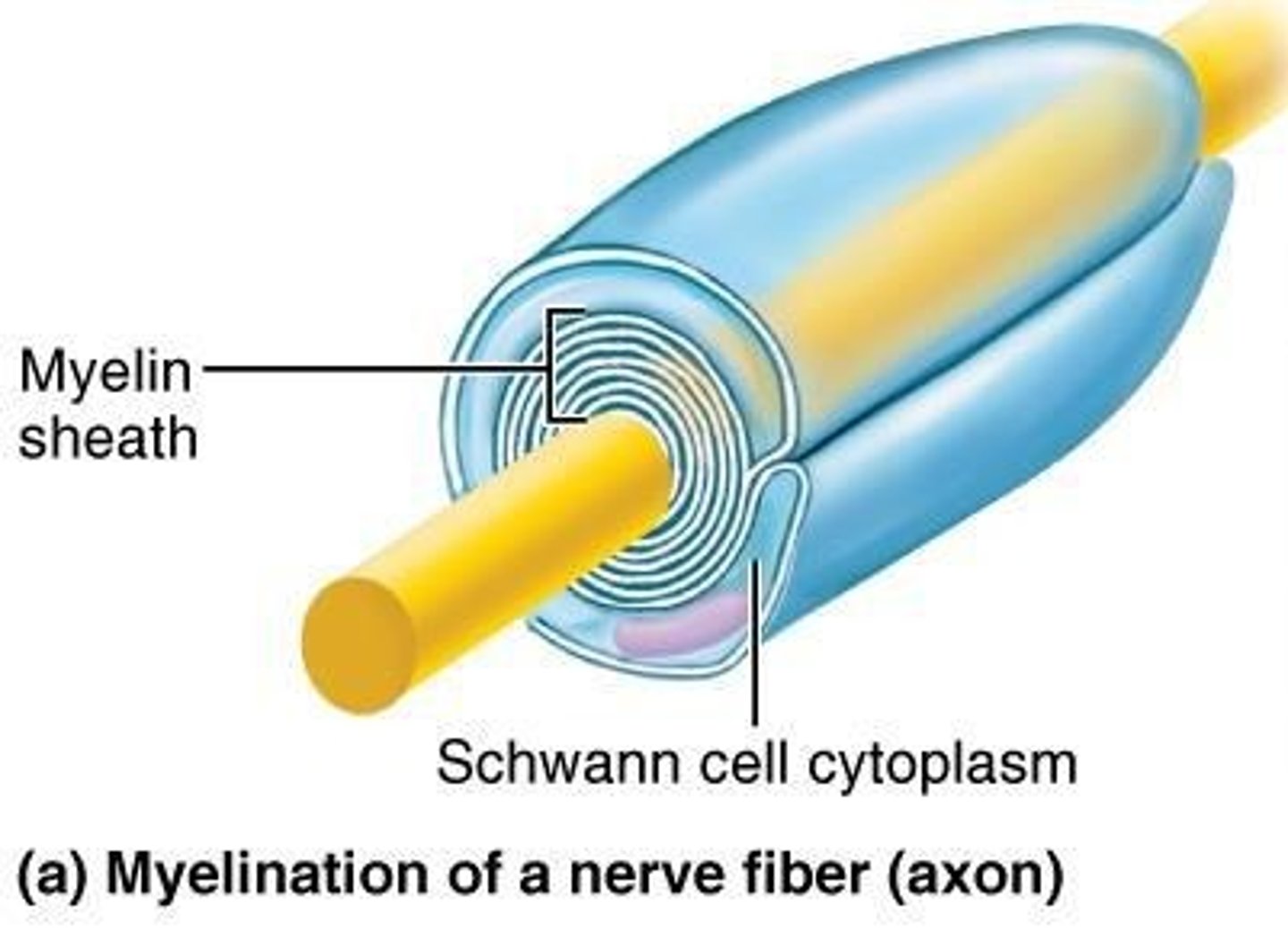
What is myelination and its significance?
Myelination is the fatty layering around axons that insulates them, increasing the speed of signal transmission.
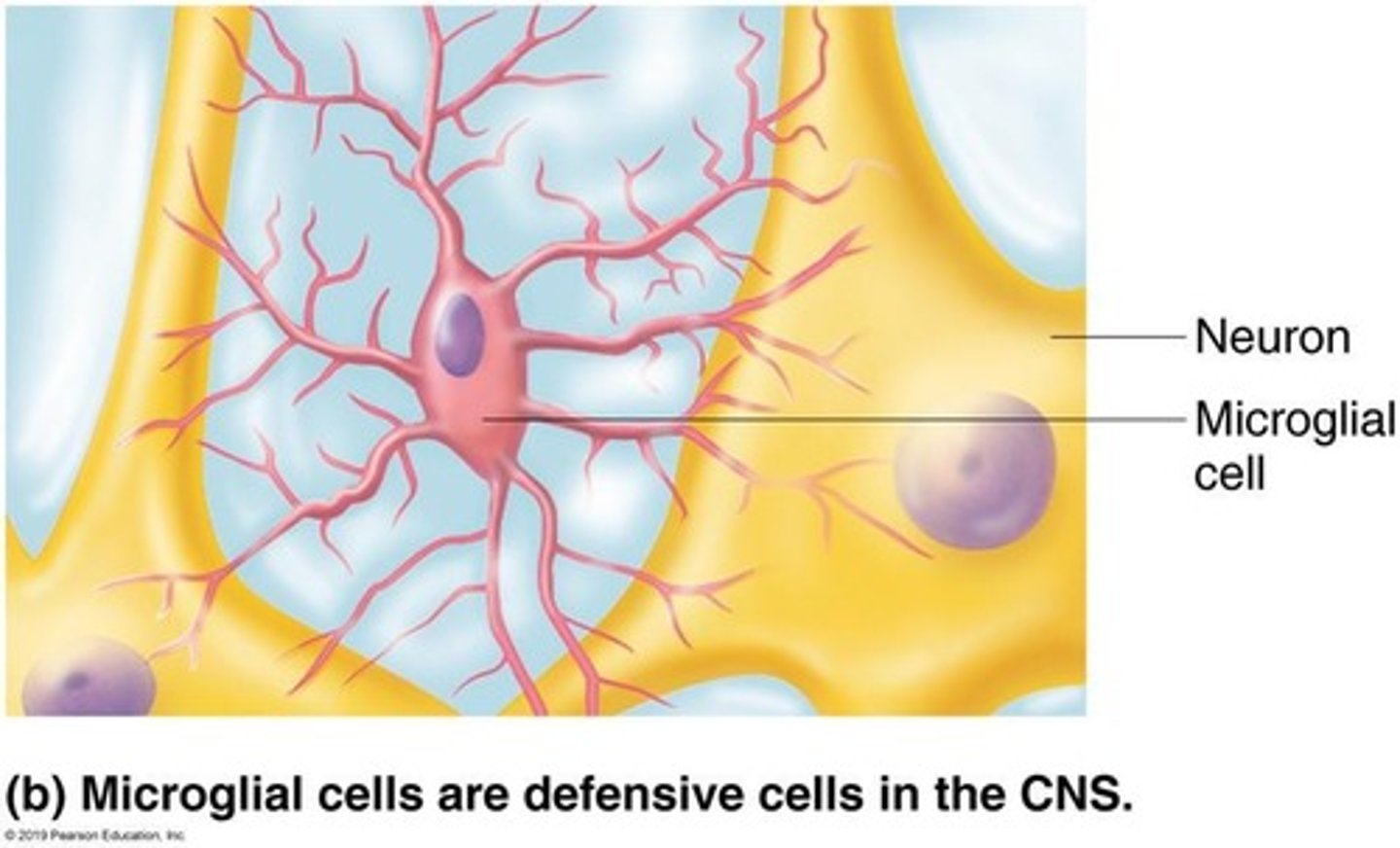
What are microglia?
Microglia are the immune cells of the CNS.
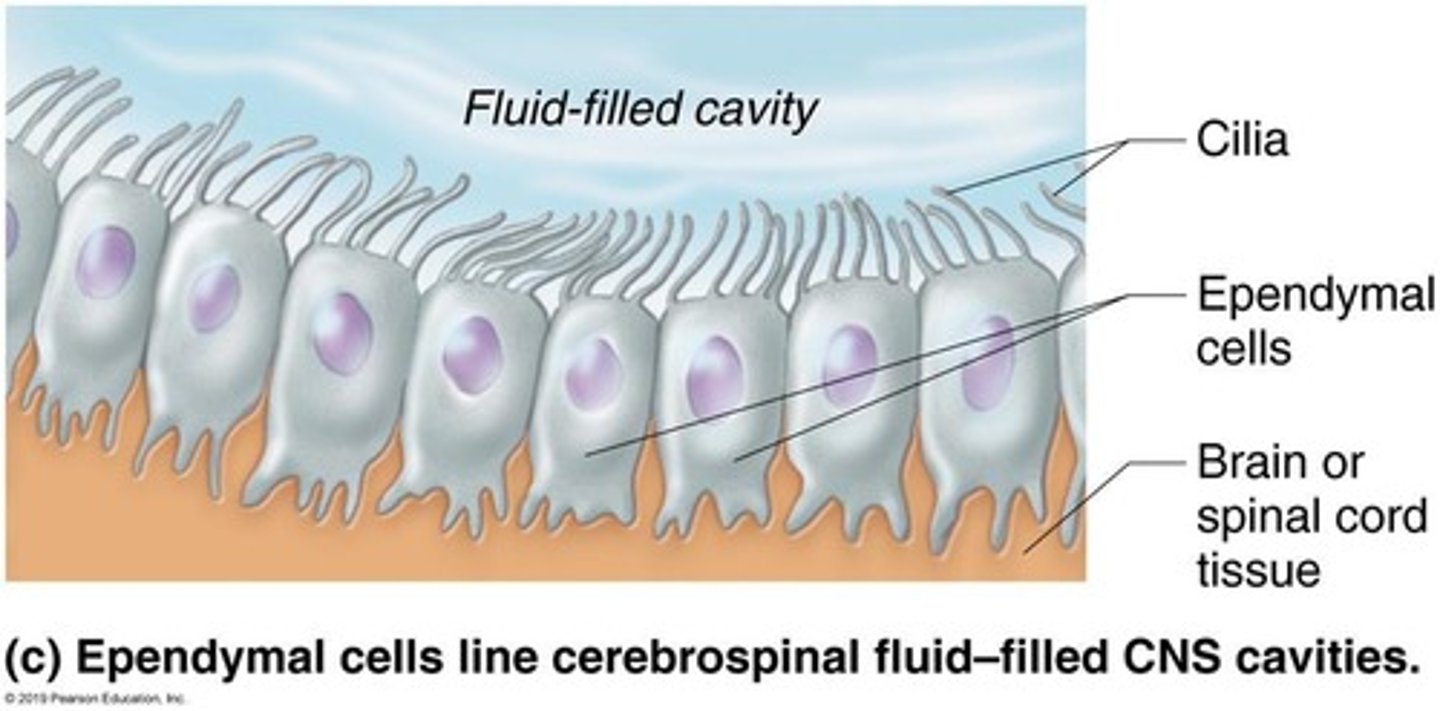
What are ependymal cells?
Ependymal cells line the ventricles of the brain.
What are the two types of glial cells in the peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
Satellite cells and Schwann cells.
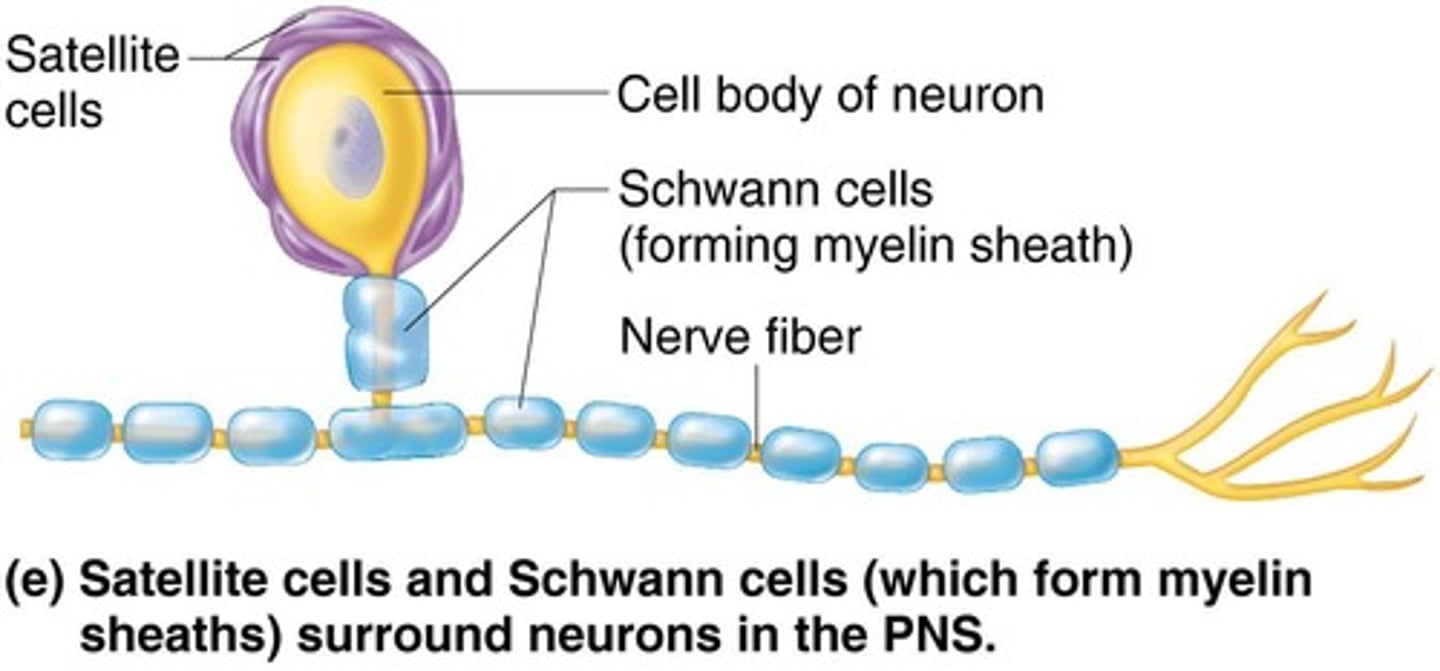
What is the function of satellite cells?
Satellite cells surround cell bodies in ganglia and regulate nutrient, gas, and neurotransmitter levels around neurons.
What is the role of Schwann cells?
Schwann cells myelinate axons in the PNS.
What is voltage in the context of the nervous system?
Voltage is a measure of the strength of the current in a circuit, measured as the potential difference between two points.
What is a membrane potential?
A membrane potential is a voltage across a cell membrane caused by a difference in the distribution of ions on each side.
What is the resting membrane potential in neurons?
The resting membrane potential in neurons is approximately -70 mV.
How is the resting membrane potential generated?
It is generated by differences in ionic composition and membrane permeability to ions.
What are the ionic differences that contribute to the resting membrane potential?
High [K+] and negatively charged proteins inside the cell, and high [Na+] and [Cl-] outside the cell.
How is the resting membrane potential maintained?
By potassium channels allowing K+ to leak out and the Na+/K+ ATPase pumping 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ in.
What is the significance of excitable cells like neurons and muscles?
They can rapidly change their membrane potential in response to stimuli, triggering electrical responses.
What is the role of voltage-gated ion channels?
They are essential for the rapid changes in membrane potential in excitable cells.