Equilibrium constants and acids & bases
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What is the thermodynamic equilibrium constant K?
uses activities
has no units
solids have an activity of 1
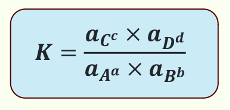
What is Kc?
Equilibrium constant using concentrations
assumes a ≈ [x]
![<p>Equilibrium constant using concentrations </p><p>assumes a ≈ [x]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/01eeca51-ba24-4512-ae5c-51ef8e6c43fa.png)
What is Kp?
Equilibrium constant using partial pressures
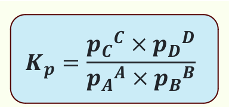
What is Q?
non equilibria
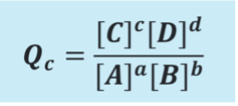
What does it mean if:
Q = K
Q > K
Q < K
Q = K at equilibrium
Q > K reaction shifts to left
Q < K reaction shifts to right
Equation for G at equilibrium and non equilibrium

What is solubility?
The amount of substance that can be dissolved in a given amount of substance
What is the equation for Ksp?
What does large/small Ksp mean?
Large Ksp = high solubility
Small Ksp = low solubility
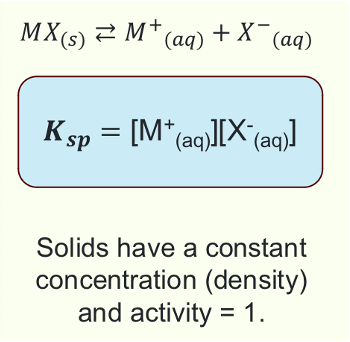
Acids and bases according to Arrhenius theory?
Acids are substances that dissociate in water to give H+ ions
Bases are substances that dissociate in water to give OH- ions
Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases
Acid = H+ donor
Base = H+ acceptor
Lewis acids and bases
Acids are substances that accept a pair of electrons
Bases are substances that accept protons
How to calculate pH?

What are the names of the H3O+ ion?
oxonium / hydronium ion
Dissociation of base equation
A- (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ HA (aq) + OH- (aq)
pOH equation
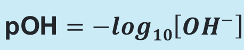
Dissociation of acid equation
HA + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + A-
How to calculate Ka?
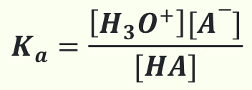
How to calculate Kb?
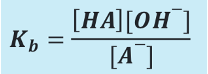
How does stability of A- ion affect POE?
The more stable the ion, the more the equilibrium will lie to the RHS
value of Ka will be larger
How are anions stabilised?
How do electronegative atoms/groups affect anions?
How else can electron density spread?
When electron density is spread over more atoms
electronegative species draw the negative charge away from the COO
electron density can be spread through delocalised p orbitals
What does polyphonic mean?
Acids/bases that are capable of donating or accepting multiple protons
What does amphoteric mean?
Can behave as an acid or a base
How does pKa change with Ka?
When Ka increases, pKa decreases
How does pKb change with pKa?
Small pKb = large pKa and vice versa
What is the fraction of dissociation (αHA) a measure of?
What is the equation?
A measure of acid strength; the fraction of acid molecules that are dissociated
FHA is the formal acid concentration
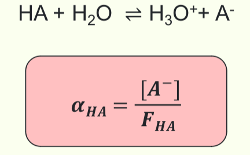
What is FHA for a weak acid?
FHA ≈ [HA]
What is pKa (in terms of pH)?
The pH at which half an acid is protonated, and half is deprotonated
What does it mean when
pH < pKa
pH > pKa
pH < pKa = lots of H3O+ ions and equilibrium is far to left (pH is low when acidic)
pH > pKa = not as many H3O+ ions, equilibrium lies to right
What is the fraction of association, αHB?
What is the equation?
The equivalent for a base
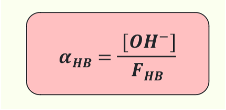
What is a buffer?
A mixture of a weak acid and the salt of its conjugate base. It resists changes in pH when acids/bases are added or if it’s diluted.
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation?
(involves pH and pKa and buffers)
What are the assumptions?
Assumes almost all HA molecules are unchanged
All A- ions come from salt
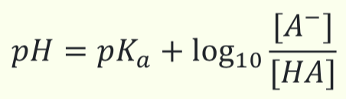
What happens when an acid is added to a buffer solution?
Equilibrium shifts to the left to reduce the concentration of H3O+
What happens when a base is added to a buffer solution?
Equilibrium shifts to the right to reduce the concentration of OH- by reacting with H3O+ ions
Equation involving Kw, Ka and Kb
Kw = Ka x Kb