Memory (multi-store model)
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
State the 3 types of memory storage commonly studied by psychlogists?
capacity
Duration
Coding
Define capacity
Quantity of info stored
Define duration
Length of time info is held in memory for
What is the coding for sensory memory
Modality specific
What is modality specific coding?
info is held in the same sense that it is registered - sight, hearing, touch, smell and taste
What sensory memory stores did most research focus on?
iconic - where visual images are kept for a short period
Echoic - where auditory senses are kept for a short period
Haptic - where physical senses of touch and internal muscle tension is stores
What is the capacity of sensory memory?
high
Outline research into capacity of sensory memory?
sperling
Used a tachistope: presented a 12 symbol grid for 1/20th of a second on a screen
Participants could recall 4 symbols but reported seeing a lot more than they had time to report
Demonstrates that the capacity of sensory memory is very large
State evaluation points for Sperling’s study into the capacity of sensory memory
Although eveidence suggests that the capacity of sensory memory is very large, it isn’t well studied, as they last so briefly and generally at a preconscious level
Lack of ecological validity as Sperlig’s study was not a realistic situation - lacks mundane realism
What is the duration of sensory memory?
0.25s-2s
What is the coding of short term memory?
acoustic
Outline research into the coding of short term memory?
visually presented students with letters one at a time to study encoding in stm
Found that: letters which are acoustically similar (rhyming) are harder to recall from STM than those which are acoustically dissimilar (non-rhyming)
Concluded that the coding in stm is acoustic
What factors need to be considered when choosing tasks for research into coding of stm?
one condition is given an acoustically similar task
Second condition is given an acoustically dissimilar task
Compare conditions
What is the capacity of stm?
7 ± 2 items
(5-9)
Outline a study that researched into the capacity of stm ?
Jacobs/Miller
Developed a technique to measure a digit span
Showed participants 4 digits
Asked to recall them aloud in the correct order
If correct, process was repeated with 5 digits, then digits and carried on until they couldn’t recall the numbers in the correct order
Results: mean span for digits was 9.3 for numbers and 7.3 for letters
What factors need to be controlled when choosing letters or digits when testing capacity of STM?
dont use letters that make up a word
No acronyms
No repititions
No acoustically similar words (would test coding)
What is the duration of STM?
15-30s
If not verbally rehearsed (maintenance reharsal)
Outline a study into duration of STM?
peterson and peterson
24 psychology students
Students had to recall trigrams at different intervals to prevent rehearsal students were asked to count back in 3/4s from a specified number
Then recalled letters
Found: 3s around 80% of trigrams recalled, 18s only 10% were recalled correctly
Conclusion: stm has a limited duration of approximately 18s
Evaluate Paterson and Paterson study into duration of stm?
Limitation: stimulus material is artificial. Trigrams given in a controlled environment. This activity does not reflect real life situations where what we are trying to remember is meaningful. So study lacks ecological validity.
Supports the explanations that the memory trace disapears after a short duration if not rehearsed. However there could be an alternative explanation which states that info in stm is displaced because stm has a limited capacity and any new info pushes out current info in stm. In study, students counted back in 3s which could have displaced info. So study lacks validity.
What is a way to expand capacity of stm and who came up with it?
chunking
Miller argued that capacity could be expanded if information was split into chunks of information which would reduce the number of individual items needed to remember
Evaluate chunking
miller might have overestimated the capacity of stm as Cowan reviewed other research and found that capacity of stm is only around 4 chunks
What is the coding of long term memory?
Semantic
Outline a study into the coding of LTM
Baddley
presented lists of 10 short words one at a time
some lists were semantically similar some wernt
tested immediately after and then after 20 min delay
found that after 20 mins they did poorly on the semantically similar words
suggests that coding in LTM is semantic so we get similar meaning things confused
evaluate Baddley’s study into the coding of LTM
used artificial stimuli such as word lists rather than meaningful material so we can’t generalise the findings to different kinds of memory tasks such as processing more meaningful information people may use semantic coding for even for STM tasks - limited application
what is the duration LTM?
unlimited
outline a study into the duration of LTM
392 Americans aged between 17&74 given a recognition test: asking participants to match names of former class mates to 59 pics in a yearbook
participants tested 48 years after graduation were 70% accurate
memories stored in LTM can last a lifetime (at least 48 years)
Evaluate Bahrick et al’s study into the duration of LTM
meaningful memories studied so research has higher ecological validity
but confounding variables are not controlled (may have looked at yearbooks since and rehearsed memory over years)
what is the capacity of LTM?
unlimited
who came up with the multi-store model?
Atkinson and Shriffrin
what is the multi-store model (just define)
structural permanent model of memory
3 fixed unitary stores (sensory, stm, ltm)
info moves in a fixed linear and passive manner
Describe the multistore model
Shows that there are 3 unitary stores for memory; sensory register, STM and LTM.
environmental input transfers info into your sensory register. The capacity of the sensory register is very large, the duration is 2.5-2s and the coding is modality specific. Paying attention transfers info into your STM. The capacity of STM is 7 +/- 2 items, the duration is 15-30s and the coding is acoustic. info can be retained in STM by maintenance rehearsal. Info is transferred to LTM by prolonged rehearsal. Info in LTM is retrieved from STM. The capacity of LTM is unlimited, the duration is unlimited and the coding is semantic
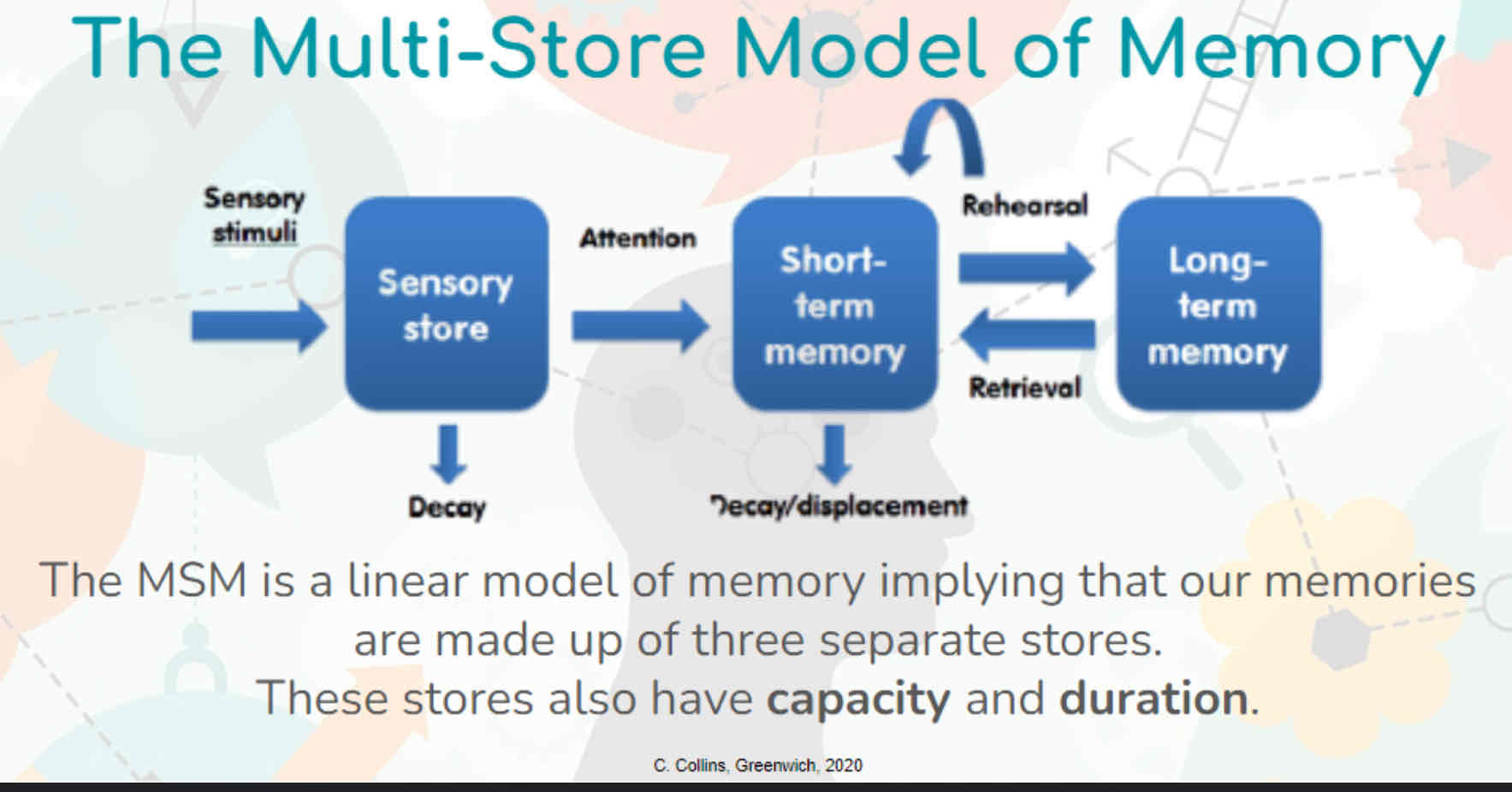
State strengths of the multi-store model
most of the studies done on memory were laboratory experiments
Research support for the existence of 2 distinct stores
Research support from clinical studies
Outline the strength that studies done on memory were lab experiments?
controlled conditions: help establish cause and effect between the variables being studied as there are fewer extraneous variables.
Controlled environment makes study more replicable.
This is a strength as it helps provide strong supporting evidence for the MSM
Explain the strength that there is research support of two distinct stores memory
studies have shown (eg Murdock) that when participants are given a list of words to learn and recall them freely in any order, they show superior recall from the beginning(primacy effect) as words have reached the LTM, and the end (recency effect), words are still in STM, of the list
Provides evidence of 2 distinct stores - STM and LTM
How are the clinical studies of amnesiacs a strength of the multi-store model?
E: HM had his hippocampus removed and whereas his STM remained intact (his digit span was normal), he couldn’t form LTM
E: supporting the MSM as this model presents memory as having separate stores located at different areas of the brain and the fact that HM’s LTM store was damaged (as he couldn’t retrieve information from the STM) suggests that the 2 stores must function seperately.
State the limitations of the multi-store model of memory?
oversimplified
Over-emphasises rehearsal
Research into MSM has used artificial meaningless stimuli
Outline the limitation of the multi-store model that it is oversimplified
P: it assumes that there is a single STM and LTM but they are much more complex than originally thought
E: There is research that supports the idea that there are different types of LTM: procedural, episodic and semantic. Fo example, Clive Wearing who’s memory was impaired due to a viral infection. His LT episodic memory was severely damaged ( he had difficulty remembering events in the past) but his procedural memory was unaffected ( he could still play the piano).
E: supports that LTM is not a unitary store like the multi-store model suggests ad that the LTM has subsections
Crticise the multi-store model using the working memory model
P: The working memory model also casts doubt on the assumption that the STM is a single unitary, passive store. It states that the STM is a multicomponent, active store.
E: Research with a patient with amnesia, patient KF, supports this idea by showing that there are seperate STM for visual information and a seperate component for auditory information. After being injured in a motorcycle accident, he could recall info from his LTM; however he had issues with his STM. He was able to remember visyal images, including faces but was unable to remember sounds.
E: this suggests that STM has subsections and is not a unitary store as shown in the multi-store model.
Criticise the fact that the multi-store model over emphasises rehearsal
P: model proposes that the transfer of info from STM to LTM is through rehearsal. It stresses in maintenance rehearsal (amount that you do). However this has been criticised by Craik and Watkins who have argued that what really matters is the type of rehearsal.
E: they believe that maintenance rehearsal only maintains info in STM but doesn’t transfer it to LTM. On the other hand, the type of rehearsal that is required to transfer info to LTM is elaborative rehearsal - when you think about that the information means and links it to existing knowledge
E: this is a limitation because it is a finding that cannot be explained by the MSM
Criticise the MSM due to it’s research support using artificial meaningless stimuli
E: Peterson and Peterson’s gave participants trigrams to memorise in a controlled artificial environment. This activity doe not reflect real life situations where what we are trying to remember is meaningful. For example, facs, names and facts. So we can say that the findings of this task lacks ecological validity.
E: as they do not reflect real life memories they therefore may not provide good support for the MSM
state the 3 types of LTM? and briefly define?
semantic - facts
episodic - personal events
procedural - muscle memories
state the differences between semantic and episodic memory?
semantic
factual knowledge
not time stamped
located in posterior region of cortex
episodic
memories of life events/personal experience
time stamped
located in anterior region of cortex
state similarities of episodic and semantic memory?
both LTM
both declarative and expressed in words
both are explicit and available for conscious inspection
Outline a study to support existence of episodic and semantic memory?
aim: to prove the existence of the existence of episodic and semantic memory as separate memory systems
method: Tulving and 5 other volunteers were injected with a small amount of radioactive gold into their bloodstream. They performed 8 trials for semantic topics and 4 for episodic topics. The trials were separated by 2 minutes of rest each. Episodic memories involved personally experienced events like holidays and semantic topics involved historical facts or knowledge acquired by learning. The brain was scanned using a PET scanner while they performed the separate memory tasks and blood flow monitored by radioactive detectors.
Results: 2 tasks gave different patterns of blood flow in the brain. Episodic memories were associated with anterior region of cortex and semantic memories led to greater activation in the posterior region of the cortex
Conclusion: provides evidence that there are at least 2 different types of LTM since it shows that episodic and semantic memories are stored in different parts of the brain.
Outline clinical evidence for the existence of episodic and semantic memory?
episodic memory in Clive Wearing and HM was severely impaired due to amnesia. However, their semantic memory was relatively unaffected. They still understood the meaning of words.
Eg: Hm would not recall stroking a dog half an hour earlier but he understood the concept of a dog.
Conclusion: This supports Tulving’s view that there are different memory stores in LTM as it supports idea that different areas of the brain are involved in LTM storage. HM had an impaired episodic memory but his semantic was intact.
State the differences between procedural memory and episodic and semantic memory
Procedural is non-declarative
Resistant to forgetting
Implicit - not available for conscious inspection
Episodic and semantic are declarative, less resistant to forgetting and explicit
Criticise the different types of LTM?
The extent to which episodic and semantic memories are different is unclear, as although different brain areas are involved, there is also a lot of overlap between the two systems, with semantic memories often originating from episodic memories. Cohen and Squire argue that episodic and semantic memories are stored together in one LTM store that they call declarative memory in contrast to procedural memories that are non-declarative
It may be that episodic memory differs from that of semantic in terms of different types of thinking and emotions. Episodic memories have emotions related to them while semantic memories are associated with objective analysis of phenomenon.
State a positive evaluation of the different types of LTM?
being able to identify different aspects of LTM allows psychologists to target certain types of memory in order to better people’s lives. It has been demonstrated that episodic memory could be improved in older people with mild cognitive impairment. The trained participants performed better on a test after training than a control group. So this enables specific treatments to be developed.
What does declarative memory mean?
info can be expressed in words