Week 3B: Light and the eye
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Three ways to look at light, three ways they ‘behave’
Rays, waves, particles
When light strikes the interface between two substances it can be
Reflected, refracted (transmission) or absorbed
Which action heats up the material the most: reflection, refraction (transmission) or absorbtion
Absorbtion
Law of Reflection
Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection
Three different types of reflection
Specular, diffuse, and spread.
Index of refraction
n = c / v
Snellius’ law
n sin(theta) = n’ sin (theta’)
Since the index of refraction of glass is higher than of air, the angle of refraction with the normal will be (…) (larger or smaller)
Smaller
Critical angle definition
Largest possible angle of incidence which still results in a refracted ray
Total internal reflection
Light cannot escape from a high density medium to a lower density medium
Critical angle degree
41.8
As a wave, light is characterized by:
wavelength, polarization (oscillation direction), intensity (amplitude of the wave)
Visible wavelengths for humans
400 till 700 (nanometer)
The spectral power distribution determines the (…) in the eye
colour
Black body radiation
The theoretical spectrum of emission from an idealized object that absorbs all incident radiation, emitting light across a range of wavelengths according to its temperature.
Black body radiation of a sufficiently high temperature is (…) (a colour)
White
Dispersion
The velocity of the wave depends on its wavelength
Diffraction and its result
Occures when a wave encountes an obstacle or a slit and causes interference
Interference with two slits: White stripes a result of (…) interference, and black stripes as a result of (…) interference
Constructive, destructive
What does the luminous efficiency curve show
The human eye is not equally sensitive to all wavelengths
Why do we need photometric units to describe light
Quantify light in ways that correlate with human vision ( allowing for accurate measurement and comparison of brightness and intensity. )
Light scattering is not absorption, it is (…) of light energy
Redistribution
Rayleigh scattering
Light interacts with particles smaller than its wavelength (leading to shorter wavelengths being scattered more than longer wavelengths)
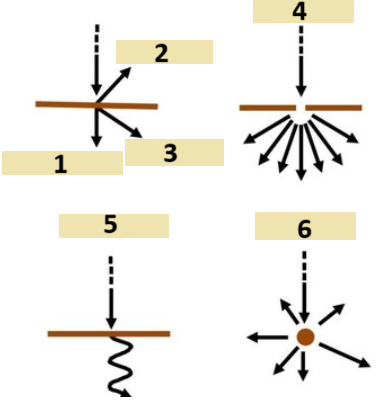
1,2,3,4,5,6
Transmission, reflection, refraction, diffraction, absorption, scattering
Focal length f of a lens
Distance where rays from infinity converge to a point
Lens formula
1/object distance + 1/ image distance = 1/ focal length
Image size scale formula
- image distance/object distance*height object
Accomodation errors: Myopic
(Nearsighted) Distant object in front of retina
Accomodation error: Hyperopic
(Farsighted) Close object focused behind retina
The smallest object humans can still see formula
Tan (alpha(visual angle)) = s(linear size) / d (viewing distance)
Pupil size can vary between (…) and (…) mm in diameter
2, 8
How is light processed from eye to brain
Light is processed by retina, transferred via the visual pathway, processed in the visual cortex
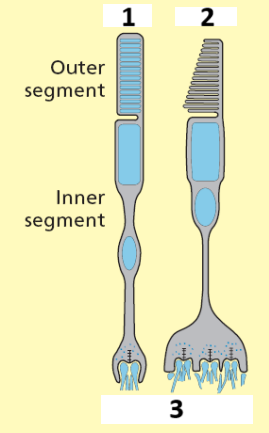
1,2,3
Rod, cone, synaptic clefts
Sensitive at low light level (cones or rods)
Rods
Location of rods in your eyes
Parafovea
Location of cones in your eyes
Fovea
If you want to see a shooting star, what should be your visual strategy and why
Use your parafoveal vision because there are more rods
Stiles-Crawford effect
Light entering the eye near the center of the pupil appears brighter than light entering near the edge of the pupil — even if the light intensity is the same
Principle of univariance
Once a photon is absorbed, its effect is independent of wavelength
Cortical cells
Produce a high response for one orientation of the stimulus
Direction selectivity
Cortical cells that produce a high response for movement of the stimulus in one direction
Binocularity (Ocular dominance)
Some cortical cells respond equally well to stimulation of either eye, while other respond better to the signal of one eye
Inner (…) degrees of the retina takes up 50% of striate cortex
10
Difference between simple cells and complex cells for cortical cells & orientation tuning
Response depends on position of stimulus in the receptive fields vs. response does not depend on position of stimulus in the receptive field