Post Seg Final
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What is the most common intraocular tumor?
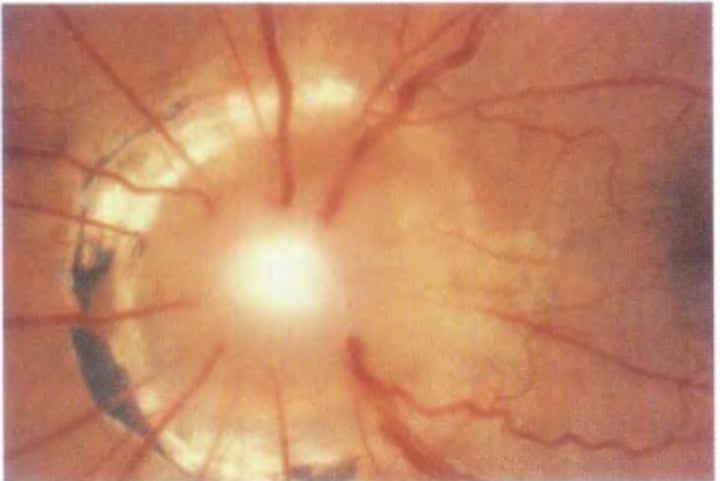
Choroidal nevus
Choroidal nevus
common benign tumor of melanocytes in choroid
acquired after puberty --> asymptomatic
Size: smaller than 5DD less sus
Color: green, blue/grey, surface drusen (good sign)
Shape: oval/round
Borders: sharpish
Location: mid-periphery (closer to ONH more risky)
__________________ is associated with an increased risk of skin cancer
Halo nevus
Amelanotic nevus
melanocytes dont produce melanin in this nevus
What characteristics make a choroidal nevus suspicious for melanoma?
blurry va, loss of vision
>5DD in size
Lipofuscin --> indicated cell death and metabolic activity
Absence of surface drusen on a thick lesion
Serous RD
Closer to optic nerve
Choroidal nevus appears how on imaging
A/B scan: localized flat lesion with *high acoustic reflectivity*
OCT: elevation but no subretinal fluid (+)thinning of overlying choriocapillaris
FAF: LP to differentiate nevus from melanoma
FA: nevi are avascular and pigmented, surface drusen hyperfluorescence
ICGA: useful for choroidal lesions
Differential for a choroidal nevus includes:
Melanocytoma of choroid
Small melanoma
Choroidal metastasis
CHRPE
CHRPE
hyperpigmented lesion within the RPE, sharp borders
OCT: shows overlying retinal thinning and PR loss, shadowing below the CHRPE. Lacunae in CHRPE will show thinner RPE and reverse shadowing
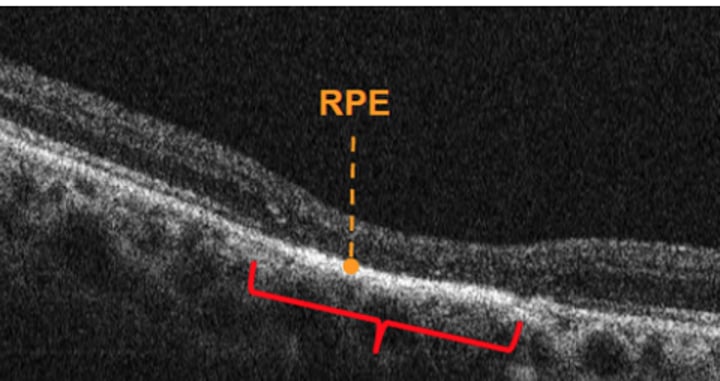
Amelanotic choroidal nevus differential includes:
Amelanotic choroidal melanoma
Choroidal cavernous hemangioma
Choroidal metastasis
Choroidal osteoma
Hypopigmented CHRPE
What is the most common primary malignant intraocular tumor?
choroidal melanoma
Choroidal melanoma
malignant tumor of melanocytes in choroid (middle aged blue eyes) --> asymptomatic
-Frequently have lipofuscin on surface
Shape: subretinal, dome shaped, elevated mass
Exudative RD common
B-scan: mushroom/button-shirt appearance when melanoma breaks through bruch's membrane
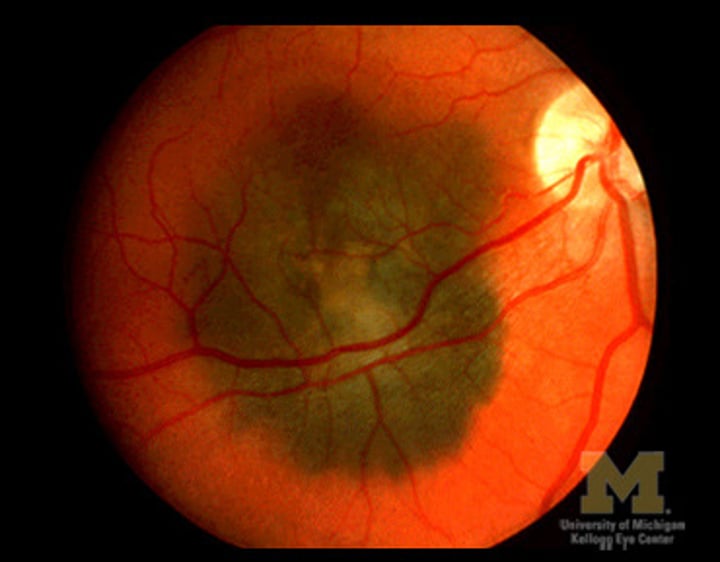
How does a choroidal melaona appear on imaging?
B-scan: hollow collar-button configuration, dome
A-scan: low to medium acoustic reflectivity
OCT: shaggy PRs, mean thickness 1025um
FAF: lipofuscin/ hyperautofluorescence
ICGA: see feeder vessels and extent of tumor
MRI
Fine needle aspiration biopsy
What are two conditions that present with shaggy photoreceptors?
choroidal melanoma
CSCR
Differential for choroidal melanoma
Choroidal nevus
Choroidal metastasis
CHRPE
Circumscribed choroidal hemangioma
RPE hyperplasia
BDUMP
Choroidal osteoma
Choroidal pigmented lesions can be grouped into what 3 categroies?
1. clearly nevi --> small flat lesions that are <2.5mm thick
2. Intermediate lesions --> pigmented choroidal lesions that are mildly elevated
3. Clearly melanomas: dome/mushroom shaped lesions >2.5mm thick
To Find Small Ocular Melanomas- Using Helpful Hints Daily
T- thickness >2mm
F- subretinal fluid
S- symptomatic
O- orange pigment (lipofuscin)
M- margin of tumor 3.0mm or less from disc
UH- ultrasound hollow
H- halo absent
D- drusen absent
To Find Small Ocular Melanoma Doing IMaging
Thickness >2mm (on ultrasound)
Fluid (subretinal on OCT)
Symptoms
Orange pigment
Melanoma hollow (B scan)
Diameter >5mm
What are the 3 most important things for detecting small melanomas?
>2mm thickness on ultrasound
Subretinal fluid on OCT
Orange pigment on FAF
Management of Typical Nevus vs. Suspicious
Typical: baseline photos, OCT, RTC 4 mo then q6mo PRN
Suspicious: photos, OCT, B-scan, RTC q3 mo
*If 3+ features are present, lesion is likely a melanoma*
Management of choroidal melanoma
Referal to ocular oncology
-aim is to prevent metastatic disease and blind/painful eye
Tx: plkaque radiotherapy, thermotherapy, aura-011 nanoparticle, enucleation
Plaque radiotherapy
tumor<20mm in diameter, vision is saveable
-tx of choice works well w/ prophylactic avastin injections
Transpupillary Thermotherapy
Infrared laser to induce tumor death by hyperthermia
-selected small, pigmented tumors especially near ONH or fovea
Aura-011 Nanoparticle Therapy
Intravitreal injection of viral-like nanoparticle that is reactive to light for tx of small choroidal melanoma that show signs of activity
-laser light shone into eye causing necrosis of melanoma and an immune response --> tumor control 70%
Side effects: A/C and vit inflammation
Radiation Retinopathy
may develop following tx of intraocular tumors by plaque therapy(bracytherapy) or external beam irradiation
-can also occur with any radiation to head and neck
-dose dependent (6mo-3yrs after) endothelial cell damage w microvascular changes/capillary occlusion
*looks like diabetic retinopathy*
Mgmt: Anti-VEGF/Steroid for ME, PRP for neo
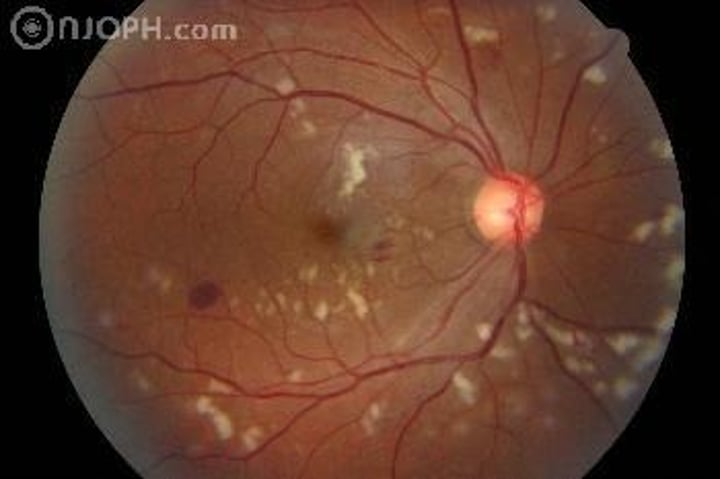
Radiation Retinopathy signs in chronological order
Capillary occlusion w/ collaterals and MA's
-severe capillary non-perfusion
-Retinal edema/exudates
-CWS/FSH/ papillopathy
-Proliferative retinopathy
COMS (Collaborative Ocular Melanoma Study) and results
1. Compared the effectiveness of brachytherapy to enucleation for med size choroidal melanomas
- No difference in 5yr morality
2. enucleation w and without preop external beam radiotherapy for large choroidal melanomas
- does not improve survival
3. small melanomas (UHHD)
- accuracy of clinical dx of choroidal melanoma is excellent
New findings of prognosis for choroidal melanomas
larger size = poorer prognosis
genetic predictors
ImmTAC for metastatic choroidal melanoma w/weekly infusion
Most common sites from which you get choroidal metastasis?
Lung
Breast
Where to look when trying to detect metastasis from the choroid into the body?
liver (palpable enlargement)
____________ is most common site for uveal metastases (90%)
Choroid (pt survival is poor 8-12mo)
Metastatic Choroidal Tumors
Fast growing creamy white placoid, oval at post pole
Multifocal deposits in some
-2ndary exudative RD common
Melanoma appears how on testing?
B-scan: diffuse choroidal thickening
A scan: med to low reflectivity
FA: early hypo with late stain
ICGA: early hypo
FAF: hypo tumor, hyperFAF of overlying lipofuscin and subretinal fluid
OCT:
Metastasis appears how on testing compared to melanoma?
B-scan: denser
A-scan: higher reflectivity
FA: dilated ret capillaries
ICGA: early hypo
FAF: brown color to lipofuscin
OCT: + lumpy bumpy appearance of tumor, (+) SRF, (+)shaggy PRs
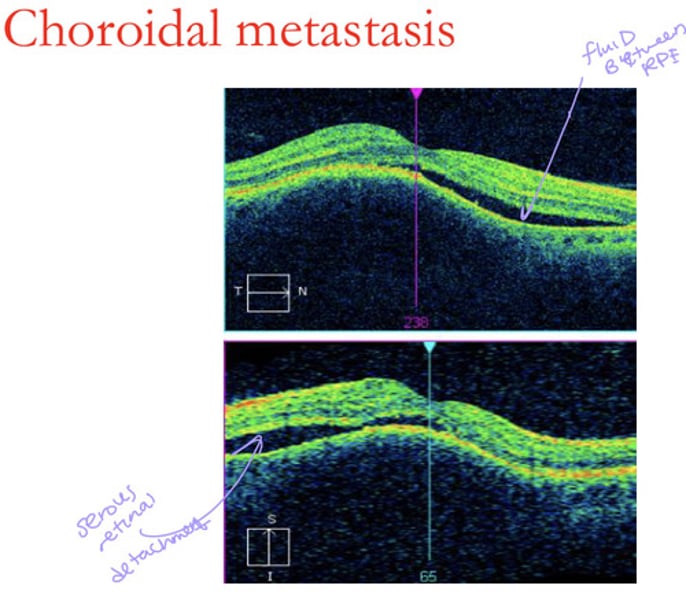
How does a choroidal metastasis appear on OCT?
lumpy bumpy tumor
Subretinal fluid
Shaggy PRs
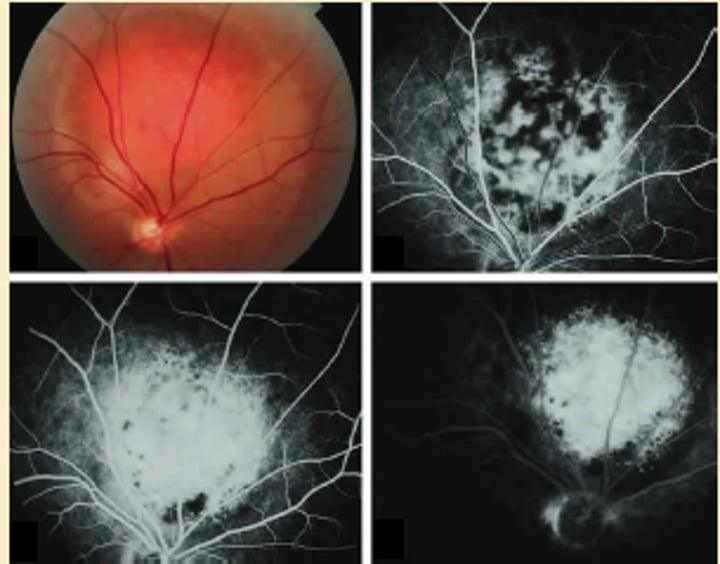
Choroidal Hemangioma
Benign Vascular tumor - solitary or diffuse congenital form
-oval mass same color as choroid, solid lesion w sharp anterior surface and choroidal thickening
-Rapid spotty hyperfluorescence on FA
ICGA
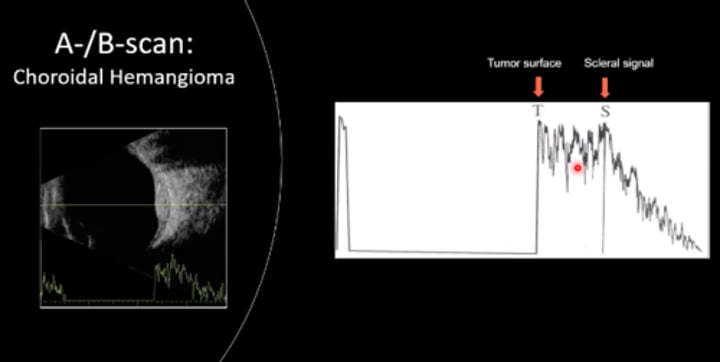
Choroidal hemangioma has what kind of internal reflectivity on A-scan?
High internal reflectivity
What kind of internal reflectivity does a choroidal melanoma have on A-scan?
Low internal reflectivity
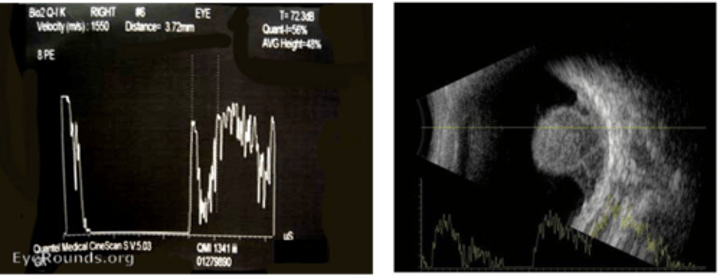
Choroidal hemangioma appears how on OCT?
Dome shaped --> does not compress the choriocapillaris
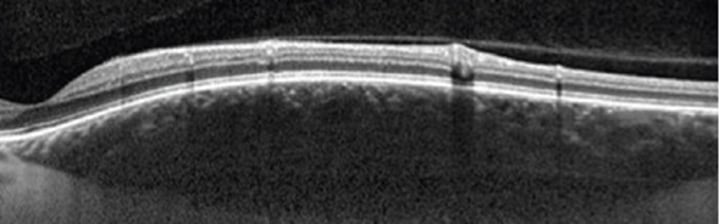
Melanocytoma
Rare unilateral pigmented females, heavy pigment nevus on or near ONH
-asymptomatic, can cause ONH dysfunction or become malignant w VF defects
No tx required
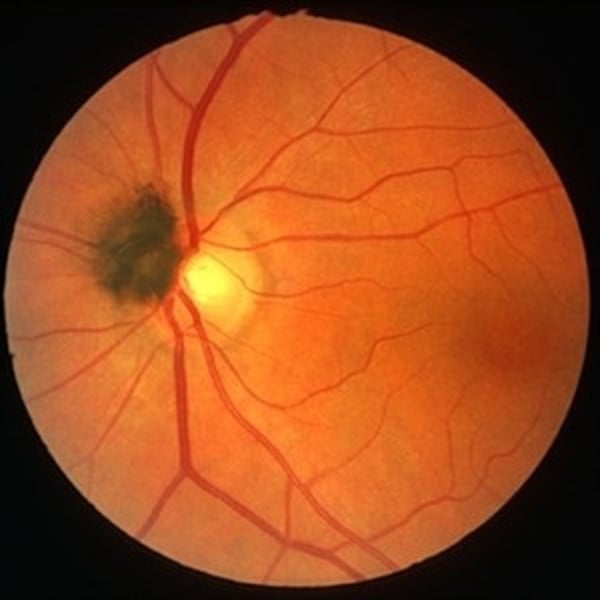
Choroidal Osteoma
VERY RARE women 20-30s, benign slow growing tumor
-tumor of mature bone w/ overlying RPE atrophy
-gradual visual impairment
Signs: peripapillary/macular region
Tx: none
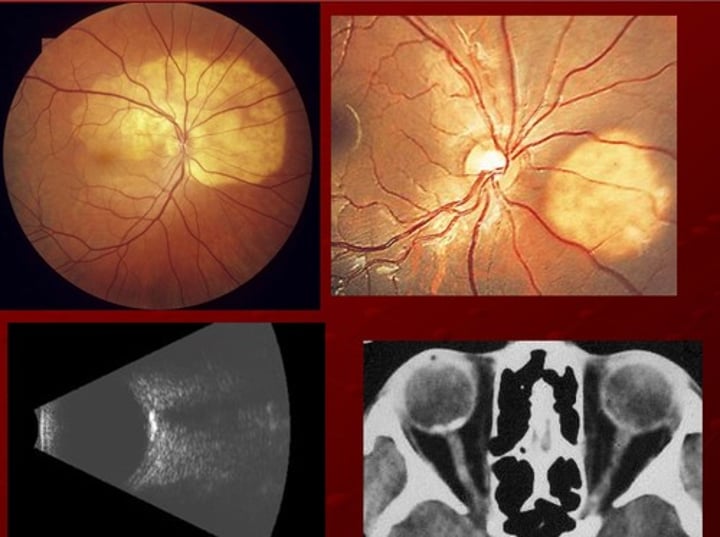
How does choroidal osteoma appear on imaging?
FA: irregular, diffues hyper
ICGA: early hypo w late staining
B-scan: very dense, highly reflective bc bone with shadowing
CT scan: bone like features
BDUMP (Bilateral Diffuse Uveal Melanocytic Proliferation)
Rare 50-80s with systemic malignancy
- paraneoplastic syndrome w diffuse thickening of entire uvea and multiple elevated tumors
-vit and A/C cells
Tx: detection of malignancy, no tx for ocular tumors
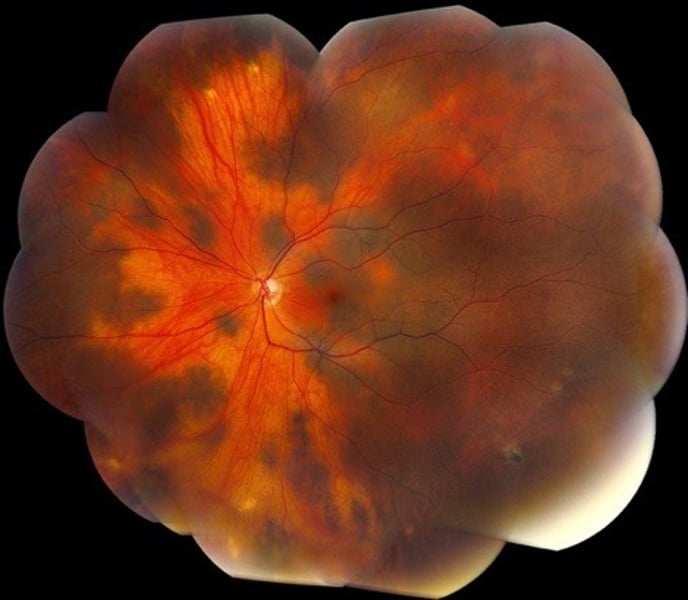
How does BDUMP appear on B-scan and FA?
B-scan: diffuse choroidal thickening
FA: masking background fluorescence by pigmented tumors, patchy hyper of RPE
Choroidal Effusion (choroidal detachment)
"kissing choroidals" on Bscan
1. Serous: release of fluid into the suprachoroidal space
2. Hemorrhagic: blood from choroidal vessel rupture
Tx: referral back to surgeon or retina
Serous choroidal effusion is typically caused by a complication of?
glaucoma surgery (hypotony)
painless no vision change (unless on vaxis), low IOP
Choroidal effusion appears how on B-scan?
"kissing choroidals"
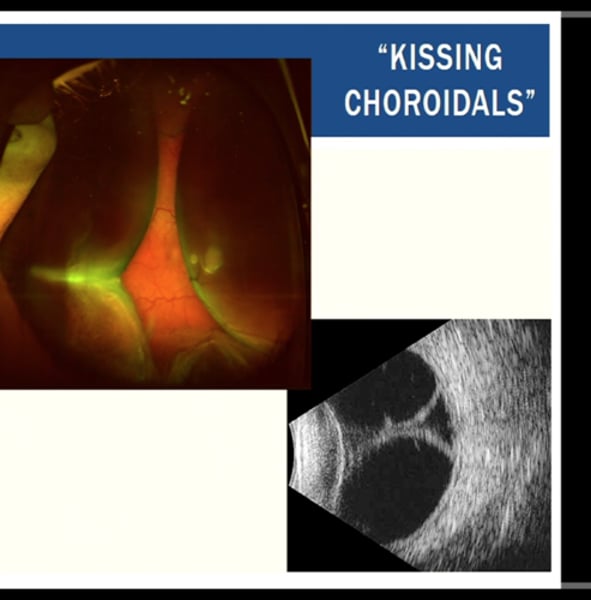
Hemorrhagic choroidal effusion is caused by
occurs during surgery or after trauma commonly in old people
-sudden onset painful decreased VA, elevated IOP
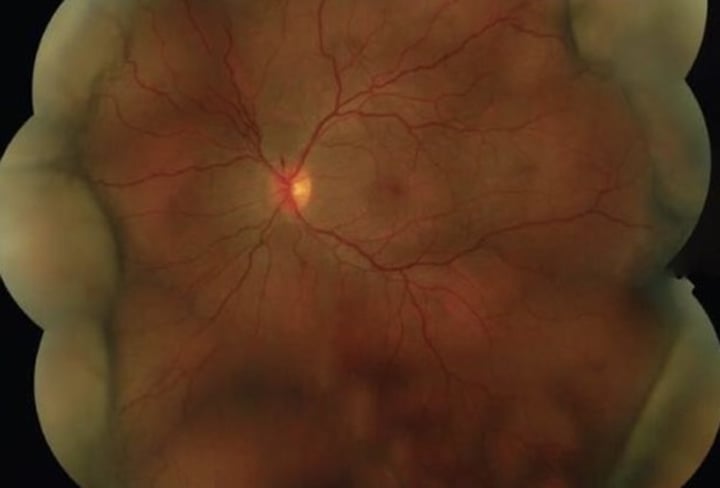
Choroidal folds
grooves involving the inner choroid, Bruchs and RPE
-retinal vessels not apart of
-classic appearance of alternating yellow/dark bands in retina
What are the causes for choroidal folds?
THIN RPE
Tumor
Hypotony
Inflammation
Neovascularization
Retrobulbar mass
Papilledema
Extraocular hardware-scleral buckle
Retinal folds
involve superficial layers of retina
-the unerlying RPE and choroid are not folded
-caused by ERM, Post uveitis, proliferative vitreoretinopathy
Ocular Embryology
week 4 gestation two optic pits form --> form hollow optic vesicles --> optic stalks --> small vessels penetrate fetal groove and form hyaloid artery and tunica vasculosa lentis --> glial cells form sheath --> adult vestiges are CRA/CRV
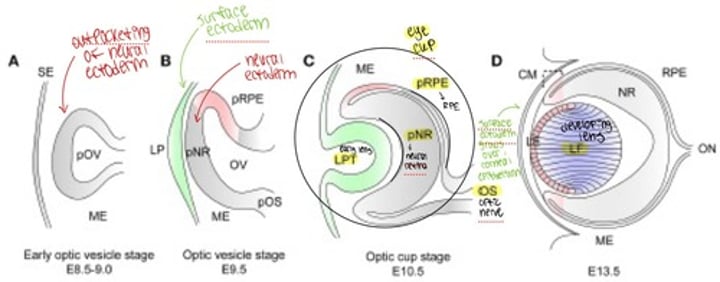
ONH is continuous with the _________________
brain (subarachnoid space and CSF)
Sclera is continous with the _____________ posteriorly
dura mater
What vessels feed the choroid, circle of Zinn, and arterial circles?
Distal SPCAs feed choroid
Paraoptic SPCAs make up circle of Zinn
Long PCAs fill arterial circles
Normal healthy ONH has what parameters?
1.7mm vertical
1.5mm horizontal
Smooth borders 360
Flat
Rose colored
distinct borders
Peripapillary crescents are usually found where?
temporal ; represent a misalignment of several layers of retina/choroid/sclera
Choroidal crescents
RPE has not abutted the optic disc so underlying RPE or choroid shows through
-darker than retina
Scleral crescent
Neither RPE or choroid abut the optic disc so underlying white sclera underneath shows through
-lighter in color
Peripapillary Atrophy (PPA)
atrophy of retinal tissue surrounding optic nerve
-alpha zone: hypo and hyper pigmented areas
-beta zone(inner): RPE and choriocapillaris are absent/atrophied
Beta zone PPA is more commonly associated with _____________________
glaucoma
Posterior Staphyloma
acquired outpuching of posterior retina near ONH (may extend to macula) seen in very high myopes due to the stretching and increased axial length --> weakens sclera and IOP pushes is out
-produces an enlarged blind spot
-Monitor --> no tx unless CNVM
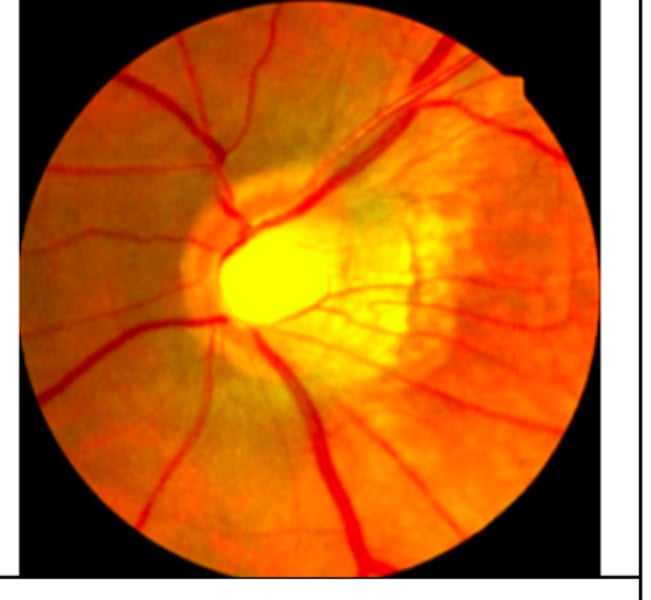
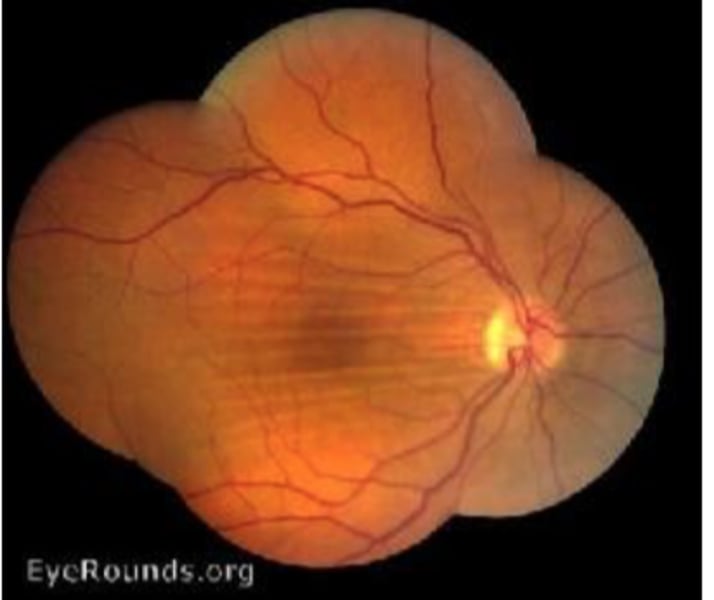
Optic nerve coloboma
incomplete closure of embryonic choroidal fissure- usually inferior
- associated with staphyloma or other colobomas(kidney) and Serous detachments
Clinic: white oval area where disc appears absent inferiorly
- increased blind spots, arcuates, scotoma
(+)APD
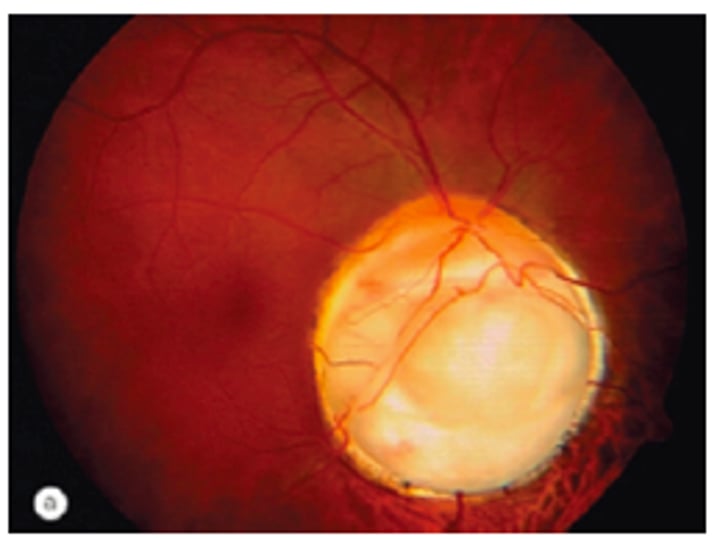
Morning Glory Disc
Unilateral Female
Funnel-shaped optic nerve that looks slightly pushed in with peripapillary pigment changes
(+)APD and 35% association with serous RD
- need full CNS and endocrine eval