Chapter 4
0.0(1)
0.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
1
New cards
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome
AIDS
2
New cards
ALT
Alanine aminotransferase
3
New cards
Antibody to hepatitis B core antigen
anti-HBc
4
New cards
anti-HBs
Antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen
5
New cards
Antibodies to HCV (Hepatitis C virus)
anti-HCV
6
New cards
ASD
Adult and Adolescent Spectrum of HIV Disease
7
New cards
Annual standardized ratio
ASR
8
New cards
ATL
Adult T-cell leukemia
9
New cards
Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma virus
ATLL
10
New cards
ATPase
Adenosine triphosphatase
11
New cards
Blood group antigen-binding adhesion
BabA
12
New cards
BLV
Bovine leukemia virus
13
New cards
Body mass index, which is a person’s weight / height. BMI = kg/m2
BMI
14
New cards
bp
Base pair
15
New cards
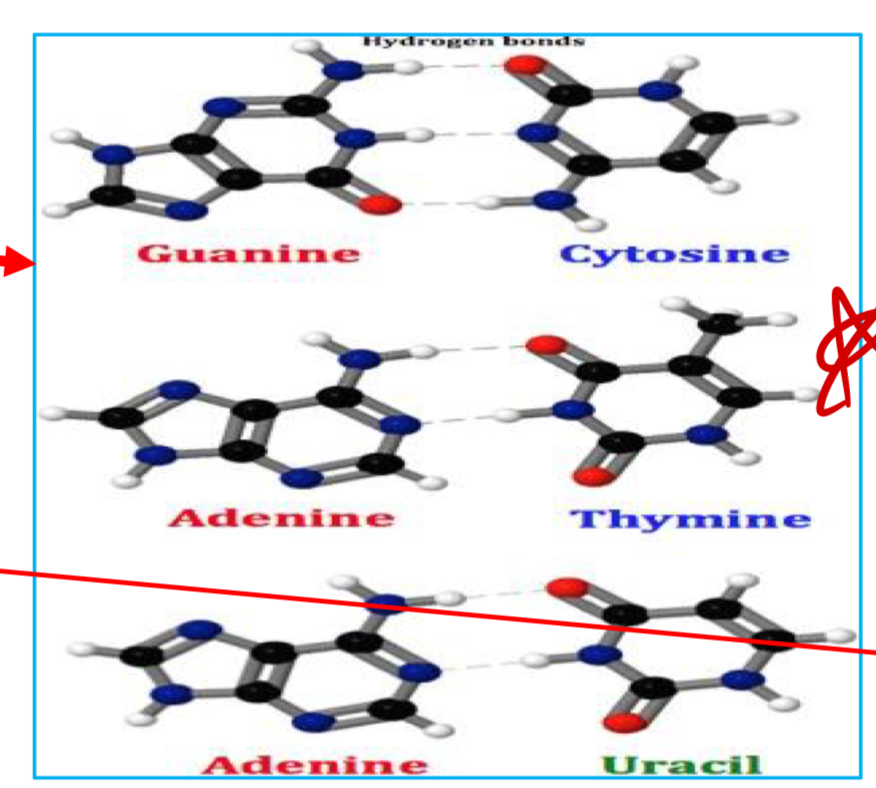
Base pair
16
New cards
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
\
\
cAMP
17
New cards
CCA
Cholangiocarcinoma
18
New cards
Covalently closed circular DNA
ccc DNA
19
New cards
SCF
Soluble complement-fixing antigen (to detect the presence of specific antibodies or antigens)
20
New cards
What SCF do?
(to detect the presence of specific antibodies or antigens)
21
New cards
Confidence interval
CI
22
New cards
CLL
When most of the cancer cells are in the bloodstream and the bone marrow, disease is referred to also Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
23
New cards
SLL
small lymphocytic lymphoma Also When the cancer cells are located mostly in the lymph nodes
24
New cards
Cytomegalovirus
CMV
25
New cards
Cryo-EM
Cryo-electron microscopy
26
New cards
Campylobacter pylori
C.pylori
27
New cards
Clonorchis sinensis a liver parasite that humans can get by eating raw or undercooked fish
C. Sinensis
28
New cards
CTAR
C-terminal activation region
29
New cards
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte
CTL
30
New cards
Cytotoxic T cells (Cytotoxic T lymphocytes)
CTLs
31
New cards
DLBCL
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
32
New cards
Dyad symmetry, which is method of E. coli. Where the when it terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). transcription termination in Regions of dyad symmetry in stall .
DS
33
New cards

What’s this
Dayd symmetry
34
New cards
EBV
Epstein-Barr virus
35
New cards
.
EBV
36
New cards
Extracellular matrix
ECM
37
New cards
EGF
Epidermal growth factor
38
New cards
Epidermal growth factor receptor
EGFR
39
New cards
EIAs
Enzyme immunoassays
40
New cards
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, The assay uses a solid- phase type of enzyme immunoassay to detect the presence of a ligand in a liquid sample using antibodies directed against the protein to be measured.
ELISAs
41
New cards
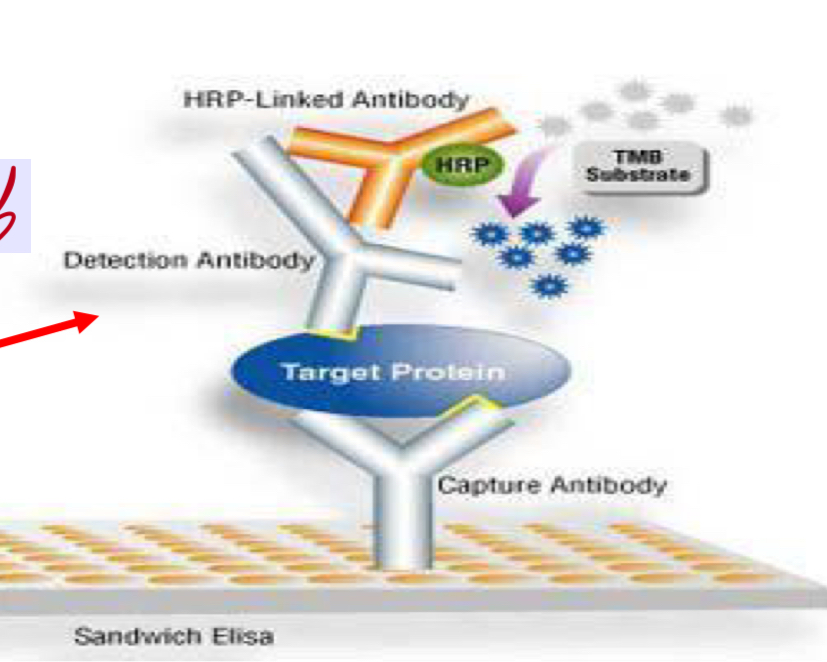
.
to detect the presence of a ligand in a liquid sample using antibodies directed against the protein to be measured.
42
New cards
Epithelial to mesenchymal transdifferentiation which contributes pathologically to fibrosis and cancer progression.
\
\
EMT
43
New cards
GLUT1
Glucose transporter 1
44
New cards
Highly active antiretroviral therapy
\
\
HAART
45
New cards
HAV
Hepatitis A virus
46
New cards
Hepatitis B virus
HBV
47
New cards
HCV
Hepatitis C virus
48
New cards
Hepatocellular carcinoma
HCC
49
New cards
cholesterol is known as the "good" cholesterol because it helps remove other forms of cholesterol from your bloodstream.
\
\
High-density lipoprotein (HDL):
50
New cards
Higher levels of HDL means
cholesterol are associated with a lower risk of heart disease.
51
New cards
HGF
Hepatocyte growth factor
\
\
52
New cards
Human herpesvirus
HHV
53
New cards
HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus
\
\
54
New cards
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
HNSCC
55
New cards
HPV
Human papillomavirus, a virus with subtypes that cause diseases in humans ranging from common warts to cervical cancer.
56
New cards
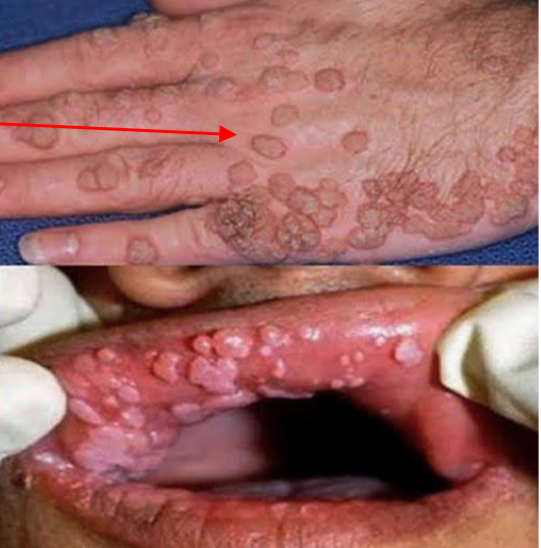
HPV
57
New cards
Hepatic stellate cells
HSCs
58
New cards
HTLV-1
Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1
59
New cards
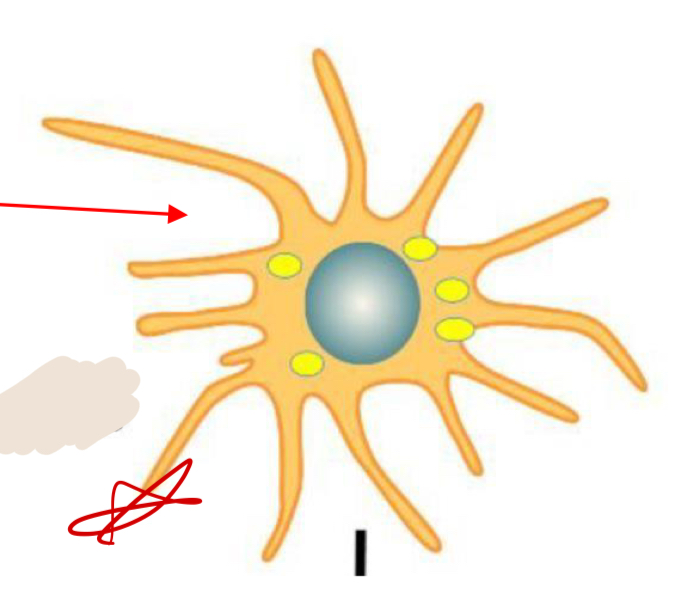
HSC
60
New cards
ICC
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
61
New cards
Insulin-like growth factor is a hormone that, along with growth hormone (GH), helps promote normal bone and tissue growth and development.
IGF
62
New cards
IgR
Immunoglobulin receptor
63
New cards
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
iNOS
64
New cards
KSHV (also known as HHV-8)
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus a type of cancer that forms in the lining of blood and lymph vessels.
65
New cards
Lymphocryptovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales.
LCV
66
New cards
LDLR
bad” cholesterol, makes up most of your body's cholesterol. High levels of LDL cholesterol raise your risk for heart disease.
67
New cards
Gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma is a clonal B-cell tumour.
\
\
MALT
68
New cards
MHC
Major histocompatibility complex which is a group of genes that code for proteins found on the surfaces of cells that help the immune system recognize foreign substances.
69
New cards
miRNA
MicroRNA is a small single stranded non-coding RNA
70
New cards
Microtubule-organizing center structure found in eukaryotic cells from which microtubules
MTOC
71
New cards
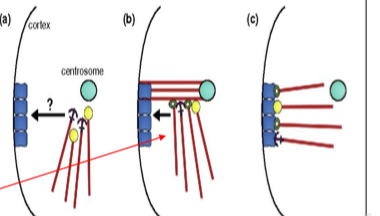
structure found in eukaryotic cells from which microtubules
72
New cards
NAFLD
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
73
New cards
Origin of replication
Ori
74
New cards
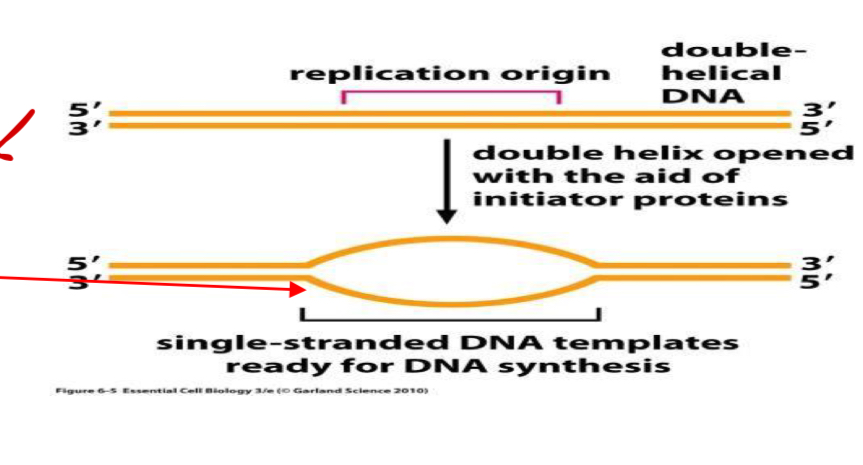
Origin of replication
75
New cards
Pase
Polymerase
76
New cards
Peripheral blood mononuclear cell
PBMC
77
New cards
PCR
Polymerase chain reaction
78
New cards
Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia
PIN
79
New cards
PKC
Protein kinase C
80
New cards
Retinoblastoma protein
\
\
pRB
81
New cards
PRKAR1α
Protein kinaseA regulatory subunit 1α
82
New cards
Primate T-lymphotropic virus
\
\
PTLV
83
New cards
RT
Reverse transcriptase
\
\
84
New cards
Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results
\
\
SEER
85
New cards
tracks the incidence of and collects follow-up information on all previously diagnosed patients until their death.
SEER
86
New cards
SHBs
Small hepatitis B surface proteins
87
New cards
Safe Injection Global Network
SIGN
88
New cards
SIR
Standardized incidence ratio is used to determine if the occurrence of cancer in a relatively small population is high or low.
\
\
89
New cards
Simian immunodeficiency virus (retrovirus)
SIV
90
New cards
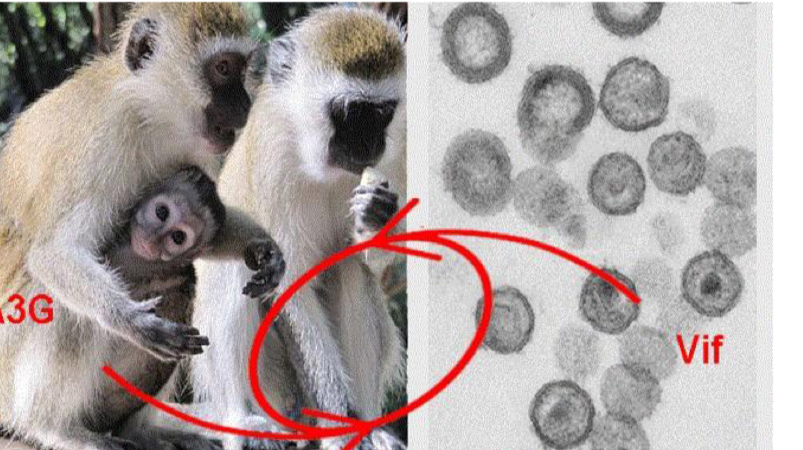
Simian immunodeficiency virus (retrovirus)
91
New cards
SNPs
Single nucleotide polymorphisms is a DNA occurring when a single nucleotide adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), or guanine (G\]) in the genome (or other shared sequence) differs between members of a species.
\
\
92
New cards
Sexually transmitted diseases
STDs
93
New cards
TNFR
Tumor necrosis factor receptor
94
New cards
is a protein receptors characterized by the to bind cells, which may be involved in inflammation-associated carcinogenesis.
TNF-receptor
95
New cards
TNF-α
Tumor necrosis factor-α responsible for a diverse range of signalling events within cells, leading to necrosis or apoptosis.
\
\
96
New cards
UVB
shorter wavelength and is associated with skin
97
New cards
longer wavelength and is associated with skin aging.
UVA
98
New cards
UV
Ultraviolet in general
99
New cards
Viral capsid antigens
VCA
100
New cards
vLDL
Very low-density lipoprotein is a type of bad cholesterol (liver), because it helps cholesterol build up on the walls of arteries.