Class 8 - Cooperation vrs. Competition
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Why is it important for organizations to grow?
To stay economically healthy
Belief non growth is stagnant & customers dont have demands met/go to competititors
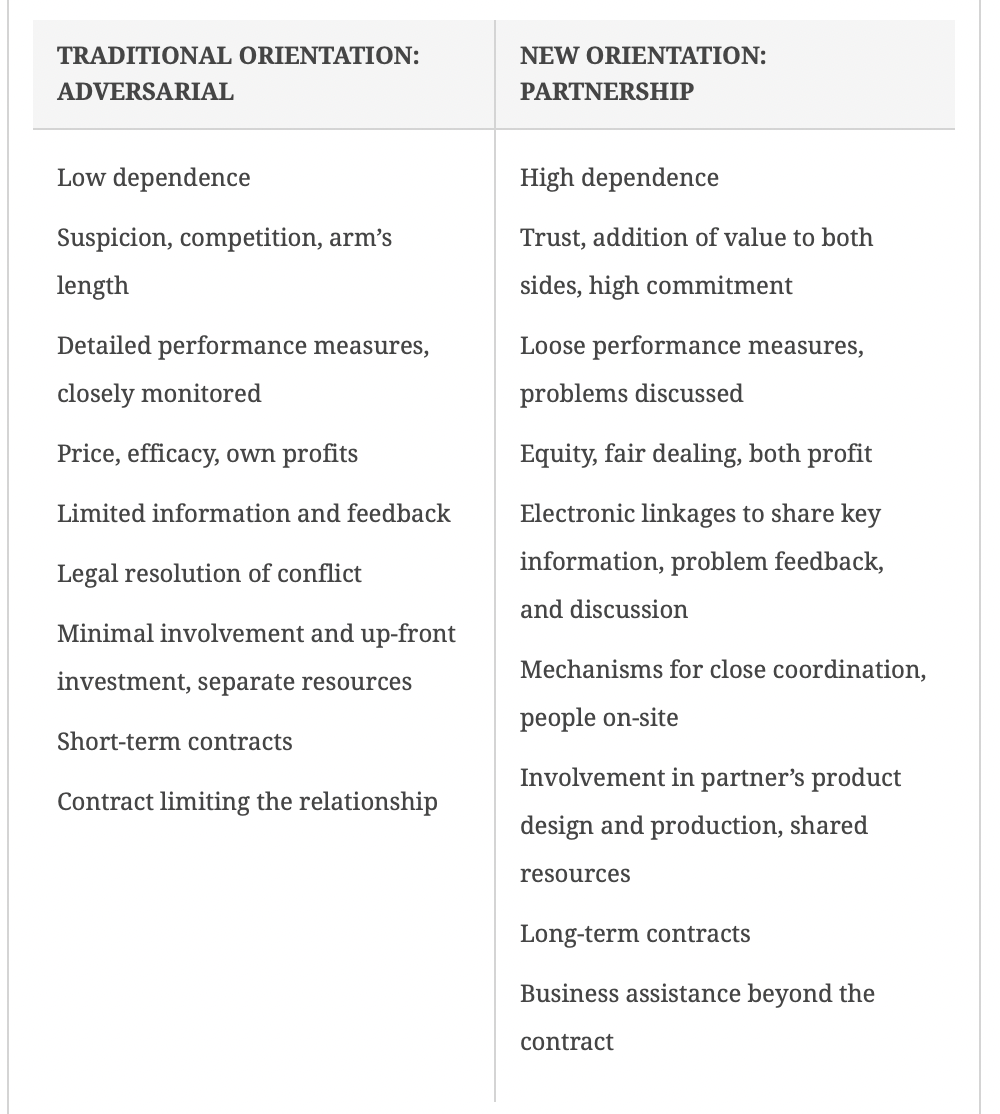
Competition causes people to act with (2)
Suspicion, keeping competition at arm’s length
Competition can affect a business by…(7)
Price of services/product
Efficiency
Own Profits
Limited info & feedback
Legal resolution of conflict
Short term contracts can limit relationships
Minimal involvement & up-front investment, separate resources
How is competition changing? (3)
Changing technology
New regulations
International competition (Corporate alliances are increasing)
Cooperation among organizations includes (8)
Trust - addition of value to both sides, high commitment
Equity - fair dealing, both profit
Electronic linkages to share key information, problem feedback & discussion
Electronic linkages to share key information, problem feedback & discussion
Mechanisms for close coordination, ppl on-site
involvement in partner’s product design & production, shared resources
long-term contracts
business assistance beyond the contract
Why collaborative networks? (4)
Share risks
Innovation, problem solving, performance
Entering global markets
Safety net
How to change adversaries to Partners (2)
Change in mind-set
From independence to interdependence and trust
Whats an example of Memetic Isomorphism?
-Ex. When all tech stores take sleek look of Apple stores
-Ex. All dessert places use insta walls/pastels for insta likes
Population Ecology focuses on
Diversity & adaptation w/in a population of orgs (set of orgs engaged in similar patterns of resource utilization & outcome)
Organizational Form:
Tech, structure, products, goals, personnel
Organizational niche
domain of unique environmental resources and needs
Population Ecology consists of: (3)
Variation → Selection → Retention
Competition involves (4)
-suspicion, competition, arm’s length
-Limited info & feedback
-Legal resolution of conflict
-Min involvement & up-front investment, separate resources
Competition can affect (3)
-Price
-Efficiency
-Own Profit
Competition has short-term contracts that can
limit relationships
How/Why is competition changing?(4)
-Technology advancements
-New regulations
-International competition
-Corporate Alliances
Cooperation can lead to
-trust, addition of value to both sides, high commitment
-equity, fair dealing, both profit
-electronic linkages to share key information, problem feedback and discussion
-mechanisms for close coordination, people on-site
-involvement in partner’s product design and production, shared resources
Cooperation can involve
-Long term contracts
-Business assistance beyond the contract
Why collab & build collaborative networks? (4)
• Share risks
• Innovation, problem solving, performance
• Entering global markets
• Safety net
How to create partners fr adversaries for Collaborative Networks:
• A change in mind-set
• From independence to interdependence and trust
Institutional Perspective is
organizations strive for legitimacy (the view that an organization’s actions are desirable, proper and appropriate) by trying to meet perceived expectations from the environment
(comprised of stakeholder norms and values)•
List the Rational, Events, Social Basis & an example for Mimetic
Rational: Uncertainty
Events: Innovation Visibility
Social Basis: Culturally Supported
Example: Benchmarking
List the Rational, Events, Social Basis & an example for Normative
Rational: Duty, Obligation
Events: Professionalism, Certification, accredition
Social Basis: Moral
Example: Accounting Standards
List the Rational, Events, Social Basis & an example for Coercive
Rational: Dependence
Events: Law, Regulation, Sanction
Social Basis: Legal
Example: Pollution Controls
Population Ecology for organizational form consists of
technology, structure, products, goals, personnel
Population Ecology for organizational niche consists of
Domain of unique environmental resources and needs
Inter-organizational Relationships
the relatively enduring resource transactions, flows, and linkages that occur among two or more organizations.
Organizational ecosystem
a system formed by the interaction of a community of organizations and their environment, usually cutting across traditional industry lines.
What is assumed in the traditional model of competition/
A distinct company is competing for survival & supremacy w other stand-alone businesses.
Why does traditional competition no longer exist?
Bc each org supports & depends on others to succeed/survive
orgs must co-evolve
Cooperation definition
the simultaneous engagement in both cooperative and competitive behaviours between two or more actors.
Managers within biz ecosystems must
learn to move beyond traditional responsibilities of corporate strategy and designing hierarchical structures and control systems
think about horizontal processes rather than vertical structures
please draw framework of interorg relationships
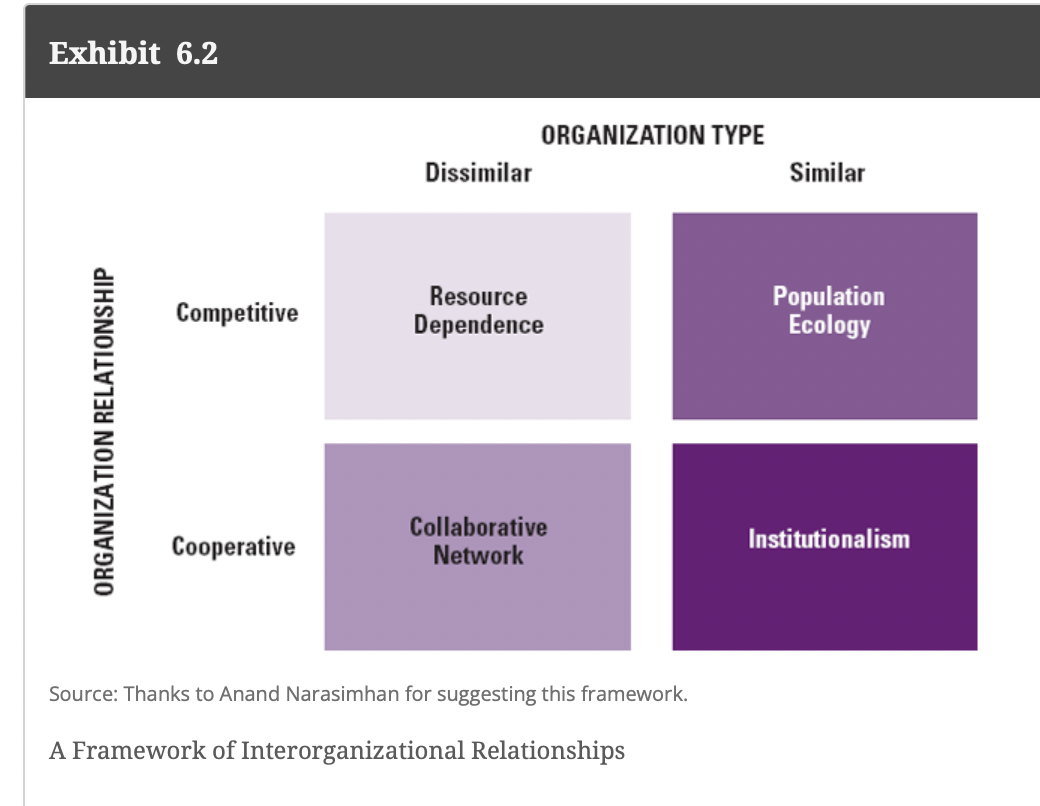
Ways that orgs can manoeuver resource dependance: (5)
adapt to or alter the interdependent relationship
Ex. purchasing ownership in suppliers, developing long-term contracts or joint ventures
use interlocking directorships
Ex. boards of directors include members of the boards of supplier companies
join trade associations to coordinate their needs
Sign trade agreements
Merge to gain resources
Collaborative Network Definition
an emerging perspective whereby organizations allow themselves to become dependent on other organizations to increase value and productivity for all.
Compare & contrast “adversarial“ vrs. Partnership
Population Ecology Perspective
a perspective in which the focus is on organizational diversity and adaptation within a community or population or organizations
Population
a set of organizations engaged in similar activities with similar patterns of resource utilization and outcomes
Organizational Form definition
an organization’s specific technology, structure, products, goals, and personnel.
Niche definition
a domain of unique environmental resources and needs.
Variation in population ecology …
appearance of new organizational forms in response to the needs of the external environment; analogous to mutations in biology
Selection in population ecology …
the process by which organizational variations are determined to fit the external environment; variations that fail to fit the needs of the environment are “selected out” and fail
Retention in population ecology
the preservation and institutionalization of selected organizational forms
Struggle of Existence
a principle of the population ecology model that holds that organizations are engaged in a competitive struggle for resources and fighting to survive.
Generalists
an organization that offers a broad range of products or services and serves a broad market.
Specialists
an organization that has a narrow range of goods or services or serves a narrow market.
Institutional perspective vs. Institutional environment
Perspective - a view that holds that, under high uncertainty, organizations imitate others in the same institutional environment.
Enviornment -norms and values from stakeholders (customers, investors, boards, government, etc.) that organizations try to follow in order to please stakeholders
Legitimacy definition
the general perception that an organization’s actions are desirable, proper, and appropriate within the environment’s system of norms, values, and beliefs.
institutional view also sees organizations as having two essential dimensions…
technical-the day-to-day work, technology, and operating requirements
institutional-part of the organization most visible to the outside public
Institutional Similarity definition
the emergence of common structures, management approaches, and behaviours among organizations in the same field
Mimetic Forces definition
under conditions of uncertainty, the pressure to copy or model other organizations that appear to be successful in the environment
Coercive Forces definition
external pressures such as legal requirements exerted on an organization to adopt structures, techniques, or behaviours similar to other organizations
Normative Forces definition
pressures to adopt structures, techniques, or management processes because they are considered by the community to be up-to-date and effective
What are the key differences b/w small & large organizations
Large Organizations:
Economies of scale, global reach, vertical hierarchy, mechanistic, complex, stable market, employee longevity, raises & promotions
Small Organizations:
Responsive, flexible, regional reach, flat structure, organic, simple, niche-finding, entrepeneurs
How was apple meant to be a hybrid (small/large org)/ keep start-up culture?
focusing the company’s strategy on one cohesive vision,
encouraging debate and eliminating passive-aggressiveness about ideas, and
setting up cross-disciplinary reviews of how the company would succeed.
life cycle definition
a perspective on organizational growth and change that suggests that organizations are born, grow older, and eventually die
Explain Organization life Cycle
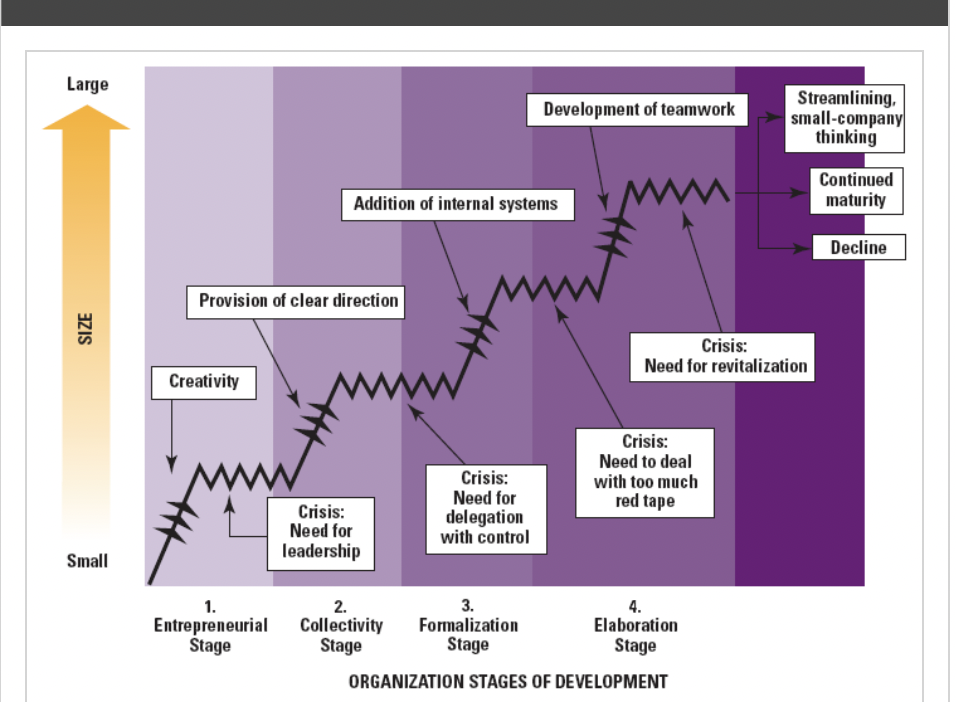
Describe the organization characteristics during all 4 stages of the life cycle:
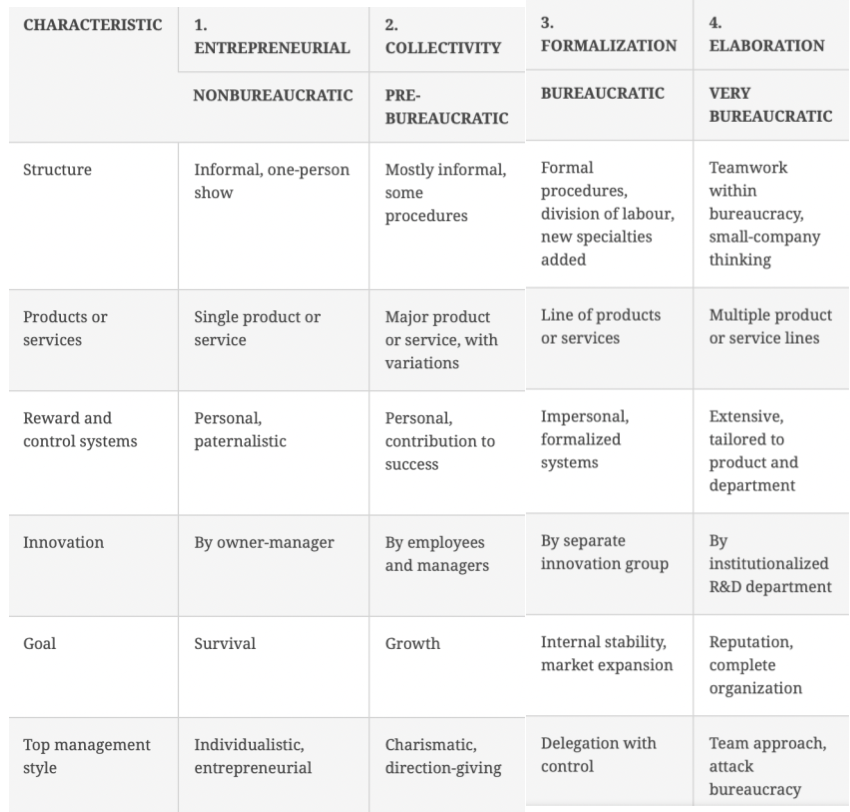
List the 6 demensions of bureaucracy:
Separate fr position holder
technically qualified personnel
hierarchy of authority
specialization & division of labour
rules & procedures
written communications and records
What is bureaucracy?
an organizational framework marked by rules and procedures, specialization and division of labour, hierarchy of authority, technically qualified personnel, separation of position and person, and written communications and records.
Formalization definition
the degree to which an organization has rules, procedures, and written documentation
Centralization definition
the level of hierarchy with authority to make decisions.
What is the relation of personnel ratios & bureaucracy?
Personnel ratios is a CHARACTERISTIC of bureaucracy, that includes admin, clerical, & professional support staff
Police/fire depts use what? to respond rapidly to emergencies?
Incident command system -developed to maintain the efficiency and control benefits of bureaucracy yet prevent the problems of slow response to crises.
Reducing bureaucracy can also be done by…
cutting layers of the hierarchy
keeping headquarters staff small → giving lower-level workers greater freedom to make decisions rather than burdening them with excessive rules and regulations.
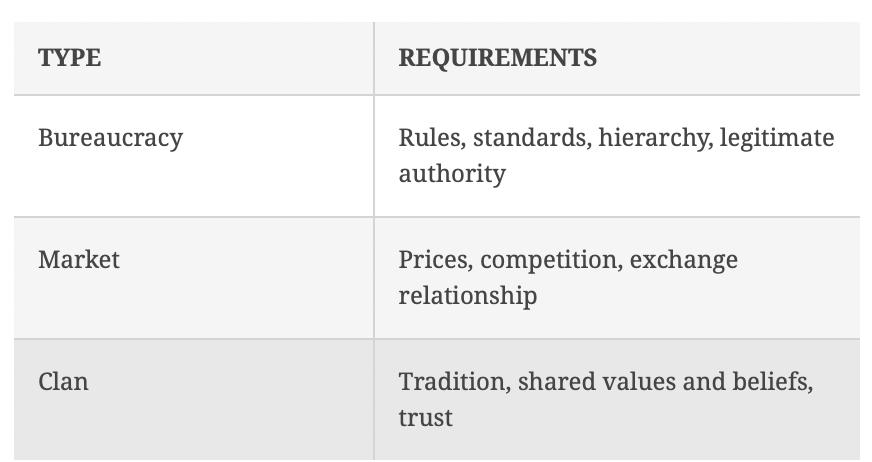
What are the 3 org control strategies & their requirements?
What are the types of authority ? (3)
Rational-legal authority
based on employees’ belief in the legality of rules and the right of those in authority to issue commands
Traditional authority
based in the belief in traditions and the legitimacy of the status of people exercising authority through those traditions.
Charismatic authority
based on devotion to the exemplary character or heroism of an individual and the order defined by them
Market control
situation that occurs when price competition is used to evaluate the output and productivity of an organization.
Clan Control
use of social characteristics, such as culture, shared values, commitments, traditions, and beliefs, to control behaviour
Organizations that use clan control require shared values and trust among employees
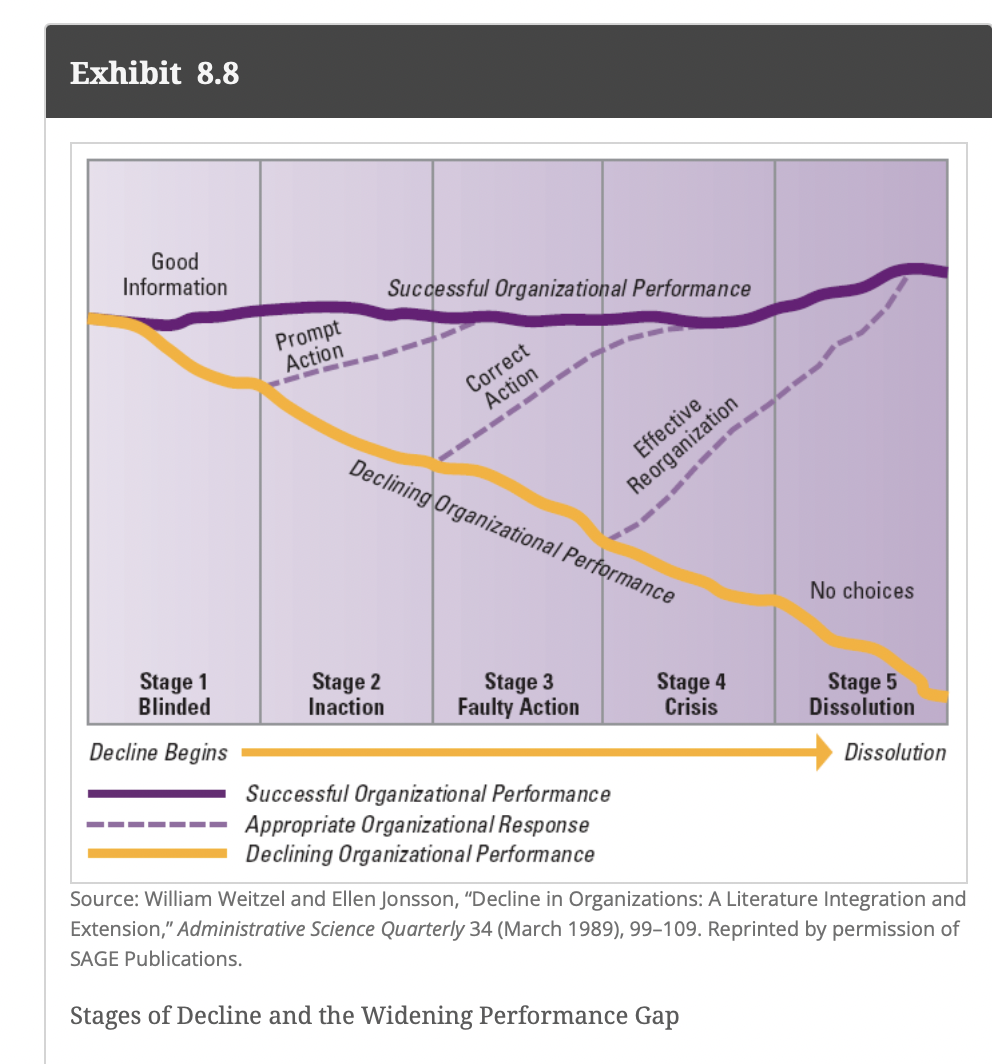
Define Organizational Decline
a condition in which a substantial, absolute decrease in an organization’s resource base occurs over a period of time
3 factors that contribute to organizational decline:
Organizational atrophy
when organizations grow older and become inefficient and overly bureaucratized. The organization’s ability to adapt to its environment deteriorates
Vulnerability
reflects an organization’s strategic inability to prosper in its environment
Environmental decline or competition
refers to reduced energy and resources available to support an organization. When the environment has less capacity to support organizations, the organization has to either scale down operations or shift to another domain
Model of org decline