Steroids Slide Set 1
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
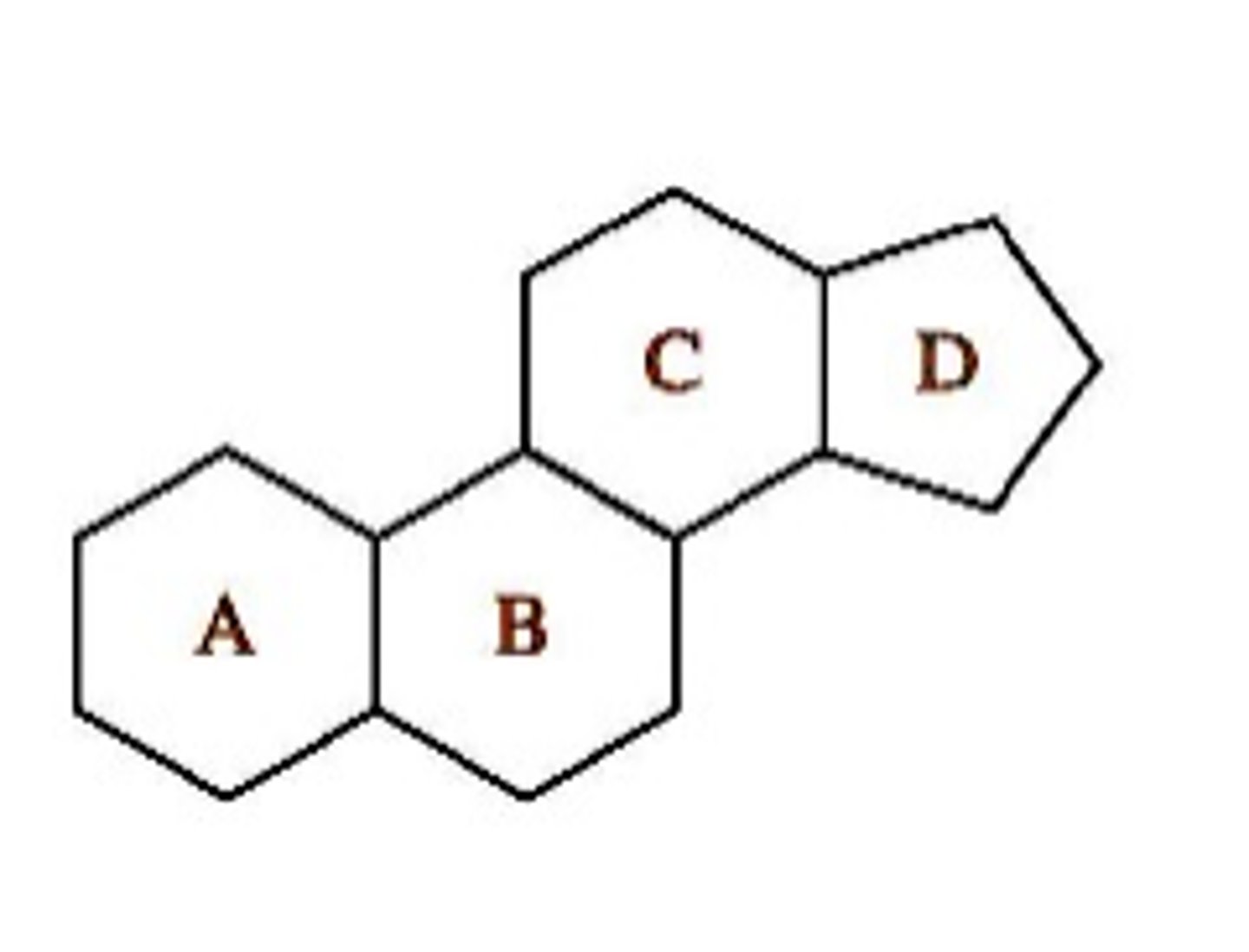
What is the basic steroid skeleton?
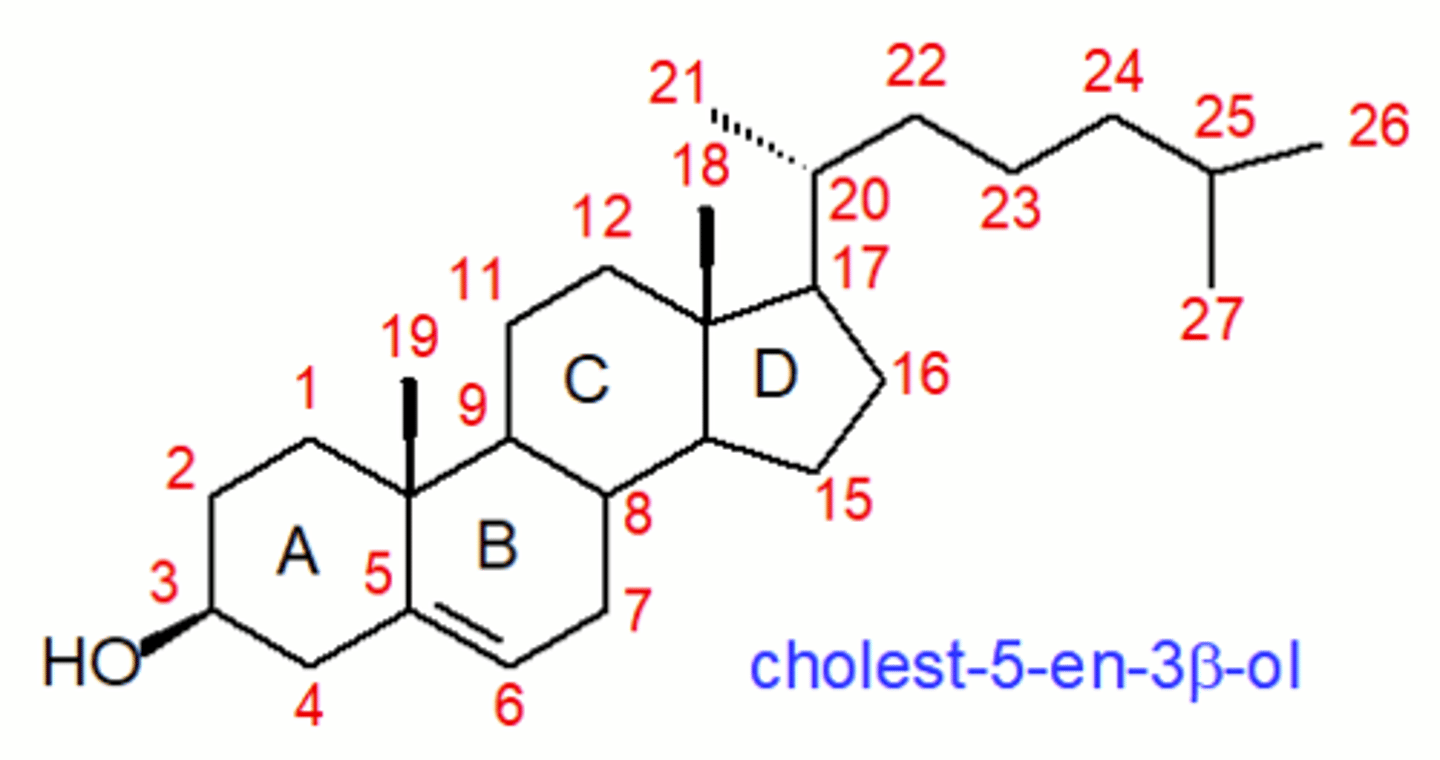
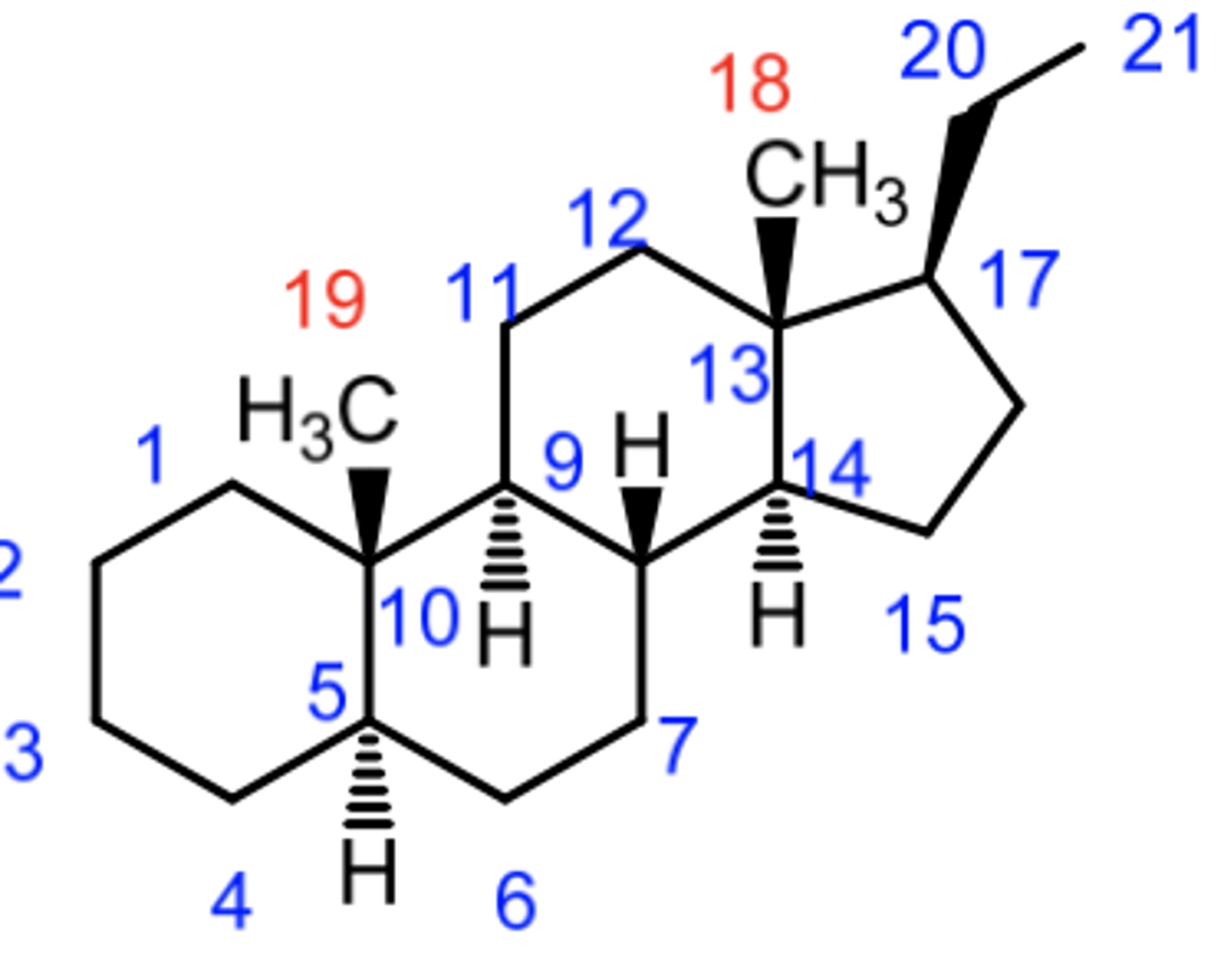
Take a minute and count the Carbons (up to 27) for Cholesterol
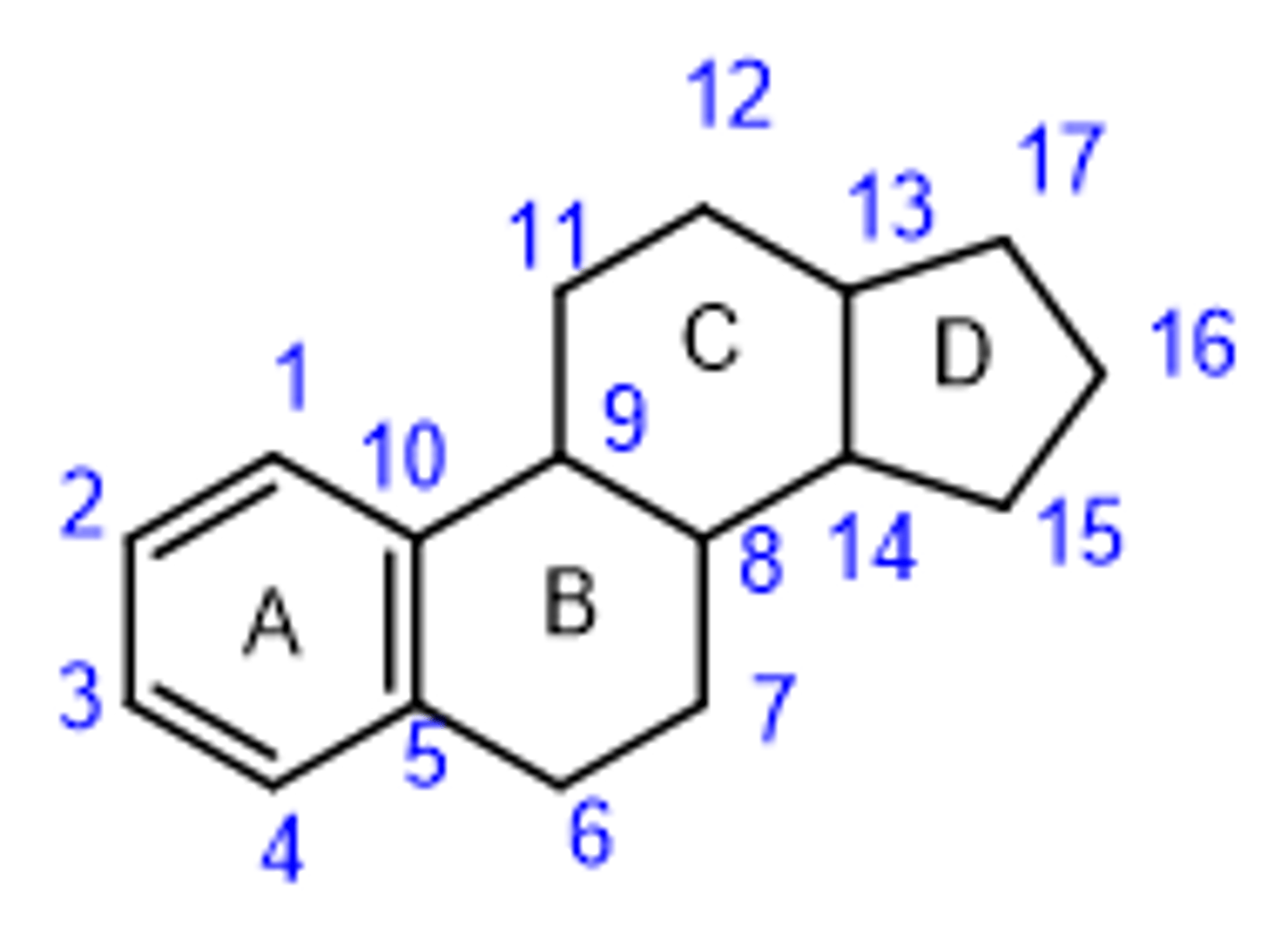
What is the basic estrogen structure? (defining features)
Look out for the aromatic ring!
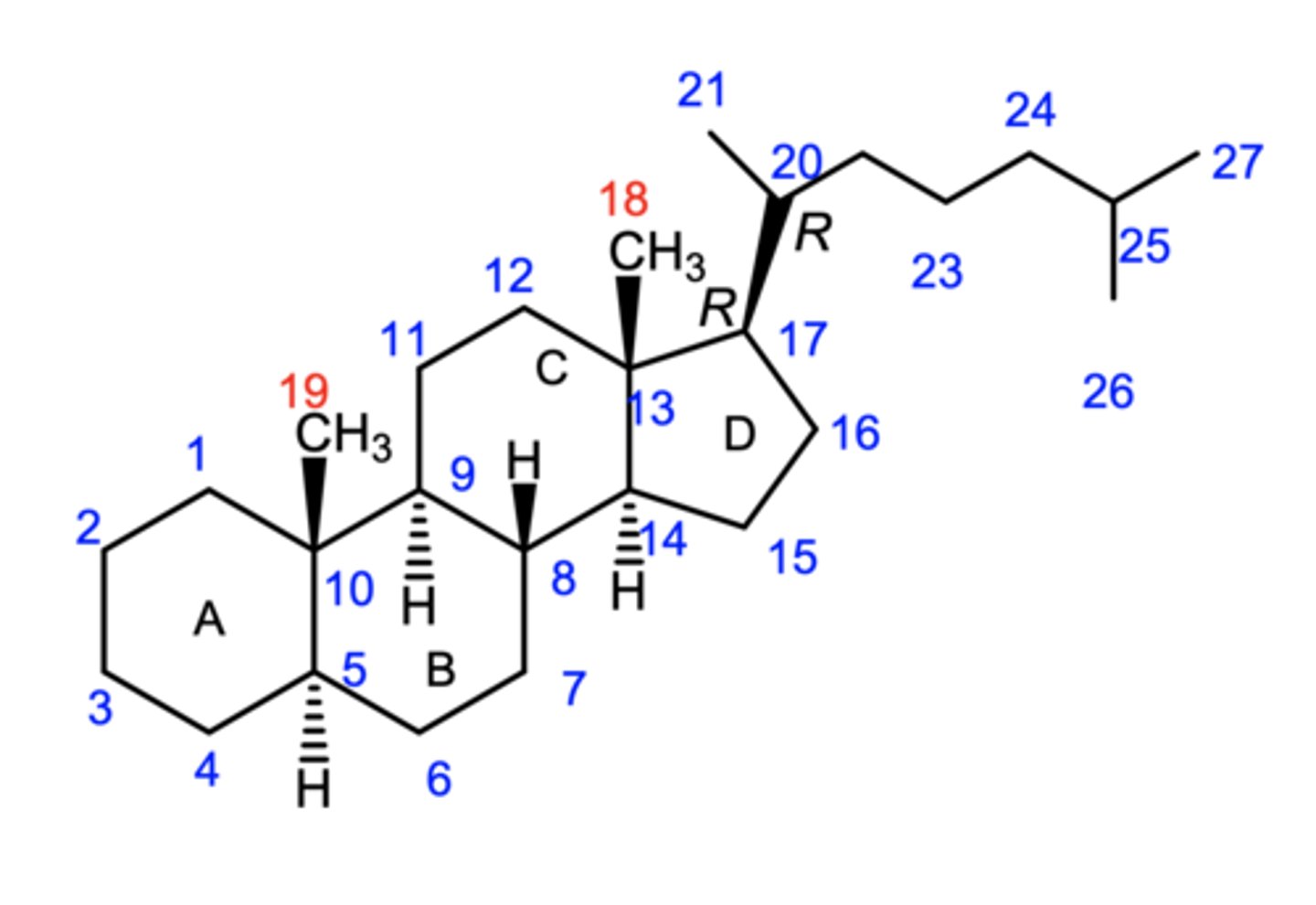
5a-cholestane
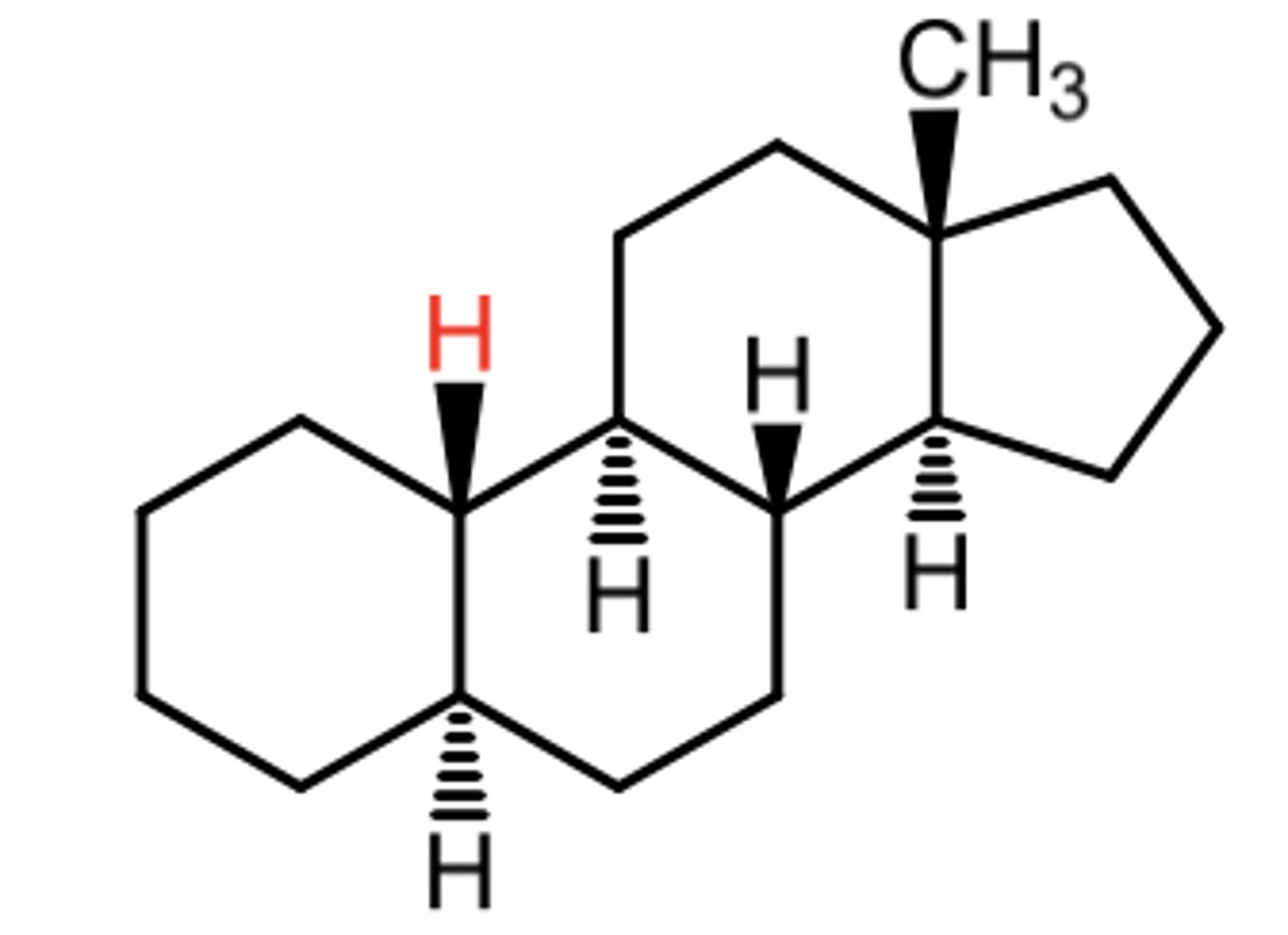
What does the "alpha" designation mean in a given steroid structure?
steroid nomenclature:
alpha = downwards (dotted lines)
https://iupac.qmul.ac.uk/steroid/3S01.html
What does the "beta" designation mean in a given steroid structure?
beta = UPwards (solid lines)
https://iupac.qmul.ac.uk/steroid/3S01.html
5a-androstane
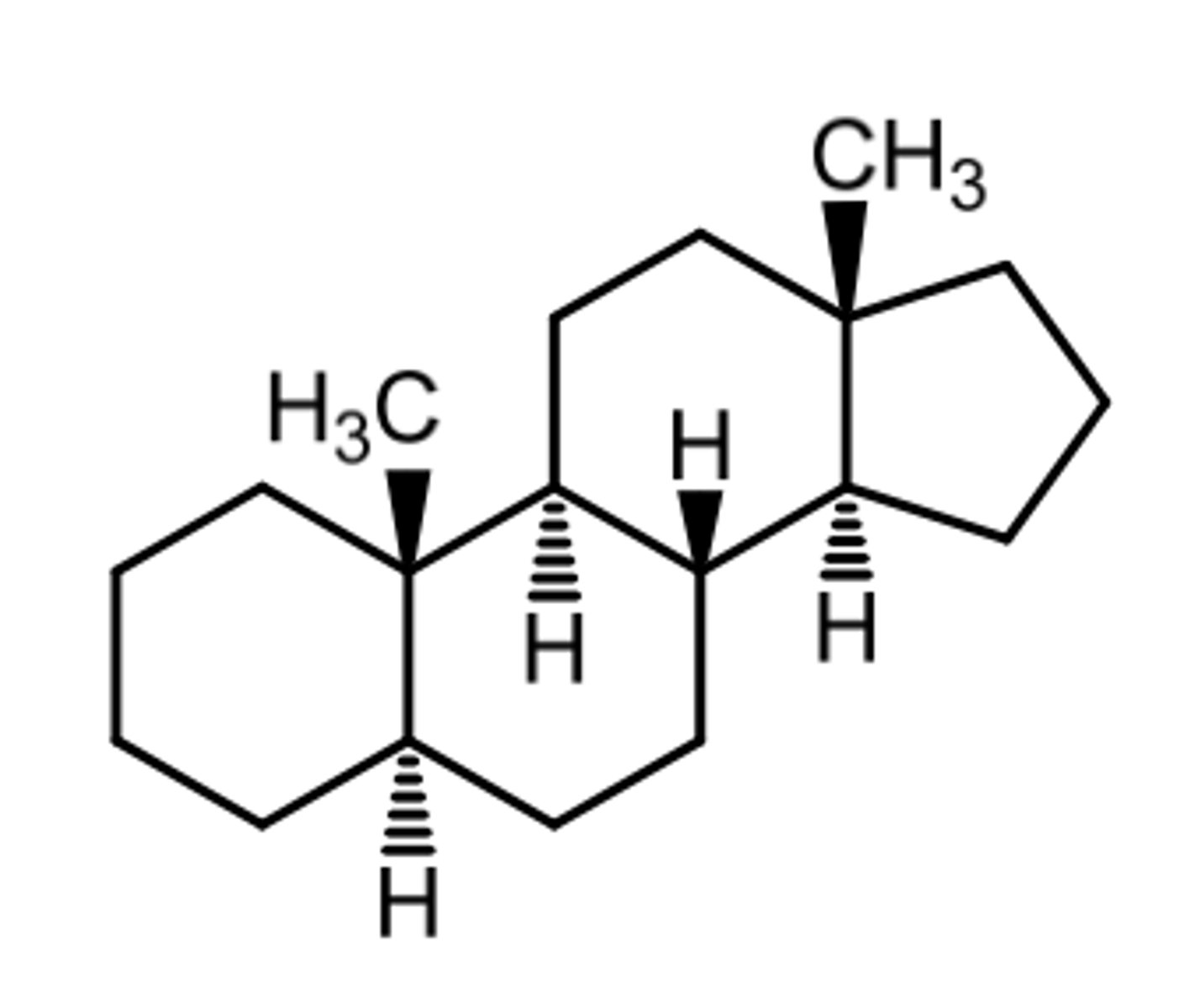
5a-pregnane
5a-estrane
5a-androst-8-ene
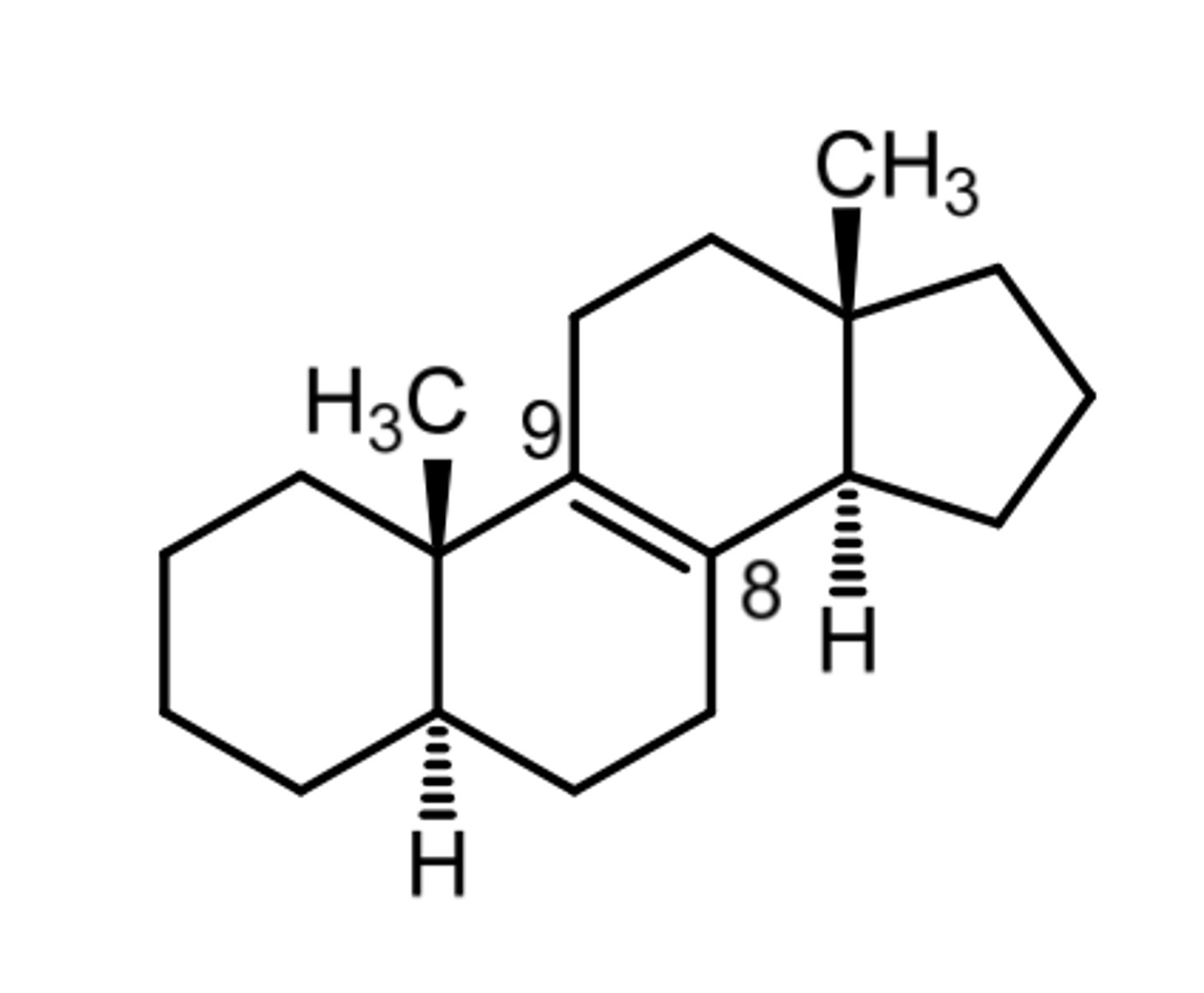
starts, ene, starting
steroid nomenclature: double bonds
double bonds are specified with the number of the position from which its ____ followed by -____.
if the bond can only be drawn in only 1 direction, or if it goes to the next highest position, only the _____ position needs to be specified.
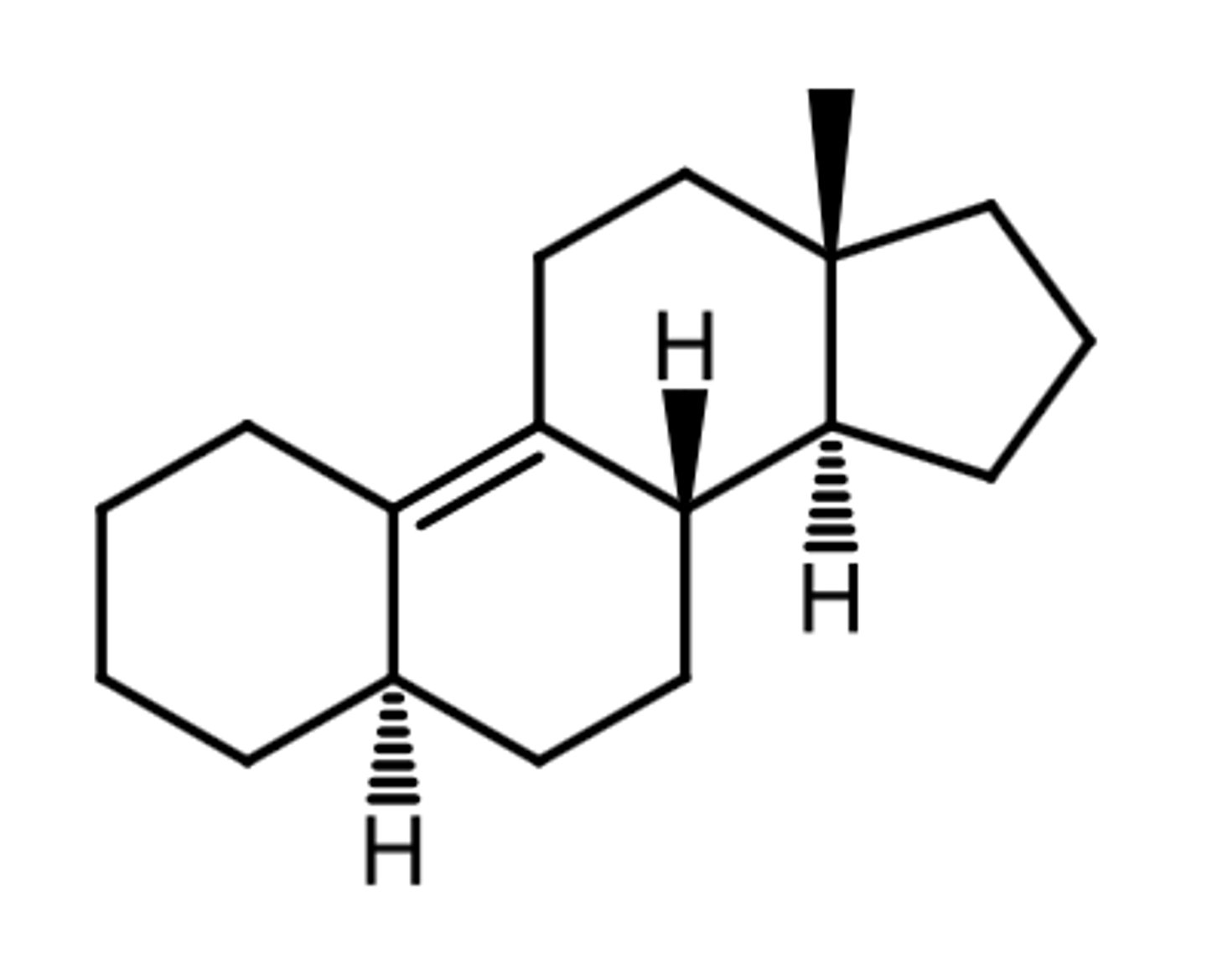
5b-estr-9(11)ene
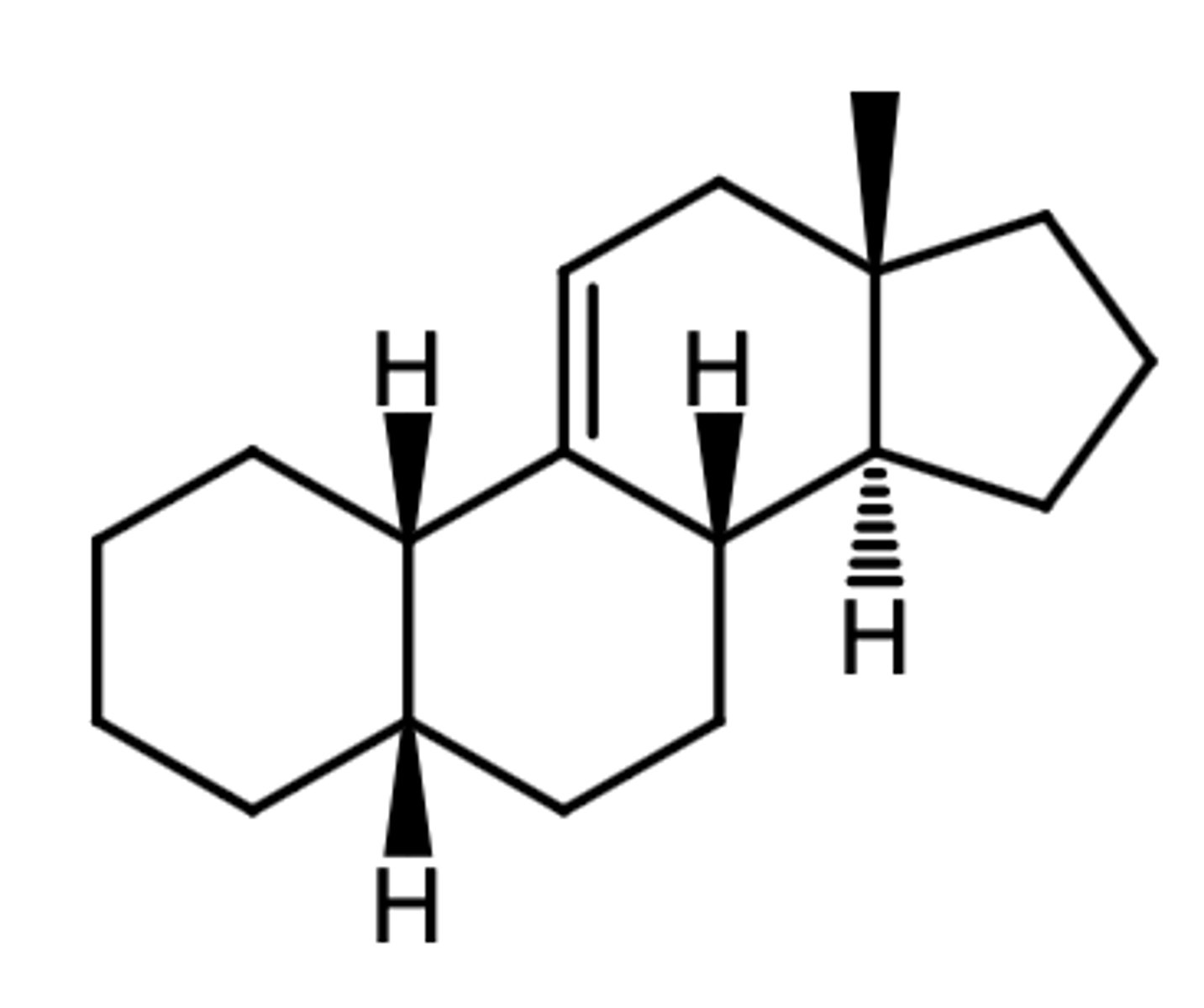
5a-estr-9-ene
What are the 2 female sex hormones?
estrogen and progestogen (and their respective derivatives)
What is the term for male sex hormones?
androgens (including testosterone etc)
What are the 3 categories of adrenocorticoids?
GLUCOcorticoids, MINERALOcorticoids, Sex hormones
What steroid hormone(s) have unsaturated ketone within its A ring?
progestins
Mineralocorticoids, Glucocorticoids do as well
What are the 2 key features of Androgen steroid structures, differentiating them from the rest?
19 methyl + 17b-OH combo
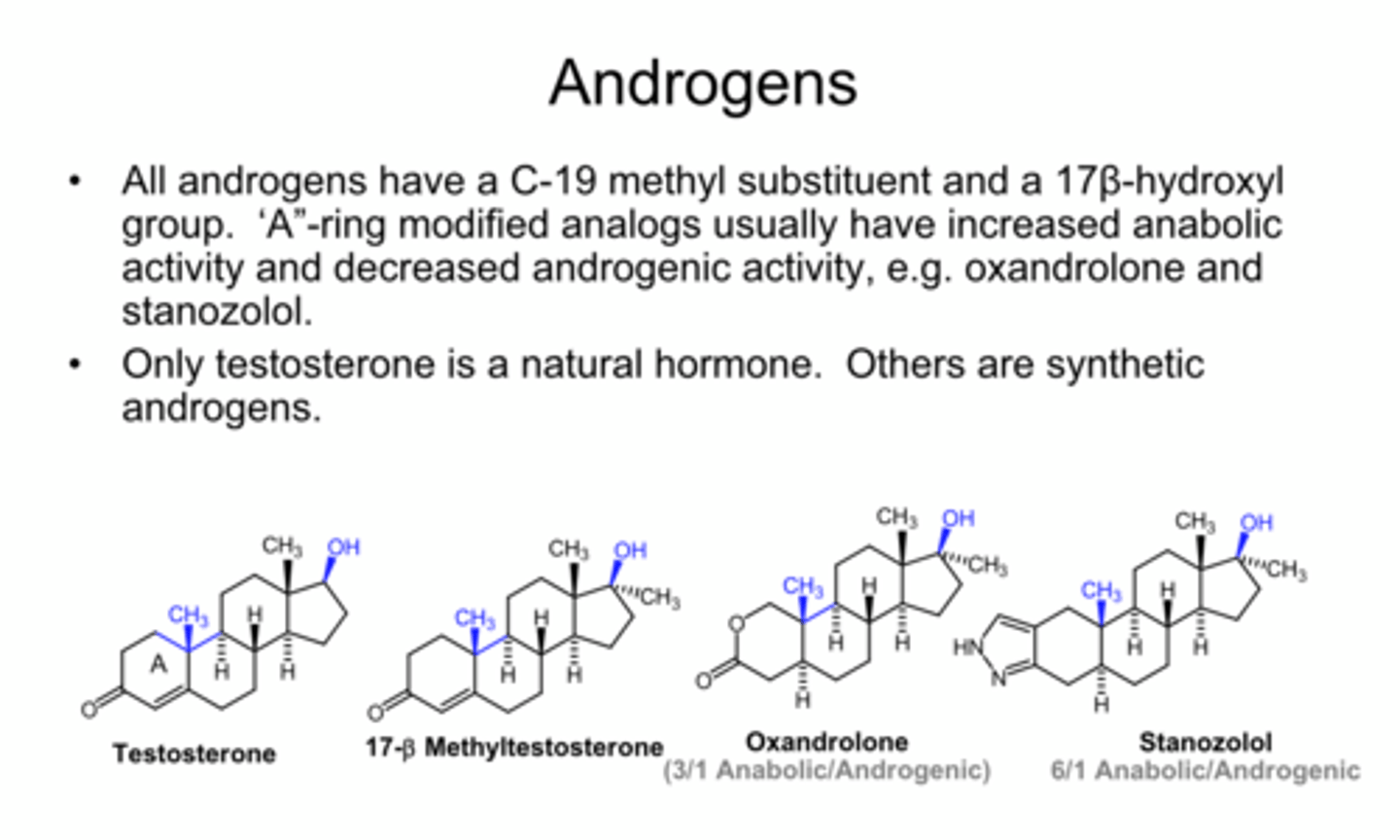
What steroid structure contains a progestin-like ring A, as well as a 21-OH or 21-Ac attached?
mineralocorticoids
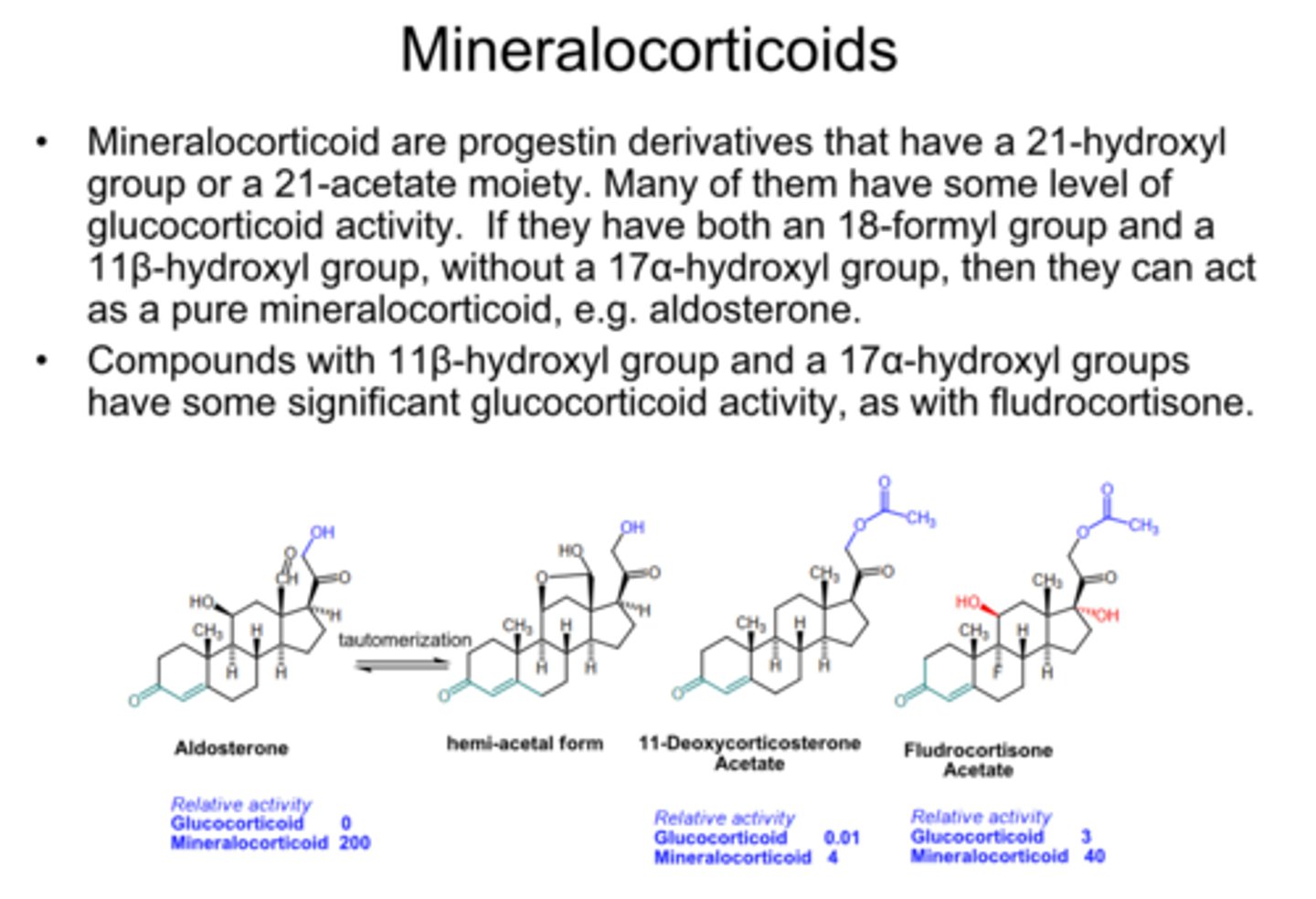
What steroid structure contains a progestin-like ring A, as well as a 17-alpha-OH and 11-beta-OH group?
glucocorticoids
transcriptional
free steroid hormones diffuse through the cell membrane + bind to high affinity receptors where they act as ______ factors by interaction with specific DNA sites
3b-dehydrogenase
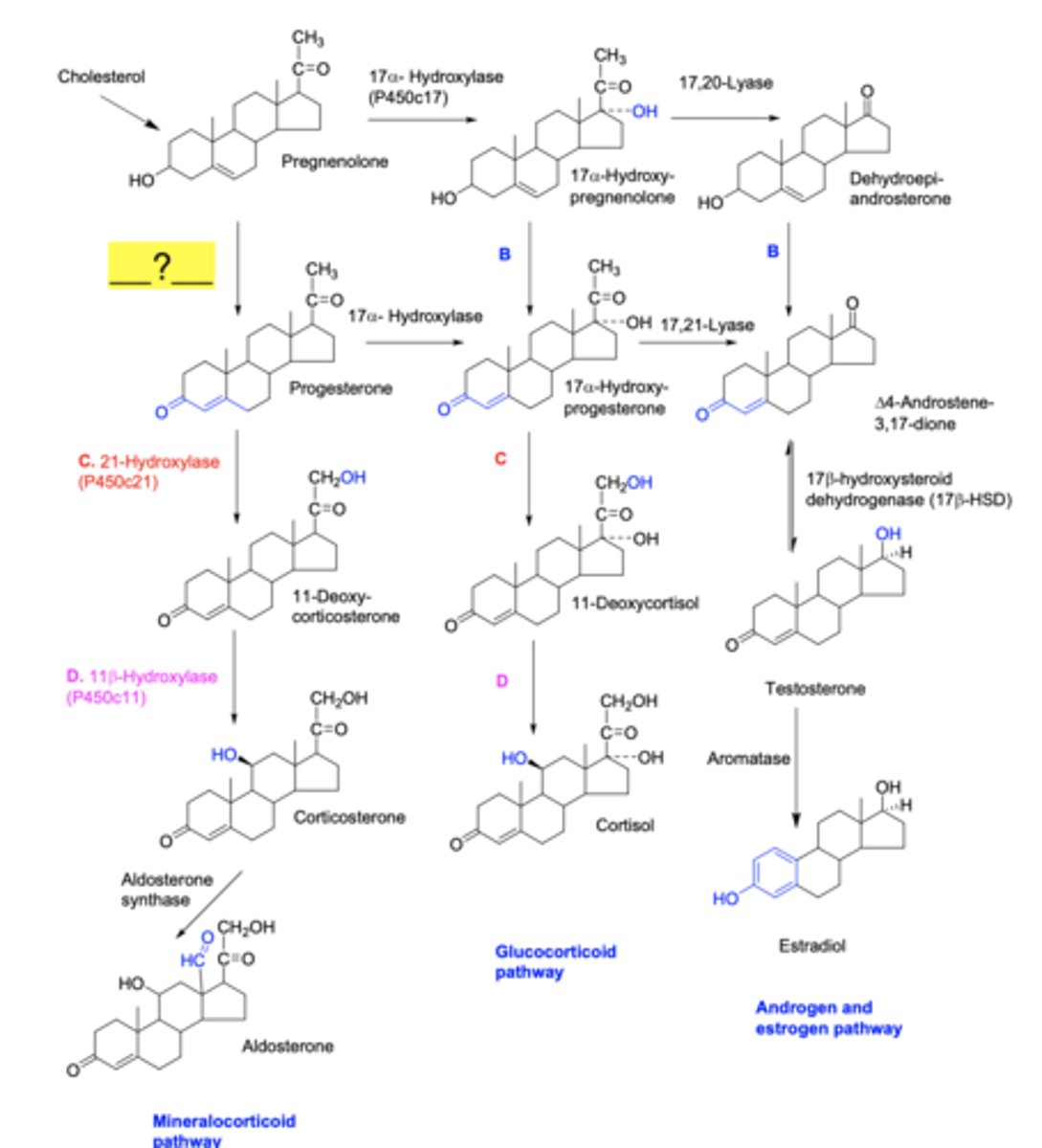
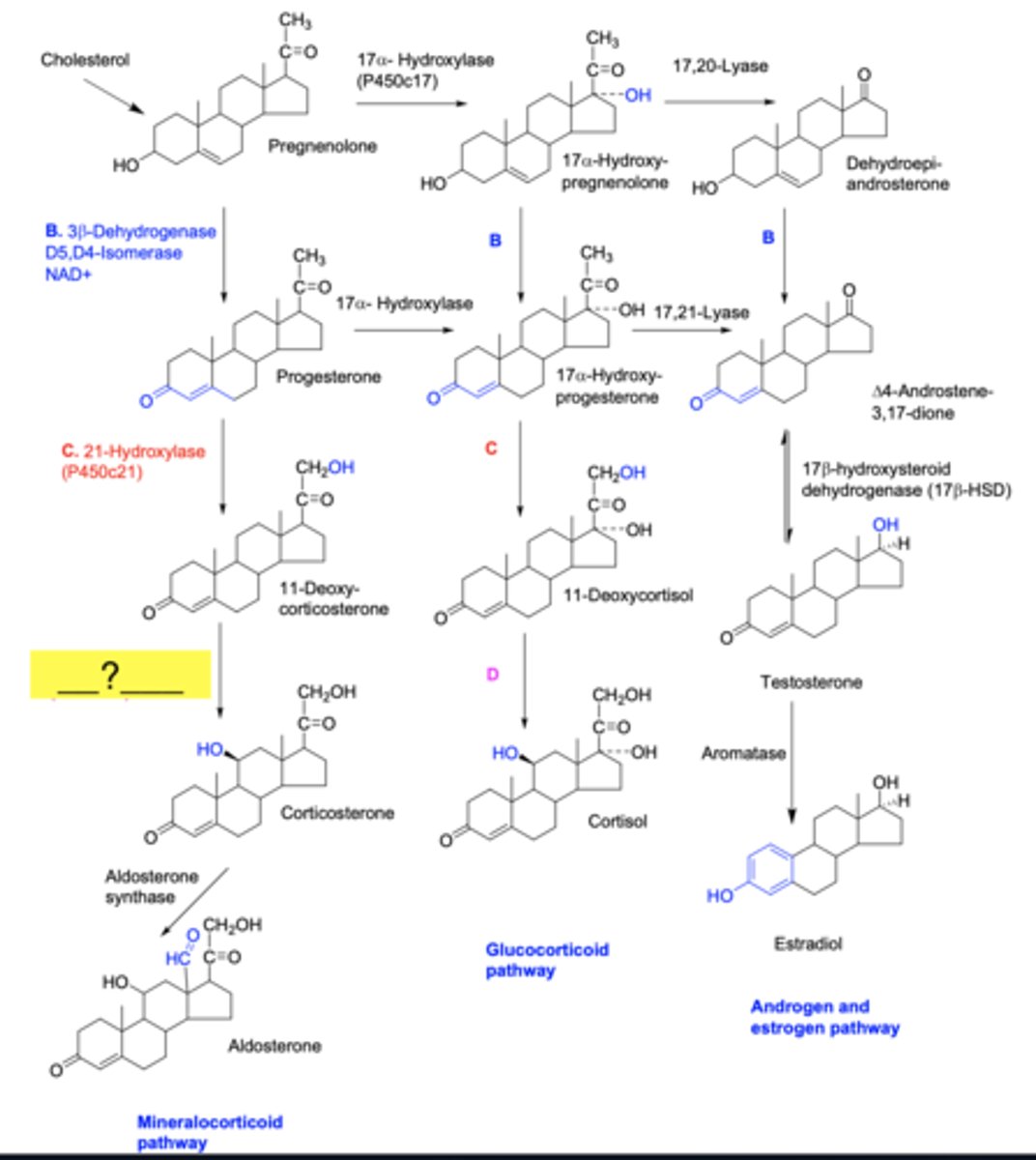
21-hydroxylase
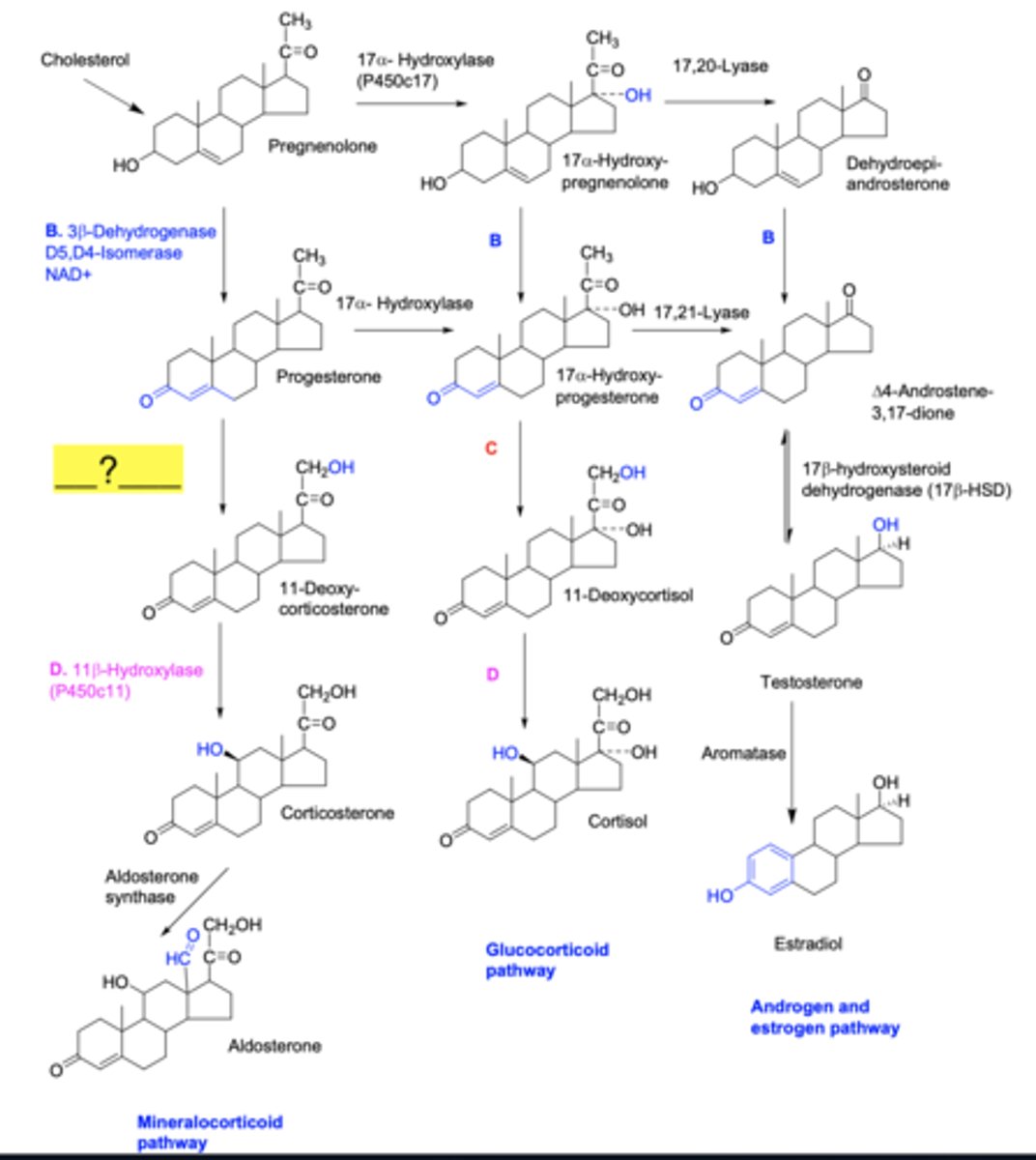
11b-hydroxylase
17-estradiol, estrone, estriol
what are the 3 main estrogens?
17b-estradiol
which estrogen is produced in the greatest amount in the body?
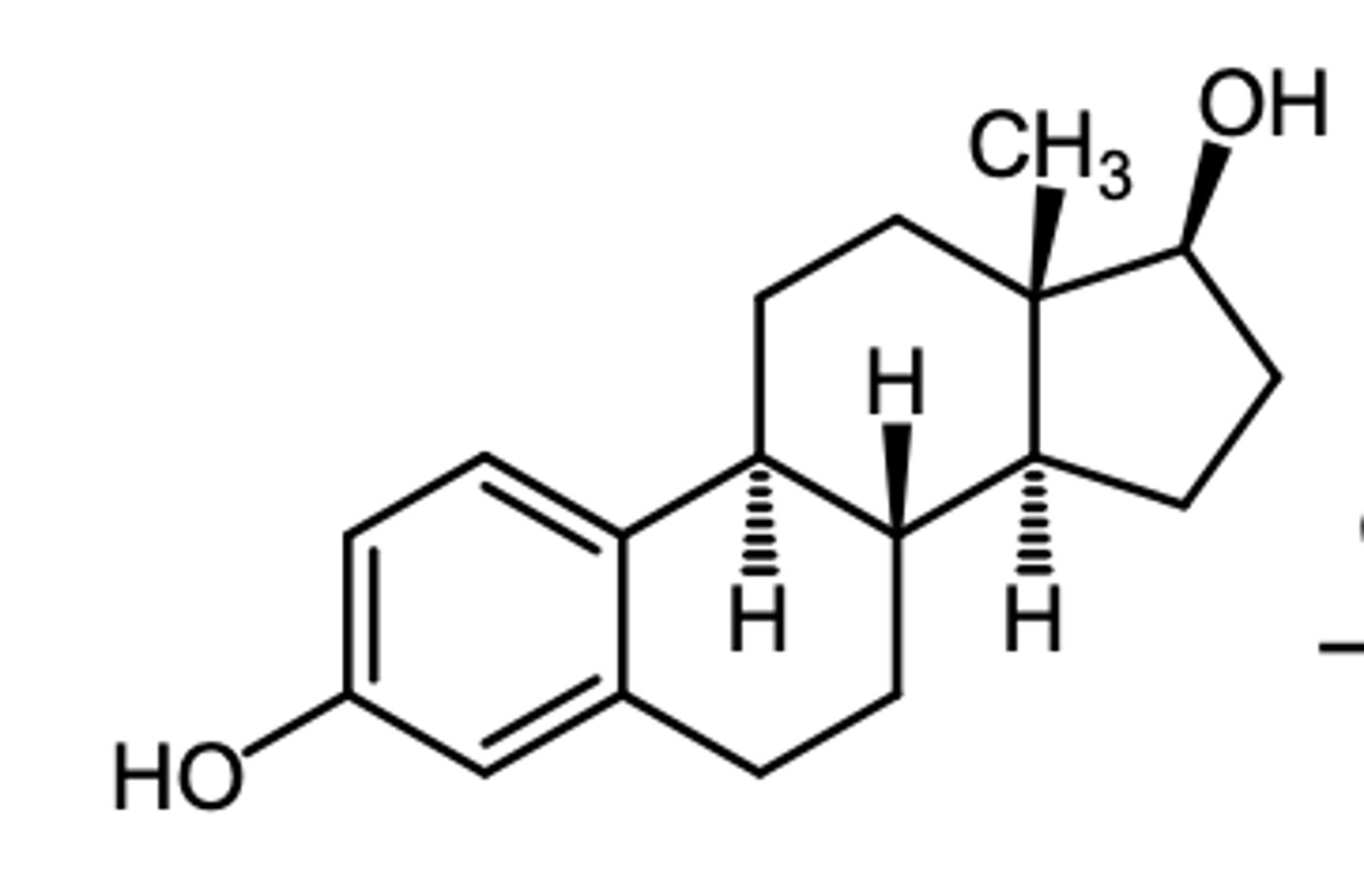
estrone (ketone version of 17b-estradiol)
which estrogen has the highest conc in the plasma?
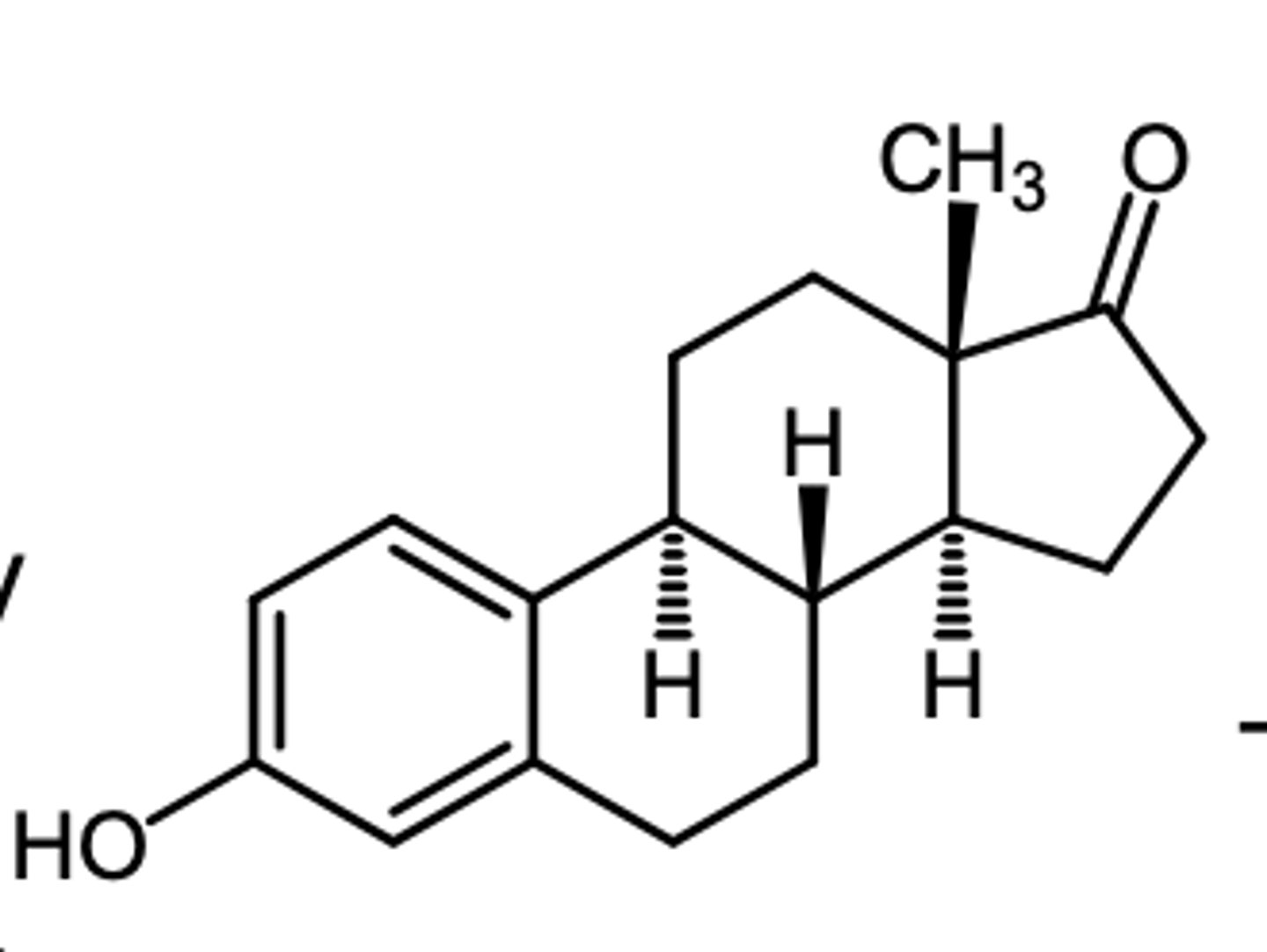
estriol
which estrogen has its highest conc in the urine?
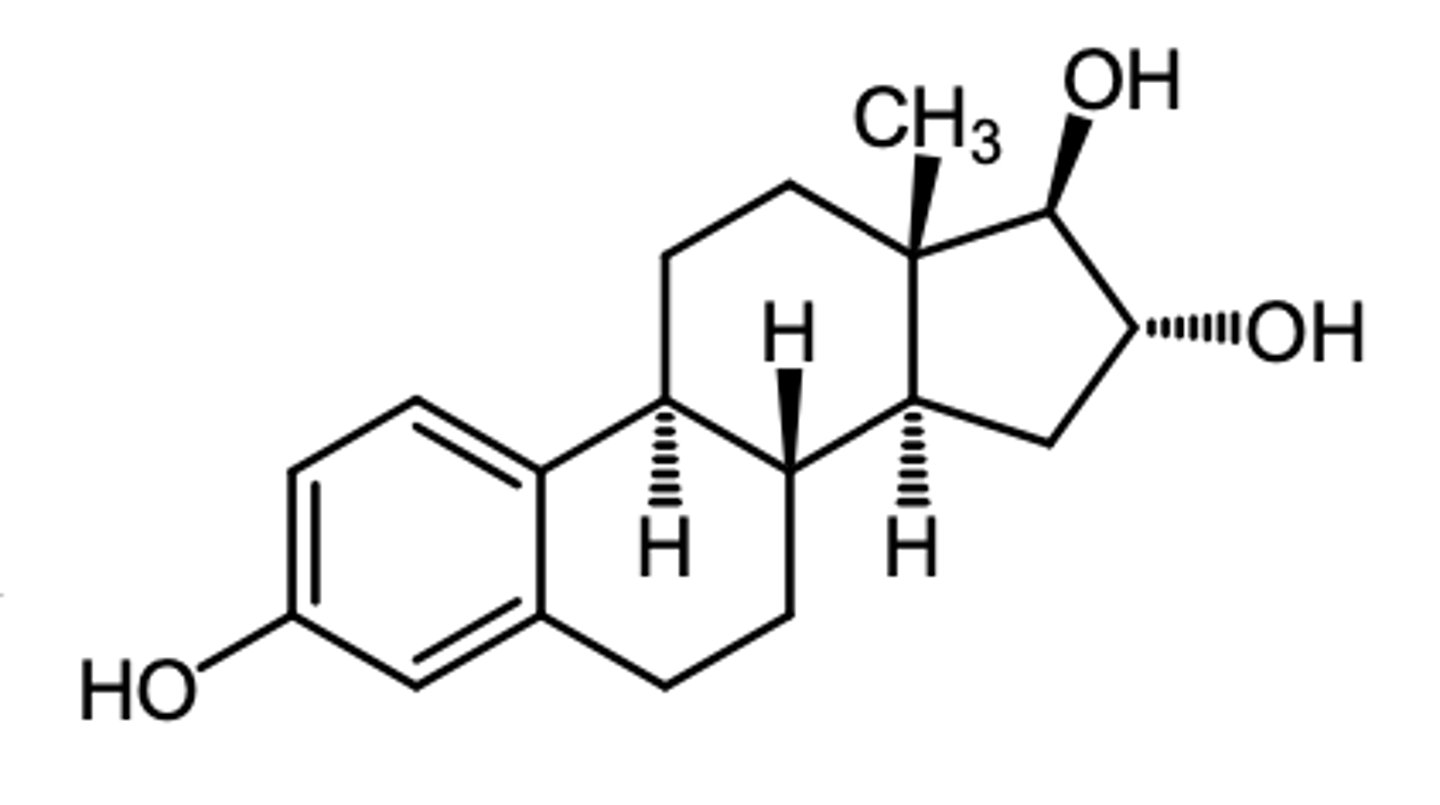
metabolite conjugates (glucuronide, sulfate)
how are insoluble estrogens and other steroids cleared from the plasma?
false
T/F. estrogens can only be used in women
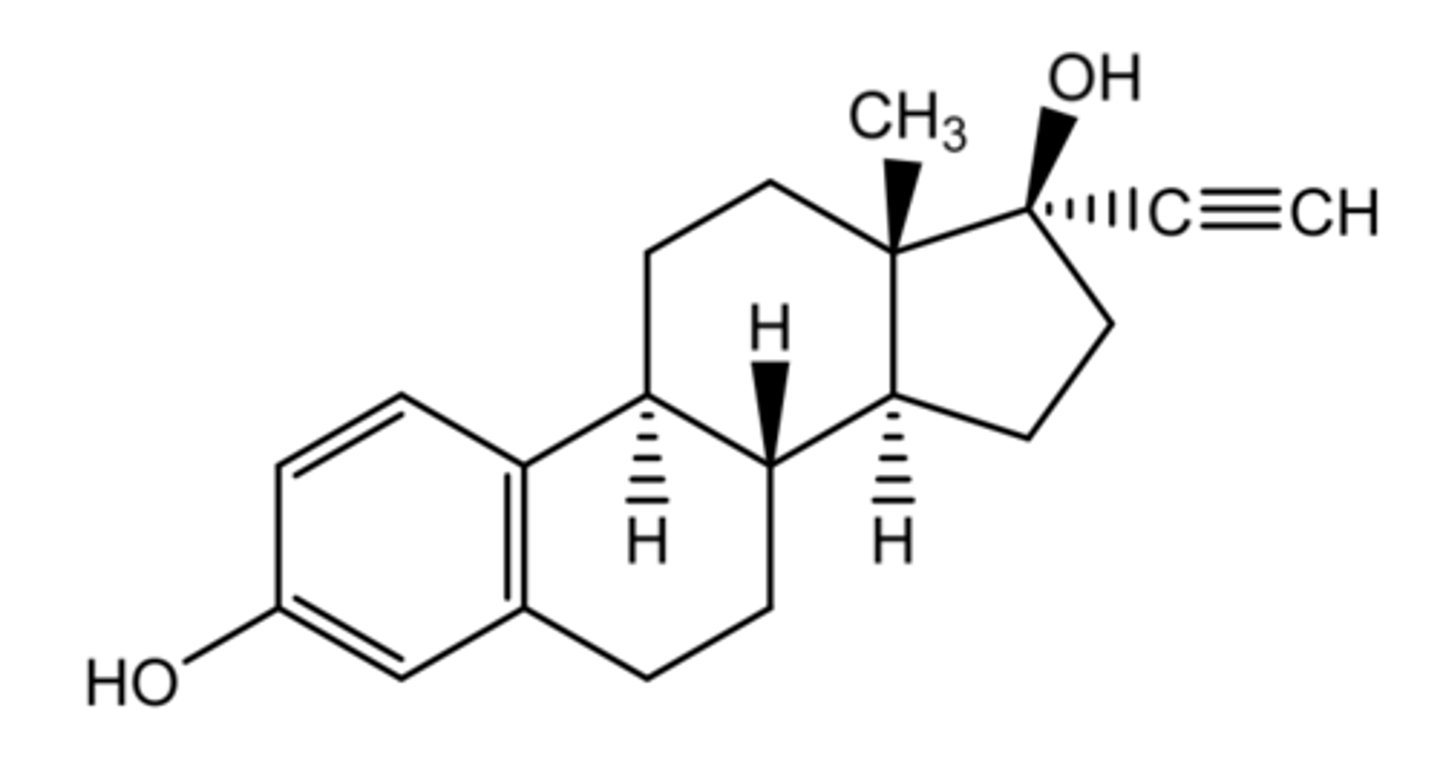
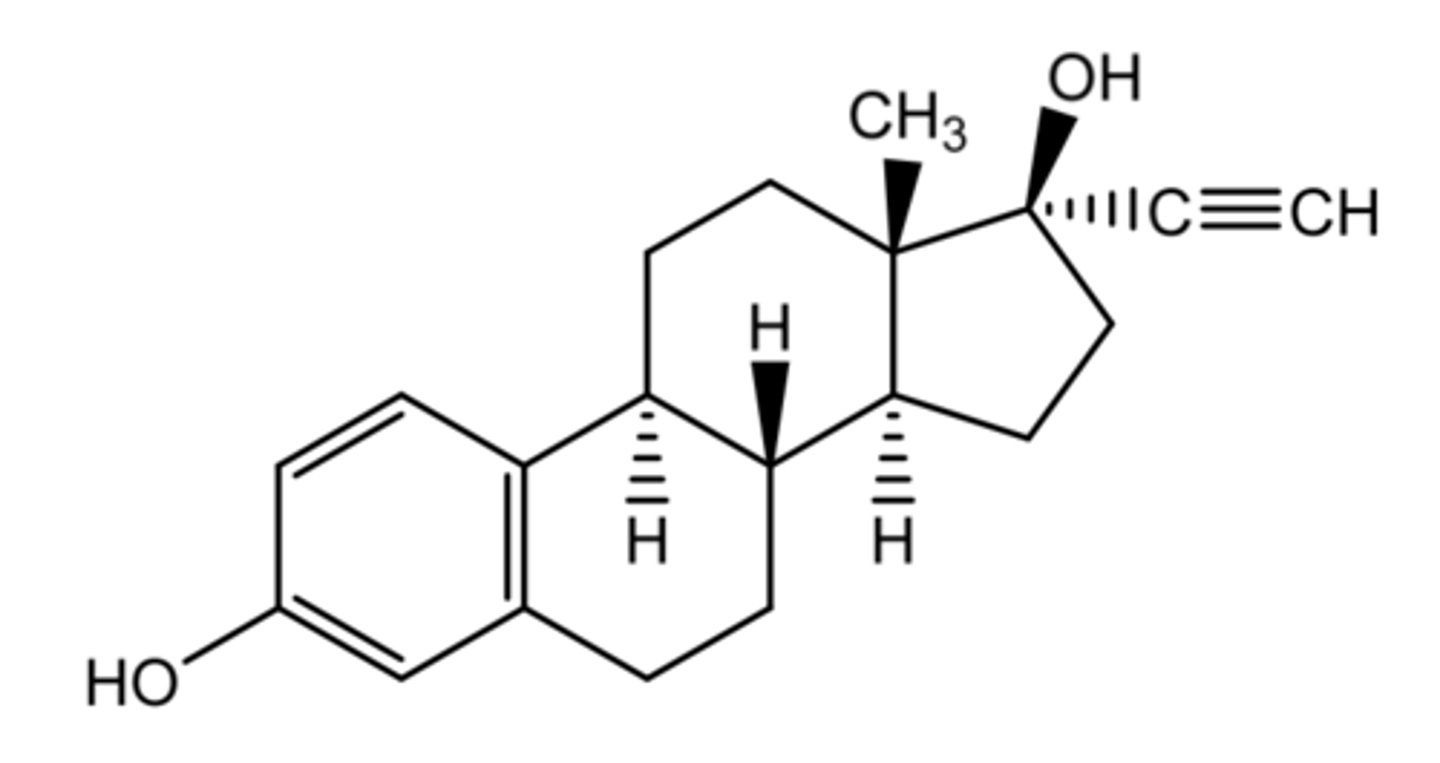
estradiol
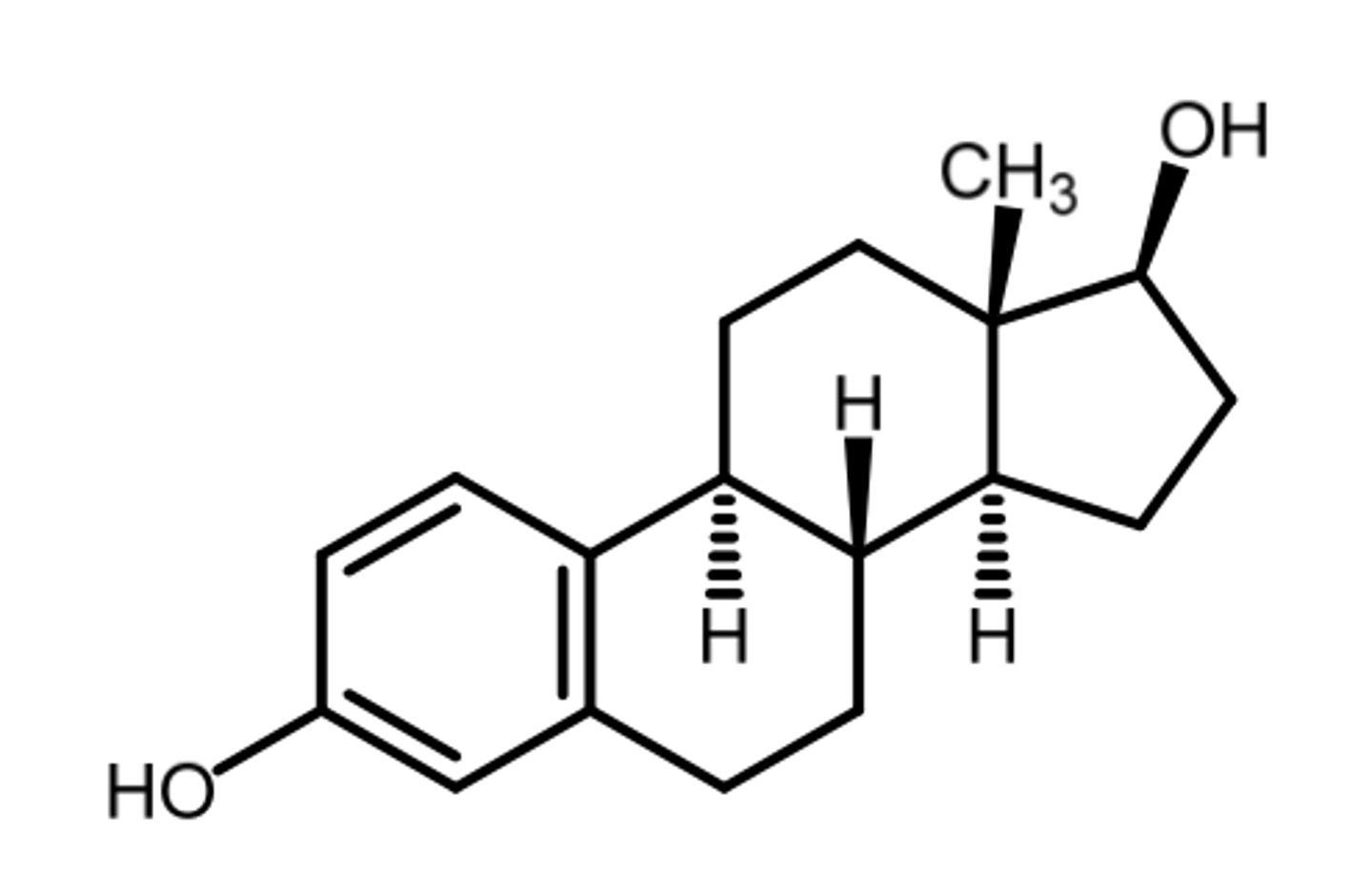
estradiol
(estrogenic)
most potent natural estrogen
ROA: oral, transdermal patch, vaginal ring
indication:
- vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause
- vulvar/vaginal atrophy associated with menopause (topical only)
ADME:
- poor OBA (5%)
- conjugate in intestine + eliminated
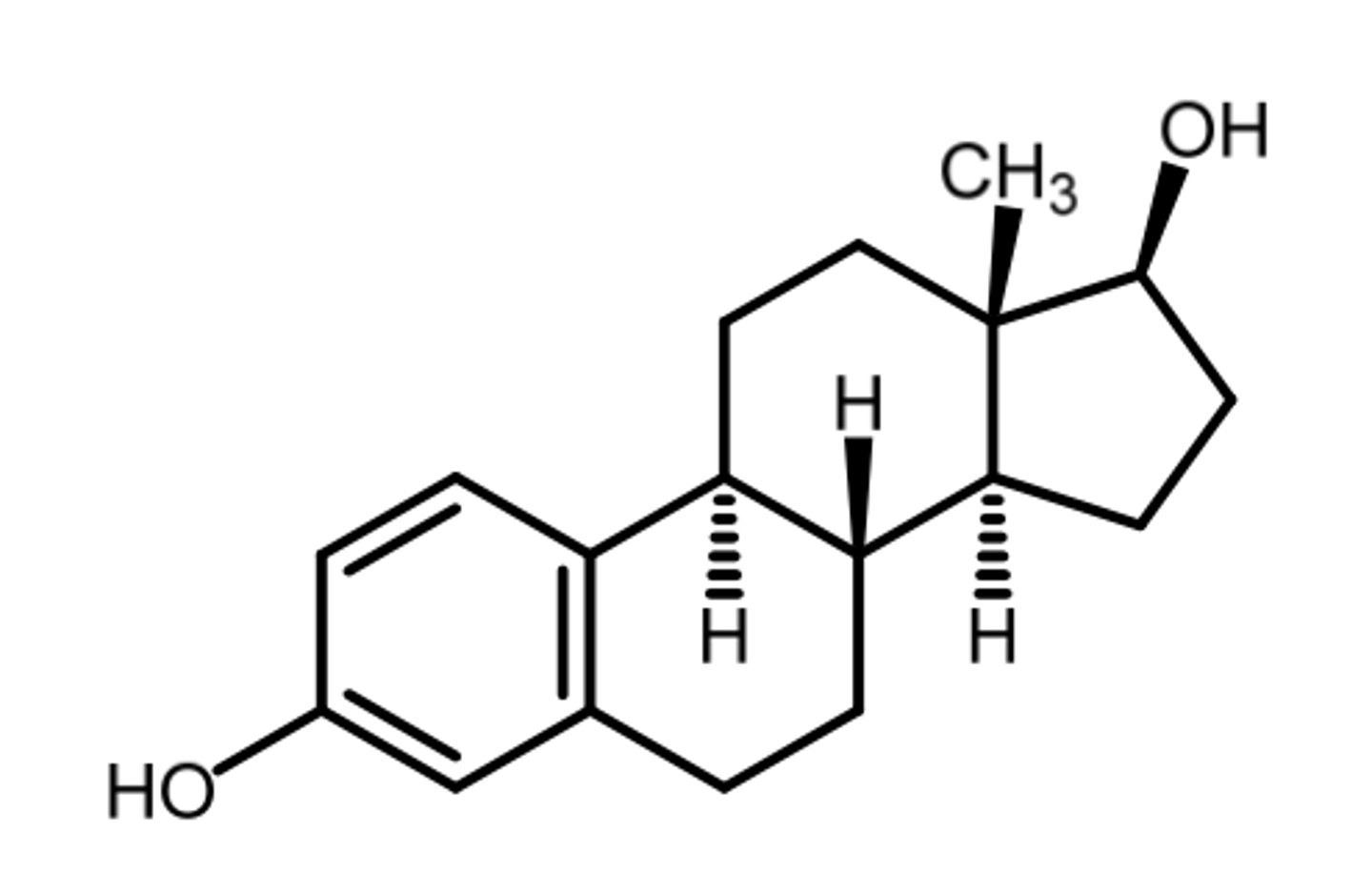
estradiol cypionate
(estrogenic)
SAR: ester prodrug
- deposited in tissue + slowly release into blood where it is hydrolyzed to estradiol
ROA: IM injection -- dosed monthly
indication: hypogonadism
- mod-severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause
BBW; inc risk of endometrial carcinoma in postmenopausal women
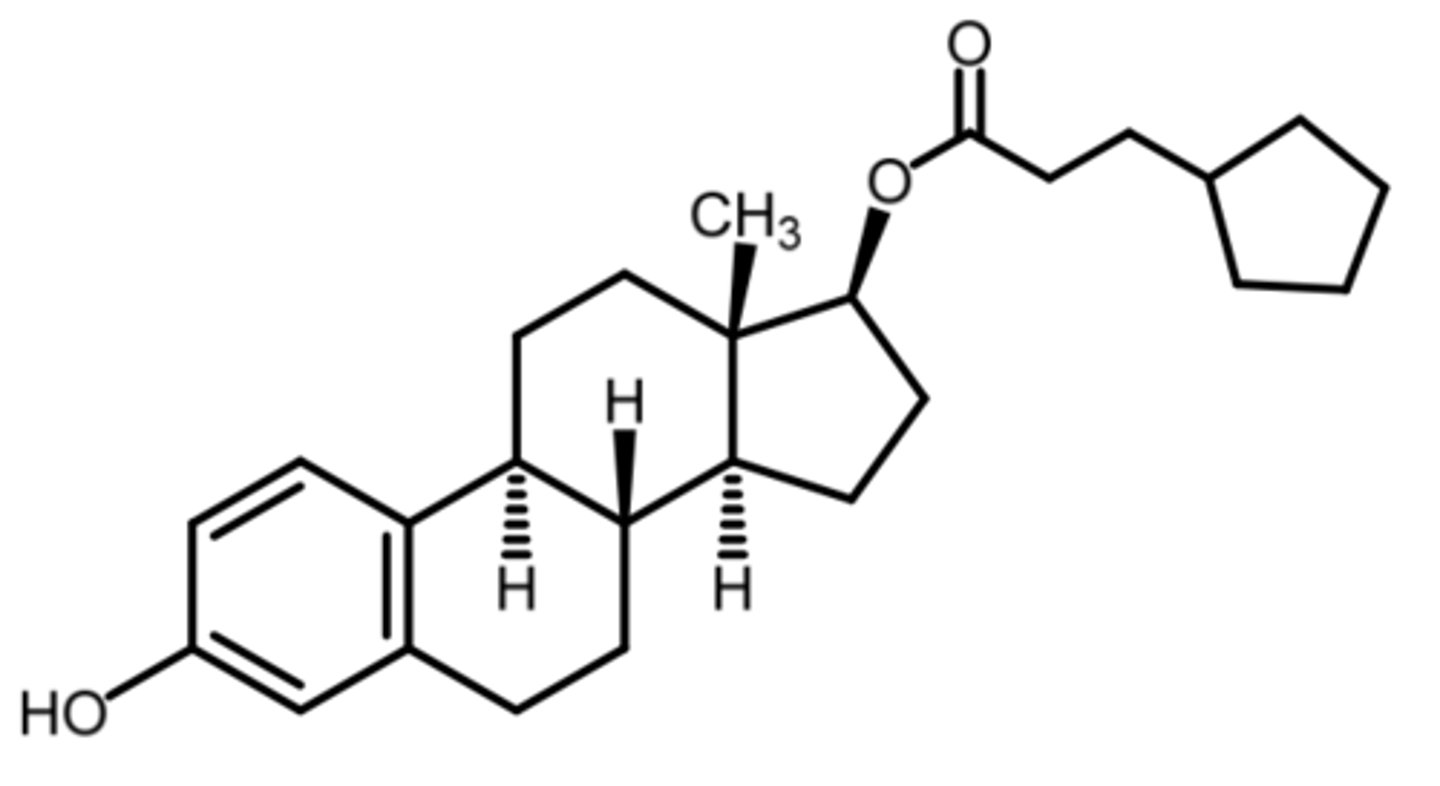
endometrial carcinoma
the BBW for estradiol cypionate has an increased risk of what?
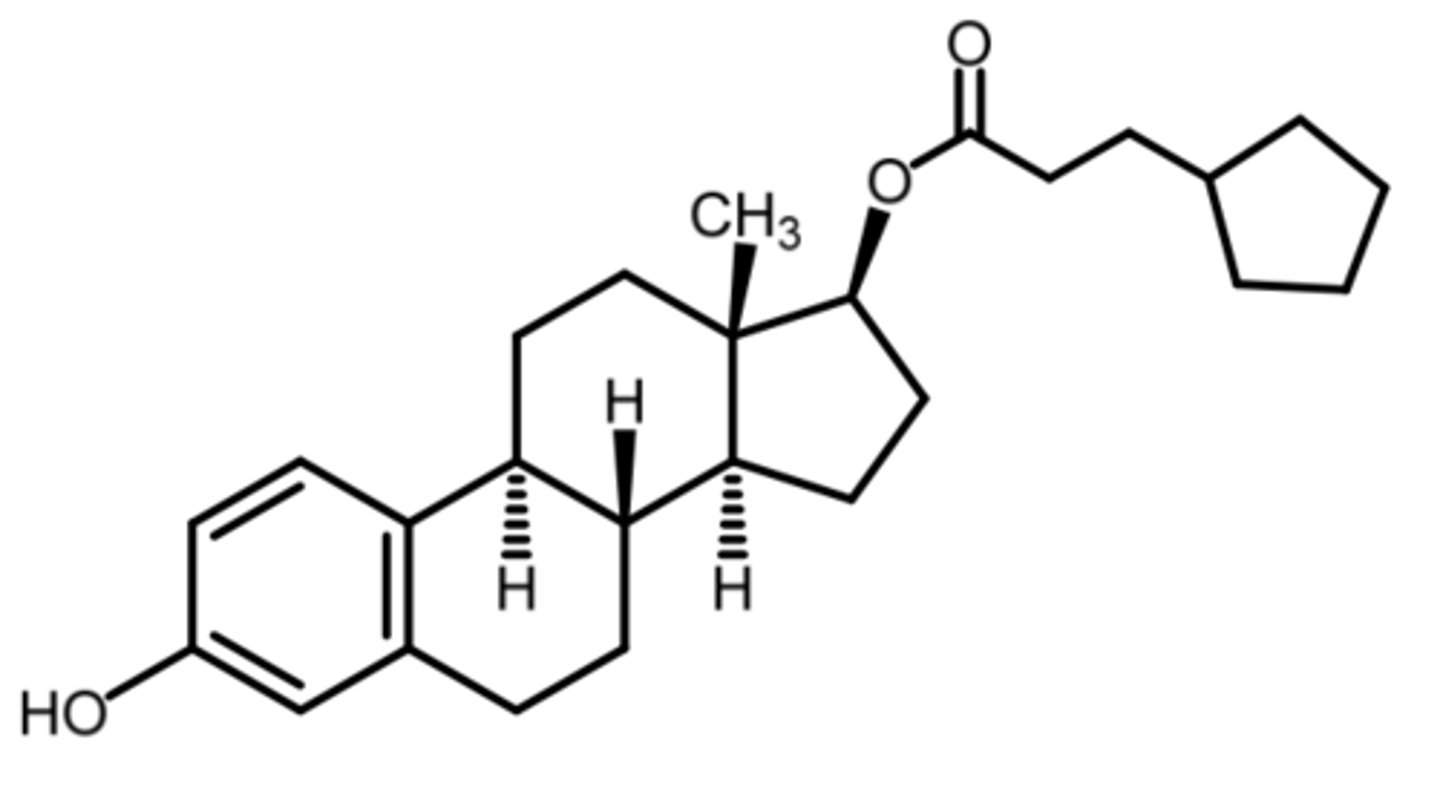
ethinyl estradiol
ethinyl estradiol
(estrogenic)
more potent + more stable than estradiol
ROA: PO, injection
indication: hypogonadism
- moder-severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause
SAR: metabolically more stable than estradiol due to C17 ethynyl group preventing oxidation
ADME:
- rapid + complete absorption after oral admin
- first pass metabolism to O-glucuronide and sulfate derivatives + enterohepatic circulation
what is the function of the C17 ethynyl group in ethinyl estradiol that increases its stability?
prevents oxidation
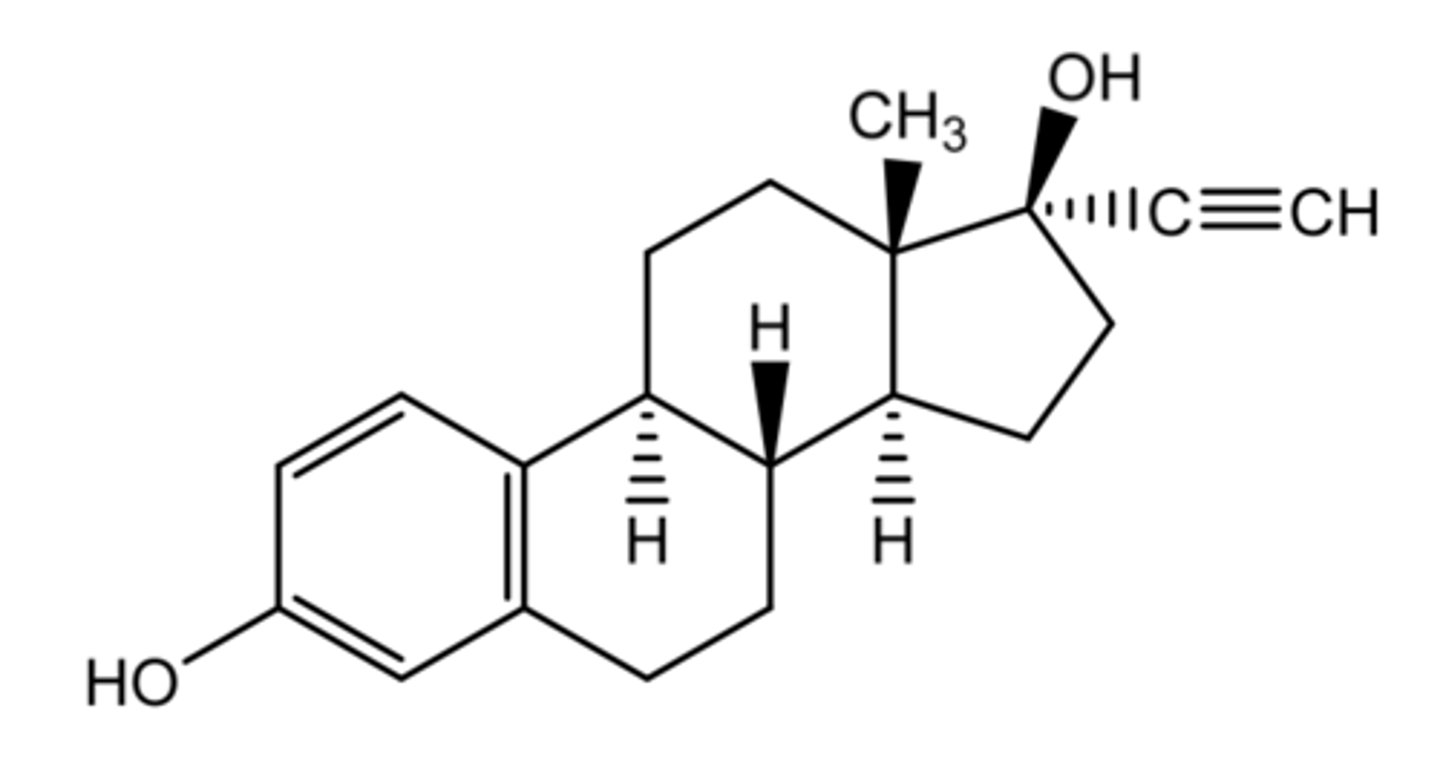
mestranol
mestranol
(estrogenic)
ROA: oral, injection, topical
- once daily dosing
indication: oral contraceptive in combo formulation
- treat hypogonadism
ADME: ether prodrug that is dealkylated in vivo via hepatic oxidative O-demethylation
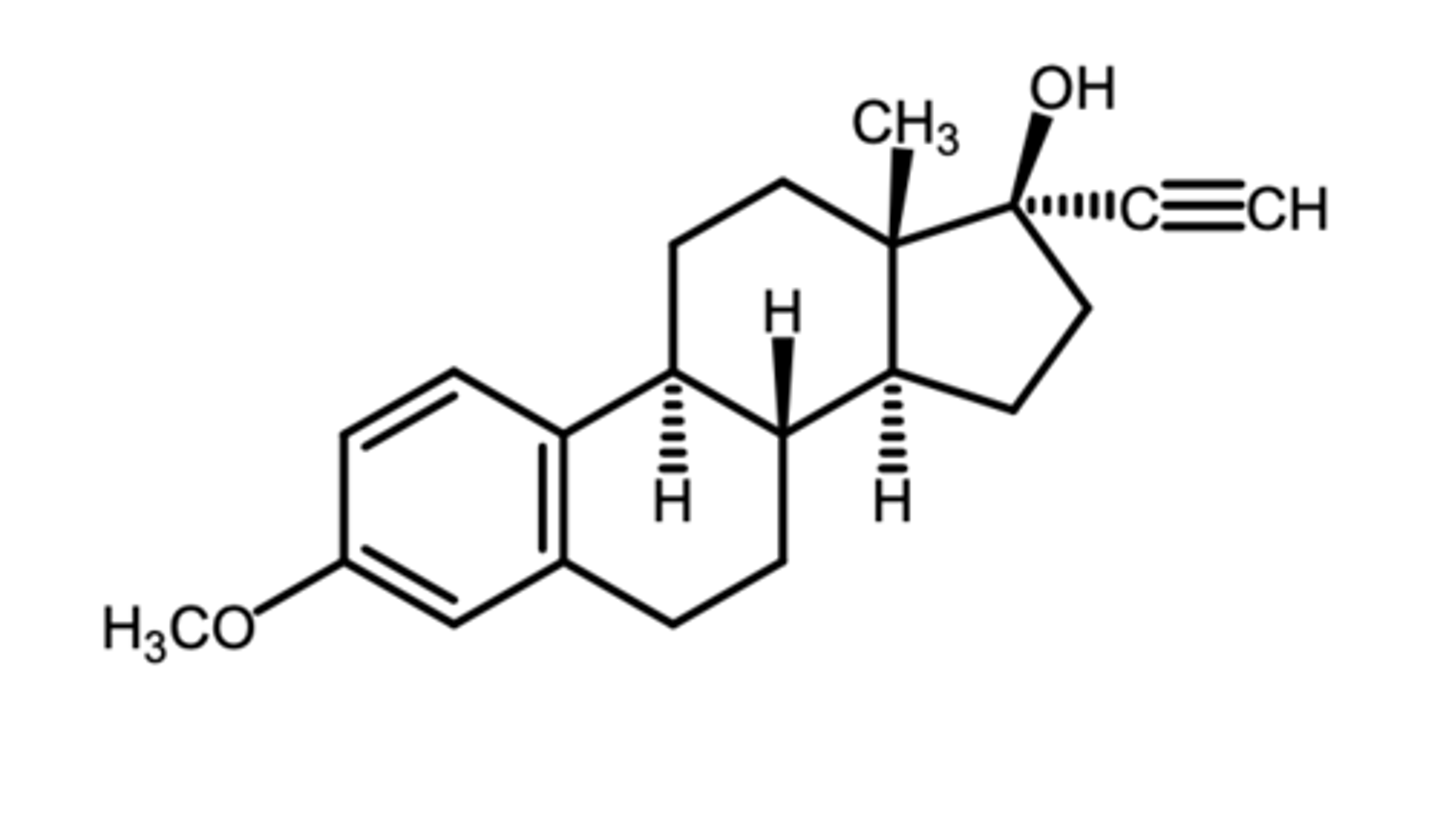
quinestrol
quinestrol
(estrogenic)
ROA: oral
- once weekly dosing
indication: oral contraceptive in combo formulation
ADME: prodrug that gets dealkylated in vivo
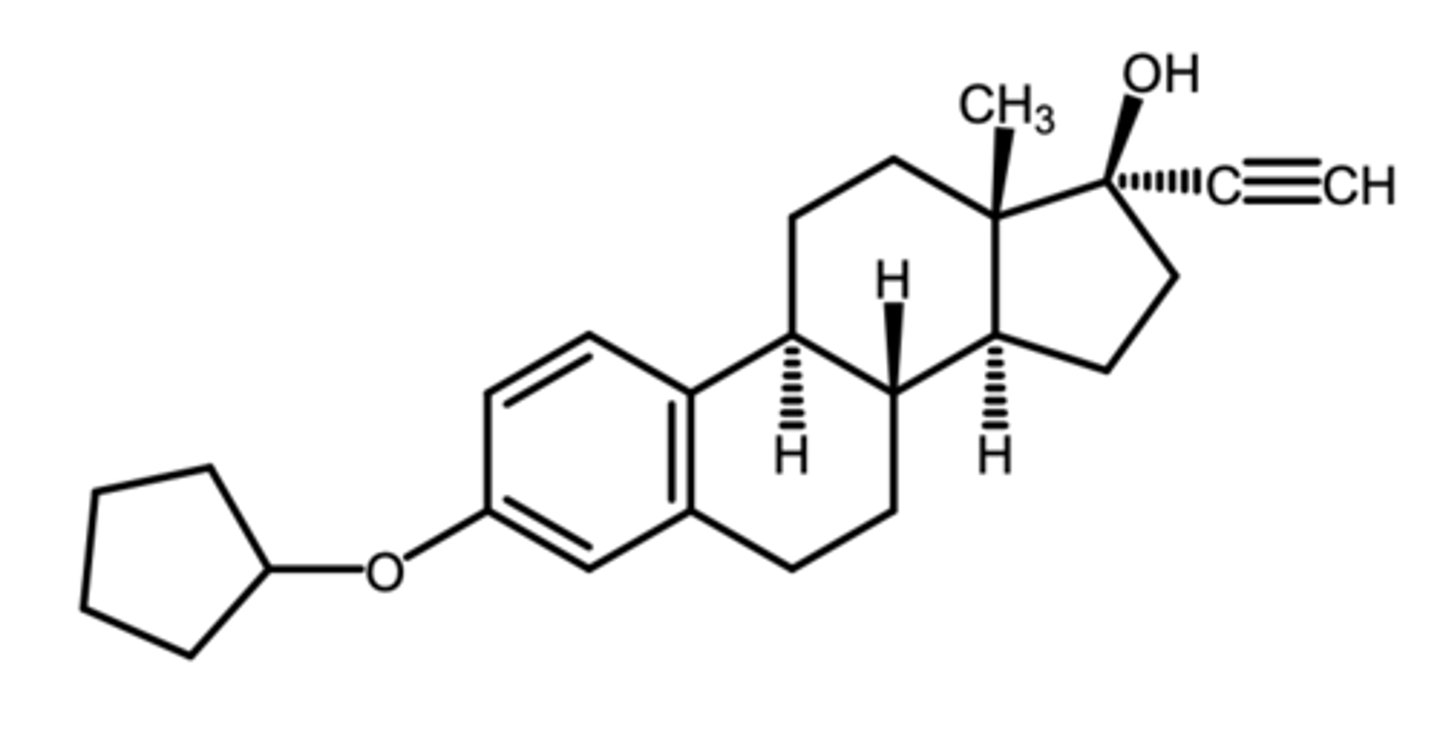
what are 2 unique estrogenic compounds excreted in the urine of pregnant mares?
equilenin, equilin
premarin
(conjugated estrogen)
combo of sodium estrone sulfate + sodium equilin sulfate
ROA: oral, IV, IM
- poor OBA
indication: uterine bleeding
BW: may cause endometrial cancer, breast cancer, or CV disorders
diethylstilbestrol (DES)
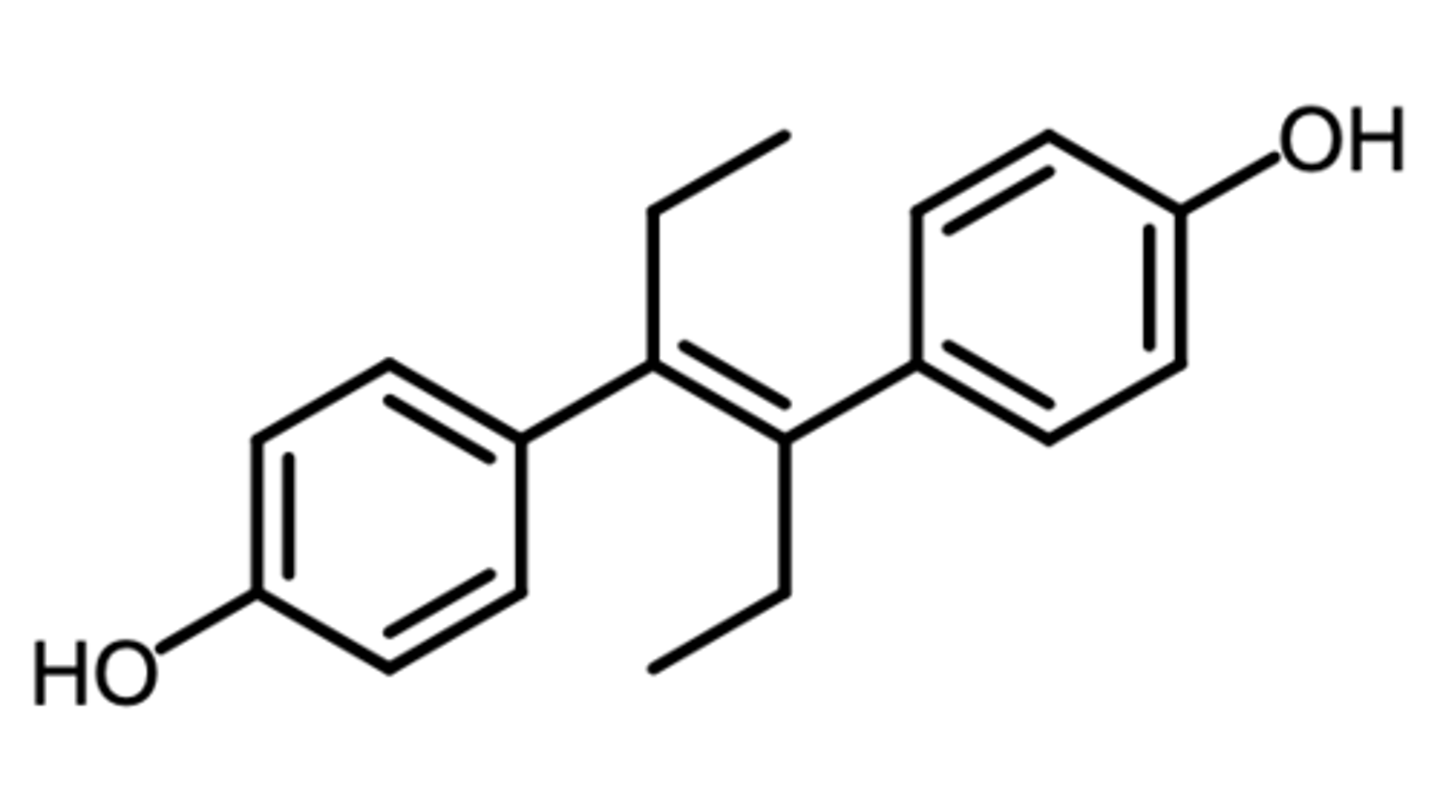
diethylstilbestrol (DES)
(non steroidal estrogen)
DISCONTINUED due to causing severe birth defects + rare tumors
SAR: E-isomer is much more active
indication: reduce risk of pregnancy complications + losses
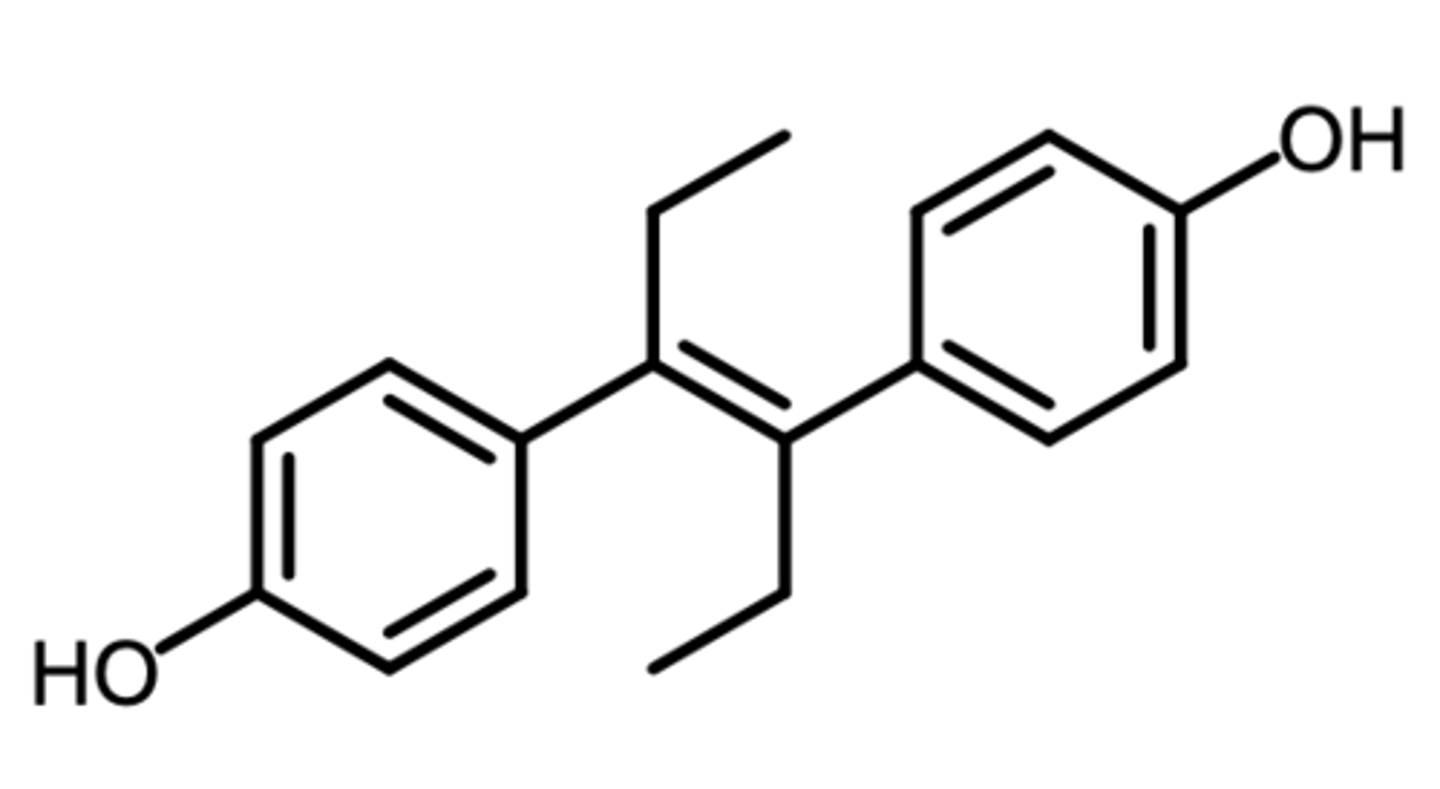
tamoxifen, toremifene, clomiphene, raloxifene
what are the 4 anti-estrogen SERMS?
tamoxifen
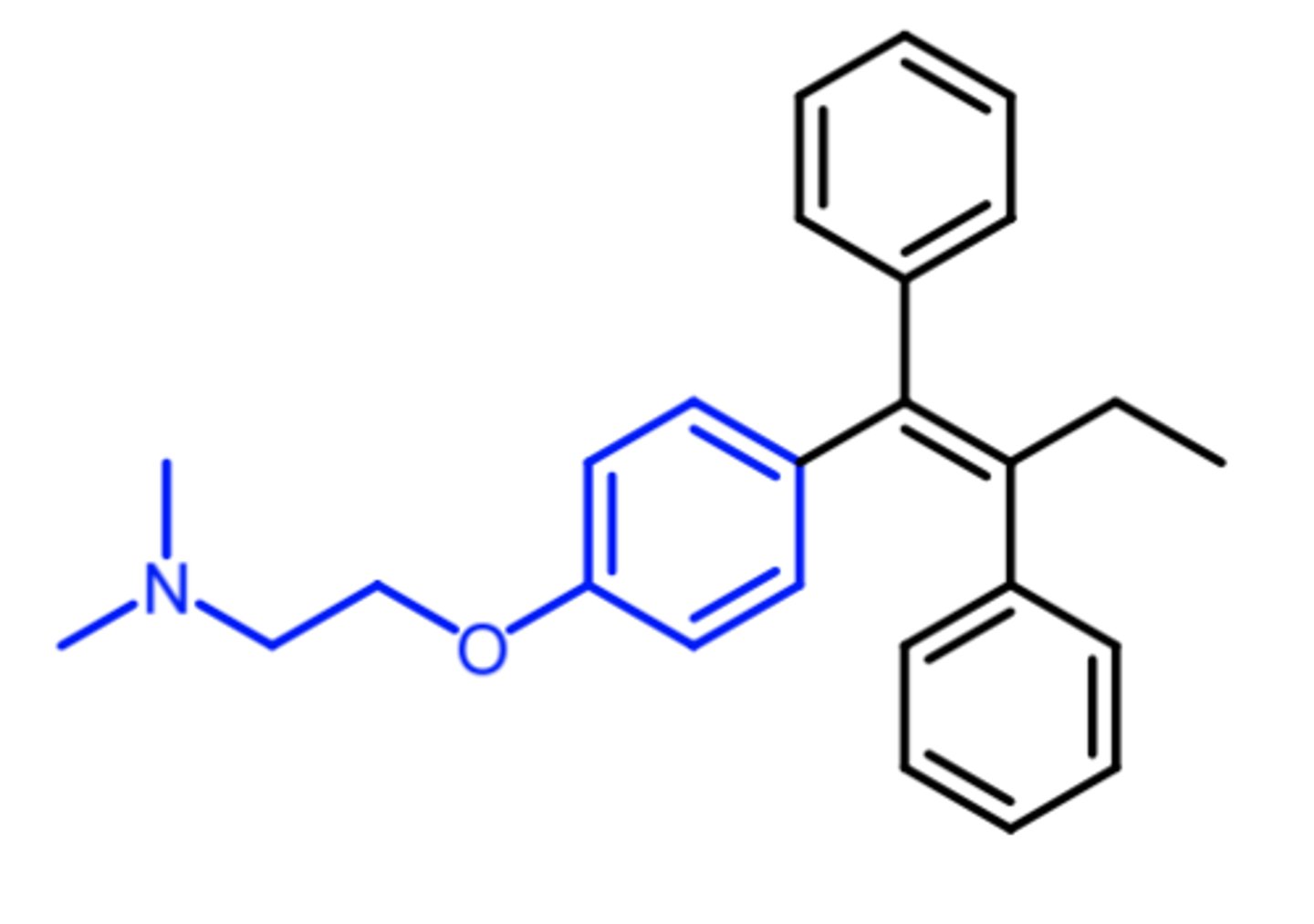
estrogen agonist or antagonist (depending on target organ and duration)
what is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM)?
tamoxifen
(anti-estrogen -- SERM)
ROA: oral
MOA: estrogen receptor antagonist in breast tissue
indication: estrogen-dependent breast cancer in women
ADME:
- minor metabolite, 4-hydroxy-N-methyltamoxifen (endoxifen) = more potent than parent
resistance: occurs after 5 years of therapy, and then agonist property takes over
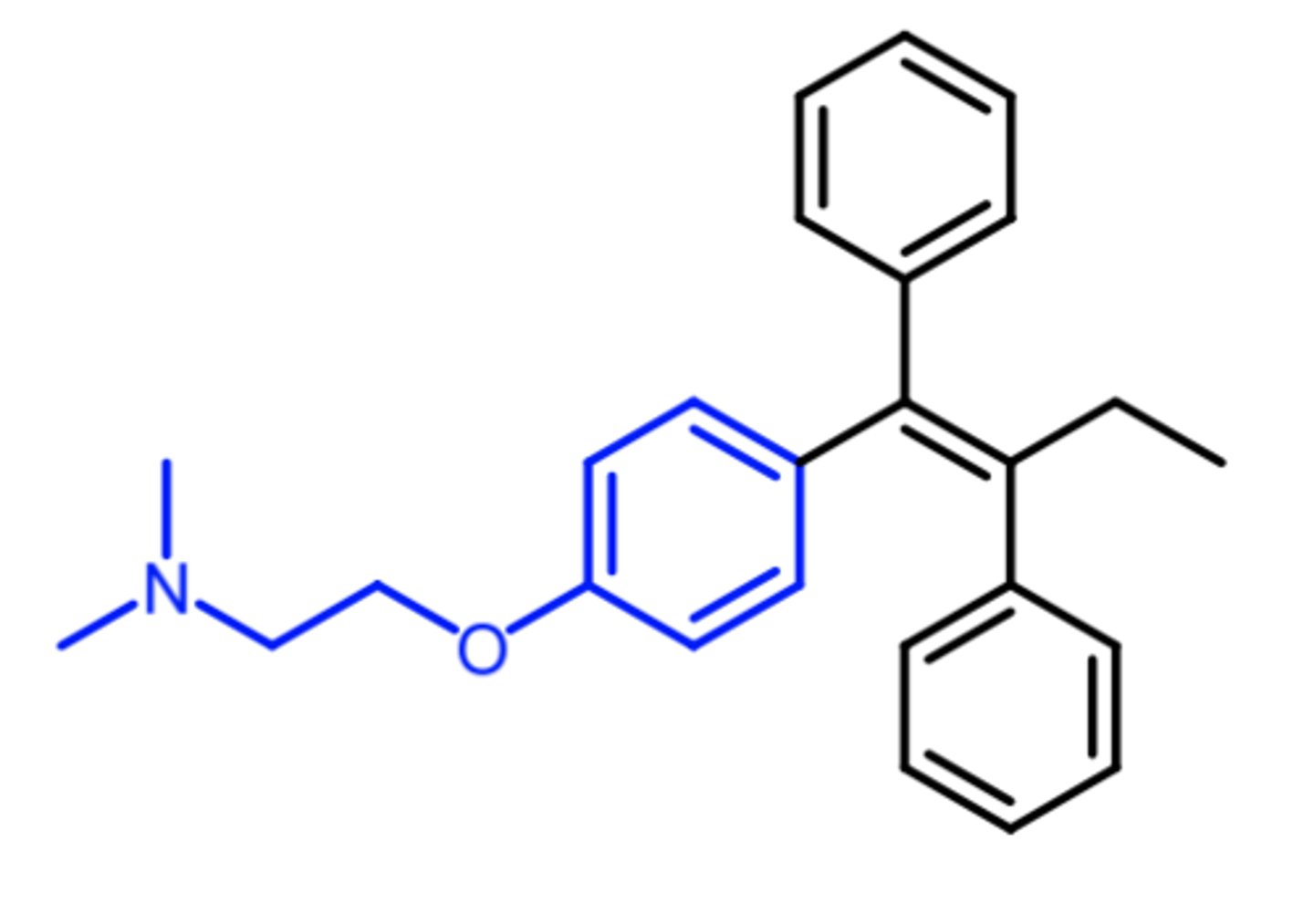
5
after how many years of tamoxifen therapy will the activity switch from being an antagonist to an agonist?
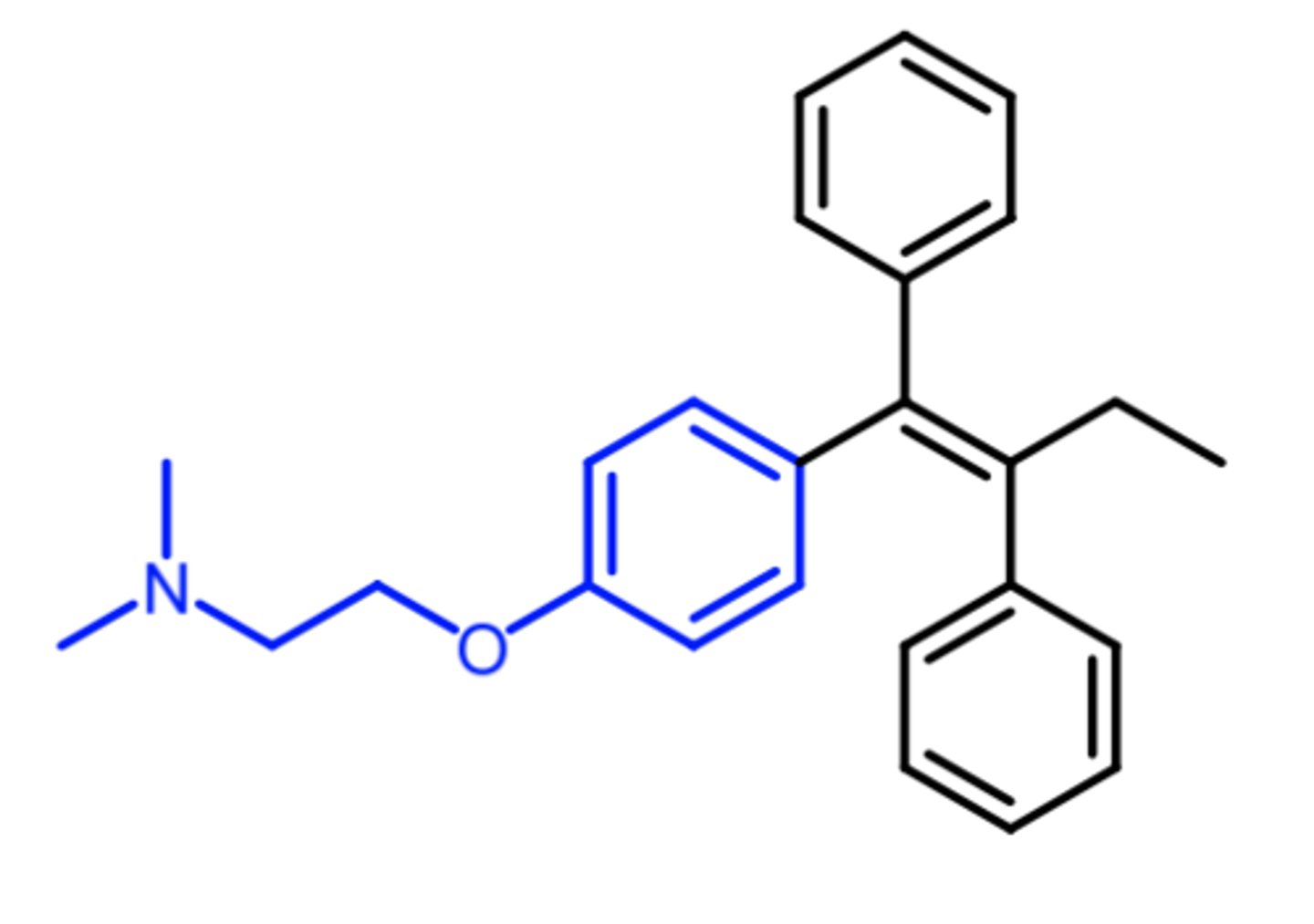
toremifene
toremifene
(antiestrogen -- SERM)
MOA: selective estrogen antagonist
indication: breast cancer
ADME: N-desmethyl toremifene = active metabolite
BBW: QTc prolongation
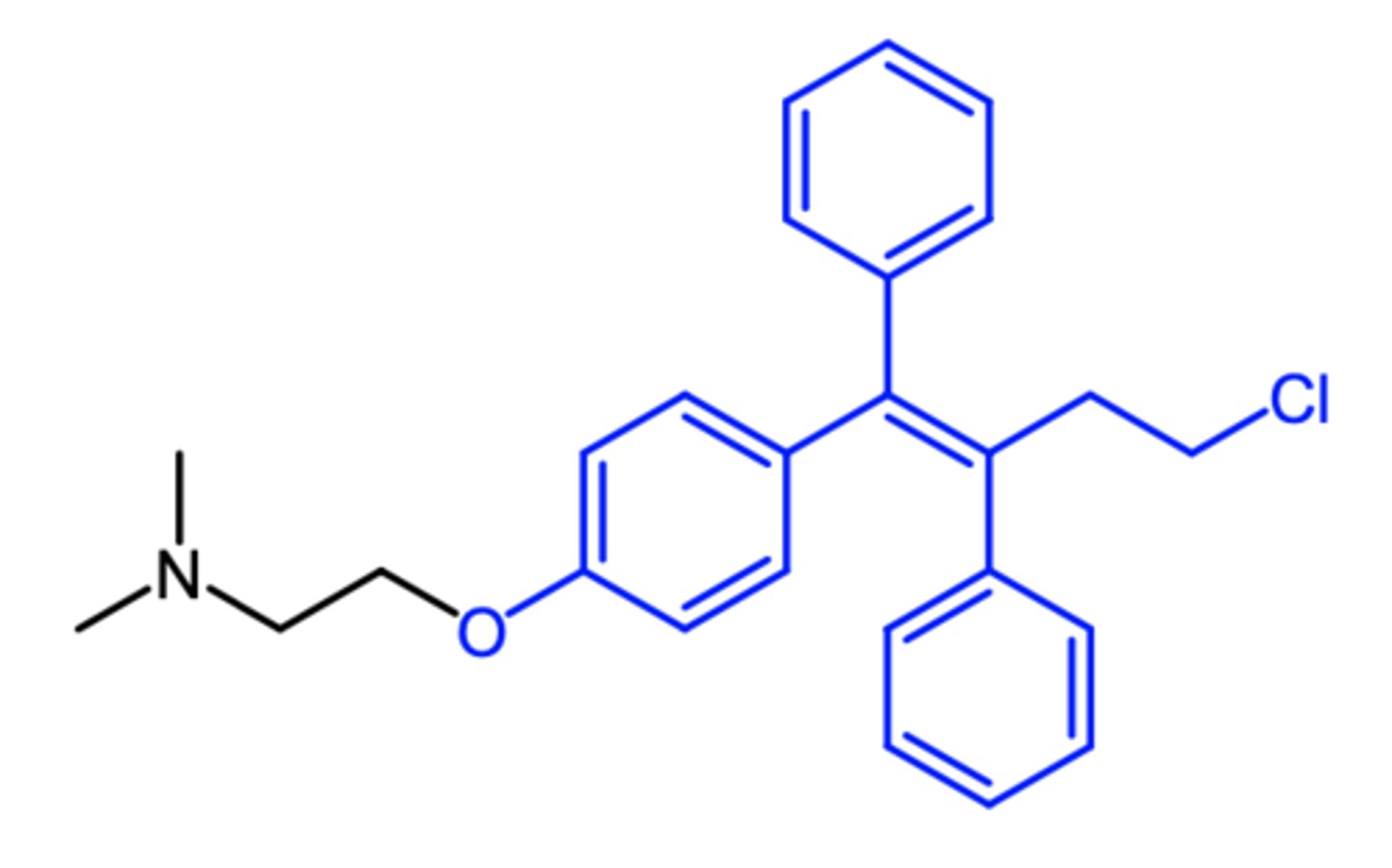
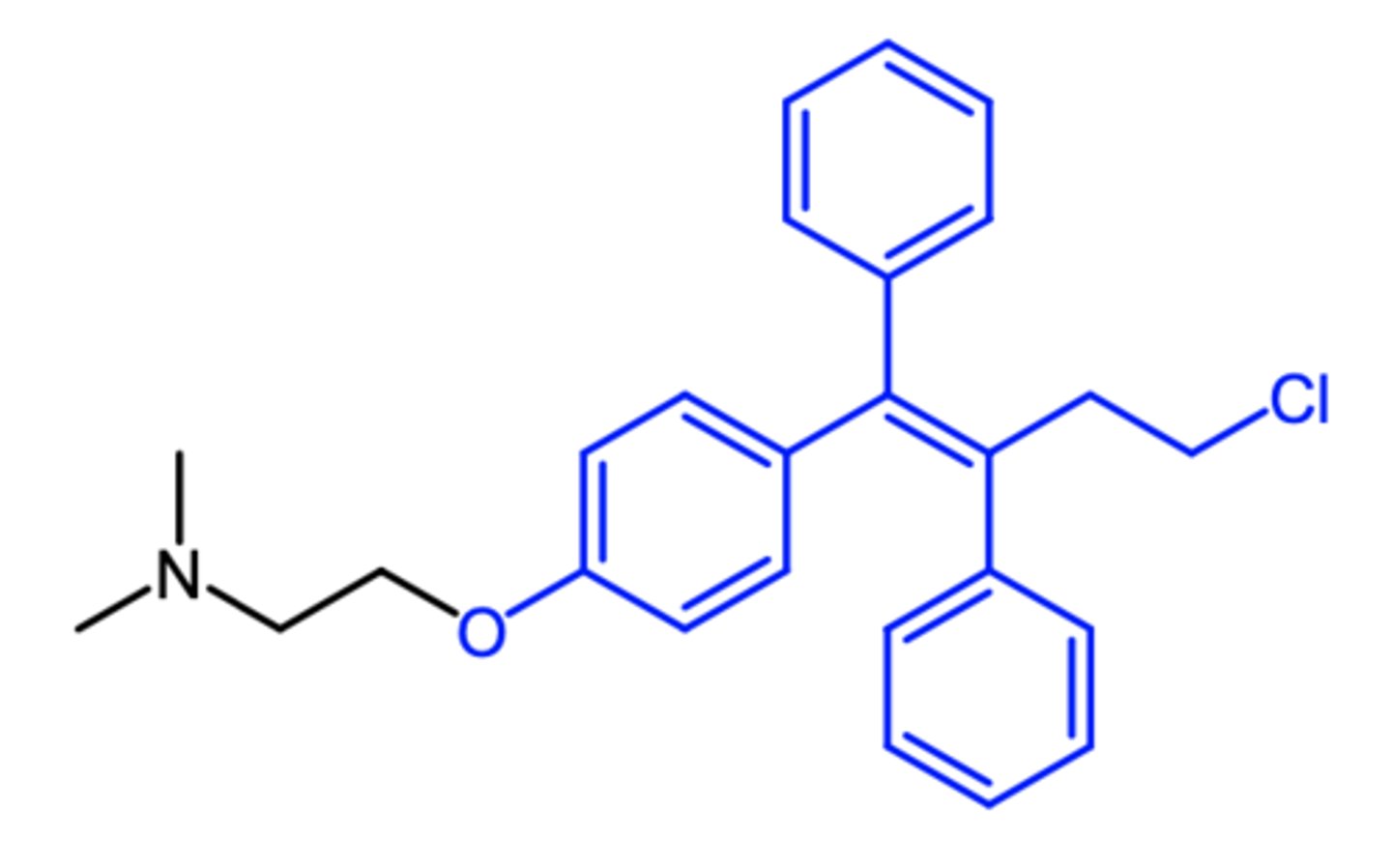
clomiphene
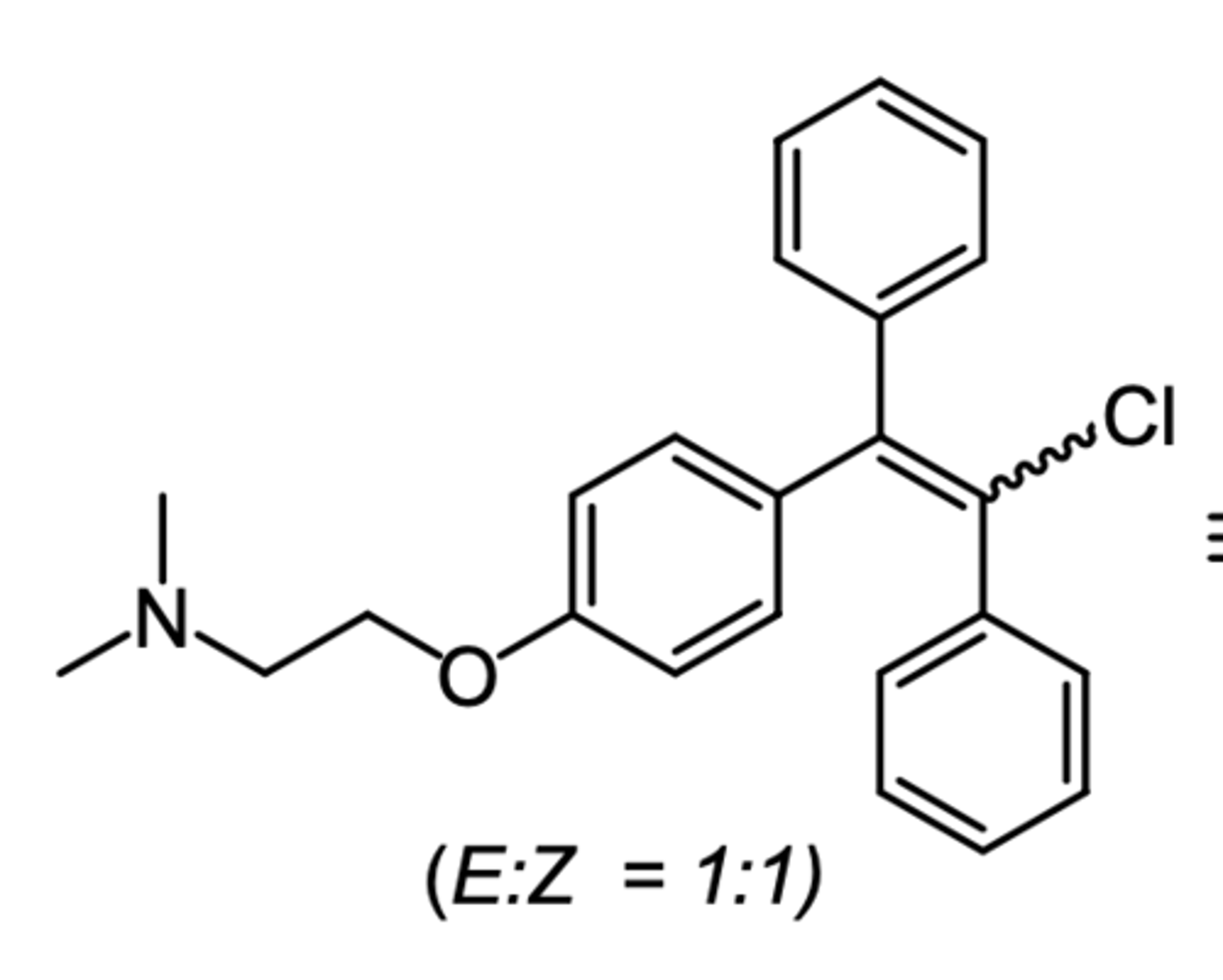
clomiphene
(anti estrogen -- SERM)
SAR: 1:1 mixture of enclomiphene and zuclomiphene
ROA: oral
MOA: zuclomiphene has estrogenic activity while enclomiphene has anti-estrogenic activity
indication: ovulation stimulant (fertility drug)
- polycystic ovary syndrome
ADME: readily absorbed from GIT, half life of 5 days
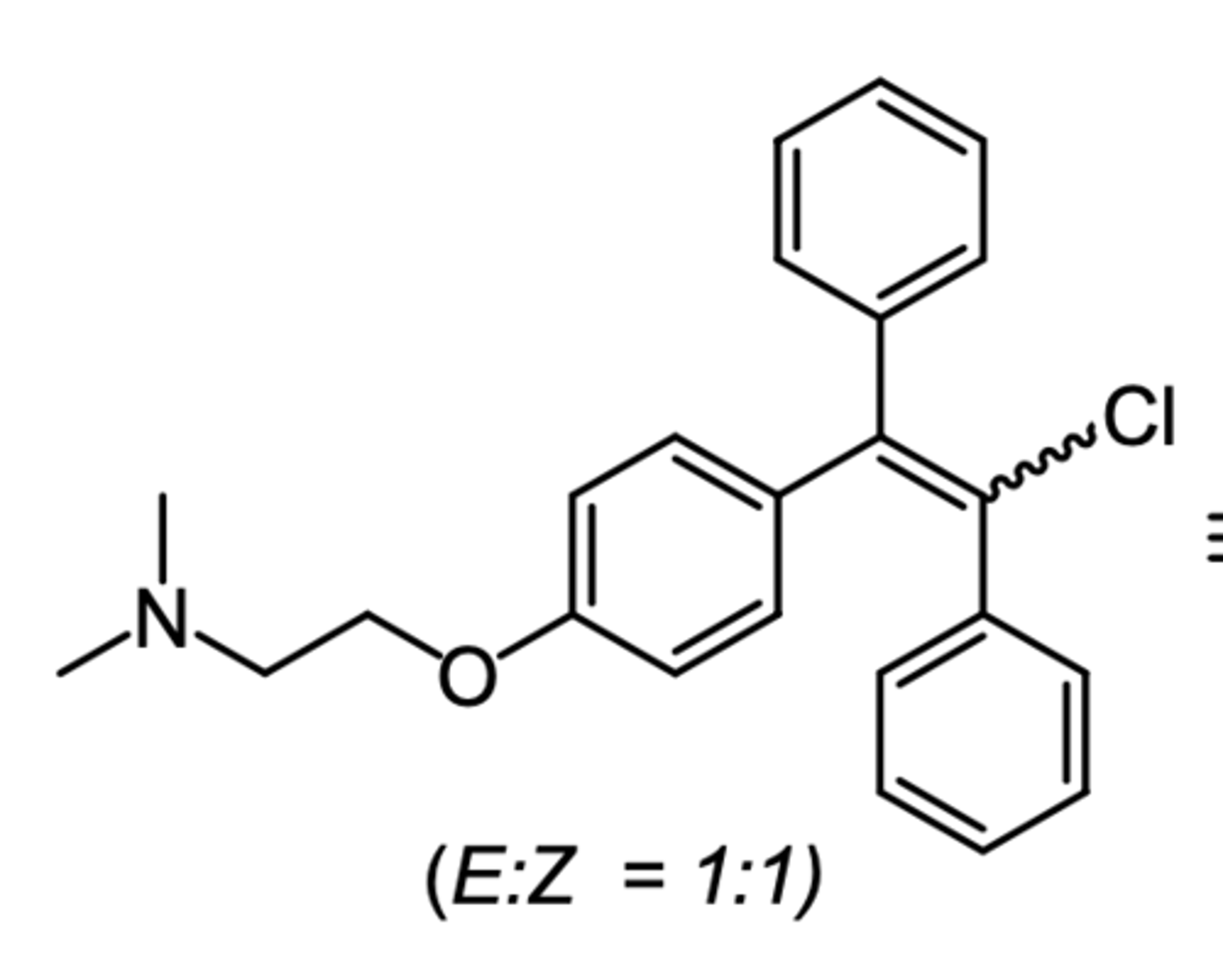
clomiphene
what is the most commonly used fertility drug?
raloxifene
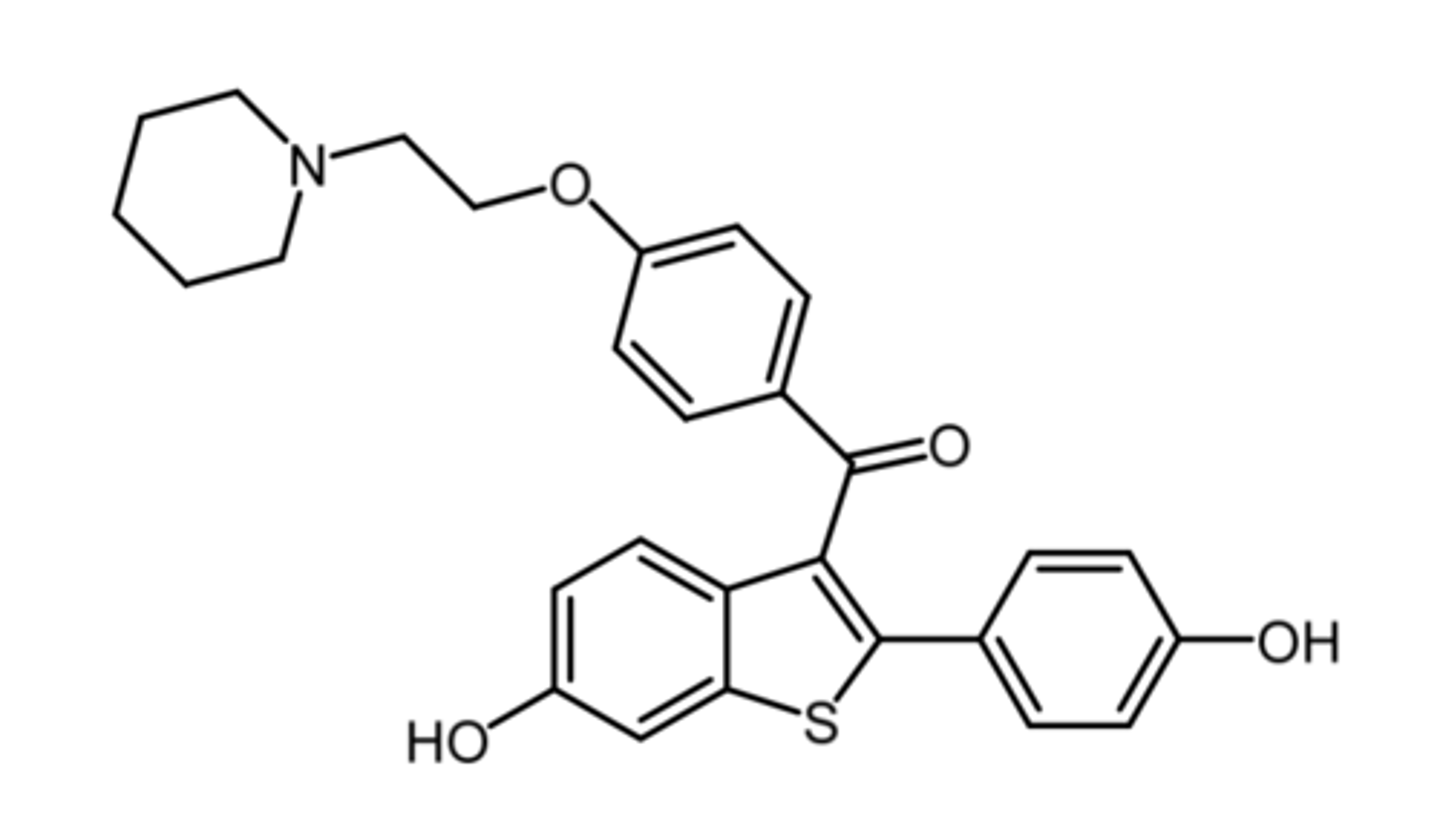
raloxifene
(anti estrogen -- SERM)
MOA: estrogen agonist on receptors of osteoblasts/clasts + antagonist at breast and uterine estrogen receptors
indication: treat + prevent osteoporosis in postmenopausal women
- dec risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women w osteoporosis or high risk women
PK: 60% absorption, low OBA (2%), rapid phase 2 metabolism, enterohepatic circulation
- dec risk of thromboembolic events + cataracts
- less resistance than tamoxifen
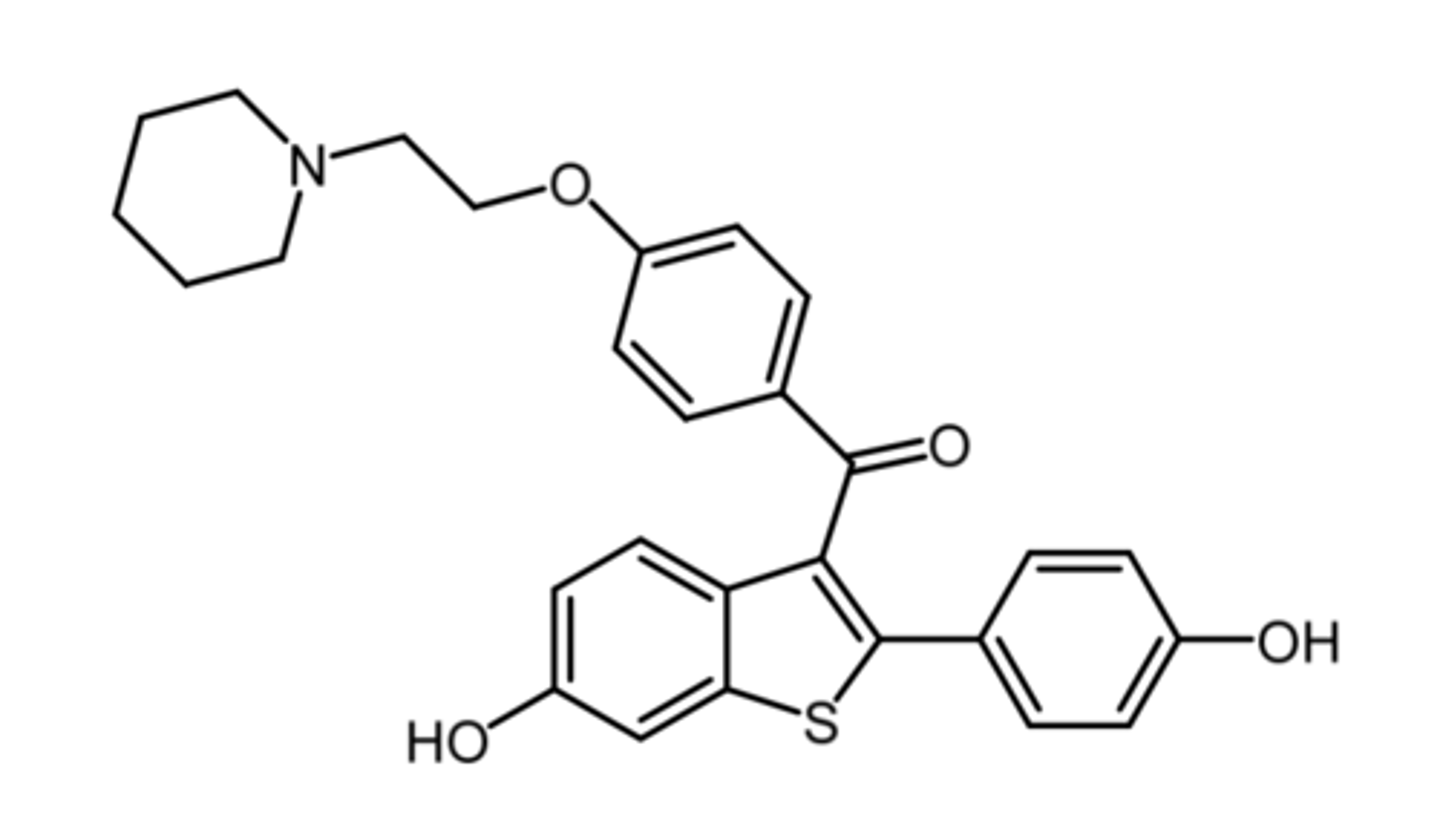
less
raloxifene has (less/more) resistance than tamoxifen
agonist, antagonist
raloxifene is an estrogen ____ on receptors in osteoblasts and osteoclasts but is an _____ in breast and uterine estrogen receptors.
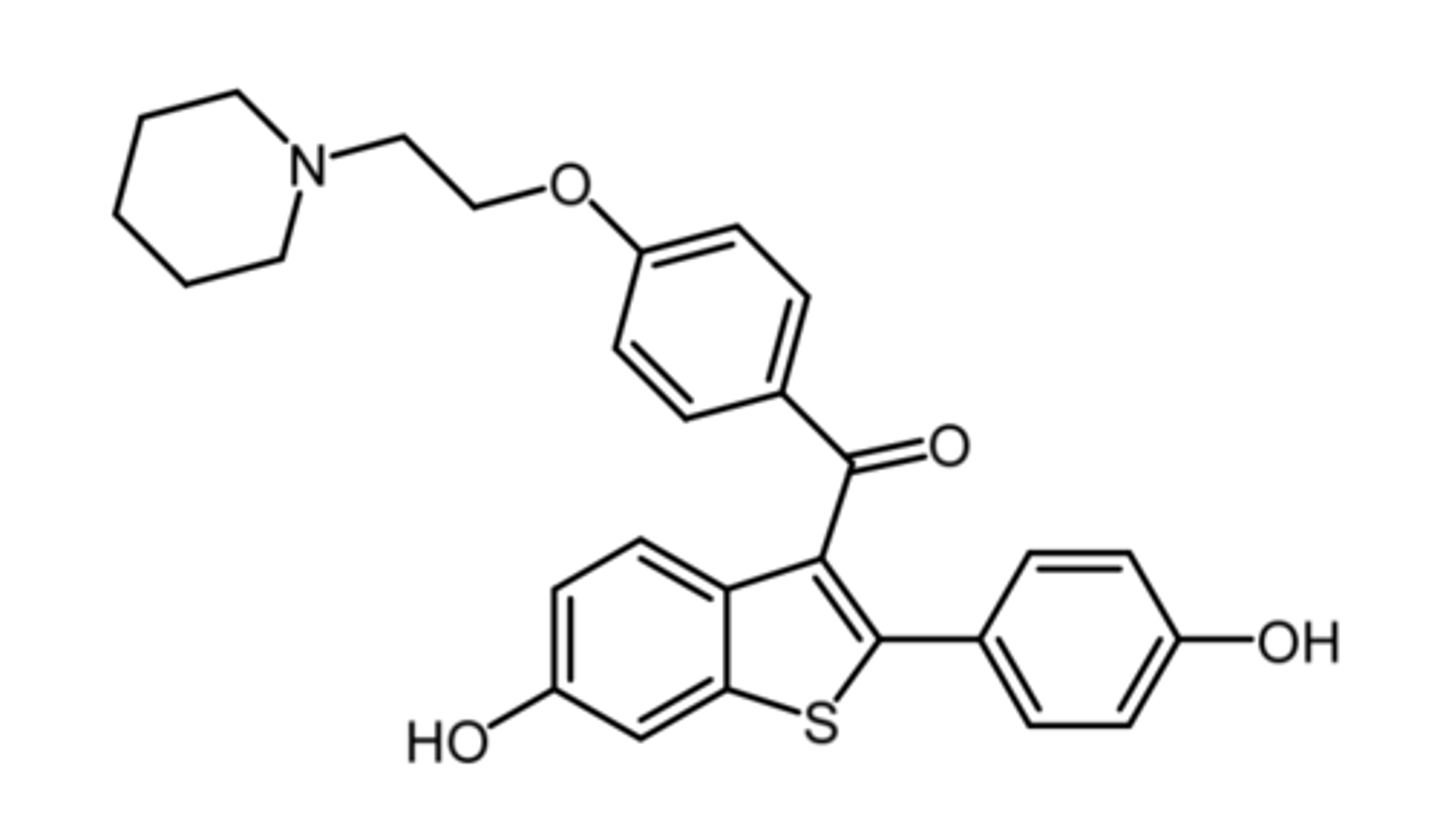
demethylate, aromatize
what are the chemical transformations that aromatase carries out?
_____ the C10 methyl group and _____ the A-ring
anastrozole, letrozole, exemastane
what are the 3 aromatase inhibitors?
anastrozole
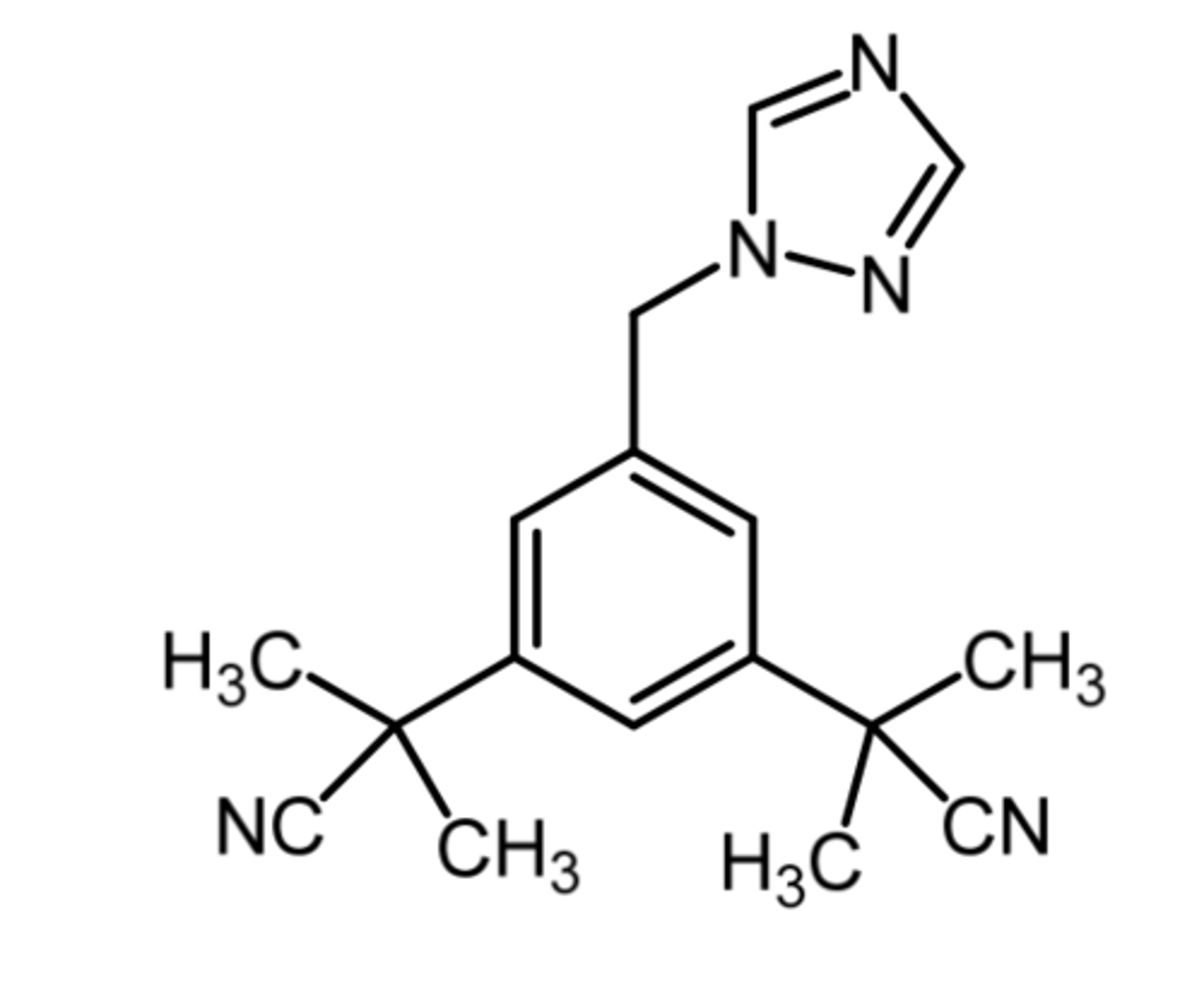
anastrozole
(aromatase inhibitor)
ROA: oral
MOA: competitive inhibitor that binds the heme portion of the enzyme
indication: 1st line for hormone receptor positive breast cancer and for relapse following tamoxifen therapy
- more effective than tamoxifen in treating breast cancer
SAR: related to non-steroidal aromatase inhibitors
advantage: no limitation on duration usage, where tamoxifen can only be used for 5 years
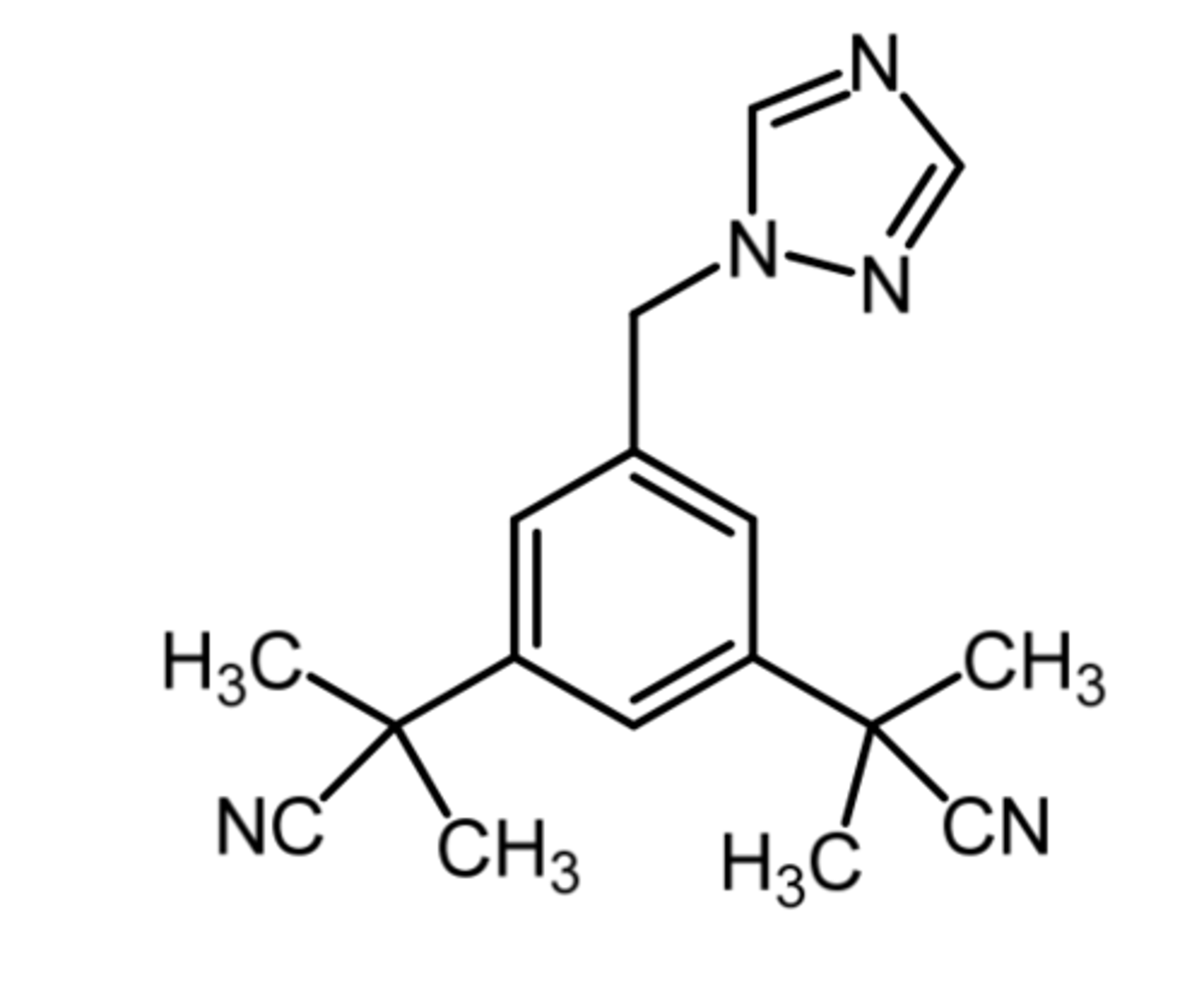
letrozole
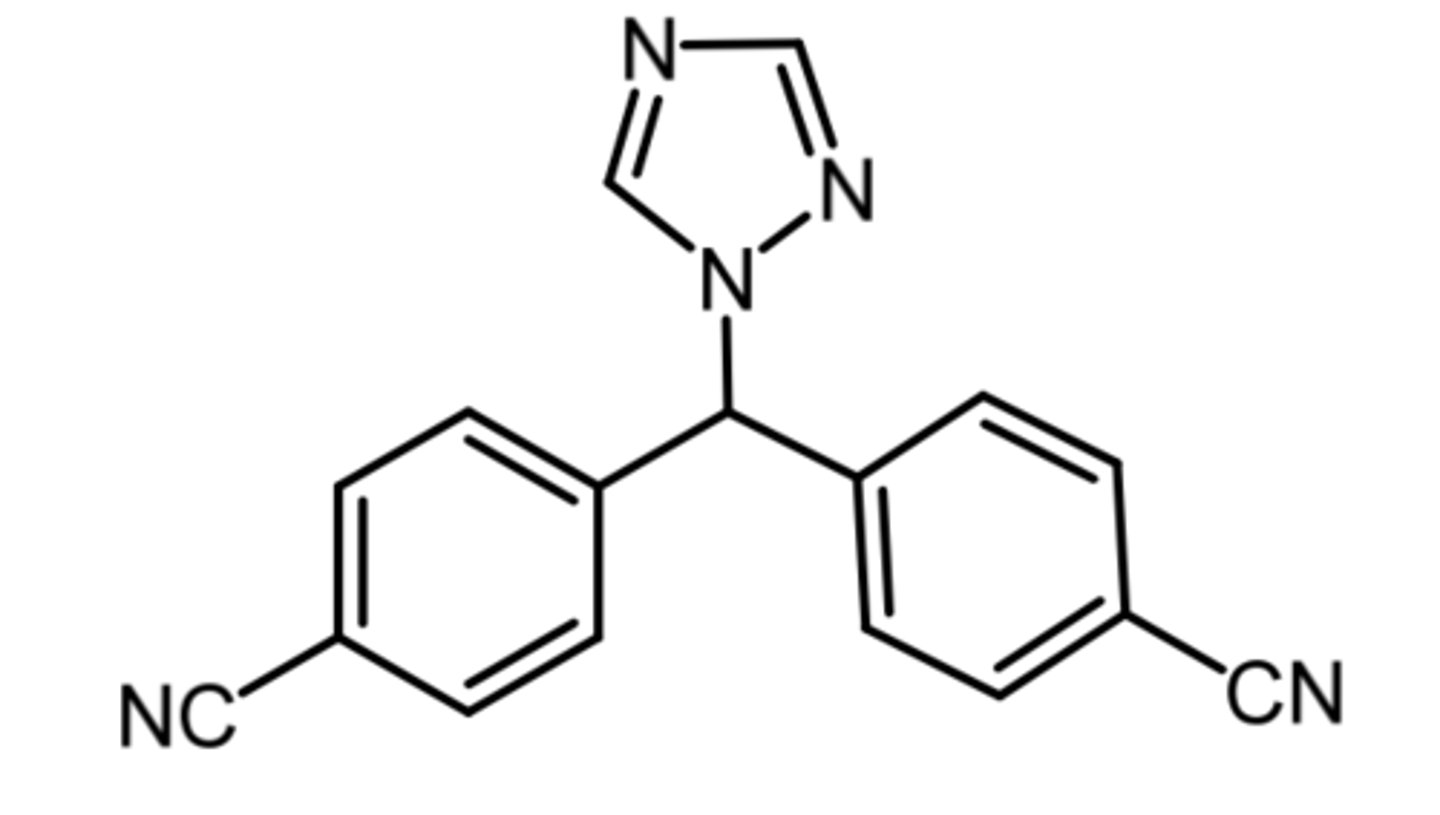
letrozole
(aromatase inhibitor)
ROA: oral
MOA: competitive inhibitor that binds the heme portion of the enzyme
indication: 1st line for hormone receptor positive breast cancer and for relapse following tamoxifen therapy
- more effective than tamoxifen in treating breast cancer
SAR: related to non-steroidal aromatase inhibitors
advantage: no limitation on duration usage, where tamoxifen can only be used for 5 years
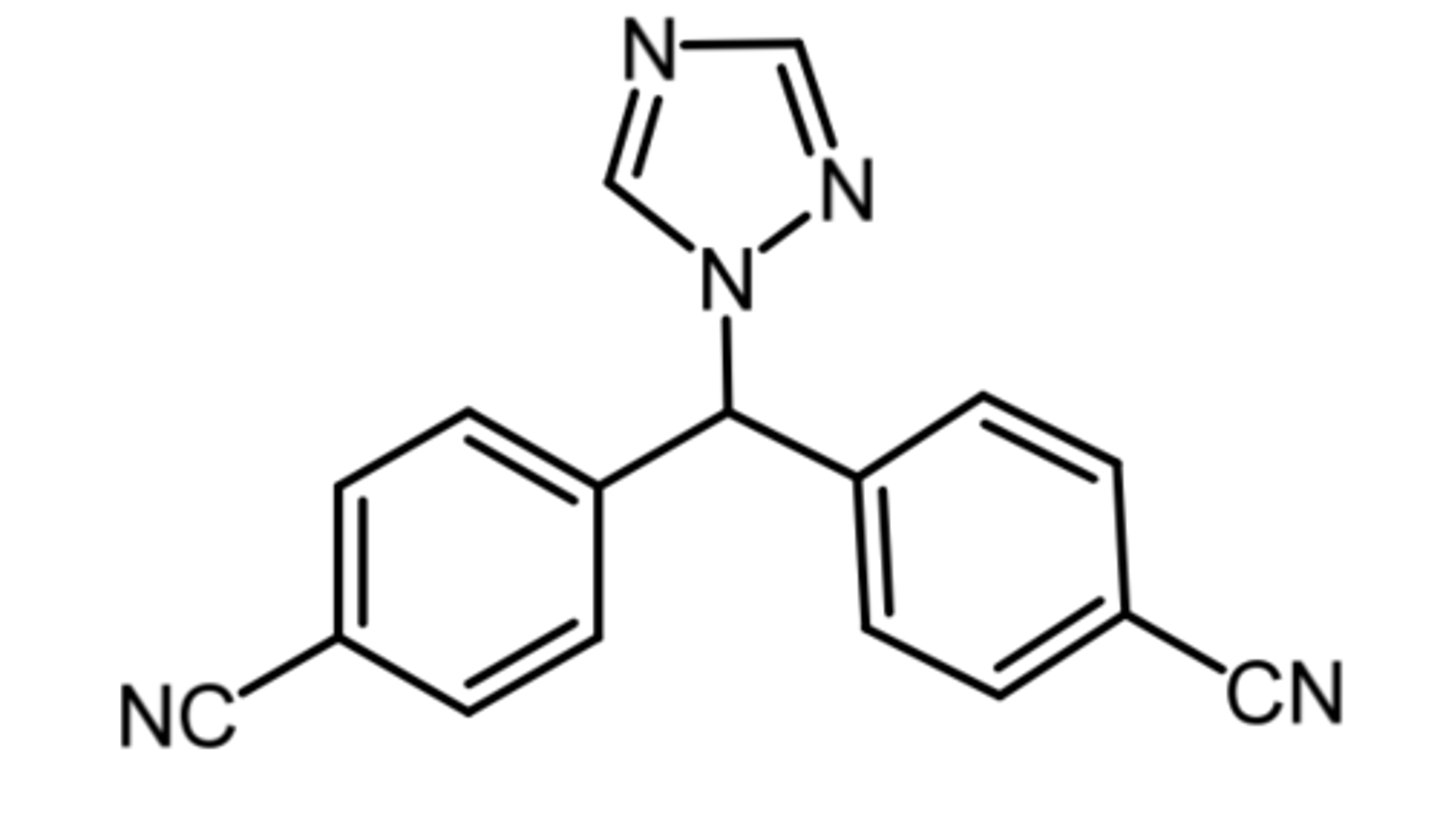
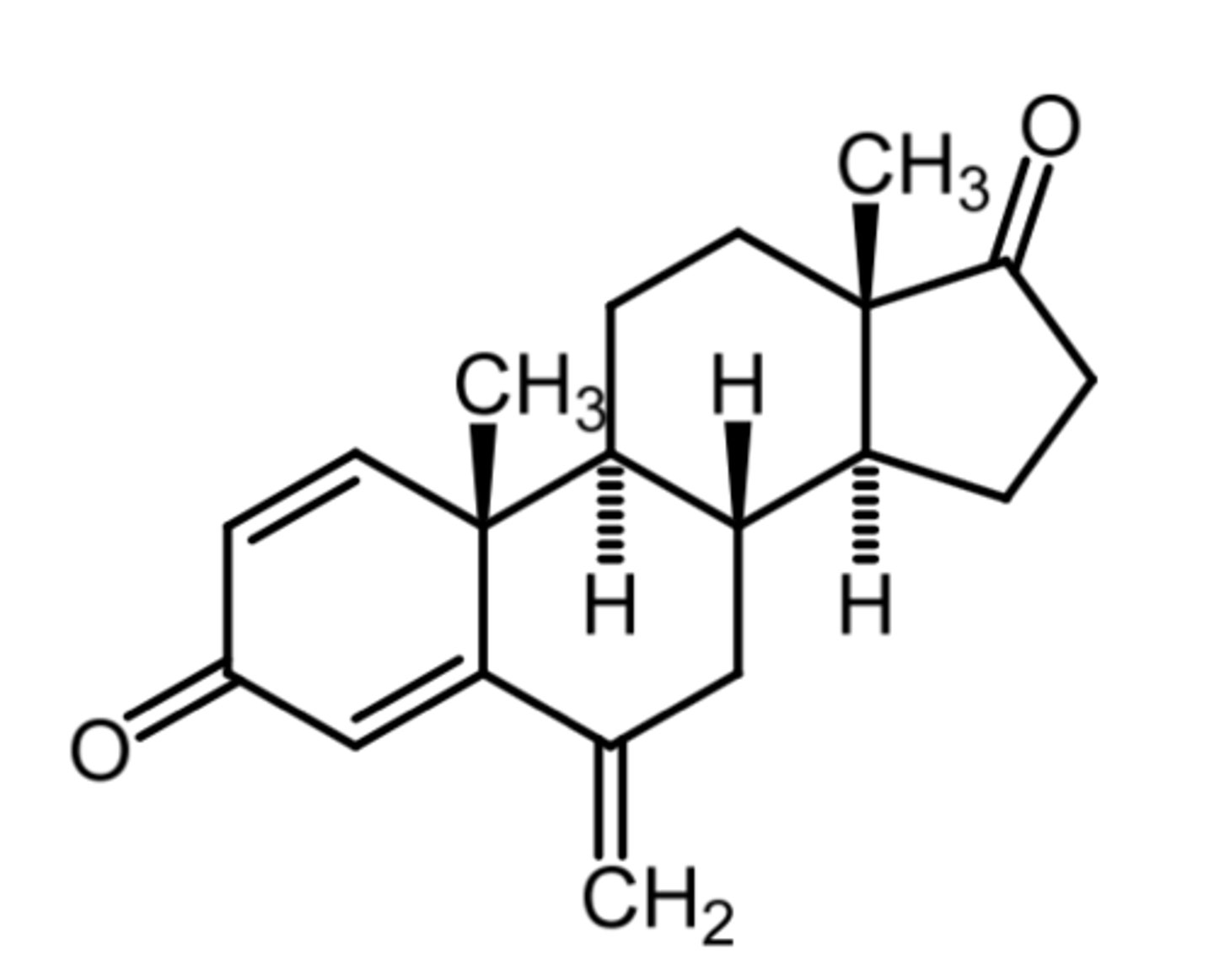
exemastine
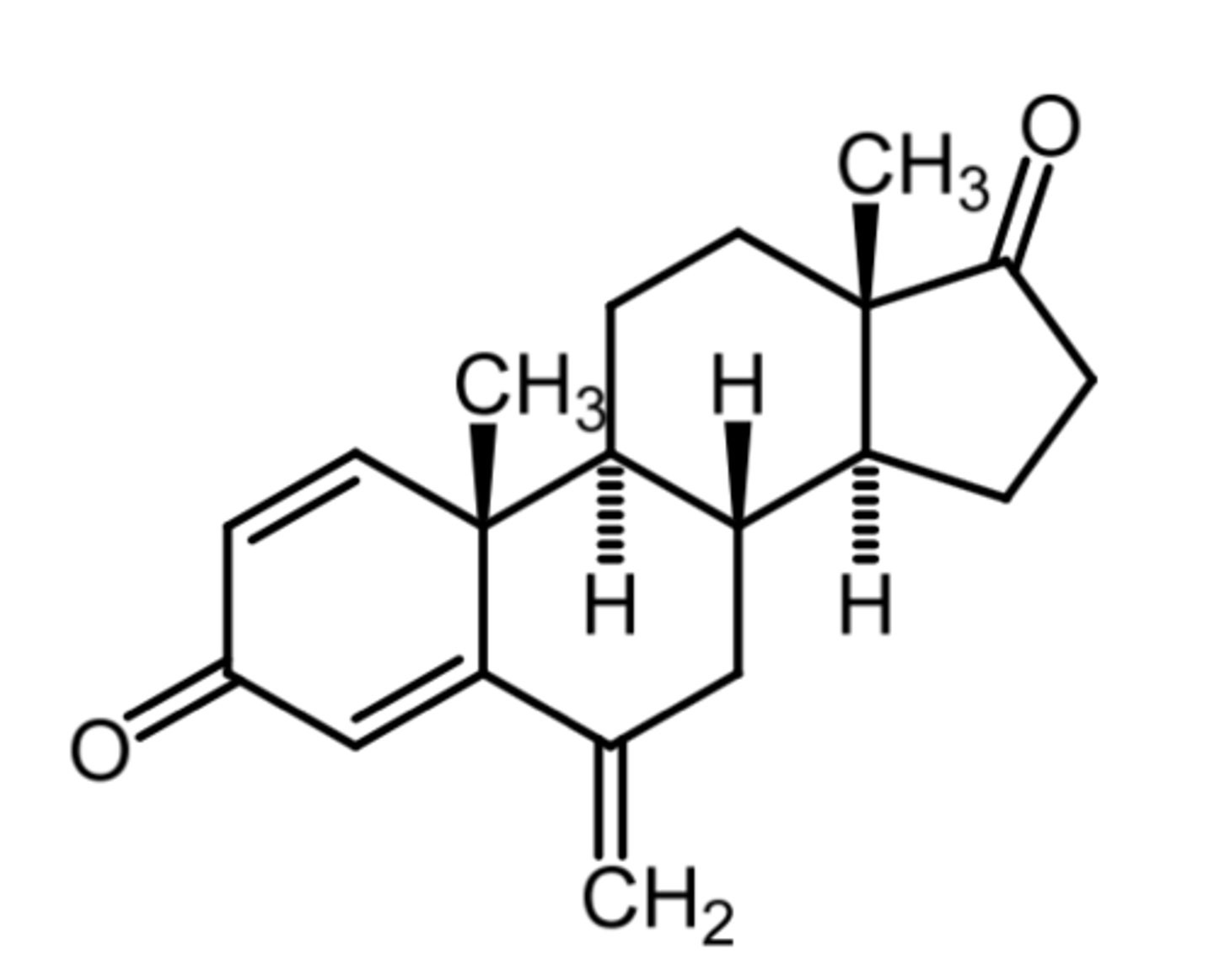
exemastine
(aromatase inhibitor)
ROA: oral
MOA: irreversible aromatase inhibitor (suicide substrate)
- forms covalent bond with cysteine
indication: estrogen +ve breast cancer in post menopausal women
- risk reduction for invasive breast cancer in post menopausal women
oral
what is the ROA for aromatase inhibitors?