Unit 1 Test: Chemistry of Life
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Hydrocarbons
organic molecules consisting of only hydrogen and carbon; major components of petroleum
Isomer
variation in the architecture of organic molecules; Has different properties because of different shape(structural, cis-trans, and enantiomers)
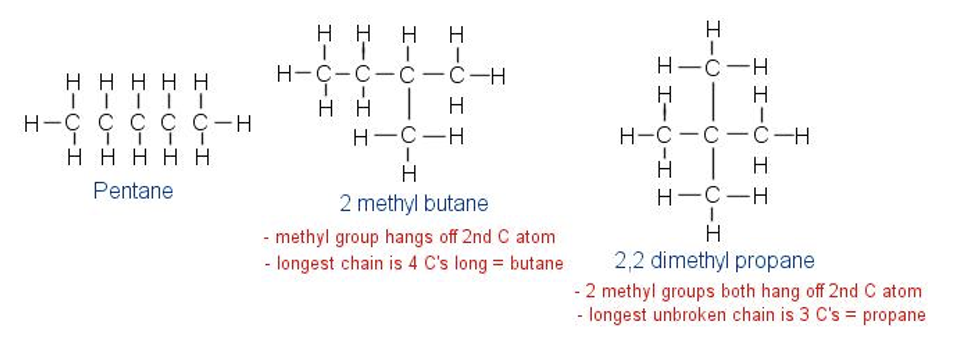
Structural isomer
differ in covalent arrangements of their atoms, may also differ in arrangement of double bonds
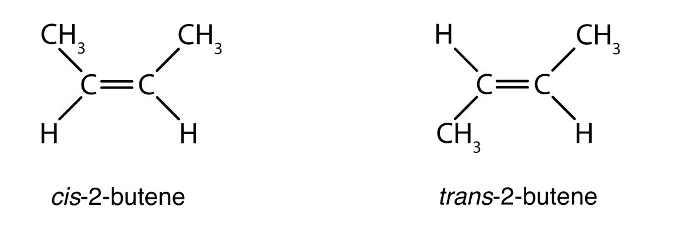
Cis-trans isomer
carbons have covalent bonds, but the atoms differ in their spatial arrangements due to the inflexibility of double bonds; They have variations in arrangement around a double bond.
enantiomer
isomers that are mirror images of each other and that differ in shape due to the presence of an asymmetric carbon
Methyl
it is a non-chemically reactive, unlike the other chemical groups, and is often used as a recognizable tag on biological molecules
polar covalent bond
results in bonding in water; a single water molecule bond
cohesion
water sticking to water
adhesion
water sticking to other substances
specific heat
is defined as the amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1g of that substance to change its temperature by 1*C; a large body of water can abosorbe and store a large amount of heat, heat regulation
evaporative cooling
moderation of temperature by evaporation
heat of vaporization
the quantity of heat a liquid must absorb for 1g of it to be converted from the liquid to the gaseous state.
solution
a liquid that is completely homogeneous mixture of two or more substances
solvent
the dissolving agent of a solution
solute
the substance being dissolved
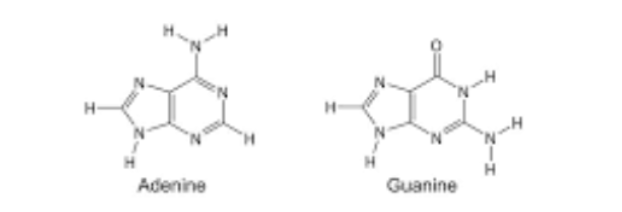
purines
adenine and guanine
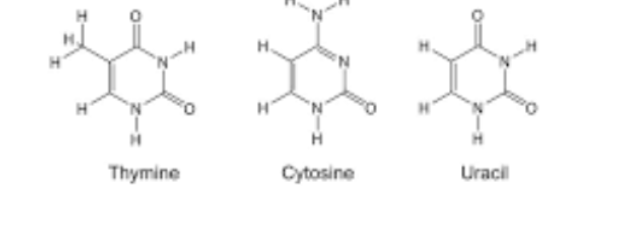
pyrimidines
thymine, cytosine, and uracil
start codon
AUG
lipids that are liquid at room temperature