unit 7: lQ/problem solving/personality (copy)
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
functional fixedness
a type of cognitive bias that involves a tendency to see objects as only working in a particular way.
flynn effect
that determined the average IQ of humans steadily increases over time
intelligence
the mental capacity to learn from experiences, adapt to new situations, understand and handle abstract concepts, and use knowledge to manipulate one's environment
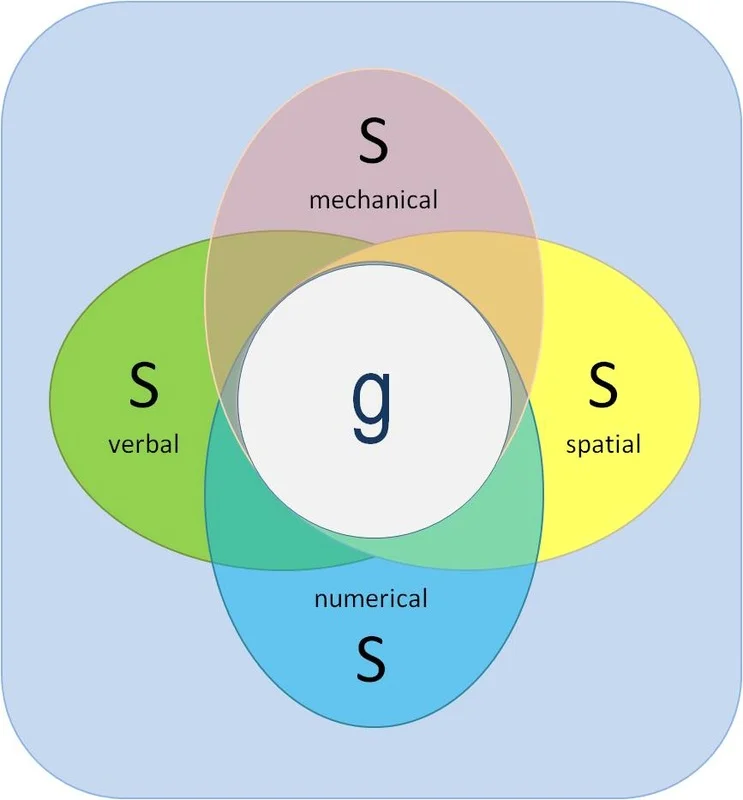
g or g-factor
source of individual differences in general ability, representing an individual's capacity to perceive relationships and derive conclusions
IQ
a number used to express the relative intelligence of a person
fluid intelligence
able to think on the fly; the ability to solve novel problems, think abstractly, and reason without relying on previously acquired knowledge or experience
crystallized intelligence
the accumulated knowledge, skills, and understanding that a person has acquired throughout their life‘ wisdom
convergent thinking
only 1 answer; a cognitive process that involves focusing on finding the best possible solution to a problem by narrowing down options and evaluating them critically
divergent thinking
creativity; a thought process used to generate creative ideas by exploring many possible solutions
validity
intelligence must be this….
the extent to which a test or measurement accurately reflects the construct or concept it's intended to measure
reliability
intelligence test must also be this….
the consistency or stability of scores obtained from an intelligence test over time and across different situation
standardization
everyone is tested the same; the process of ensuring that a test is administered and scored consistently across all participants, allowing for meaningful comparisons of results
normed (percentile rank)
the percentage of individuals in a specific group (the norm group) who scored at or below a particular score on a test, providing a way to compare an individual's performance to others; percentile rank
achievement
ACT and AP exams; Measure how much you have learned in a given subject area
aptitude (predictive validity)
SAT; designed to assess an individual's potential to succeed in a certain area, even if they haven't received training or education in that field
ghrelin
a hormone that is known as an appetite increaser
leptin
a protein, manufactured and secreted by fat cells, that may communicate to the brain the amount of body fat stored and may help to regulate food intake
hypothalamus
control center for many automatic functions including hormone production, temperature regulation, hunger, thirst, sleep cycles, and emotional responses
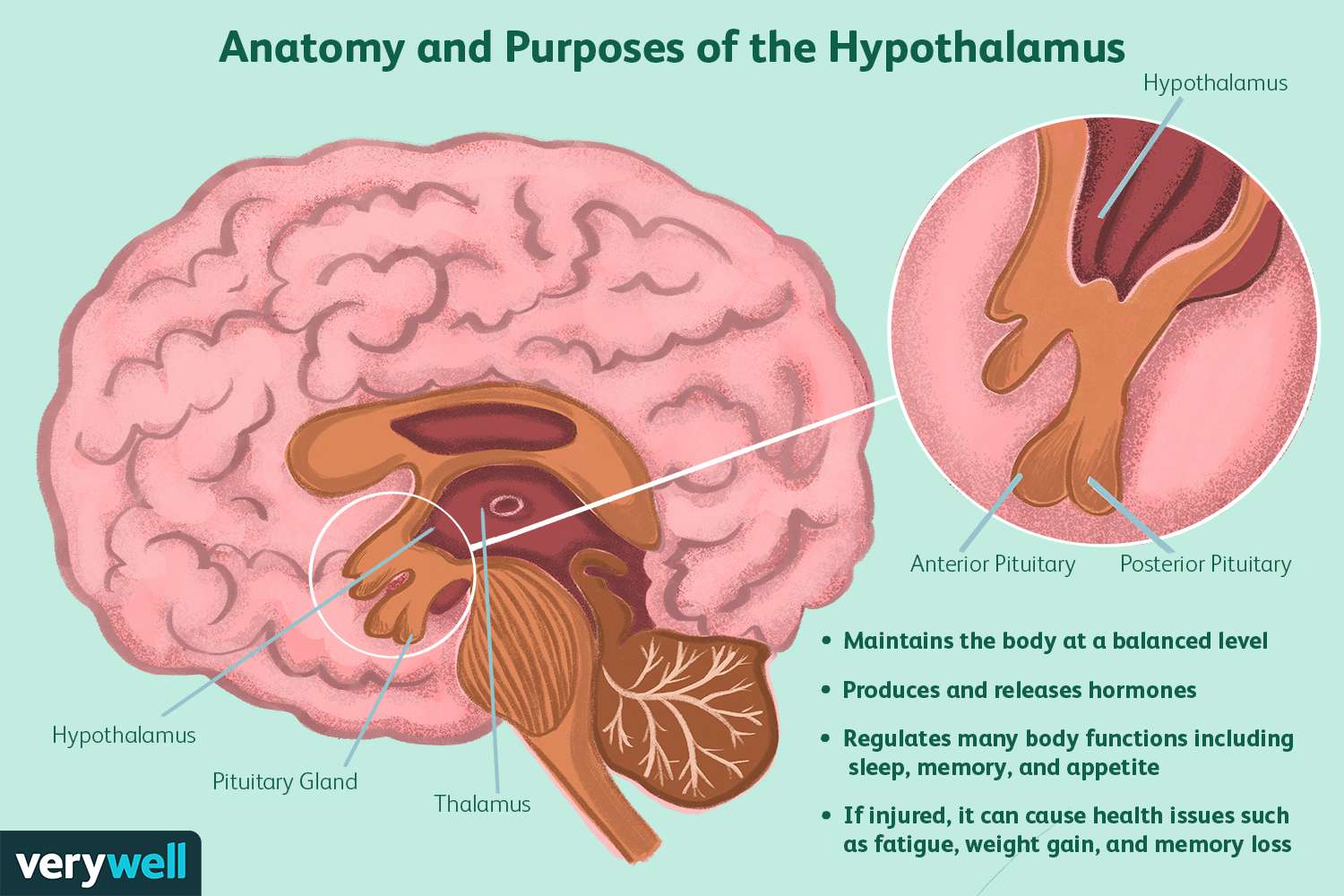
pituitary gland
it regulates other endocrine glands and controls growth, metabolism, and other bodily functions, including stress response
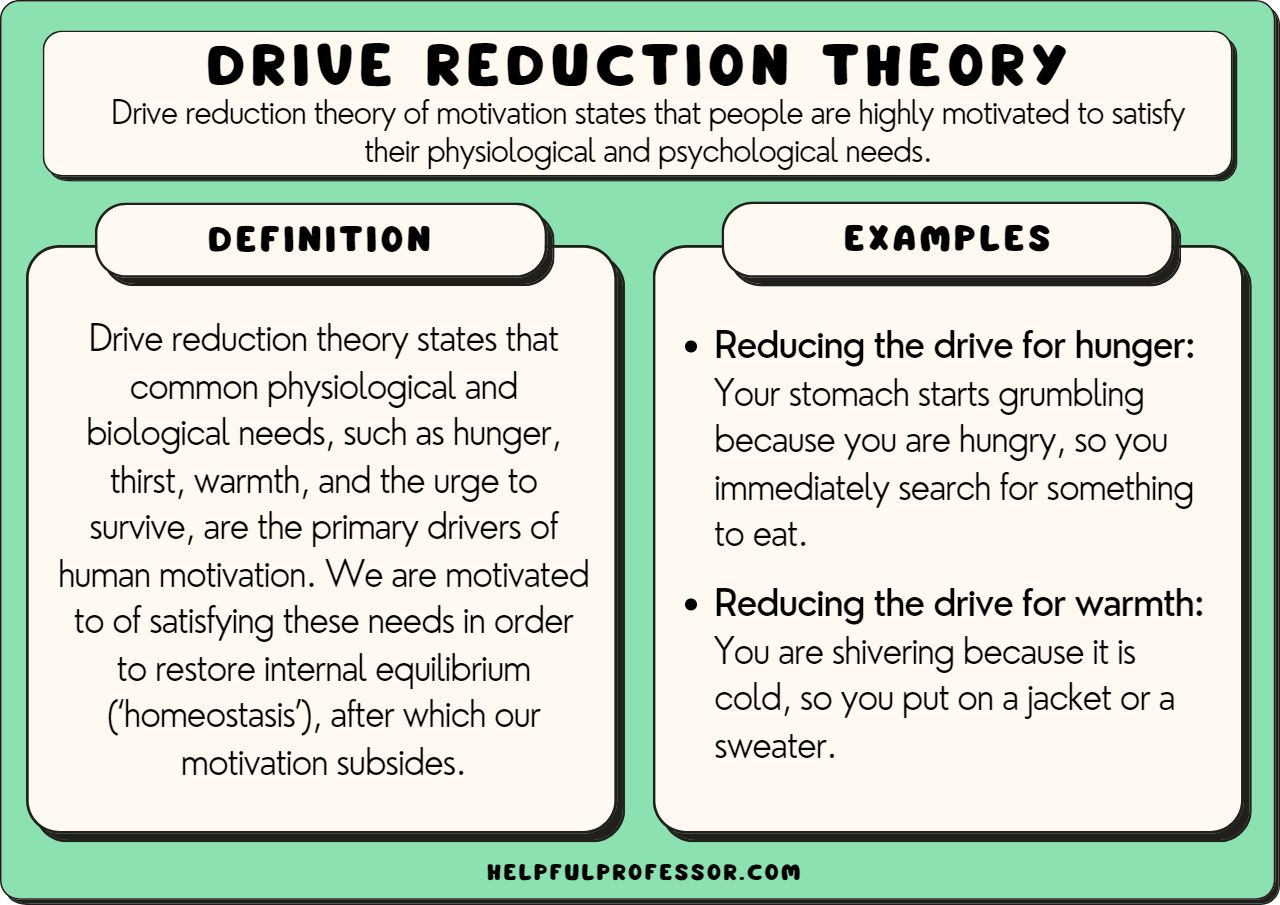
drive reduction theory
the actions we take are motivated by a need to reduce the tension created by physiological drives
homeostasis (satiety)
homeostasis refers to the body's ability to maintain a stable internal environment, while satiety is the feeling of fullness that signals the end of eating and inhibits further food intake
anorexia
an eating disorder characterized by restriction of food intake leading to low body weight, typically accompanied by intense fear of gaining weight and disturbed perception of body weight and image
bulimia
an eating disorder that causes you to eat large amounts of food at one time (binge) and then get rid of it (purge)
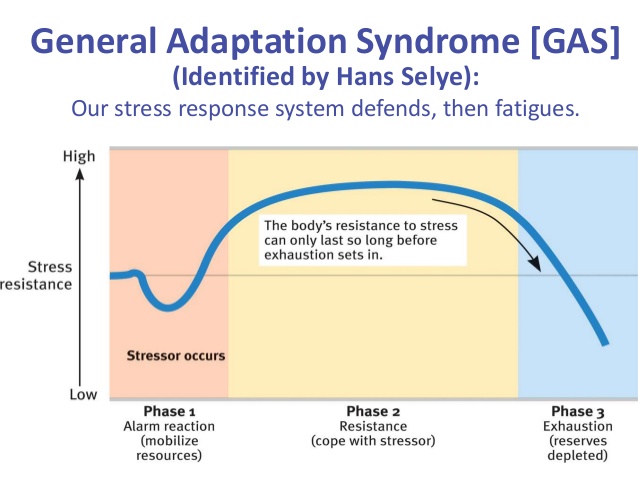
general adaption syndrome (GAS)
a three-stage response that the body undergoes when exposed to prolonged stress
STAGE 1: alarm - sympathetic NS
STAGE 2: resistance - drive reduction
STAGE 3: burn out/sickness
trait
a relatively stable, consistent, and enduring internal characteristic that is inferred from a pattern of behaviors, attitudes, feelings, and habits in the individual
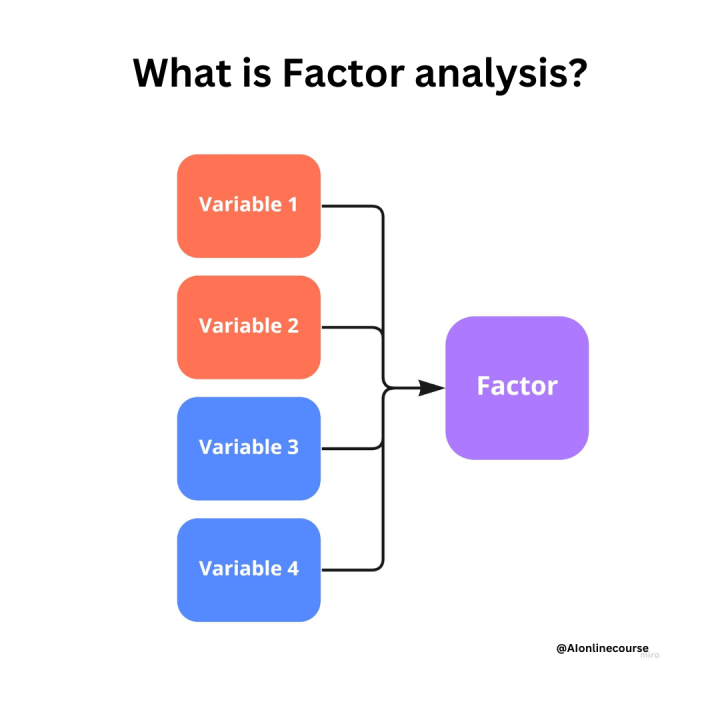
factor analysis
a statistical method for identifying clusters of items that tend to be answered the same way
personality inventory
a psychological assessment tool that measures and evaluates various aspects of an individual's personality, such as traits, behaviors, and attitudes
big 5 (OCEAN)
Openness
Conscientiousness
Extraversion
Agreeableness
Neuroticism
Openness
curious, original, intellectual, creative, and open to new ideas
Conscientiousness
organized, systematic, punctual, achievement oriented, and dependable
Extraversion
outgoing, talkative, sociable, and enjoys being in social situations
Agreeableness
affable, tolerant, sensitive, trusting, kind, and warm
Neuroticism
anxious, irritable, temperamental, and moody
difference between emotions, feeling, and mood
emotions: seconds
feeling: minutes
mood: days
how many emotions are there
7
name of emotions
surprise, fear, disgust, anger, happiness, sadness, and contempt
emotions
conscious mental reactions (such as anger or fear) subjectively experienced as strong feelings usually directed toward a specific object and typically accompanied by physiological and behavioral changes in the body
display rules
culturally-defined norms or conventions that dictate when, where, and how emotions should be expressed, suppressed, or exaggerated
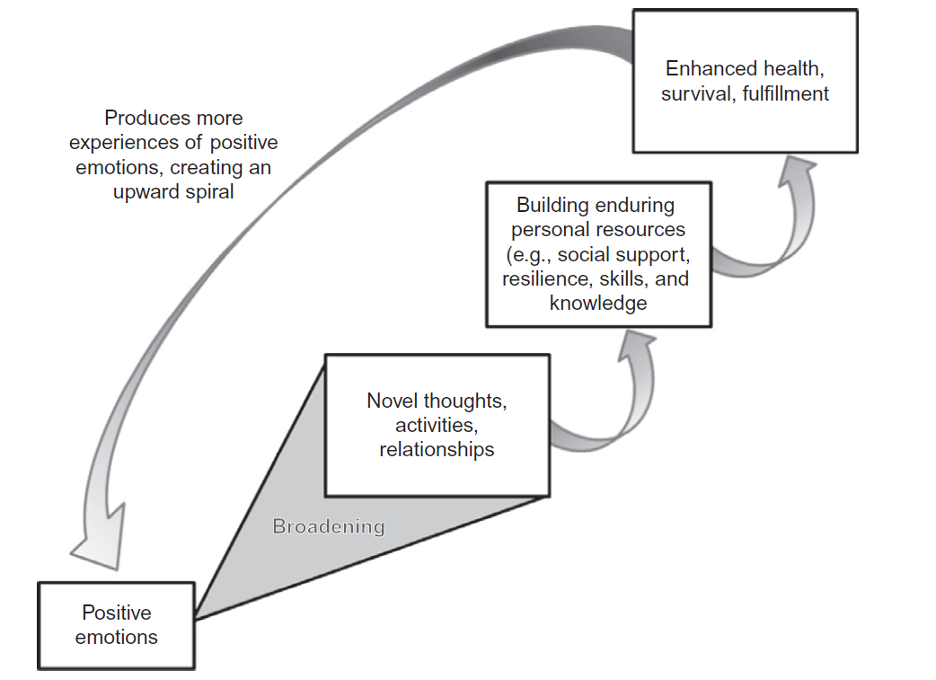
broaden & build theory
positive emotions broaden an individual's momentary thought-action repertoires, leading to the building of enduring personal resources
facial feedback hypothesis
suggests that individuals' emotional experiences are influenced by their facial expressions
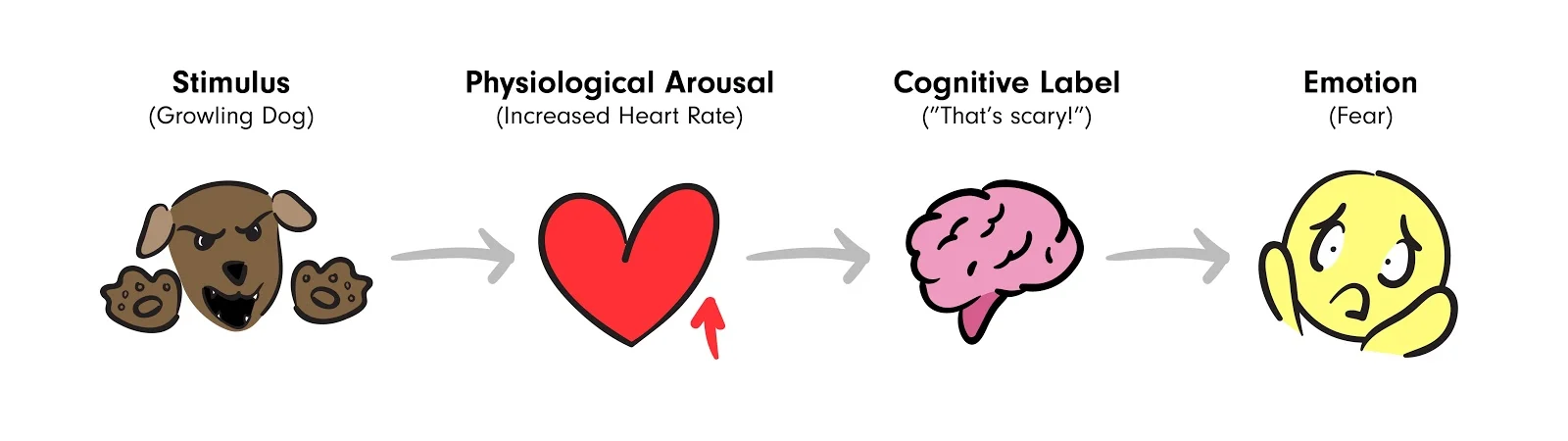
schachter’s two-factor theory emotion
people use cues from their immediate environment to inform their emotions
psychoanalytic/psychodynamic approach
explains personality in terms of unconscious psychological processes
id
the primitive, instinctual, and unconscious part of the personality that drives basic needs and desires, operating on the pleasure principle seeking immediate gratification
ego
the realistic part of personality that strikes a balance between our primal urges and moral conscience
superego
the ethical component of the personality and provides the moral standards by which the ego operates/what society thinks you should do
defense mechanisms
unconscious strategies used to protect oneself from anxiety or distress, often distorting reality to cope with internal conflicts or external stressors
repression
a defense mechanism where the unconscious mind pushes unacceptable or anxiety-provoking thoughts, feelings, or memories out of conscious awareness, though they may still influence behavior
denial
a psychological defense mechanism in which an individual refuses to acknowledge or accept painful or threatening realities
displacement
a defense mechanism where an individual redirects an emotional reaction, like anger or fear, from its original source to a less threatening target
fantasy
a broad range of mental experiences, often involving vivid imagery and the expression of desires through imaginary scenarios, which can be conscious or unconscious and serve various psychological purposes
projection
a defense mechanism in which an individual attributes their own unacceptable thoughts, feelings, or behaviors to others
rationalization
a defense mechanism where a person justifies their thoughts, feelings, or actions with seemingly logical reasons, often to avoid confronting uncomfortable truths or underlying motives
reaction formation
a defense mechanism in psychology where a person unconsciously expresses the opposite of their true feelings or impulses
regression
a defense mechanism where an individual returns to earlier stages of development or behavior
sublimation
a healthy defense mechanism where unacceptable or socially undesirable impulses or desires are channeled into socially acceptable and constructive behaviors
free association
a psychoanalytic technique where a patient is encouraged to express their thoughts, feelings, and memories without censorship or self-criticism
projective test
presents ambiguous stimuli (like inkblots or pictures) to elicit responses that reveal underlying personality traits, unconscious thoughts, and emotions, as individuals are believed to "project" their internal world onto the stimuli
grit
a personality trait characterized by perseverance and passion for achieving long-term goals
growth mindset
people believe that their most basic abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work
fixed mindset
the belief that abilities are innate and unchangeable
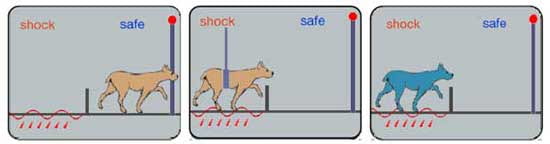
learned helplessness
a state where an individual, after repeated exposure to stressful or painful situations they believe they cannot control, develops a passive and apathetic response, even when opportunities for change or escape arise
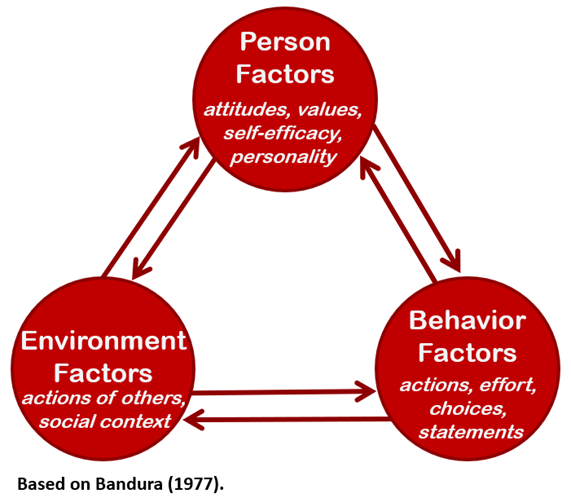
reciprocal determinism
the theory set forth by psychologist Albert Bandura which states that a person's behavior both influences and is influenced by personal factors and the social environment
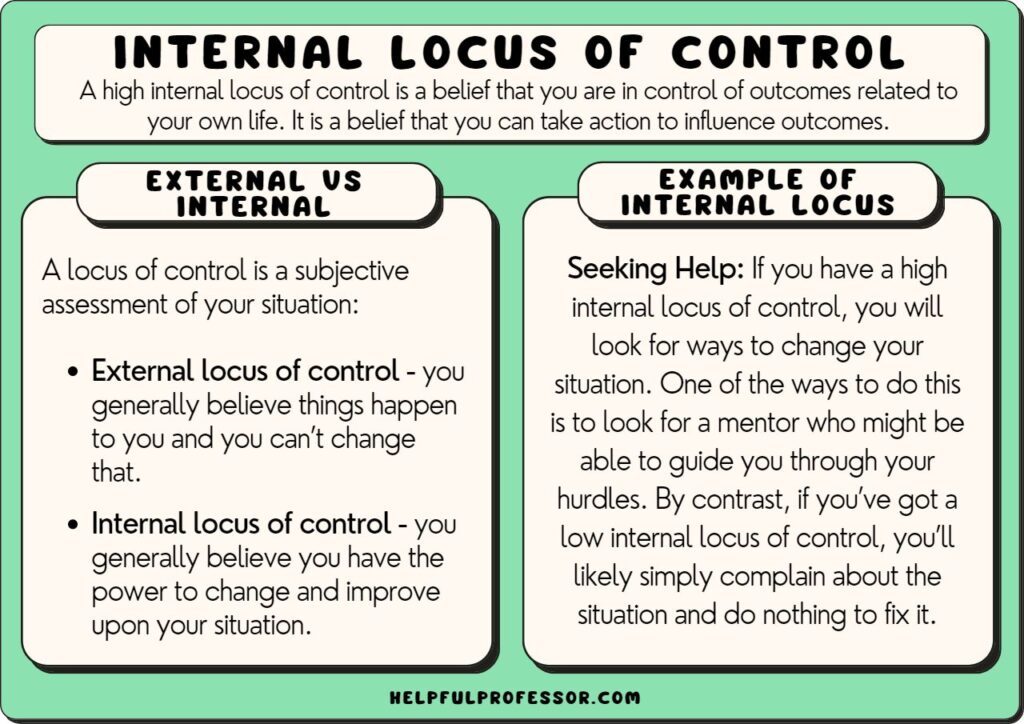
internal locus of control
the belief that individuals have control over their own actions and outcomes, and that their choices and efforts directly influence the results they experience
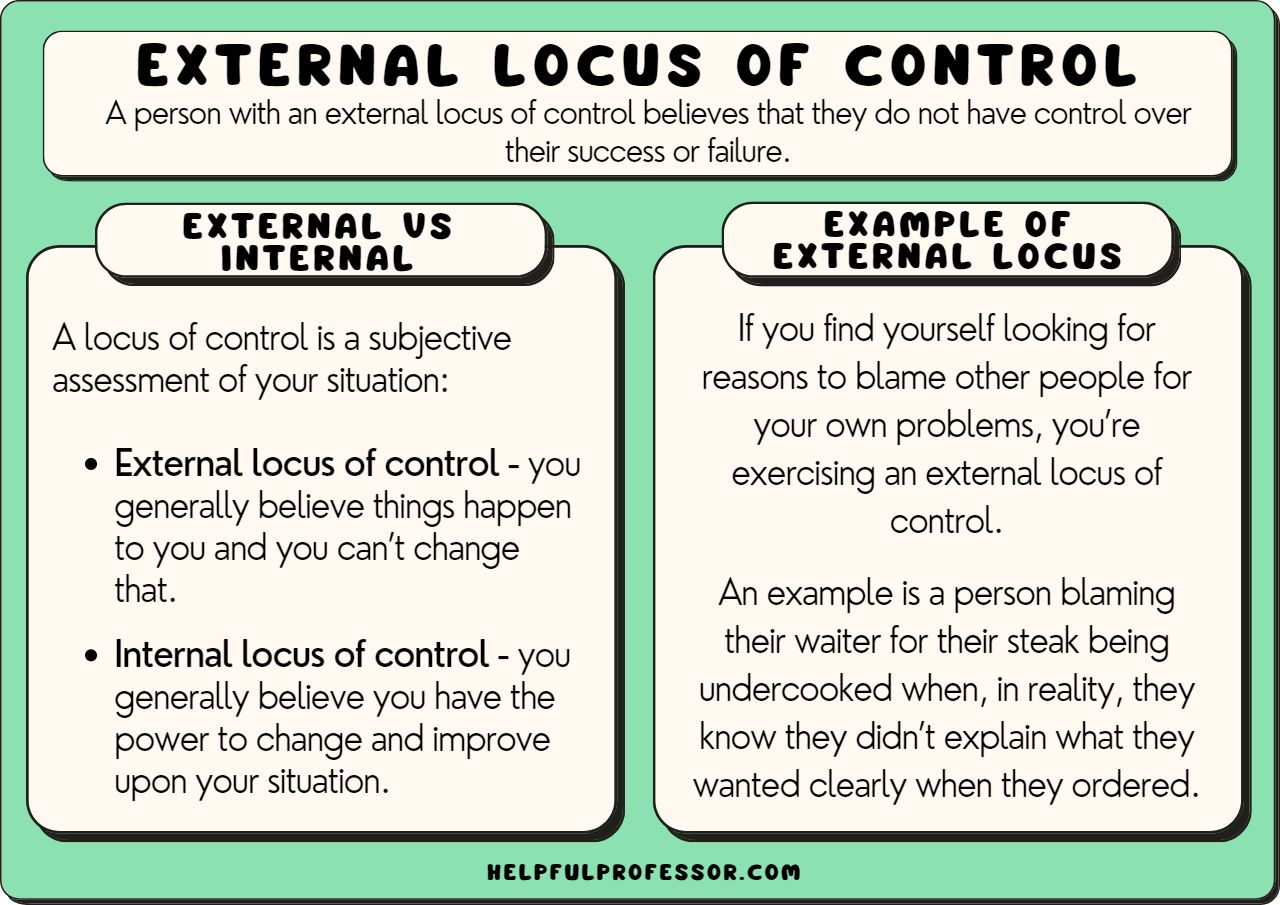
external locus of control
the belief that external factors, rather than one's own actions, determine life outcomes, such as luck, fate, or powerful others, leading to a sense of helplessness or resignation
explanatory style
the way a person creates a narrative about a specific event in their life