Breeding Management Tutorials
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
What are the key livestock species to evaluate the impact of breeding on health and welfare?
Holstein cows, Belgian Blue cattle, sows, and meat birds.
What is the primary focus of the group task regarding livestock breeding?
To research and evaluate the impact of breeding on health and welfare of specific livestock species.
What is one reason for breeding livestock?
To fit their systems, such as dairy versus beef cows.
How do traits differ between dairy cows and beef cows?
Dairy cows are bred for high milk production, while beef cows are bred for meat quality and growth rate.
What is the purpose of designing the 'perfect animal' in the activity?
To understand the traits required for different production systems.
What are two examples of livestock systems discussed in the activities?
Extensive dairy system and pig breeding unit.
What ethical considerations are discussed regarding breeding in companion animals?
The implications on animal health of extreme breed traits.
What are exaggerated features in dog breeds, and why are they important?
Certain features can cause pain and suffering and make dogs prone to specific disorders.
What is an EBV (Estimated Breeding Value)?
A measurement of genetic potential used to assess breeding merit for a certain trait.
What does a Selection/Breeding Index indicate?
It differs from an EBV by incorporating multiple traits into a single value for breeding decisions.
What should clients look for when choosing a puppy breeder?
Reputation, health testing, and ethical breeding practices.
What primary concerns should be discussed with a client wishing to breed their family dog?
Health risks, complications of mating, gestation, and parturition.
What is the significance of understanding genetic reports in breeding?
To make informed decisions about breeding for desired traits.
How does breeding in companion animals differ from breeding in large animals?
Companion animal breeding often focuses on aesthetics and temperament, while livestock breeding focuses on production traits.
What is the impact of high milk production in Holstein cows?
It can lead to health issues such as mastitis and metabolic disorders.

What are the implications of double musculature in Belgian Blue cattle?
It can result in increased muscle mass but may lead to birthing difficulties.
What is the health impact of breeding for a high number of piglets in sows?
It can lead to increased stress and health complications for the sow.
What is the importance of fast growth rates in meat birds?
While it improves production efficiency, it can lead to health issues such as skeletal problems.
What is the goal of comparing traits in different animal functions?
To understand how breeding affects the suitability of animals for specific purposes.
What should be included in the presentation on the impact of breeding?
At least 5 references and a comprehensive evaluation of the chosen livestock species.
What is the role of environmental effects in estimating breeding values?
They are adjusted for factors like age, lactation number, and herd performance.
What are Estimated Breeding Values (EBVs) expressed in?
EBVs are expressed in the unit of measurement for that trait, such as kg for weight.
How are EBVs represented in relation to genetic differences?
EBVs are shown as positive or negative differences between an animal's genetic difference and the genetic base to which it is compared.
What is the significance of genetic worth in breeding?
Only half of the genetic worth will be passed to its progeny.
What is a Selection Index or Breeding Index?
It combines the EBVs of several traits with economic weighting on each trait to produce a single selection index value for a specific breeding objective.
What are some examples of selection indices in the UK dairy industry?
Examples include £PLI (Profitable Lifetime Index), £SCI (Spring Calving Index), and £ACI (Autumn Calving Index).
How are breeding indexes expressed in the UK dairy industry?
Most breeding indexes are expressed as Predicted Transmitting Abilities (PTAs), predicting the amount of a trait offspring will receive from parents.
What does the Profitable Lifetime Index (£PLI) represent?
The £PLI value represents the additional profit that a daughter of a high £PLI bull is expected to earn over her lifetime compared to a daughter sired by an average bull.
What is the significance of PTAs for a bull with no daughter/performance data?
Genetic indexes will be based on the bull's parents and his own traits until he is 7 years old and has a high reliability daughter proof.
What does the Autumn Calving Index (£ACI) reflect?
The £ACI is suitable for autumn block-calving herds and reflects the costs of feeding for winter milk production and the higher milk price per litre received at that time.
What is the purpose of the Spring Calving Index (£SCI)?
The £SCI is developed to breed cows that produce lower volumes of milk of higher quality, specifically for spring block-calving herds.
What does the Feed Advantage PTA indicate?
It indicates the tendency to transmit good feed conversion to daughters, expressed as PTA in kg of DMI saved during each lactation.
What does the Lifespan PTA indicate?
It indicates the increase or reduction in days or lactations that daughters of a bull are predicted to survive in the herd relative to a bull with a PTA of zero.
What is Direct Calving Ease?
It refers to the ease with which the calf is born by a sire.
What is Maternal Calving Ease?
It refers to the ease with which the daughters will give birth to their calves.
How is Somatic Cell Count (SCC) expressed?
SCC is expressed as PTAs, where a negative %PTA SCC indicates a reduction and is therefore considered good.
What does a higher Maintenance value indicate?
A higher value indicates a heavier animal and a greater cost associated with the maintenance (feeding) of that animal.
What is Type Merit in dairy breeding?
Type Merit is a genetic index for conformation, indicating the sire's ability to transmit genes for physical traits to the next generation.
What should be considered regarding size in dairy breeding?
Bigger isn't always better; practical considerations should be taken into account, such as teat length and stature.
What is the breeding goal for Derek's high input Friesian herd?
Derek aims to increase fat and protein percentages and improve his Somatic Cell Count (SCC) to better position himself for contract changes.
What are the two main aims for suckler herds?
To improve calf growth rates and enhance maternal traits.
What is the purpose of Estimated Breeding Values (EBVs) in beef sires?
EBVs are used to predict the genetic potential of sires for traits such as birth weight, calving ease, and growth rates.
List three EBVs used in beef sires.
Birth weight, calving ease direct, and 400 day growth.
What are Selection Indexes in the context of beef sires?
Selection Indexes are tools used to evaluate the overall genetic value of a bull based on multiple traits, such as calving value and terminal index.
What is the significance of using sexed semen in dairy herds?
Sexed semen is used to improve fertility and increase the likelihood of producing female calves for replacement.
What is double musculature in Belgian Blue cattle?
Double musculature is a genetic condition caused by a mutation in the myostatin gene, leading to excessive muscle development.

What are the advantages of Belgian Blue cattle?
High carcass yield, tender meat, and improved feed efficiency.
What are the typical weight ranges for adult Belgian Blue bulls and cows?
Bulls weigh between 1100-1250 kg, while cows weigh between 850-900 kg.
What is the typical coat color of Belgian Blue cattle?
Coat colors can range from white, blue roan, black, or a combination, and sometimes red.
Why might a farmer choose a bull for a finishing operation?
To improve carcass and meat quality, as well as profitability.
What factors should be considered when advising a dairy farmer on bull selection?
Fat and protein percentage, somatic cell count, and proven sires.
What challenges might Alan face with his suckler herd?
Increasing mature cow size and more difficult calvings.
What is the goal of using a terminal sire in sheep farming?
To enhance the growth rate of lambs for quicker slaughter.
What should John consider when selecting a ram for his ewe flock?
The ram's ability to improve litter size and weight gain of progeny.
What is the impact of declining scanning and weaning percentages in sheep?
It indicates potential reproductive issues and lower productivity in the flock.
What is the importance of maternal calving ease in beef sires?
It affects the ease with which calves are born, impacting both calf survival and the health of the cow.
How does the genetic mutation in Belgian Blue cattle affect their appearance?
It results in larger and more defined muscles, particularly in the hindquarters.
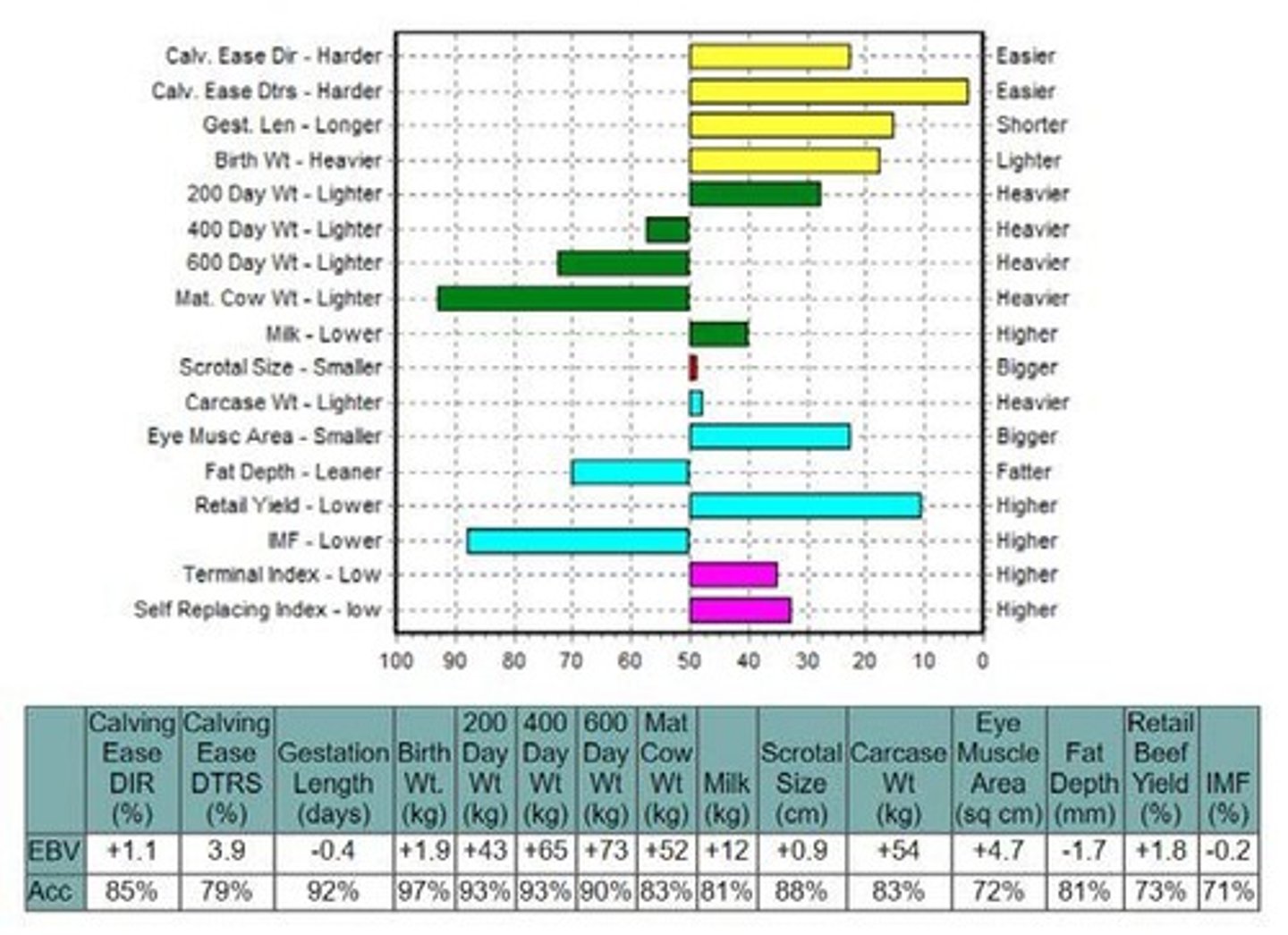
What is the relationship between EBVs and carcass quality in beef cattle?
EBVs help predict traits that influence carcass quality, such as muscle depth and fat depth.
What is the significance of feed efficiency in double-muscled cattle?
It indicates that these cattle can convert feed into body mass more effectively, reducing feeding costs.
How can a farmer improve the profitability of a beef operation?
By selecting bulls that enhance carcass quality and yield.
What considerations should be made when selecting bulls for dairy herds?
Focus on traits that improve milk production, fertility, and health of the herd.
What is the role of maternal ability in sheep breeding?
It influences the ewe's capability to care for and raise her lambs effectively.
What is feed efficiency in double-muscled cattle?
Double-muscled cattle are more efficient at using feed, leading to a higher proportion of expensive meat cuts and more profit for farmers.
What are the fertility rates of double-muscled cattle?
Double-muscled cattle have lower fertility rates.
What is dystocia and how does it relate to double-muscled cattle?
Dystocia is a complication during birth, and double-muscled cattle are more likely to experience it, often requiring assistance.
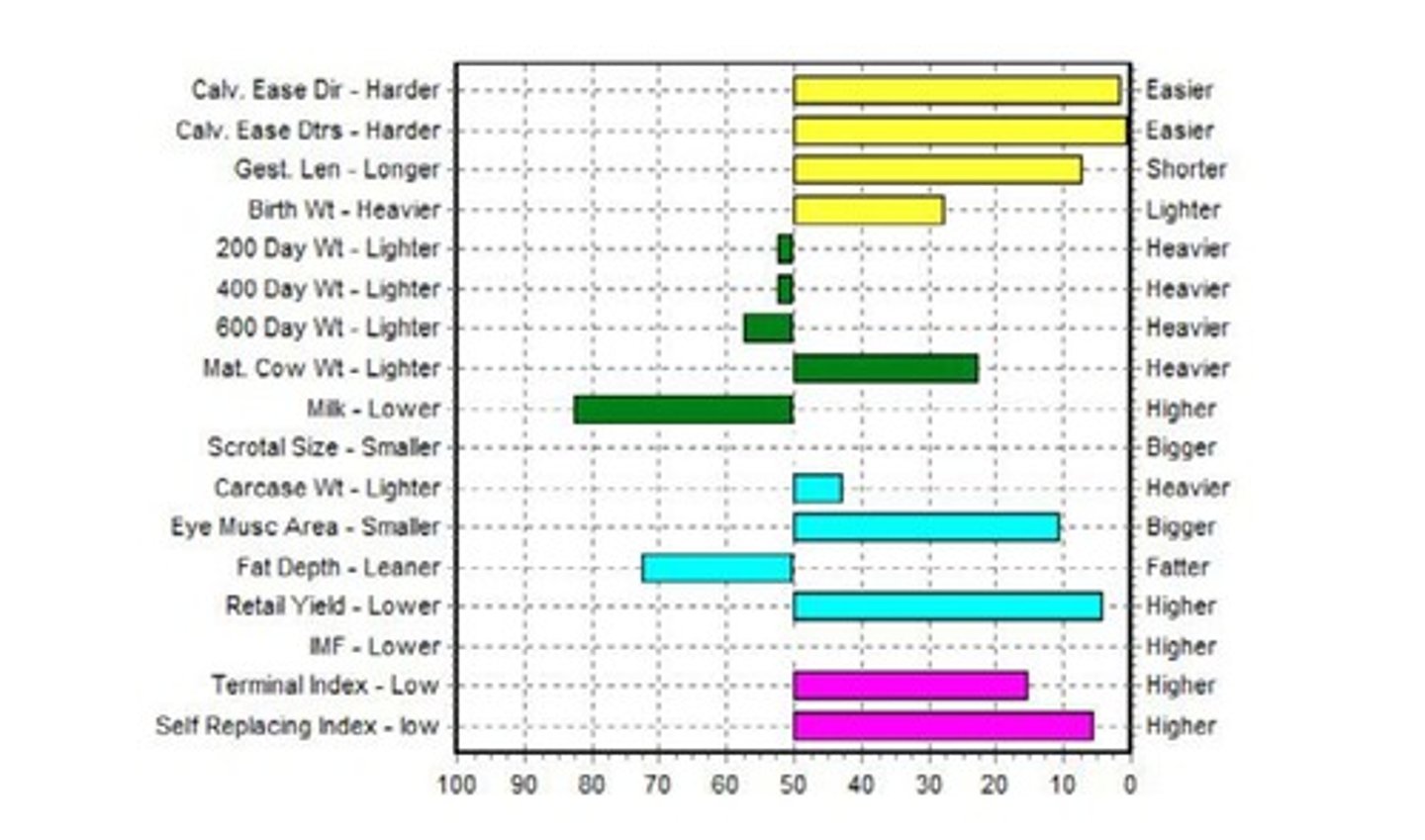
What diseases are double-muscled cattle more susceptible to?
They are more susceptible to respiratory disease, stress, and white muscle disease.
What is a common issue with the reproductive tracts of double-muscled cattle?
They often have underdeveloped reproductive tracts.
What dietary need is increased in double-muscled cattle?
They may need more selenium in their diet.
What are some welfare complications associated with dystocia in double-muscled cattle?
Dystocia can cause maternal injuries such as uterine rupture, which puts the mother's life at risk.
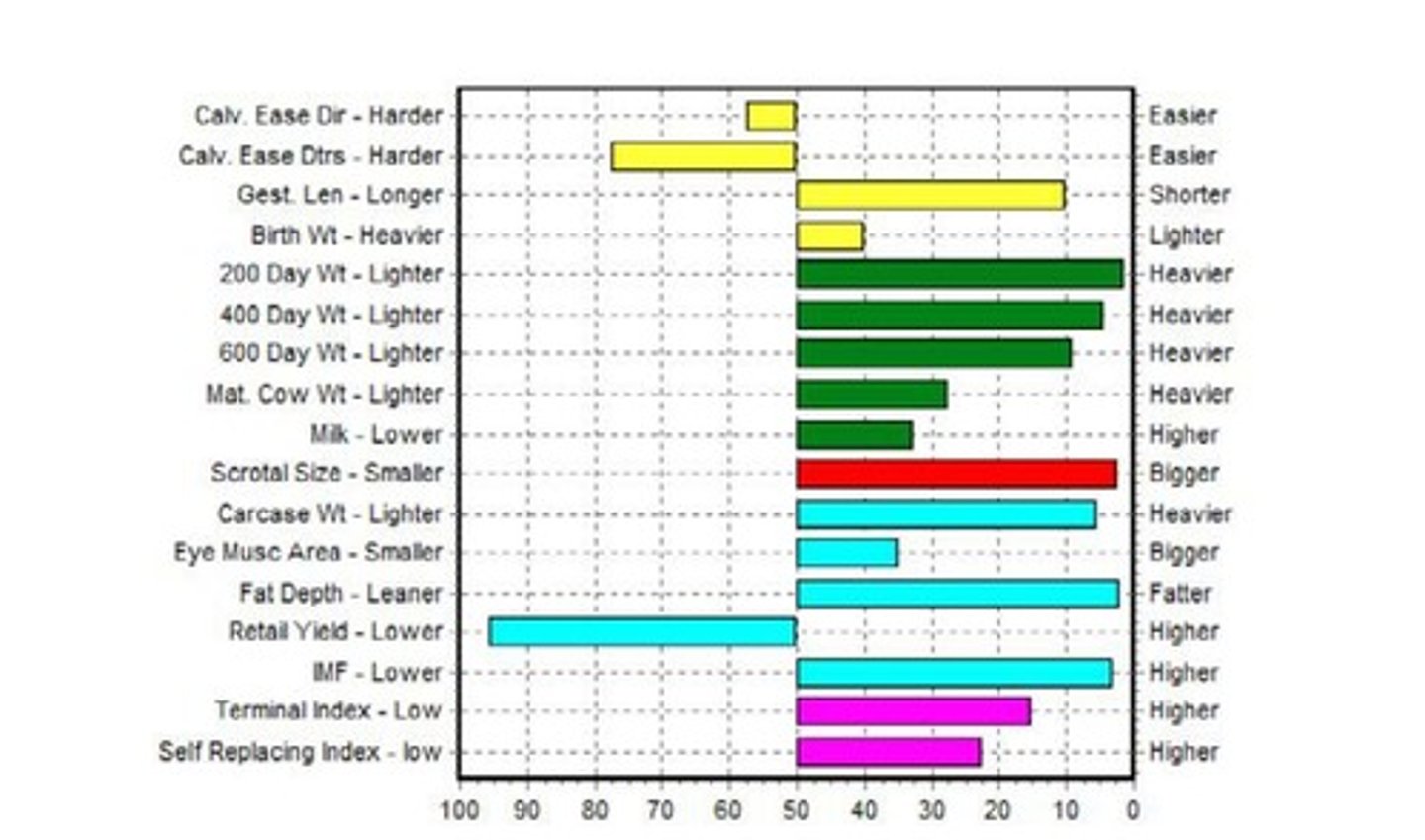
How does excessive muscle development affect double-muscled cattle?
It can strain joints, making them more susceptible to lameness and arthritis, and increase oxygen requirements, leading to respiratory stress.
What environmental stressors do double-muscled cattle face?
They are at risk of heat stress and may suffer from heat exhaustion.
What are some methods to improve the welfare of double-muscled cattle?
Methods include selective breeding, C-sections, closely monitoring pregnancies, providing access to cooling systems, and ensuring a large area for movement.
What are the economic justifications for breeding double-muscled cattle?
Producing more lean meat with fewer resources is efficient and sustainable, especially with a growing population.

How does high economic value affect the care of double-muscled cattle?
High economic value often ensures that farmers invest in better veterinary care, housing, and nutrition.
What consumer demand exists for double-muscled cattle?
There is a demand for lean, tender meat, which is considered a legitimate goal if animals are treated humanely.

What are the animal welfare concerns regarding double-muscled cattle?
Severe health issues arise, prioritizing human benefit over animal well-being.
What is unnatural selection in the context of double-muscled cattle?
Extreme selective breeding violates natural evolutionary processes, leading to animals struggling to live normal lives.
What challenges do high milk-yield dairy cows face?
They face challenges in mobility and birth, which could lead to chronic pain and distress.
What is the global demand for milk?
782 million liters of milk per day is consumed globally, with demand continuing to increase.
What is the UK's contribution to global milk production?
The UK is the thirteenth largest milk producer, producing up to 15.3 billion liters per year.
What breed is recommended for high milk yields?
The Holstein-Friesian breed is recommended for high milk yields.
What is the typical weight and height of a mature Holstein?
A mature Holstein weighs about 1500 pounds and stands 58 inches tall at the shoulder.
What is the normal productive life of a Holstein cow?
The normal productive life of a Holstein is six years.
What health implications arise from breeding dairy cows for high milk yields?
Intensive genetic selection has led to reduced fertility and increased postpartum clinical problems.
What is a challenge faced by high-yielding dairy cows in early lactation?
They often experience a negative energy balance and must mobilize body reserves for milk.
What are the health risks associated with negative energy balance in dairy cows?
Higher incidence of metabolic disorders, impaired fertility, and other health problems.
How does high milk production affect reproductive performance in dairy cows?
High-producing cows exhibit low intensity and short duration oestrus, leading to extended intervals to first breeding and conception.
What is the average duration of oestrus in high-producing cows compared to low-producing cows?
High-producing cows have shorter oestrus periods (5.5 hours) compared to low-producing cows (11.1 hours).
What genetic factor is associated with higher milk production in Holstein cows?
A variant of the GH gene called the A allele.
What is the primary purpose of broilers in poultry production?
Broilers are chickens raised for meat.
What is the feed conversion ratio in broilers?
Broilers require less food for rapid growth due to an efficient feed conversion rate.
What are some negative health implications of fast growth in broilers?
Weak legs leading to splayed legs, increased risk of heart and pulmonary conditions, and susceptibility to leg and foot disorders.
What are some consequences of high energy demand in fast-growing broilers?
High basal metabolic rate, oxygen deficits, and increased pressure on the pulmonary artery.
What is ascites in broilers and what causes it?
Ascites is caused by hypertrophy of the right ventricle, increasing thoracic and abdominal pressure.
What are some common leg and foot disorders in broilers?
Bacterial chondronecrosis with osteomyelitis, angular bone deformity, femoral bone degeneration, hock burn, and foot pad dermatitis.
How does the rapid growth of broilers affect their mental welfare?
It restricts their ability to perform natural behaviors, leading to increased inactivity and stress.
What impact does modern broiler breeding have on organ size?
Modern broilers have smaller organ size as a percentage of body weight, which may reduce functional capability.
How does stress and pain in broilers affect their immunity?
It can lead to immunosuppression, making them more susceptible to disease and infection.
What is the economic consequence of declining fertility in high-producing dairy cows?
Increasing reproductive costs for dairy cattle.
What role does behavior play in the reproductive performance of high-producing cows?
Behavior may contribute to lower reproductive performance due to poor oestrus detection.