anat3
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/99
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
1
New cards
4 different classifications of bones
flat, irregular, long, short
2
New cards
example of bone classifications (flat)
rib bones
3
New cards
example of bone classifications (irregular)
sacrum
4
New cards
example of bone classifications (long)
humerus
5
New cards
example of bone classifications (short)
carpal bones
6
New cards
where is the periosteum located
around your bones
7
New cards
what is the function of the periosteum
anchor point for tendons and ligaments
8
New cards
epiphysis
ends of the bone
9
New cards
diaphysis
middle of the bones
10
New cards
location of the medullary cavity
hollow region within the diaphysis
11
New cards
function of the medullar cavity
stores area for bone marrow
12
New cards
yellow marrow
high in fat; found in diaphysis
13
New cards
red marrow
produces red blood cells; found in epiphysis
14
New cards
function of articular cartilage
create smooth movement; protects bones from rubbing against each other
15
New cards
where is the articular cartilage found
end of bones/joints
16
New cards
compact bone
dense, less space in between
17
New cards
spongy bone
large spaces
18
New cards
4 types of bone cells involved in bone growth and formation and their function
osteoprogenitor - immature bone cells that grow into blasts or clasts
osteoblasts - immature bone cells that secrete calcium
osteocytes - mature bone cells
osteoclasts - break down bone
osteoblasts - immature bone cells that secrete calcium
osteocytes - mature bone cells
osteoclasts - break down bone
19
New cards
where is the epiphyseal plate located
middle/end of long bones
20
New cards
function of the epiphyseal plate
growth
21
New cards
what is a joint
where two bones connect
22
New cards
what is a ligament
connects bone to muscle
23
New cards
what is a tendon
connects muscle to bone
24
New cards
what are the 3 main categories of joins - what are their movement
synovial - free moving
fibrous - no moving
cartilaginous - slight moving
fibrous - no moving
cartilaginous - slight moving
25
New cards
what are the 6 synovial joints
gliding
pivot
hinge
ball and socket
condyle
saddle
pivot
hinge
ball and socket
condyle
saddle
26
New cards
function/location of gliding joint
function - flat surfaces glide across one another
location - clavicle to scapula
location - clavicle to scapula
27
New cards
function/location of pivot joint
function - rotational movement
location - shake head no
location - shake head no
28
New cards
function/location of hinge joint
function - motion in one plane
location - elbow, knee
location - elbow, knee
29
New cards
function/location of ball and socket joint
function - motion in all directions
location - shoulder
location - shoulder
30
New cards
function/location of condyle joint
function - significant rotation isnt allowed
location - wrist joint
location - wrist joint
31
New cards
function/location of saddle joint
function - all motion except rotation
location - thumb
location - thumb
32
New cards
adduction
moves towards midline
33
New cards
abduction
moves away from midline
34
New cards
retraction
pulling body part back
35
New cards
protraction
pushing body forward
36
New cards
pronation
turn downward
37
New cards
supination
turn upward
38
New cards
flexion
decrease angle of bone; flexing
39
New cards
extension
increase angle of bone stretch
40
New cards
hyperextension
extend a joint past its natural boundaries
41
New cards
eversion
foot outwards
42
New cards
inversion
foot inwards
43
New cards
what is scoliosis
abnormal curving of the spine; C or S shaped
44
New cards
what is arthritis
joint inflammation; cartilage, tendons, joints - less flexible and decrease range of motion
45
New cards
what is osteoporosis
bones break down prematurely; bones break easily
46
New cards
types of bone fractures
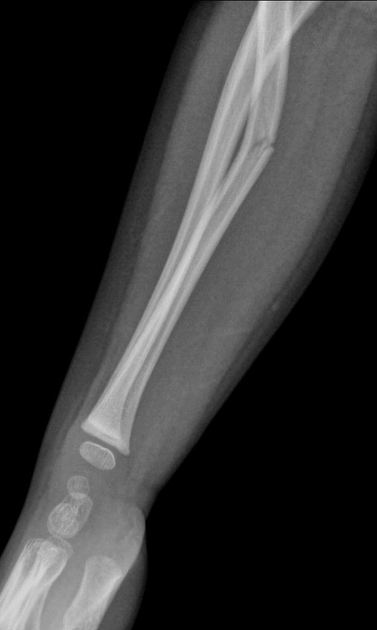
simple, hairline, compression, greenstick, spiral, comminuted, compound
47
New cards
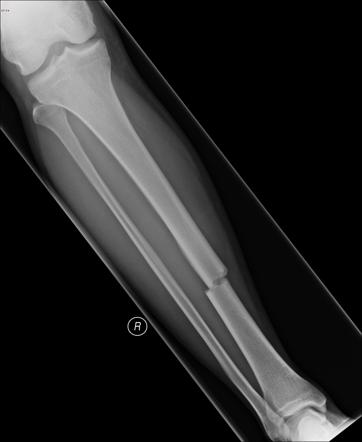
\
simple fracture
48
New cards
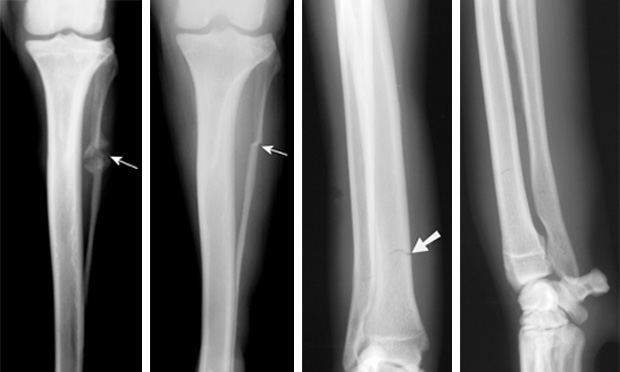
hairline fracture
49
New cards
compression fracture
50
New cards
greenstick fracture
51
New cards
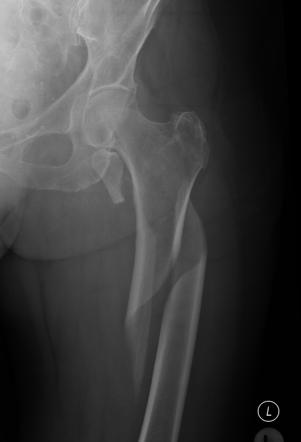
spiral fracture
52
New cards
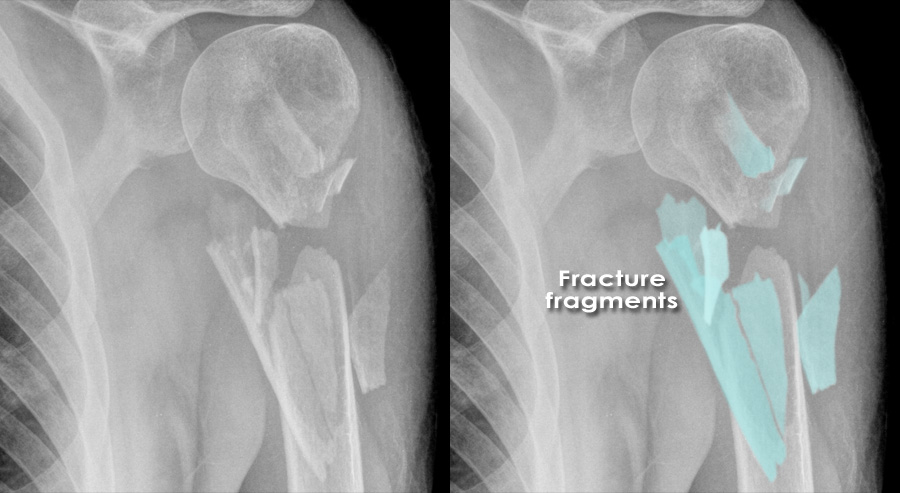
comminuted fracture
53
New cards
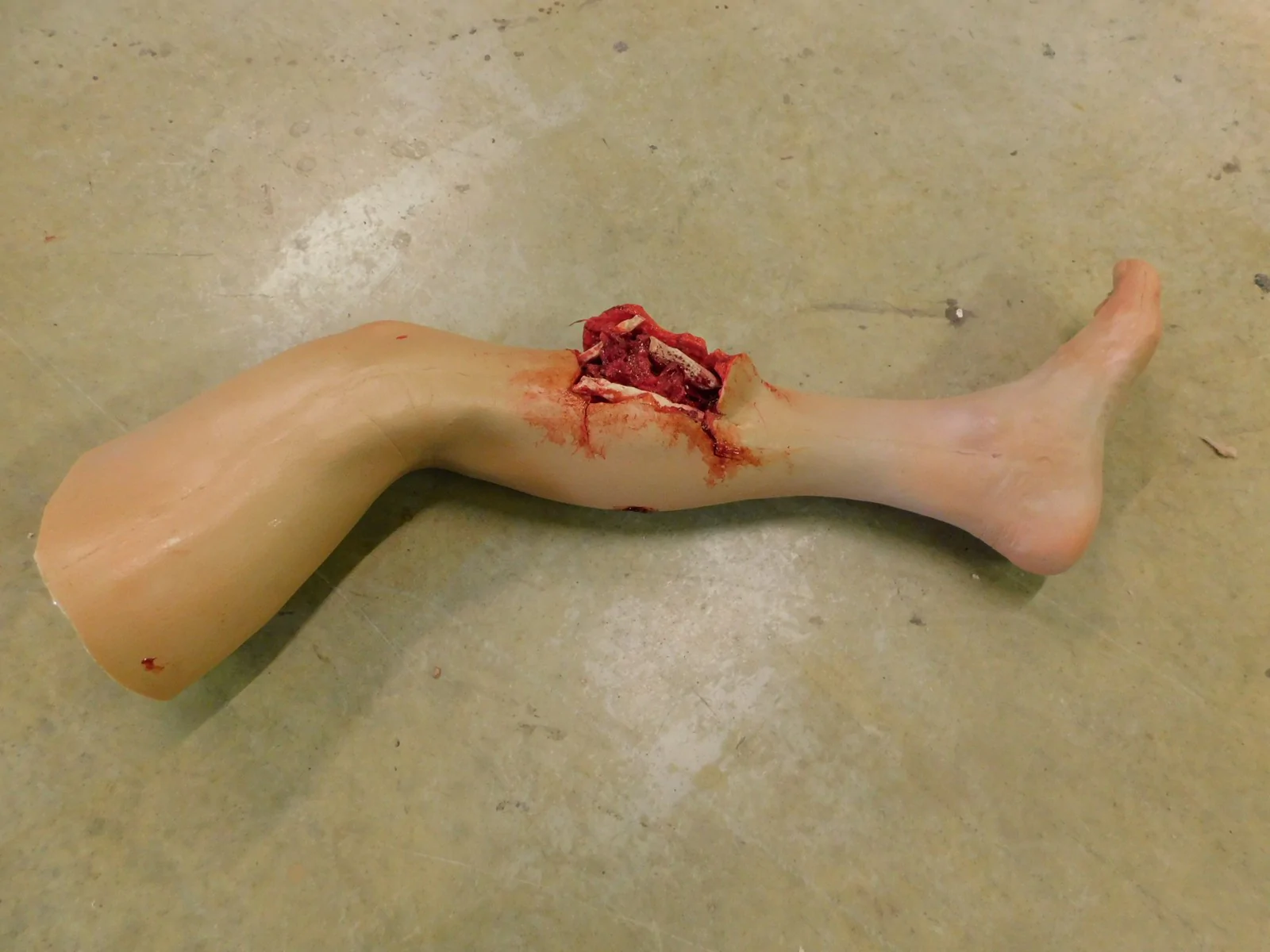
compound fracture
54
New cards
how do bones heal
1. bone breaks and severs the blood vessel
2. blood clots and forms a **fracture hematoma**
3. strengthened by collagen and **soft callus**
4. osteoblasts produce bone cells to form **bone callus**
5. osteoclasts and osteoblasts work together to replace bone callus with harder compact bone
55
New cards
56
New cards
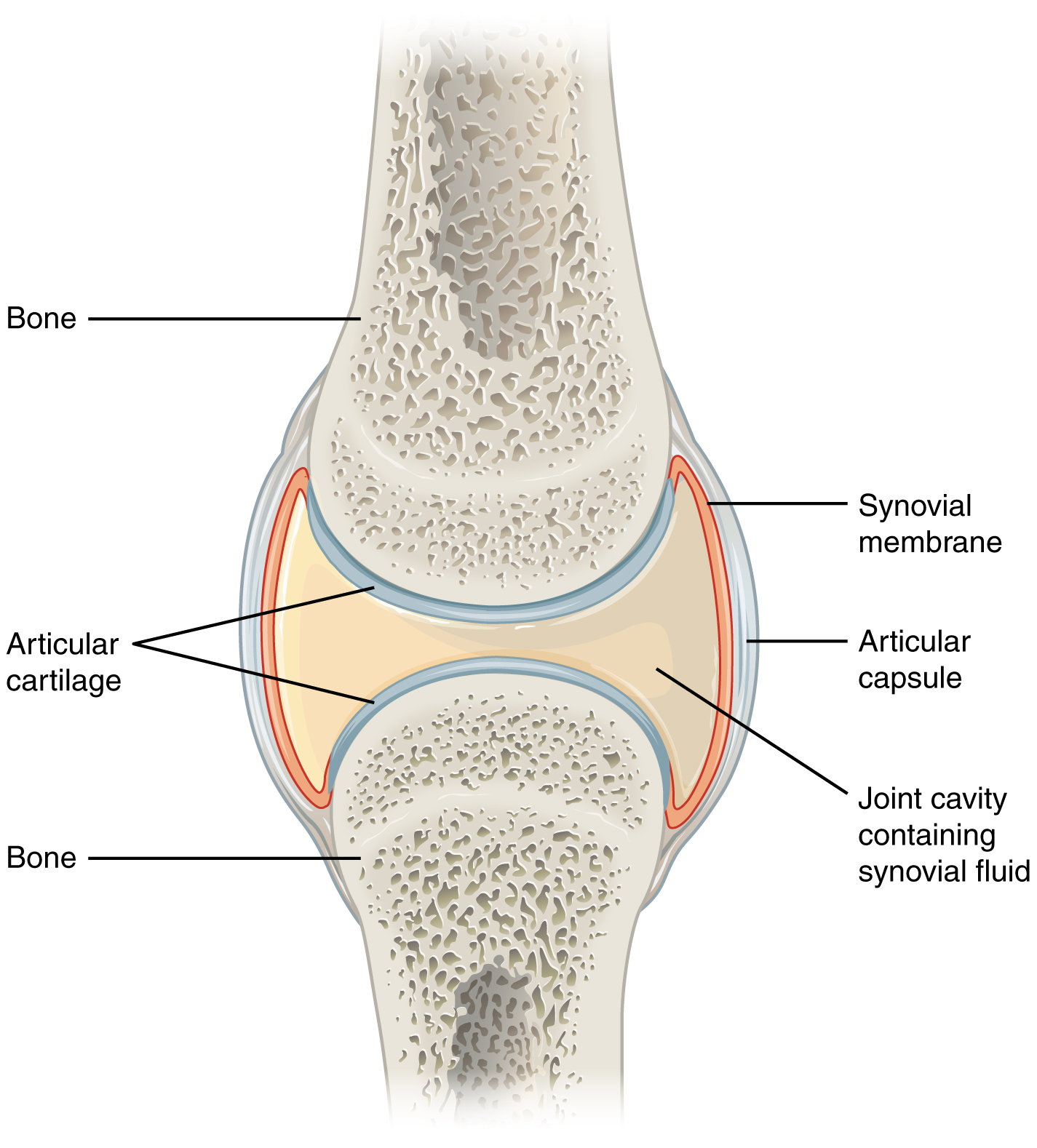
57
New cards
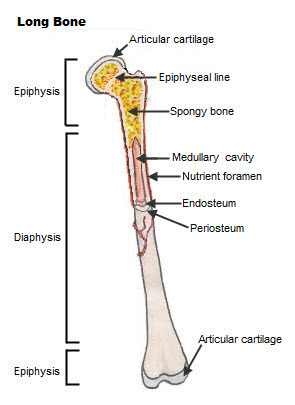
58
New cards
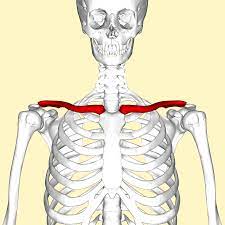
clavicle
59
New cards
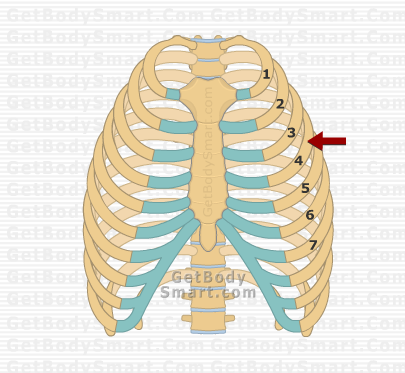
true ribs
60
New cards
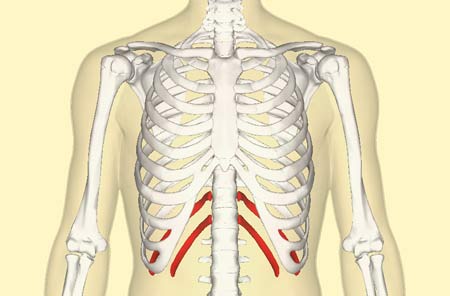
false ribs
61
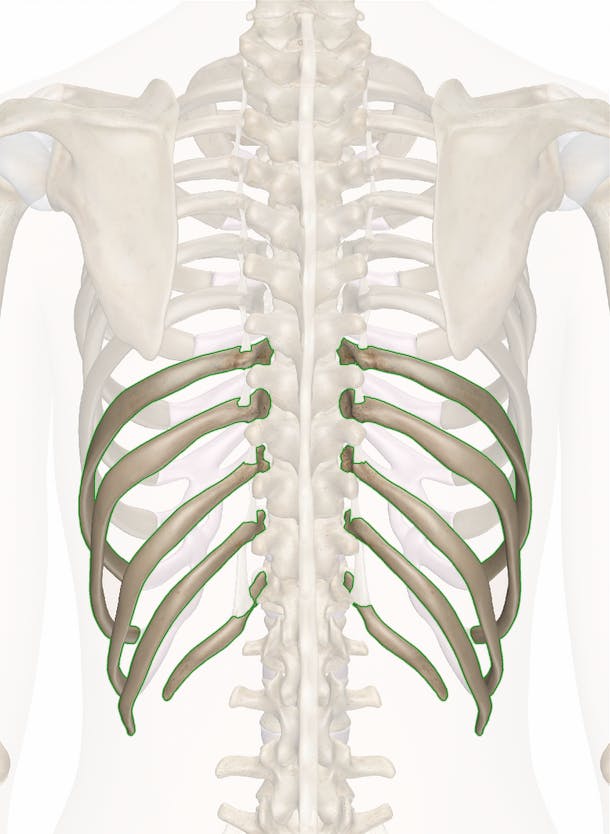
New cards
floating ribs
62
New cards
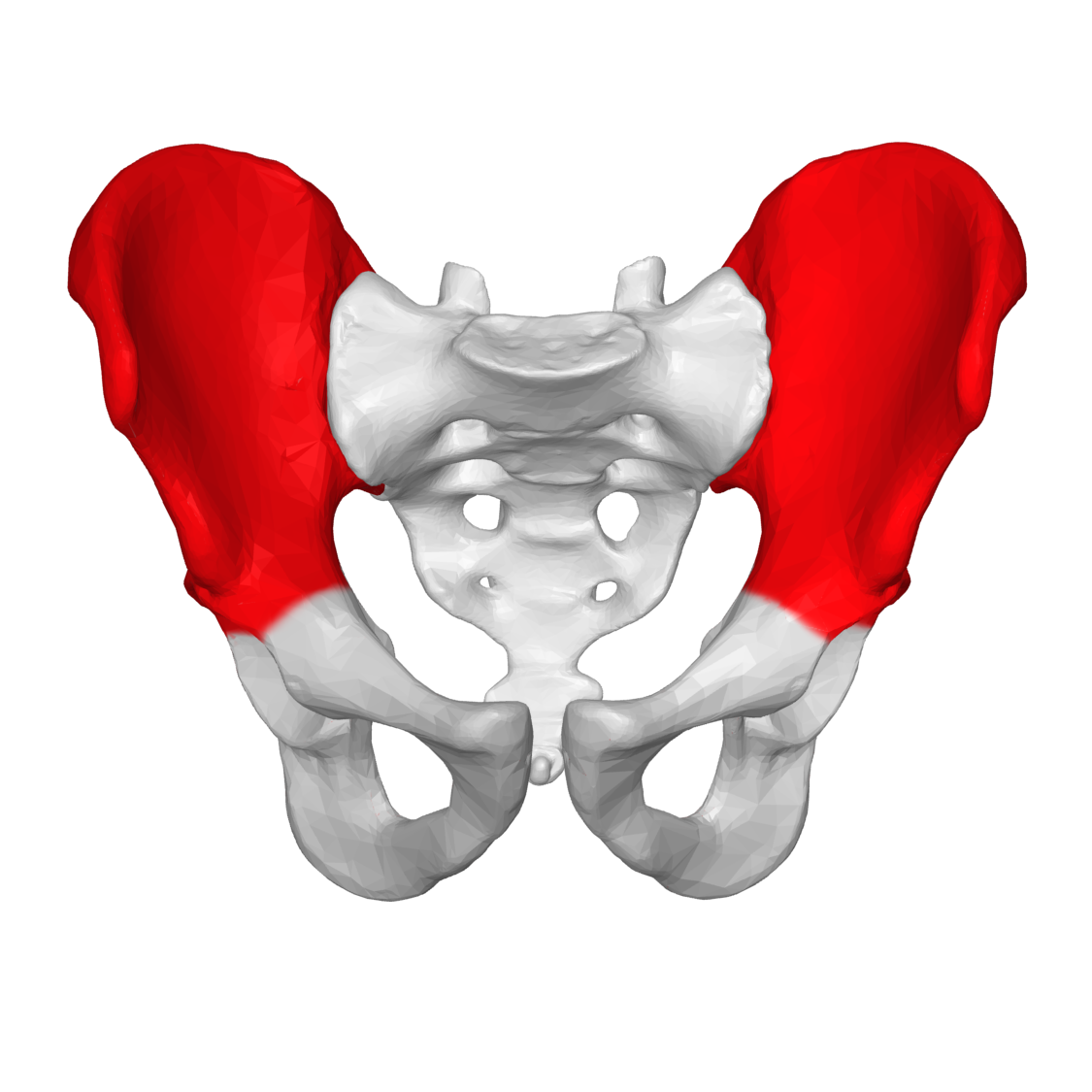
ilium
63
New cards
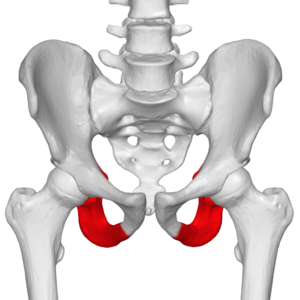
ischium
64
New cards
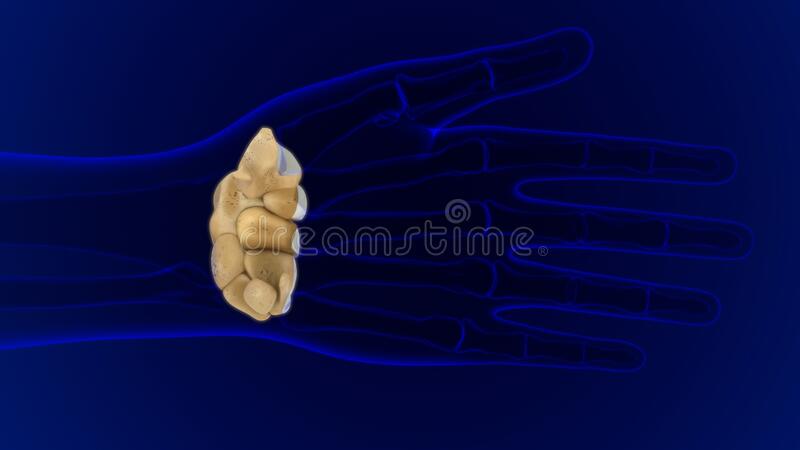
carpals
65
New cards
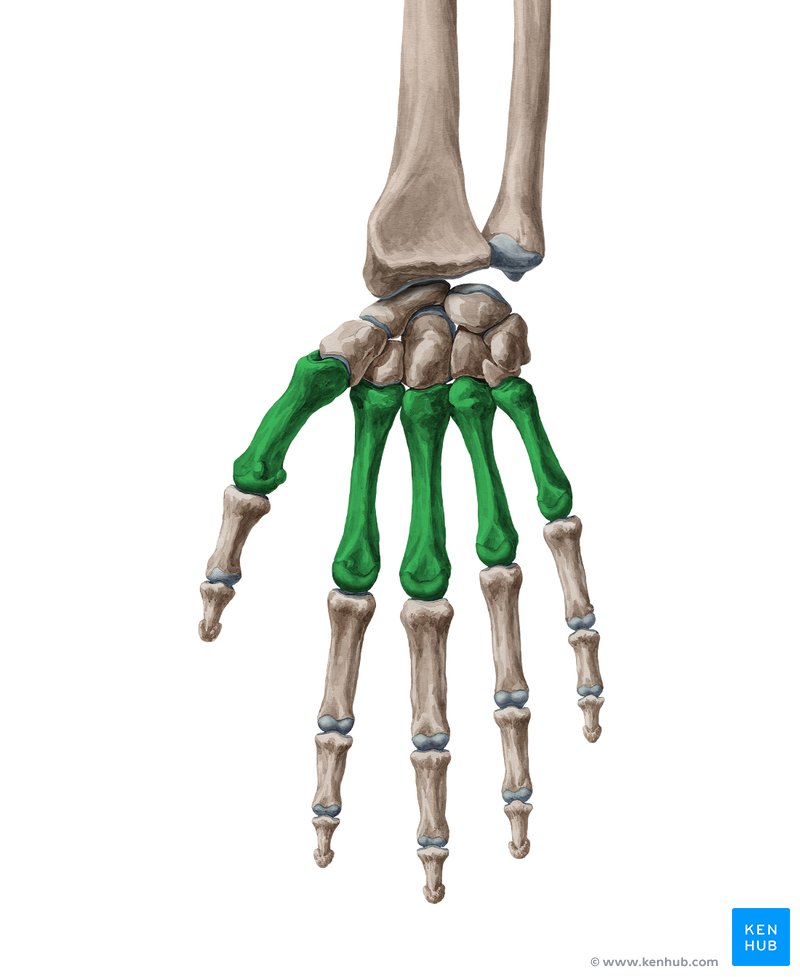
metacarpals
66
New cards
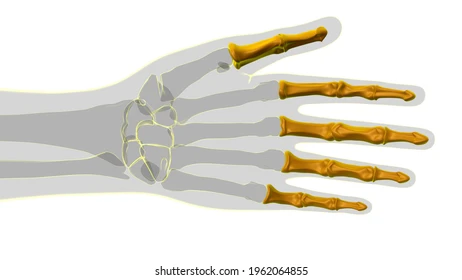
phalanges
67
New cards
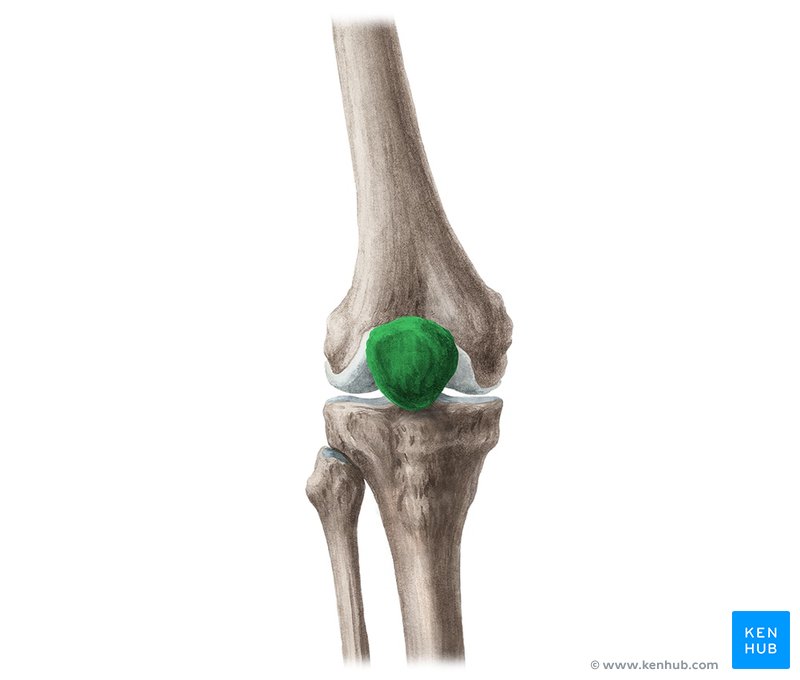
patella
68
New cards
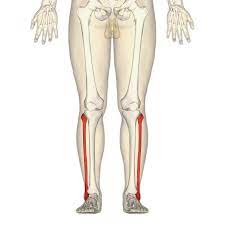
fibula
69
New cards
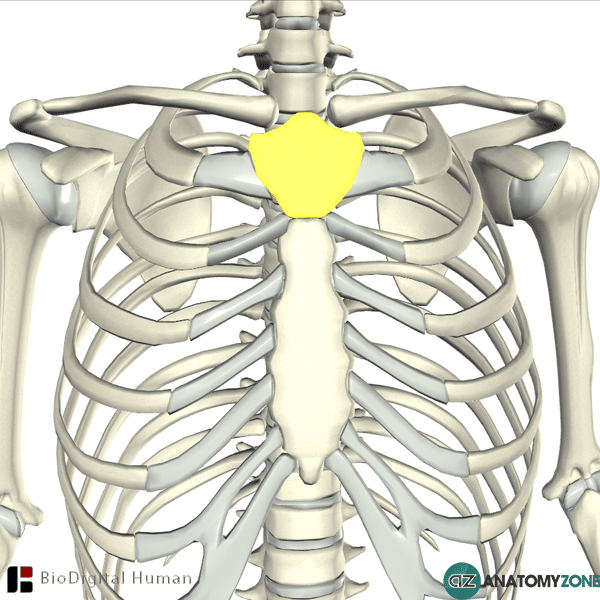
manubrium
70
New cards
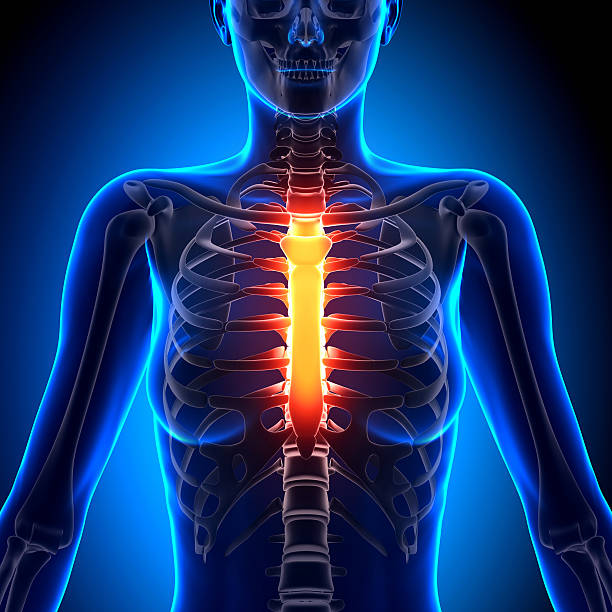
sternum
71
New cards
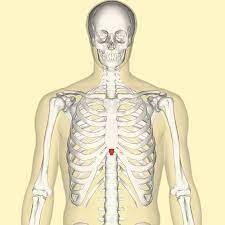
xiphoid process
72
New cards
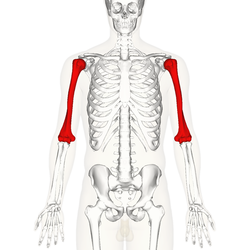
humerus
73
New cards
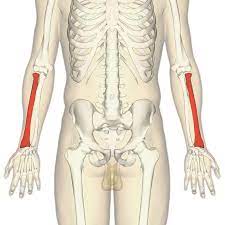
radius
74
New cards
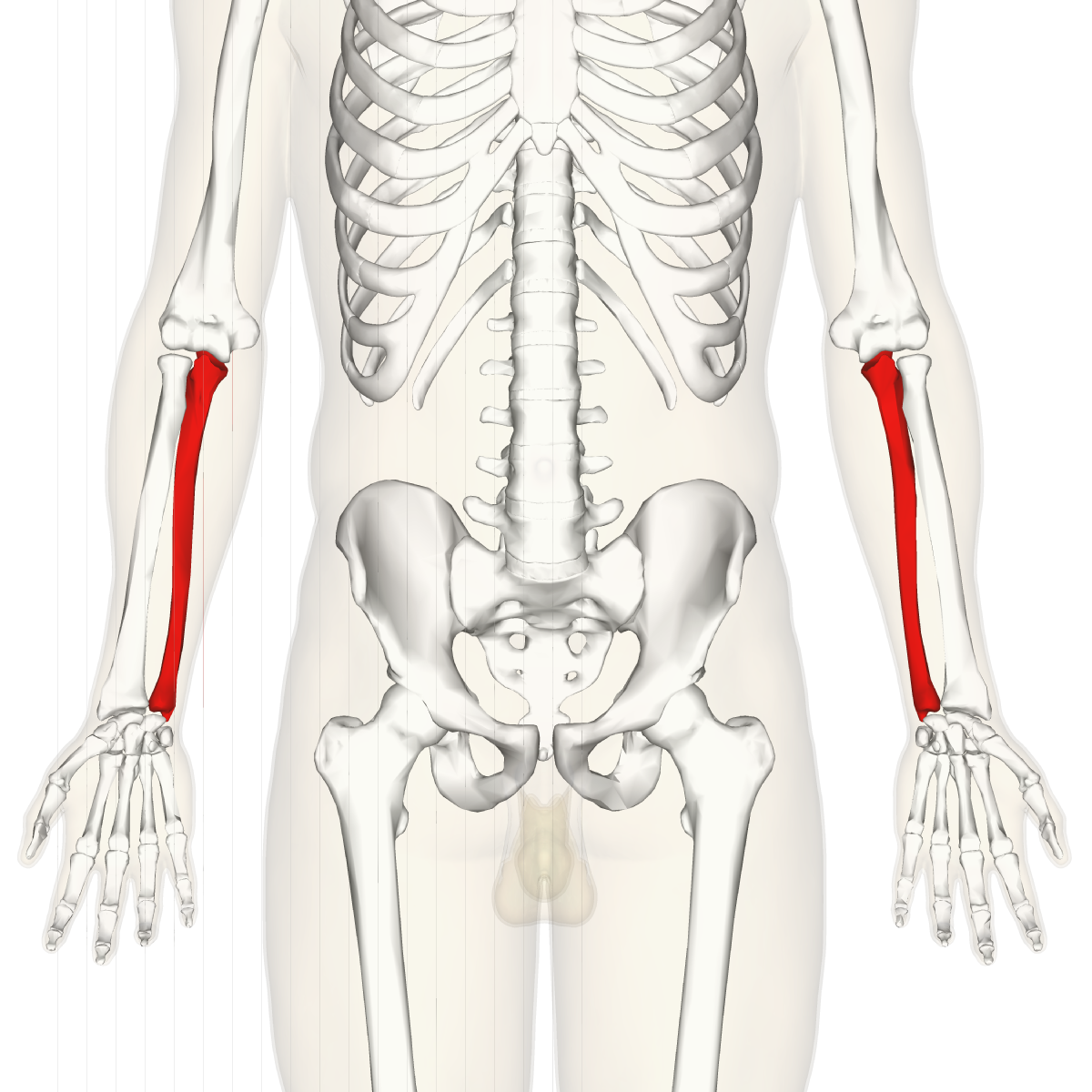
ulna
75
New cards
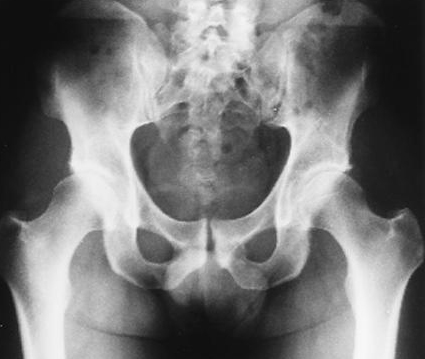
pubis
76
New cards
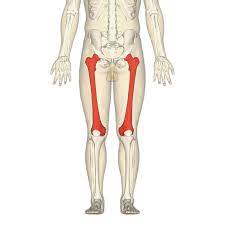
femur
77
New cards
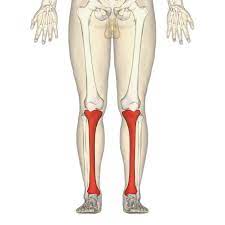
tibia
78
New cards
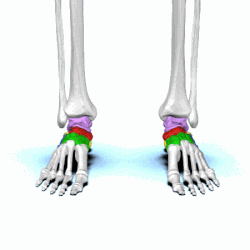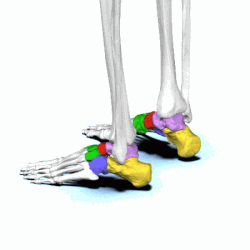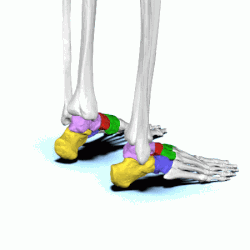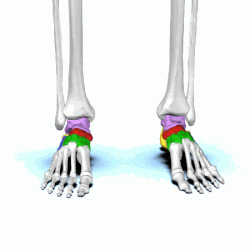
tarsals
79
New cards
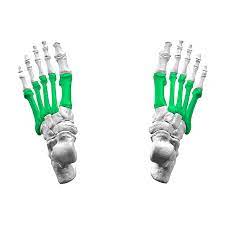
metatarsals
80
New cards
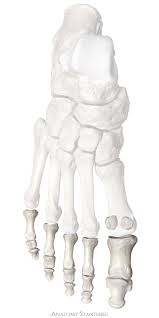
phalanges
81
New cards
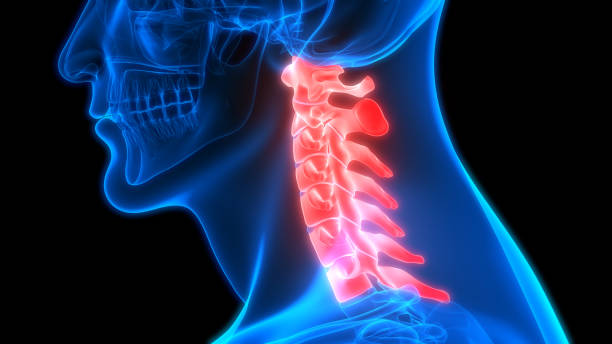
cervical
82
New cards
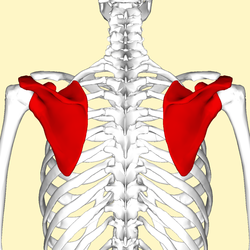
scapula
83
New cards
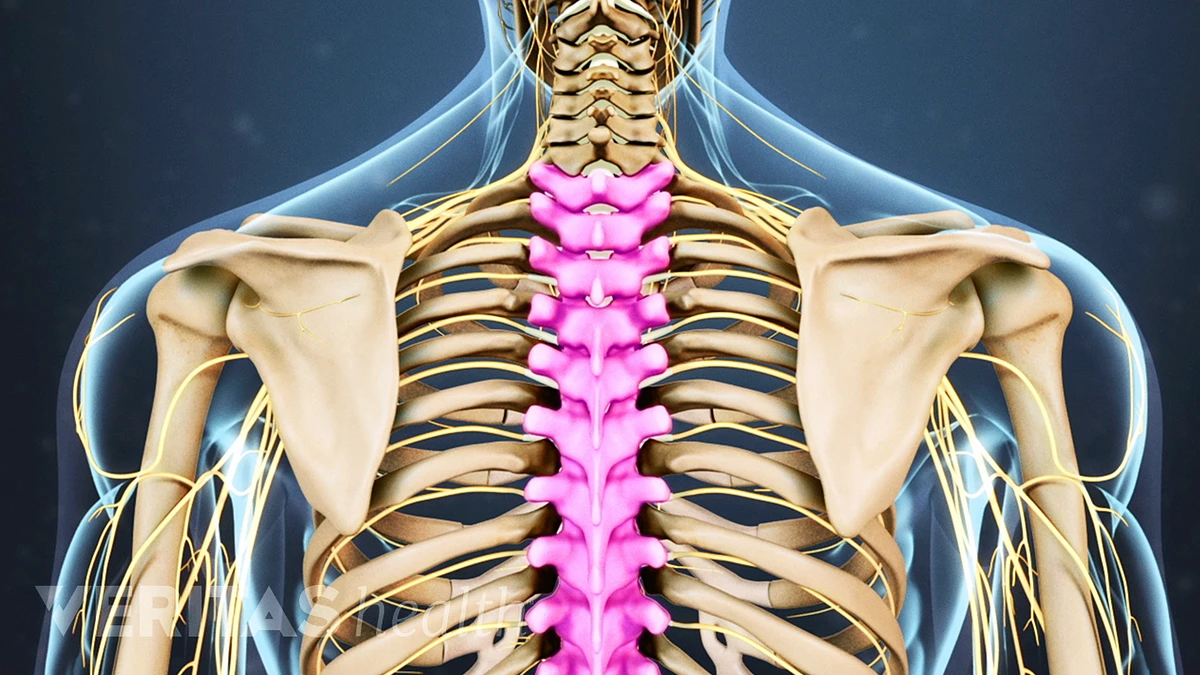
thoracic
84
New cards
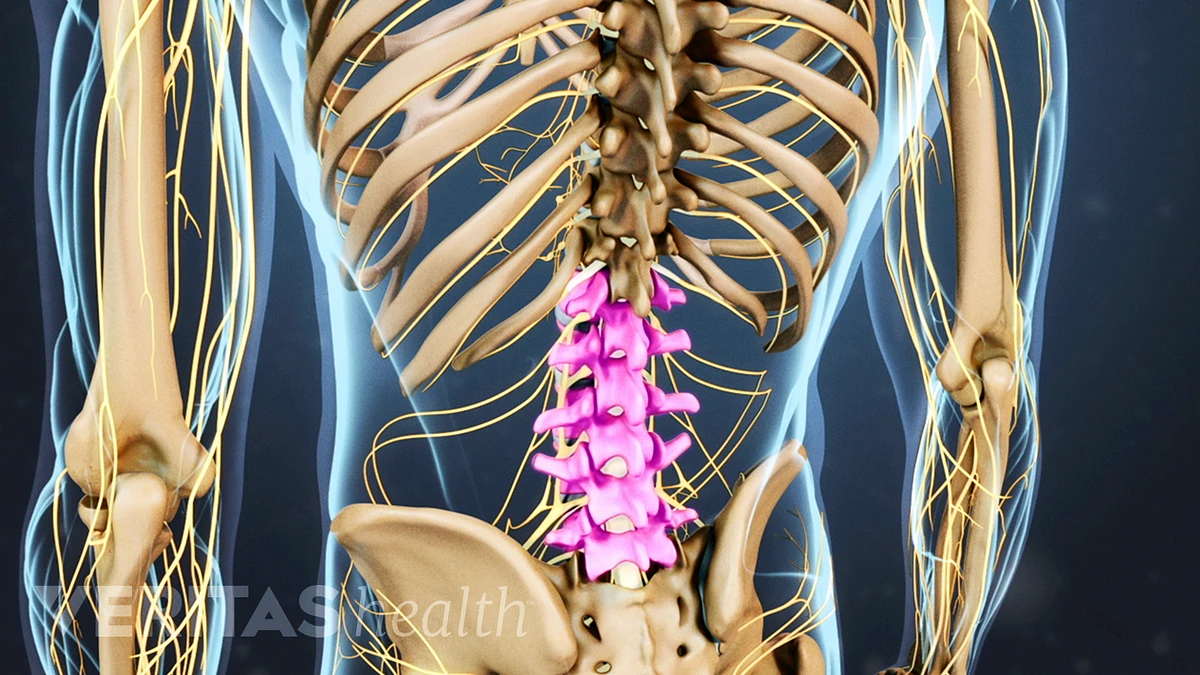
lumbar
85
New cards
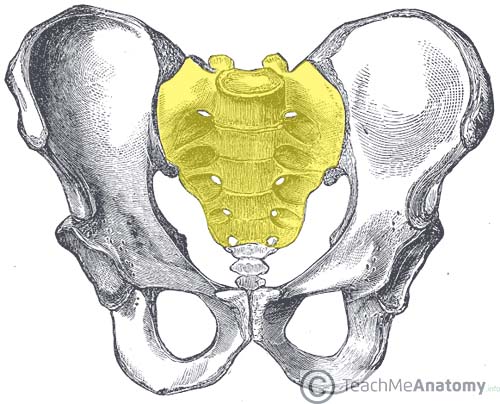
sacrum
86
New cards
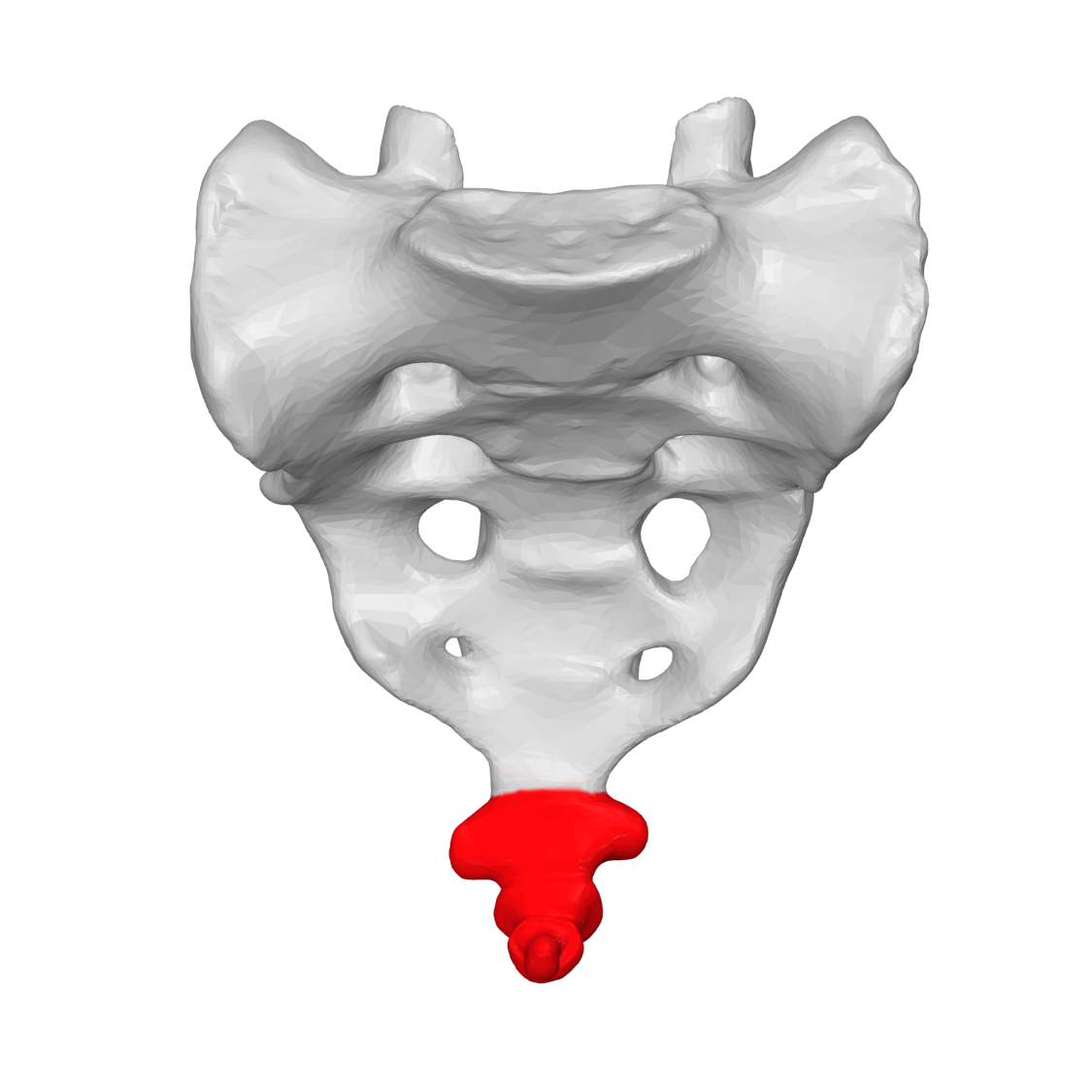
coccyx
87
New cards
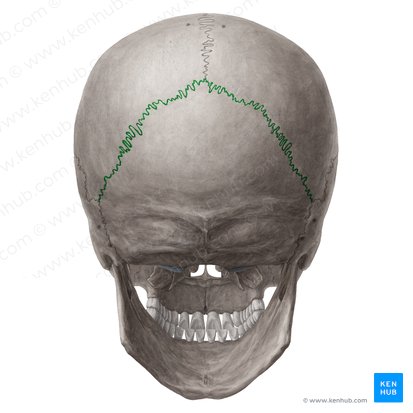
suture
88
New cards
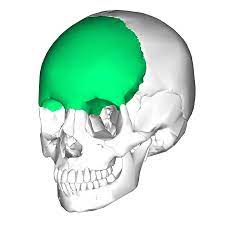
frontal
89
New cards
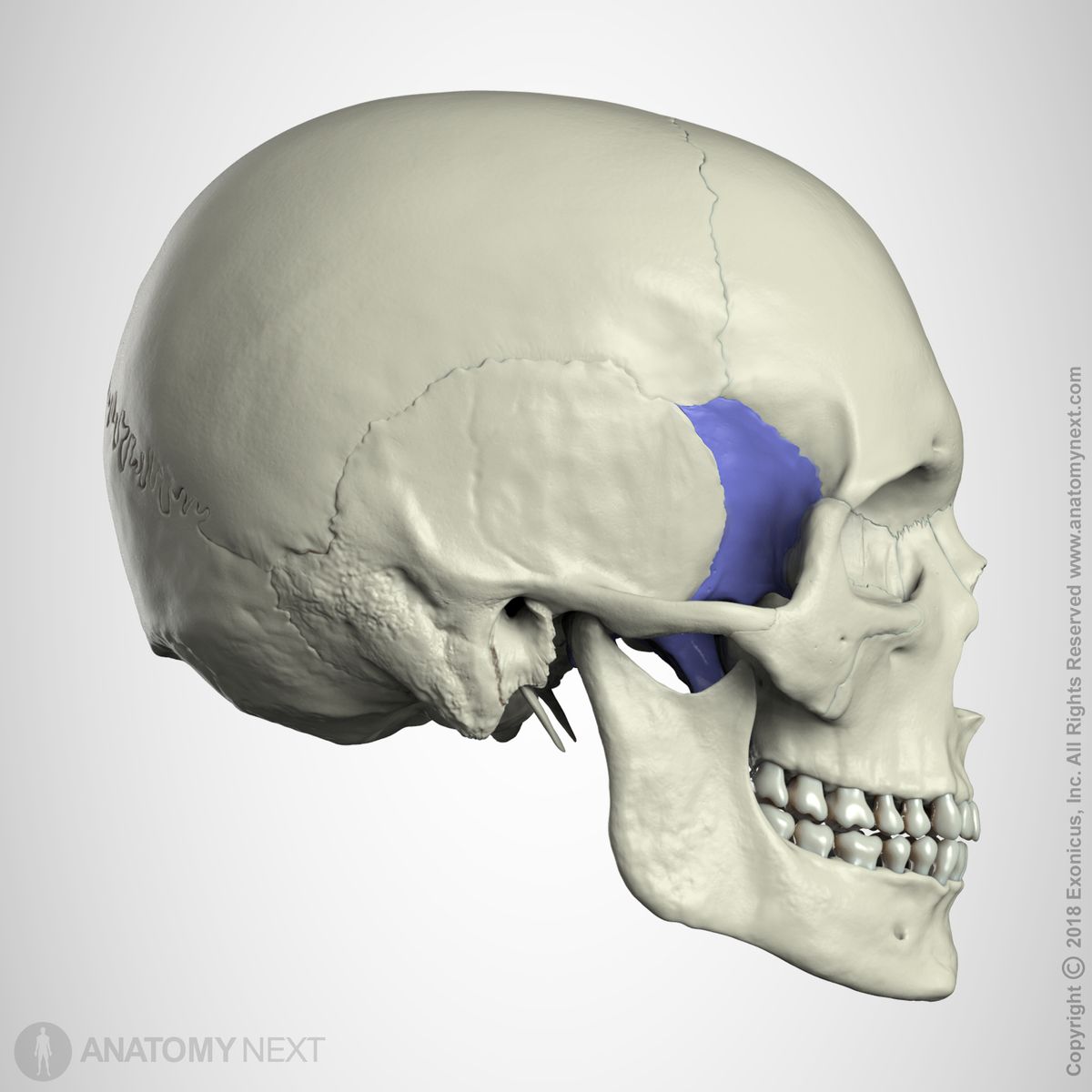
\
sphenoid
90
New cards
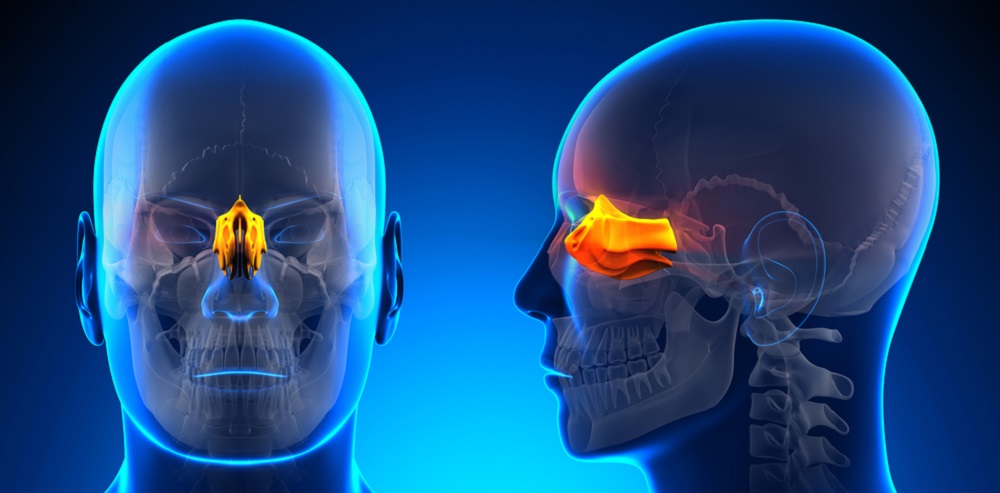
ethmoid
91
New cards
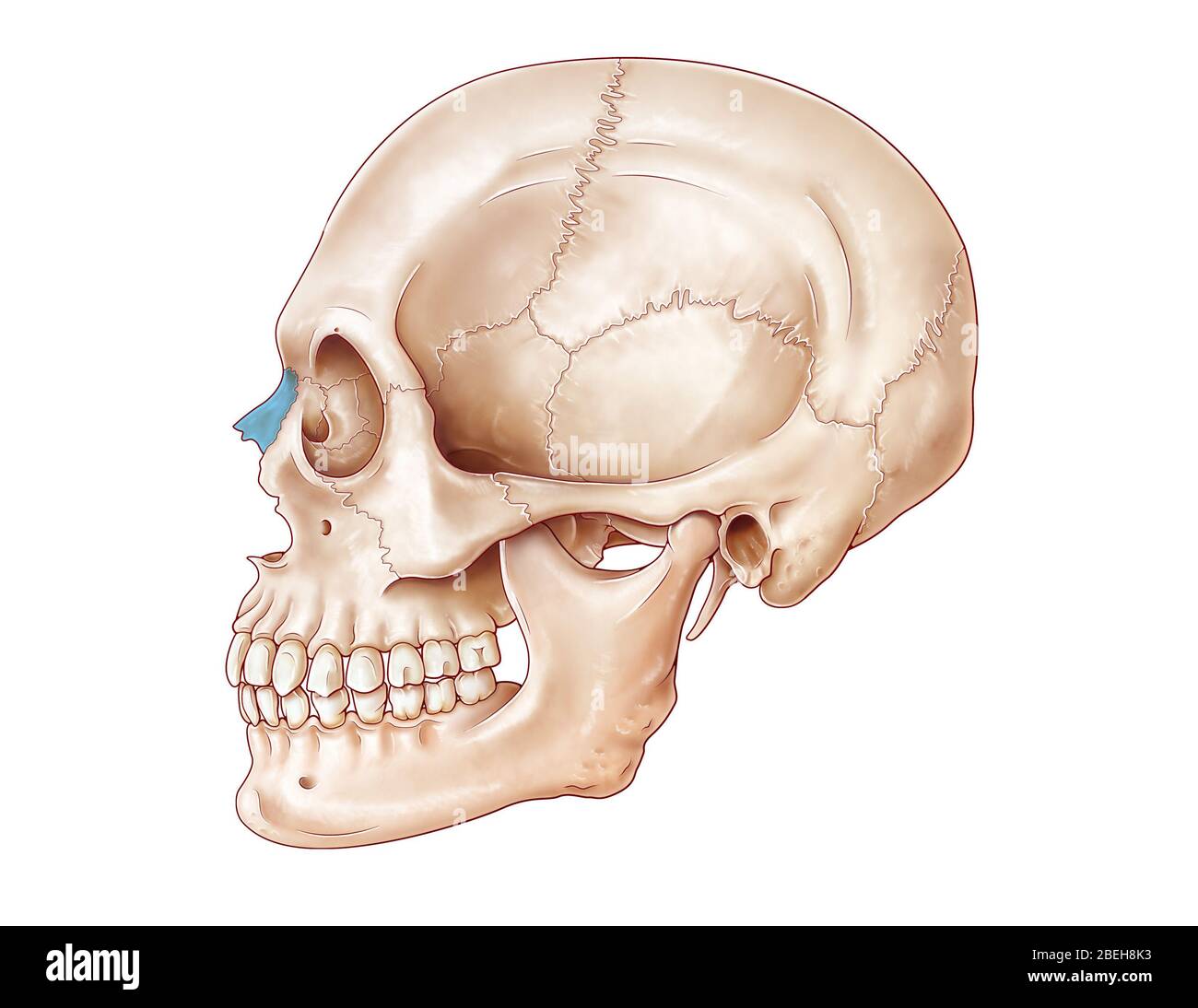
nasal
92
New cards
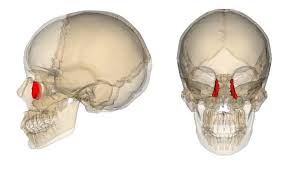
lacrimal
93
New cards
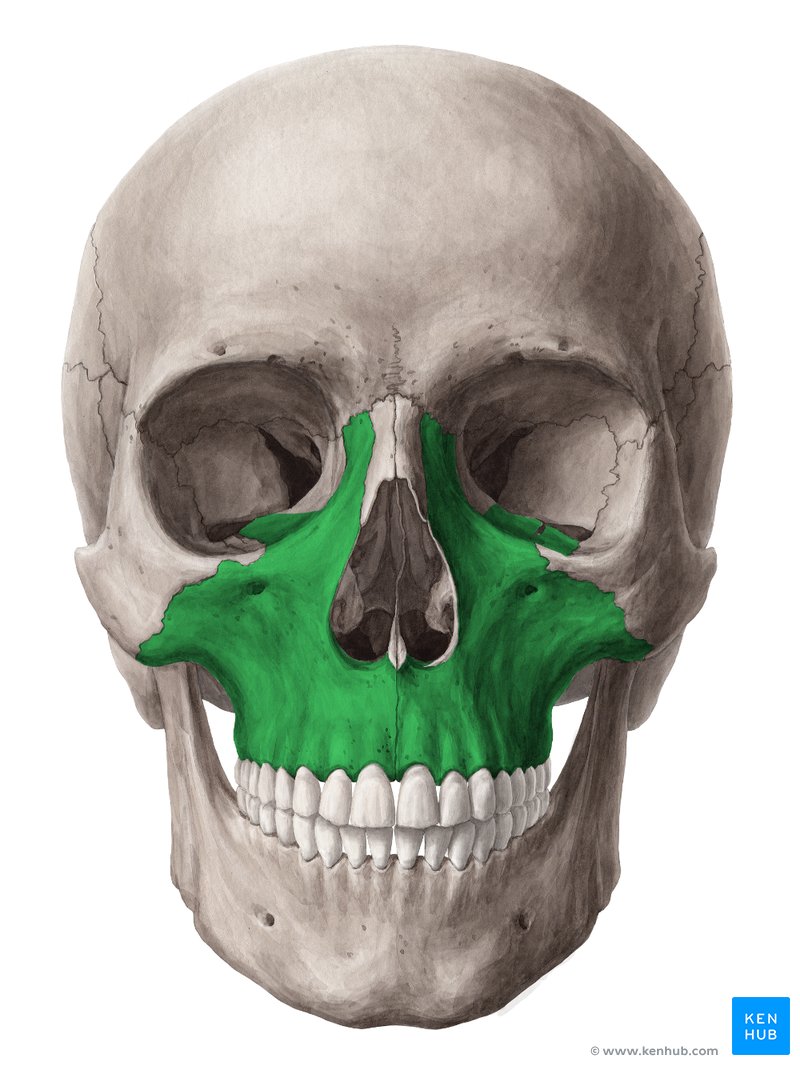
maxilla
94
New cards
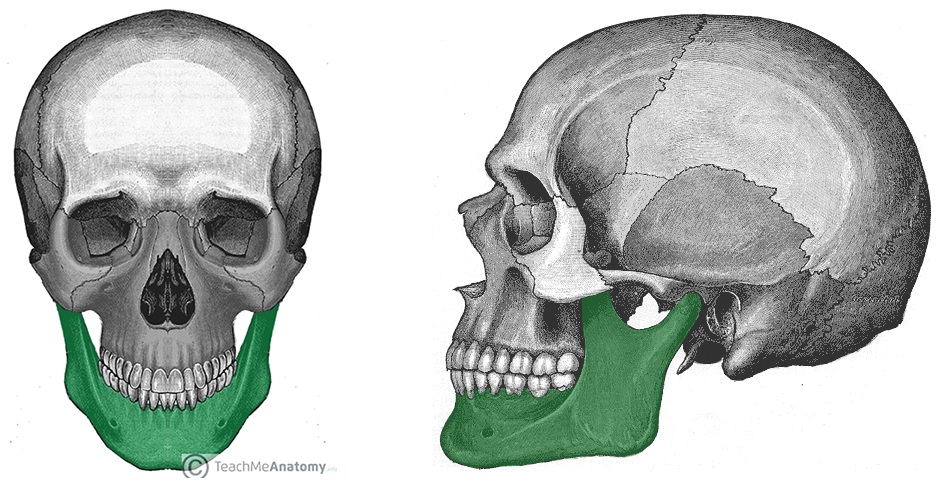
mandible
95
New cards
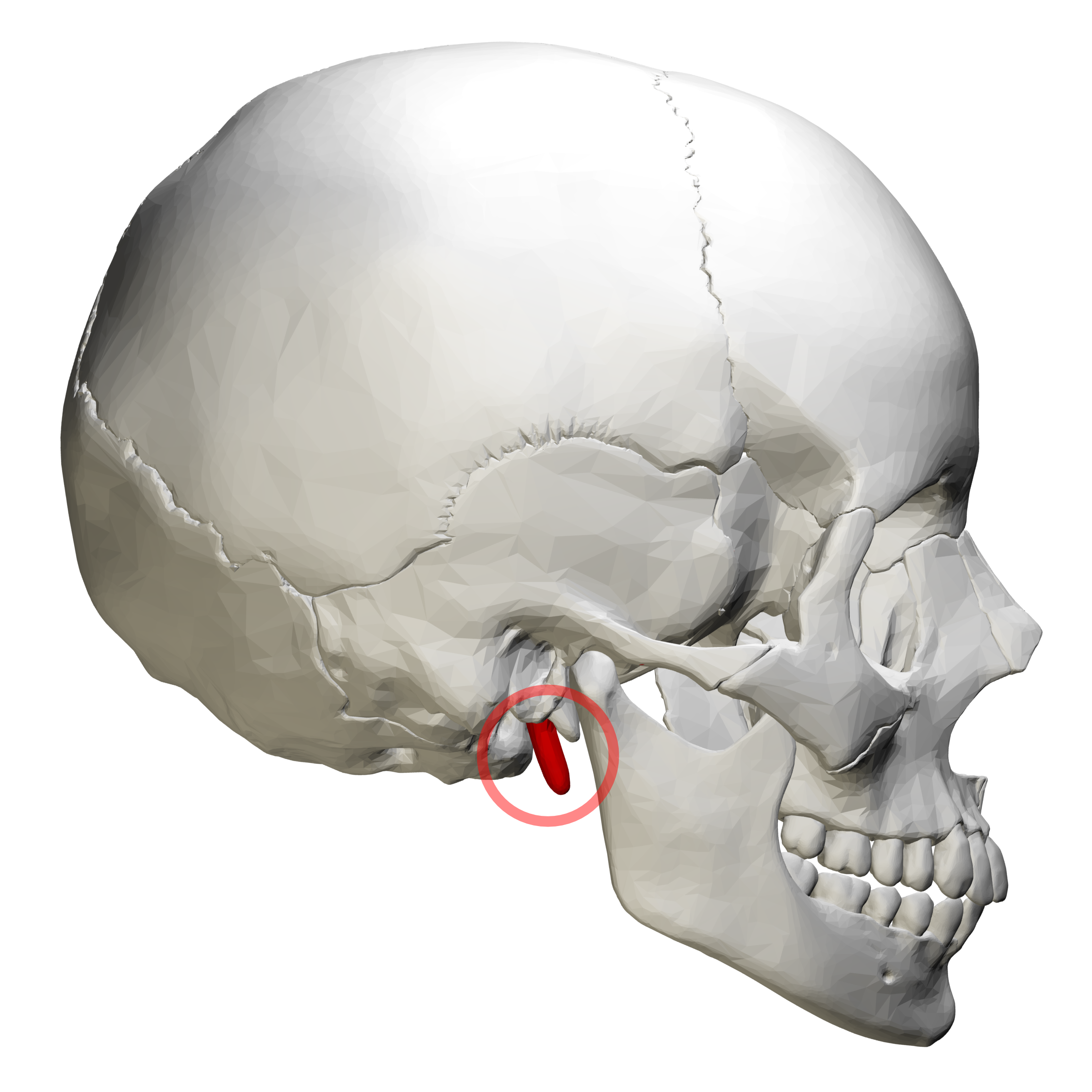
styloid process
96
New cards
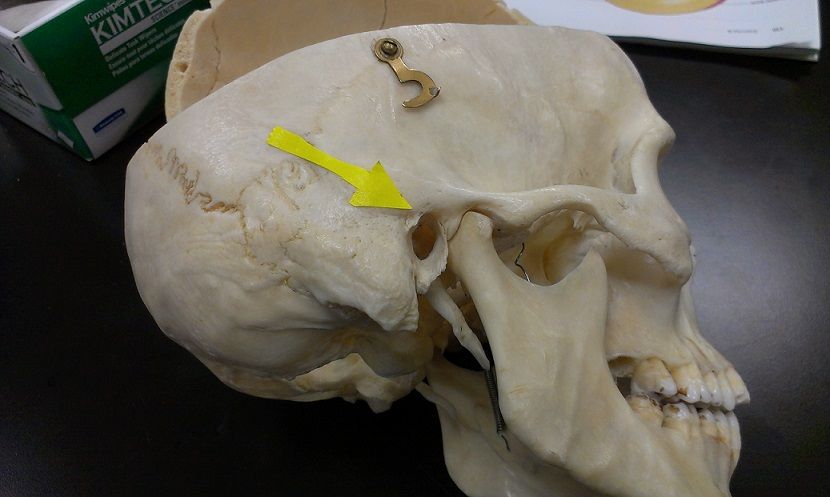
external auditory canal
97
New cards
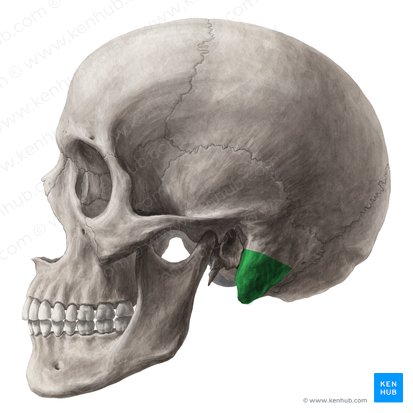
mastoid process
98
New cards
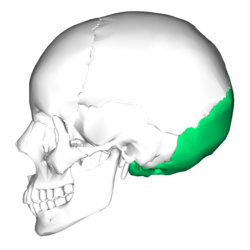
occipital
99
New cards
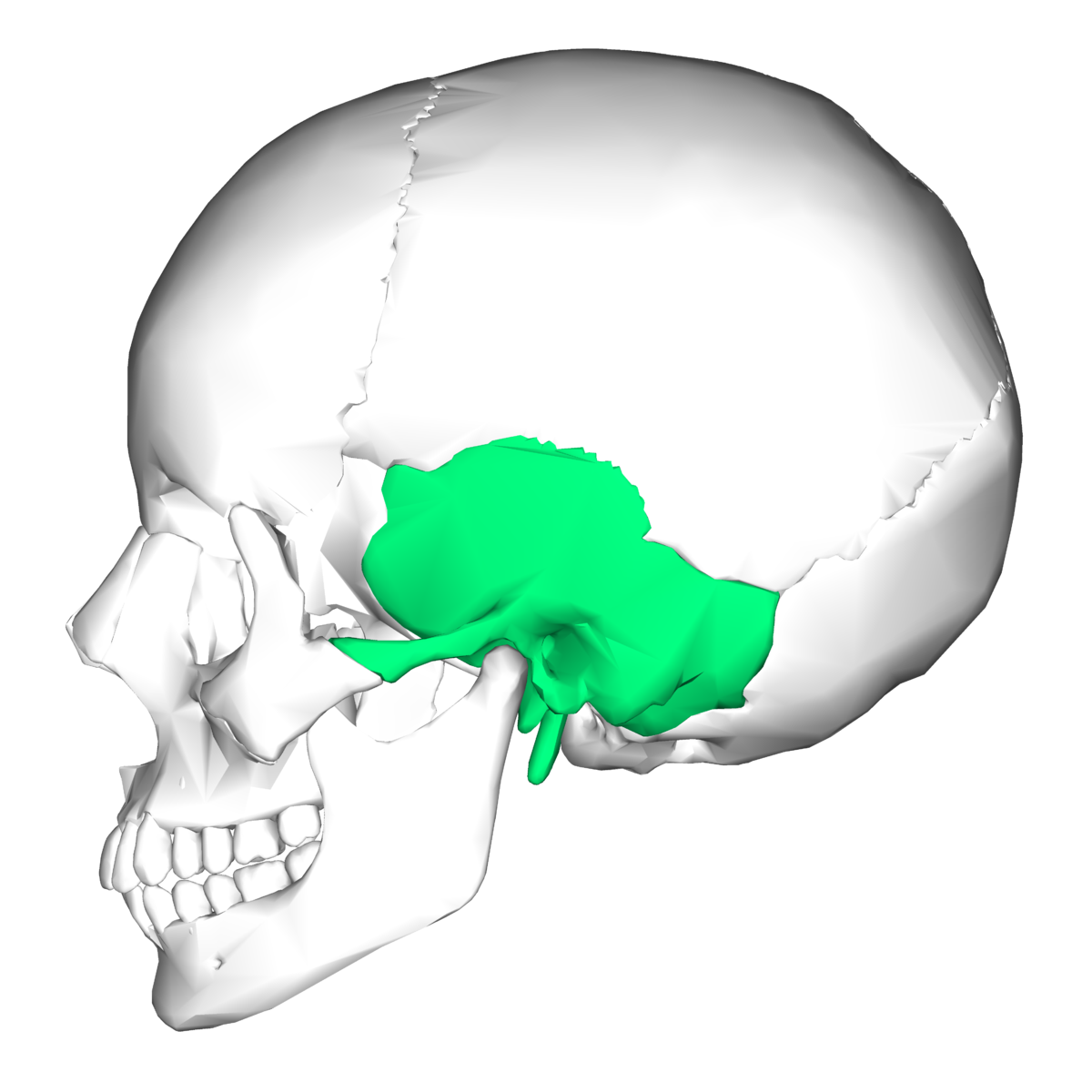
temporal
100
New cards
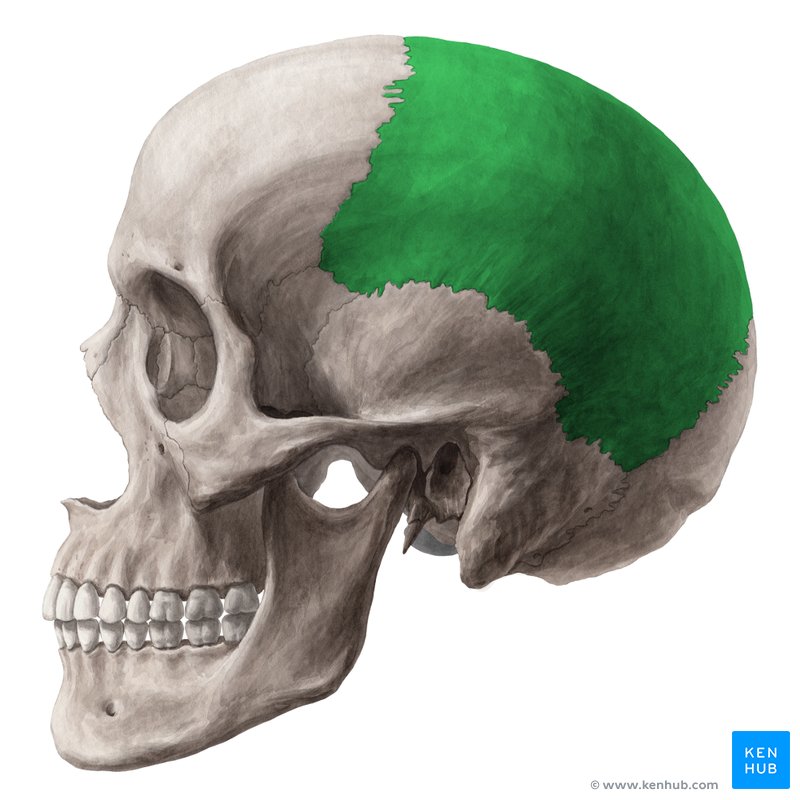
parietal