Histology and Integumentary System Flashcards - Biology Lab 1
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
Histology
the study of tissues
Tissues
a group of similarly structured cells that work together to accomplish a specific function
Four major tissue categories
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
epithelial tissue
- lines and covers organs (as well as their internal passageways
- create boundaries from different environments
- forms glands
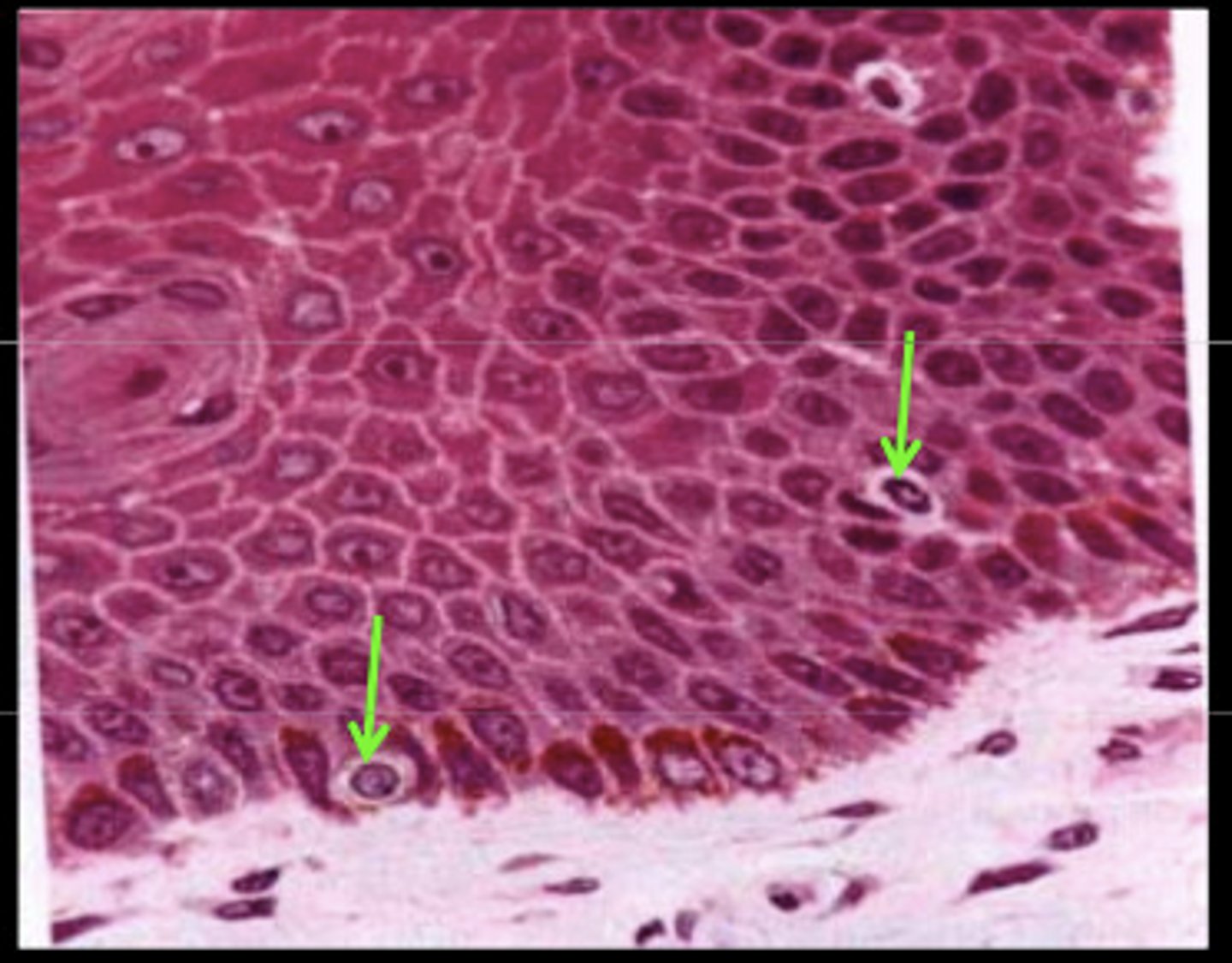
epithelia functions (6)
filtration, absorption, protection, secretion, excretion, and sensory reception
free or apical surface
- surface of the epithelium that is exposed to either the external environment or to an internal passageway or cavity
how the apical surface obtains nutrients
by diffusion of substances from connective tissue underlying the epithelia
basal lamina
- attaches epithelia to the boy (located between the epithelium and connective tissue layer)
- not cellular
- formed by glycoprotein secretions from epithelial cells plus collagen fibers
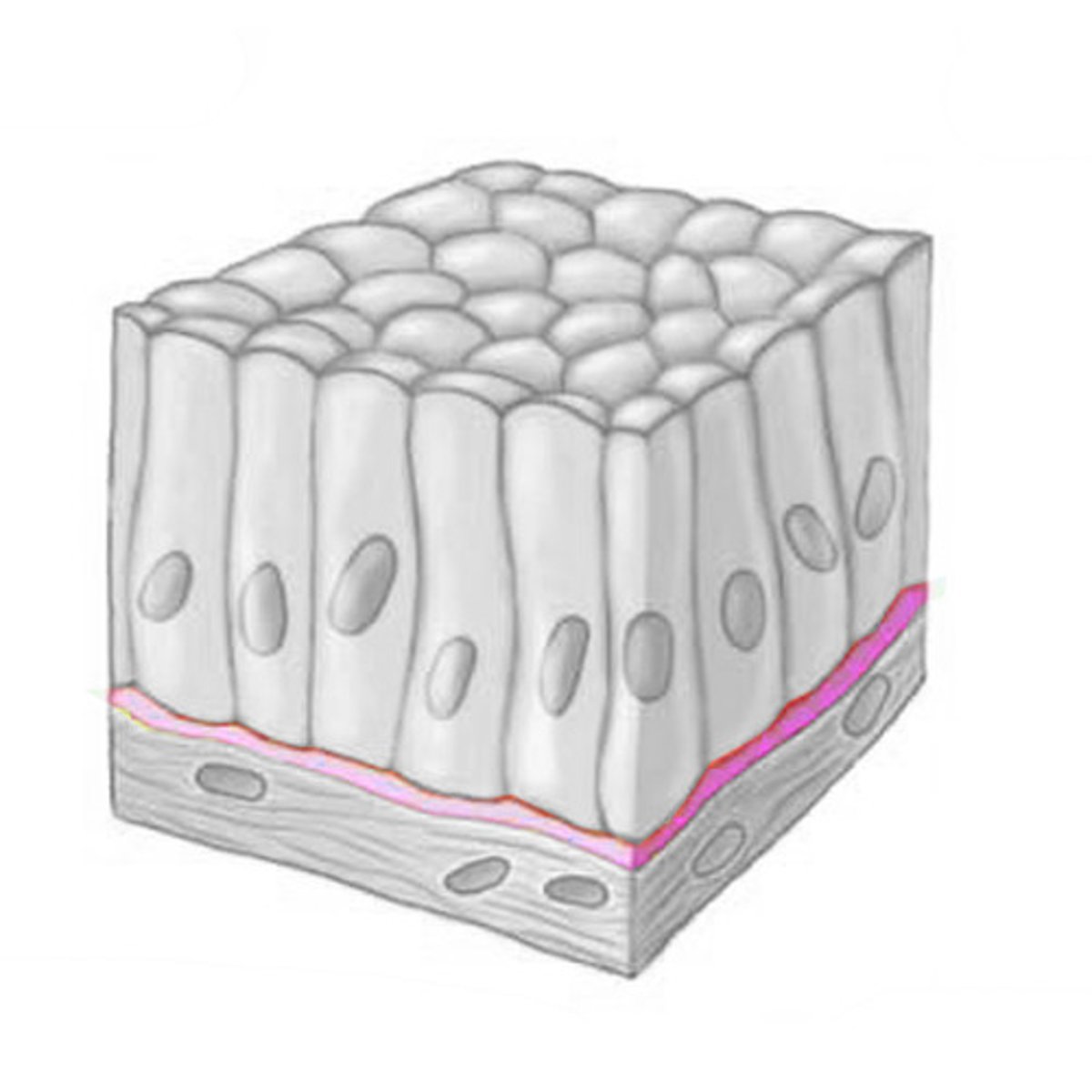
basal lamina function
a filter at the base of the epithelium and can form a scaffold for wound repair
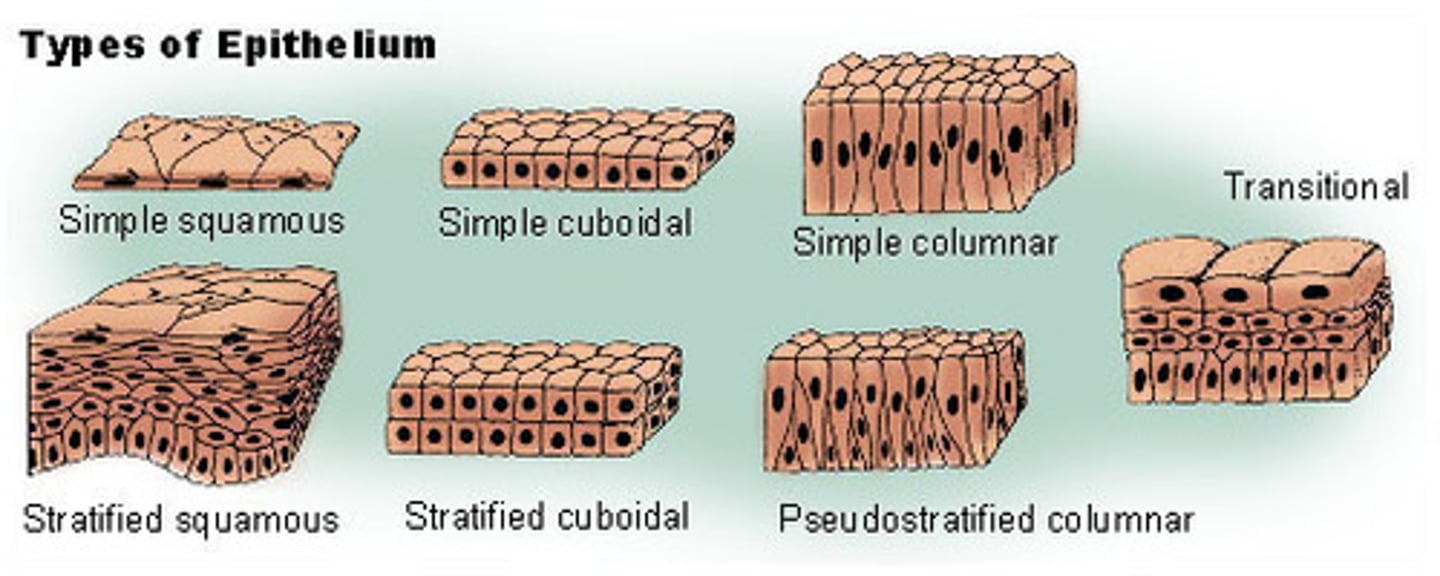
how epithelial are named
according to their shape and number of cell layers
simple epithelia
- only has one layer
- found in places with less friction (arteries, lymphatic system)
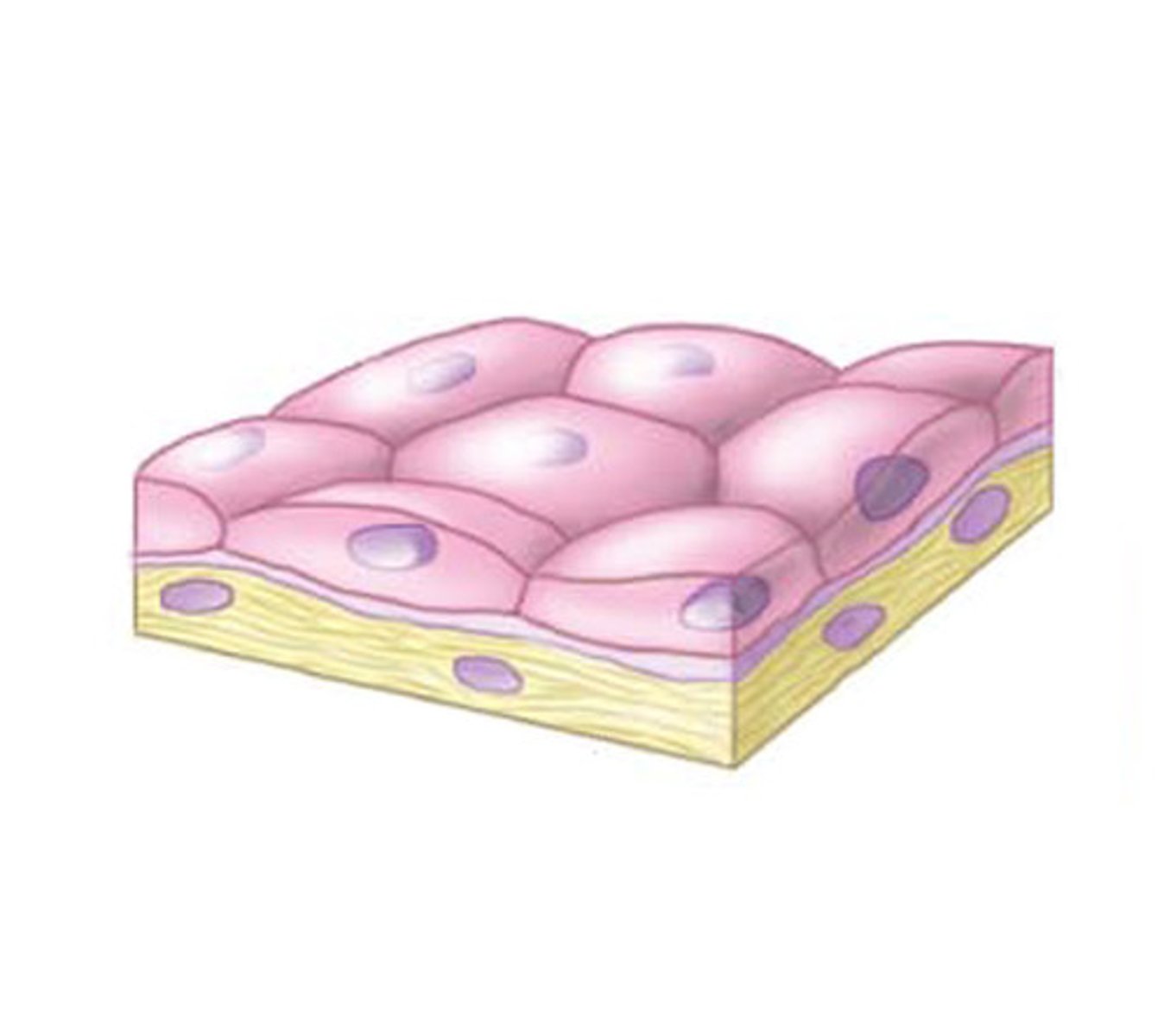
simple epithelia function
diffusion, absorption, filtration, and secretion
things found on simple epithelia
microvilli, goblet cells, and cilia
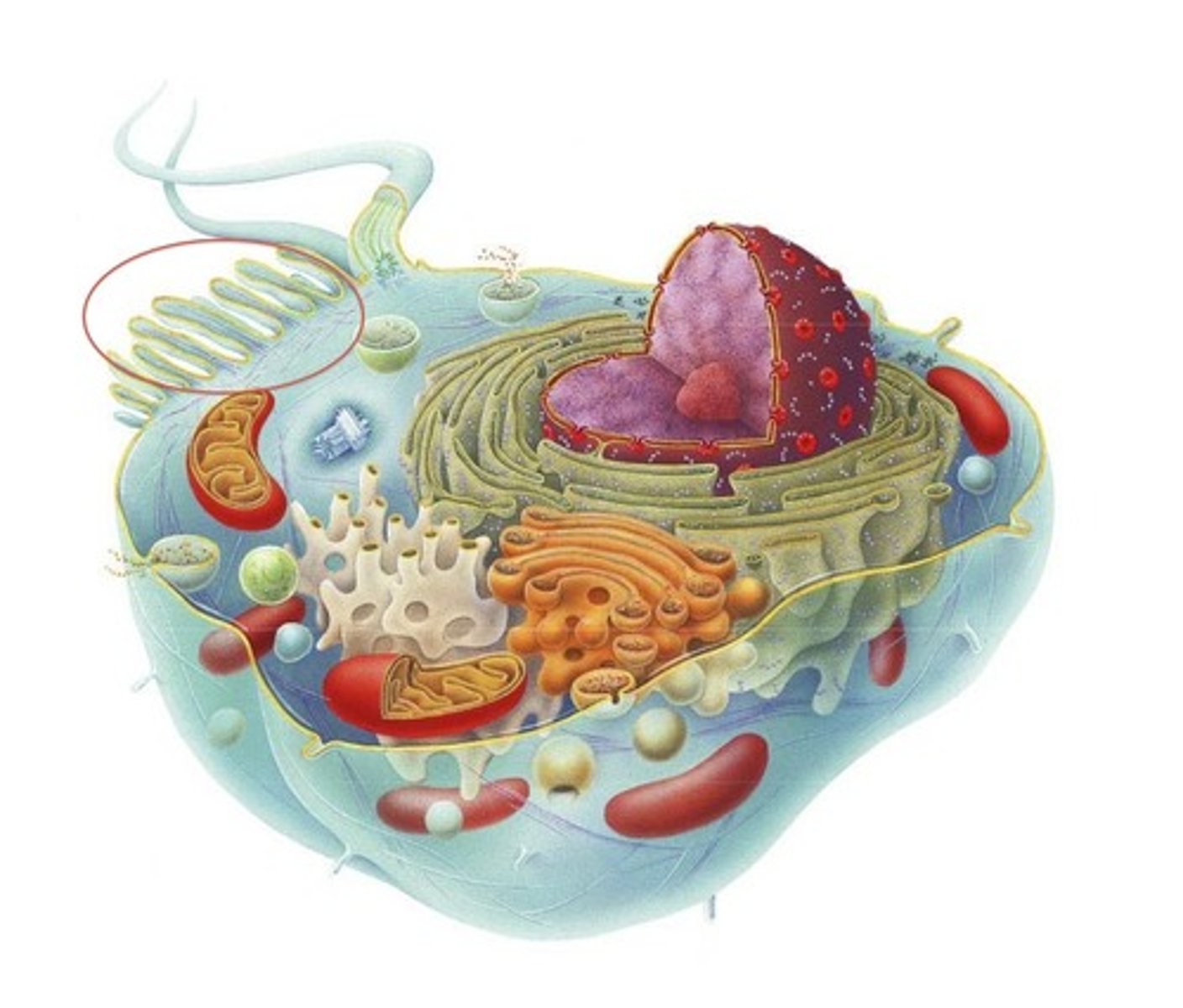
microvilli
increase surface area available for absorption
goblet cells
cells that secrete mucus that coats the cells to protect them at the free surface
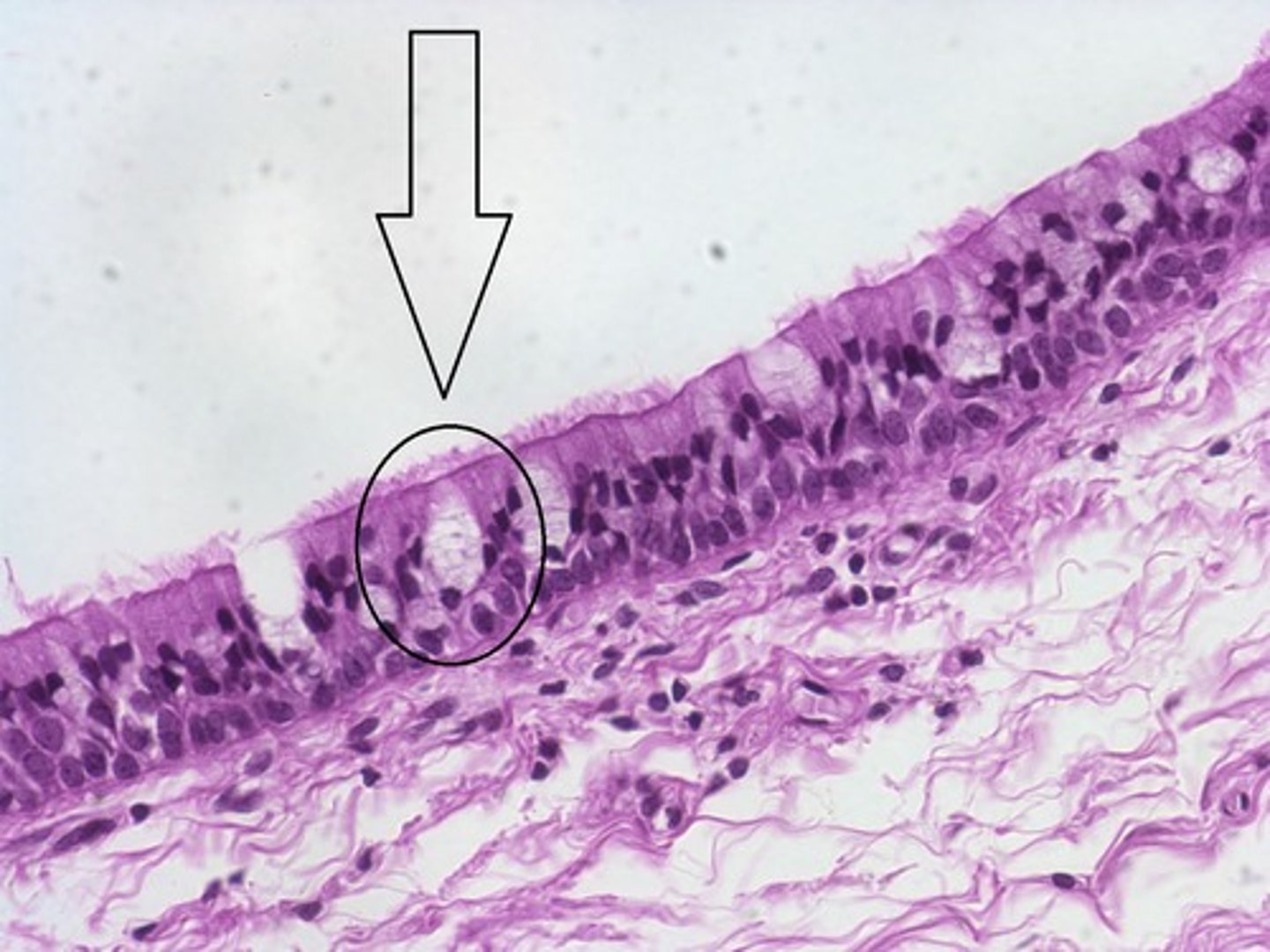
cilia
- small motile hair-like projections from apical surface
- sweep substances like mucous and debris (for removal) along apical surface
stratified epithelia
- more than one layer
- found in areas with higher abrasion and friction (body surface upper GI tract)
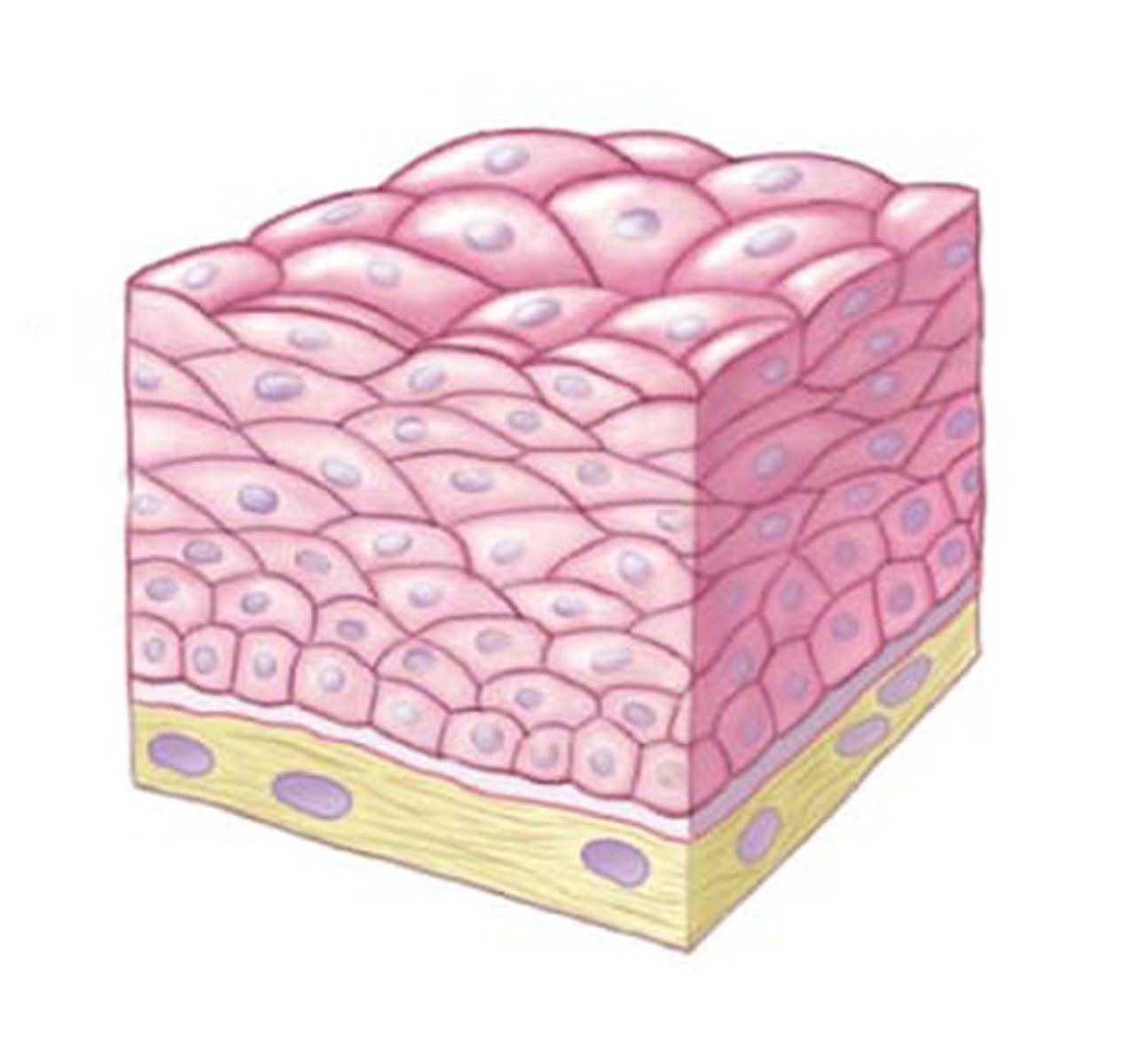
stratified epithelia function
mostly protection
how stratified epithelia is classified
based on the type of epithelial cell at the free surface
good to excellent tissue regeneration capacity
epithelial, bone, areolar, dense irregular connective, blood-forming
moderate tissue regeneration capacity
smooth muscle and dense regular connective
weak tissue regeneration capacity
skeletal muscle and cartilage
no to almost none tissue regeneration capacity
cardiac muscle and nervous tissue
distinguish epithelial tissues from other tissues
1. regeneration
2. polarity
3. cellularity and specialized contacts
4. supported by connective tissue
5. avascularity (no blood supply)
6. innervated
basement membrane
- helps epithelia resist tearing and stretching
- reinforces structural integrity
- creates a boundary
glandular epithelial tissue
- vascular
- make up glands within the body (sebaceous, exocrine, etc.)
- function is directly related to location
simple squamous epithelium
- single layer of flattened cells with disc-shaped central nuclei and sparse cytoplasm (simplest of all epithelia)
- diffusion and filtration, secretes lubricating substances in serosae
- located in kidney glomeruli, air sacs in lungs, heart lining, blood and lymphatic vessels, and lining of ventral body cavity
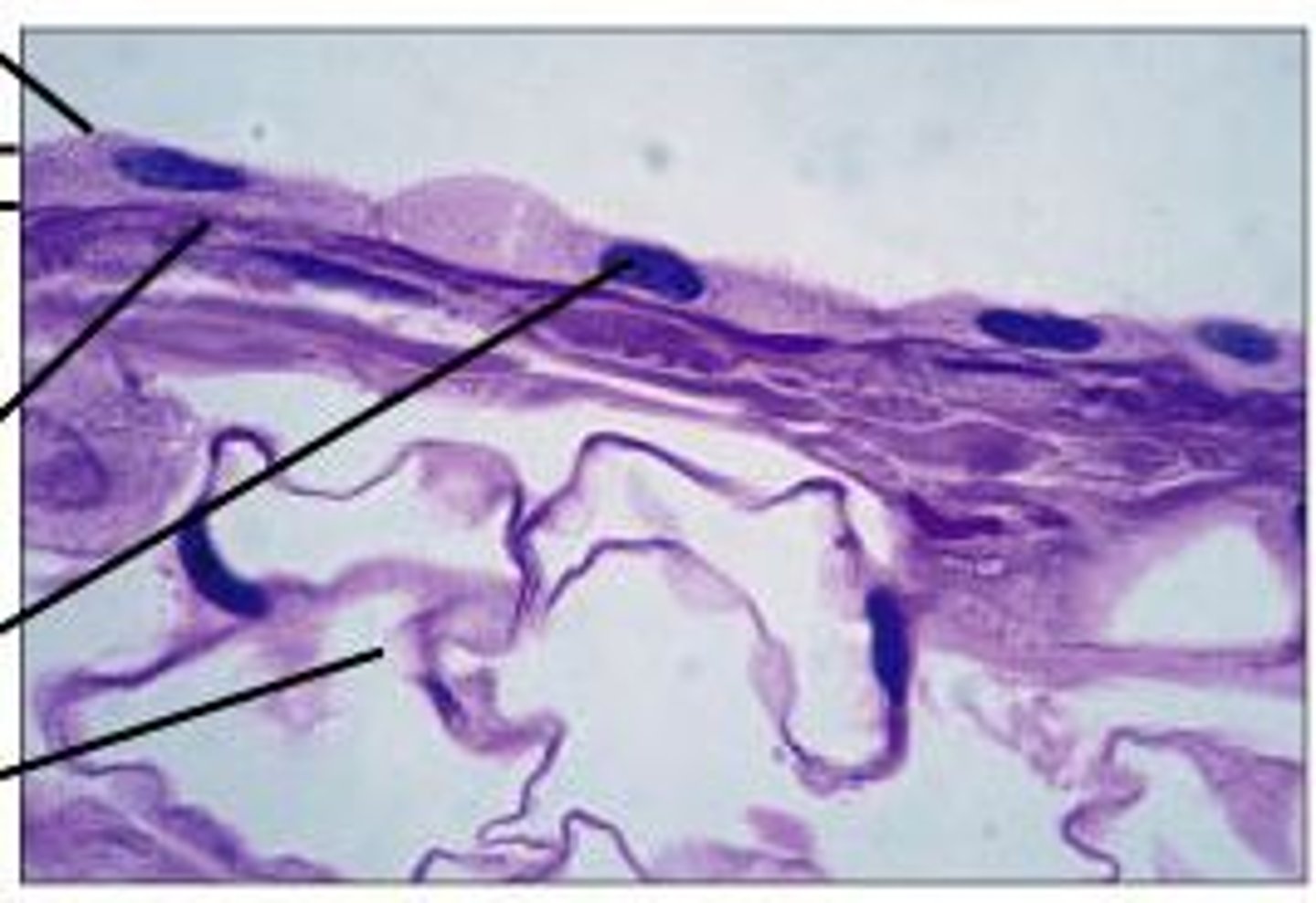
serosae
tissue lining of a body cavity or outer lining of an organ
endothelium (simple squamous epithelium)
provides a slick, friction-reducing lining in hollow organs that transmit body fluids (lymph, blood)
mesothelium (simple squamous epithelium)
epithelium found in serous membranes lining the ventral body cavity and covering its organs
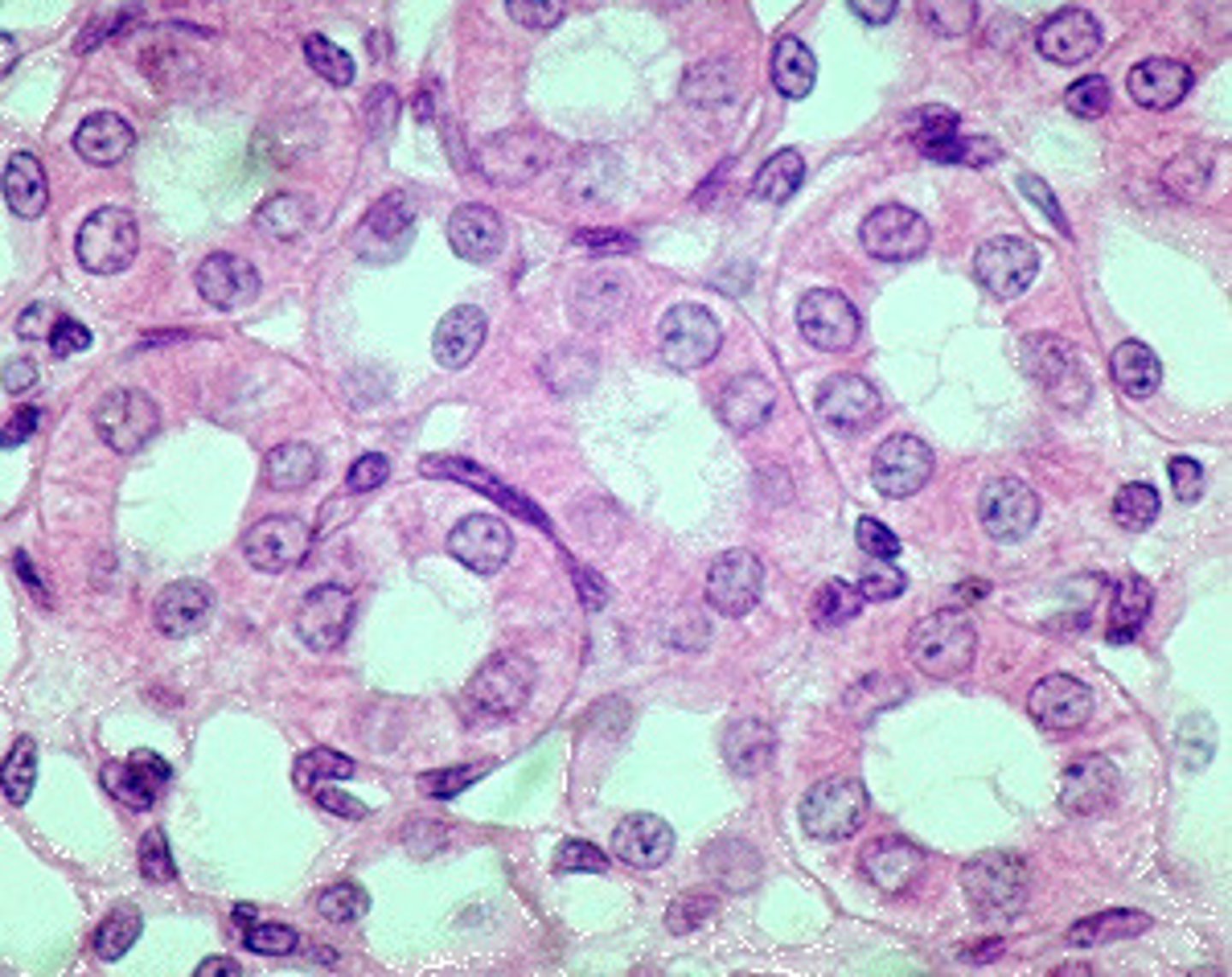
simple cuboidal epithelium
single layer of cube-like cells with large, spherical central nuclei
- function is secretion and absorption
- located in kidney tubules, ducts and secretory portions of small glands, and ovary surface
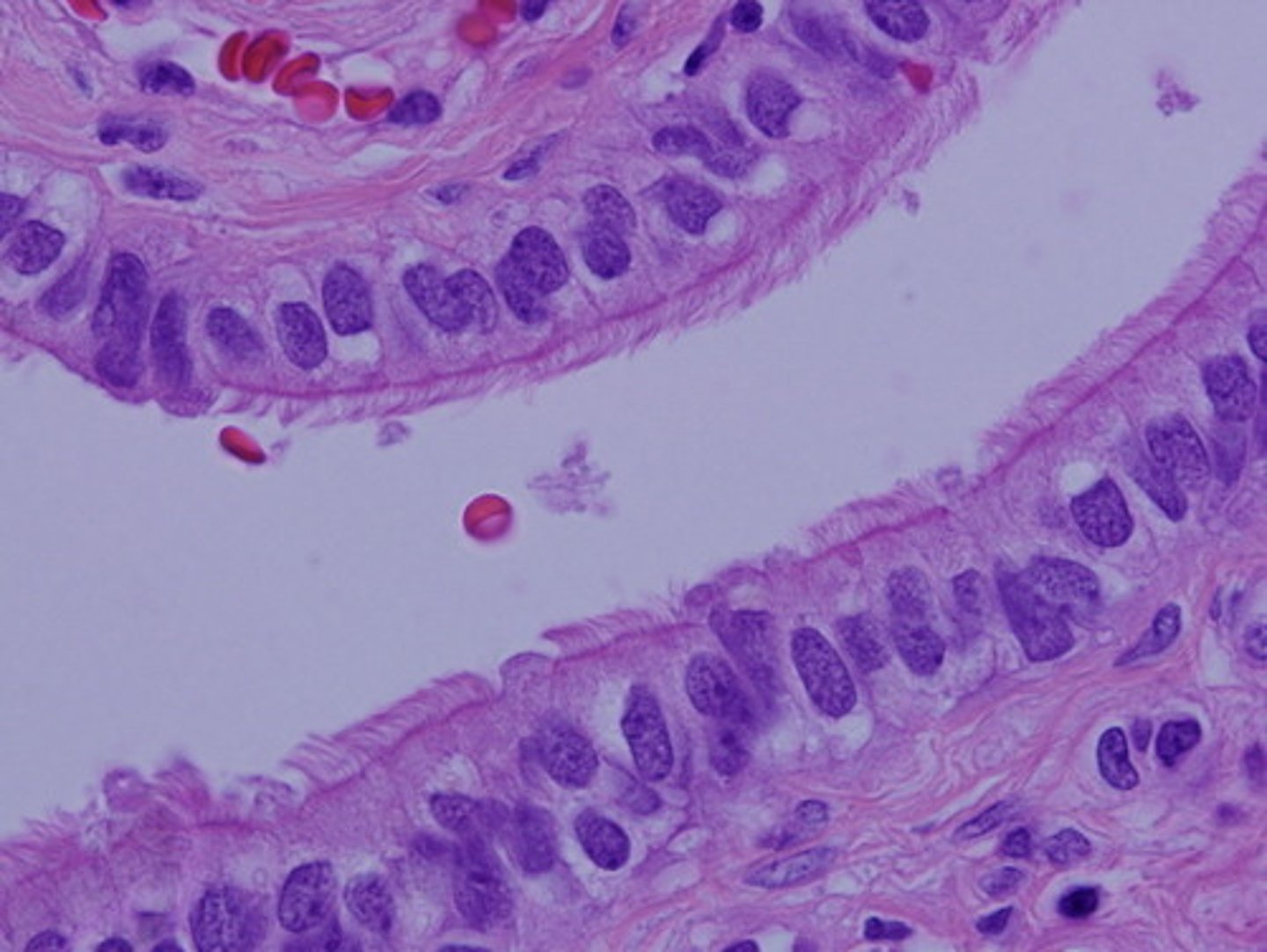
simple columnar epithelium
- single layer of tall cells with round/oval nuclei; some with cilia, sometimes have goblet cells
- function is absorption, secretion of mucus/enzymes/other substances; ciliated propels mucus by ciliary action
- non-ciliated located in digestive tract lining (stomach to anus), gallbladder, and excretory ducts of glands
- ciliated located in lining of small bronchi, uterine tubes, and some regions of the uterus
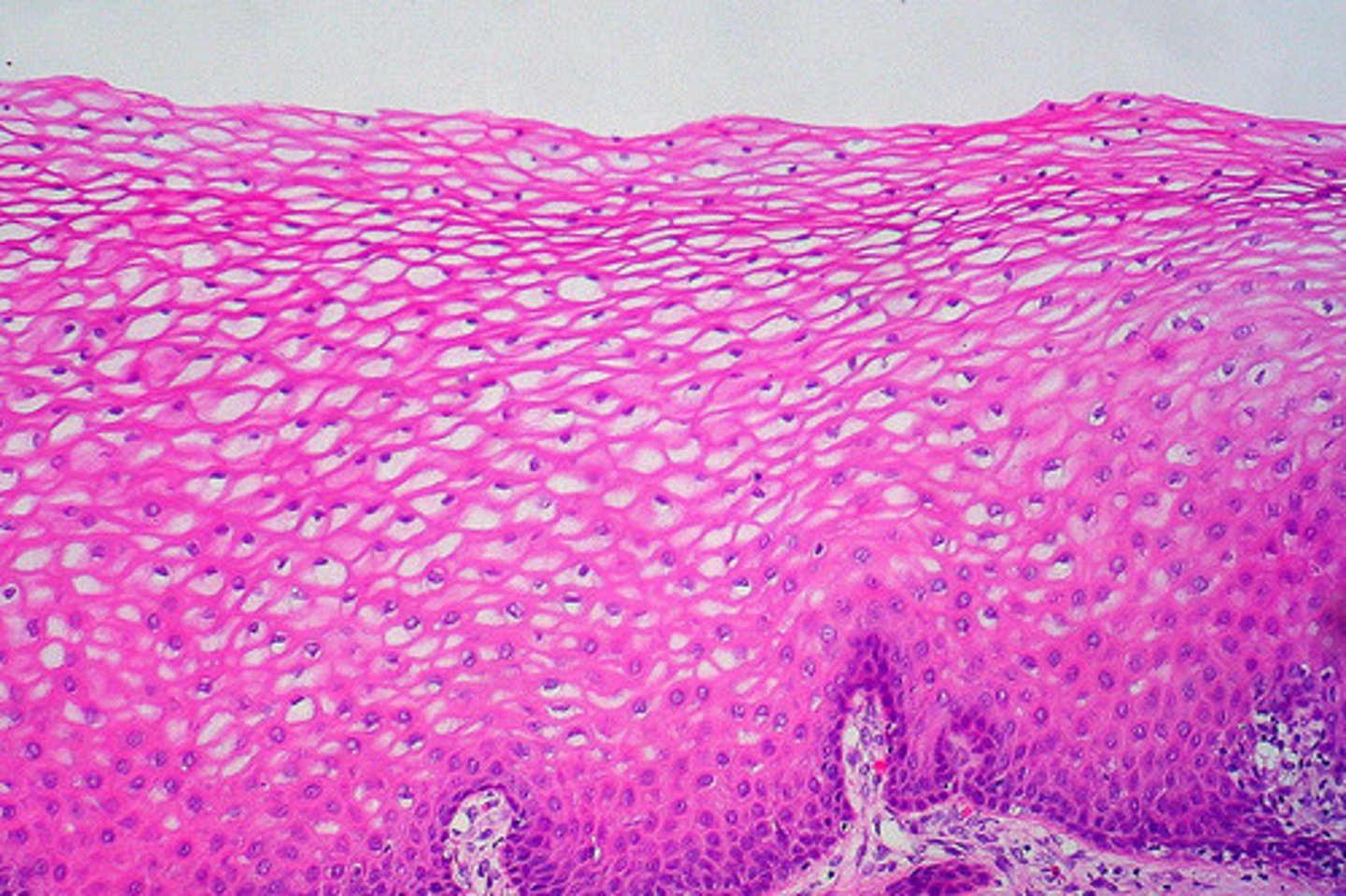
stratified squamous epithelium
- most common stratified epithelial type
- thick membrane composed of several layers
- has cuboidal or columnar basal cells and they're metabolically active
- surface cells are squamous (keratinized: dead)
- protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion
- nonkeratinized: moist lining of the esophagus, mouth, vagina
- keratinized: epidermis of the skin (dry membrane)
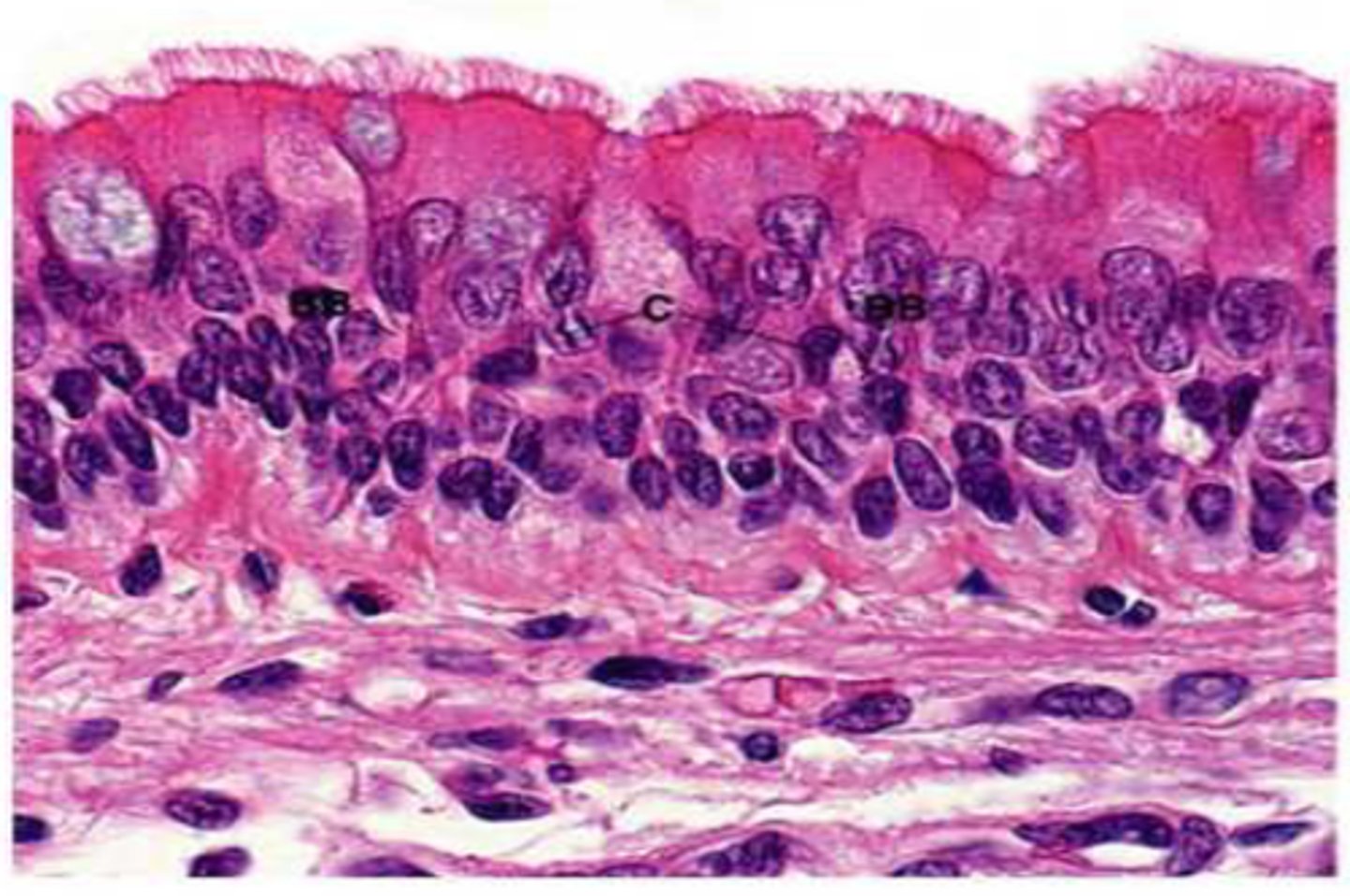
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
- single layer of cells that differ in height, nuclei at different levels, mucus-secreting cells and bear cilia
- function is secretion, particularly of mucus by ciliary action
- non-ciliated in male's sperm-carrying ducts/ducts of large glands
- ciliated lines trachea and most of the upper respiratory tract
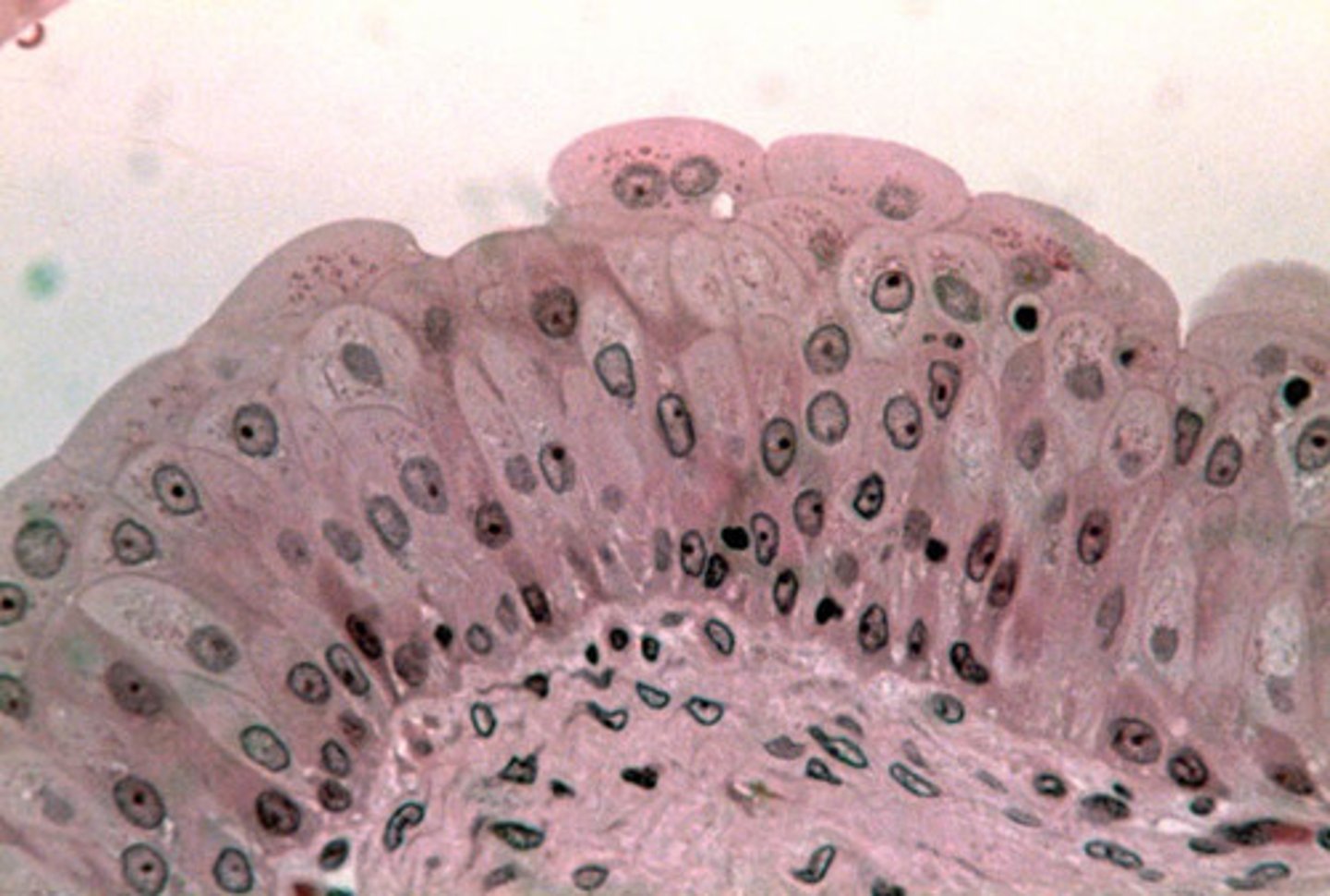
transitional epithelium
- resembles stratified squamous and stratified cuboidal; basal cells cuboidal or columnar, surface cells are dome shaped/squamous like (depends on organ stretch)
- stretches readily and permits distension of certain hollow organs (bladder)
- lines the ureters, urinary bladder, and part of the urethra
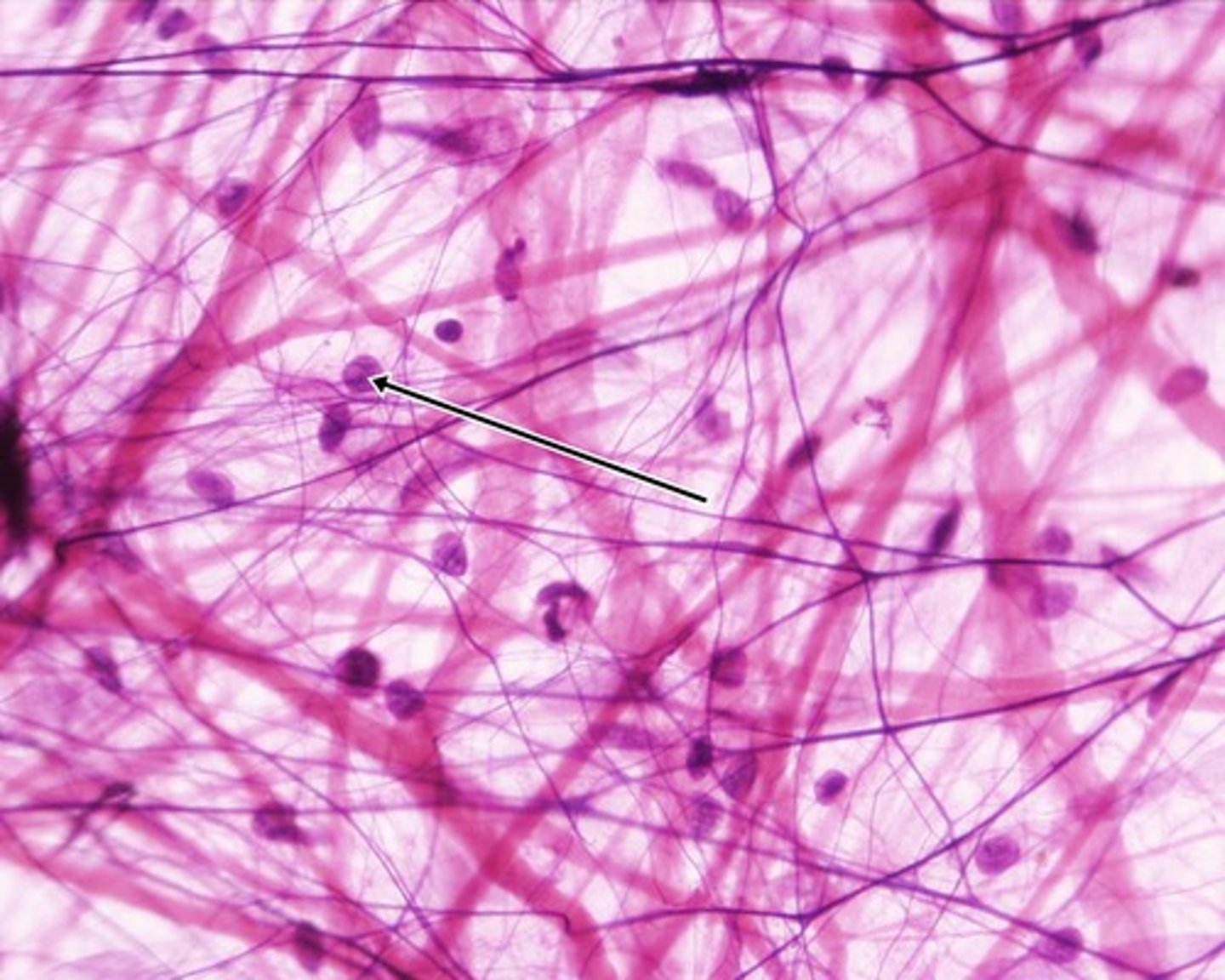
mesenchyme
the common embryonic connective tissue for all tissue types
connective tissue proper
- fibroblast then fibrocyte
- consists of loose and dense connective tissues
loose connective tissue
- areolar, adipose, reticular
- open network of protein fibers in a thick, syrupy ground substance
dense connective tissues
- regular and irregular
- made of protein fibers (thick collagen bundles) and elastic fibers
cartilage
- chondroblast then chondrocyte
- consists of hyaline, fibro, and elastic
- rubbery, avascular, non-innervated
- gelatinous matrix and fibers
- provides support, but is more flexible than bone
osseous (bone)
- osteoblast then osteocyte
- consists of compact and spongy (cancellous)
- solid matrix composed of calcium phosphate salt (hydroxyapatite)
- supports and protects body
- provides cavities for blood cell synthesis and fat storage
- highly vascularized and innervated
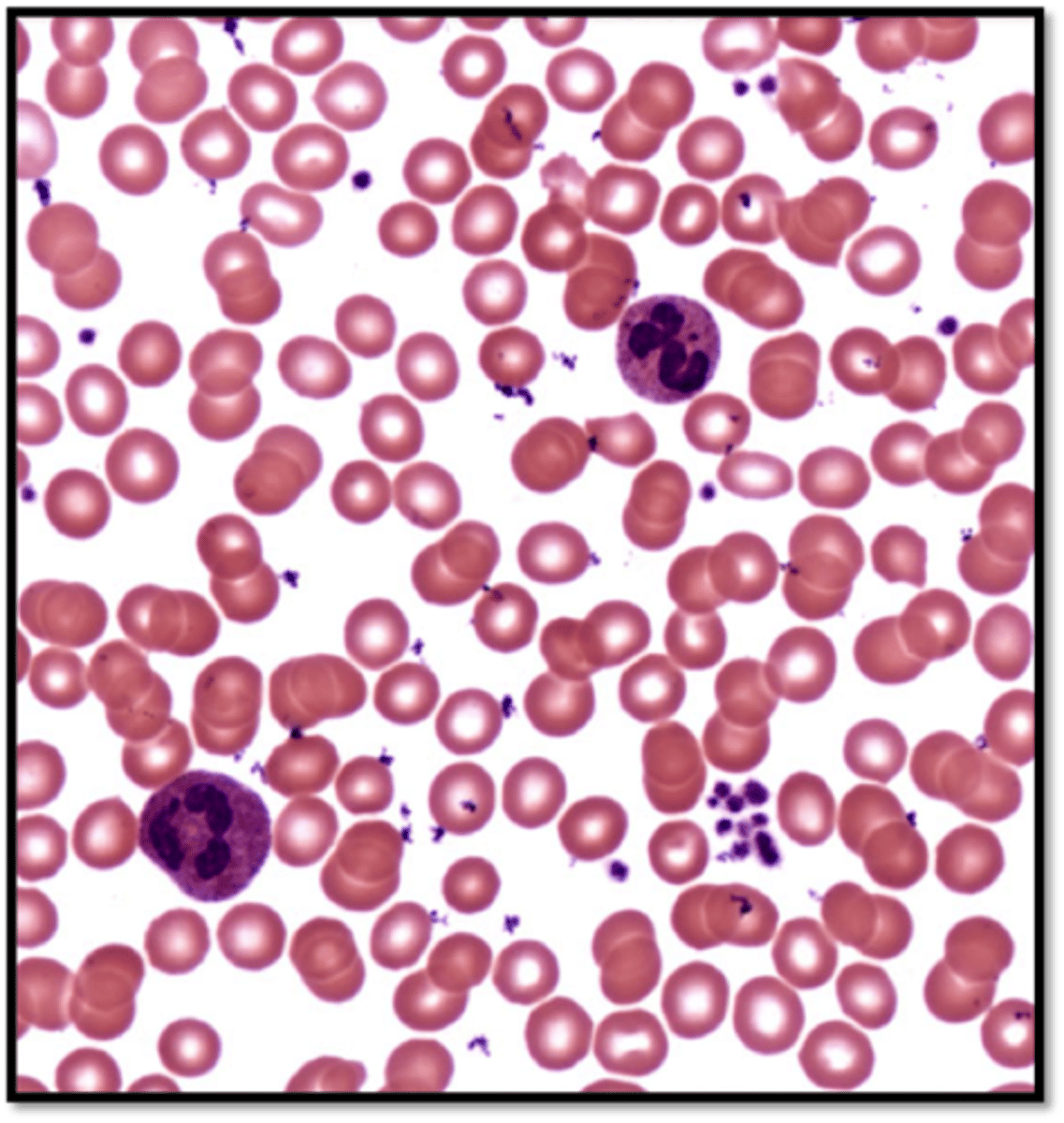
blood
- hematopoietic stem cell then blood cells
- contains red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes)
extracellular matrix
made of protein fibers and ground substance
ground substance
made up of collagen fibers, elastic fibers and reticular fibers
collagen fiber
made of many cross-linked collagen fibrils that gives the fibers their strength
elastic fibers
made of elastin, a protein that forms a branching network to provide stretch and recoil
reticular fibers
short, fine fibers made of a different collagen chemistry that form fuzzy nets and give more give/play
once matrix is generated
when blast cells become less active and mature into cyte cells
fibroblasts
stationary cells that secrete proteins that join other molecules in the matrix to form
macrophages
patrol tissues and are mobilized during infection or injury, migrate to the site of disturbance, and phagocytize damage tissue cells/microbes
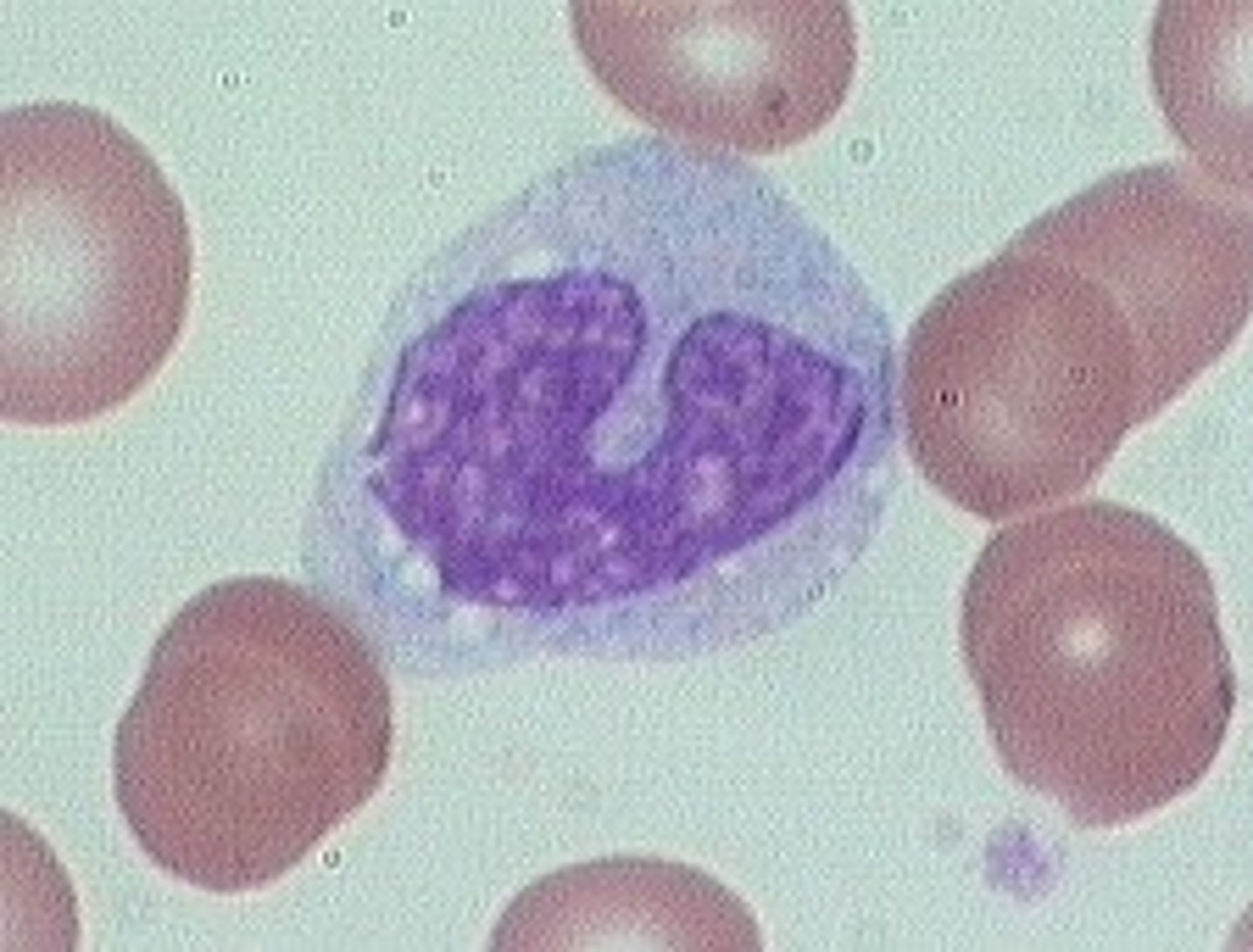
mast cells
detect foreign microorganisms and initiate immune responses against them (causes inflammatory response)
adipocytes
fat cells and contain vacuoles for the storage of lipids
dense irregular tissue
- fibers run in many different directions
- exerted from many different directions
- found in organ capsules and joints, dermis of the skin, submucosa of digestive tract
fluid connective tissue
blood and lymph
supporting connective tissue
- bone and cartilage
- contain strong matrix of fibers capable of supporting body weight and stress
perichondrium
- membrane that surrounds all supporting connective tissue in cartilage
- produces chondroblasts
- nutrients received by diffusion
chondroblasts
secrete fibers and the ground substance of cartilage matrix
lacunae (cartilage)
small spaces where the chondroblasts get trapped in matrix and become chondrocytes
chondrocytes
function to maintain mature cartilage tissue
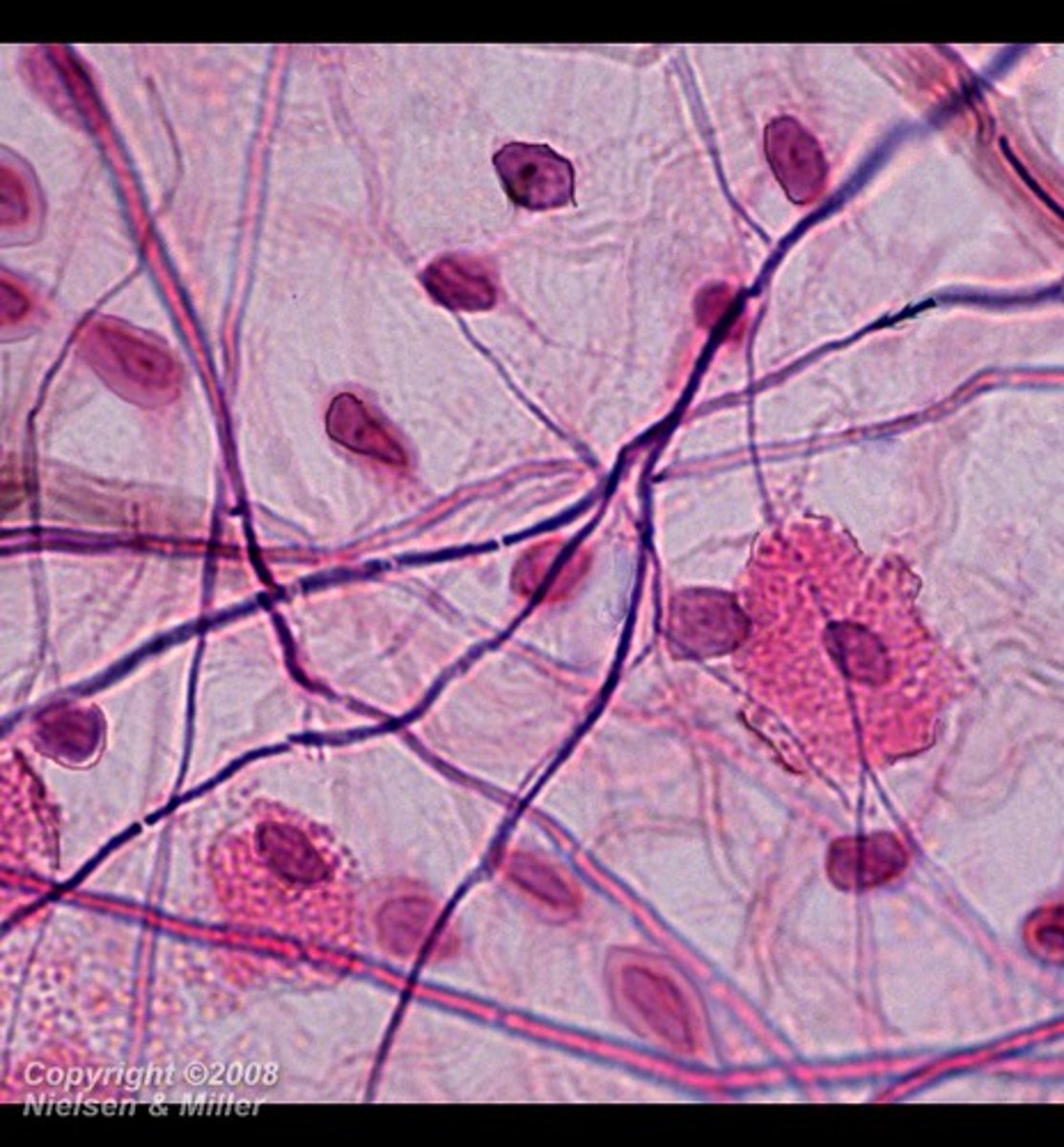
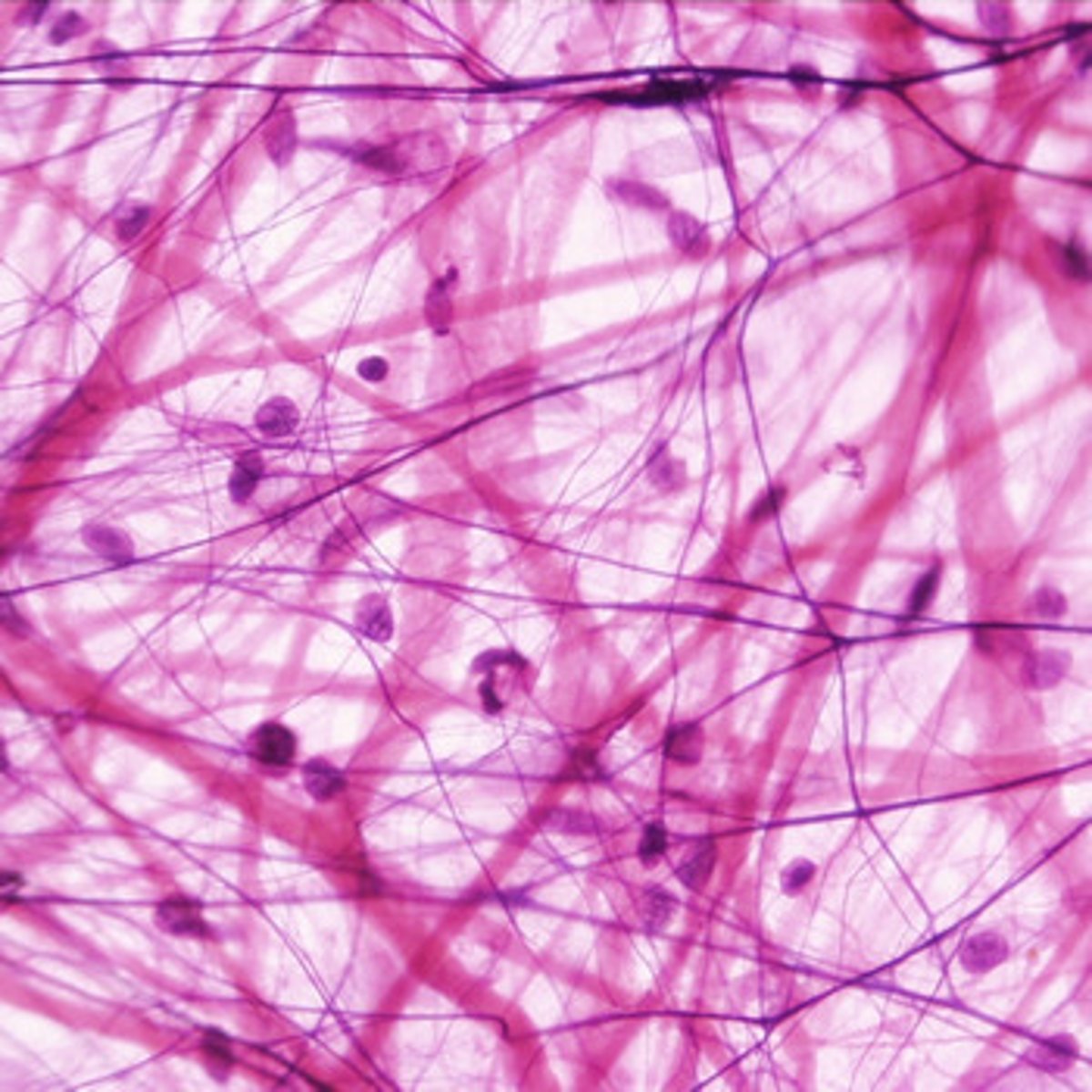
areolar tissue
- loose connective tissue
- gel-like matrix with all three fiber types (fibroblasts, macrophages, and mast cells) and some white blood cells
- wraps and cushions organs; plays important role in inflammation; holds and conveys tissue fluids
- located/widely distributed under the skin
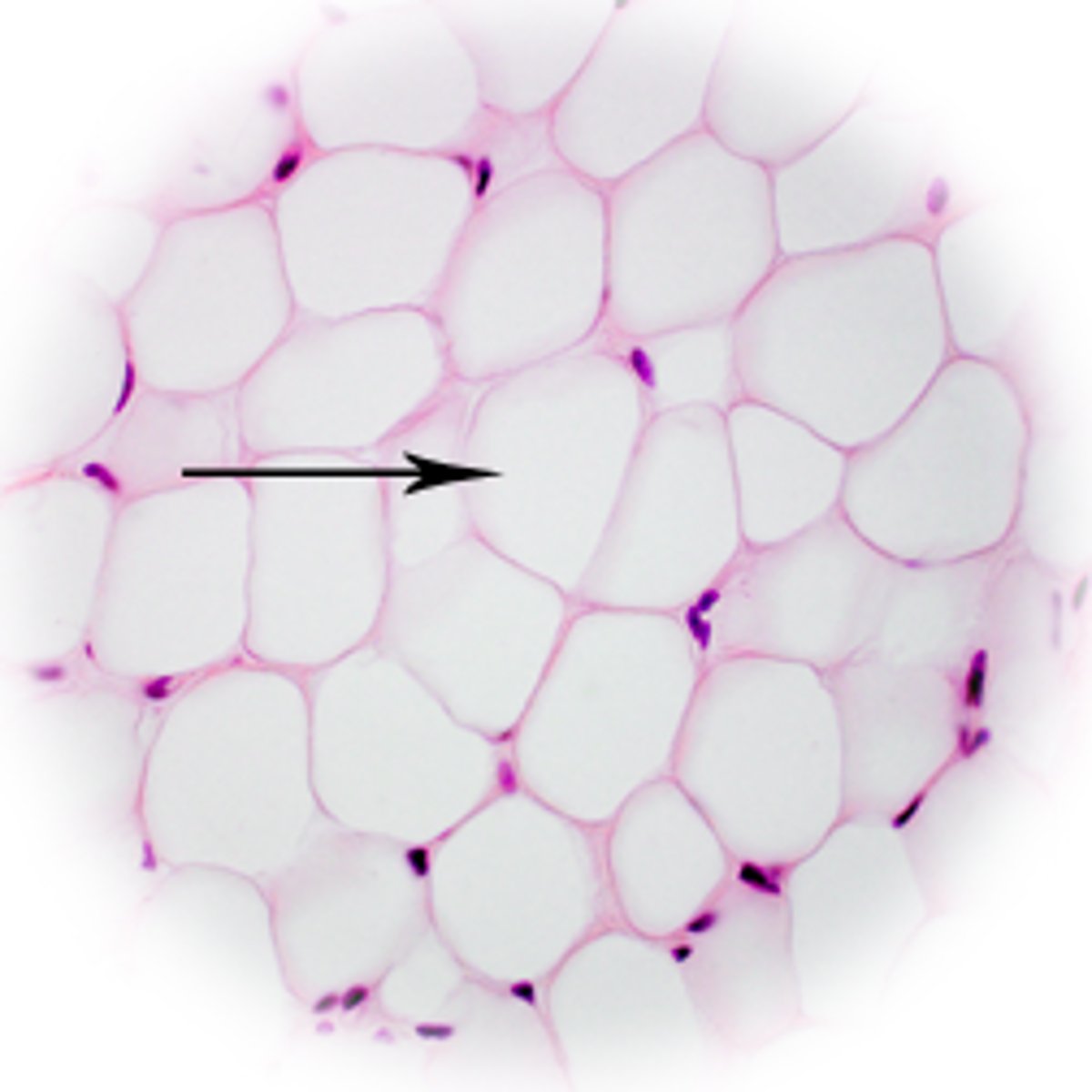
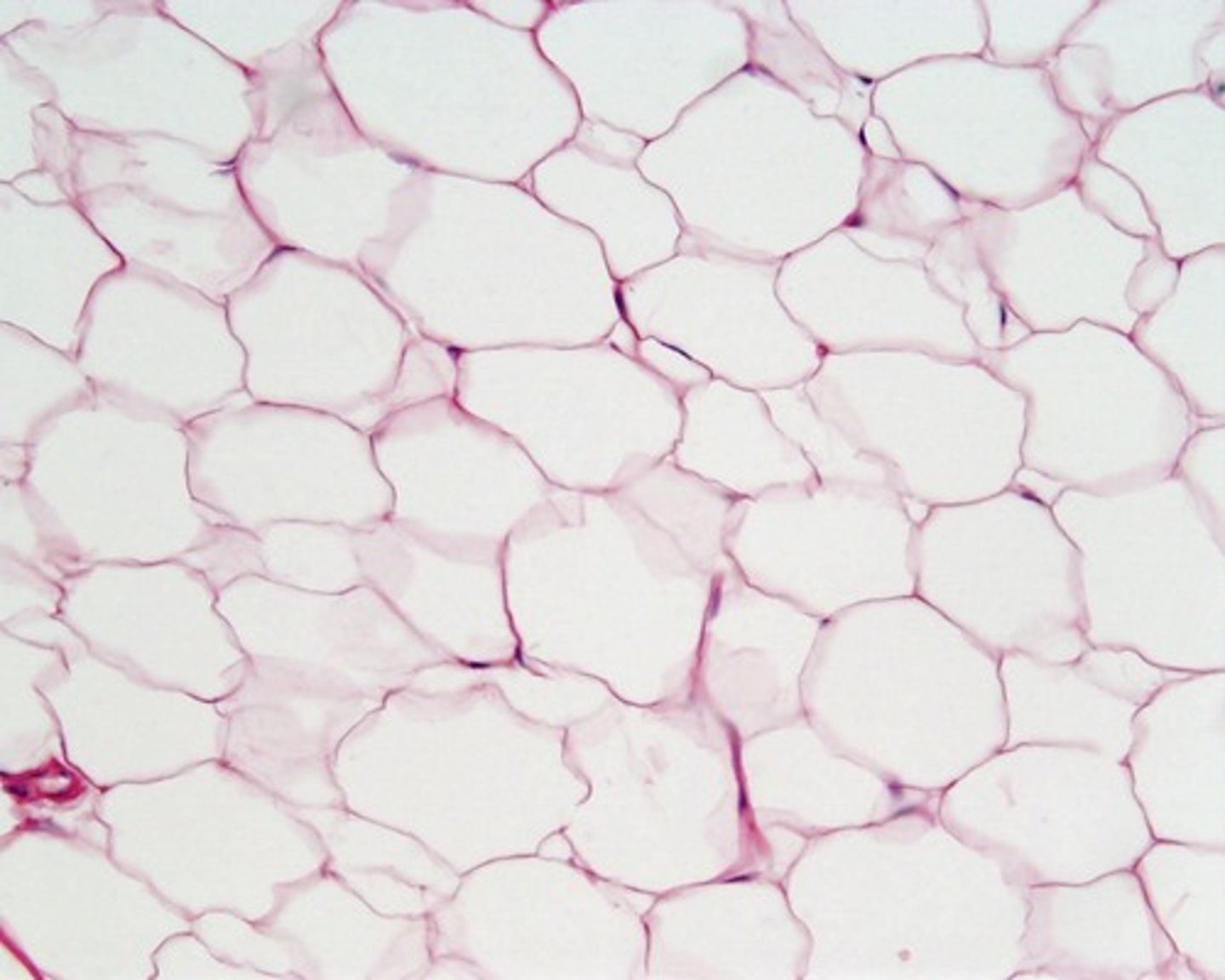
adipose tissue
- loose connective tissue
- matrix like areolar tissue, but sparse; has closely packed adipocytes and nucleus pushed to side by fat droplets
- provides reserve food fuel; insulates against heat loss; supports and protects organs
- located under skin in subcutaneous tissue; around kidneys and eyeballs; within abdomen; in breasts
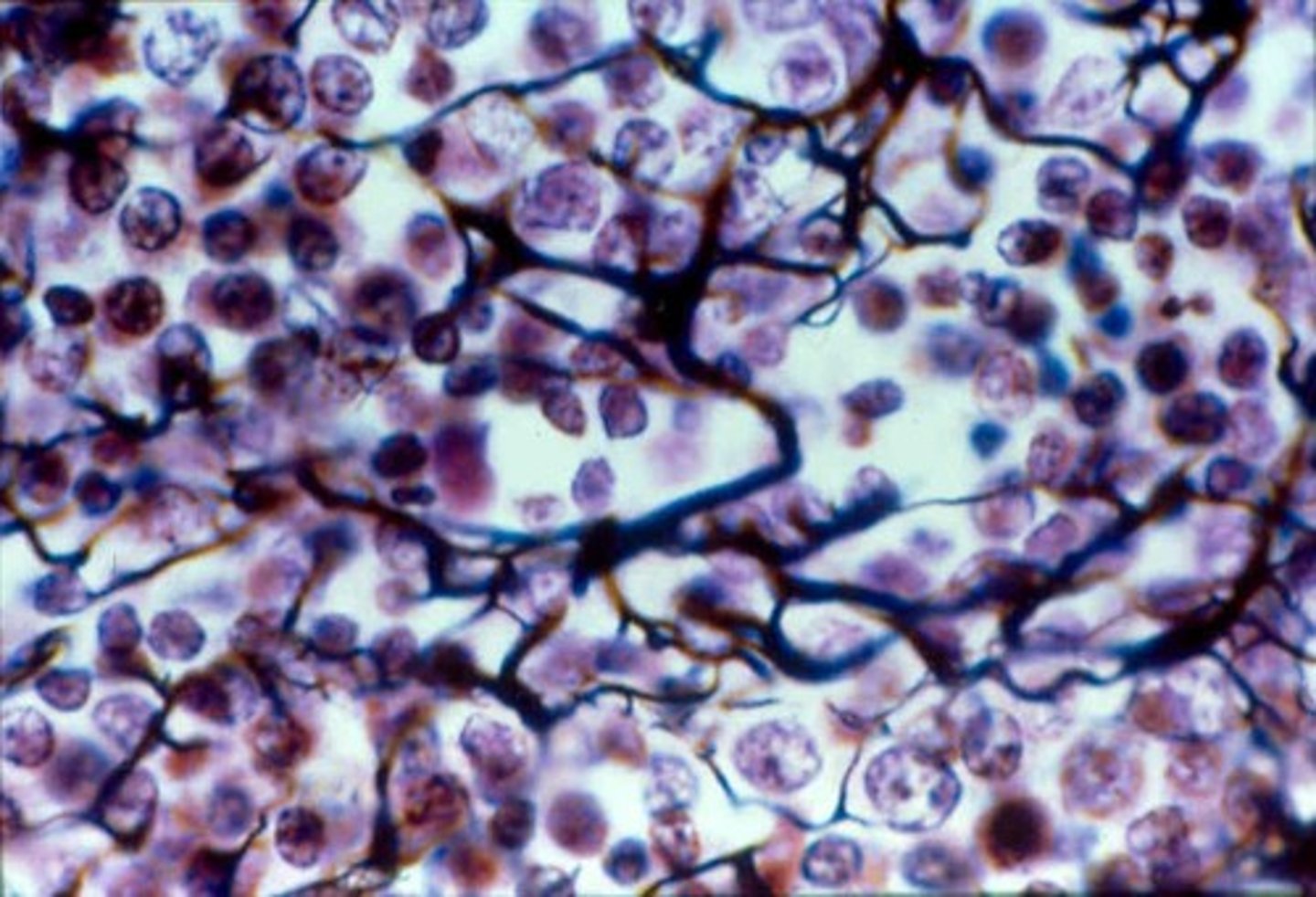
reticular tissue
- loose connective tissue
- network of reticular fibers in a typical loose ground substance; reticulocytes lie on network
- fibers form a soft internal skeleton (stroma) that supports other cell types including white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages
- located in lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, bone marrow, spleen)
dense regular connective tissue
- primarily parallel collagen fibers with few elastic fibers; main cell type is fibroblast
- attaches muscle to bones or to muscles; attaches bone to bone; withstands great tensile stress when pulling force is applied in one direction
- located in tendons, most ligaments, and aponeuroses
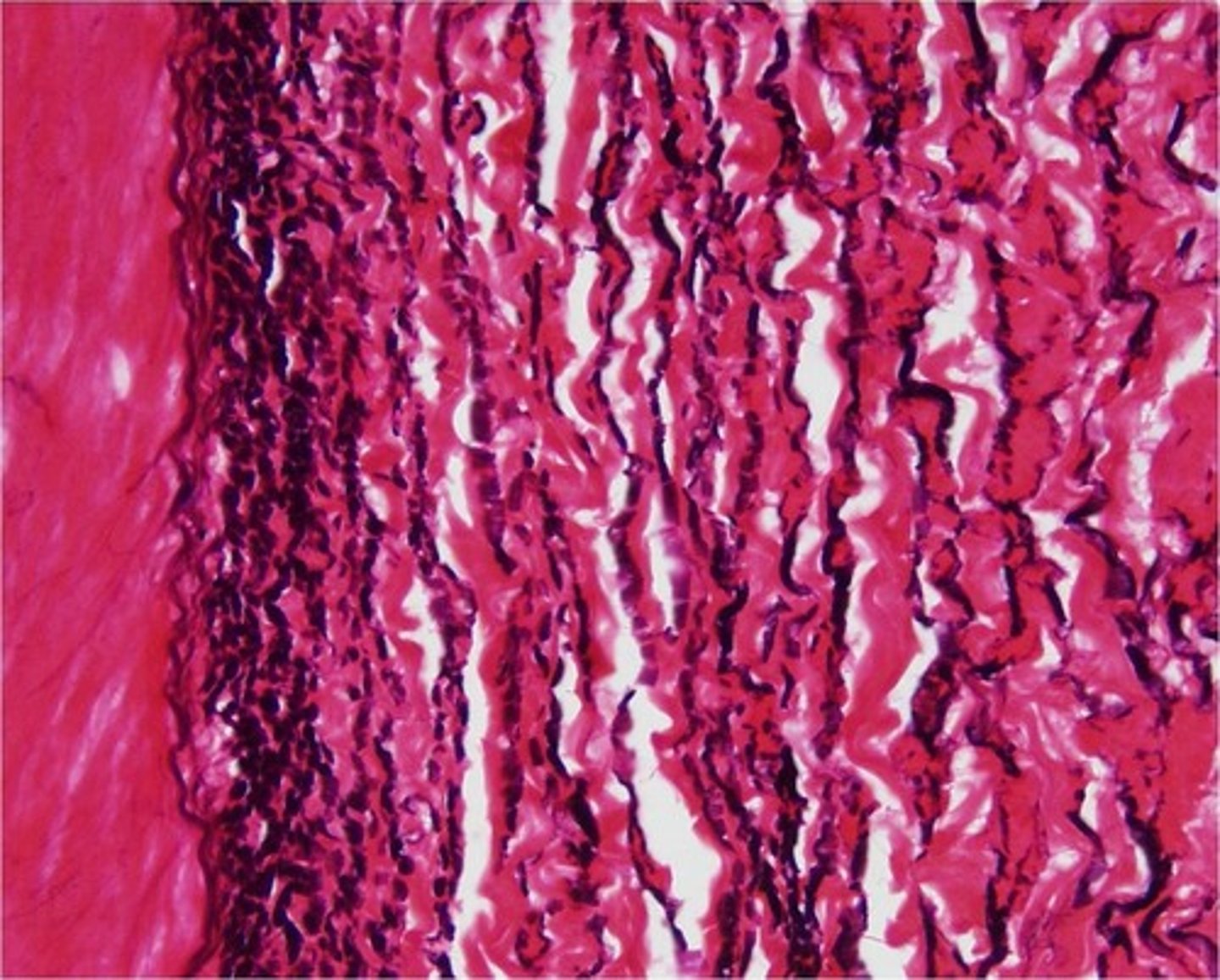
dense regular elastic tissue
- contains a high proportion of elastic fibers, but also has collagen fibers and fibrocyte nuclei
- allows recoil of tissue following stretching; maintains pulsatile blood flow through arteries; aids passive recoil of lungs following respiration
- located in the walls of large arteries, certain ligaments within/associated with the vertebral column, within the walls of bronchial tubes
blood fluid connective tissue
- composed of mostly formed elements suspended in a liquid ground substance called plasma
- red and white blood cells in a fluid matrix
- function is the transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances
- contained within the blood vessels
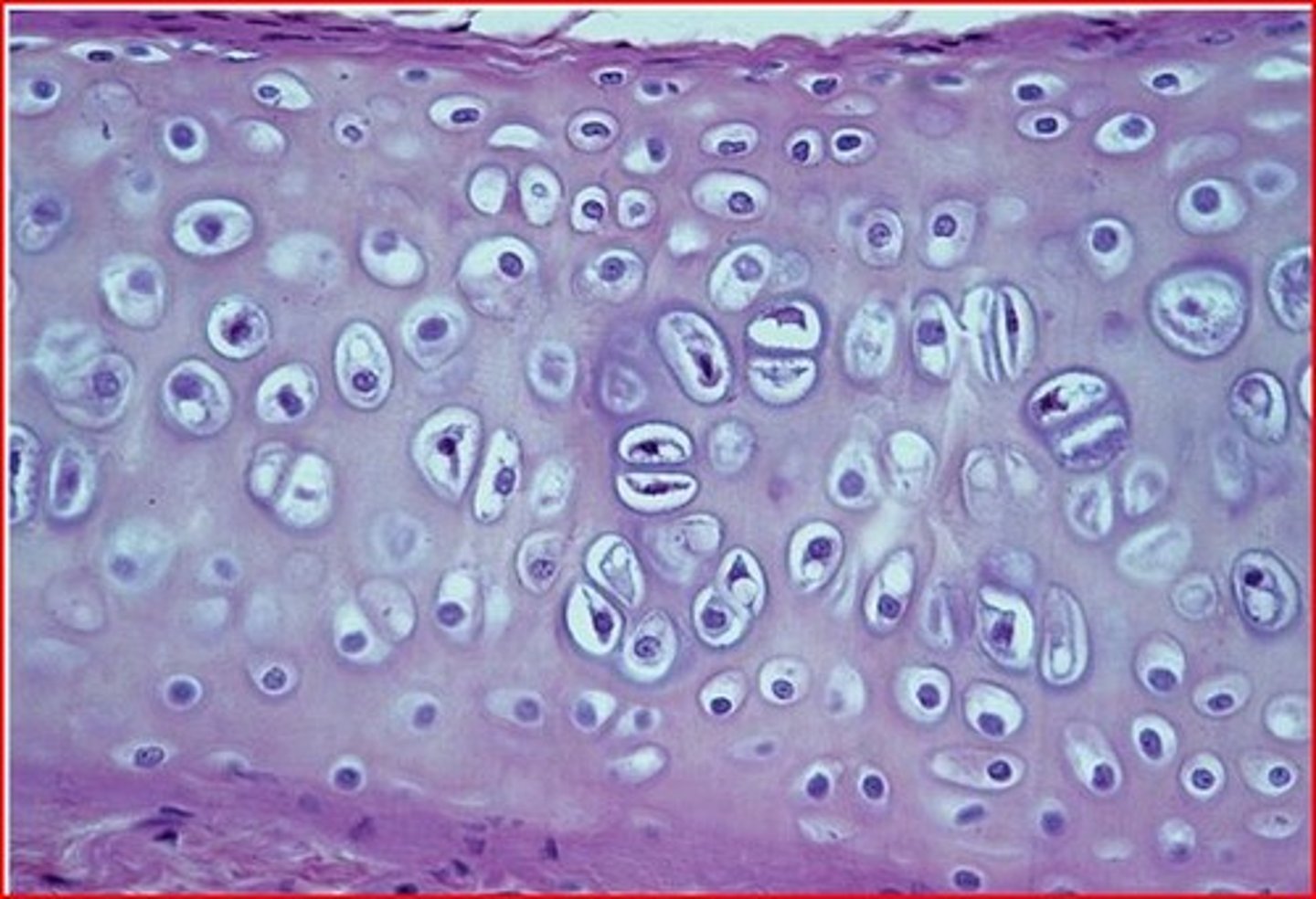
hyaline cartilage
- most common cartilage in the body
- amorphous but firm matrix, collagen fibers form an imperceptible network; collagen and elastic fibers not visible
- supports and reinforces; has resilient cushioning properties; resists compressive stress
- forms most of the embryonic skeleton, covers the ends of long bones in joint cavities, forms costal cartilages of the ribs, cartilages of the nose, trachea, and larynx
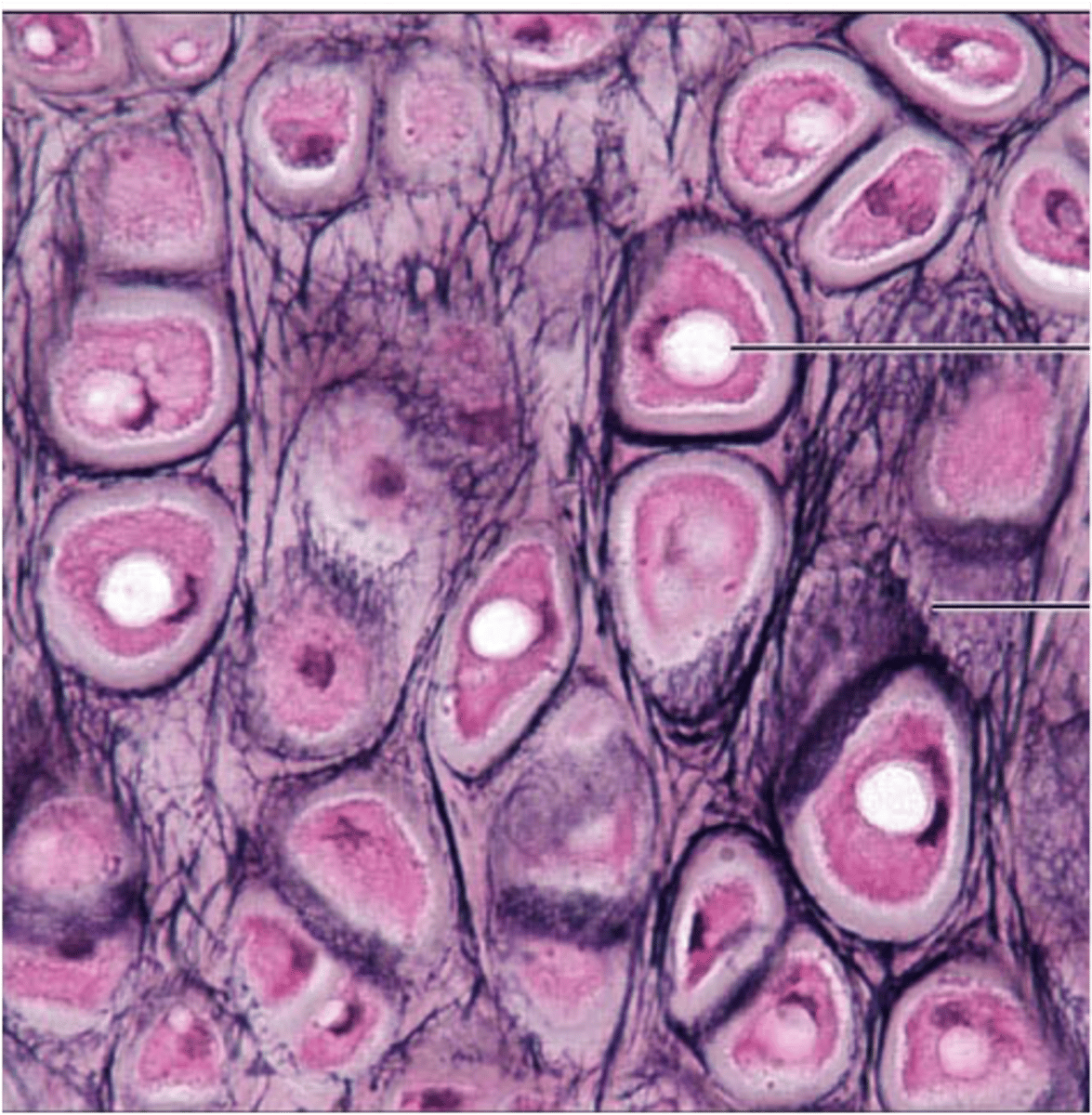
elastic cartilage
- similar to hyaline cartilage, but more elastic fibers are visible
- maintains the shape of a structure while allowing great flexibility
- supports the external ear (pinna) and epiglottis
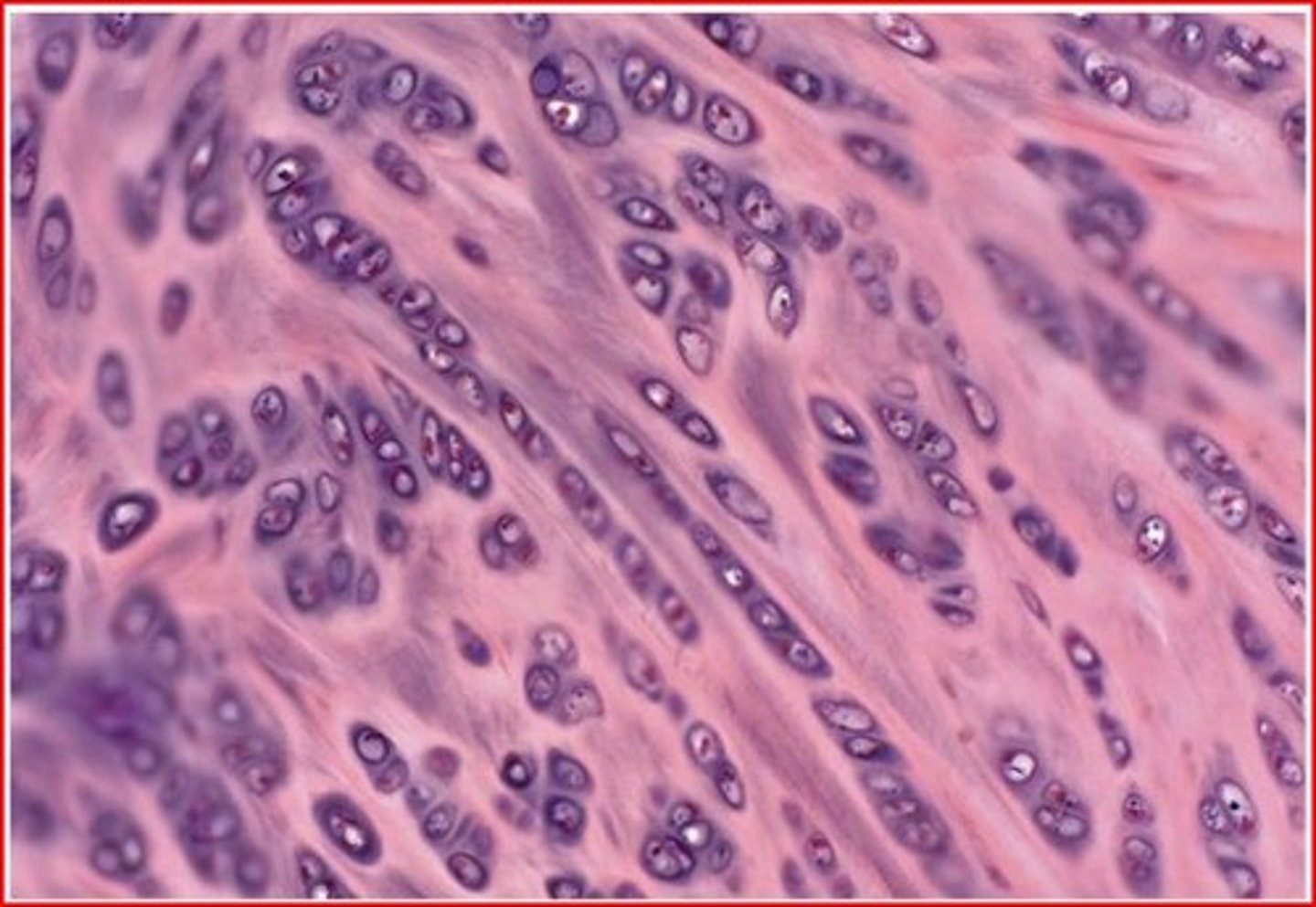
fibrocartilage
- matrix similar to but less firm than hyaline cartilage; thick collagen fibers predominate
- tensile strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock
- located in invertebral discs, pubis symphysis, and discs of knee joint
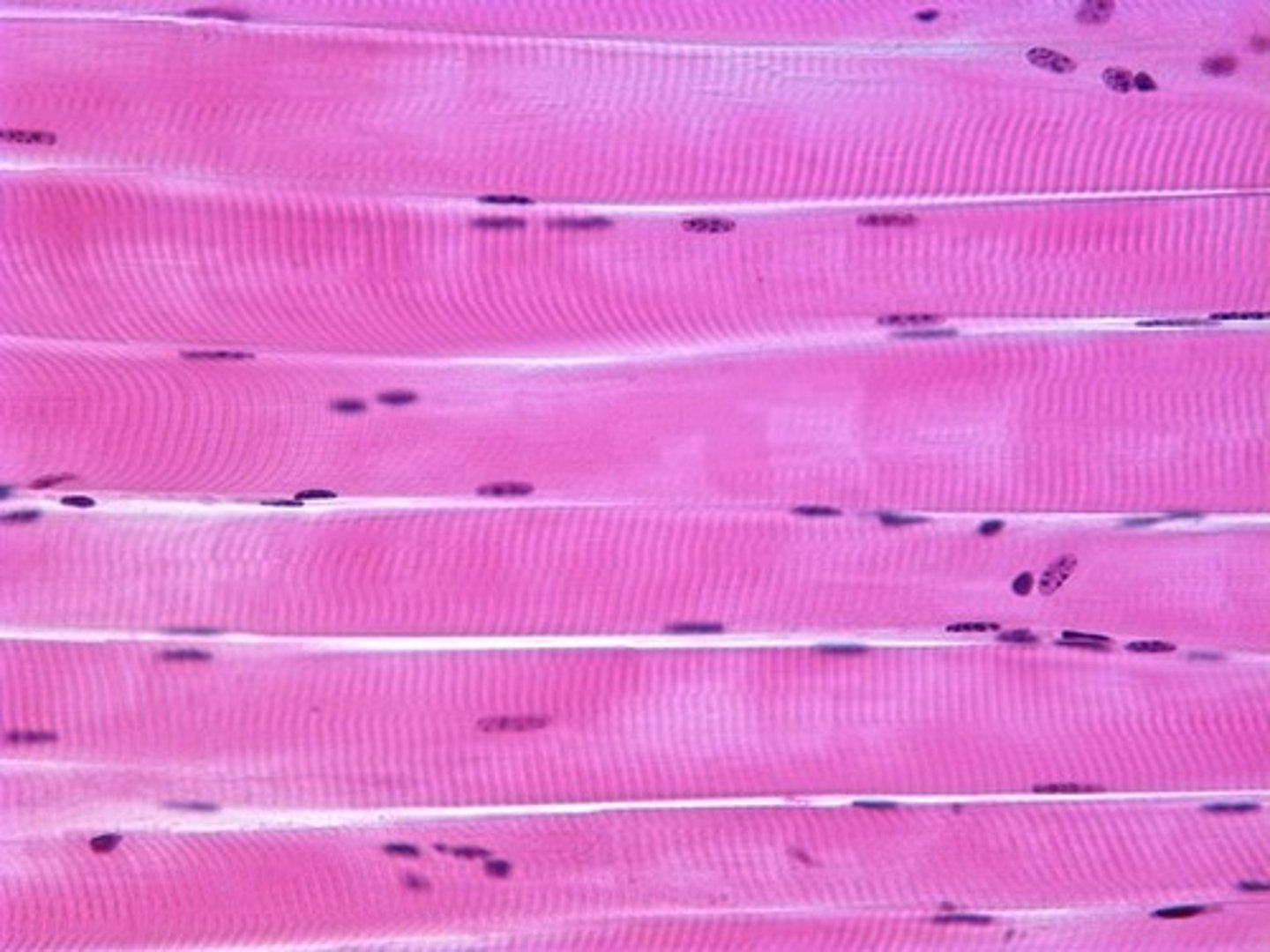
skeletal muscle tissue
- long, cylindrical, multinucleate cells with obvious striations (caused by myofilaments like actin and myosin)
- aid in voluntary movement; locomotion; manipulation in the environment; facial expressions
- located in skeletal muscles attached to bones or occasionally to skin
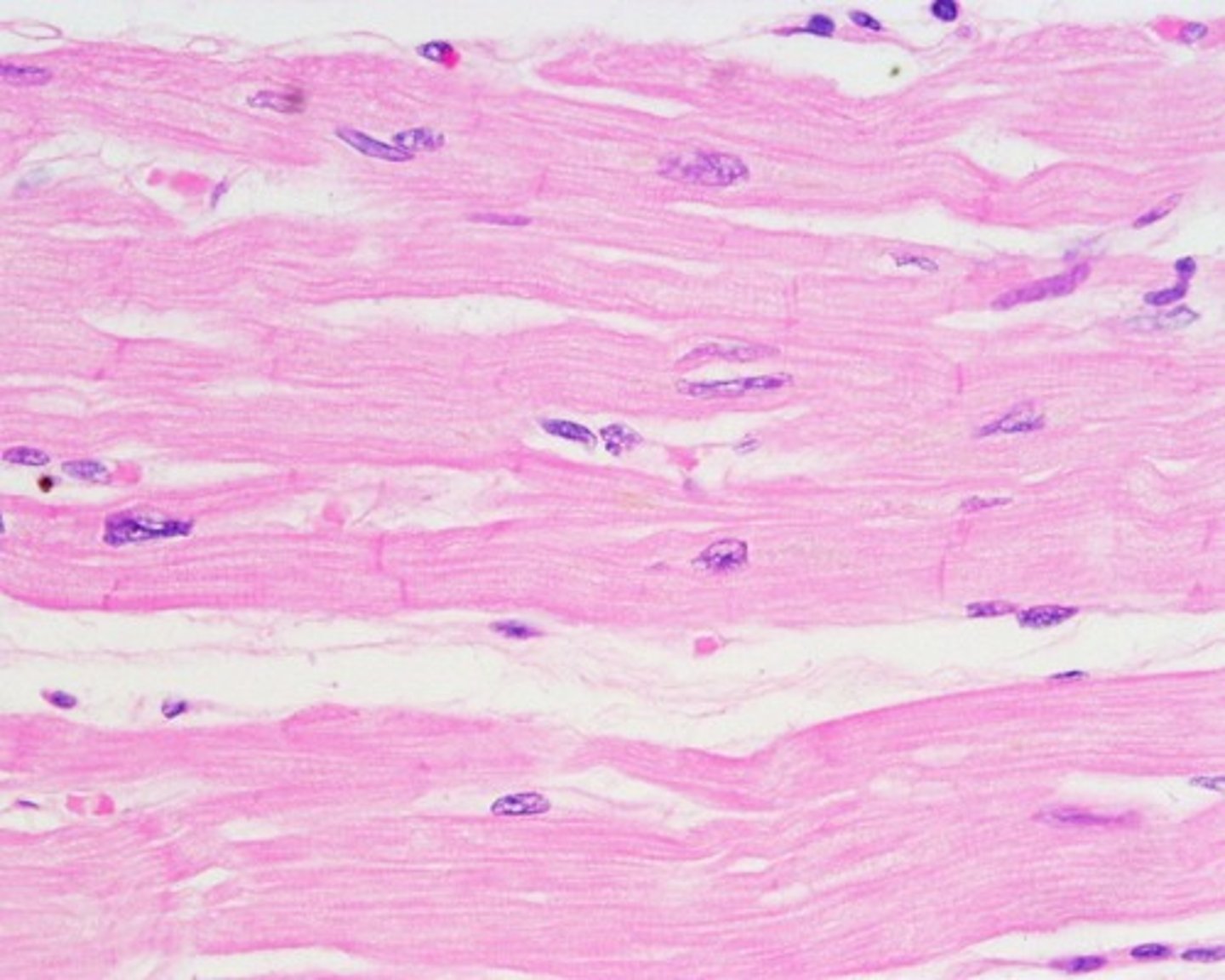
cardiac muscle tissue
- branching, striated, generally uninucleate cells that interdigitate at specialized junctions (intercalated discs)
- as it contracts, it propels blood into the circulation; involuntary control
- located in the walls of the heart
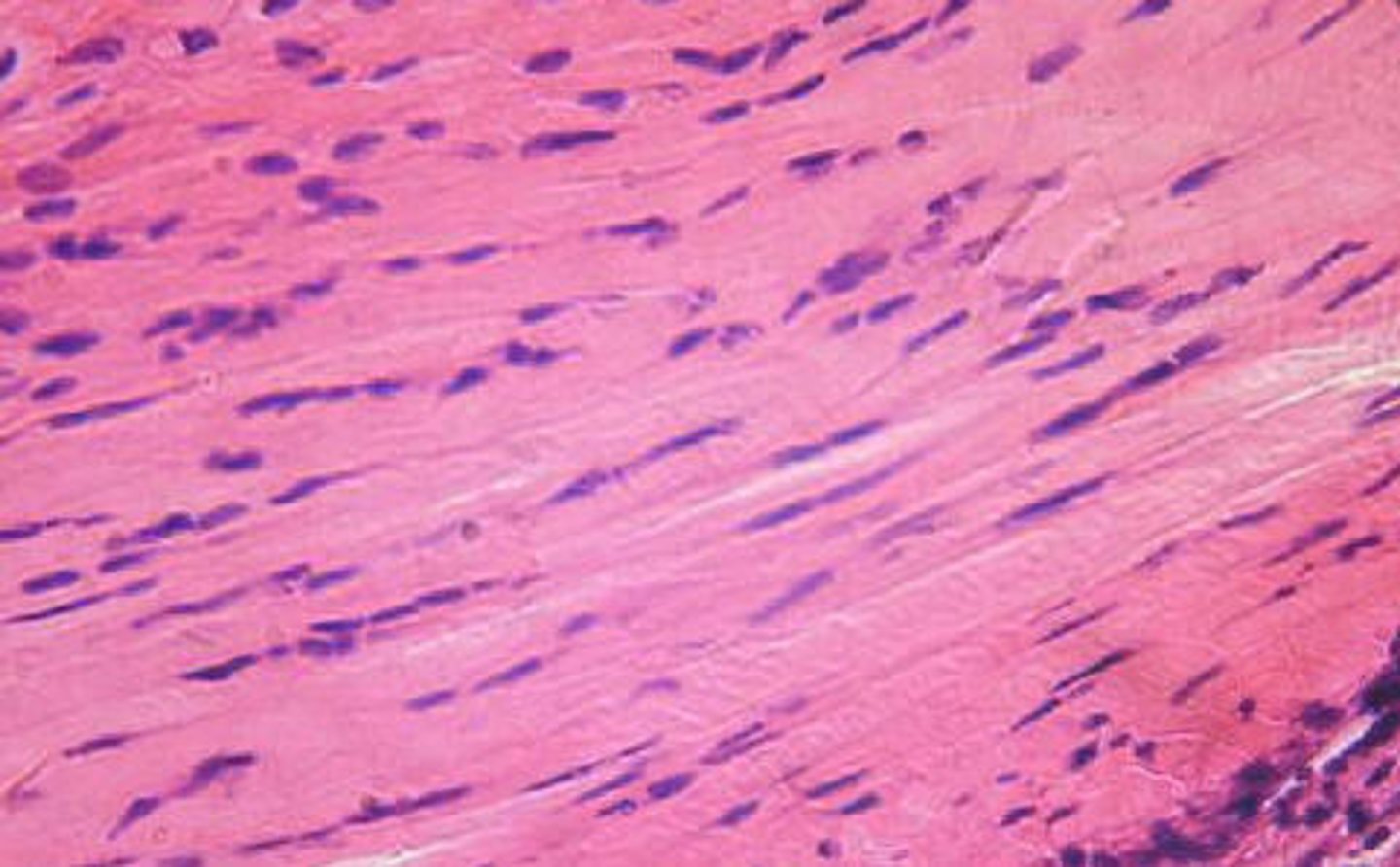
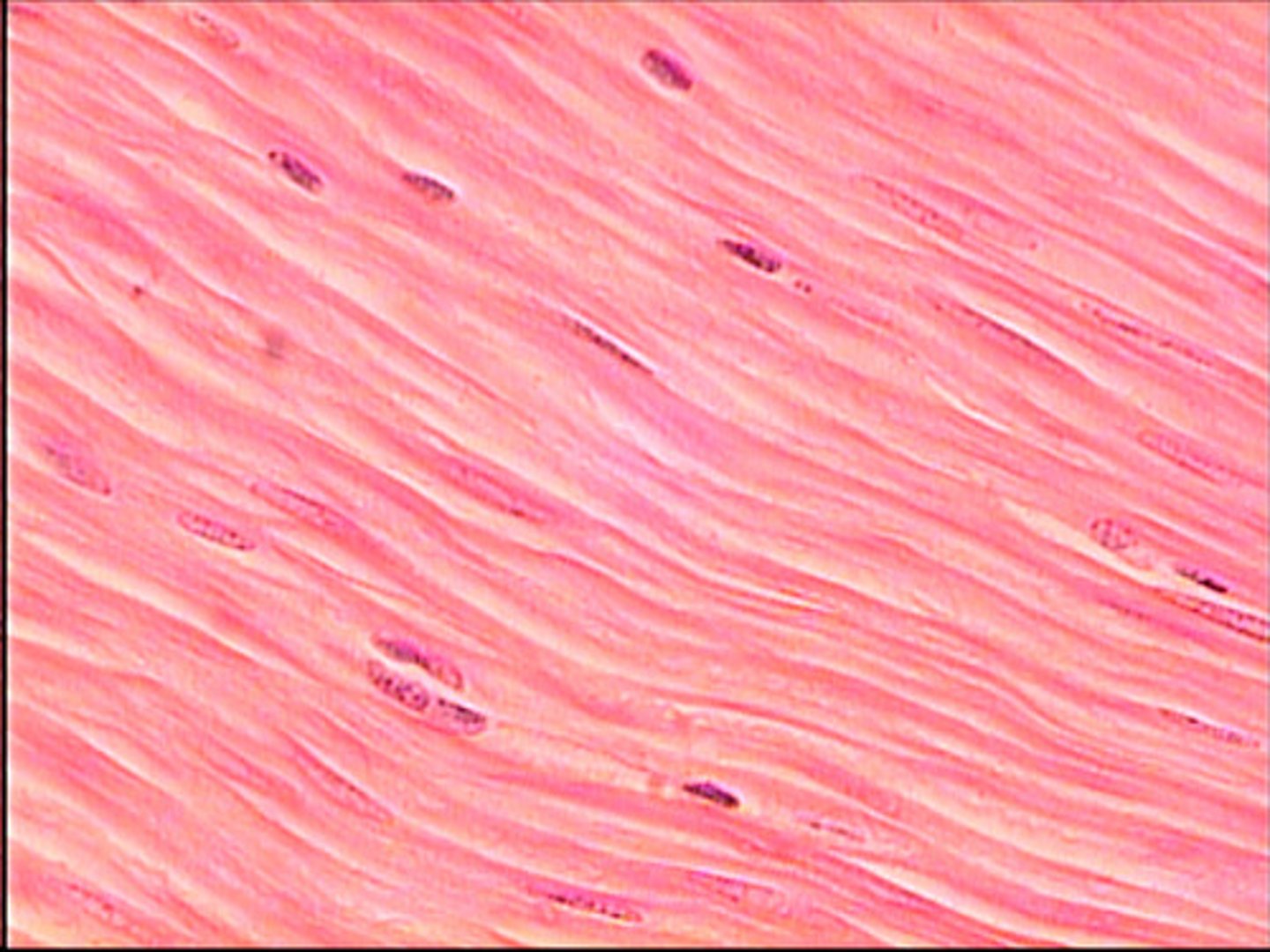
smooth muscle tissue
- spindle-shaped cells with central nuclei; no striations; cells arranged closely to form sheets
- propels substances or objects (food, urine, baby) along internal passageways; involuntary control
- located mostly in the walls of hollow organs
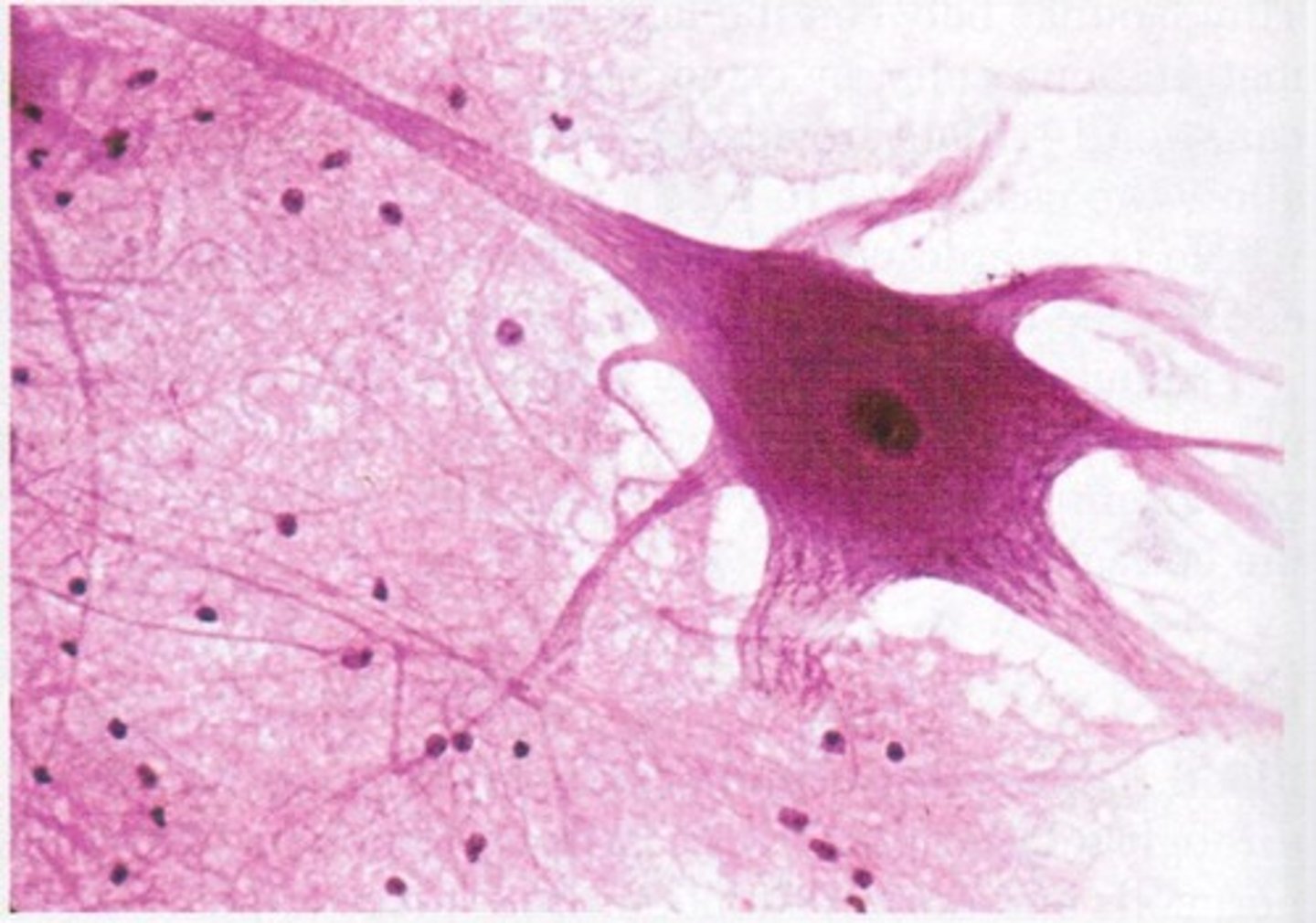
nervous tissue
- neurons are branching cells, cell processes that may be quite long extended from the nucleus containing body (soma); also have non-irritable supporting cells (glial cells)
- transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors (muscles and glands)
- located in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves
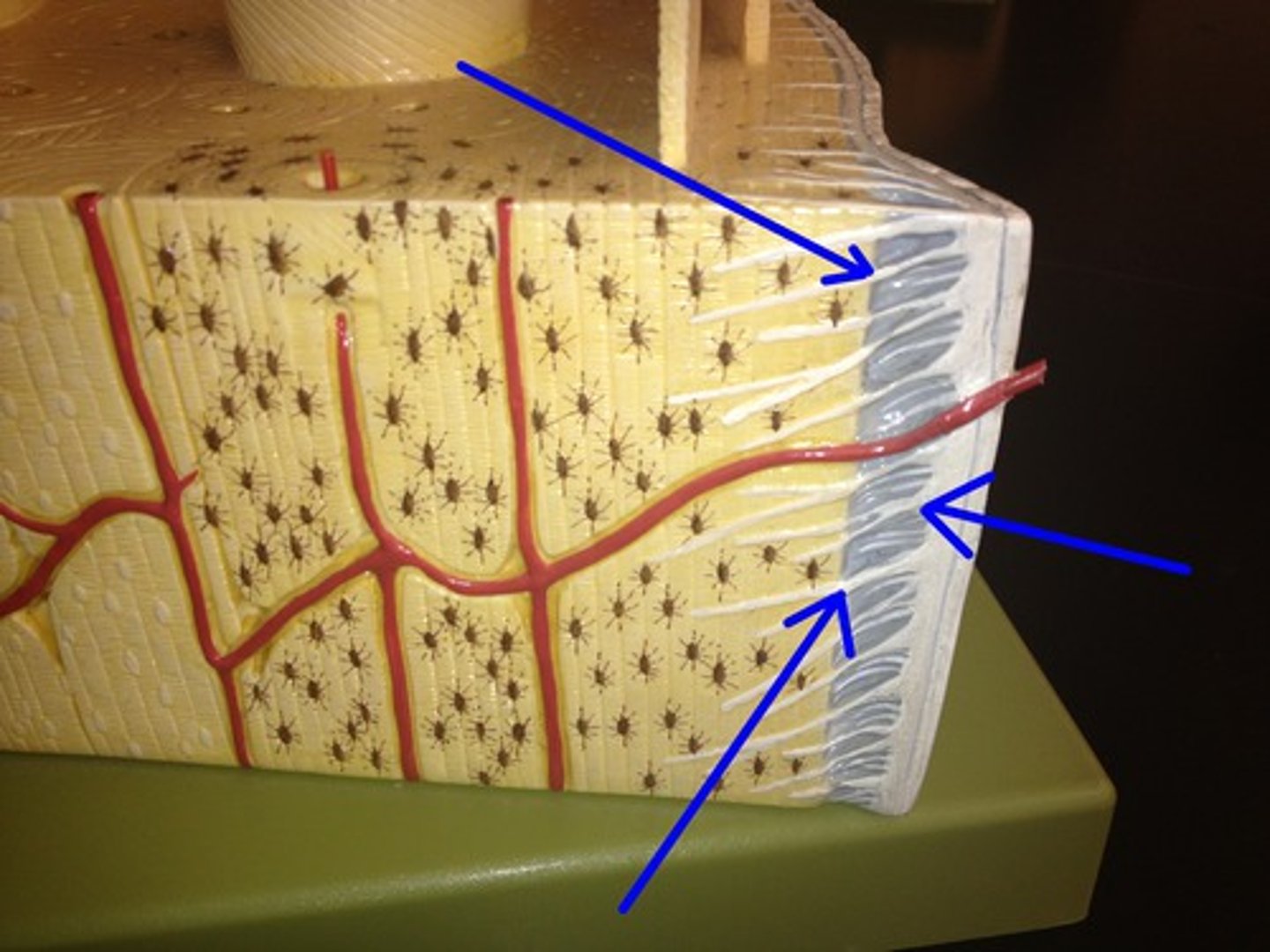
periosteum
membrane surrounding bone tissue that contains osteoblasts
osteoblasts
bone building cells (growth and repair)
osteocytes
mature osteoblasts stuck in lacunae (bone maintaining cells)
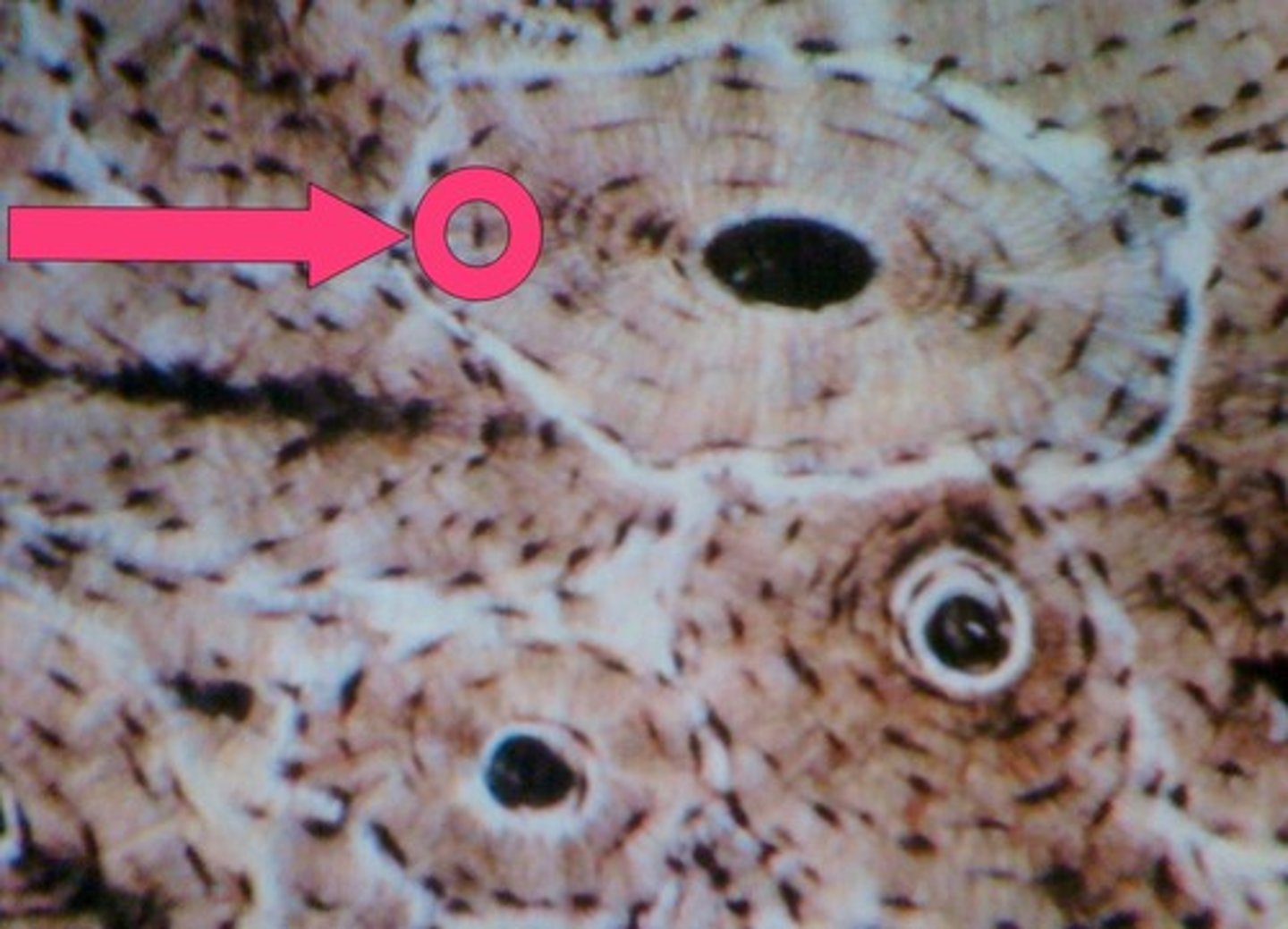
osteoclasts
bone destroying cells
intramembranous bone
- cranial and clavicle bones
- develop/ossify from fibrous membranes and endochondral bone
hyaline cartilage (bone development)
what all other bones develop/ossify from
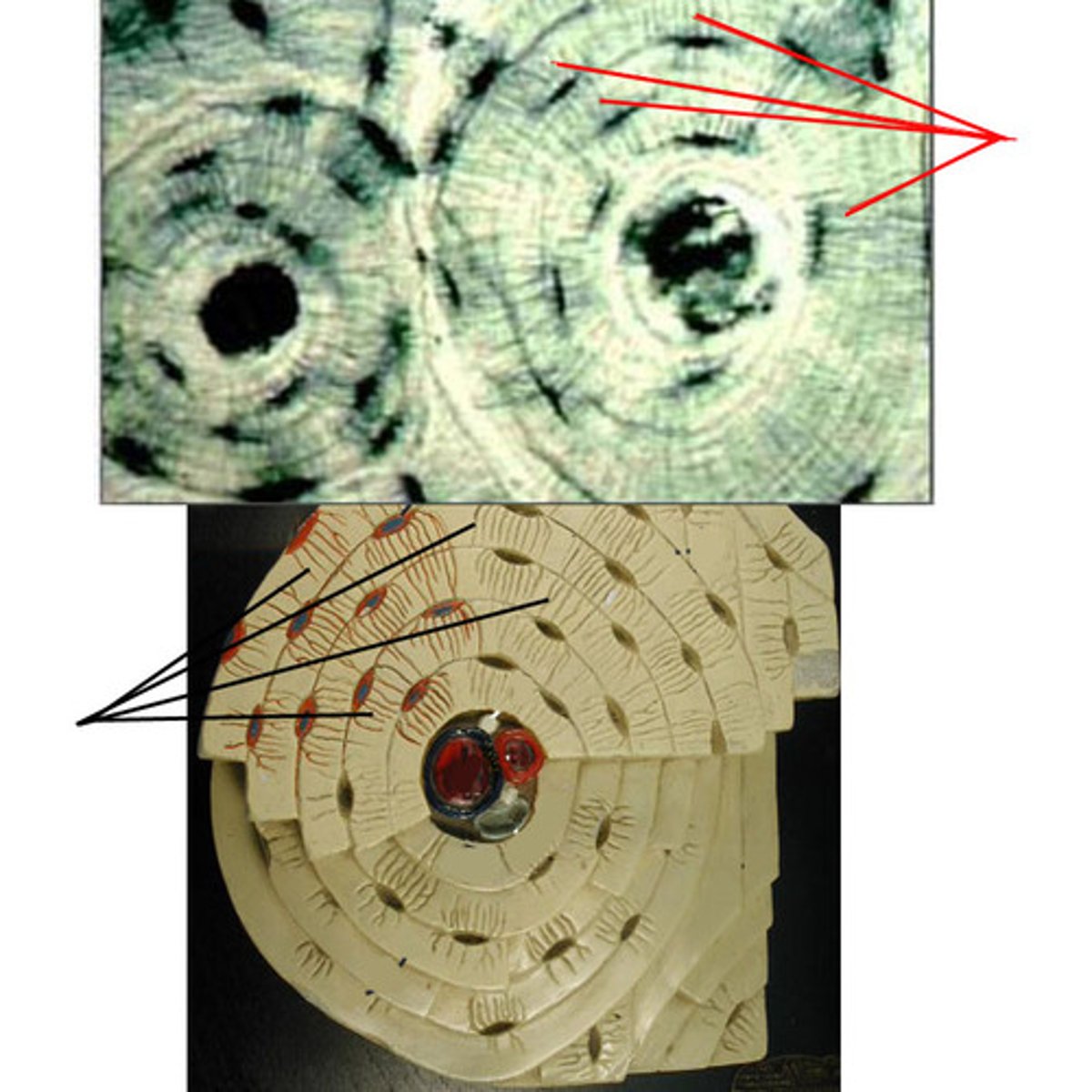
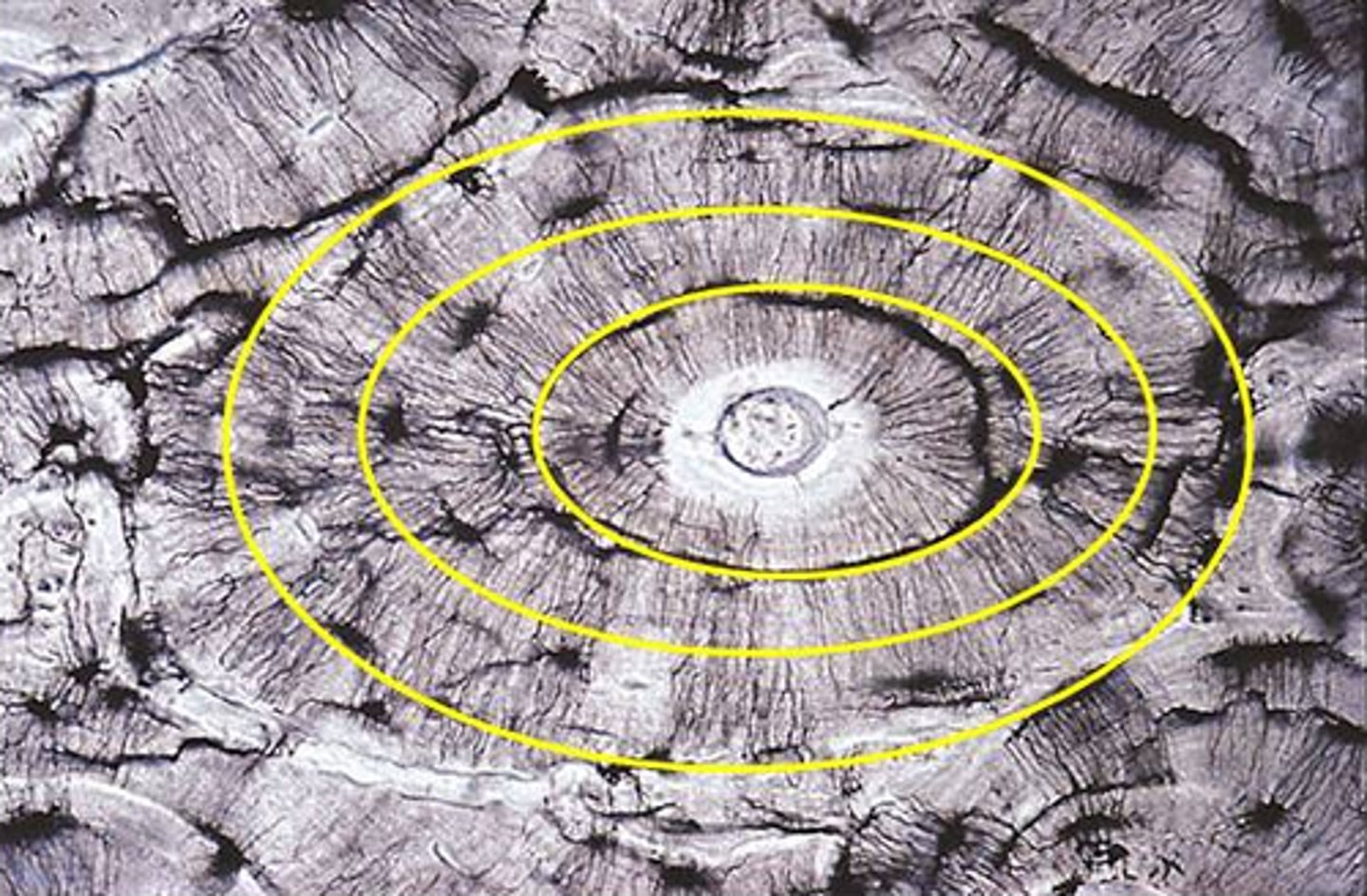
osteon (Haversian system)
- structural unit of bone
- round set of rings in the bone
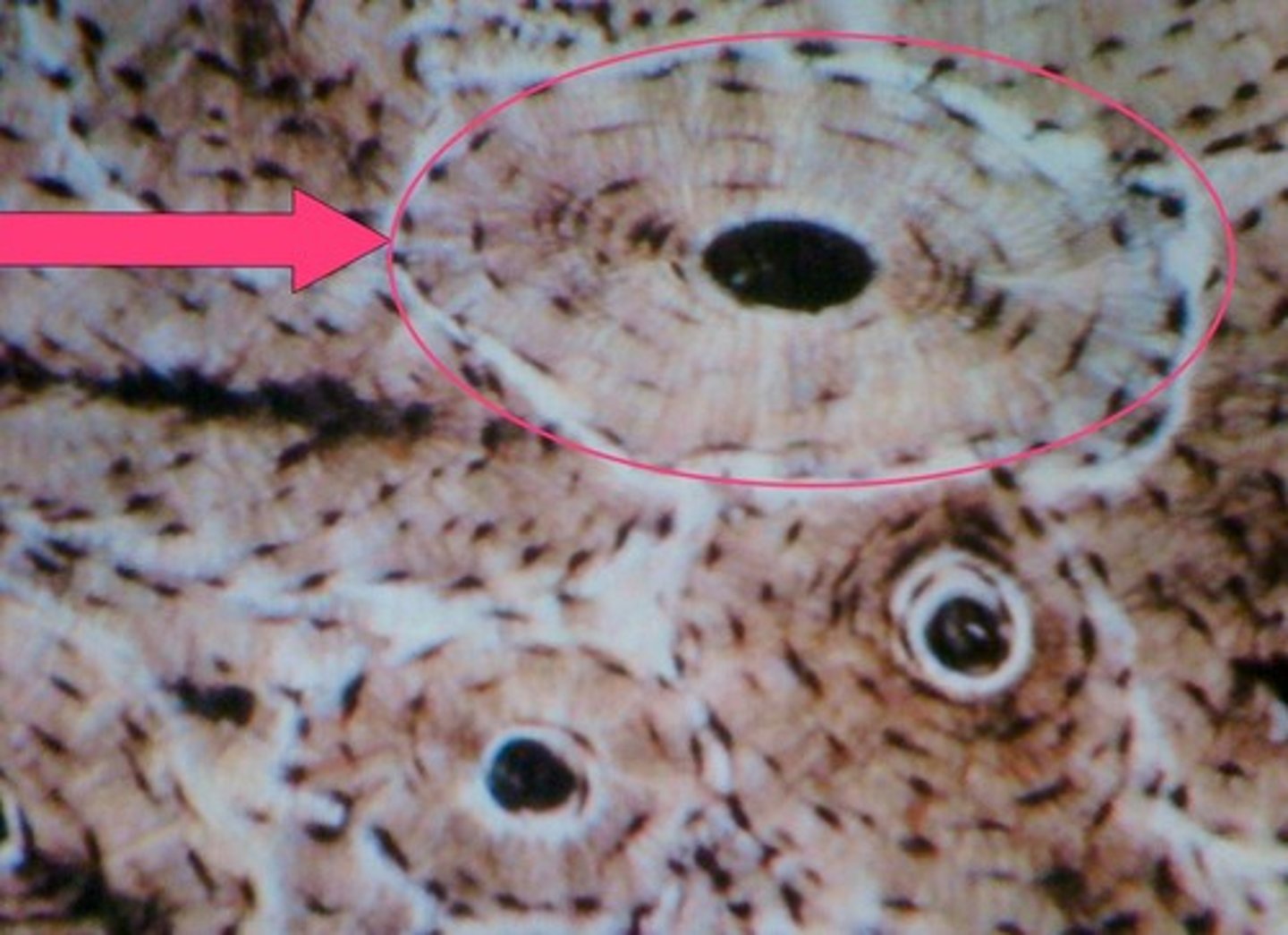
concentric lamellae
the many rings of calcified matrix within each osteon
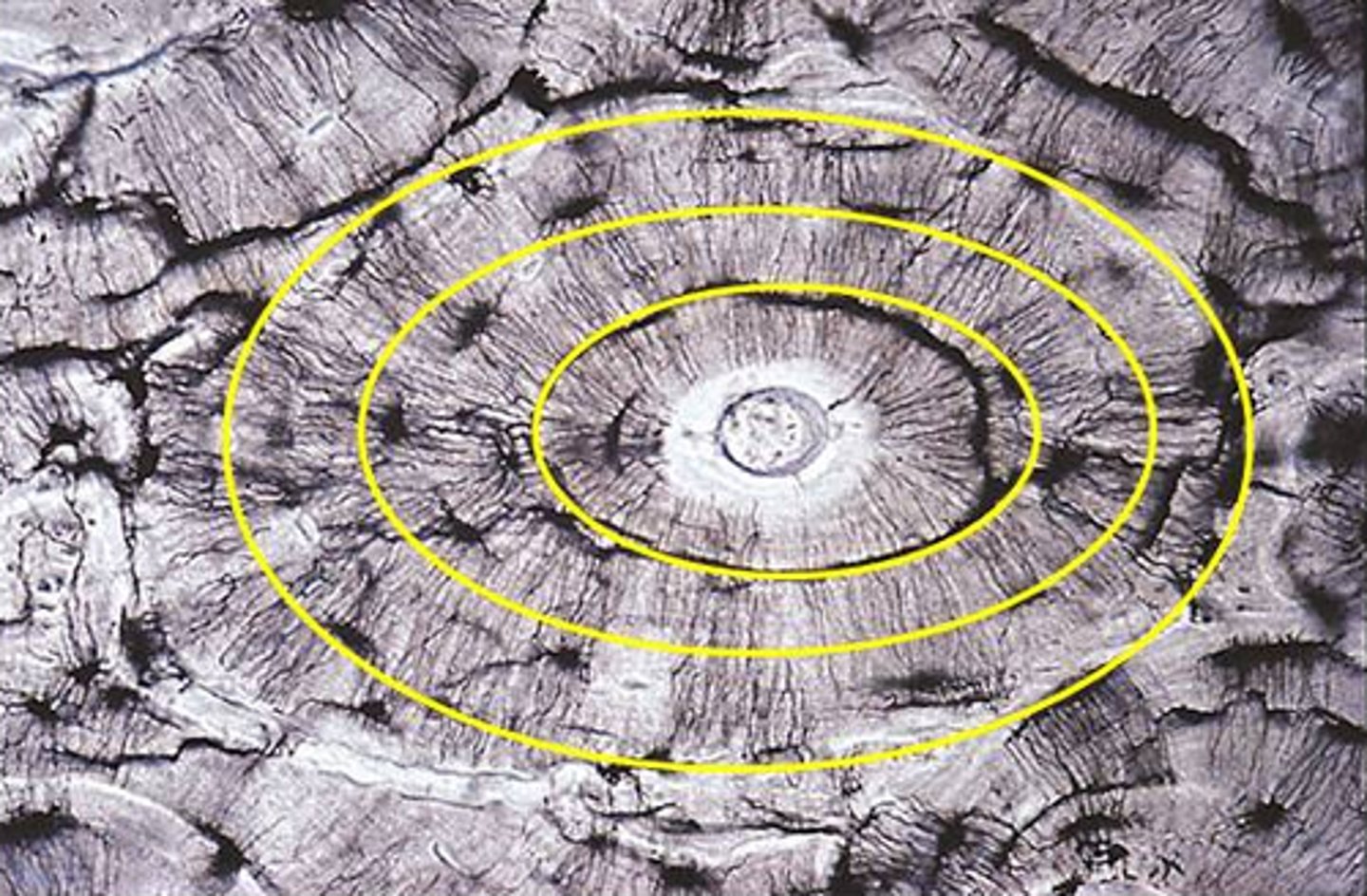
lacunae (bone)
small spaces between the lamellae where osteocytes are found
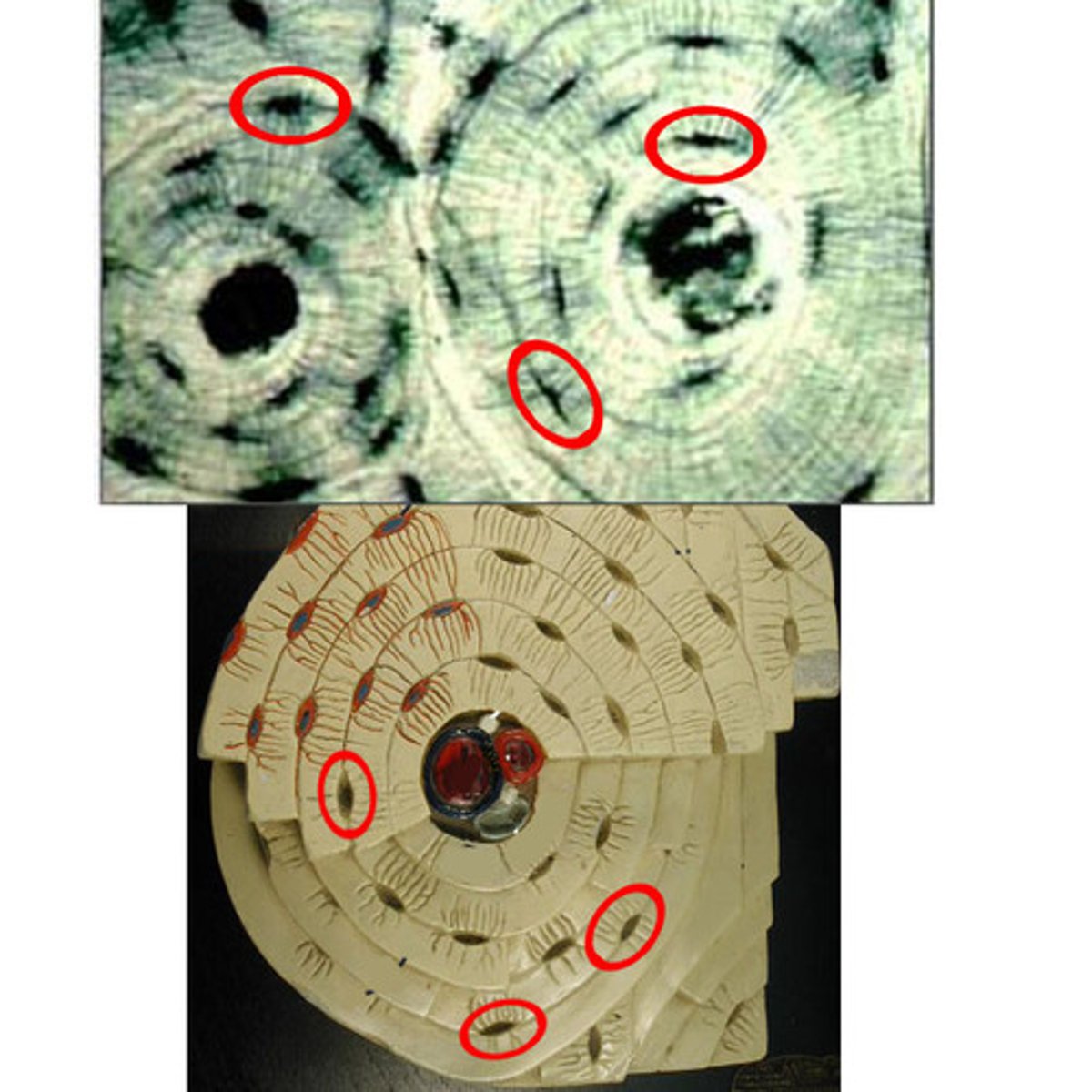
Volkmann's canal (perforating canal)
where nerves, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels all pierce the periosteum and enter the bone (perpendicular to the osteon)
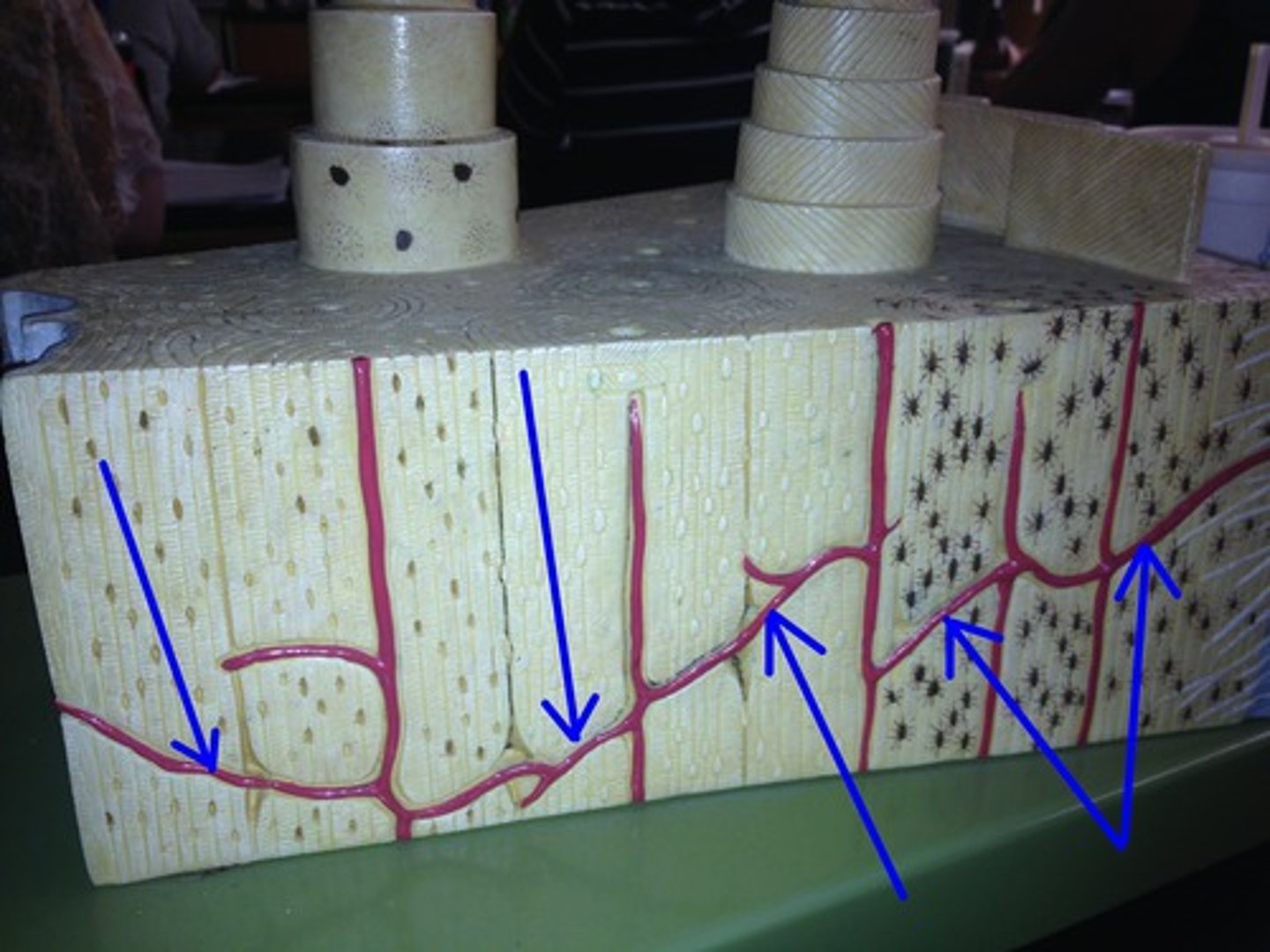
Haversian canal (central canal)
canal at the center of each osteon
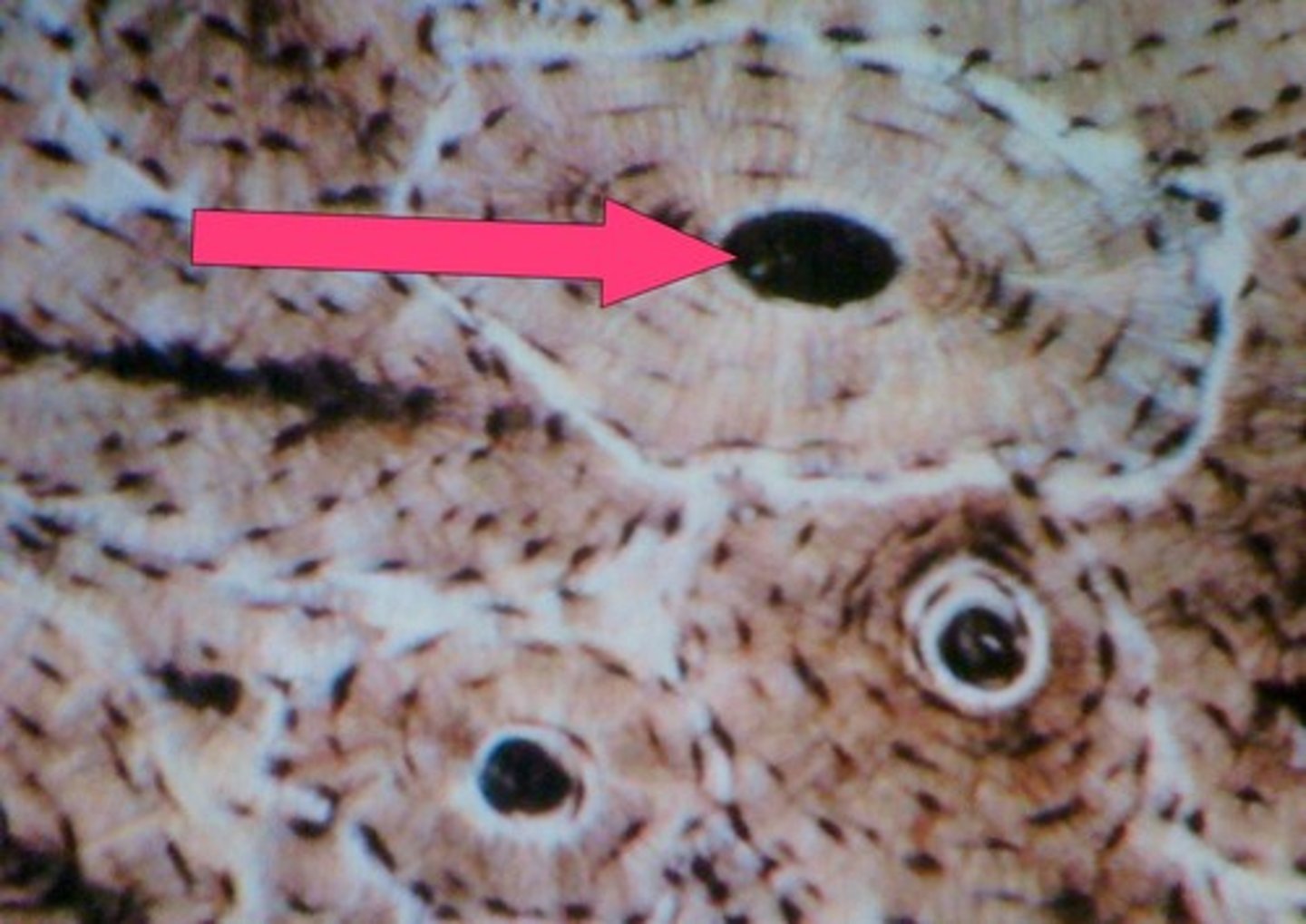
canaliculi
smaller canals that radiate from the Haversian canal and facilitate nutrient, gas, and waste exchange with the blood
Sharpey's fiber
secure periosteum to underlying bone
Spongy bone
Layer of bone tissue having many small spaces and found just inside the layer of compact bone.
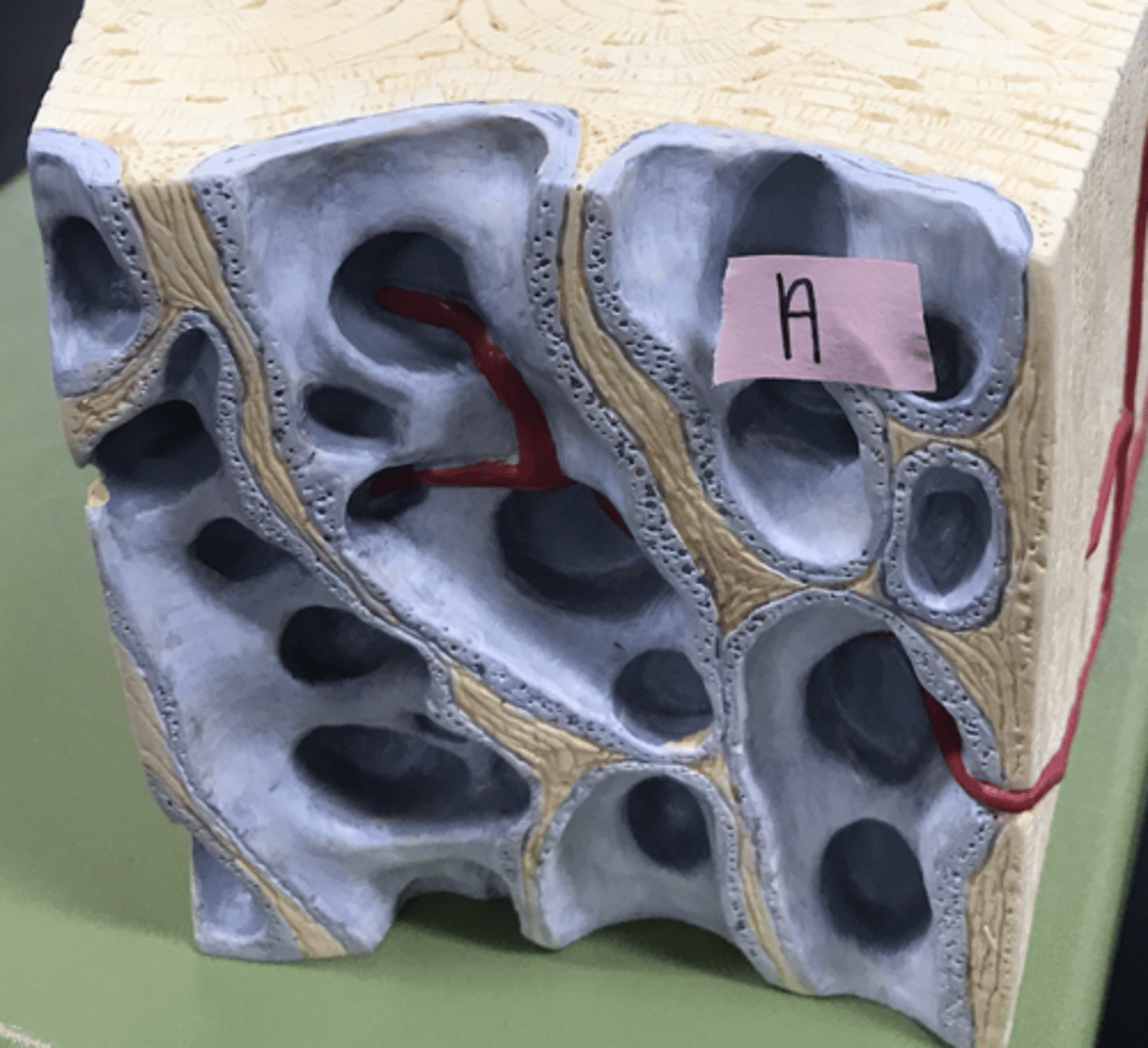
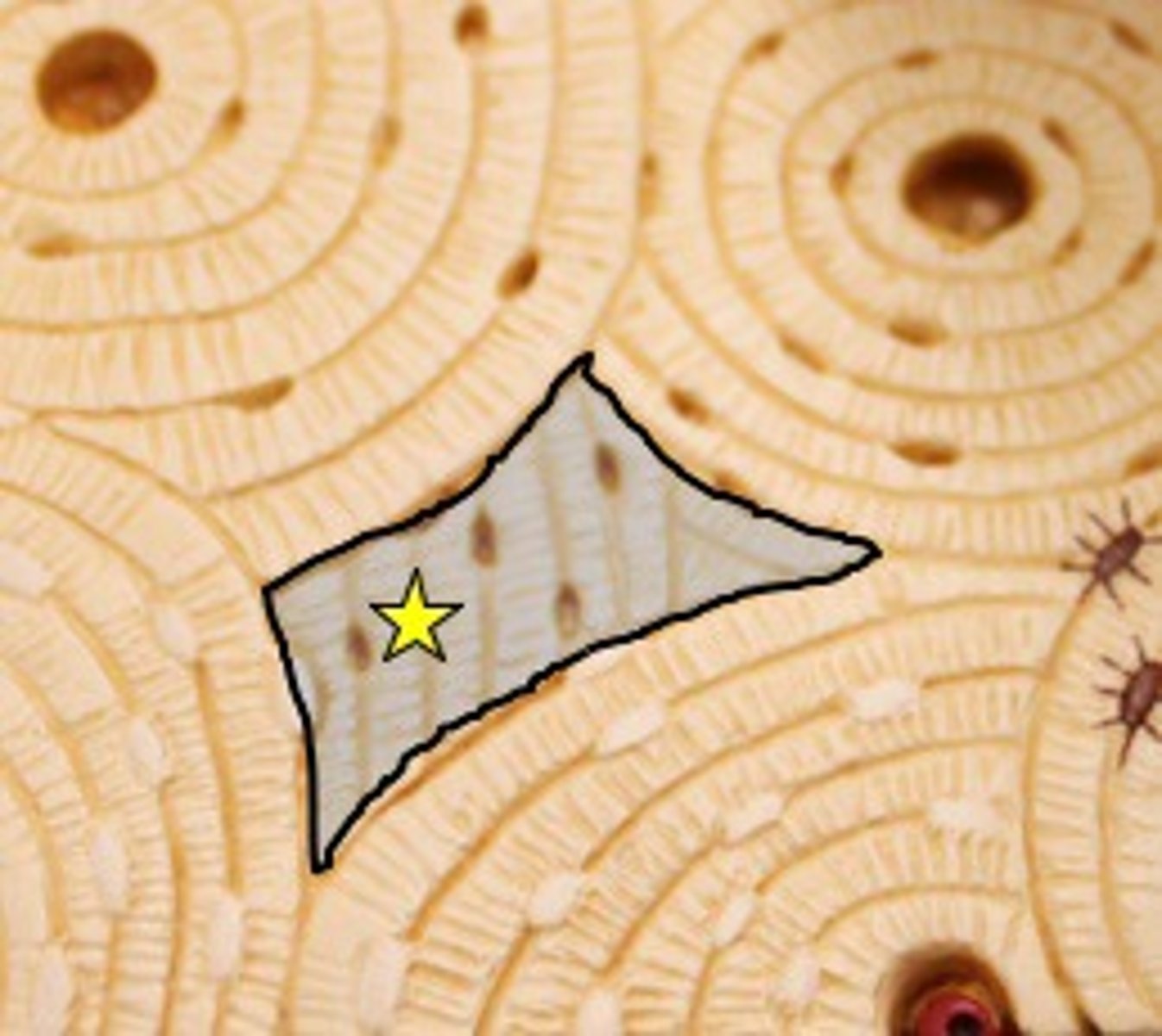
interstitial lamella
fills space in between osteons

concentric lamella
type of lamella that makes up the bulk of the osteon
integumentary system
- comprises the skin, sweat and oil glands, hair, and nails
- gives the body a protective barrier that is resistant yet flexible (keeps bacteria and mechanical insult at a minimum)
- regulates body temp, houses sensory receptors, ensures water homeostasis, and manufactures vitamin D3
epidermis and dermis
two main tissue layers of the integument
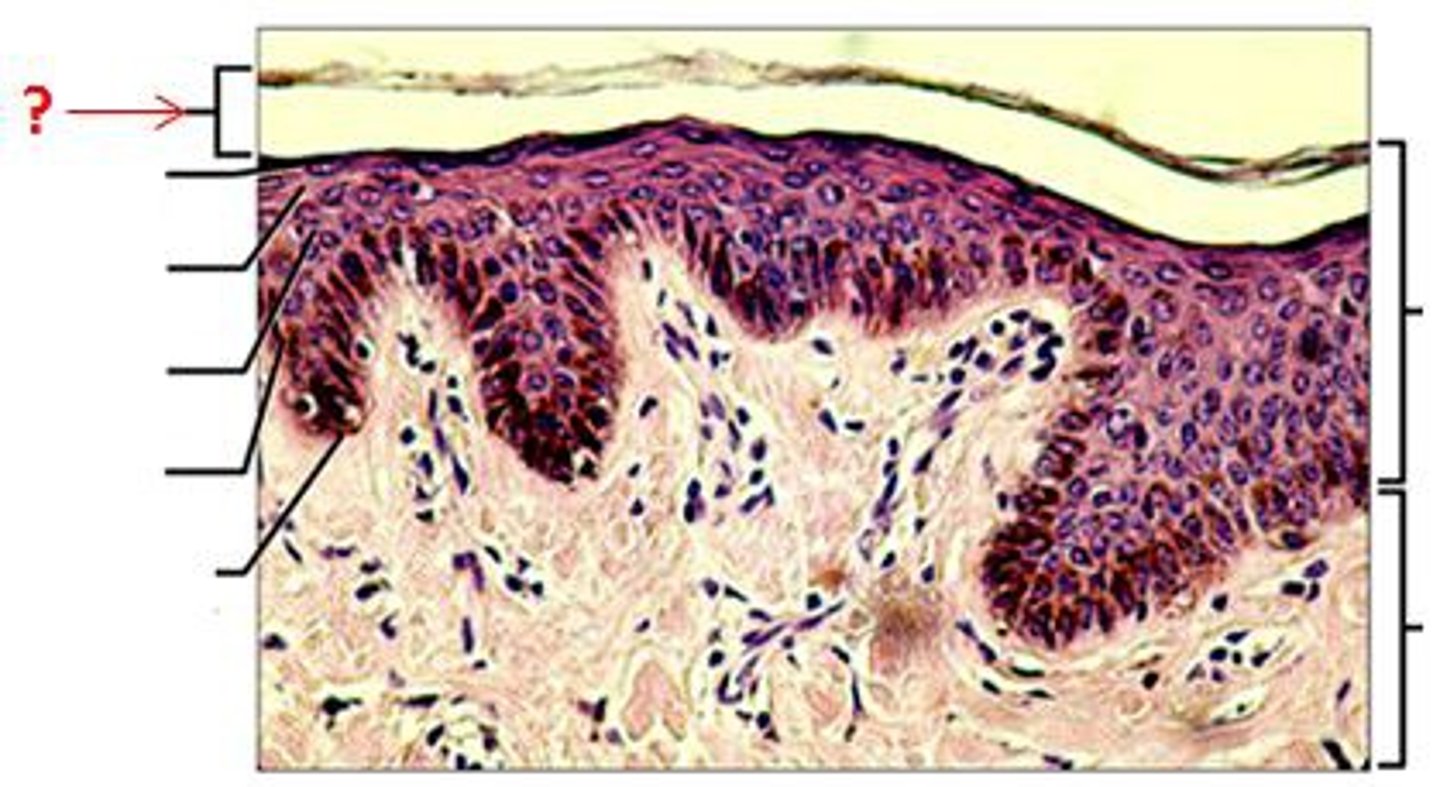
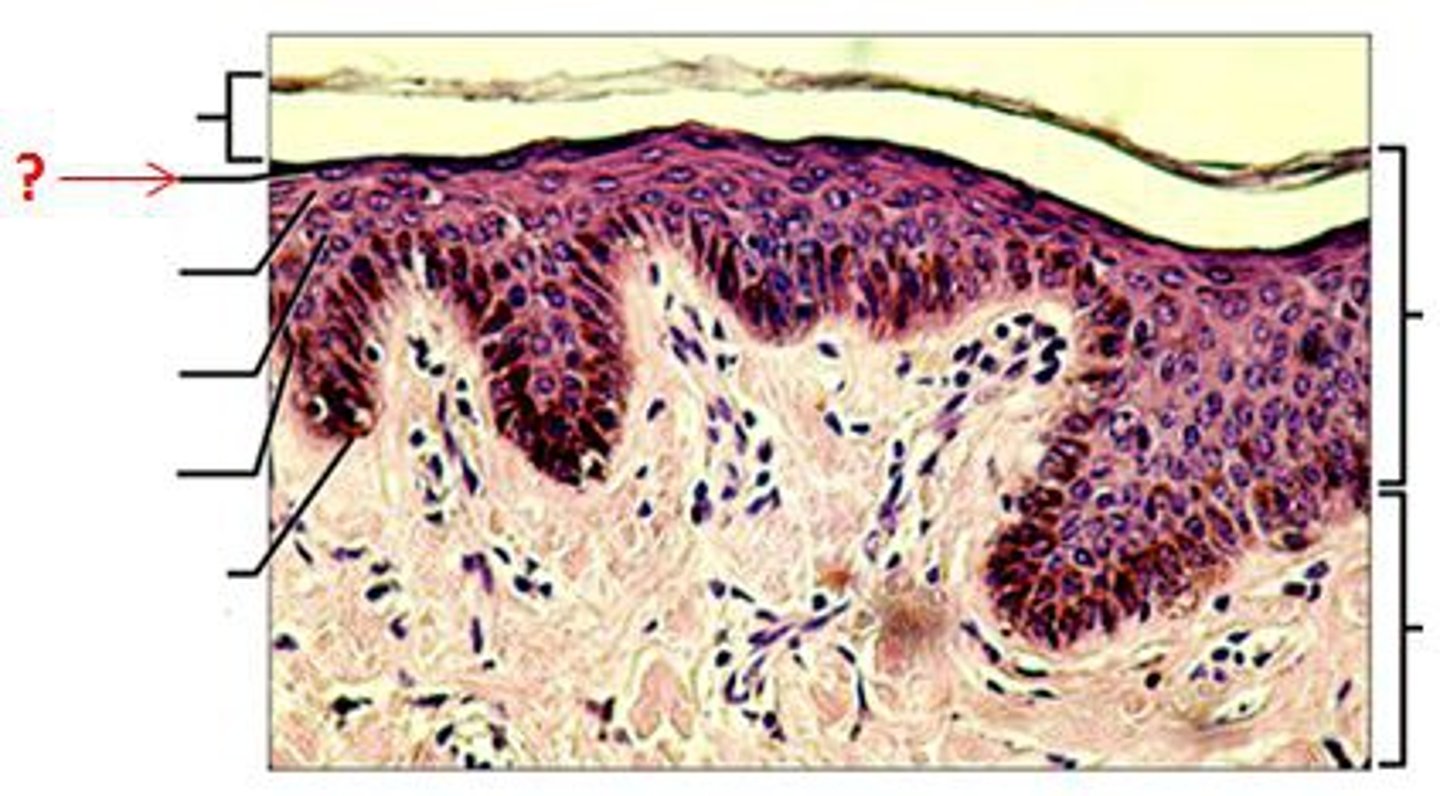
epidermis
- consists of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium organized into strata (layers)
- most cells are keratinocytes
- thick or thin skin is determined by the thickness of this
- accelerated friction can produce a callus
keratinocytes
- produced by basal layer of epidermis and migrate out
- fill with keratin as they move and gradually lose function
- slough off after 25-45 days
five layers of epidermis
stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale
stratum corneum (horny layer)
- most superficial layer
- contains 20-30 layers of dead squamous, anucleate cells that make up 2/3 of the epidermis thickness (contain keratin)
- keratin and thick plasma membranes protect against abrasions
- glycolipid between cells waterproofs skin
stratum lucidum (clear layer)
- thin, transparent layer of cells
- found in only the palm of hand and sole of feet
- protects underlying strata from abrasions
- keratohyalin granules from the stratum granulosum cling to the keratin filaments within dying cells to cause them to aggregate and form tonofilaments
stratum granulosum (granular layer)
- deep to the stratum corneum (unless lucidum is present)
- contains 4-6 layers of dark cells that synthesize keratohyalin (help form keratin in superficial layers)
- produce lamellar granules that contain water-resistant glycolipid (released into extracellular space)
- keratinization occurs in this layer to increase durability and prevent water loss
- water barrier and long distance from capillaries dooms superficial layers to death
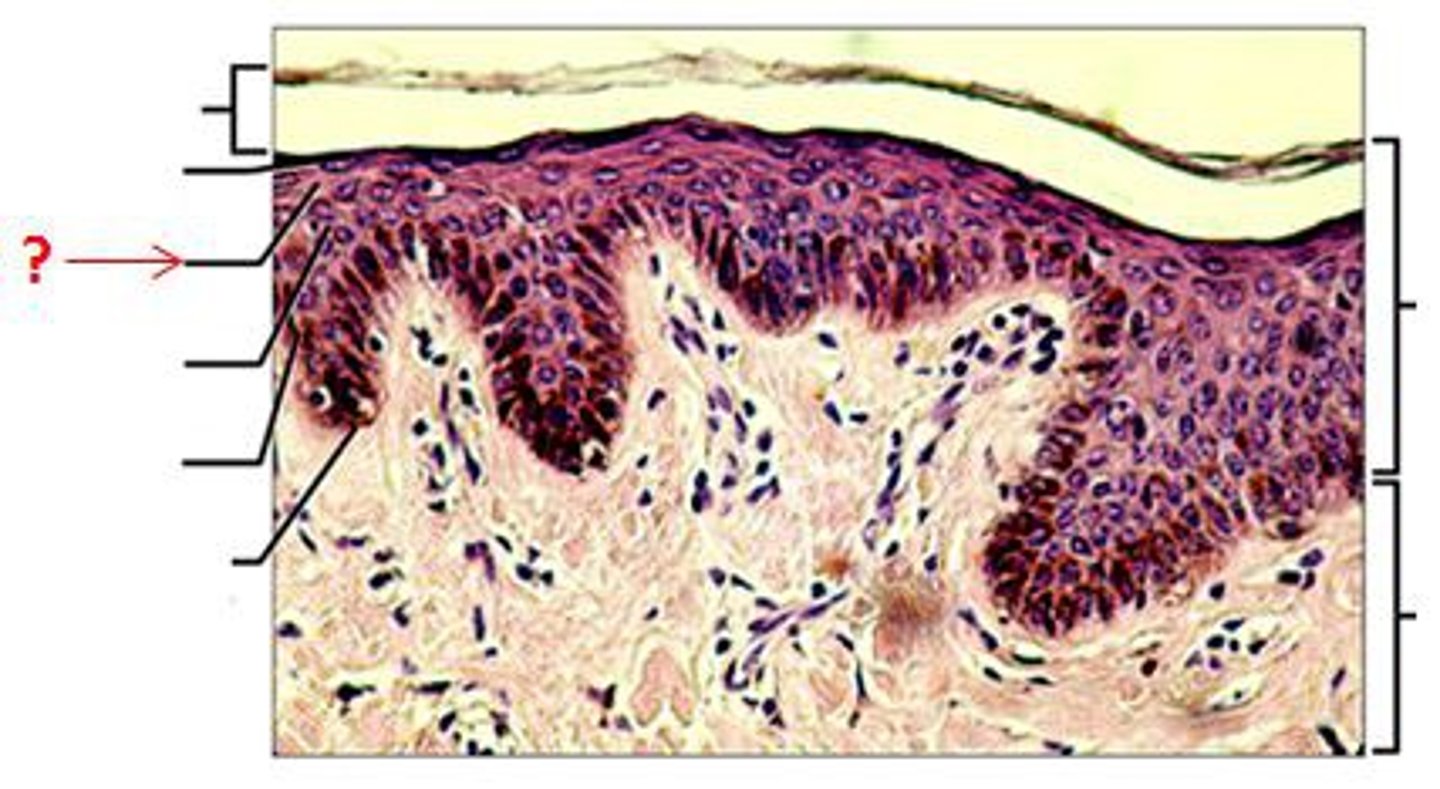
stratum spinosum (prickly layer)
- deep in stratum granulosum
- consists of 5-7 cells that form cell attachments via desmosomes
- keratinocytes appear to have spines (hence prickly) but this appearance is actually an artifact in cell preparation (not prickly when alive)
- melanin granules and dendritic cells scattered among keratinocytes
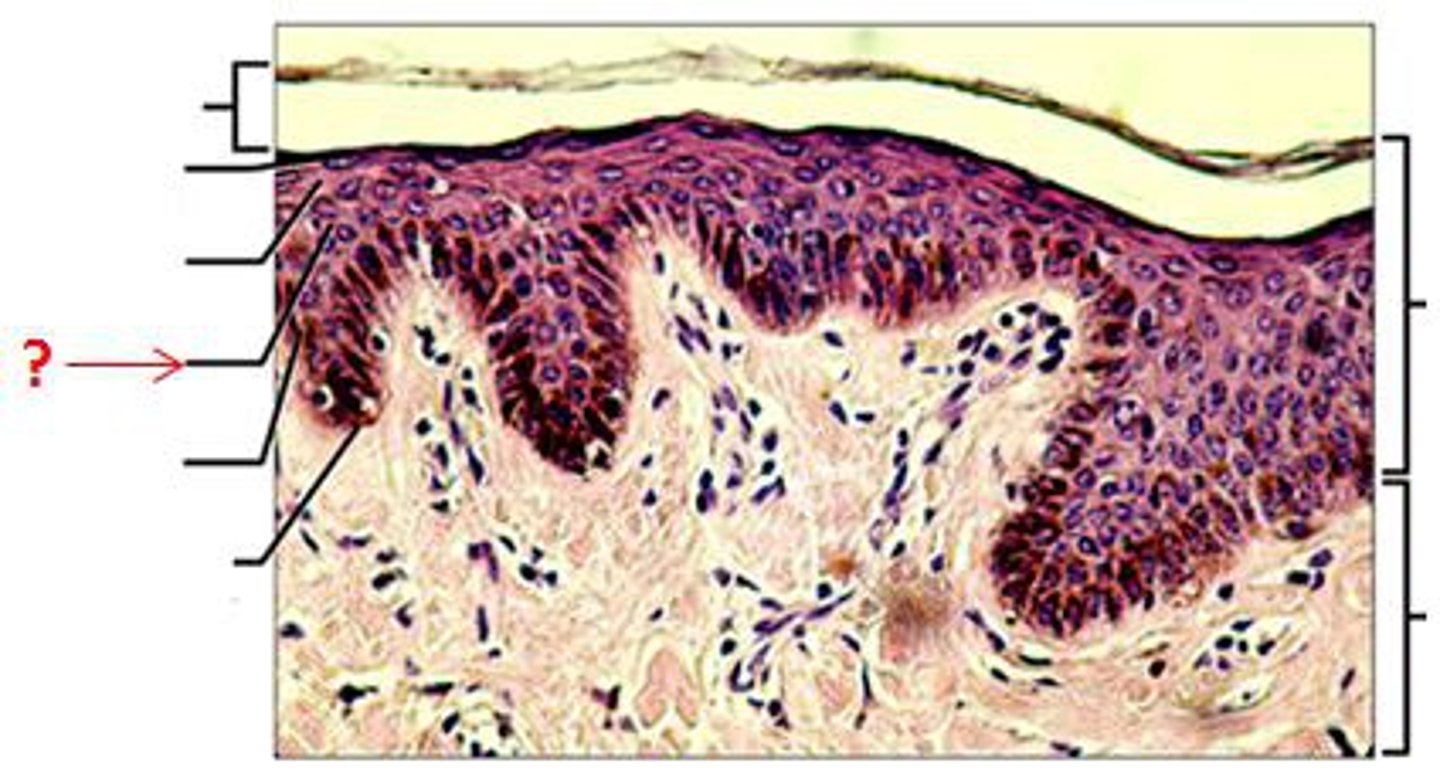
desmosomes
connected to intracellular pre-keratin filaments that form a tension-resisting web within cells
stratum basale (basal layer)
- deepest epidermal layer
- single layer of stem cells attached to the dermis
- constantly undergoing mitosis
- one daughter cell pushed to spinosum, one stays here
- as the cells migrate, they take on the function of the new layer
- melanocytes found in this layer
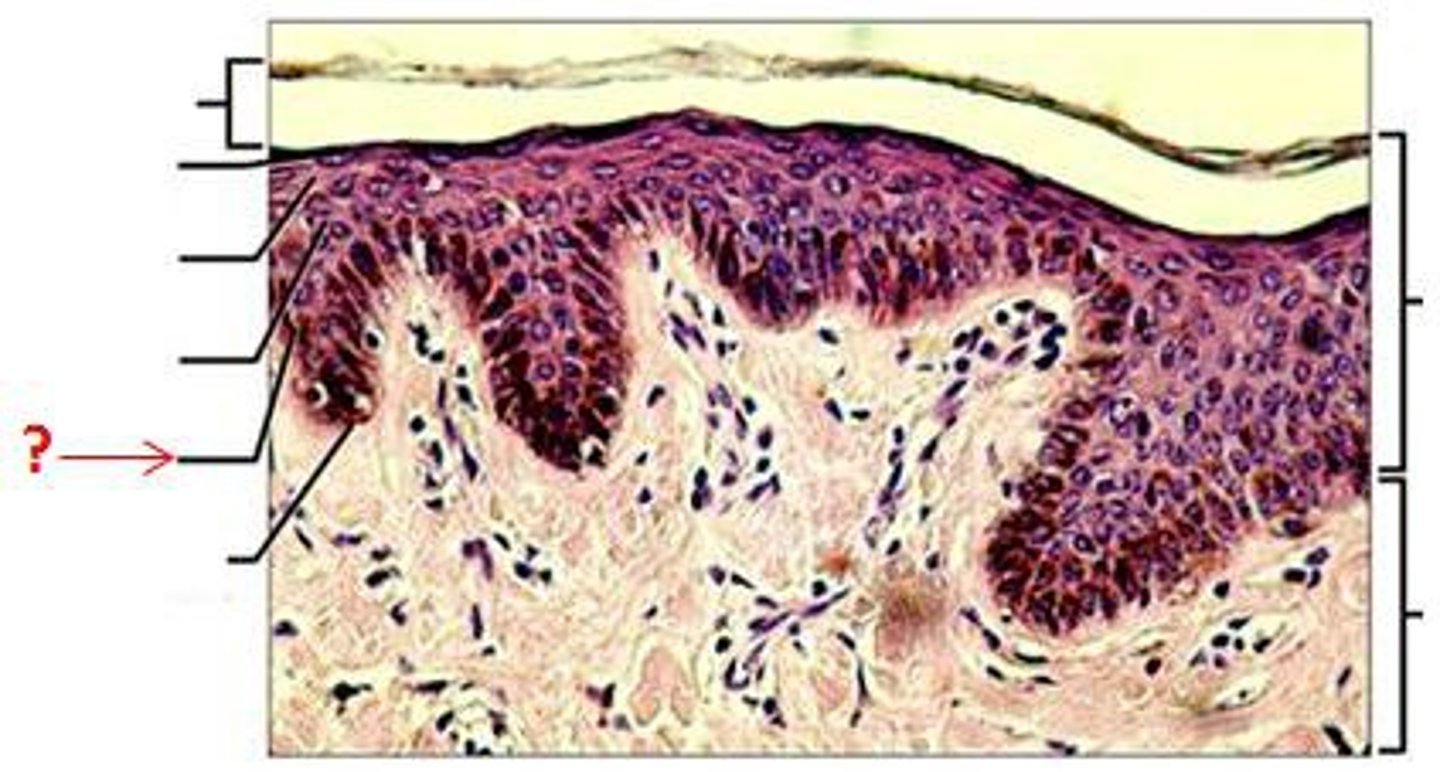
melanocytes
- produce melanin
- melanin is packed into melanosomes for secretion at tip
- melanin is taken up by keratinocytes to accumulate on superficial, sun exposed side of the nucleus to protect DNA within from UV light exposure damage