Human Anatomy - Muscle Lecture
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What are the 3 types of muscle tissue?
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
Smooth muscle
visceral muscle (nonstriated) involved in involuntary movement
Where can smooth muscle be found?
walls of hollow organs, blood vessels, intestines, and urinary bladder
cardiac muscle
myocardium that is striated and involved in involuntary movement
Where can cardiac muscle be found?
heart
skeletal muscle
striated and voluntary; the muscular system refers to skeletal muscle
Functions of skeletal muscle
1. Production of skeletal movement
2. Maintenance of posture/body position
3. Support for soft tissues
4. Guarding entrances and exits of the body
5. Maintaining body temperature (85%)
exercising; bed- or wheelchair-bound
individuals
What 3 layers of connective tissue surround skeletal muscle?
Epimysium ("epi" -- upon)
Perimysium ("peri" -- around)
Endomysium ("endo" -- inside)
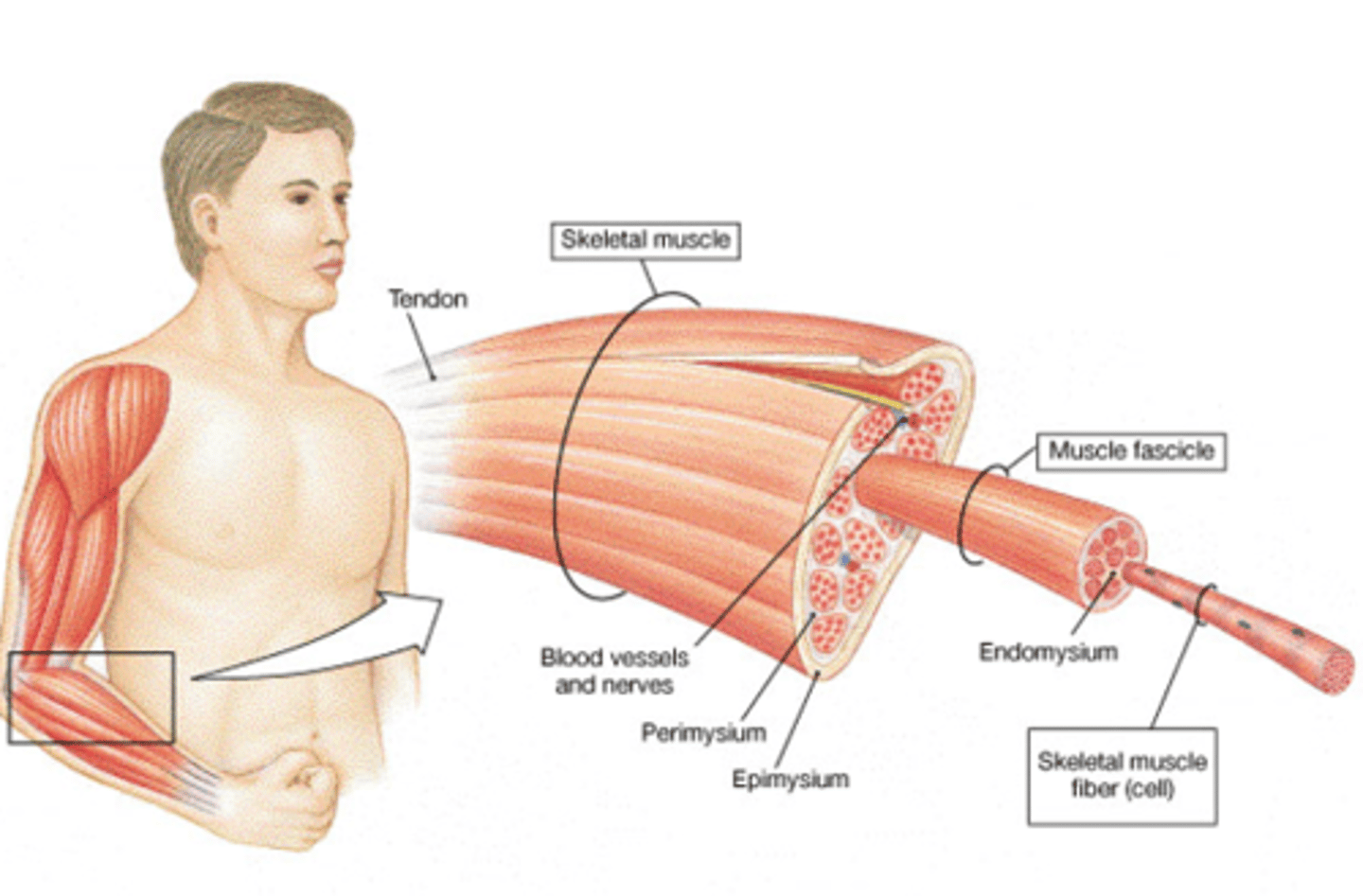
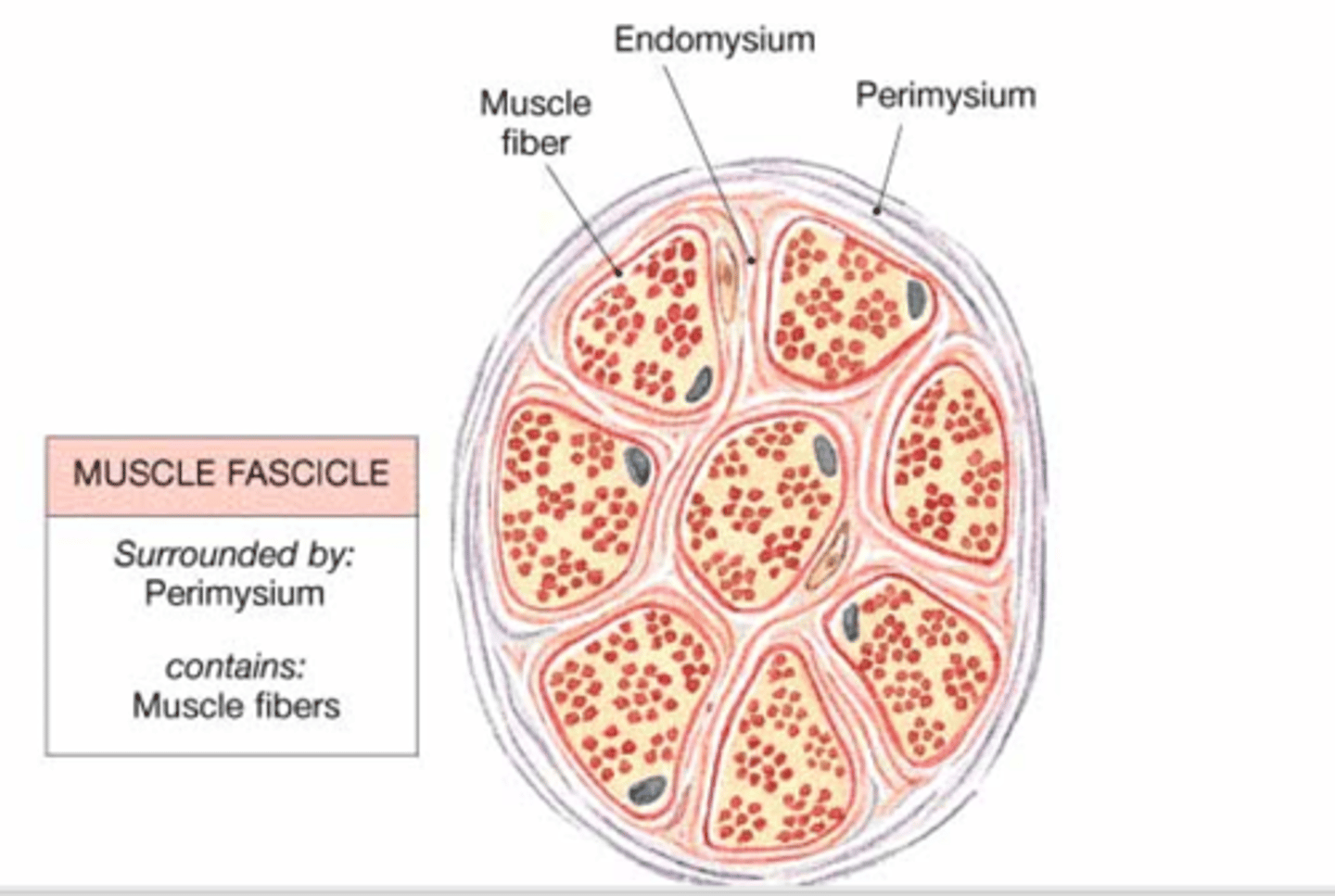
Muscle fasicle diagram
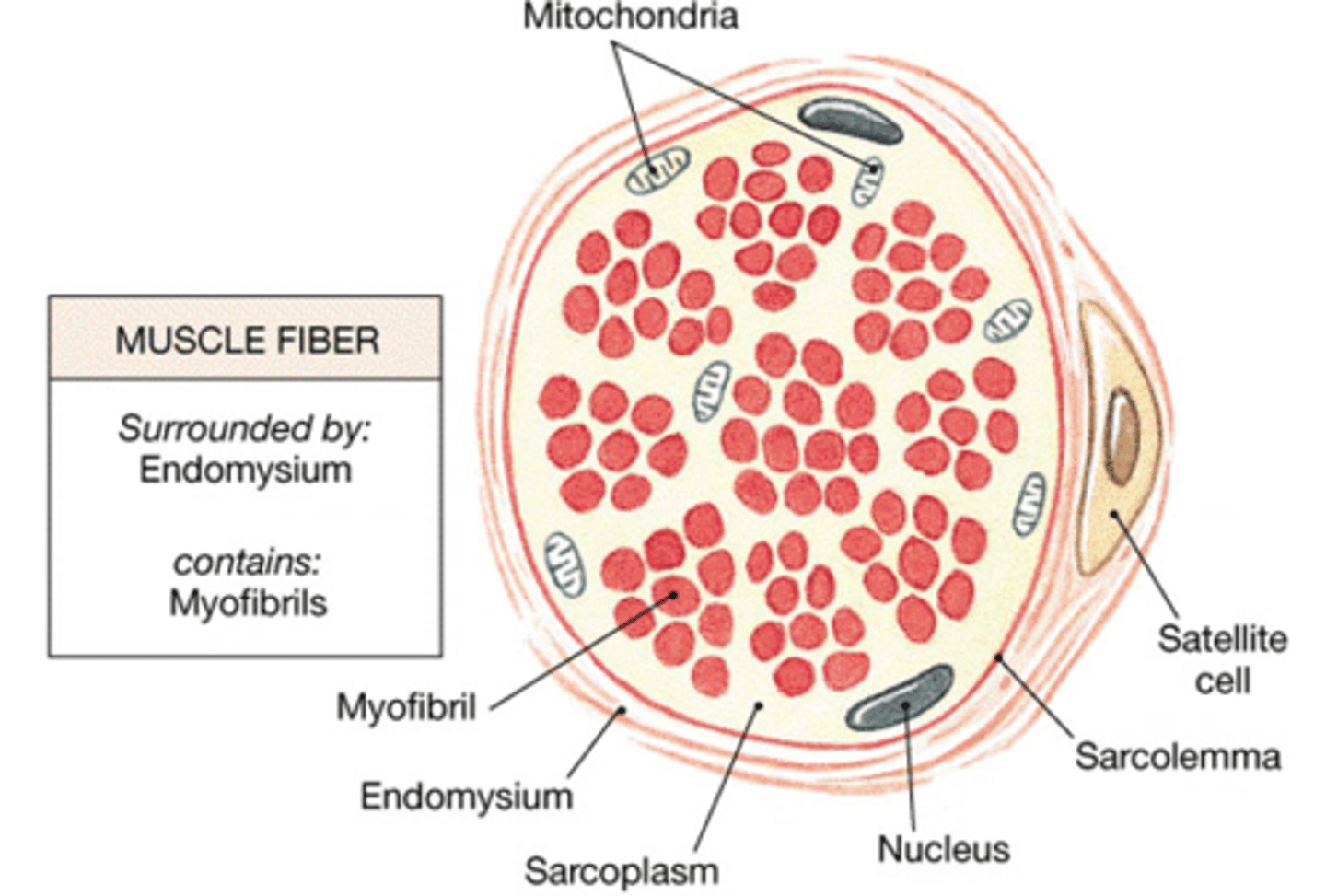
Muscle fiber diagram
What do the collagen fibers of the skeletal muscle layers do?
they blend together forming the cord-like tendons and sheet-like aponeuroses. Here, there are no muscle fiber enclosed and they are used to attach muscles to other structures
sarcolemma
muscle sheath, analogous to the cell membrane and surrounds sarcoplasm (cytoplasm)
sarcoplasm
contain multiple myofibrils; sarcoplasmic reticulum, or internal membrane system, surrounds each myofibril
sarcomeres
contractile units of skeletal muscle (myofilaments made of actin and myosin)
myofibrils
bundles of myofilaments
myofilaments
proteins (actin and myosin) that are arranged in repeating units
Actin and Myosin are organized into repeating units called _________.
sarcomeres
How many of sarcomeres does each myofibril consist of ?
10,000
z-line
defines the end of the one sarcomere and the beginning of the next
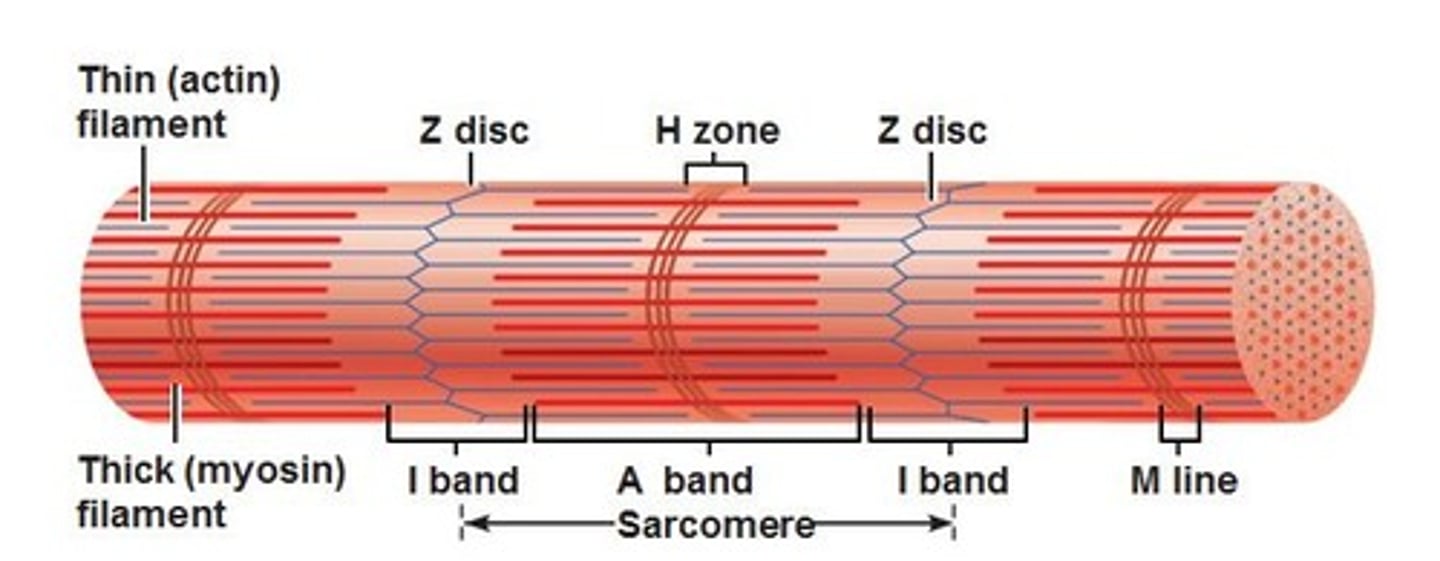
M-line
middle of a sarcomere; supports myosin (thick) filaments
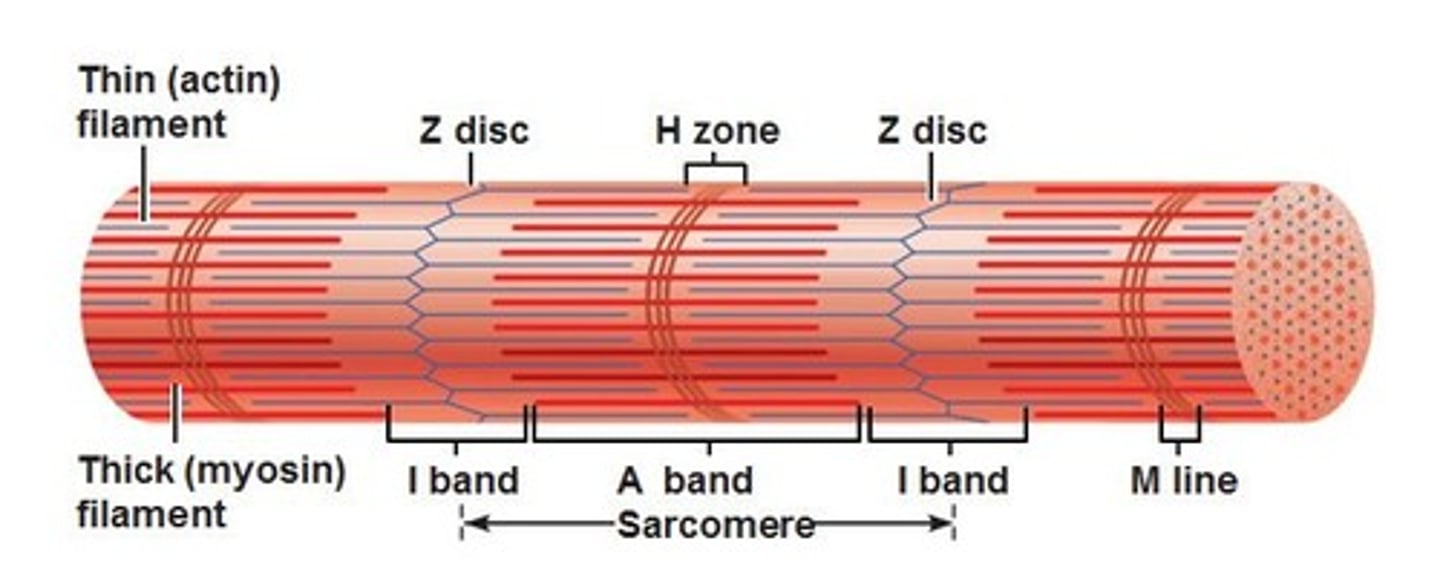
A band
entire length of thick filament (myosin) and overlap thin (actin) filaments
H zone
zone of thick filaments only, centered within the "A band"
I band
thin filaments only
sliding filament theory
muscle contraction, which is a shortening of sarcomeres
when does sliding occur? What does this movement require?
myosin heads bind to active sites on actin filaments and literally pull actin filaments inward. Requires calcium and ATP (acetycholine initiates contraction)
Actin
resemble a double strand of pearls twisted together (thin filaments)
Myosin
hockey stick or golf club (the heads are flexible); handles oriented toward the center, heads sticking out in all directions (THICK FILAMENTS)
Muscle fibers are arranged in bundles called..?
fascicles
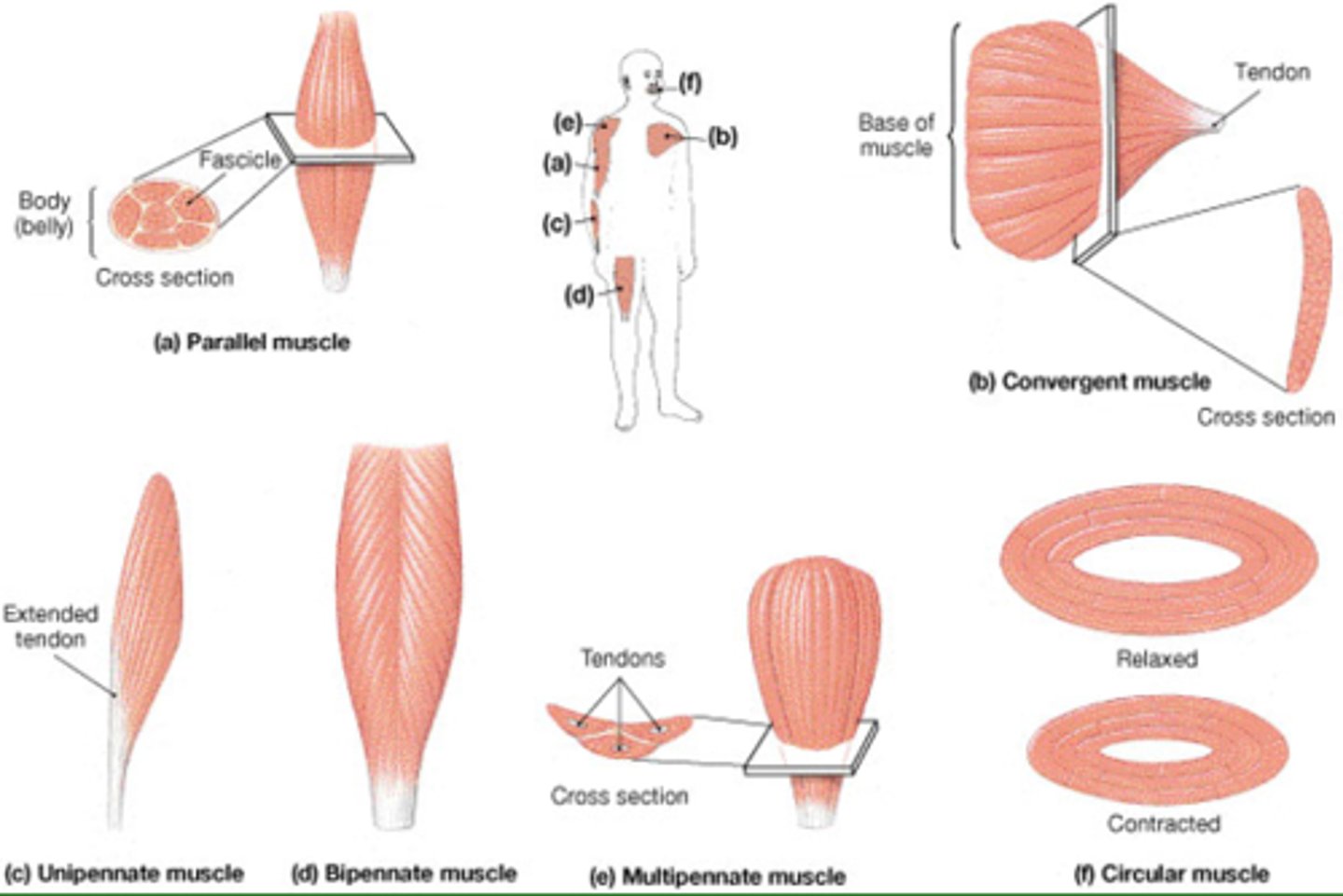
What are the 4 patterns of muscle in the body?
1. parallel muscles
2. convergent muscles
3. pennate muscles
4. circular muscles
Motor unit
1 motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it controls
Each muscle fiber works on an "____-or-____" principle
all-or-none
recruitment
increasing number of motor units
What is the innervation ratio for most muscles?
1 motor neuron for each 100 to 150 muscle fibers (contains myofibrils)
What is the innervation ratio for precise, dexterous movements (eye muscle)?
1:10
What is the innervation ratio for massive muscles responsible for gross body movement (thigh)?
exceeding 1:500
What can increase the size of muscle fibers?
exercise; increasing exercise means more myofilaments (actin and myosin) are synthesized
hypertrophy
Increase in size of muscle fibers (myofilaments) by increasing exercise
muscular atrophy
a wasting away of muscles because of progressive loss of myofibrils due to disuse or denervation
3 types of skeletal muscle fibers
fast, slow, and intermediate fibers
fast skeletal muscle fibers
fact acting; high energy requirements; fatigue easily
slow skeletal muscle fibers
more myoglobin as a reservoir for oxygen; slow contraction, but can be sustained
Intermediate skeletal muscle fibers
combination of both fast and slow; can be trained to function more aerobically or anaerobically
Muscle soreness
Not just the result of lactic acid buildup but can result from damage to contractile proteins (actin and myosin) within muscle
lockjaw/tetanus
Bacterial infection enters through puncture wound; neurotoxin results in tetany (continous contraction of muscle). Mandible's muscle is affected first
Shinsplints
result of stress fracture or periosteum damage of tibia
Rigor Mortis
Lasts for 24 hrs, disappears as tissues begin to disintegrate. Caused by attachment of myosin heads to actin which freeze in place
Origin
point of attachment that is less moveable; fixed end
Insertion
the point of attachment of a muscle to the part that is more moveable; where the action is exerted
Action
the movement or effect; muscle fibers pull the insertion toward the origin
Belly
the area mid-way between the origin and insertion
Prime movers
muscles conducting the major motion
Synergists
assists, complements, stabilizes, or prevents unwanted motion
Antagonists
acts against the prime mover and will be prime movers in restoring body position
How are muscles named?
1. Origin/Insertion
2. muscle fiber direction
3. position of muscle
4. size of muscle
5. action of muscle
What is the musculotendinous cuff (rotator cuff) made of?
1. Supraspinatus m.
2. Infraspinatus m.
3. Teres minor m.
4. Subscapularis m.
What makes up the quadriceps femoris?
1. Rectus femoris m.
2. vastus lateralis m.
3. vastus medialis m.
4. vastus intermedius m.
What makes up hamstrings?
1. Biceps femoris m.
2. Semitendinosus m.
3. Semimembranosus m.
muscles of mastication (chewing)
1. Masseter m.
2. Temporalis m.
3. Pterygoids mm.
muscles of facial expression
1. Orbicularis oris m.
2. Buccinator m.
3. Occipitofrontalis m.
4. Platysma m.
Why are joints of your hand partially fixed even when the hand is relaxed?
Antebrachial muscles that flex these joints are larger and stronger than those that extend the joints