Airway Lecture 4: Techniques of Intubation
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
Before intubating checklist
- Performed an adequate airway evaluation of patient
- Checked out airway equipment
- Suction is present
- Patient is positioned correctly
- ASA monitors are on
- Patient is apneic, unconscious
- Demonstrate ability to mask ventilate effectively
How many blades/handles should you have available when intubating?
Two (one for backup)
When in an OB case, what may be different about your airway equipment?
Use a shorter handle for your laryngoscope setup
What is the typical size ETT used for a male?
8.0 or 7.5 for males
What is the typical size ETT used for a female?
7.5 or 7.0 for females
What to do after opening ETT
Tighten the connector, test cuff for leaks
Oral Airways come in what sizes?
90, 100, 110 mm
What to also have handy when using oral airways
Tongue depressor

Nasal Airways are measured in what units?
french diameters
Nasal Airways come in what sizes?
28-34 french diameters
What to also have handy when using nasal airways
KY jelly/water soluble lube
LMA sizes
3-5 for adults
LMA sizing is based upon
weight/mouth opening
What other equipment may you need to use if using an LMA?
lube
20mL syringe to inflate the cuff
What instrument should be available in the case of a nasal intubation
magill forceps
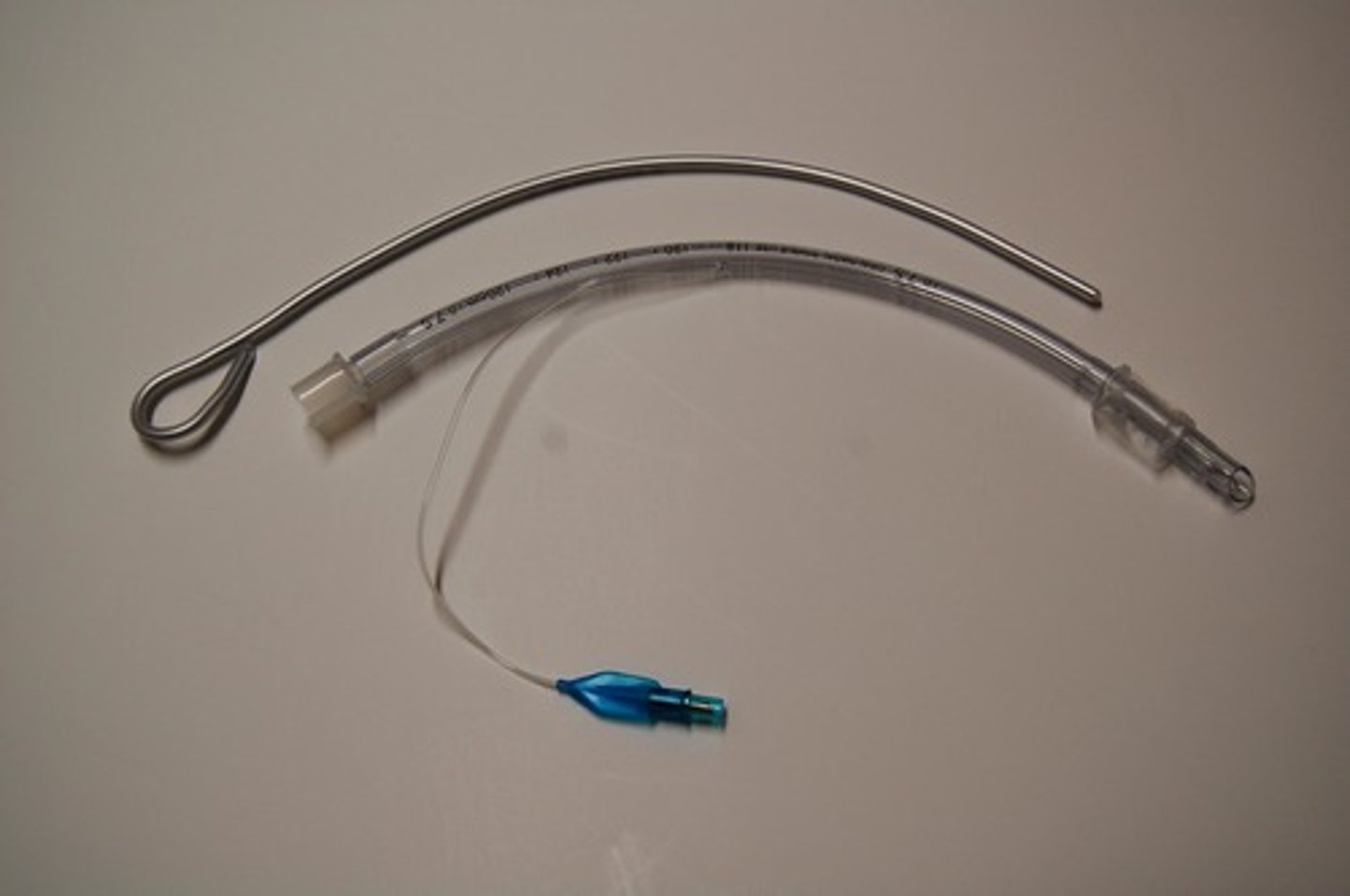
What instrument should be available when using an ETT
stylet/bougie

What needs to be in every room, every case, no exception
Ambu bag
What color tape is put over the eyes
Clear
What color tape is used to anchor the ETT
pink
What is the use of the stethoscope during intubation
To hear bilateral breath sounds
Where should suction be when intubating
Within reach without looking away from vocal cords
What tip should be on the suction while intubating
Yankauer

When intubating, how should the patient be positioned?
- head at top of table
- patient centered on bed
- mattress at level of belly button
- xiphoid process aligns with patient head
Sniffing Postion includes these two motions:
atlanto-occiptal extension
cervical flexion
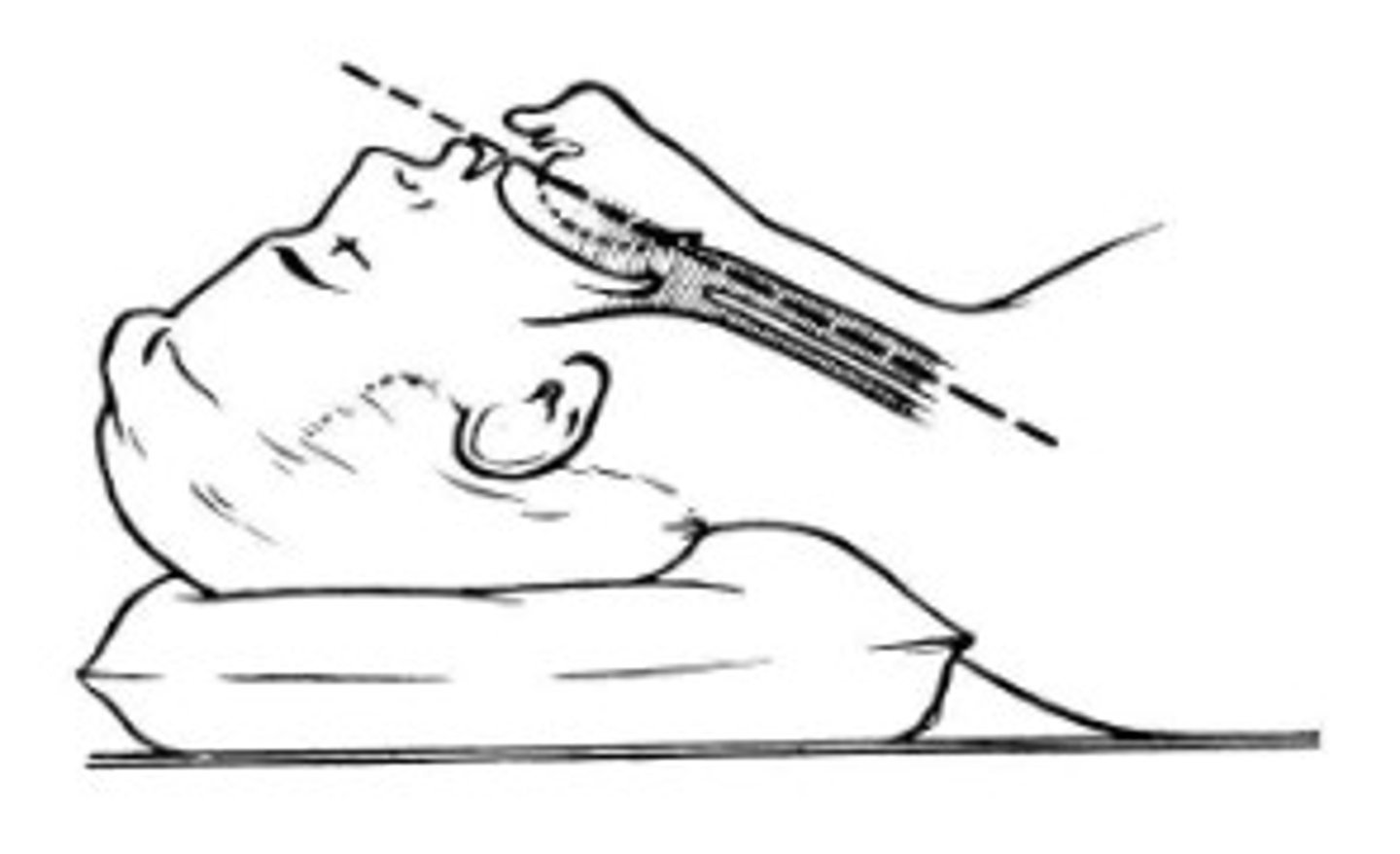
The sniffing position is done to achieve what?
alignment of three axes
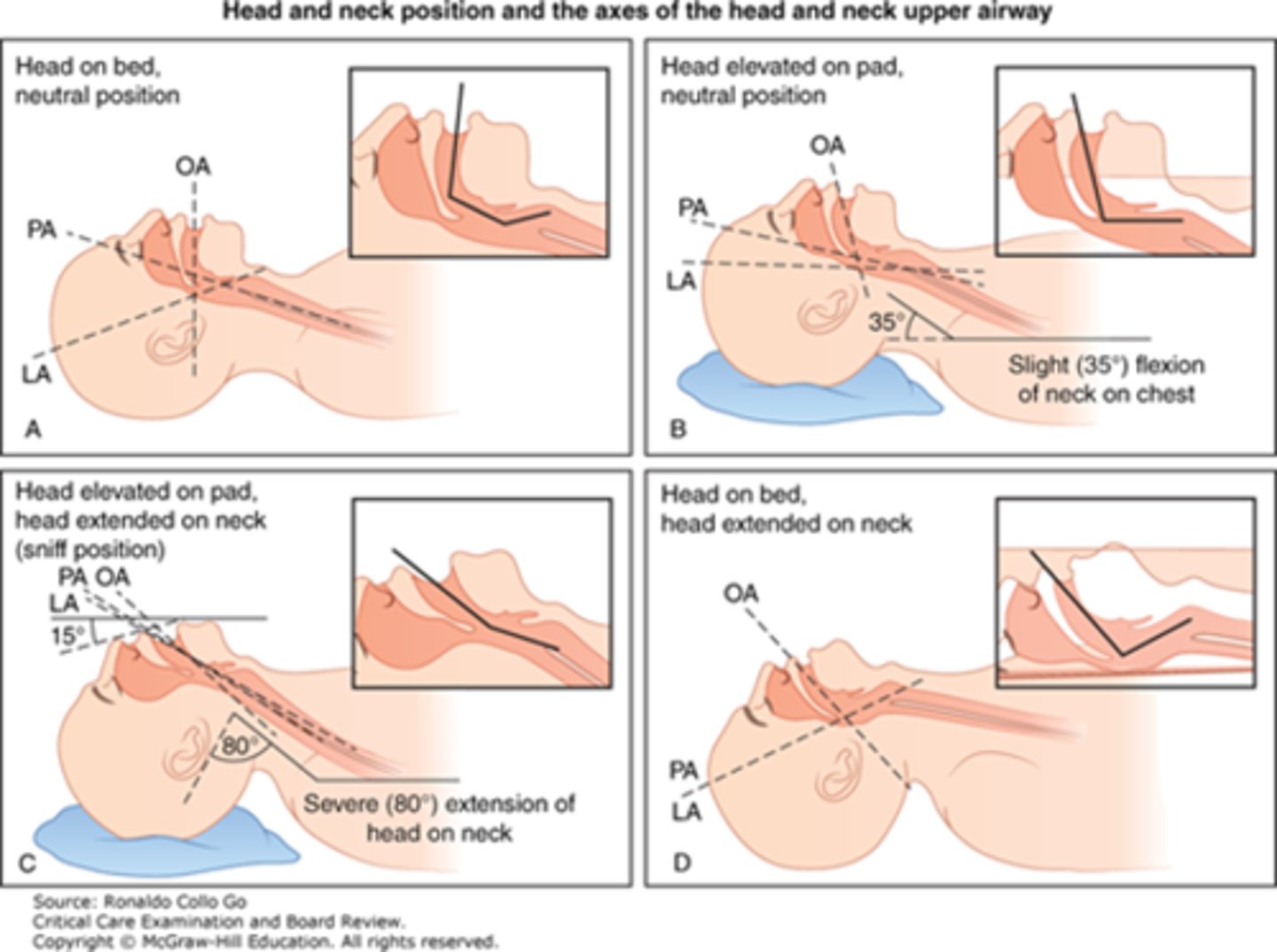
What are the three axes?
oral, pharyngeal, laryngeal
Oral axis is the axis of the
cavity of the mouth
Pharyngeal Axis is the axis of the
cavity of the pharynx
laryngeal axis is the axis of the
larynx and trachea
Sniffing Position + Head support: two methods
double folded pillow
trifold sheet with donut pillow on top
How many cm of pillow should be the head support
10cm
Why might you run into issues when positioning a morbidly obese patient?
Fat pad at base of neck may make it harder to extend atlanto occipital joint well in the flat position
How could you relieve this potential issue w/ morbidly obese patients?
build up/ramp up bed with sheets to allow for neck extension
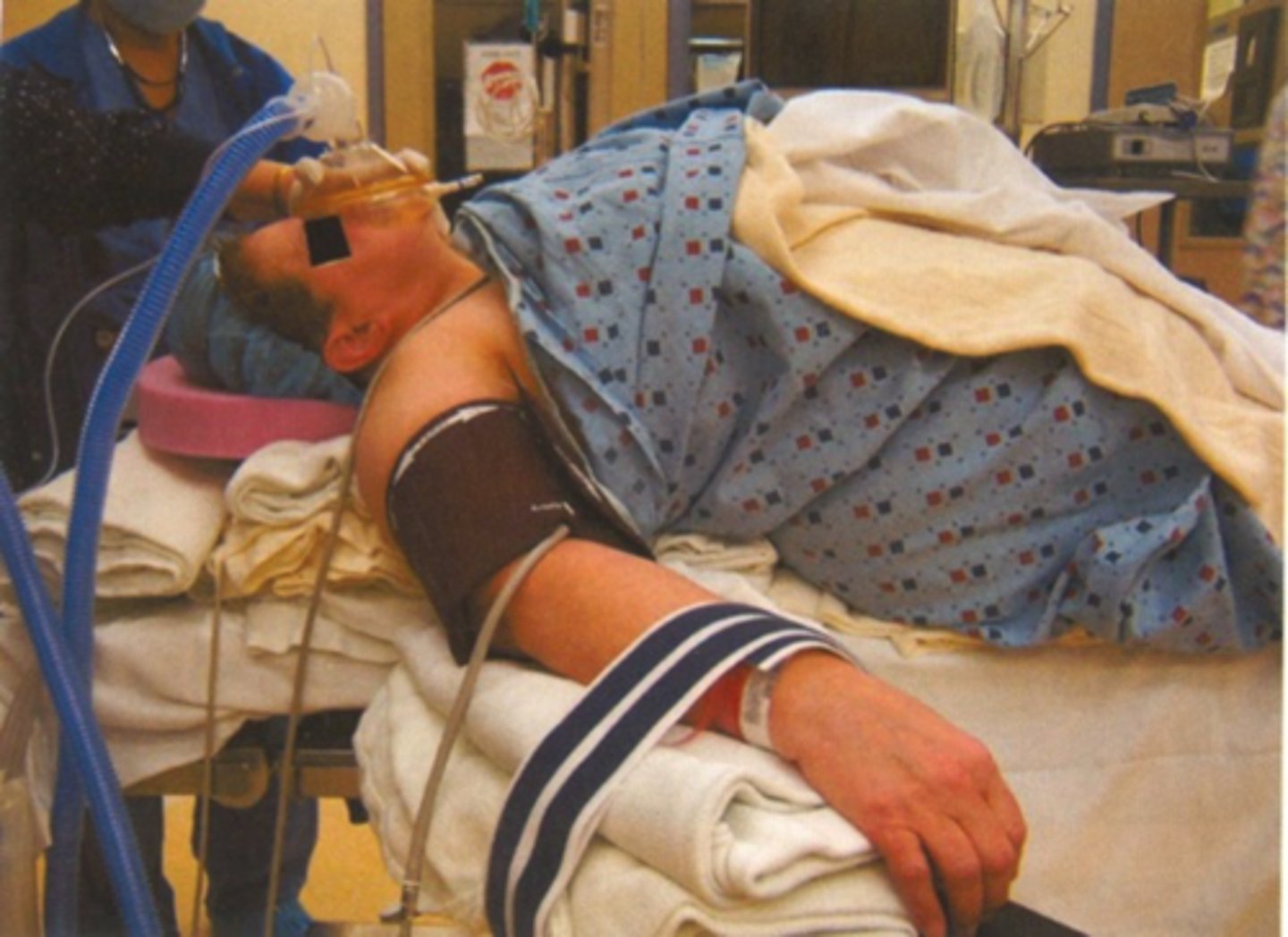
How does ramp up help the laryngoscopist
Displaces chest inferiorly
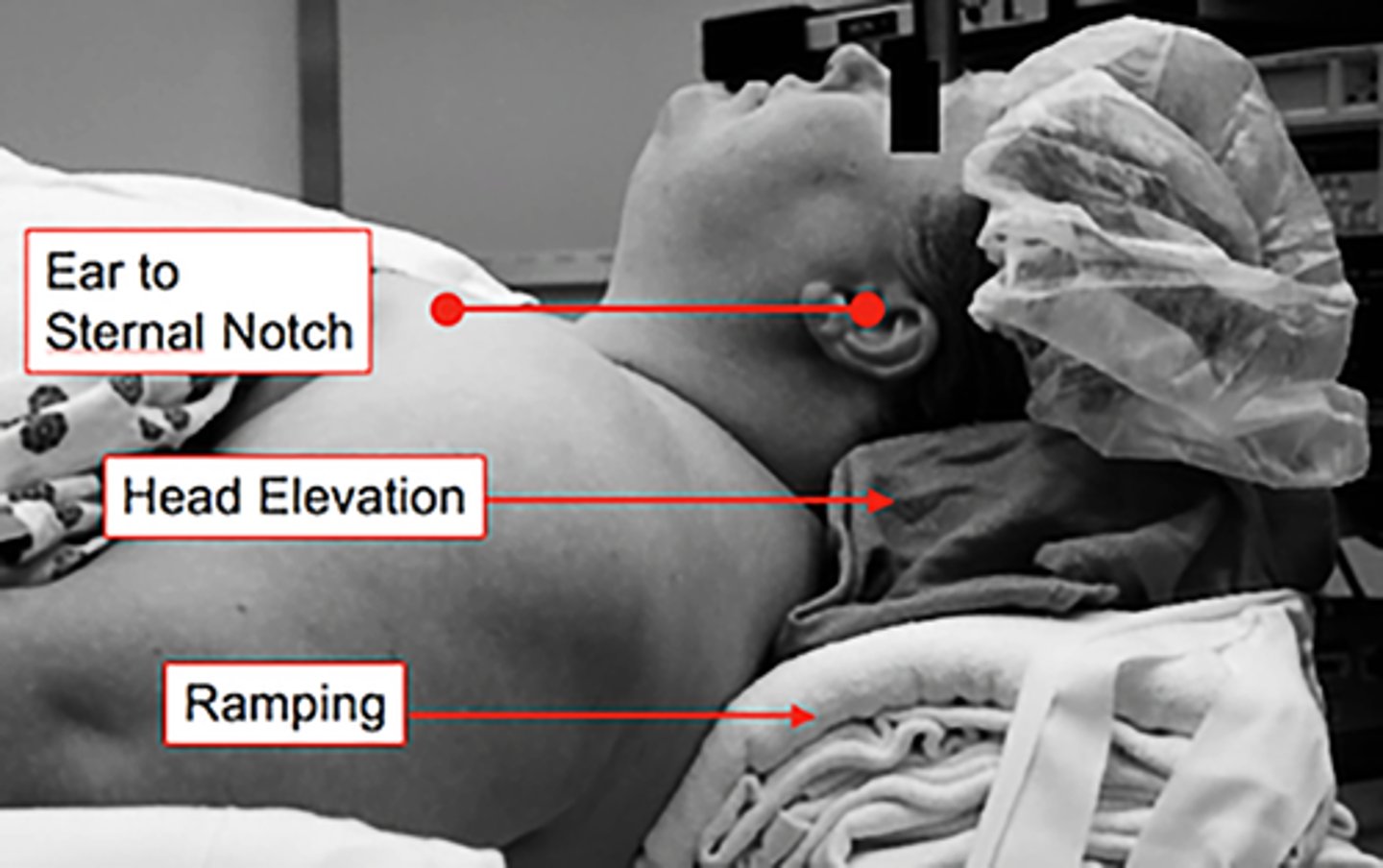
In addition to neck flexion and atlanto-occipital extension, what can you look at to see if the patient is aligned properly?
ear to sternal notch alignment
How do you know that a patient is adequately pre-oxygenated?
FEO2 > 90% is optimal (≥85% is acceptable)
Why do we preoxygenate?
to delay the onset of hypoxia (5-9 min delay)
When is pre-oxygenation most important
- Difficult airway (need more time)
-obese (desaturate quickly)
What should always be worn when managing airway
Gloves

How do we verify patient is unconscious by IV agents
Loss of eyelid reflex
What to do while waiting for optimal relaxation provided by paralytic agents
Mask ventilate
Onset time: Roc intubating dose
1-2 min
Onset time: Roc RSI
30 seconds
Roc RSI dose
1.2 mg/kg
Two techniques for opening mouth
no-touch
scissor
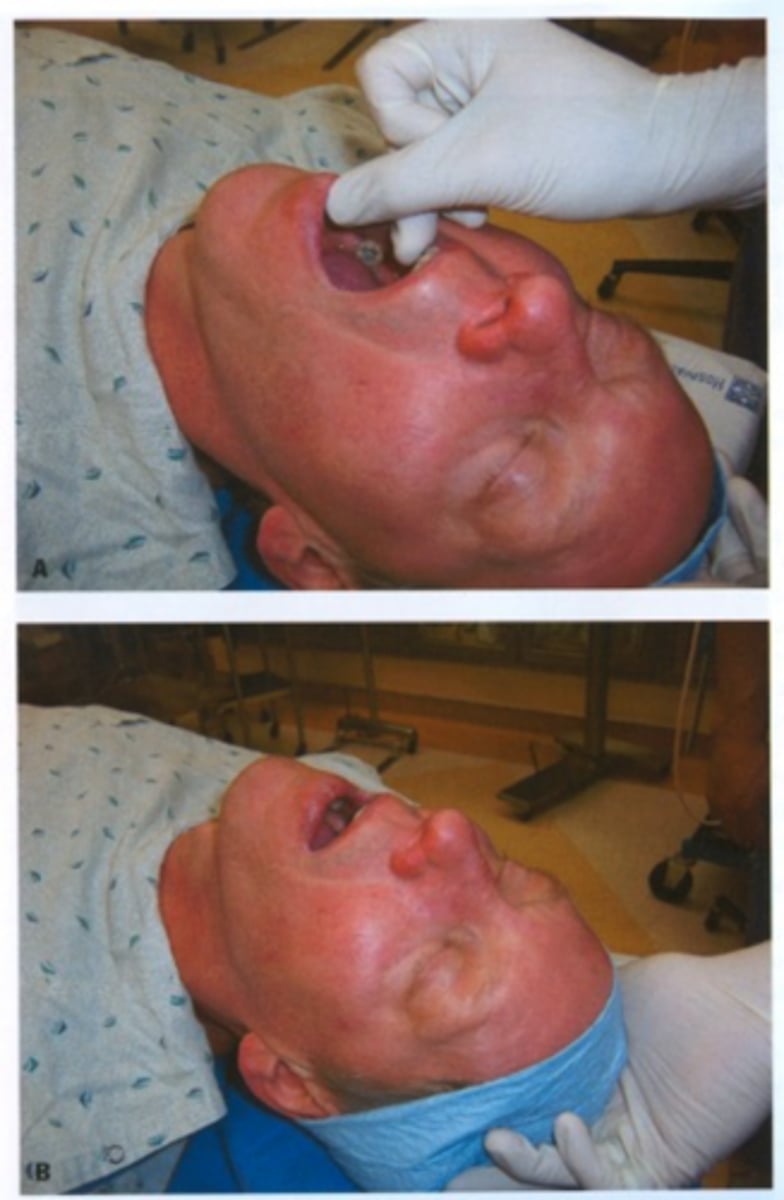
What to be careful of when inserting laryngoscope blade
Pinching the lower lip against the teeth
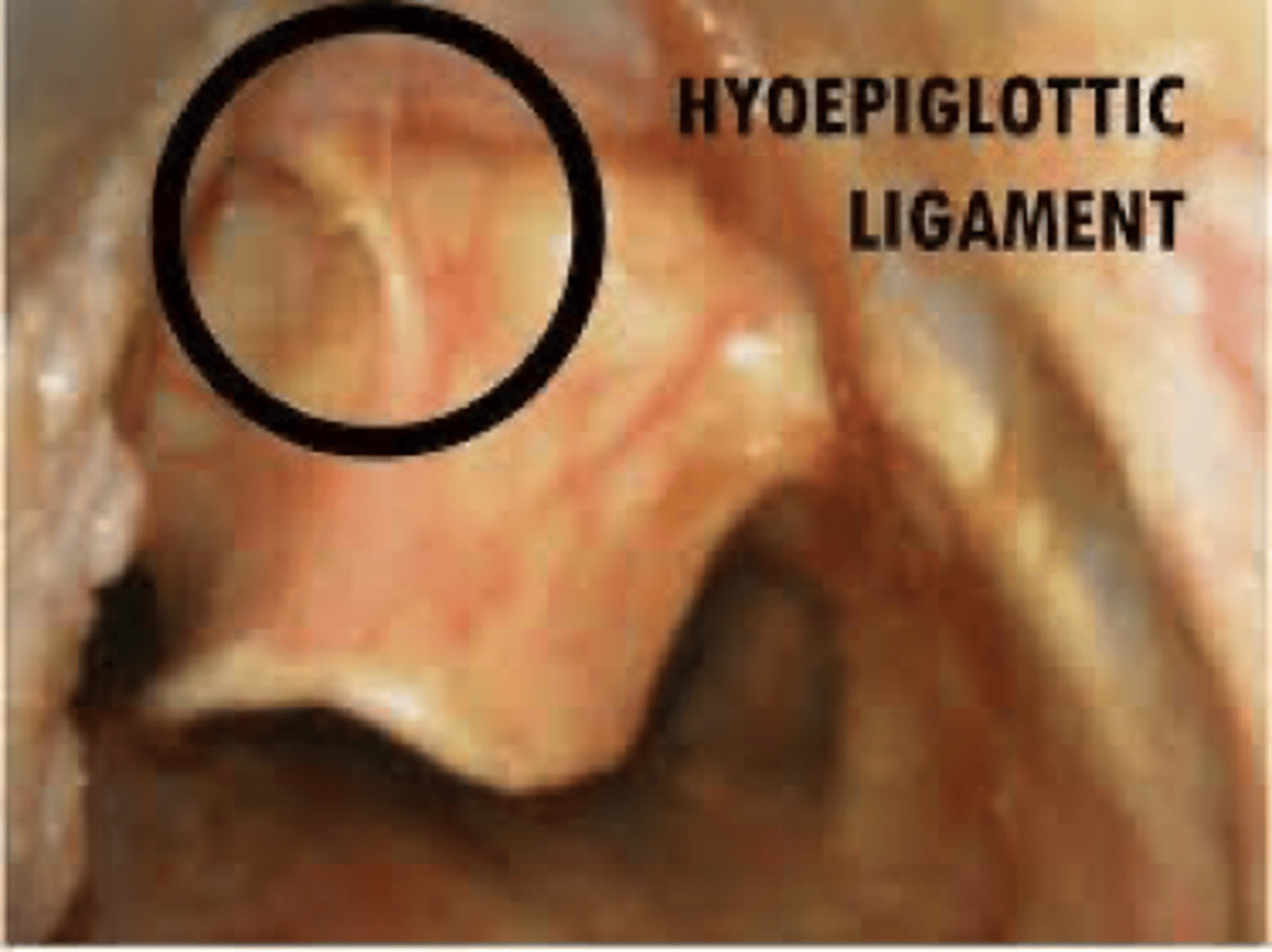
Where do you place the blade if using a mac blade?
in vallecula (base of tongue)
Once you are in the vallecula with a mac blade, what do you do?
push up and away tensing the hyoepiglottic ligament
How does intubating with a miller blade differ?
Push blade deep
Epiglottis is being pinned to the anterior laryngeal wall
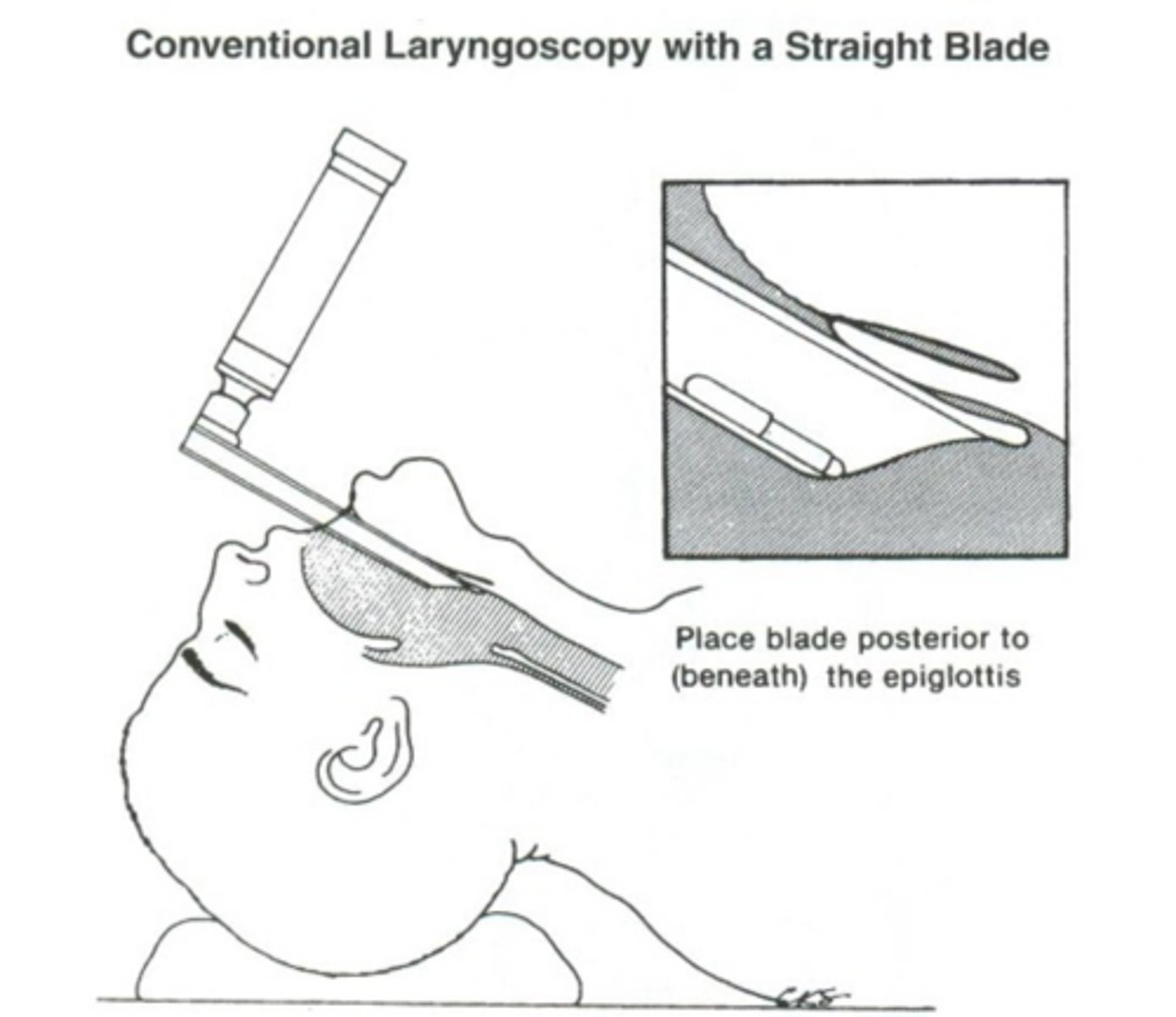
What are the two approaches to intubating with a miller blade?
- blade coming in at center
- paraglossal approach (from the right)
What is a potential disadvantage to a miller intubation?
epiglottic trauma
What is an external technique you can use to improve your view while intubating?
BURP
Backwards, Upwards, and Rightwards Pressure on external larynx region
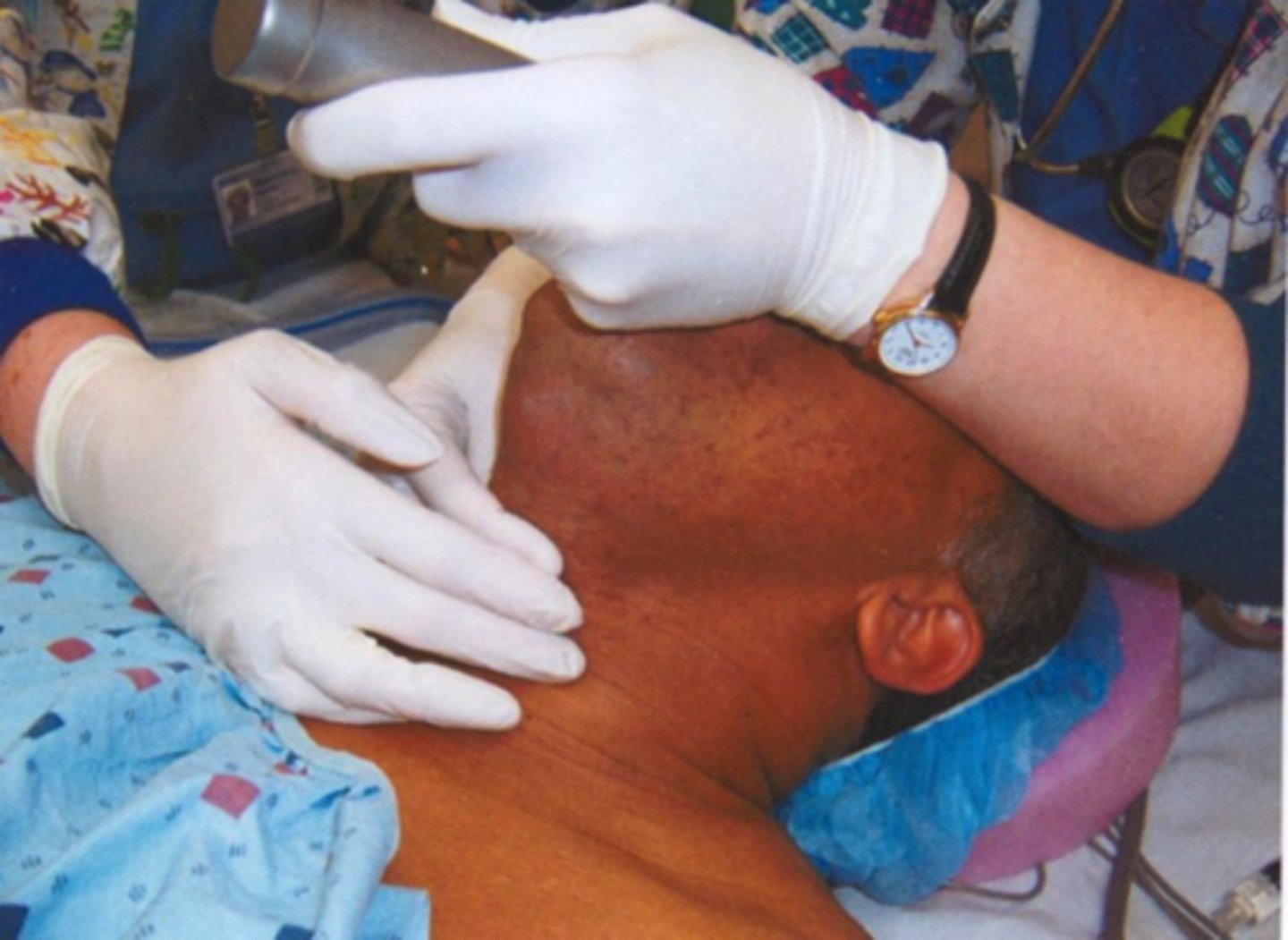
Misleading alternate name of optimal external laryngeal manipulation
Cricoid pressure
Who performs the initial cricoid pressure (BURP)
Laryngoscopist
How far in do you push the ETT tube?
x3 ETT size at level of teeth
After you are through the glottis with the ETT tube, how much further do you advance?
2-3cm into the trachea
What may happen if you insert the Mac blade too deep?
may only see the esophagus
What is the purpose of the flange on a blade?
to keep the tongue off to the left
How to hold ETT tube after intubating
Braced against the patient's cheek
How much air should you push into the cuff? ml and cmh20
6ml of air or 20-30cm H2O
Why is the first attempt at intubation typically the best?
- Airway is relatively dry
- Patient is pre-oxygenated
- drugs are active
How do you confirm that the tube is actually in the trachea? (2)
sustained etco2 using capnography
chest rise
How do you confirm where in the trachea the tube is? (2)
Bilateral breath sounds
Lack of sound over epigastric area
What are the two ways to monitor end tidal carbon dioxide
- capnography (waveform, more common)
- capnometry (number)
What would your capnograph display if you were in the stomach/esophagus?
EtCO2 diminishing over time
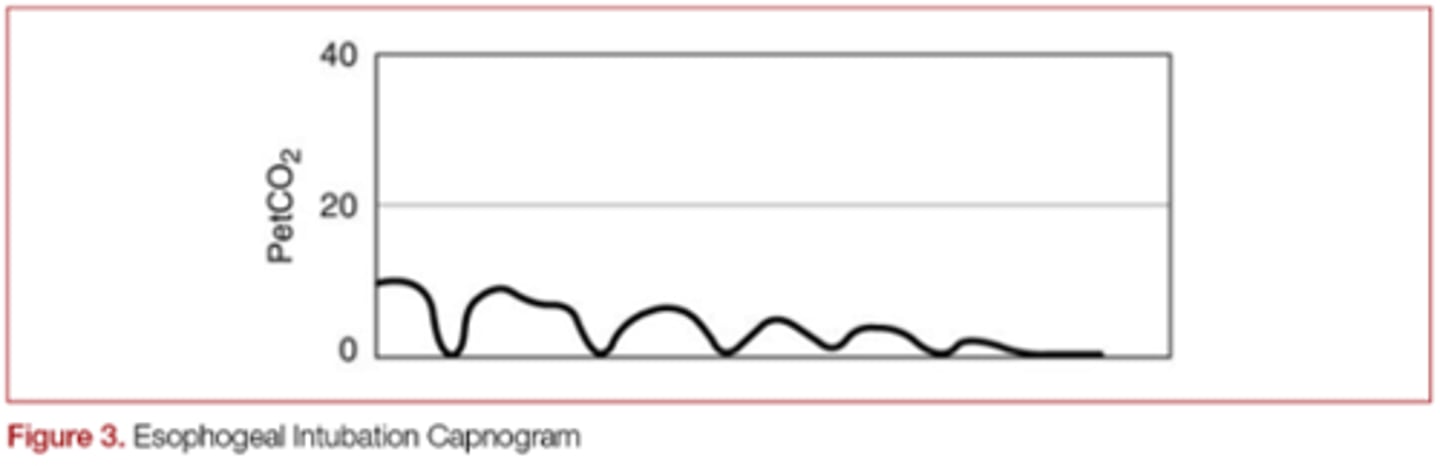
Although carbon dioxide measurement is the gold standard, why is not infallible?
if there is no pulmonary circulation to produce co2, none may be detected
EtCO2 is proportional to...
Cardiac output
A quick EtCO2 drop could be indicative of
cardiac arrest or pulmonary embolism
Ngeative Pressure devices to check confirmation of tube placement is based on the theory that
the tracheobronchial tree is semi rigid, and the esophagus is collapsable
Negative pressure device example
Self-inflating bulb (SIB)
Negative Pressure Devices: If you are in the trachea, what would happen to your bulb?
bulb would reinflate
Negative Pressure Devices: If you are in the esophagus, what would happen to your bulb?
No inflation of bulb
Advantages of using negative pressure devices
Practical and cheap
Immediately following intubation, where should you listen while manually ventilating the patient
Bilateral axillae
In what situations may chest rise be diminished ?
barrel chested, obese patients
Which fiberoptic device may be used to confirm ETT tube placement?
fiberoptic bronchoscope
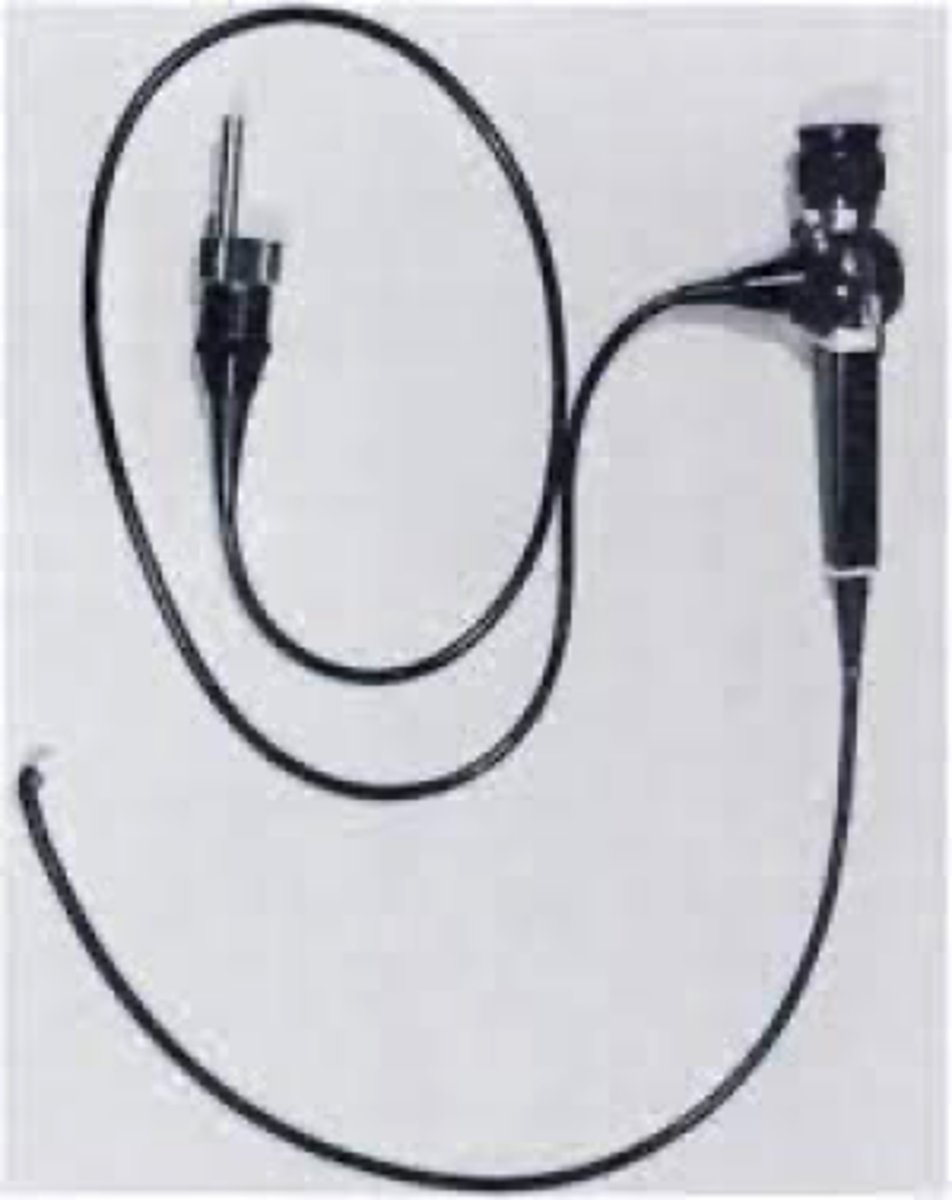

Disadvantages of using fiberoptic bronchoscope
Expensive, impractical
Which types of intubations always require you to use an fiberoptic bronchoscope?
double lumen enodbronchial tube
Can you verify tube placement with a pulse oximeter?
NO, but serves as a warning device is patient is desaturating due to hypoventialtion
Mainstem intubation occurs when:
The tube is advanced too far and therefore enters the mainstem bronchus
Mainstem intubation may also occur if...
Patient's head is repositioned
Which bronchus is the tube more likely to go into?
right
Outside of the OR, how can you confirm tube position?
chest x-ray
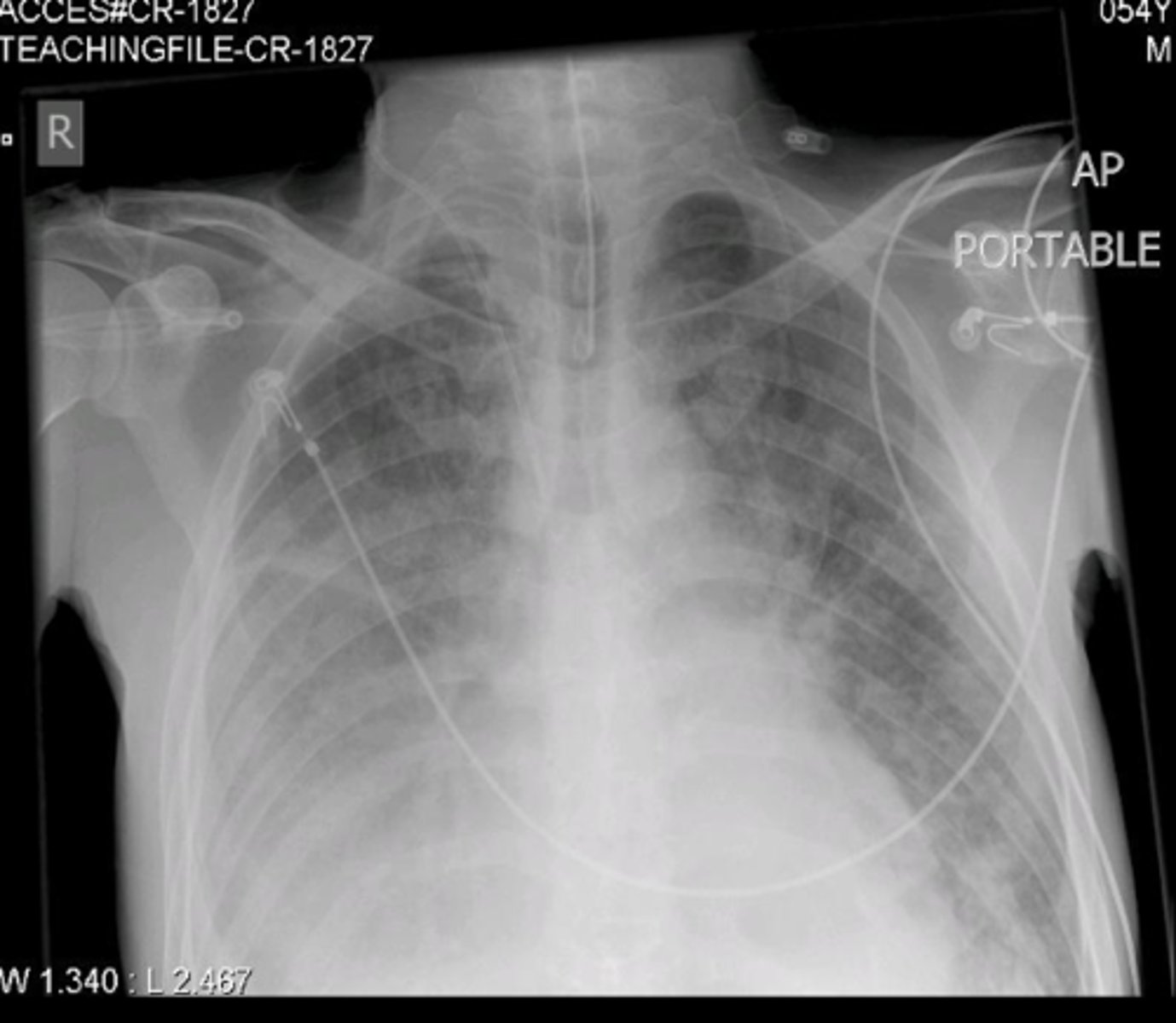
Minimum check of tube placement
Continuous capnography
Auscultation of lungs and stomach
Test to check tube placement outside the OR
Negative presssure test
Where should you tape the tube on patients face?
Maxilla to maxilla
In a prone positioned patient, what might you consider to REALLY secure the airway
- using two pieces of tape secured from 2 diff. positions
What to do if the tape is not sticking well
Benzoin
What should you be mindful of when securing the tube? (2)
- do not tape all the way around head (will restrict venous return)
- be sure not to catch the lip
If tape on the face is not desirable, how can the tube be secured?
wire tube to upper incisors via sutures
BIte blocks are used to accomplish what?
- To reduce chances of patient biting/occluding the tube
What can happen is the tube is occluded?
negative pressure pulmonary edema (NPPE)
When nasally intubating, what should you ask the patient prior to intubation?
which nostril is more patent
When nasally intubating sprays can be utilized to vasodilate or vasoconstrict?
vasocontstrict
Nasal Vasoconstrictors examples
-Oxymetazoline spray
-Phenylephrine spray
What side of the nose is the spray used with nasal intubation
both
In comparison to a oral tube, how do you size nasal tube?
1/2 size smaller than normal
7 for women, 7.5 for men
Two things that you can do to tube itself to facilitate easier movement?
warm tube up, and lube tip
Methods to warm up nasal tube?
soak in warm saline
wrap in warm blankets
When do you always use lube
When inserting anything through the nose