Pancreas Pathology
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Islet Cells (Langerhans)
Endocrine cells produced in the pancreas. Produces Alpha and Beta cells
Alpha and Beta cells
types of islet cells responsible for insulin and glucagon production in the pancreas.
Islet Cell Tumors
rare tumors (7%) that arise from abnormal growth of islet cells.
Can be functioning or non-functioning.
Most common: Insulinomas, glucagonomas
Insulinoma
a type of islet cell tumor that secretes excess insulin, leading to hypoglycemia.
Benign
Small, well-encapsulated, good vascular supply
Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)
Best imaging modality for pancreatic masses < 2cm
Sensitivity: 87-100% vs. CT 66-86%
Assists with FNA
Best for SOLID lesions
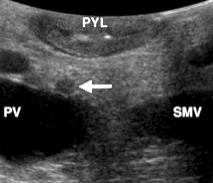
Gastrinoma
20% of islet cell tumors
Usually malignant
Hard to locate
Cystic Neoplastic Lesions
Pancreatic tumors that form cysts
10% of all pancreatic growths are cystic, the rest are solid
Two types: Benign Serous and Malignant Mucinous
Differentiate from pseudocyst (elevated amylase/lipase/inflammation)
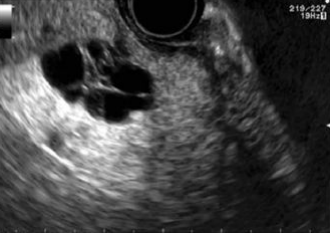
Benign Serous Cystadenoma
< 2cm
Cystic/septated on US
Head of pancreas
thin, well-defined capsule with septations/fluid-filled cysts
“Central star” appearance
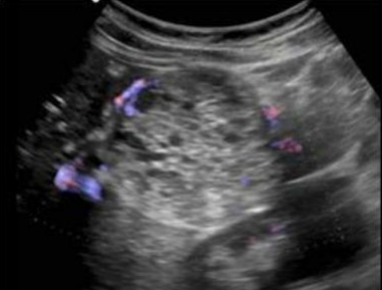
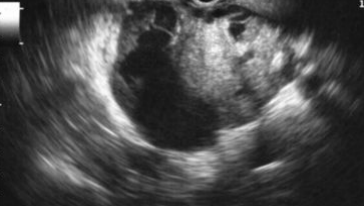
Malignant Mucinous Cystic Adenoma (AKA cystadenocarcinoma)
> 2 cm
Peripheral rim calcifications
Large, uni or multilocular, encapsulated mass
Most found in the tail = good prognosis
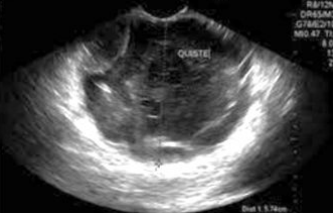
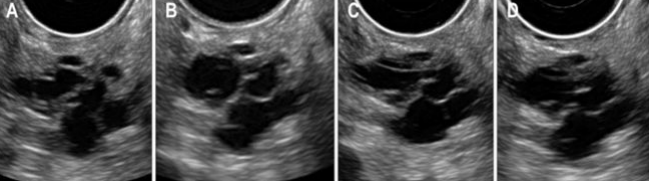
Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor (IPMT)
A type of mucinous cystic neoplasm
Origin = pancreatic duct
Slow growing (60-70s)
Benign then malignant
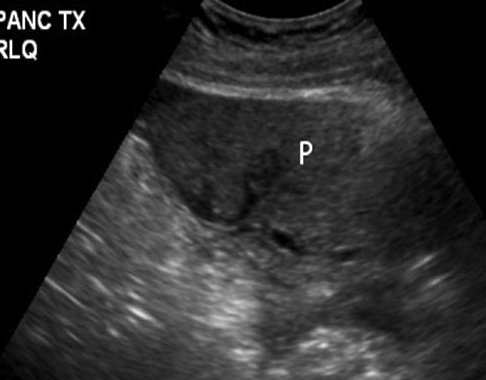
Pancreas Transplant
Treats diabetes
Placed in the pelvis
Von Hippel-Lindau Disease (VHL)
Autosomal dominant disorder (genetic)
Causes tumors and cysts to grow
Affects the CNS and other organs (65-75% of pt’s have pancreas involvement)
Sono: rim-like peripheral calcifications. Carcinoma is solid and irregular plus liver mets
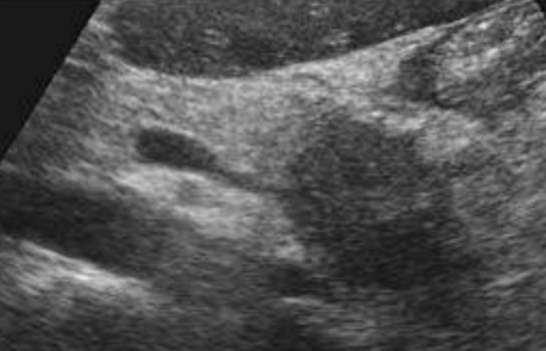
Biliary/ductal dilatations
When sweeping through the liver, if you see dilated structures, investigate the surrounding organs and make sure to confirm whether it’s a duct or a vessel (color, turn on it)
Why are we seeing these?
What hereditary disease causes excessive production of mucous by the endocrine glands?
Cystic Fibrosis
Sudden inflammation of the pancreas caused by inflamed acini cells that release pancreatic enzymes to surrounding parenchyma?
Acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis is associated with:
Biliary disease, ETOH (alcohol) abuse, trauma, drugs, infection
Ultrasound appearance of severe pancreatitis
Fibrotic
Ultrasound appearance of pseudocysts
Phlegmon
Sonographic appearance of Chronic Pancreatitis
Signs of atrophy and calcifications, very bright with hyperechoic areas, possibly smaller in size
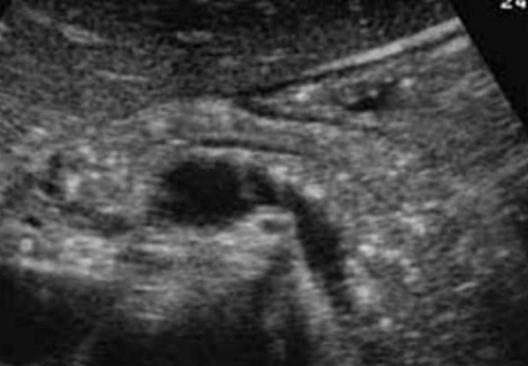
Sonographic appearance of Acute Pancreatitis
Swelling, fluid around the pancreas, increase in size
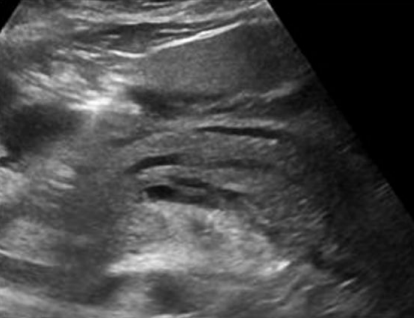
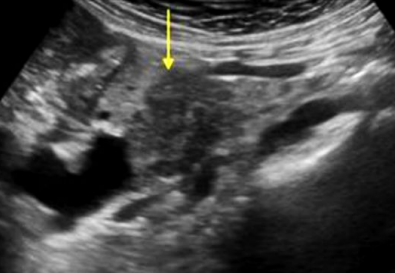
Sonographic appearance: adenocarcinoma
Ill-defined/irregular borders, hypoechoic, solid lesion
Also shows dilated ducts and biliary obstruction, no vascularity
(ie. Abnormally dilated CBD due to mass in head of pancreas, jaundice, weight loss)
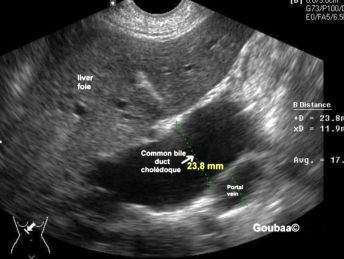
Indications for Pancreas ultrasound
Epigastric pain
Assess for malignancy, pancreatitis, complications
Abnormal labs (elevated LFTs or enzymes)
Jaundice
Hx of cholelathiasis
Labs to look for
Elevated amylase, lipase, fat in feces, bilirubin, LFTs
Abnormal Amylase levels:
elevated: acute pancreatitis/pancreatic disease
low: pancreas damage, hepatitis, cirrhosis
Abnormal Lipase
Elevated: sudden acute pancreatitis, ductal dilatation, pancreatic carcinoma, acute cholecystitis
Fecal fat removal
undigested fat ~ pancreatitis
Abnormal bilirubin/LFTs
enlargement/neoplasia of pancreas head → stenosis or complete obstruction of the distal common bile duct
(when there’s a mass or inflammation in panc head, it compresses or obstructs CBD so bile can’t drain and bilirubin rises)
“head hits the hepatic highway”
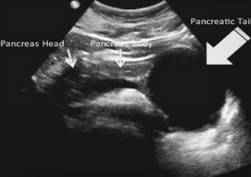
Pancreas location
Retroperitoneum (except tail)
Sits between the duodenal loop and splenic hilum
12.5-15 cm
Pancreatic duct = < 2 mm
Landmarks
Left liver lobe
Splenic vein (elongate to follow tail)
SMA posterior to it
Congenital diseases
Cystic Fibrosis (CF) - inherited that causes damage to lungs, digestive system, other organs by overproducing mucus, sweat, and digestive juices
Decreased enzyme production (exocrine failure in children)
Improper digestion
Causes recurrent pancreatitis
Cystic Fibrosis ultrasound
Makes pancreas hyperechoic and small
Hypoechoic areas can represent pancreatic fibrosis
Small cysts/calcifications, gallstones, liver disease associated with CF
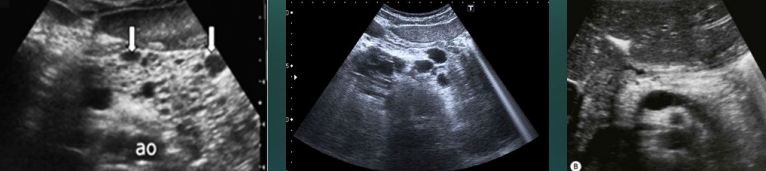
Acute pancreatitis with stone obstructing the pancreatic duct
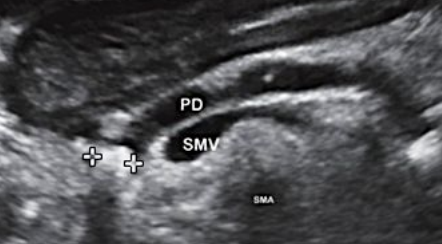
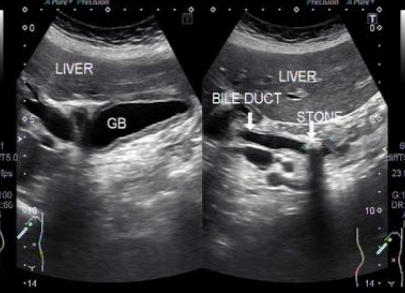
Describe this image
Diagnosis?
Gallbladder with wall thickening and a stone obstructing the common bile duct causing dilatation (posterior shadowing). Results in pancreatitis
Dx: gallstones/pancreatitis
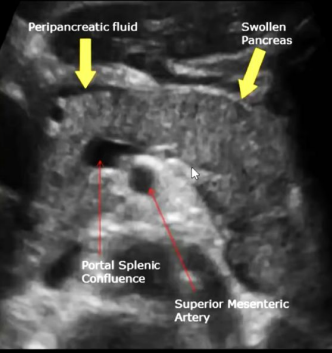
Describe this image
Diagnosis?
Transverse view of the pancreas
Pancreas appears to be swollen/enlarged with increased echogenicity and has peripancreatic fluid
Dx: acute pancreatitis
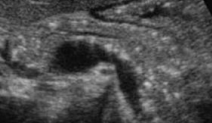
Describe this image
Diagnosis?
Transverse image of pancreas
Pancreatic parenchyma appears hyperechoic with echogenic foci (calcifications) throughout.
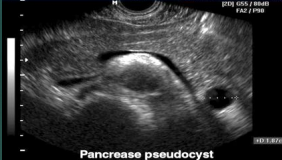
Pseudocyst
Most common cystic lesion of the pancreas
Fluid-filled loculus with no epithelial lining
Located outside the pancreas often in lesser sac
Pancreatic tissue is damaged and leaks enzymes and body fluid to form a cyst
Often occurs in the tail
Complications of pseudocyst (fatal)
Hemorrhagic pancreatitis (high mortality rate) *see image
Ruptured pseudocyst
Phlegmonous pancreatitis
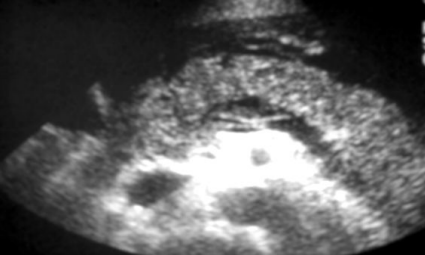
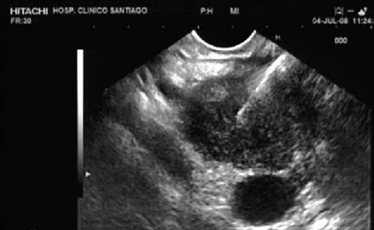
Describe this image
US guided FNA of a pancreatic tumor located in the head of the pancreas (based on landmarks)
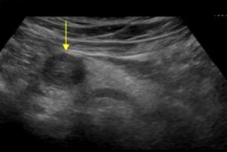
Adenocarcinoma
Most common malignant mass of pancreas
Poor prognosis (7% chance u live 5 years)
Most common in pancreas head
Can’t differentiate without bx
Hard to diagnose
Often shows increased vascularity around the tumor
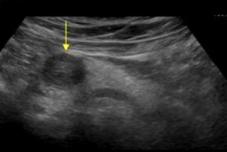
Describe this image
Differential dx?
A well-defined, solid, round, hypoechoic mass located in the head of the pancreas. Most likely adenocarcinoma but needs to be confirmed with biopsy
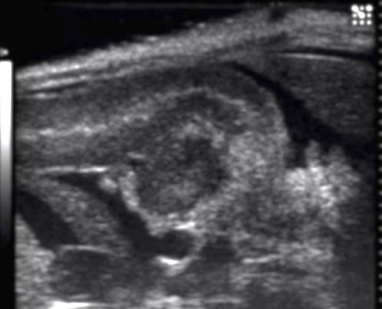
Describe this image
Dx?
A well-defined, hypoechoic, complex mass located in the head of the pancreas
Dx: adenocarcinoma
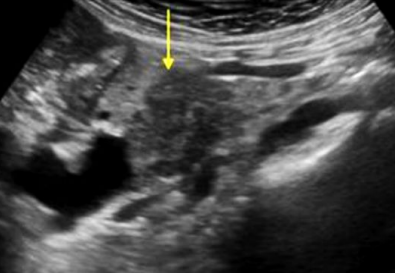
Describe this image
Dx:
An ill-defined, irregularly shaped, hypoechoic, solid lesion located in the head of the pancreas.
Dx: Adenocarcinoma
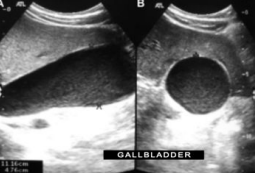
Describe this image
Dx:
Gallbladder in both the longitudinal and transverse planes with low level echoes suggestive of sludge and distention (gallbladder hydrops).
Dx: Likely diagnosis is choledocholithiasis
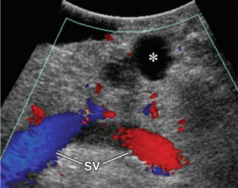
Describe this image
Dx?
A small, well-defined, hypoechoic, cystic lesion located in the body of the pancreas towards the tail end.
Dx: most likely a cystadenoma
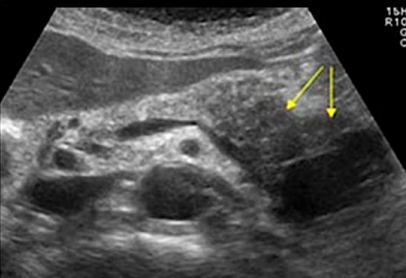
Describe this mass
Dx?
A large, ill-defined, hypoechoic, complex mass located within the pancreatic tail.
Dx: most likely cystic adenocarcinoma but requires biopsy
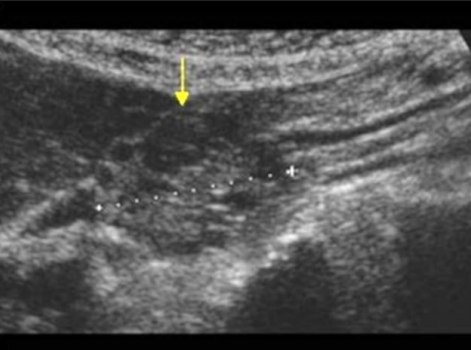
Describe this image
Dx?
A large, hypoechoic, complex mass with both solid and cystic components.
Dx: pancreatic adenocarcinoma with cystic mass
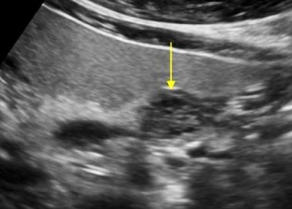
Describe this image
Dx?
A small, hypoechoic, complex mass with microcysts located in the body of the pancreas
Dx: microcystic adenoma of pancreas
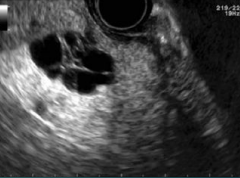
Describe this image
Dx?
An EUS image of a well-defined, hypoechoic cyst with a “central star” and microcysts/septations.
Dx: benign serous cystadenoma