Equine Limb Palpation Online Practical
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is the coronary band?
hairline on the equine foot
How can the coronary band be identified?
by change in texture at transition from hoof (hard) to skin (soft)
when palpating in a proximal direction from hoof onto skin
Name all of the features the arrows are pointing at:
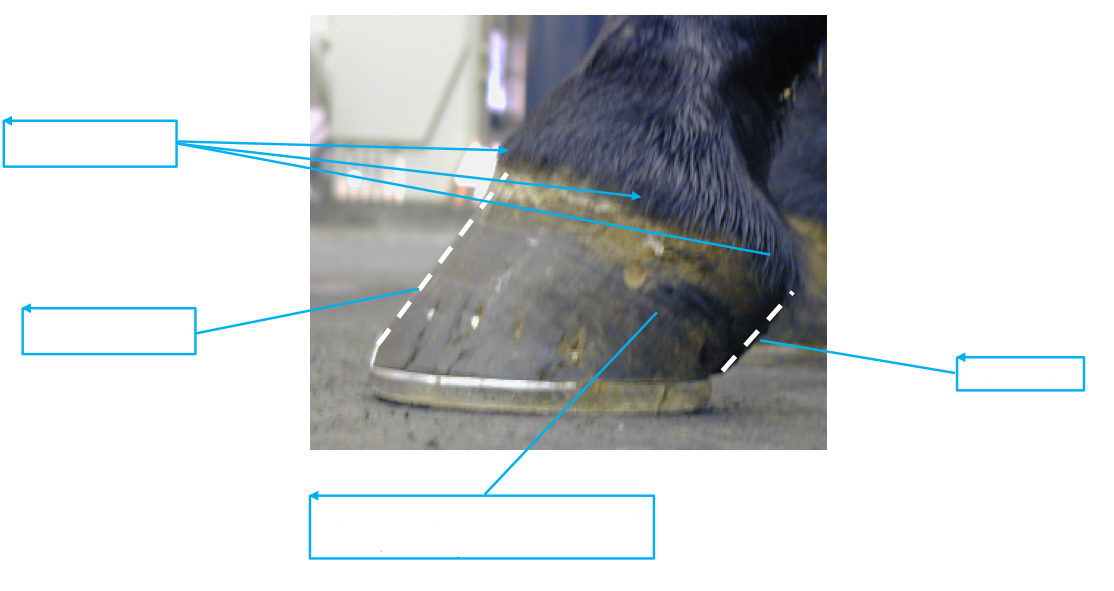

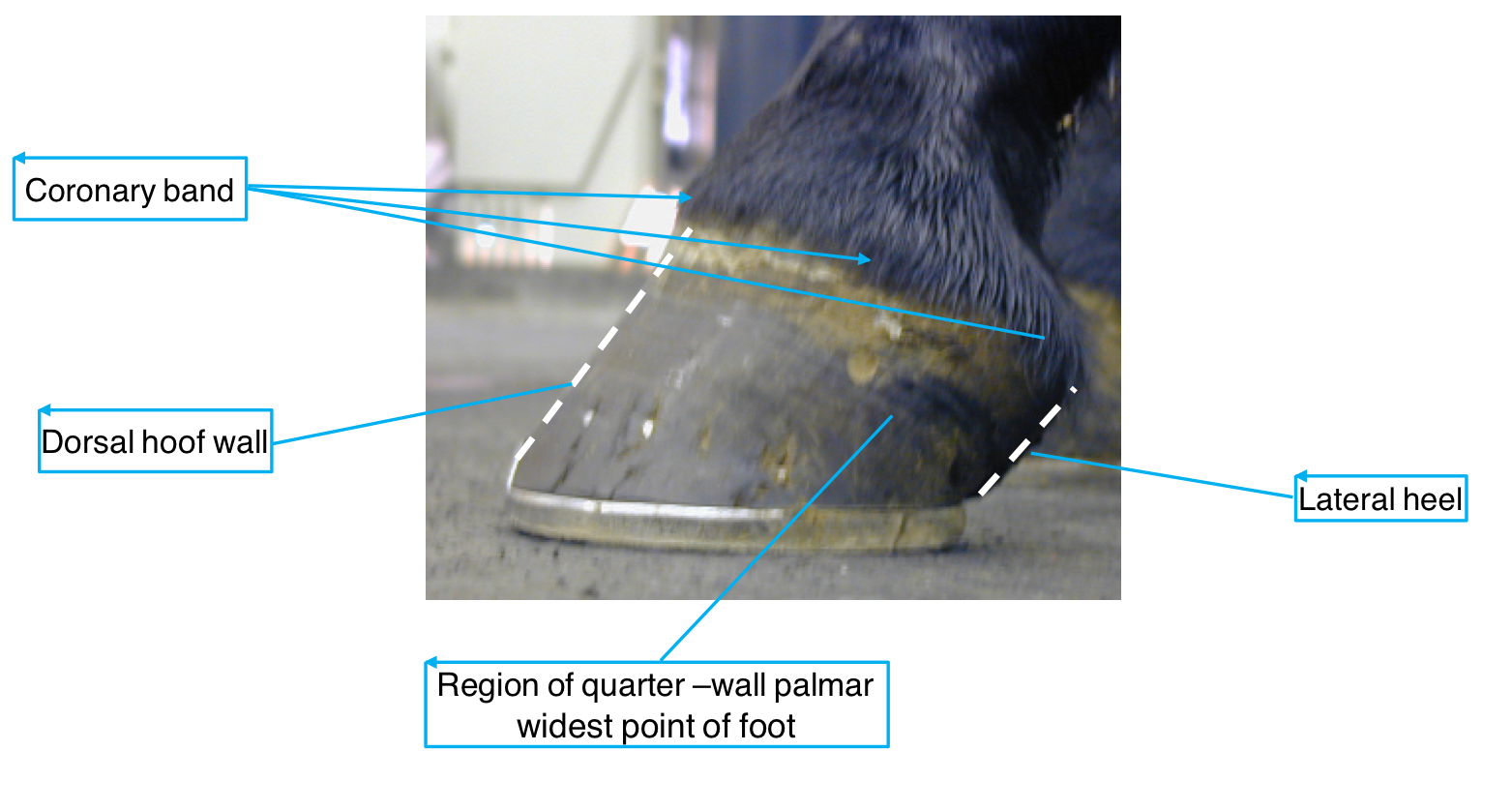
Name the features of teh equine foot
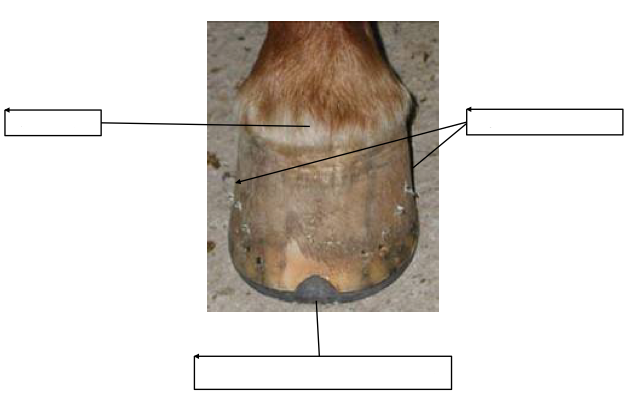
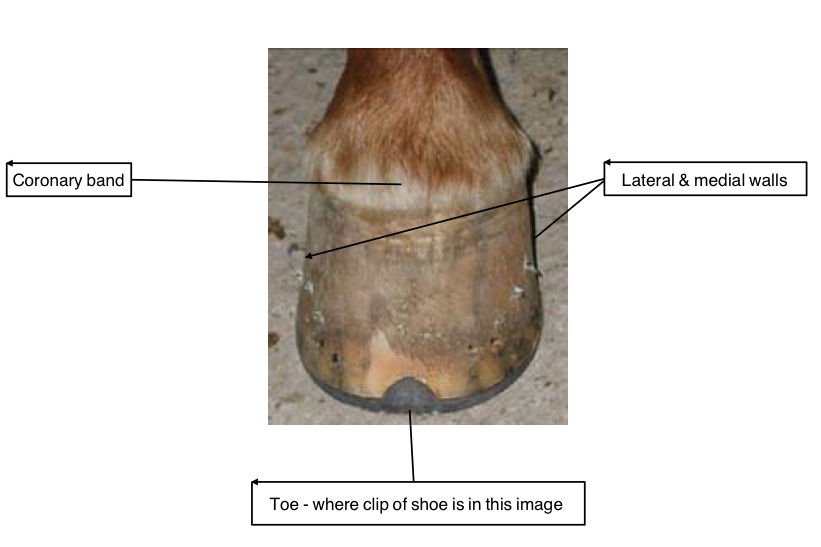
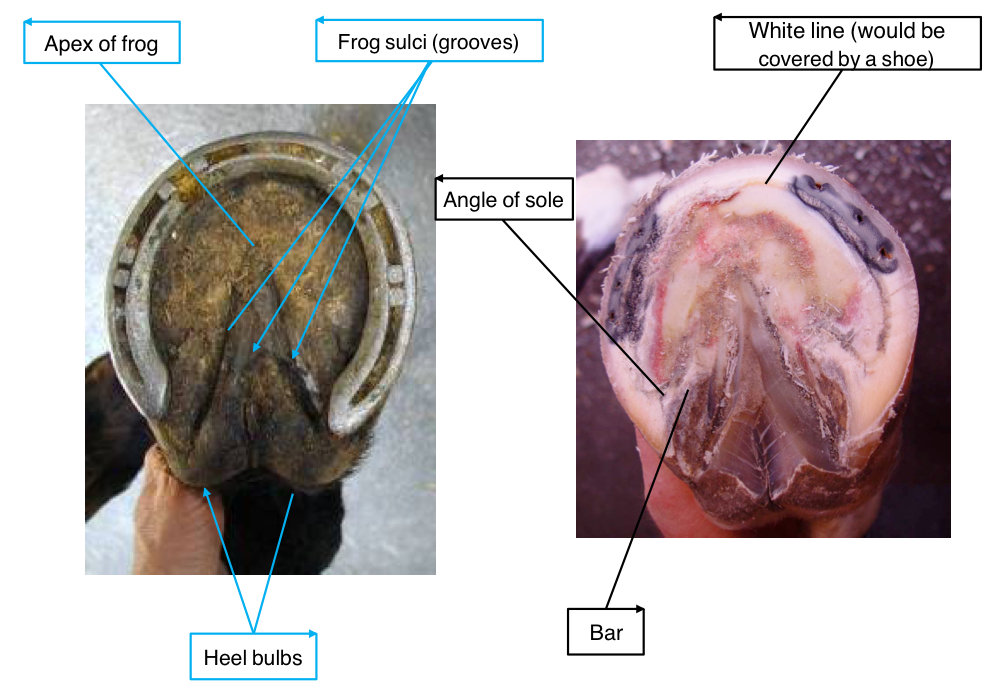
Name the anatomical features:
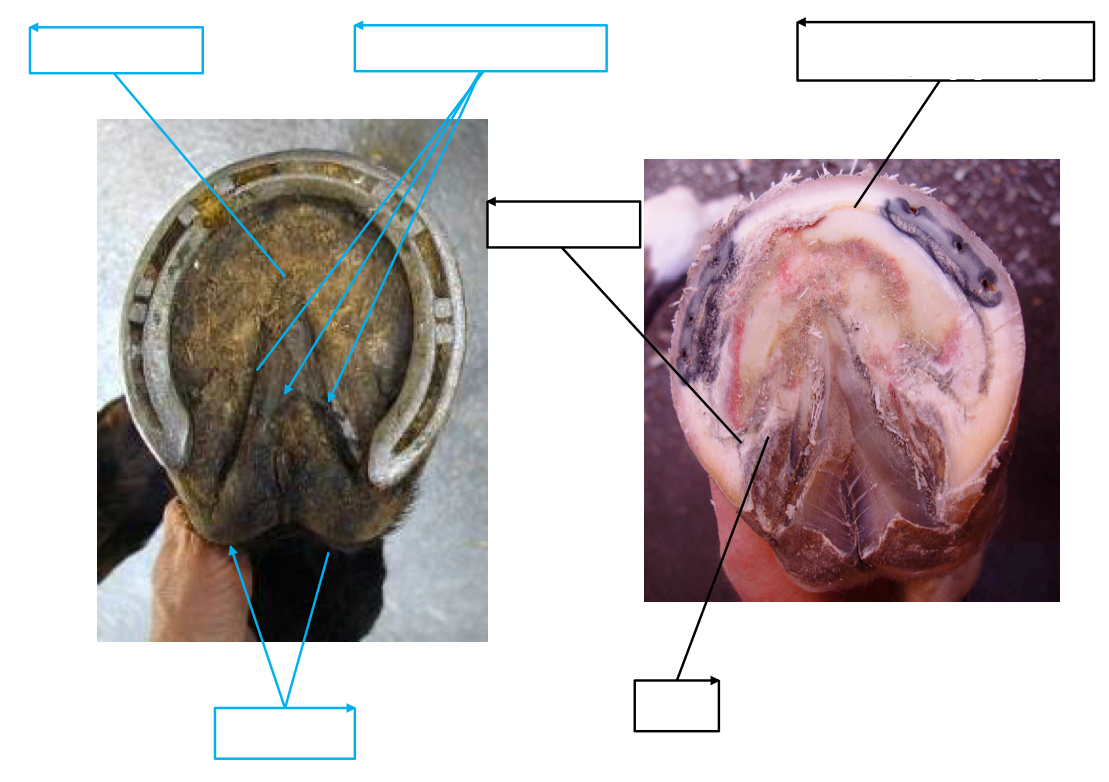
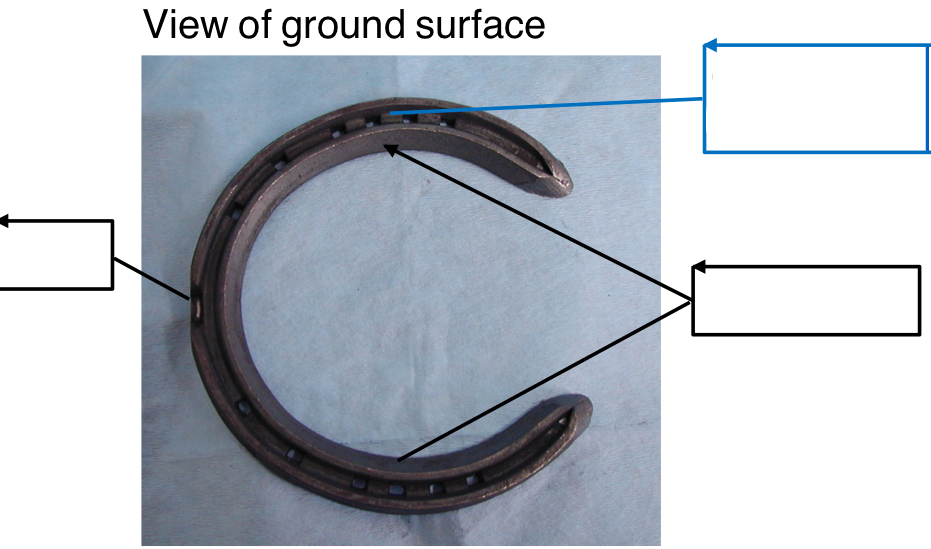
Name the anatomical features of a shoe:
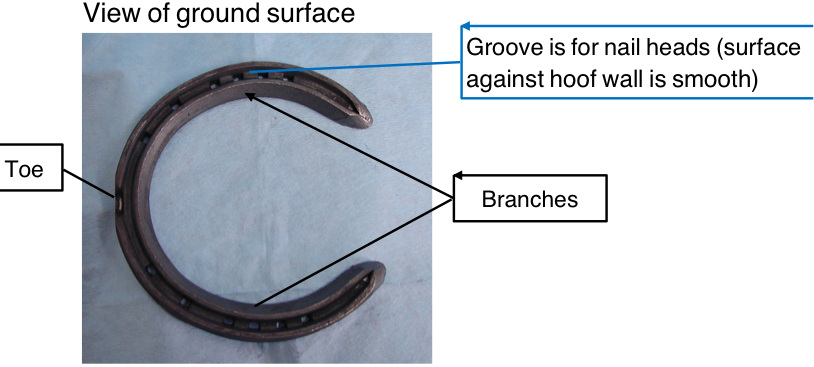
Name the anatomical feature of the shoe:
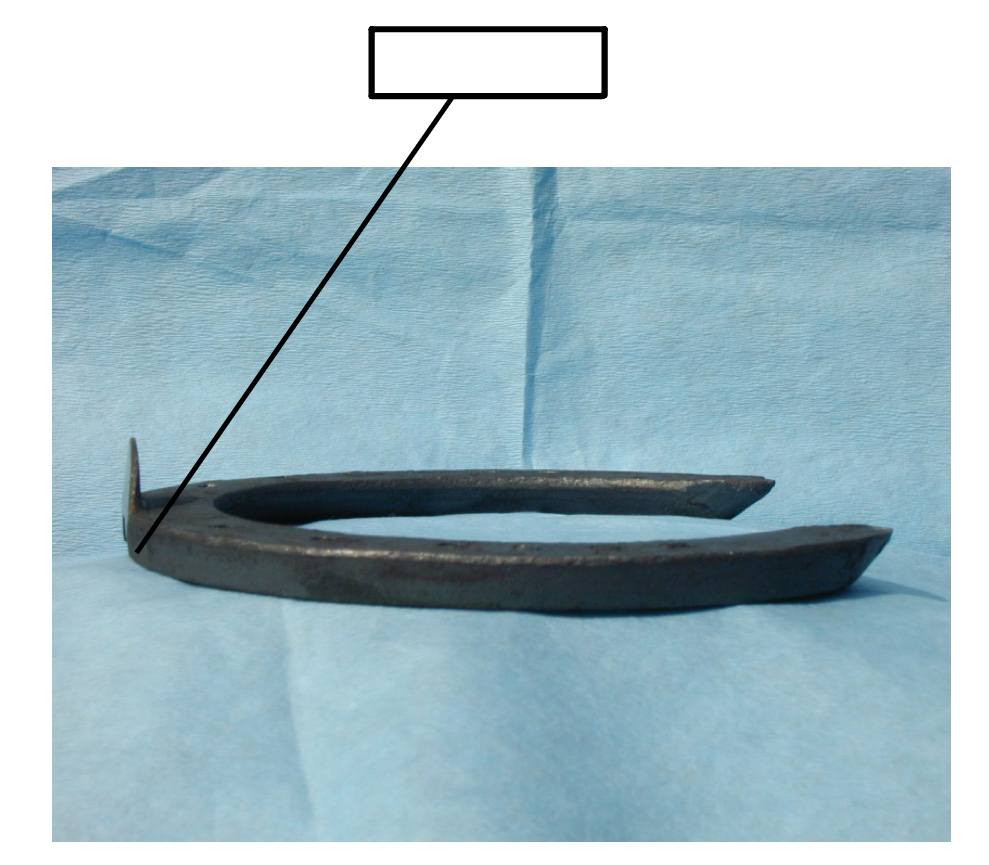
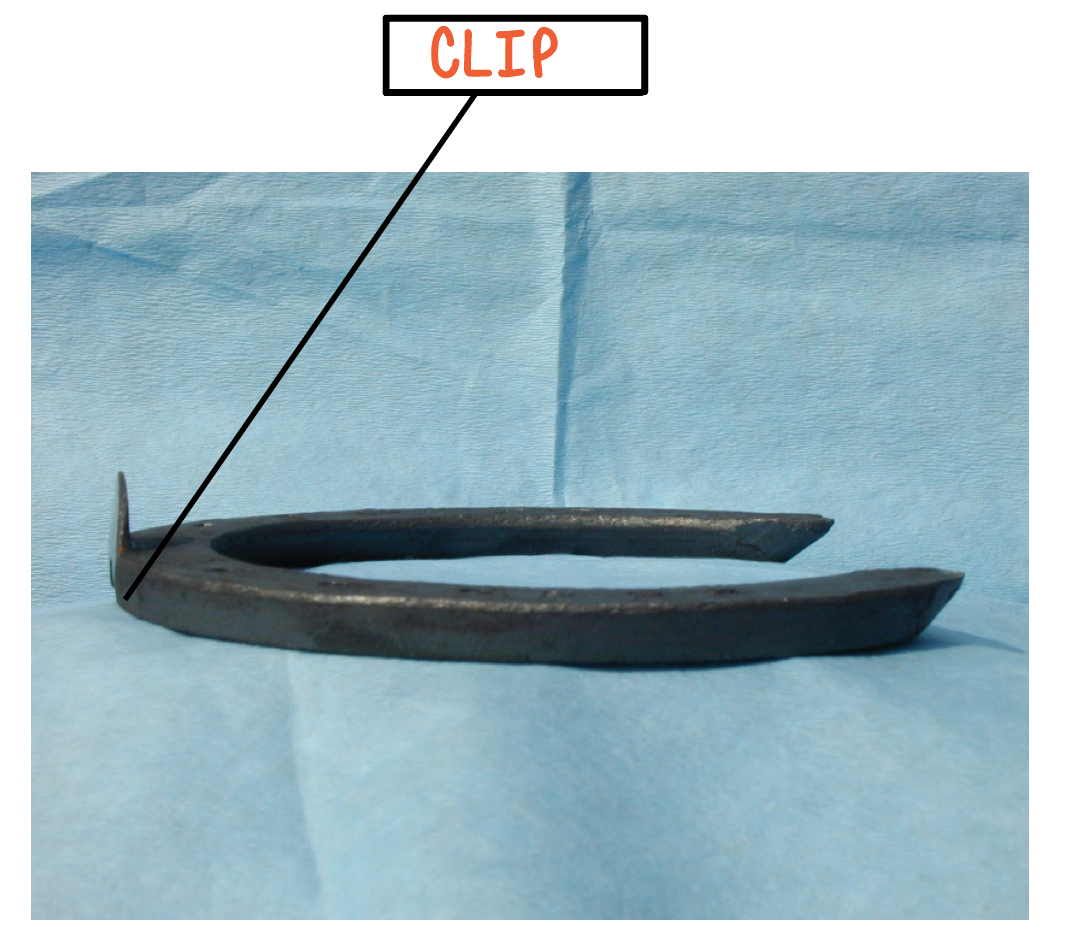
What is the purpose of the clip?
help to keep the shoe on by protecting the nails (also called clenches) from the shear forces created during the stance phase
How many clips will a regular front shoe have?
one toe clip
How many clips will a hind shoe have?
two, one on either side of the toe
What is synovitis?
inflammation in the synovial membrane that lines joints
What are some signs of synovitis?
Fetlock joint distension
Digital flexor tendon sheath distension
Distal interphalangeal joint distension
what is the fetlock joint also known as in the forelimb and hindlimb?
metacarpo - or metatarsophalangeal joint
Name the labeled structures:
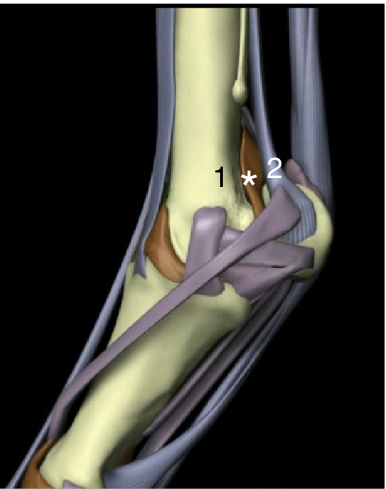
1 - Metacarpus III
2 - Suspensory ligament branch
* = Fluid “bubble” at bottom groove between metacarpus III and suspensory ligament branch
True or False: Palpate with the horse weightbearing?
TRUE
Name the labeled structures:
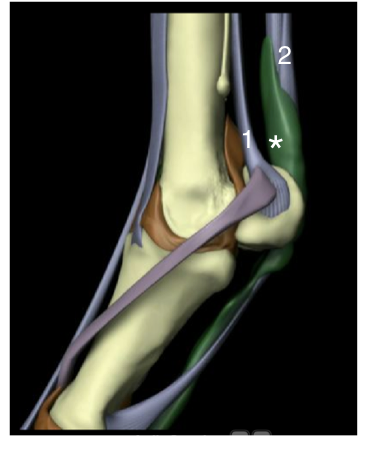
1 - suspensory ligament branch
2 - flexor tendons
* - fluid bubble at bottom of groove between suspensory ligament branch and the flexor tendons
Name the labeled structures:
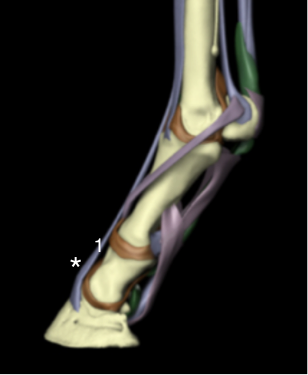
1 - Common digital extensor tenson (long DE in hindlimb)
* - fluid “bubble” in dorsal midline/just off midline
Name the labeled structures:
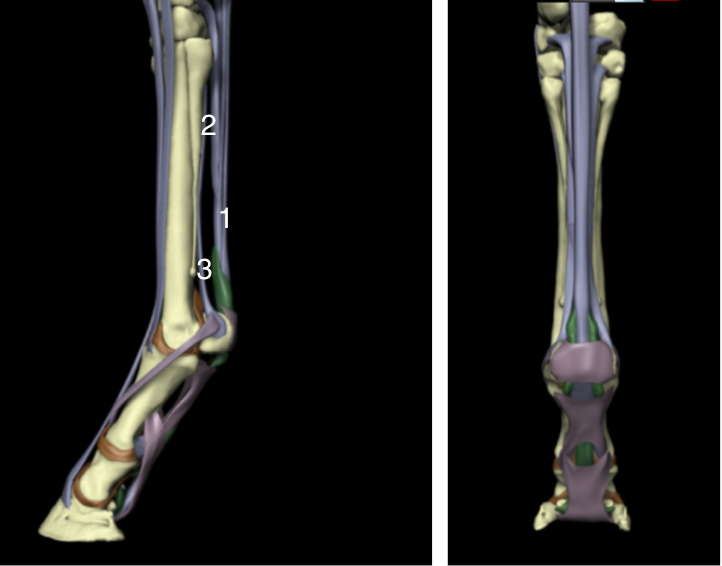
1 - flexor tendons
2 = accessory ligament of the deep digital flexor tendon
3 = suspensory ligament (in region of branches)
When palpating soft tissues of palmar metacarpus/plantar metatarsus, what are you aiming to detect?
any increase in temperature
increase in size
pain response to palpation (check repeatable)
change in texture
What positions should the limb be in when palpating the soft tissues of palmar metacarpus/plantar metatarsus?
weight bearing
limb lifted
Which direction should you palpate when the horse is weight bearing?
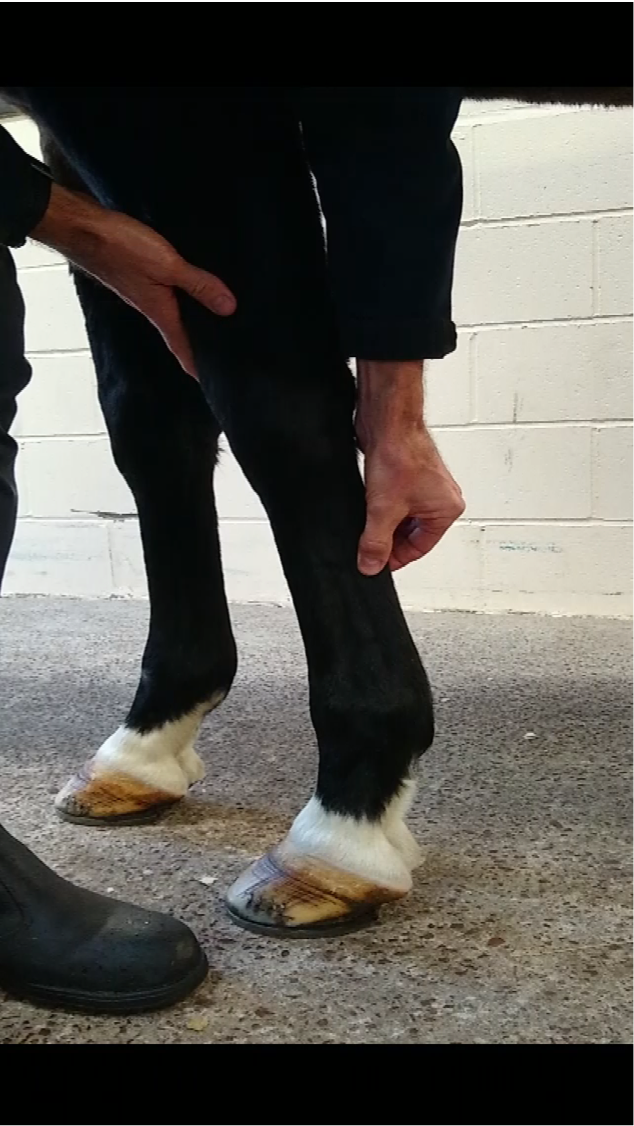

proximal to distal, along each structure in turn
How does the limb lifted affect the structures when palpating?
structures more pliable (not under tension)
can partially separate flexor tendons
What technique should you use to locate digital arteries?
Abaxial sesamoid nerve block technique
What does it mean when you can not detect the digital pulse strength?
normal (most likely)
poor technique
decreased strength
What does it mean when digital pulse is ‘just palpable’?
*takes 4-5 secs to be confident
normal
what does it mean when the digital pulse is immediately palpable?
increased strength
What is the significance of decreased strength of digital pulse?
poor peripheral perfusion caused by shock or loss of blood supply
What is the significance of increased strength of digital pulse?
distal limb inflammation
Which synovial cavity is most likely to be penetrated by this wound?
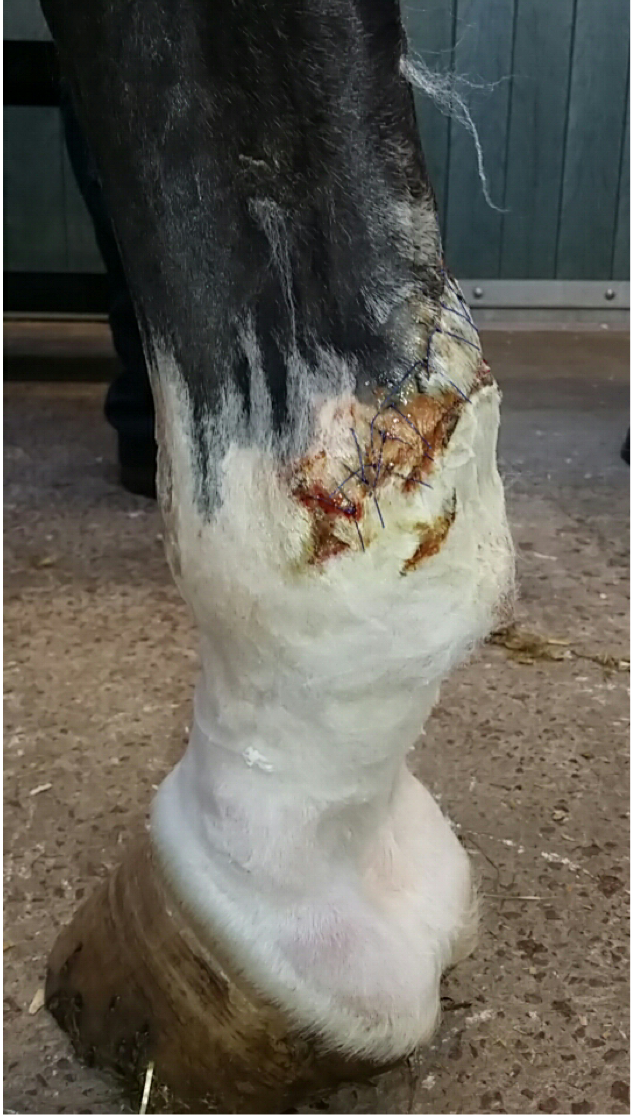
digital flexor tendon sheath
fetlock joint less likely as more dorsal
Your patient is severely lame of its right forelimb. Digital pulse strength in this limb is increased (“bounding”), right front hoof wall temperature is increased and there is a marked, localized response to hoof testers at the lateral sole. What are the likely causes of lameness?
foot abscess, solar bruise, laminitis (usually dorsal sole), fracture (often generalized)
Your patient has been showing signs of severe abdominal pain but is now obtunded (dull). It’s heart rate is very high. The distal limbs are cold to touch and you cannot palpate digital pulses. Why are the digital pulses not palpable?
Profound shock (likely to be caused by endotoxemia) causing very poor peripheral perfusion