medical interventions final sem 1
1/212
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
213 Terms
what holds together the antigen binding sites heavy and light chains?
disulfide bridges
antibodies are also called
glycoproteins
antibodies are a vital part of the…
immune system
where are antibodies found?
in the blood and other bodily fluids
antibodies are produced by…
b-cells
what do antibodies belong to?
a class of proteins called immunoglobulins (Ig)
main function of antibodies
recognize and initiate removal of foreign substances in the body (ex. bacteria or viruses)
antibodies consist of four _________________
polypeptide chains
what types of polypeptide chains make up antibodies?
two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains
what does the structure of antibodies form?
a y-shaped protein molecule
what are the 5 antibody isotype classes?
Ig: D, E, A, M, G
isotype
related antibodies but variations in heavy chain
isotypes vary _______ the antibody class
within
what is the same in isotype classes?
the two heavy and light chains
variations in isotypes occur within the
Ig
variations are due to differences in the __________ region
variable
what part of the antibody is extremely variable?
the region at the tip
what do isotypes allow for?
millions of antibodies to exist
many antigens to be recognized
antigens
foreign substances or materials that do not belong in the body (bacteria or viruses)
explain antibody recognition of antigen
recognizes on specific region of antigen called epitope
what is the region called that is recognized on the antigen?
epitope
explain antibody (epitope) recognition
specific “induced fit” between the antibody variable regions
what can antibodies bind to?
only their binding antigen
when the antibody binds to the antigen
the antigen is tagged to be destroyed by immune system
antibody survival
must undergo activation to survive
activation
causes rapid proliferation of B-cells
makes more copies of antibodies
how often does the body make antibodies?
continuously
what happens to antibodies that do not recognize an antigen?
they are destroyed
what are ELISA tests based on?
immune system antibody molecules
what does ELISA stand for?
Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay
what does ELISA utilize?
enzymes (enzyme-linked)
enzyme linked
enzymatic reastion produces colorimetric changes
linked (attached) to an antibody
immuno
based on immune system “component”
sorbent
antibody or antigen must be “affixed” to surface
assay
qualitative and quantitative investigative procedure
ELISA determines
the presence of a substance
what substance is usually being determined in ELISA?
an antigen, in a liquid sample or wet sample
what kind of tool is ELISA
a common health diagnostic tool
what is ELISA performed on?
ELISA plates that contain multiple “wells”
ELISA is based on
antigen/antibody interactions
previous assays required
radioactivity
ELISA developed year
1960
radioactive substance linked to
antibodies or antigens
what did sensitive equipment detect in previous ELISA?
the emitted radioactive signals
what’s the problem with radioactivity?
radioactivity kills
why did they change from old ELISA?
a safer, non-radioactive, signal was desired
some enzymative reactions can produce _______
color
what is the enymatic reason equation?
enzyme + substrate —enzyme substrate complex—> product
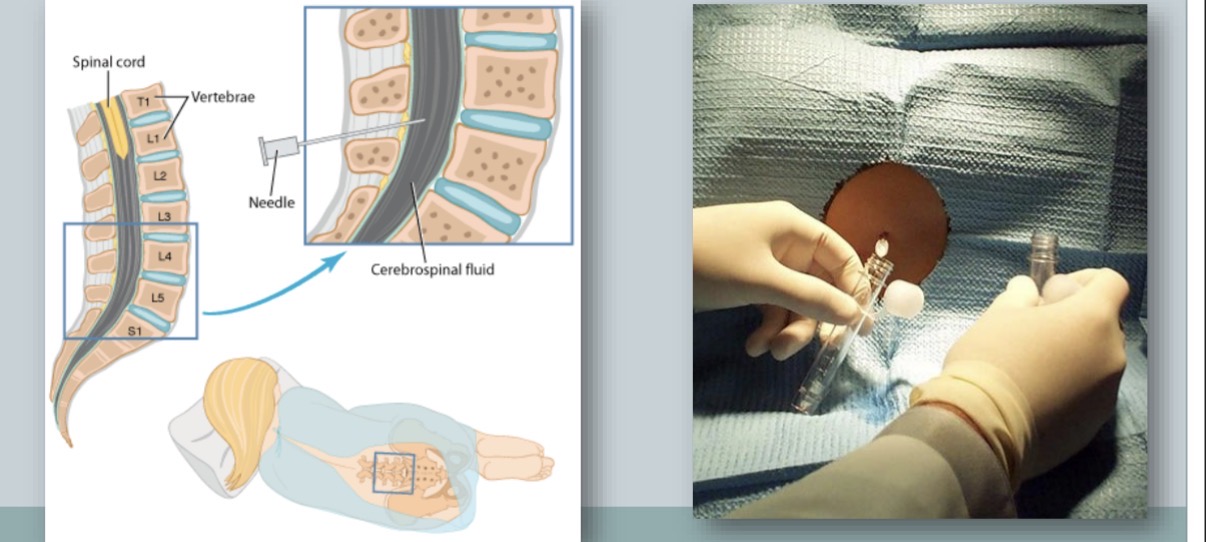
lumbar puncture procedure to obtain cerebrospinal fluid (CS)
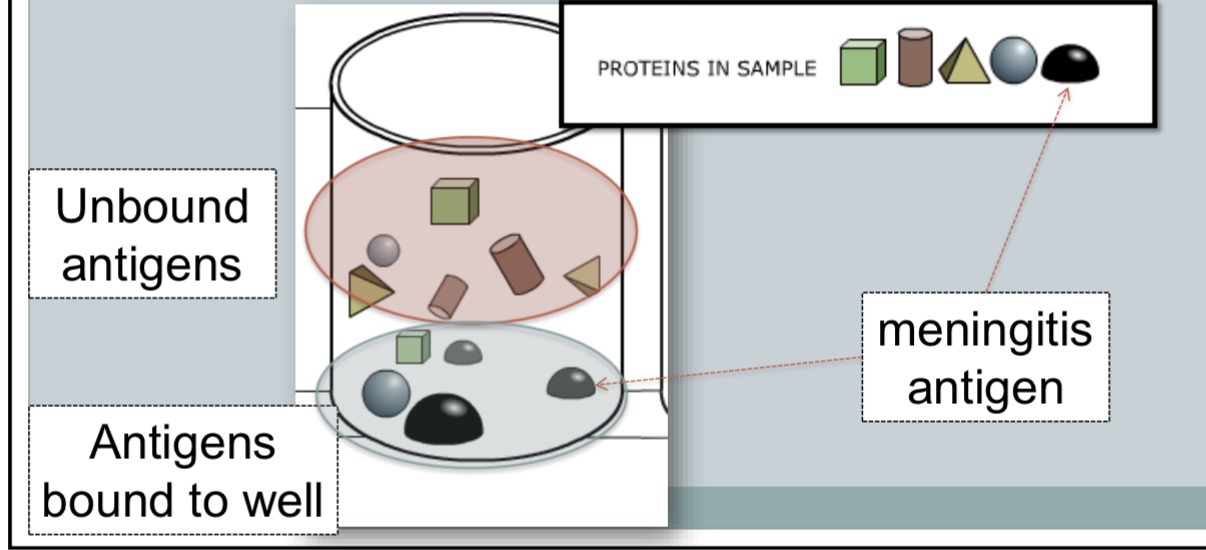
analyte (CSF) placed into well
proteins in analyte bind to plastic wells
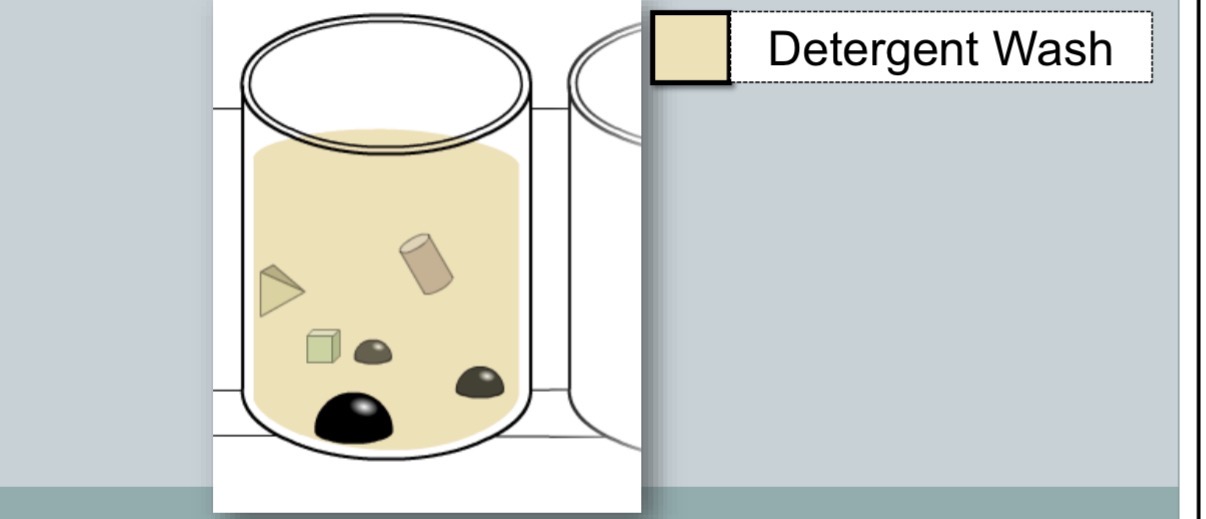
detergent wash to remove unbound antigen
block remaining surface of wells
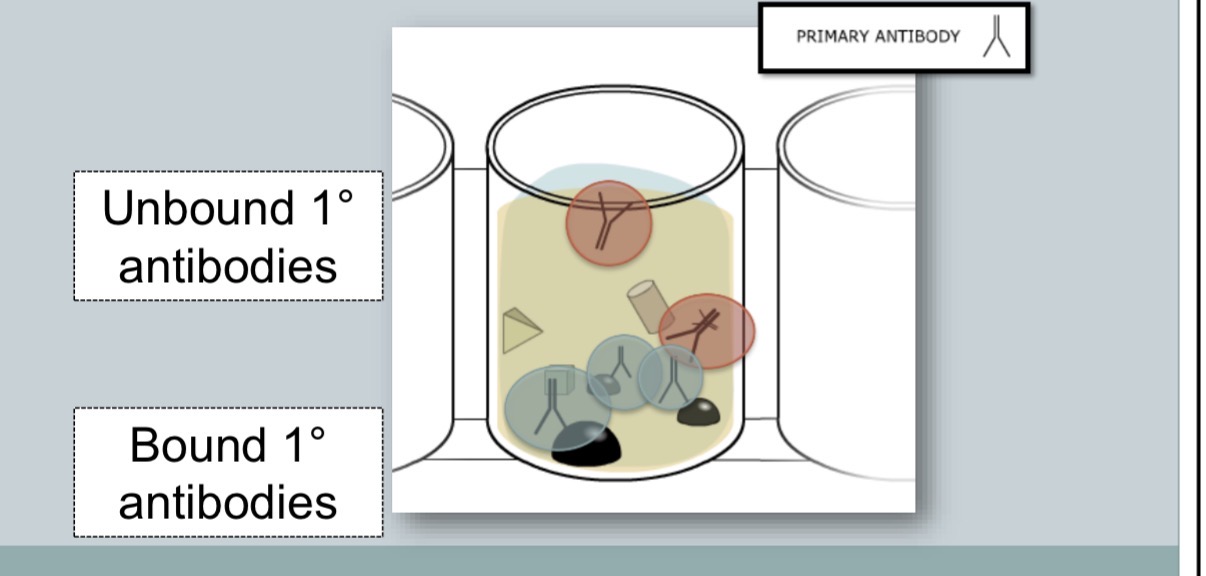
primary antibody binds to specific antigen
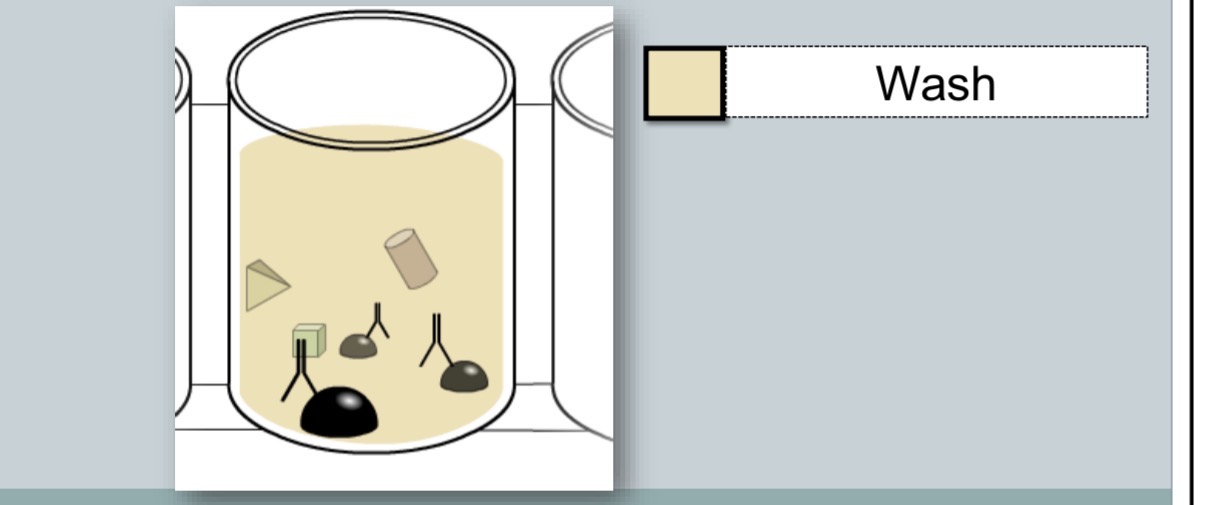
common wash steps
unbound primary antibody is washed away
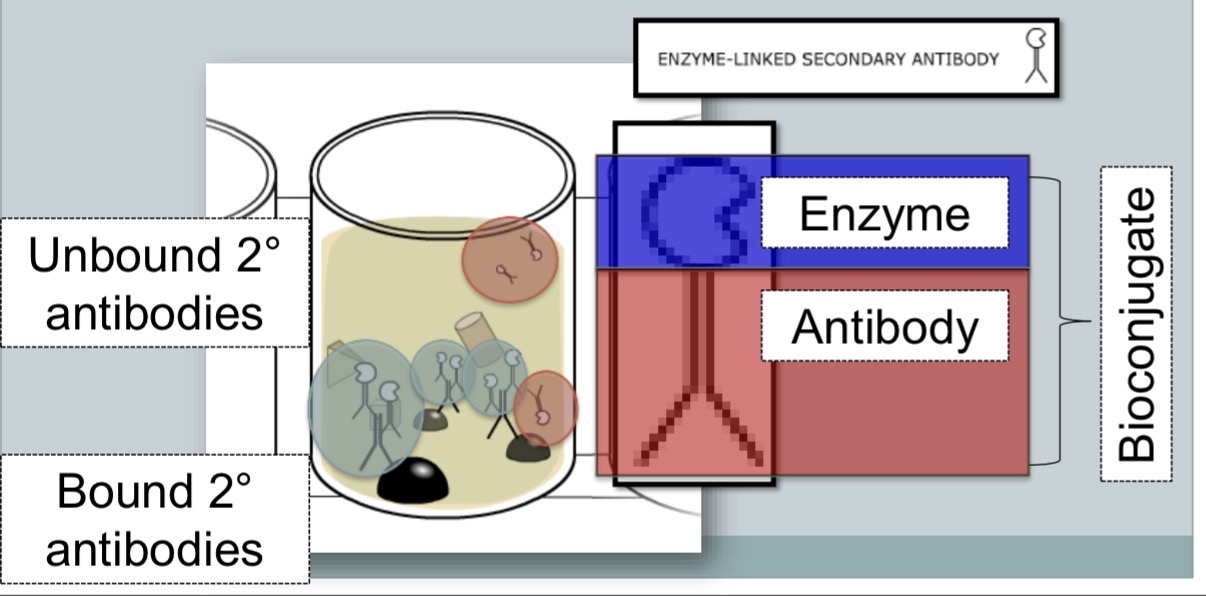
enzyme linked secondary antibody (bioconjugate) binds to primary antibody
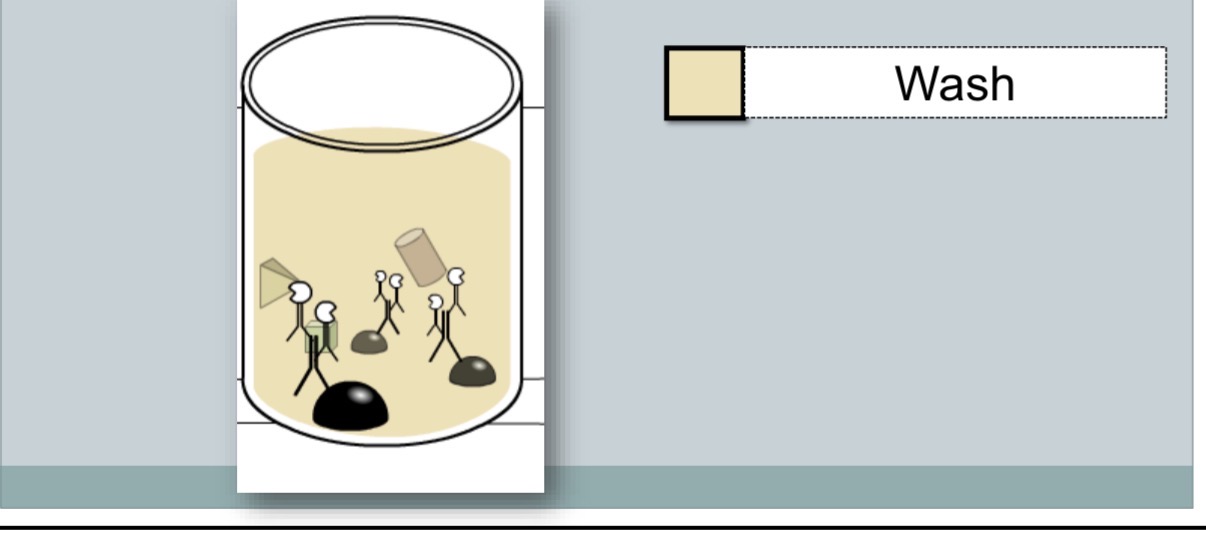
common wash steps
unbound secondary antibody is washed away

enzyme substrate is added
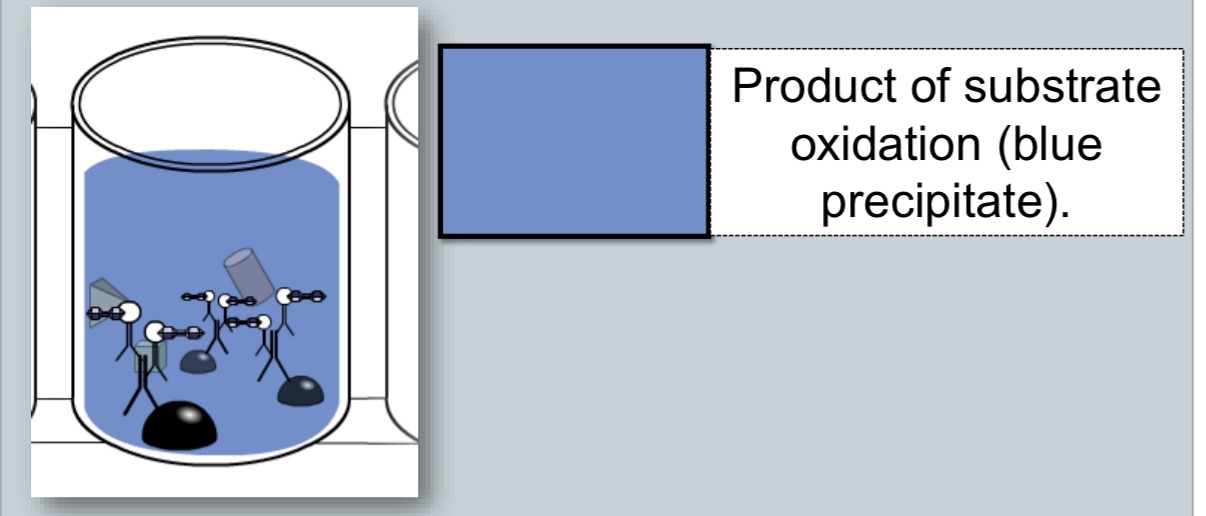
common ELISA enzyme
peroxidase
common ELISA substrate
3,3, 5,5 tetramethylbenzidine (TMB)
peroxidase/TMB reaction
enzymme (peroxidase) + substrate (TMB) —> colorimetric product
what does it mean to add the enzyme to the antibody?
it is enzyme linked, taking advantage of color changes
when was modern ELISA born?
1971
what are the three types of ELISA?
competitive
direct/sandwich
indirect
explain the 5 steps of direct ELISA
the ELISA plate it coated with the primary antibody (specific to antigen)
2. non-reacting protein added to block any plastic surface remaining uncoated by the antigen (wash buffer)
antigen introduced to well and bind to the antibody if recognized
secondary enzyme linked antibody is introducted, specific for antigen of interest and binds to antigen
substrate TMB added to reaction
explain the 5 steps of indirect ELISA
analyte is added to each well where proteins adhere to the plastic (charging interactions of plastic and antigens)
non-reacting protwin is added to block and plastic remaining uncoated
primary antibody introduced and binds to bound antigens if recognized
secondary enzyme linked antibody introduced and binds to primary antibody
substrate TMB added to reaction (colorimetric)
ELISA test results are both ________ & _______________
qualitative and quantitative
the colorimetric change is directly proportional to the ______
amount of anitgen
nucleoid
region within bacteria visible in transmission electron micrographs
most DNA is here
not bounded by a membrane
plasmid
small circular DNA fragments found in cytoplasm
contain code responsible for antibiotic resistance
can be transferred between bacteria
flagella
purpose is motility
long rotating appendages, rotate by means of a motor in cell envelope
bacteria can have one or many
ribosomes
where protein synthesis occurs
mRNA is read by ribosome and amino acids are made into a protein
cell wall
rigid structure that provides shape to cell and protects it from osmotic pressure
endotoxins
toxic lipopolysaccharides found in outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria
can trigger immune responses in the host
plasma (cell) membrane
phospholipid bilayer responsible for diffusion & transport of materials between cytoplasm and environment
capsule
layer of polysaccharide (sometimes proteins)
protects call & is often associated with pathogenic bacteria because it is a barrier against phagocytosis by white blood cells
can be seen by viewing bacteria in india ink
pili
hollow, hairlike strucutres made of protein
allow bacteria to attach to other cells
the sex pilus allows transfer of plasmid DNA from one cell to another
also called fimbriae
what color does each type of bacteria stain?
gram-negative: red
gram postive: blue
penicilins
disrupt formation of peptidoglycan layer
works on both gram positive and negative
tetracyclines
inhibits the 30s ribosomal subunit, which disrupts protein synthesis
works on both gram positive and negative
fluroquinolones
target enzymes gyrase and topiosomerase
mainly affect gram negative
sulfonamids
attack metabloic pathways through folic acid synthesis
works on gram positive and gram negative
what type of bacteria is Neisseria meningitidis
gram negative
bacteriocidal
destroys bacterial cells
bacteriostatic
delaysdisrupts future cell growth
wht is gram status based on
graim stain devloped by hans christian gram
what are gram stain based on
cell wall/envelope
characteritics of gram positive bacteria
thick peptidoglycan layer
no lipopolysaccharides present
simple cell wall
characteristics of gram negtaive bacteria
thin peptidoglycan layer
lipopolysaccharides present
complex cell wall
peptidoglycan lager (PGL)
mesh of peptides (proteins) and sugars
lipopolysacharise (LPS)
mesh of fats and sugars
coccus
round
bacillus
rod-shaped
curved
vibrio
spirillium (spyrogyra)
spiral
singular arrangement
by itself
cocus
bacillus
diplo
pairs (2)
diplo coccus
diplo bacillus
stepto
string of 3 or more
staphylo
clustered (grapelike)
tetrad
stacked pairs
ampicillin characteristics
invented in 1961
penicillin class
traets both gram neg and pos
inhibits a bacterial enzyme that helps build cell wall
B lactamase disrupts ring structure of ampicilin