Parallel and Series circuits
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
what happens to resistance in a parallel circuit when more components are added
adding more components to a parallel circuit decreases the total resistance ® of the circuit. Connecting more components into the circuit in parallel causes more current to flow through the cell, not less.
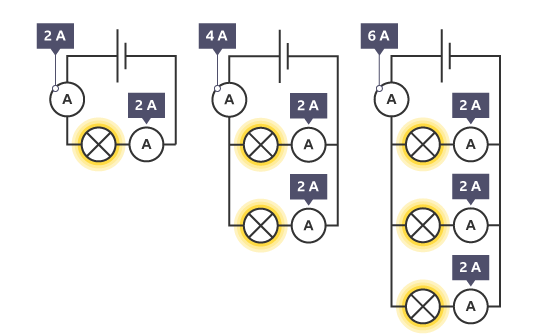
what happens If the components in a parallel circuit have different resistances
a different amount of current will flow through each branch but more current flows through paths of less resistance which can help you work out which components for more resistant than others
The total current into a junction equals the total current out of a junction.
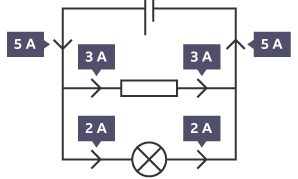
what happens to resistance in series circuit when components are added
-resistance increases when more components are added to a series circuit so the current decreases
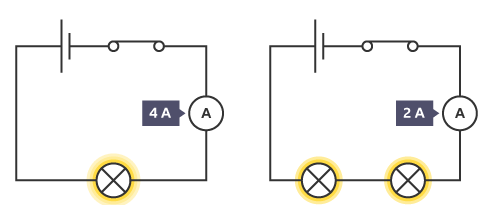
describe the current in a series circuit
-the current remains constant throughout the circuit as there is only one path for the current to flow
describe the current in a parallel circuit
current can have different values in different parts of a parallel circuit. This is because there are multiple paths for current to flow.
The current is shared between the different branches of the circuit
what happens to the potential difference in a series circuit
The potential difference produced by the cell is shared equally between the identical resistors, so there is 3 V of potential difference across each resistor.
If the components in a series circuit have different resistances, the potential difference does not divide equally across them but will still divide
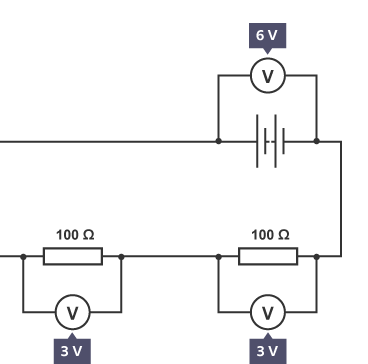
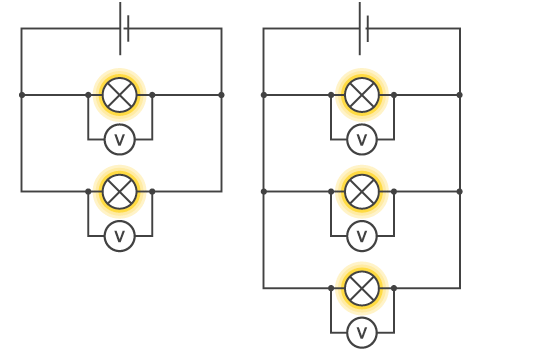
what happens to the potential difference in a parallel circuit
In a parallel circuit, the potential difference across each branch of the circuit remains constant between components
If more lamps are added to a parallel circuit, all the lamps continue to glow brightly because the potential difference is the same across all branches of a parallel circuit. All the lamps in these circuits will glow with the same brightness.
ohms law
V = IR
v=potential difference
I = current
R = resistance
states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference (voltage) across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance of the conductor.
why does current increase in a parallel cricuit
The circuit has more paths for current.
Each new path draws its own current.
The source works harder to supply the total needed current by more charge flowing per second but the amount of charge the source is constant