Forensic Anthropology Exam 2
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
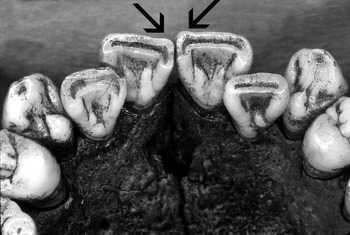
Shovel-shaped incisors
A dental trait most commonly found in East Asian and Native American populations.
Double shoveling
A dental trait largely observed in New World populations.
Four-cusped first molars
A dental trait more common in Northern Europeans.
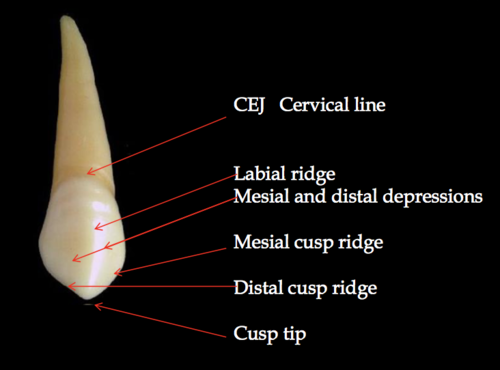
Mesial canine ridge (Bushman canine)
A trait most common in San and West Africa, with low frequency elsewhere.
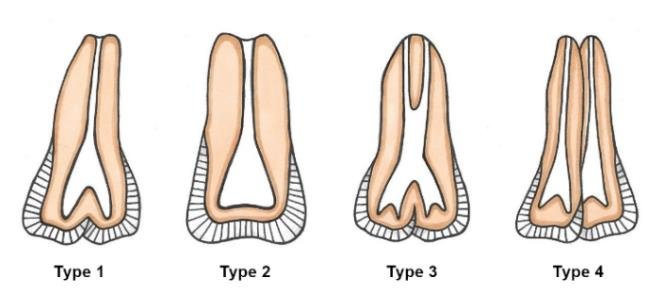
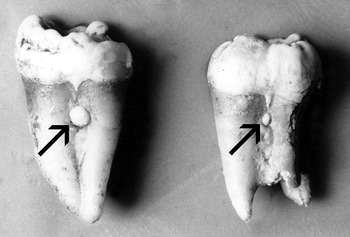
Double root occurrence
A trait occurring in about 5% of Europeans but nearly absent in other populations.
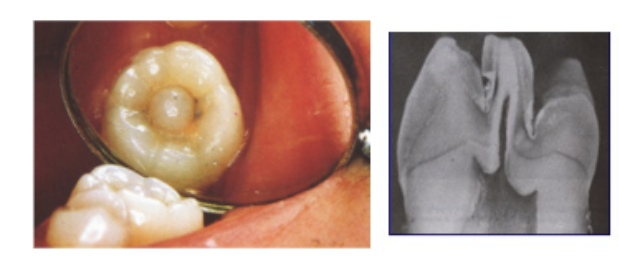
Odontomes
Dental anomalies most common in East Asia, occurring at a rate of 4-7%.
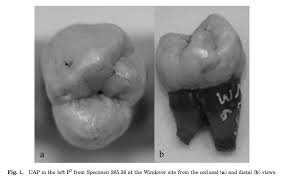
Distosagittal ridge
A dental trait only found in Aztec-derived populations. (Uto-Aztec premolar)
Hypocone absence
A dental trait most common in Northeast Siberia/Arctic and Western Europe, least common in Sub-Saharan Africa and Sahul-Pacific regions.
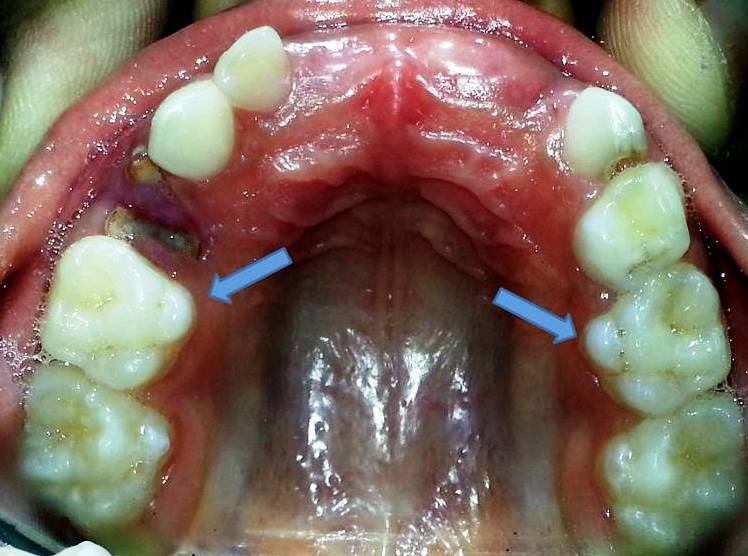
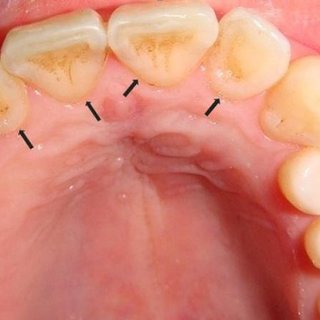
Carabelli's cusp
Dental trait not common in East Asia but moderately common elsewhere, especially in Europe.
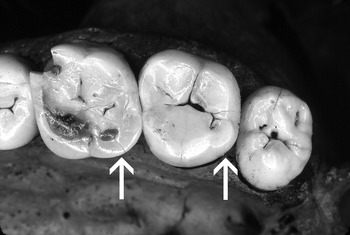
Cusp 5 on lower molars
A dental trait most common in West Africa and Australia.
Enamel extension and enamel pearls
A dental trait most common in East Asia and nearly absent elsewhere.

Hypoconulid absence on M1
A dental trait that shows varying frequencies across populations, more common in Northern and Western Europe.
Hypoconulid absence on M2
A dental trait more pronounced absence in Northern Europe compared to other regions.
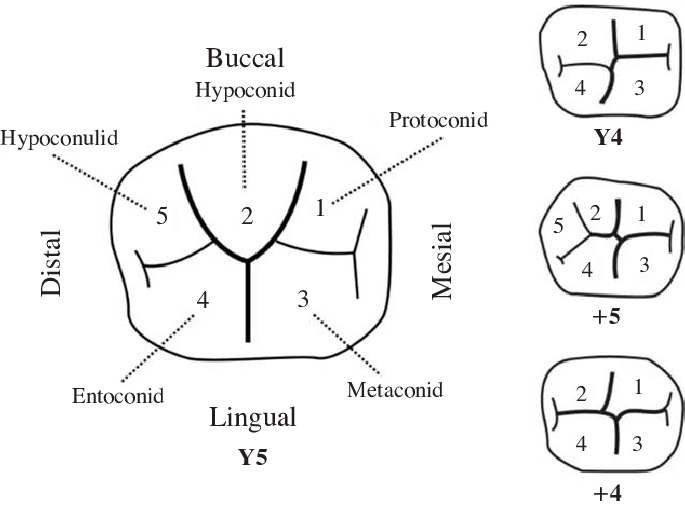
Y5 groove pattern
A dental trait most common in the San population, with less than 30% frequency elsewhere.
Cusp 7 on lower molars
A dental trait that has a high frequency in Sub-Saharan Africa.
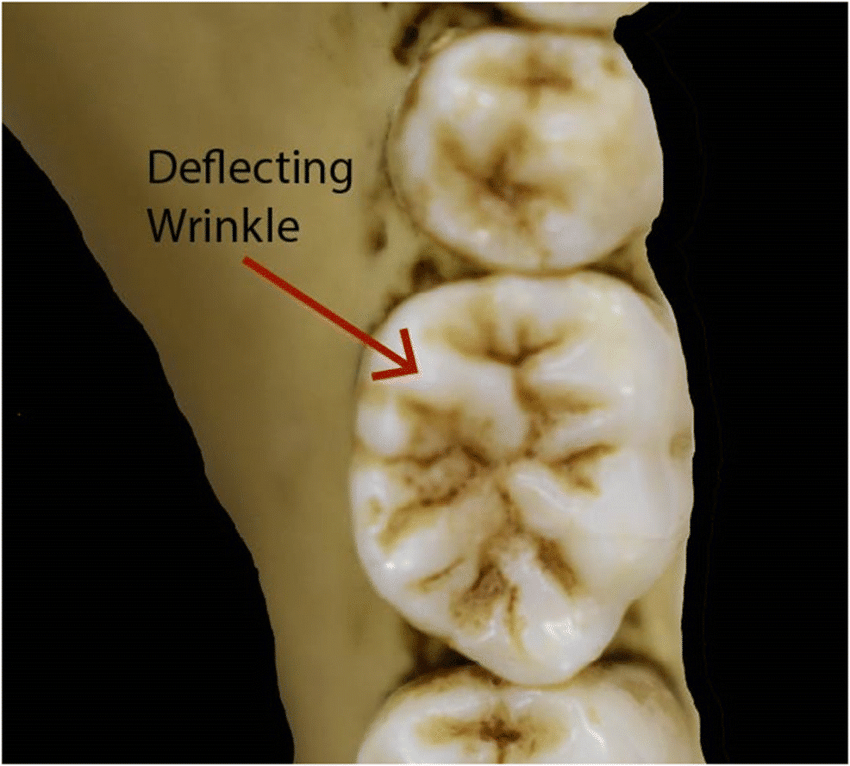
Deflecting wrinkle on lower molars
A dental trait highly frequent in West Africa, moderate in the rest of Africa, and rare elsewhere.
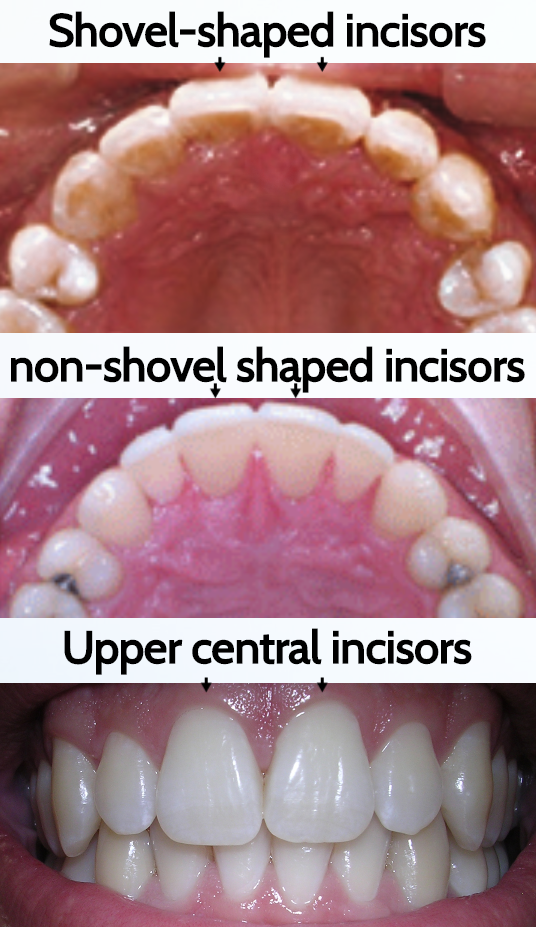
Sinodonty
A dental morphology pattern characterized by shoveled upper incisors and specific root structures, historically associated with East Asian and Native American populations. (the name for these combination of traits)
Eruption of last permanent molar
Typically occurs between 17-21 years of age.
Deciduous Teeth Size and Shape
A dental trait generally smaller than their permanent counterparts, have thinner enamel, and shorter roots.
Number of Deciduous Teeth
20
Number of Permanent Teeth
32
Presence of Premolars in Deciduous Dentition
Deciduous dentition does not include premolars; the deciduous molars are replaced by the permanent premolars.
Timing of Permanent Teeth Eruption
Begin to erupt around 6 years of age and continue into early adulthood.
Root Development in Permanent Teeth
As permanent teeth develop and erupt, the roots of the deciduous teeth resorb, leading to the eventual shedding of the baby teeth.
Sexual Dimorphism
Morphological differences that are influenced by hormones and functional differences.
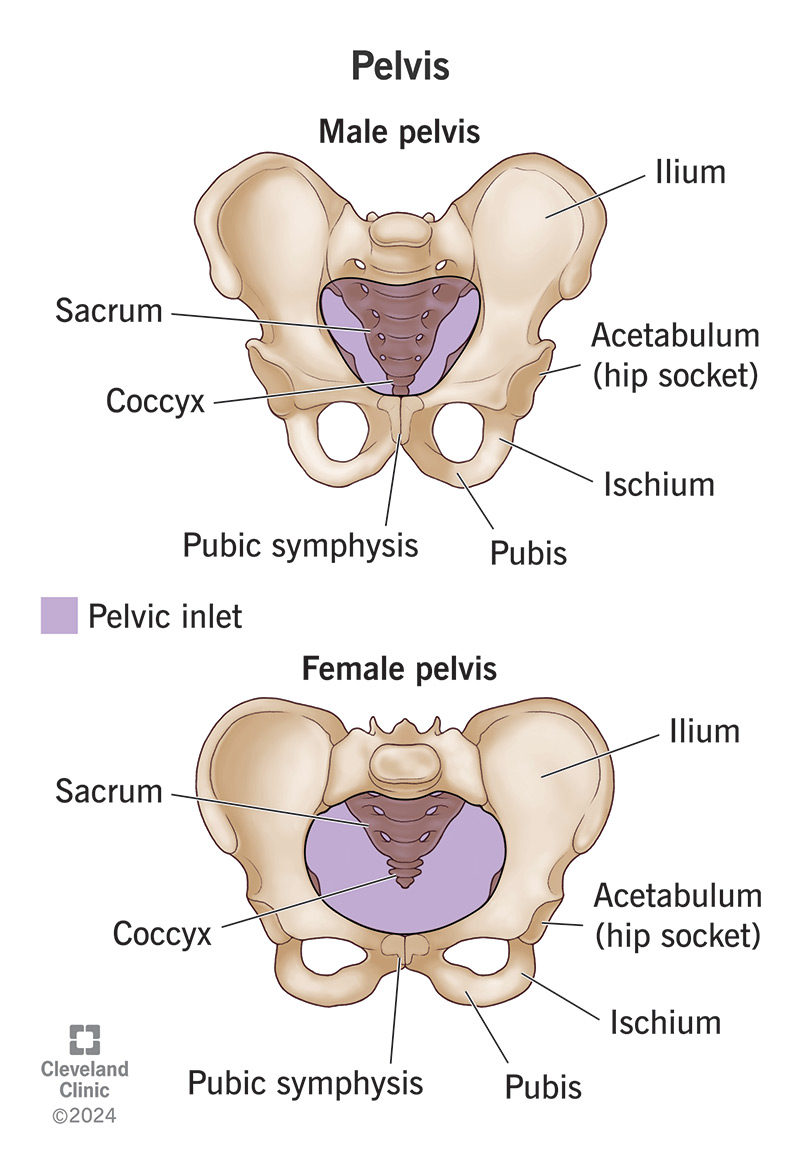
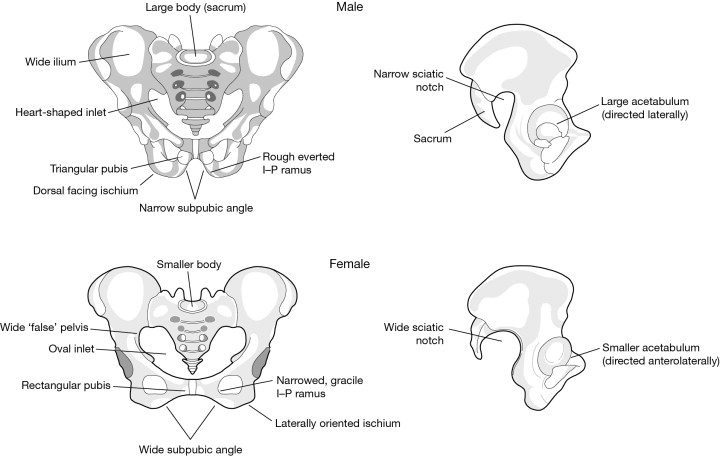
Pelvic Inlet in Males
Heart-shaped, constricted pelvic inlet.
Pelvic Inlet in Females
Ovoid and open pelvic inlet.
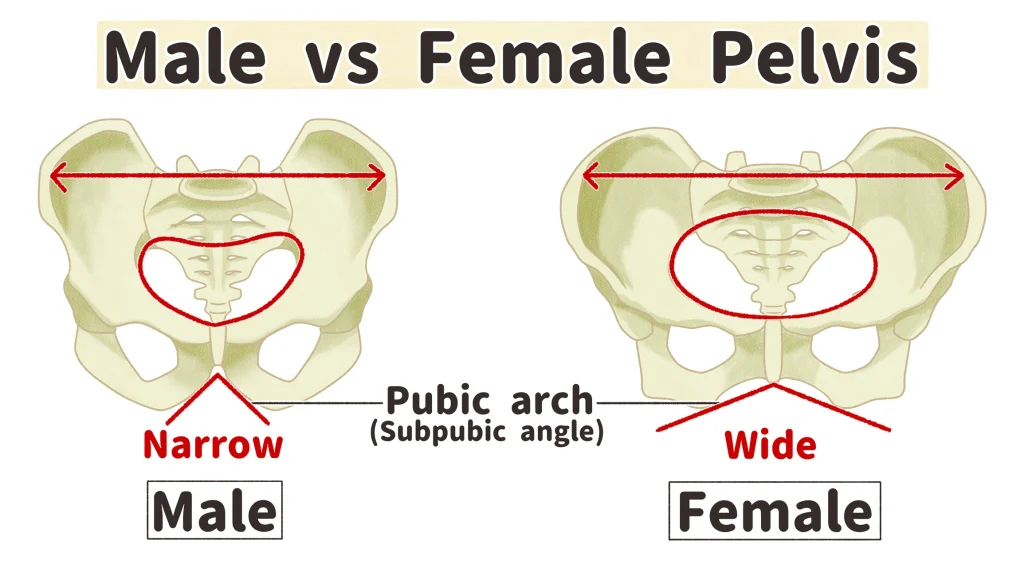
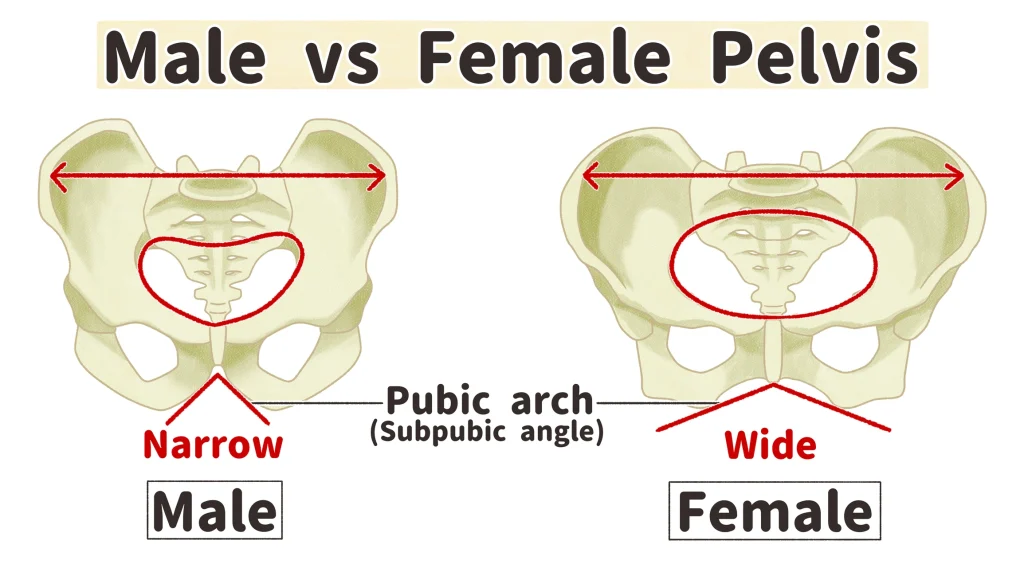
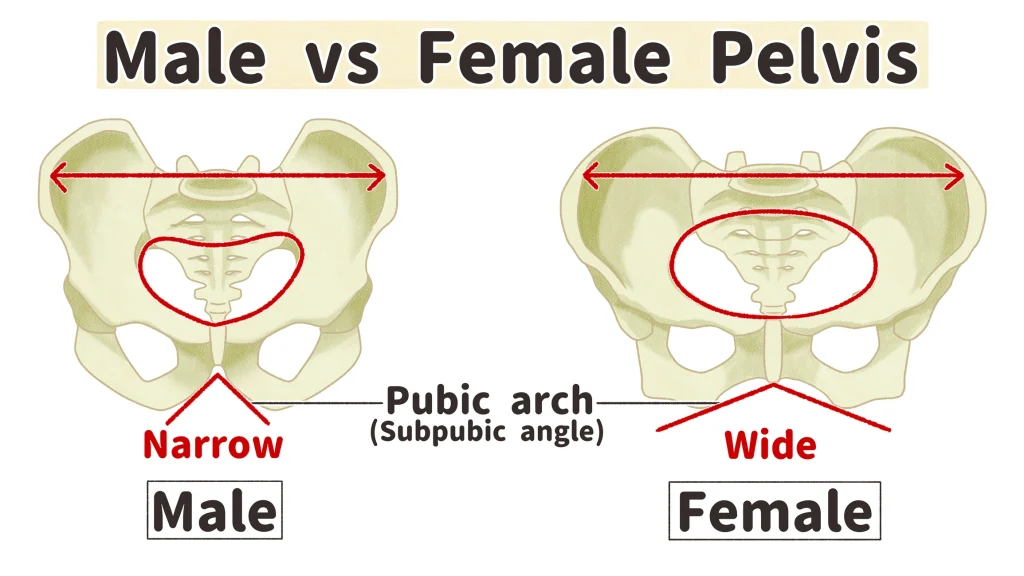
Subpubic Angle in Males
The angle formed where the two pubic bones meet is less than 90° (acute) males.
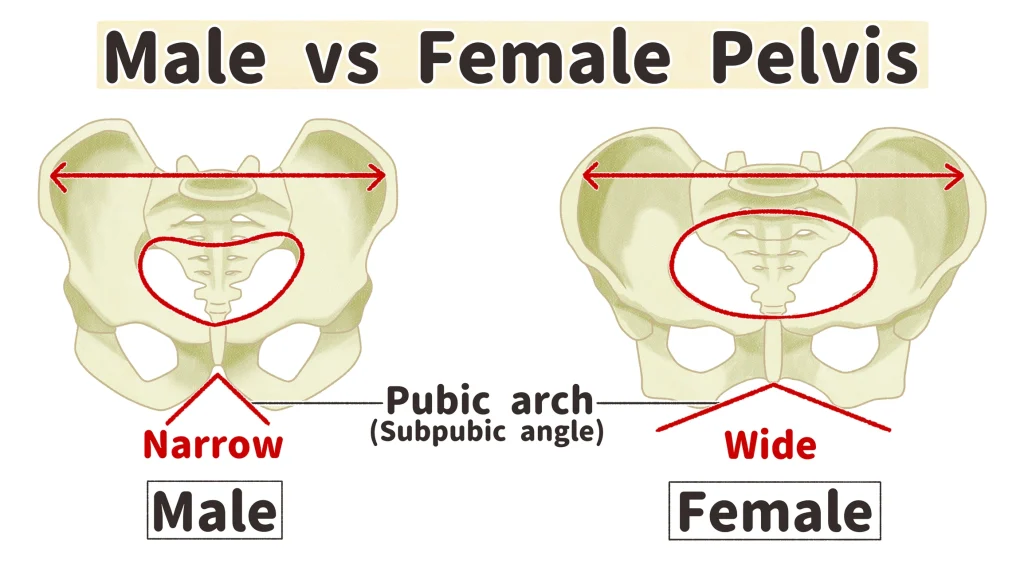
Subpubic Angle in Females
Angle is greater than 90° (obtuse).
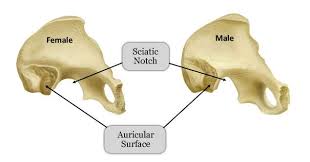
Greater Sciatic Notch in Males
The sciatic notch is narrow and acute.
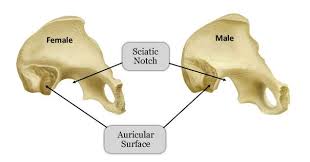
Greater Sciatic Notch in Females
Sciatic notch is wider and more sloping.
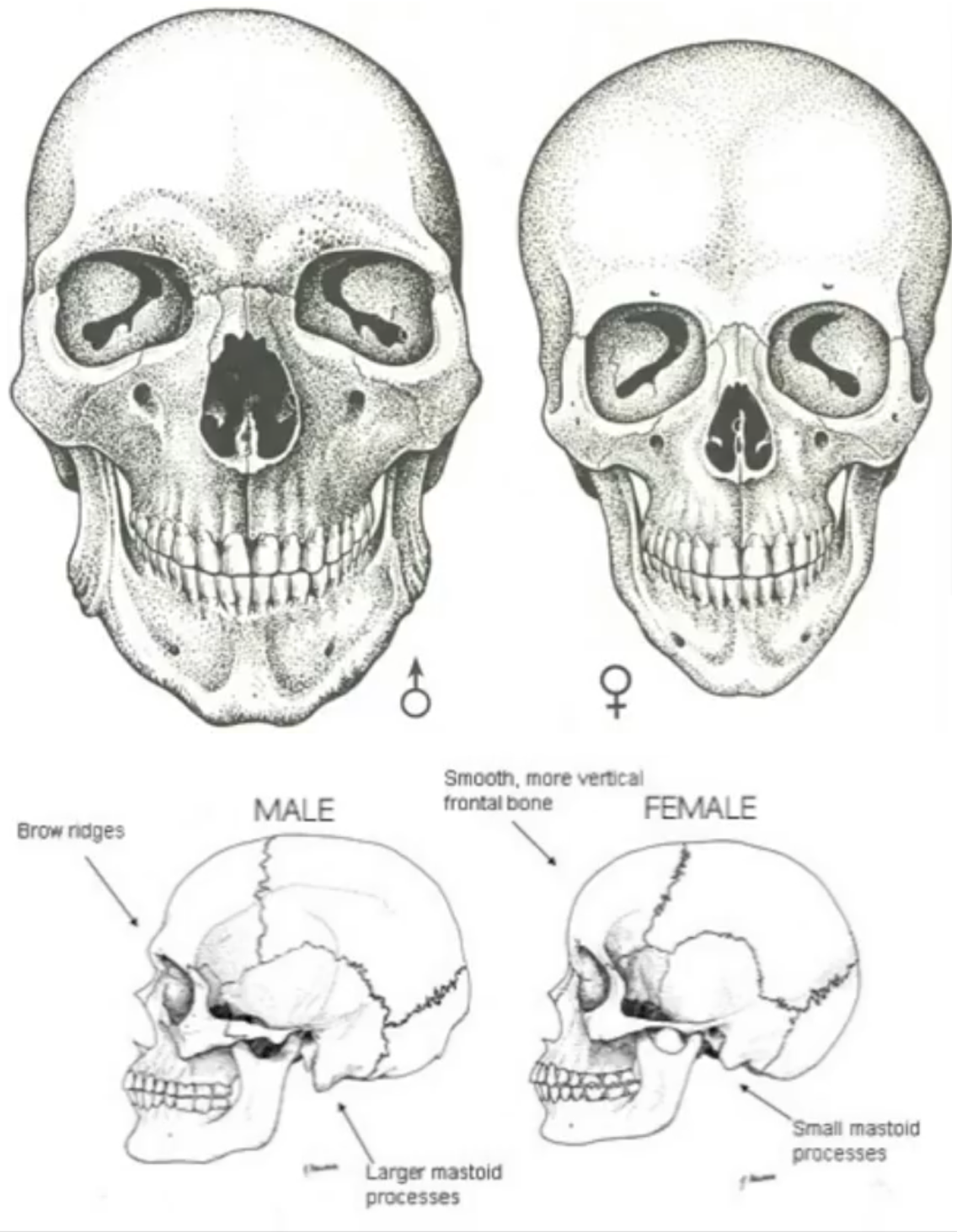
Ilium in Males
The ilium tends to be more vertical and higher.
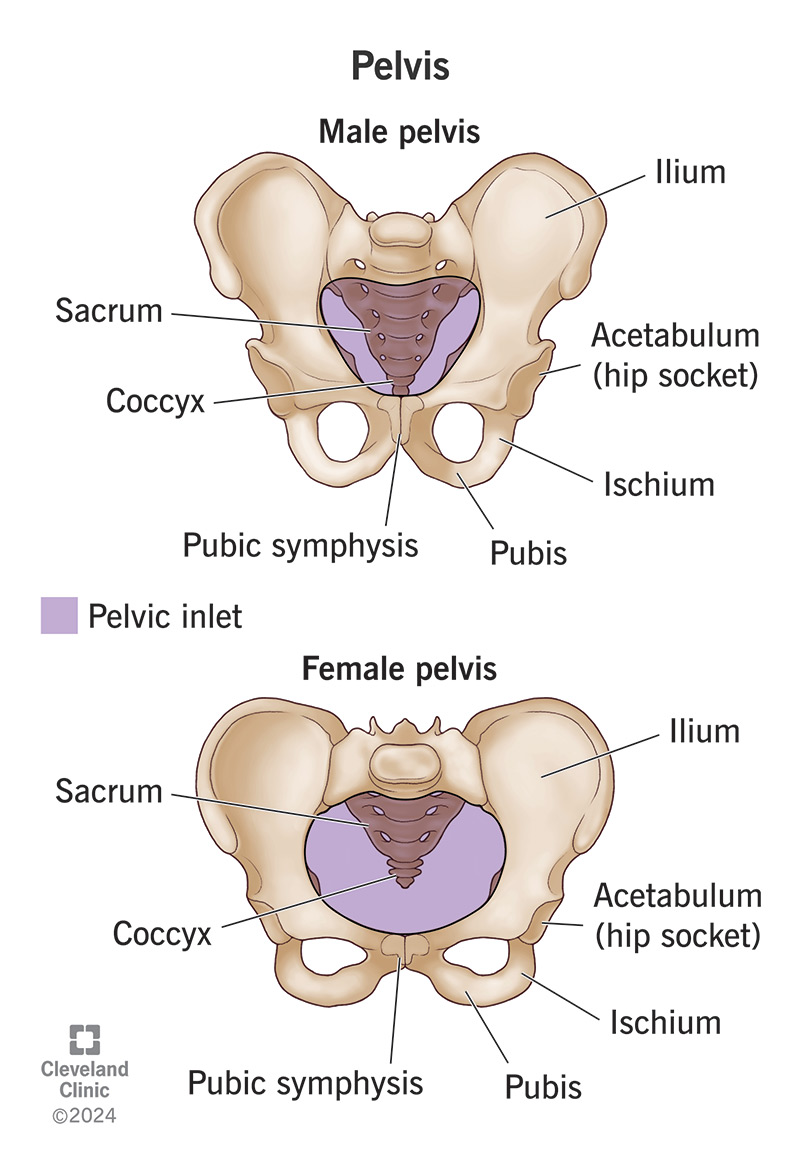
Ilium in Females
The ilium is often more flared and wider.
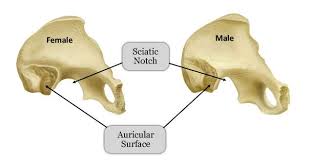
Auricular Surface Shape in Males
The auricular surface tends to be longer and narrower.
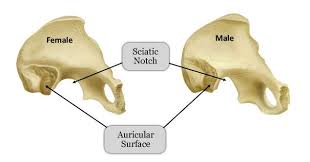
Auricular Surface Shape in Females
The auricular surface tends to be shorter and wider.
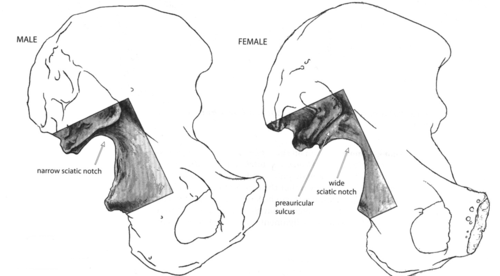
Preauricular Sulcus in Females
The preauricular sulcus is often wide and present.
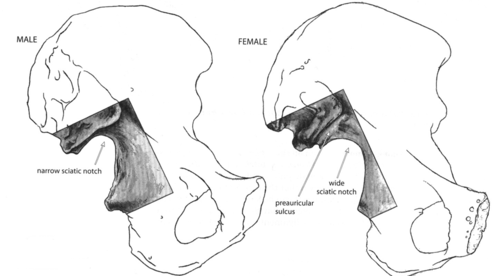
Preauricular Sulcus in Males
Preauricular sulcus is typically absent or less pronounced.
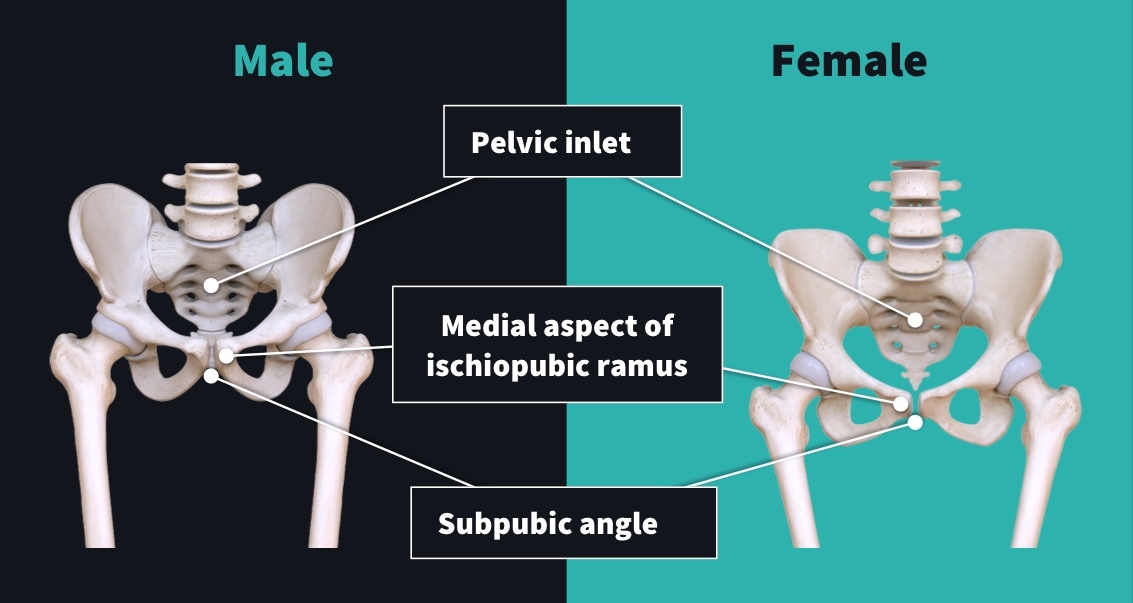
Medial Aspect of the Ischiopubic Ramus in Females
The medial aspect of the ischiopubic ramus is narrow with a ridge.
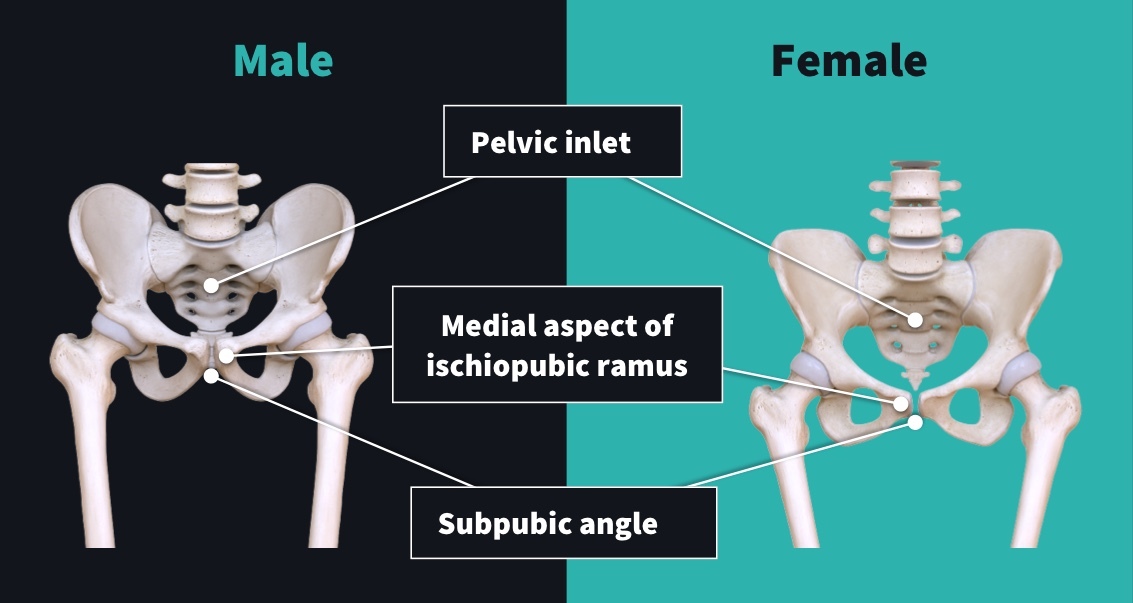
Medial Aspect of the Ischiopubic Ramus in Males
The medial aspect of the ischiopubic ramus is broad with no ridge.
Ischial Spines in Males
The ischial spines tend to be more medially projecting.
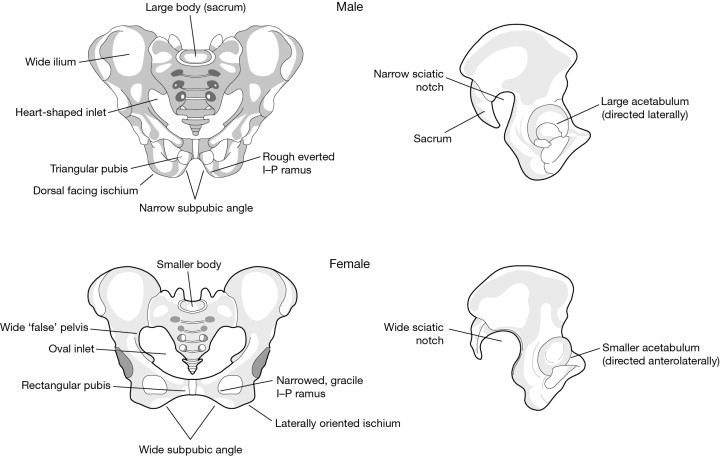
Ischial Spines in Females
The ischial spines tend to be less projecting.
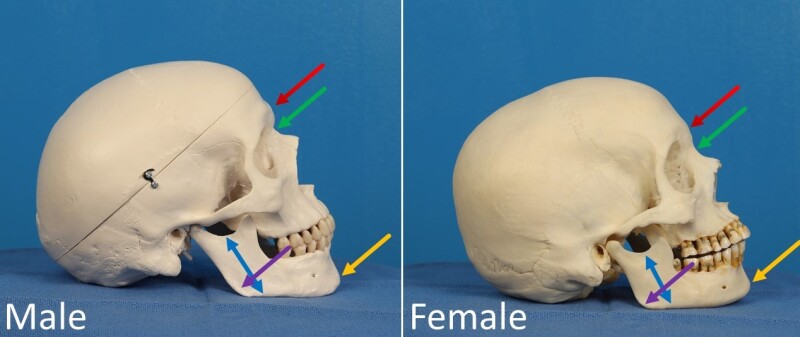
Overall Size and Robusticity of Male Skull
The skull is generally larger and more robust with thicker bones and more pronounced muscle markings.
Overall Size and Robusticity of Female Skull
The skull is typically smaller and more gracile.
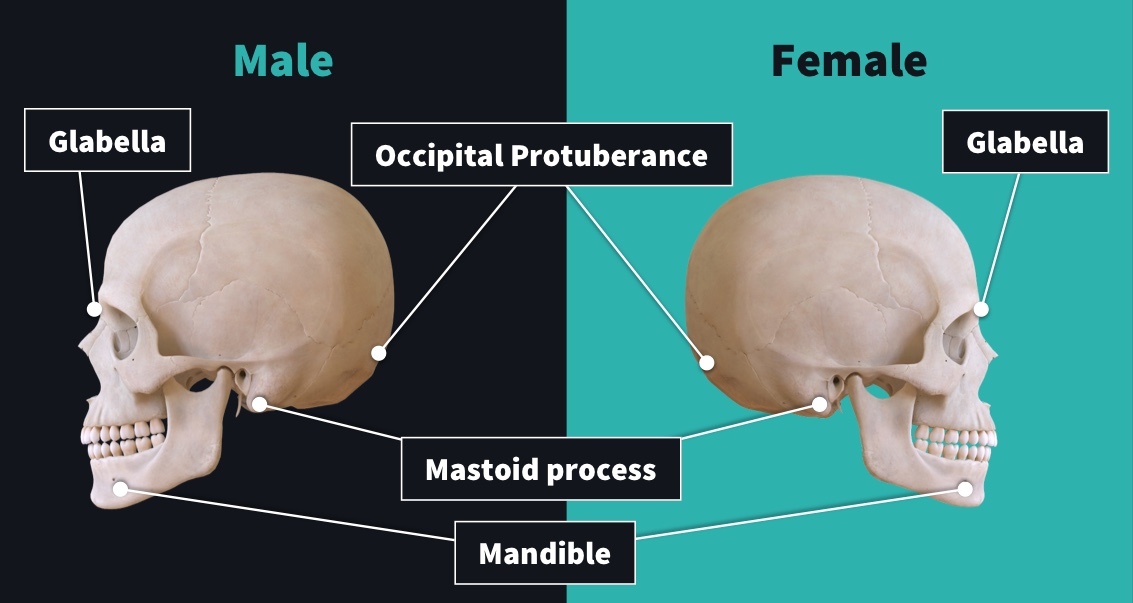
Glabella in Males
The glabella is more pronounced, leading to a more sloping forehead.
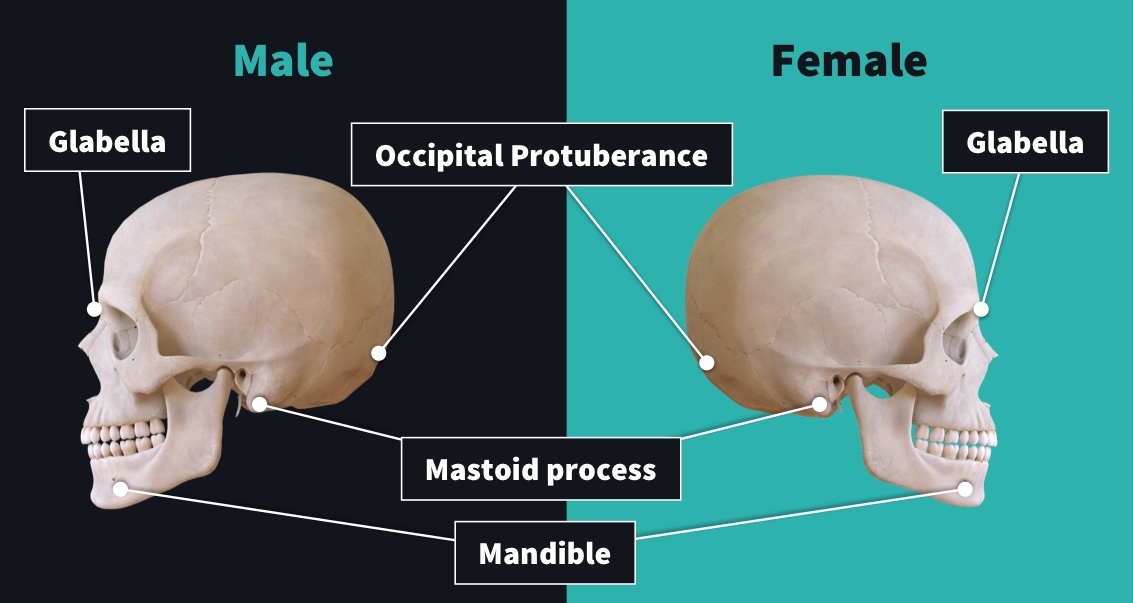
Glabella in Females
The glabella is flatter and has a taller forehead.
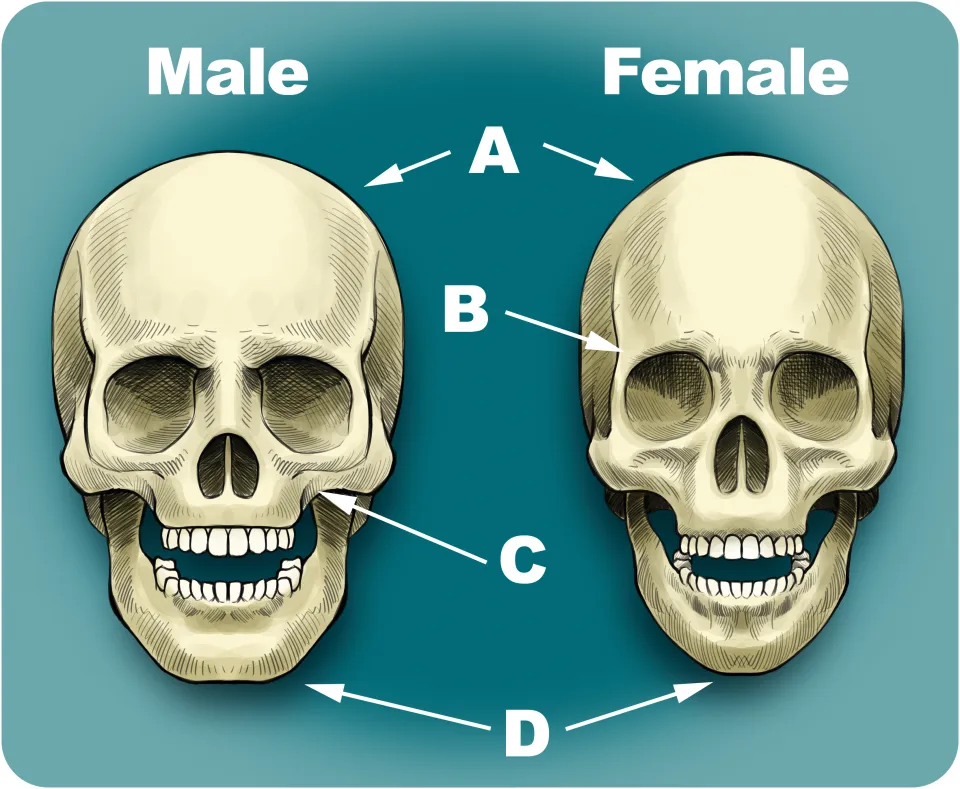
Supraorbital Torus in Males
A more pronounced supraorbital torus.
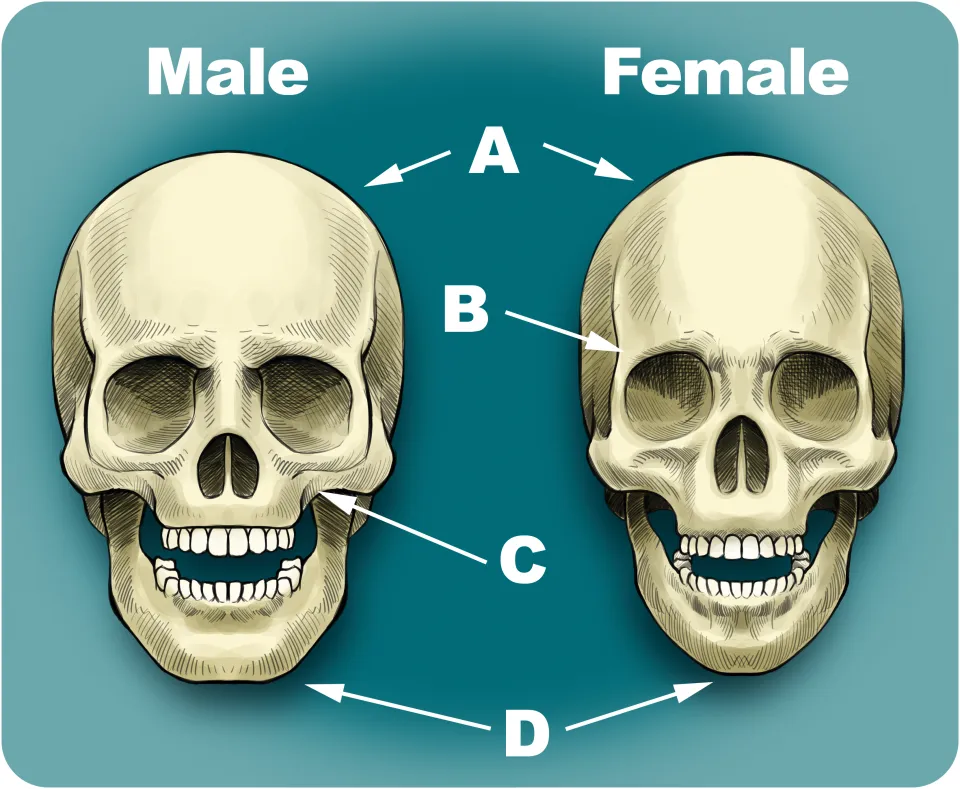
Supraorbital Torus in Females
The brow ridges are typically smaller or absent.
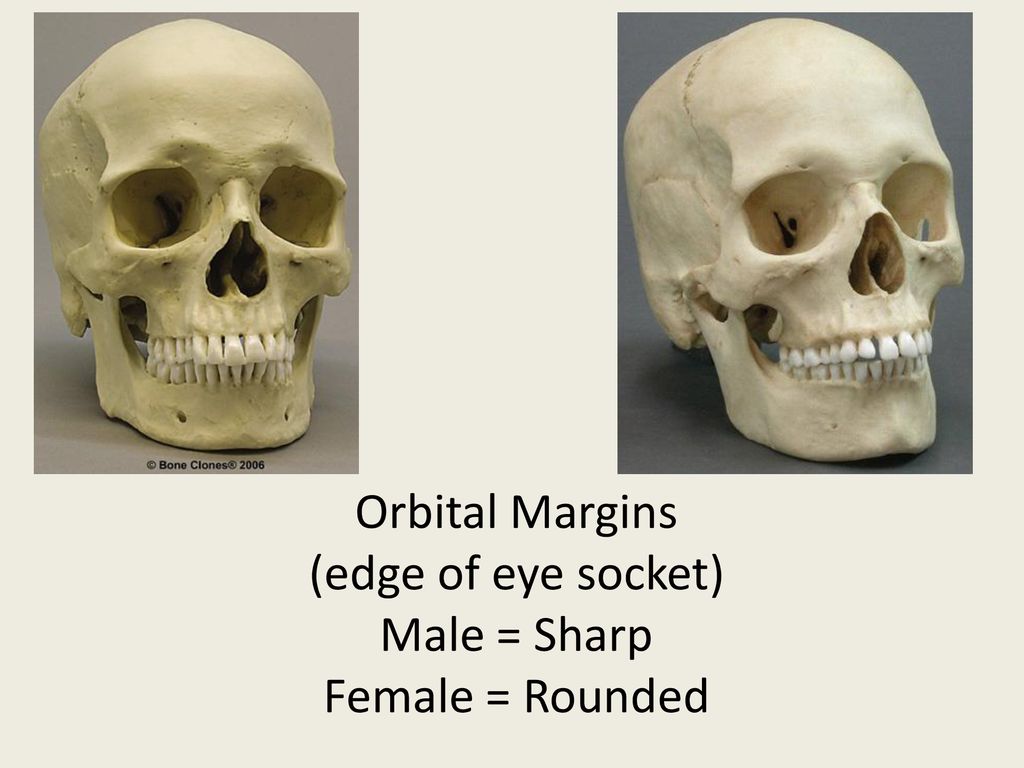
Orbital Margins in Males
Tend to be more square in shape with rounded margins.
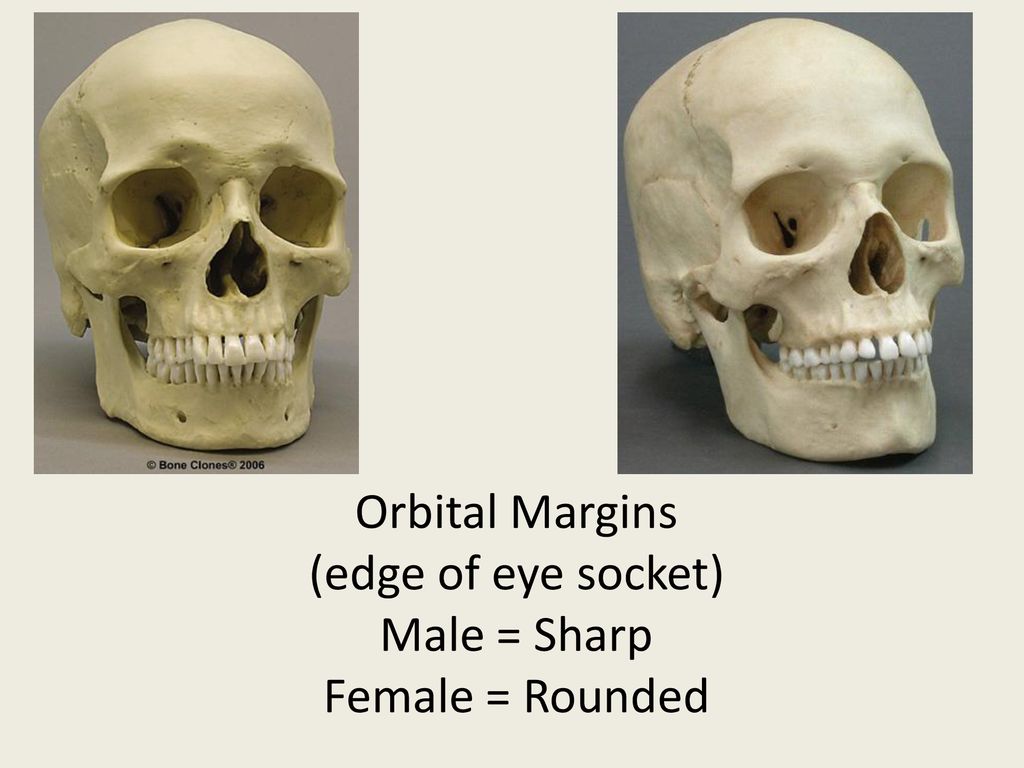
Orbital Margins in Females
Often more rounded in shape with sharp margins.
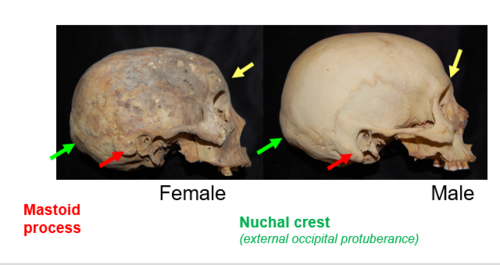
Nuchal Crest in males
The nuchal crest is typically more protruding, even hook-shaped, with the inion being more pronounced. the nuchal crest is usually rounded and non-protruding.
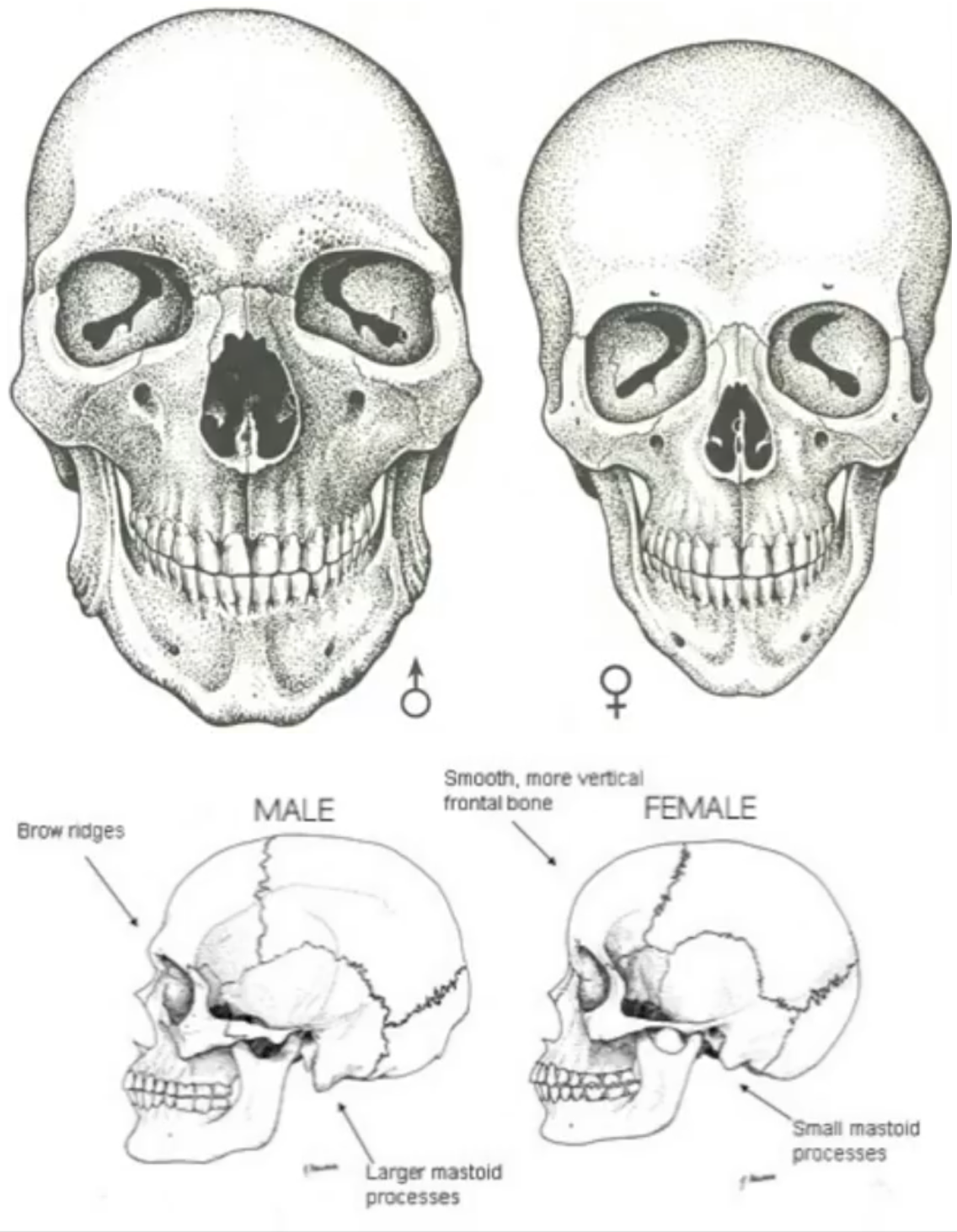
Zygomatic Arch in females
The zygomatic arch is generally thinner and does not extend as far past the external auditory meatus.
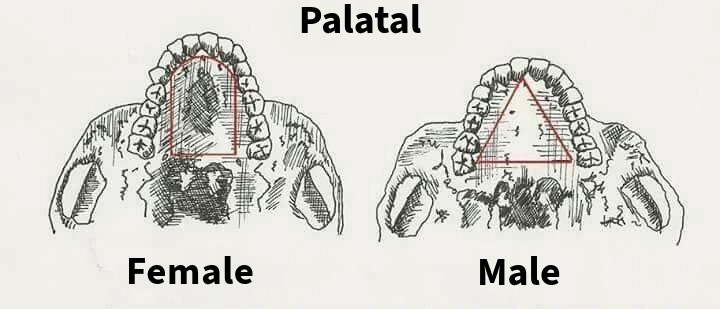
Male palate
The palate tends to be wider.
Long Bone Measurement Steps
To measure long bones like the femur and humerus and determine possible sex using a chart, follow these steps: Identify the correct bone and landmarks, take standardized measurements, and consult the appropriate chart.
Humerus Measurements
Examples of measurements for the humerus include maximum length, glenoid fossa height, and vertical head diameter.
Radius Measurements
Examples of measurements for the radius include maximum and minimum radial head diameter.
Femur Measurements
An example of a measurement for the femur is the head diameter.
Sexual Dimorphism
The concept that there is about 7-15% sexual size dimorphism in our species, with overlap between smaller males and larger females.
Long Bone Measurements
Specific measurements such as humerus maximum length, glenoid fossa height, humerus vertical head diameter, radius head diameters, and femur head diameter used to determine sex.
Pubic Symphysis Changes
Morphological changes in the pubic symphysis that occur with aging, including the presence of:
ridges
furrows
eventual pitting and erosion.
Auricular Surface Changes
Alterations in the:
texture
porosity
overall topography
Of the auricular surface of the ilium as individuals age.
Suchey-Brooks method
This method divides the aging process into six distinct phases (I-VI) based on the appearance of the symphyseal face.
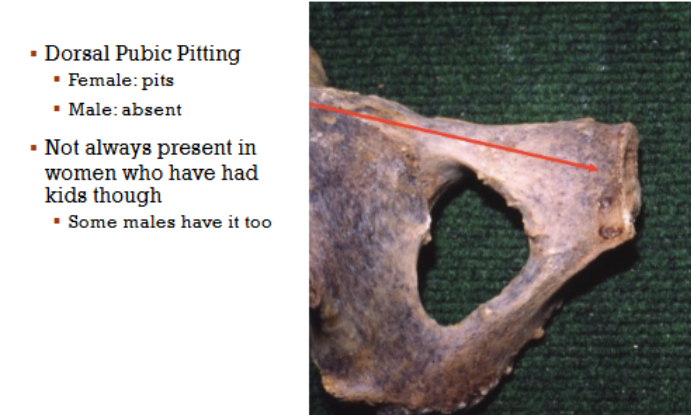
Pitting
A feature of the pubic symphysis that can be observed to help estimate age.
Skeletal Maturity
Typically occurs around 18-22 years of age when an individual's skeletal development is complete.
Long Bone Length Measurement
You would locate the measurement you took for a particular long bone on the chart and find the corresponding estimated stature range.
Height Calculation
Calculate an estimated stature by plugging in the length of the long bone (in millimeters or centimeters) into the formulae.
Stature Calculation
The process of determining a person's height based on measurements of long bones.
FORDISC
A statistical method used by forensic anthropologists to estimate ancestry from skeletal remains.
Asian Crania
Cranial characteristics typically associated with individuals of Asian ancestry, such as narrow concave nasal bones and prominent cheekbones.
Black Crania
Cranial characteristics typically associated with individuals of Black ancestry, including wider interorbital distance and broad nasal apertures.
Total Facial Prognathism
The overall forward projection of the entire face.
Cranial Traits for Asian Ancestry
This cranium is likely of Asian ancestry due to the presence of shovel-shaped incisors, prominent zygomatics, and relatively circular orbits, which are traits that occur with higher frequency in individuals of East Asian and Native American descent.
Consider Visual Assessment
It's important to remember that if you cannot get a likely assessment of ancestry through visual methods, metric methods like FORDISC are also likely to struggle.
Stature Estimation
The process of estimating the living height of an individual from the measurements of their bones, primarily the long bones. Formulae and charts are used for this, and using multiple bones increases accuracy.
FORDISC
A computer program used in forensic anthropology to estimate ancestry by statistically comparing skeletal measurements to a database of individuals with known biological profiles.
Dental Non-Metric Traits
Morphological variations in teeth (e.g., shovel-shaped incisors, Carabelli's cusp) that are not measured but are observed and their presence or absence is noted.
Subpubic Concavity
A concave curvature on the inferior aspect of the pubic bones, typically present in females.
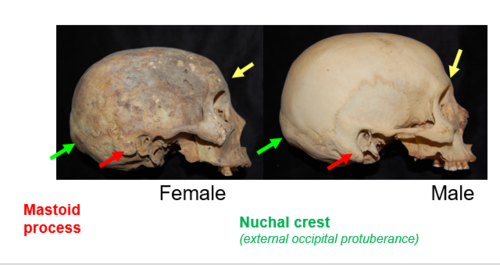
Nuchal Crest in females
the nuchal crest is usually rounded and non-protruding.
Zygomatic arch in males
the zygomatic arch is typically thicker, extends past the meatus, and is more pronounced.
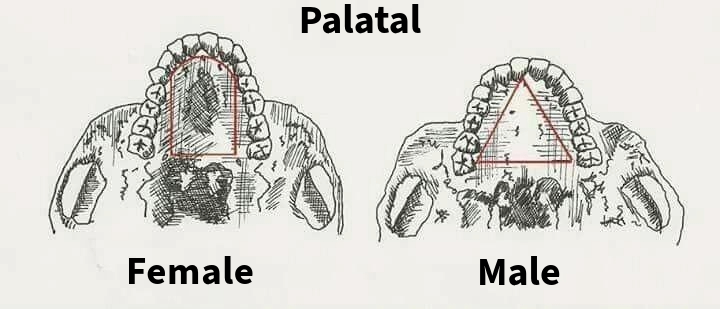
Female palate
The palate tends to be narrower.
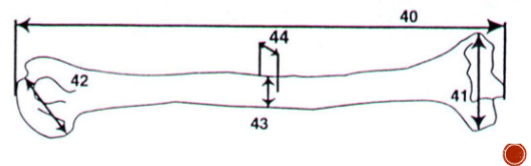
Humerus vertical head diameters for males and females
Female: <43 mm, Male: >47 mm
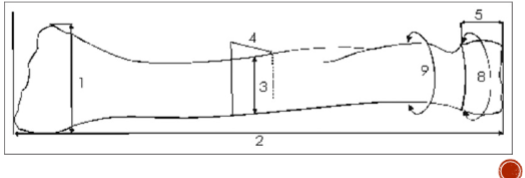
Maximum and minimum radial head diameter for males and females
Max: Female <21 mm; Male >24 mm
Min: Female <20 mm; Male >23 mm
Femur head diameter for males and females
Female: <40 mm; Male: 47.5 mm
Long bone measurement formula
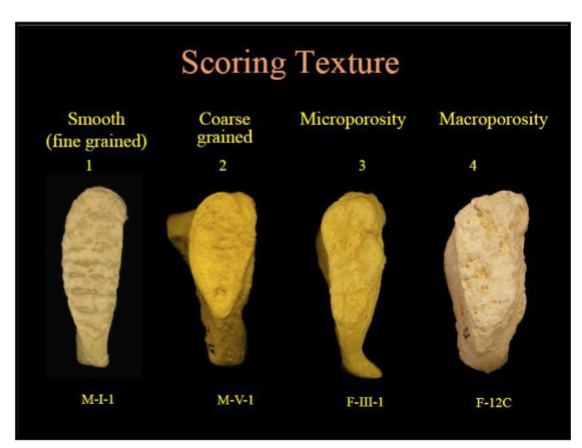
what are the four scales of measuring bone texture
1: smooth (fine grained)
2: coarse grained
3: microporosity
4: Macroporosity