Lecture 6: Rumenotomy and laparotomy
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Indications for rumeostomy
Chronic bloat
Feeding mechanism (tetanic cattle, severe oral damage)
Rumen fistula placement
Indications for rumenotomy
Hardware to remove wires
Dumping contents for acidosis
Choke retrograde retrieval of items
Removing fiber in hay belly cases
General considerations for rumenotomy
Standing surgery
If possible withhold food for 24-48 hours and water for 12-24 hours
Butorphanol/xylazine/ketamine used for standing sedation
Pre-op/ post-op antibiotics
Assistance usually needed depending on urgent nature
NSAID pre-op
May need to pass kingman tube before surgery to relieve pressure or use needle to deflate
What side to you perform rumenotomy?
Left flank
What are the flank anesthetic options for rumenotomy?
Line block
Inverted L or reverse 7
Proximal paravertebral
Distal or transverse paravertebral
High volume caudal epidural or lumbosacral epidural
General anesthesia
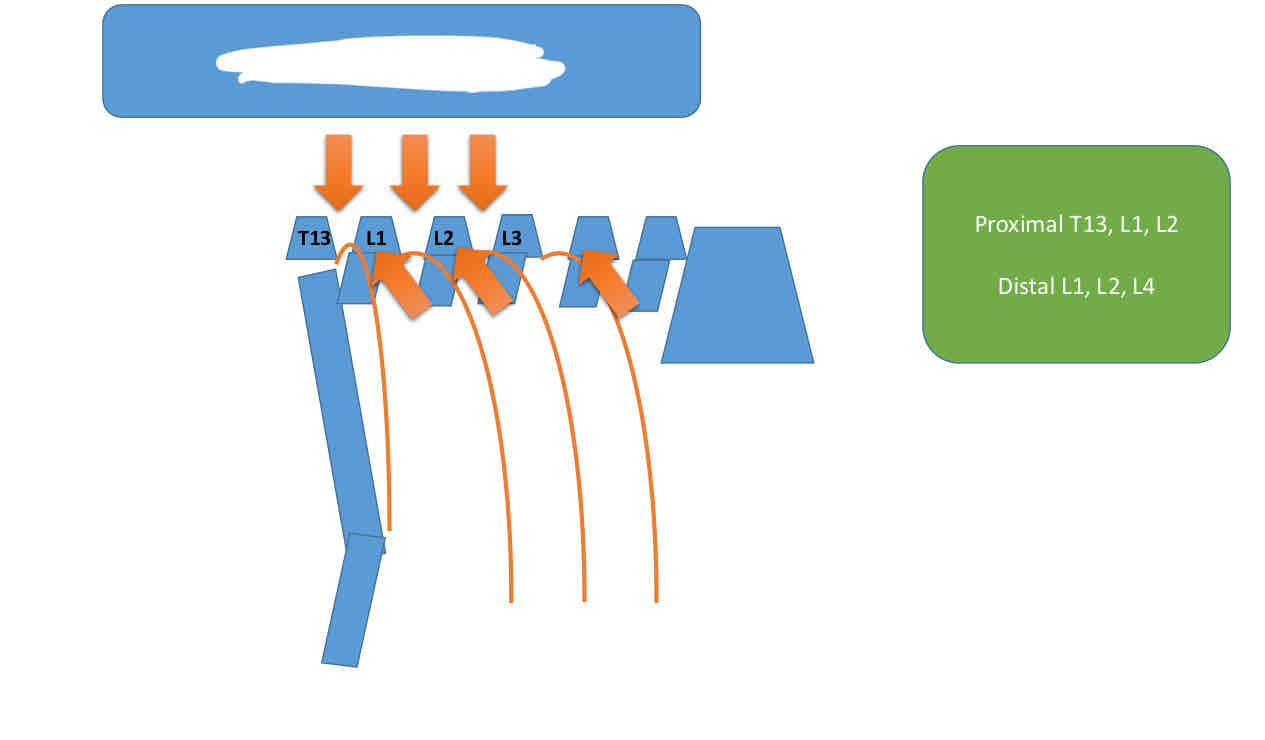
What block is shown in the picture?
Paravertebral
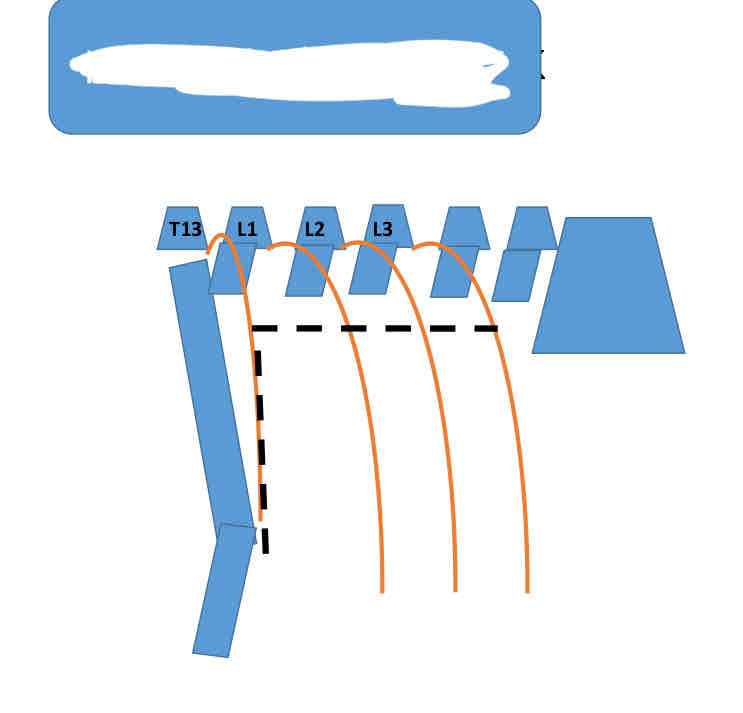
What block is being shown?
Inverted L/Reverse 7
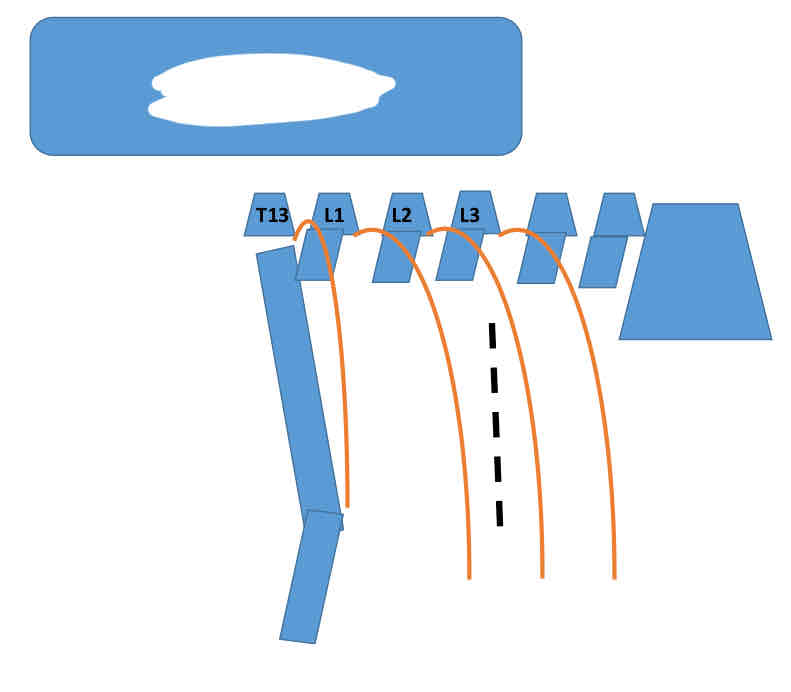
What block is being shown?
Line block
What should you keep in mind with location of stoma?
Consider if bloated where it will be when its deflated
Fit rumen cannula in it
Steps for rumenostomy
Aseptic prep (clip/prep). Draping and gowning.
Skin incision in dorsal 1/3. SQ tissues removed and disposed of. Muscle griddled, sharply incised, circle removed.
Go through the muscle layers: External abdominal oblique,internal abdominal oblique, transversus
Incise peritoneum ONLY. Suture peritoneum and transversus to deep dermis. Seal it shut. Use absorbable suture on cutting needle. Tack first at 0, 3, 6, 9 o’clock. Simple continous to make a circle.
Tack rumen to skin at 0,3,6,9 o’clock. Use simple continuous to create seal. Insert rumen cannula. Use stay sutures.
Postop care of rumenostomy
Daily cleaning
Post-op medications (PPG and NSAIDs)
Rumenostomy post op complications
Incisional infection
Peritonitis
Continues primary problems
How do you close a stoma?
Remove the cannula
Freshen edges and 2 layer closure if chronic fistula
What are you at risk with complete stoma closure?
Peritonitis
What can you used to close the rumen?
Taper needle
Absorbable suture monofilament (Monocryl, PDS)
Urecht, Lembert, Cushings
May need double layer
How do you close the skin for an rumenotomy?
1-3 muscle layers (peritoneum and transversus, internal abdominal oblique, external abdominal oblique)
Reverse cutting needle and absorbable suture (Vicryl, monocryl, PDS, chromic gut)
Non-absorbable (Nylon) for skin
What approach is used for exploratory laparotomy?
Right sides into abdomen same as rumenotomy. Location found at the paralumbar fossa.
Indications for exploratory laparotomy
Intestinal disease (SI disease)
Cecal disease
Liver disease
No US
Unexplained pings
Type 3 or 4 vagal indigestion
Peek and shriek
Compare a standing vs. recumbent exploratory laparotomy
Standing gives you best approach and visualization. UNLESS YOU ARE GOING TO MANIPULATE SI
Recumbent is better for tugging on
If you want to open rumen, remove contents and close, which surgery will you do?
A. Rumenotomy
B. Rumenostomy
A. Rumenotomy
Which sided approach will you do in case of TRP?
A. Left
B. Right
A. left
Which is the correct order you will cut through from external to internal
A. Skin, external abdominal oblique, internal abdominal oblique, transverse
B. Skin, transverse, external abdominal oblique, internal abdominal oblique
C. Skin, internal abdominal oblique, external abdominal oblique, transverse
A. Skin, external abdominal oblique, internal abdominal oblique, transverse
What is one indication for performing a rumenotomy?
a. Chronic bloat
b. Severe oral damage
c. Liver disease
d. Intestinal disease
a. Chronic bloat
Which of the following is a step in performing a rumenotomy?
a. Incise the skin in the ventral 1/3
b. Close the stomach with non-absorbable suture
c. Suture the peritoneum and transversus to deep dermis
d. Use a right-sided approach
c. Suture the peritoneum and transversus to deep dermis
What type of anesthesia is commonly used for a standing surgery?
a. General anesthesia
b. Local anesthesia
c. Standing sedation
d. Epidural anesthesia
c. Standing sedation
Which of the following is NOT an indication for rumenostomy?
a. Hepatic lipidosis
b. Hardware disease
c. Feeding mechanism failure
d. Cecal disease
b. Hardware disease
What is a common postoperative care step for rumenostomy?
a. Immediate feeding
b. Daily cleaning
c. Withhold water for 48 hours
d. No medication needed
b. Daily cleaning
During a rumenotomy, which layer is the surgeon NOT supposed to incise?
a. Skin
b. Peritoneum
c. Rumen
d. Transversus
c. Rumen
What complication is associated with rumenostomy?
a. Incisional infection
b. Abdominal distension
c. Hemorrhage
d. Anemia
a. Incisional infection
Which anesthetic technique involves a line block?
a. Inverted L block
b. Proximal paravertebral block
c. Distal paravertebral block
d. All of the above
d. All of the above
Which structure is checked first during an exploratory laparotomy?
a. Gall bladder
b. Rumen
c. Omentum
d. Liver
c. Omentum
What is the purpose of rinsing the abdomen during rumenotomy closure?
a. To remove excess blood
b. To prevent contamination
c. To enhance the healing process
d. To reduce pain
b. To prevent contamination
What is the recommended size of the skin incision for a rumenostomy?
a. 1 cm
b. 2 cm
c. 4 inches
d. 5 cm
c. 4 inches
What is a common postoperative medication for rumen surgeries?
a. NSAIDs
b. Corticosteroids
c. Vaccines
d. Antihistamines
a. NSAIDs
Which surgical approach is used for exploratory laparotomy?
a. Left-sided
b. Right-sided
c. Ventral midline
d. Parametrial
b. Right-sided
What type of suture is typically used for skin closure in rumenotomy?
a. Non-absorbable
b. Absorbable
c. Silk
d. Nylon
a. Non-absorbable
Which of the following is a possible postoperative complication of exploratory laparotomy?
a. Coughing
b. Peritonitis
c. Vomiting
d. Constipation
b. Peritonitis
What is a key consideration when performing a rumenostomy?
a. The location of the stoma
b. The size of the incision
c. The type of anesthesia
d. The age of the animal
a. The location of the stoma
Which block would you use for pain relief in rumen surgery?
a. Epidural block
b. Inverted L block
c. Intramuscular block
d. Topical anesthetic
b. Inverted L block
When should the pre-op antibiotics be administered?
a. 12 hours before surgery
b. 24-48 hours before surgery
c. After the surgery
d. During the surgery
b. 24-48 hours before surgery
Which of the following is a reason to perform an exploratory laparotomy?
a. Hardware disease
b. Unexplained pings
c. Chronic bloat
d. Severe oral damage
b. Unexplained pings
What is the purpose of using absorbable suture for closing the rumen?
a. To allow for future surgeries
b. To avoid the need for suture removal
c. To minimize scarring
d. To enhance cosmetic appearance
b. To avoid the need for suture removal