1.16 - neurophysiology II - action potentials and synaptic transmission
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
what does the movement of a dissolved, charged particle depend on?

what is Ohm’s law?

what factors make up Nersts potential?

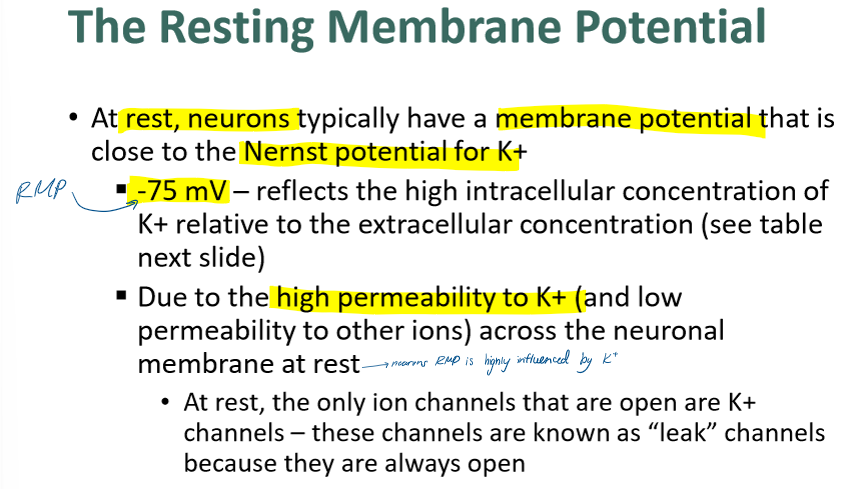
how is K+ concentration related to resting membrane potential?
what does membrane potential of a cell depend on?
goldman field equation is updated nernst potential equation that incorporates otehr ions

what does it mean if the membrane potential is close to the Nernst potential of a particular ion?
usually means that the membrane is more permeable to that ion
what does movement of charges particles across a membrane depend on?

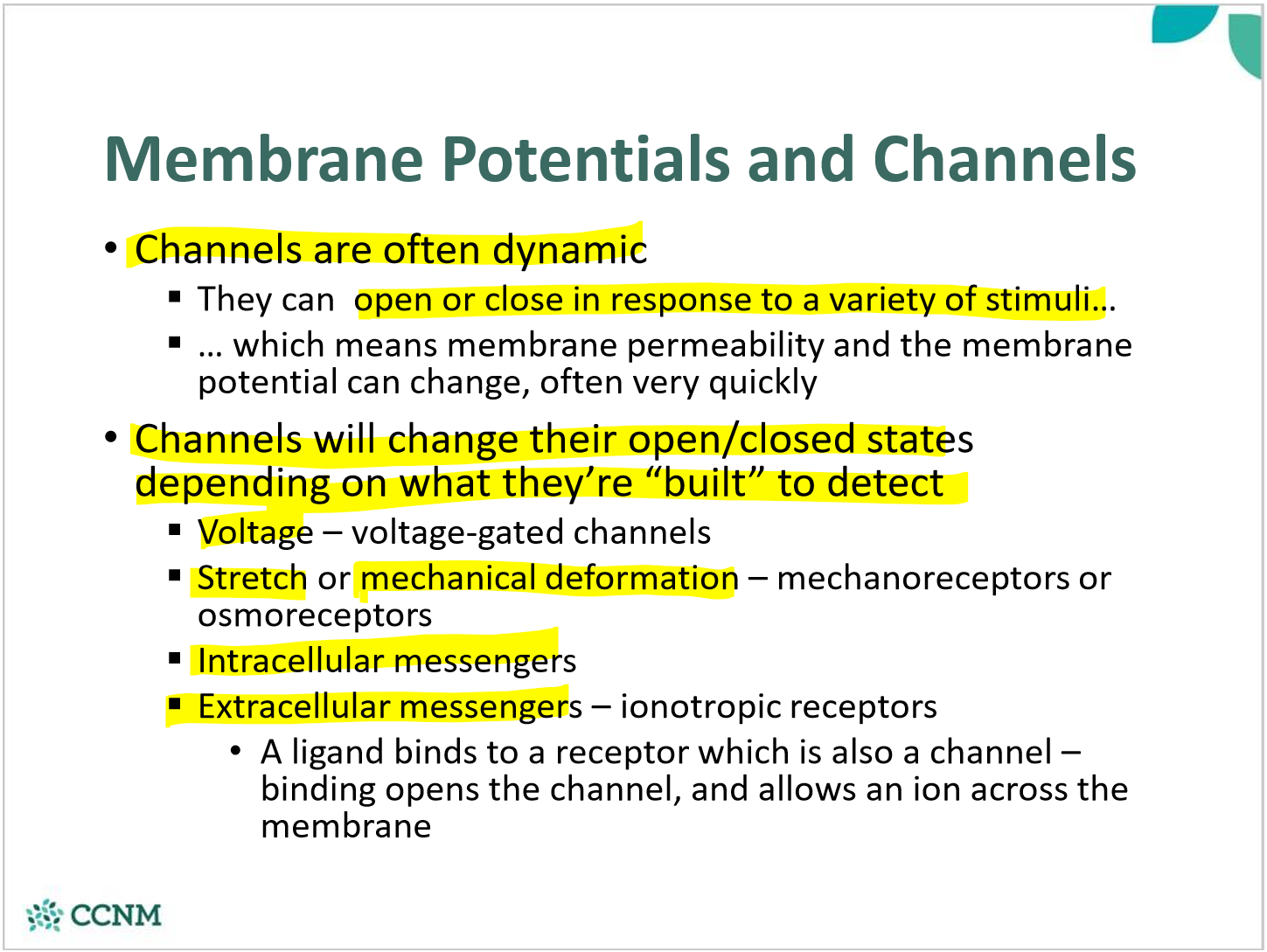
explain how channels are dynamic
where in a neuron is an action potential generated?

what do action potentials require?

at rest does the cell have more K+ or Na+
K+ is higher in the cell
Na+ is higher outside the cell
describe what happens during step 1: resting membrane potential

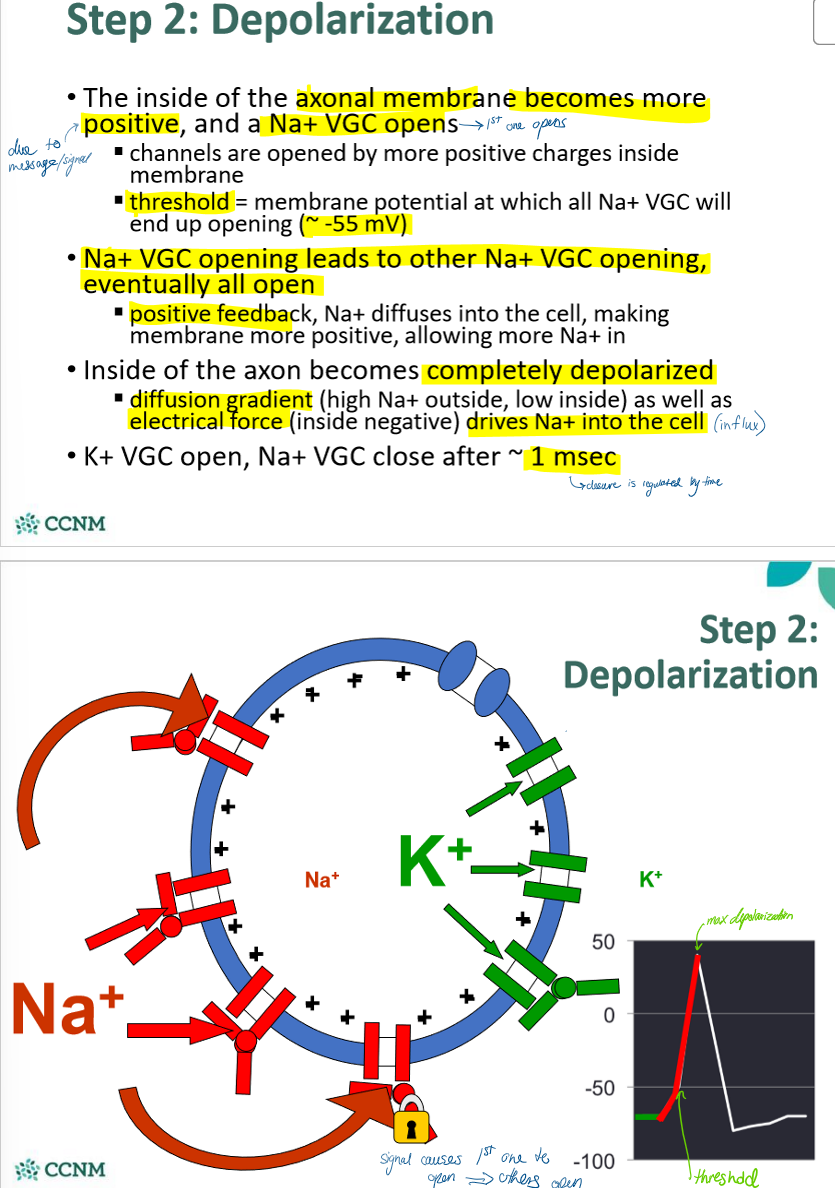
describe what happens during step 2: depolarization
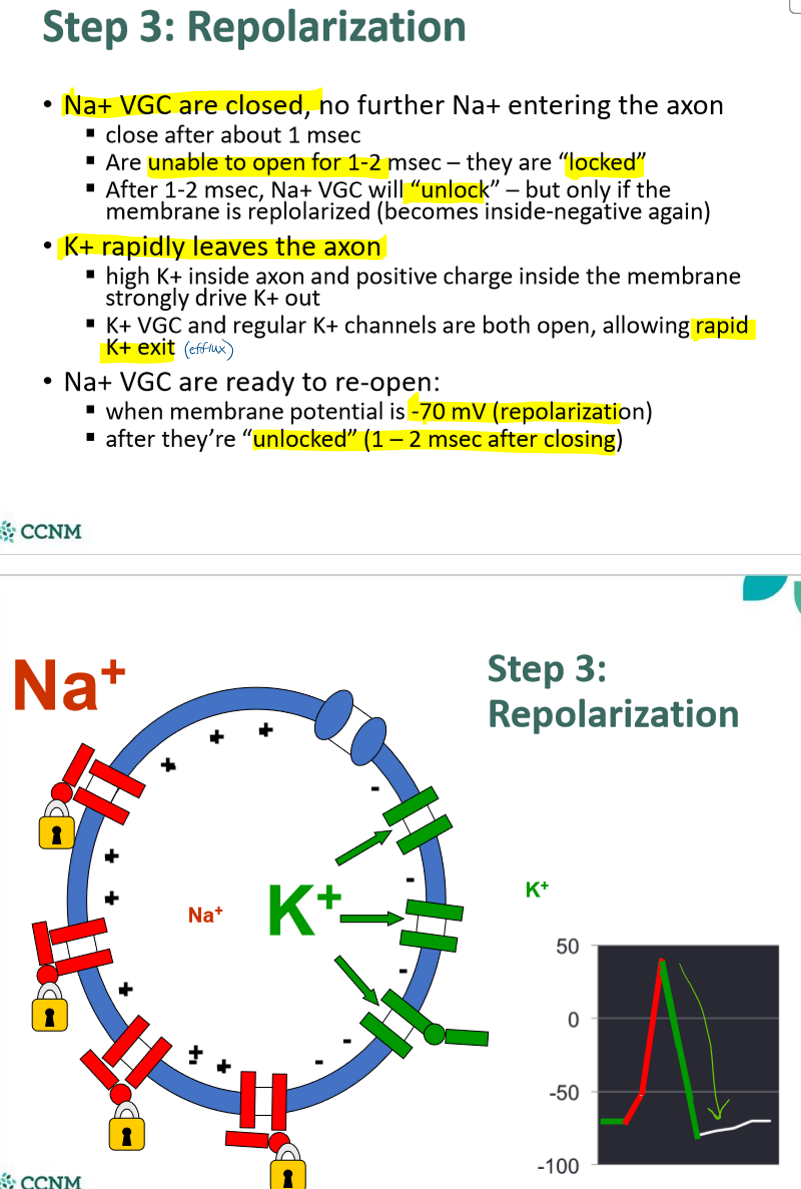
describe what happens during step 3: repolarization
what are the 2 gates on sodium-voltage-gated channels? how is each regulated?

how are postaasium voltage gated channels regulated?

describe the absolute refractory period
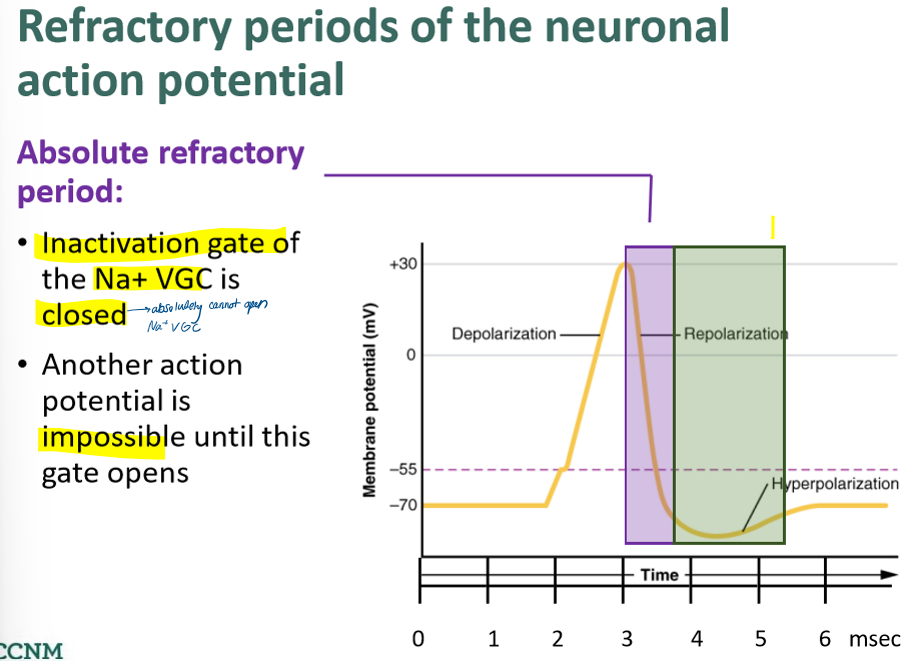
describe the relative refractory period
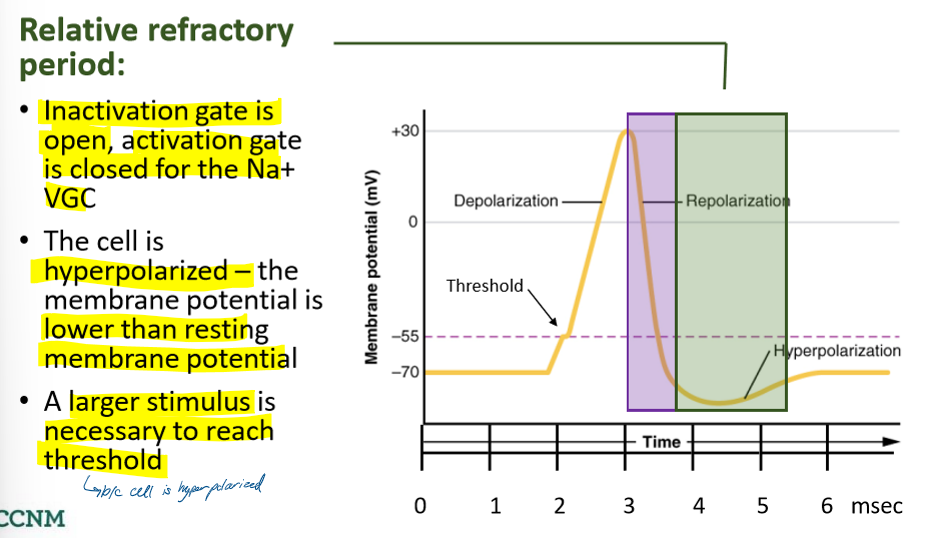
how are APs initiated?
depolarization
explain how APs are all or nothing events

explain why APs have constant amplitude

explain how fiber diameter changes speed of AP
larger diameter conducts APs faster than small fibers
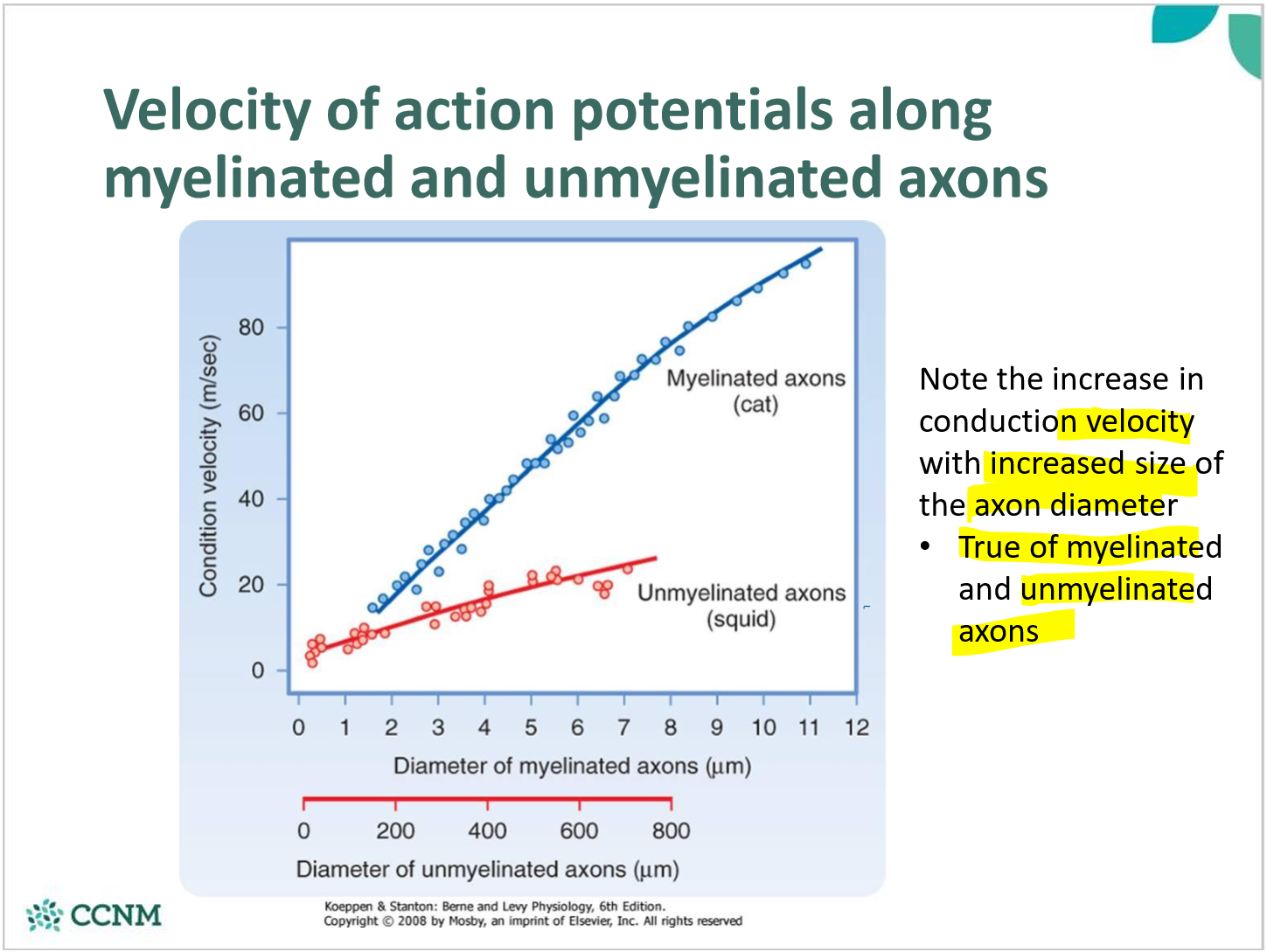
describe A fibers
size
myelination
speed
function

describe B fibers
size
myelination
speed
function

describe C fibers
size
myelination
speed
function

describe continuous conduction
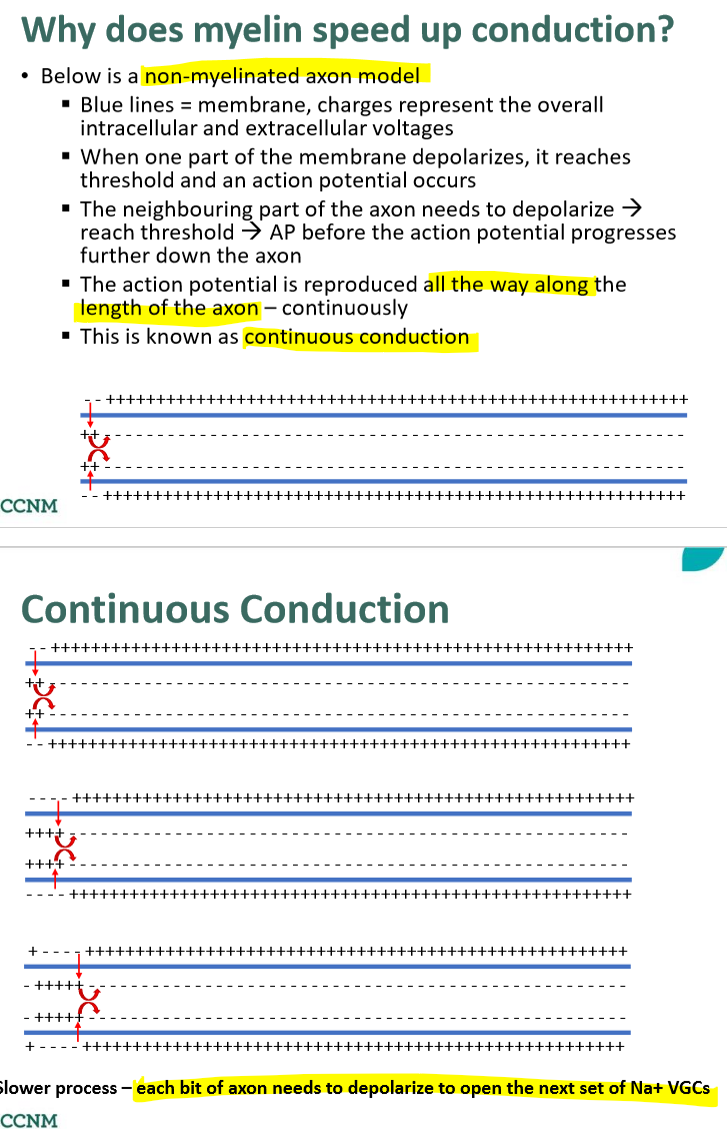
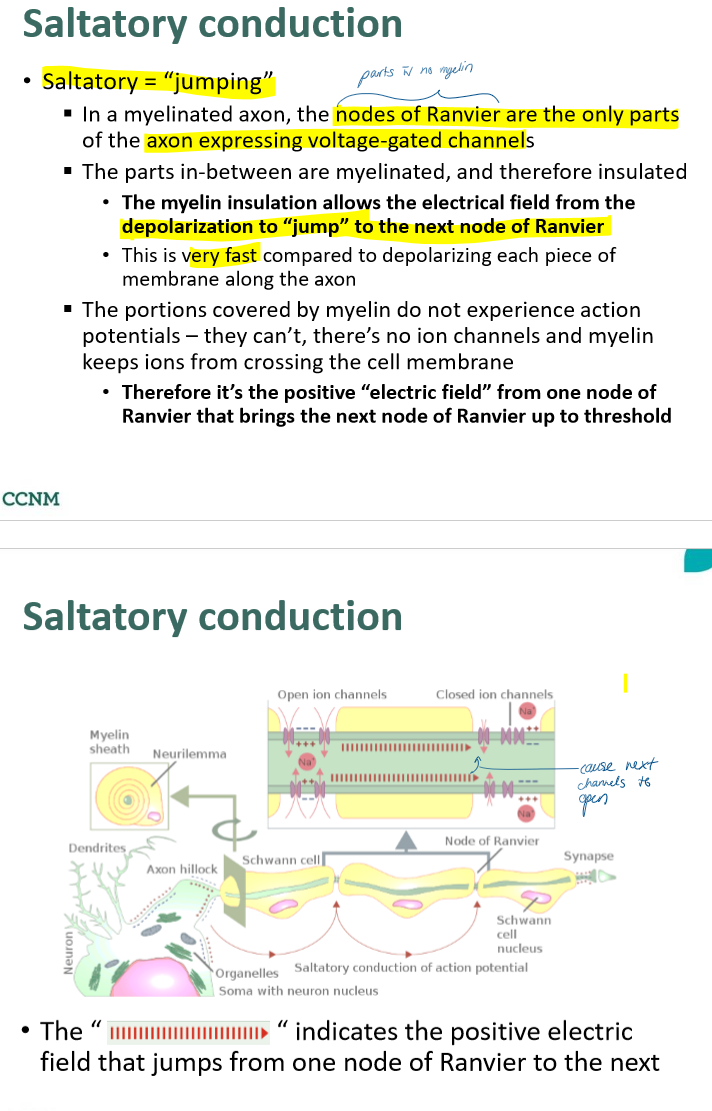
describe saltatory conduction
describe the chemical synapse
what cells is it associated with
what happens at the pre-synaptic neuron? cleft?
how are NT vesicles packaged? transported to synpase?
what are the basic steps of NT release?
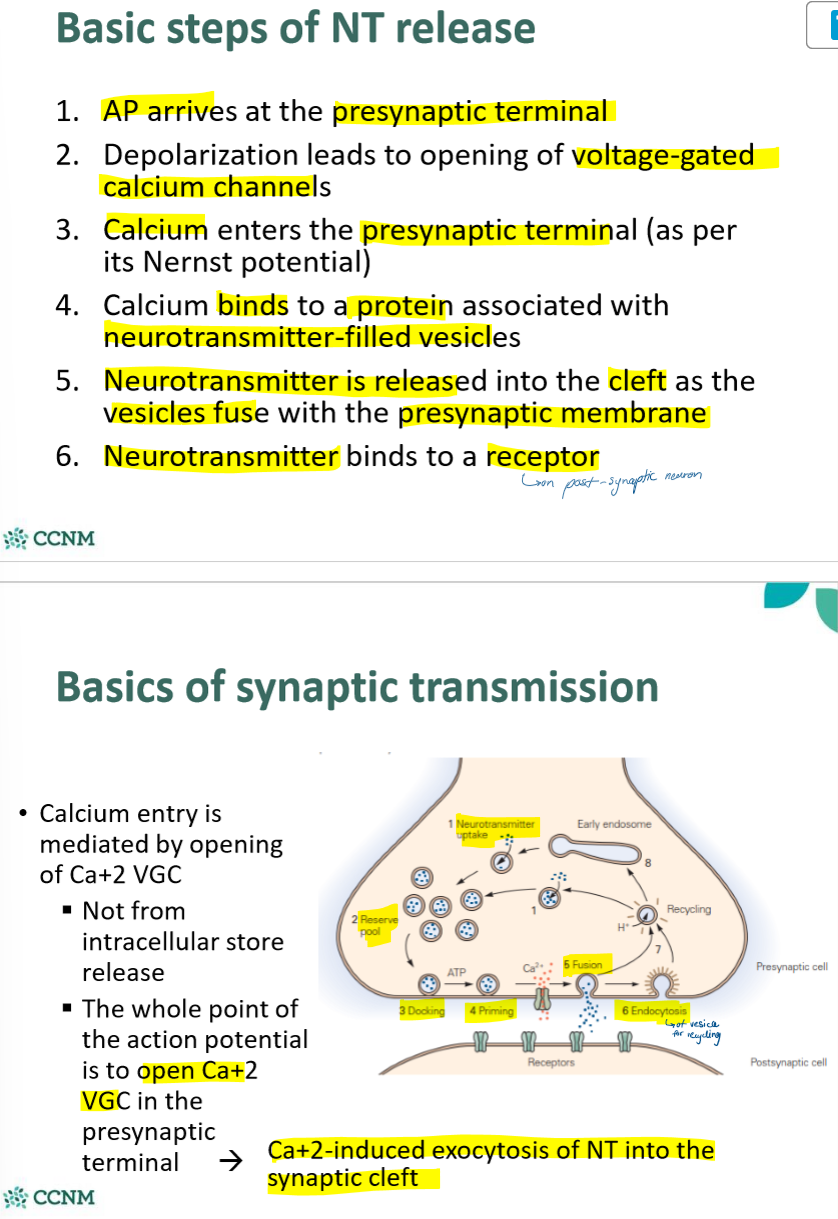
requirments of vesicle release
must be quick
must be highly regulated
name the molecules involved in vesicle release regulation
vSNAREs
tSNAREs
complexins
synaptotagmin
what are v-SNAREs?

what are t-SNAREs
what are complexins

what are synaptotagmins

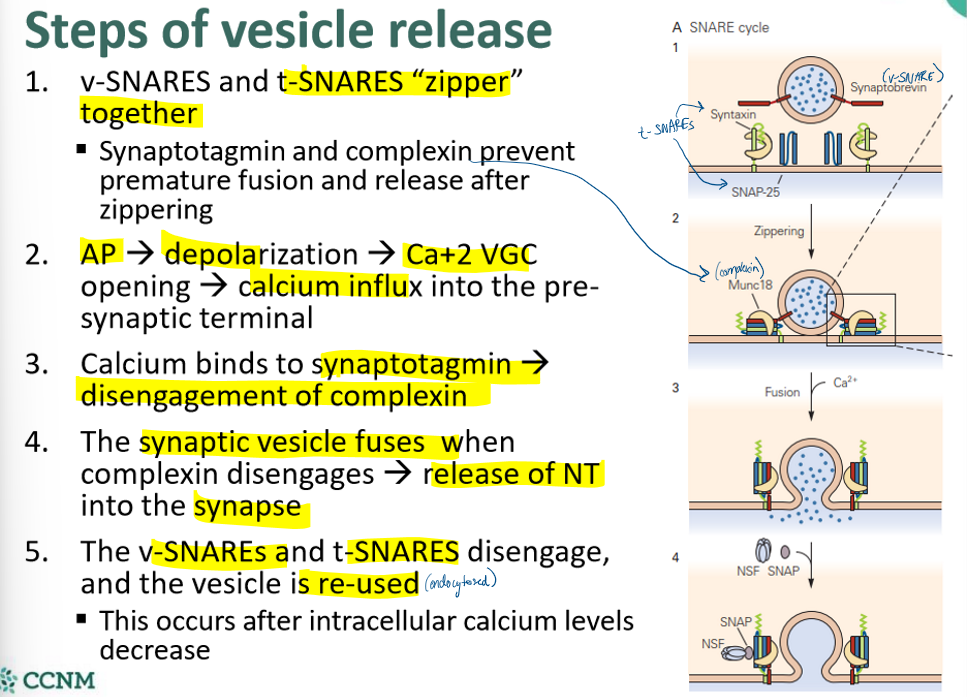
explain the steps of vesicle release
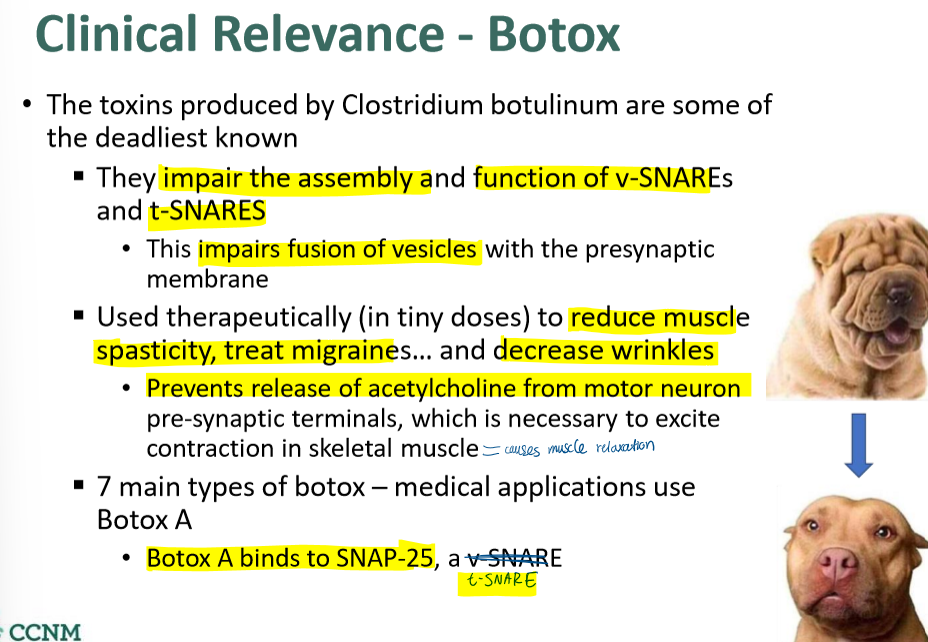
explain how v-SNAREs and t-SNARES are used in botox
what are the mechanisms that remove NTs after release?

how can the effects of NTs vary?
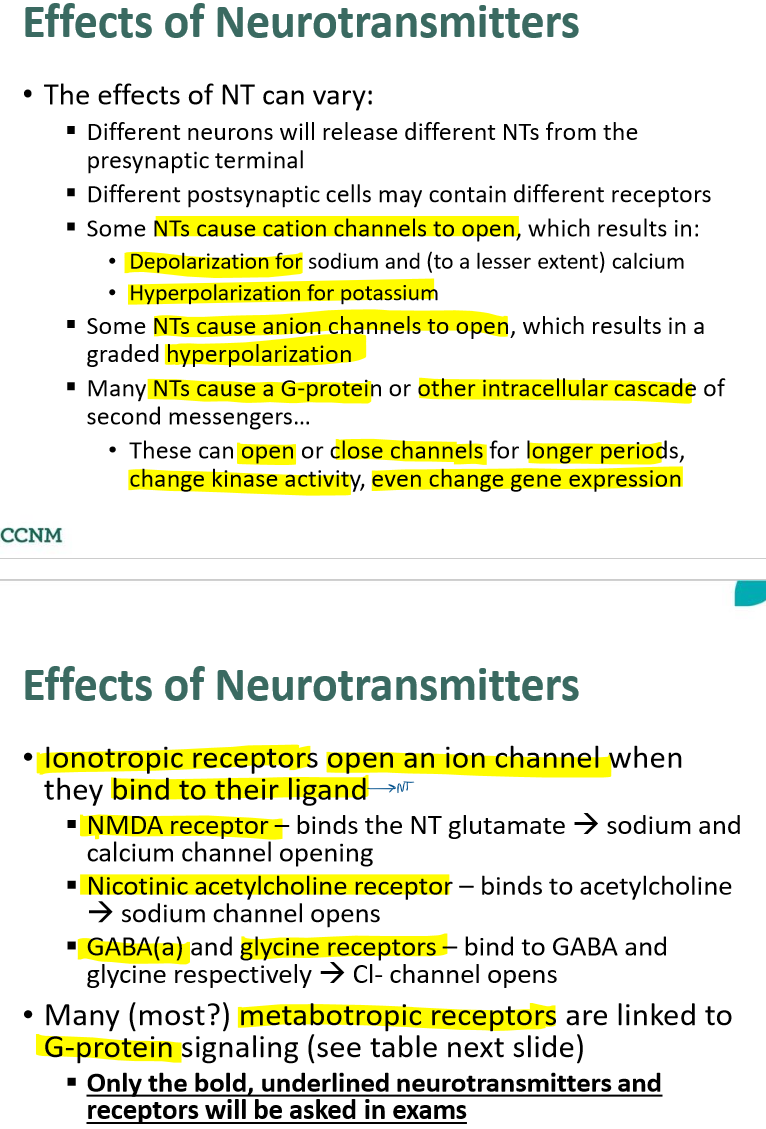
what does NT behaviour depend on?
receptor type
NT: acetylcholine (Ach: excite)
behaivour
receptor
signal

NT: acetylcholine (Ach: inhibit)
behaivour
receptor
signal

compare the different dunctions of Ach

NT: GABA (inhibit)
behaivour
receptor
signal

NT: glutamate (excite)
behaivour
receptor
signal

NT: glycine (inhibit)
behaivour
receptor
signal

NT: norepi (excite)
behaivour
receptor
signal

what is the most important inhibitory NT of the intracranial CNS?
GABA
what is the most important inhibitory NT of the spinal cord?
glycine
what is the most common excitatory NT of CNS?

what are the excitatory functions of norepi?

what happens when an NT binds to an inhibitory ionotropic receptor?

what happens when an NT binds to an excitatory ionotropic receptor?

what is the consequence of ionotropic receptor activation?

what are graded potentials? what are their propreties?
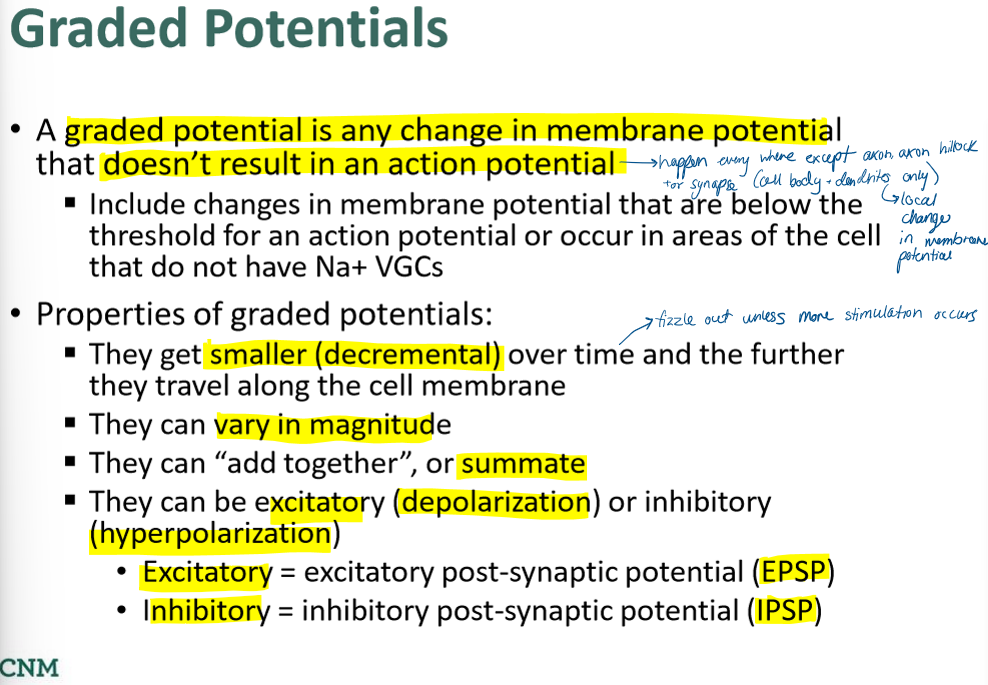
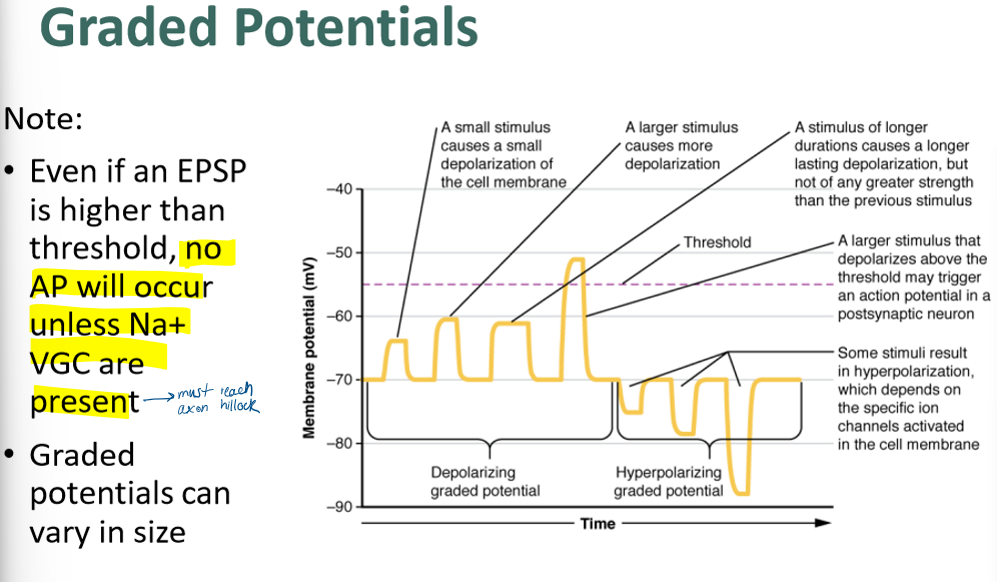
when can graded potentials become APs?
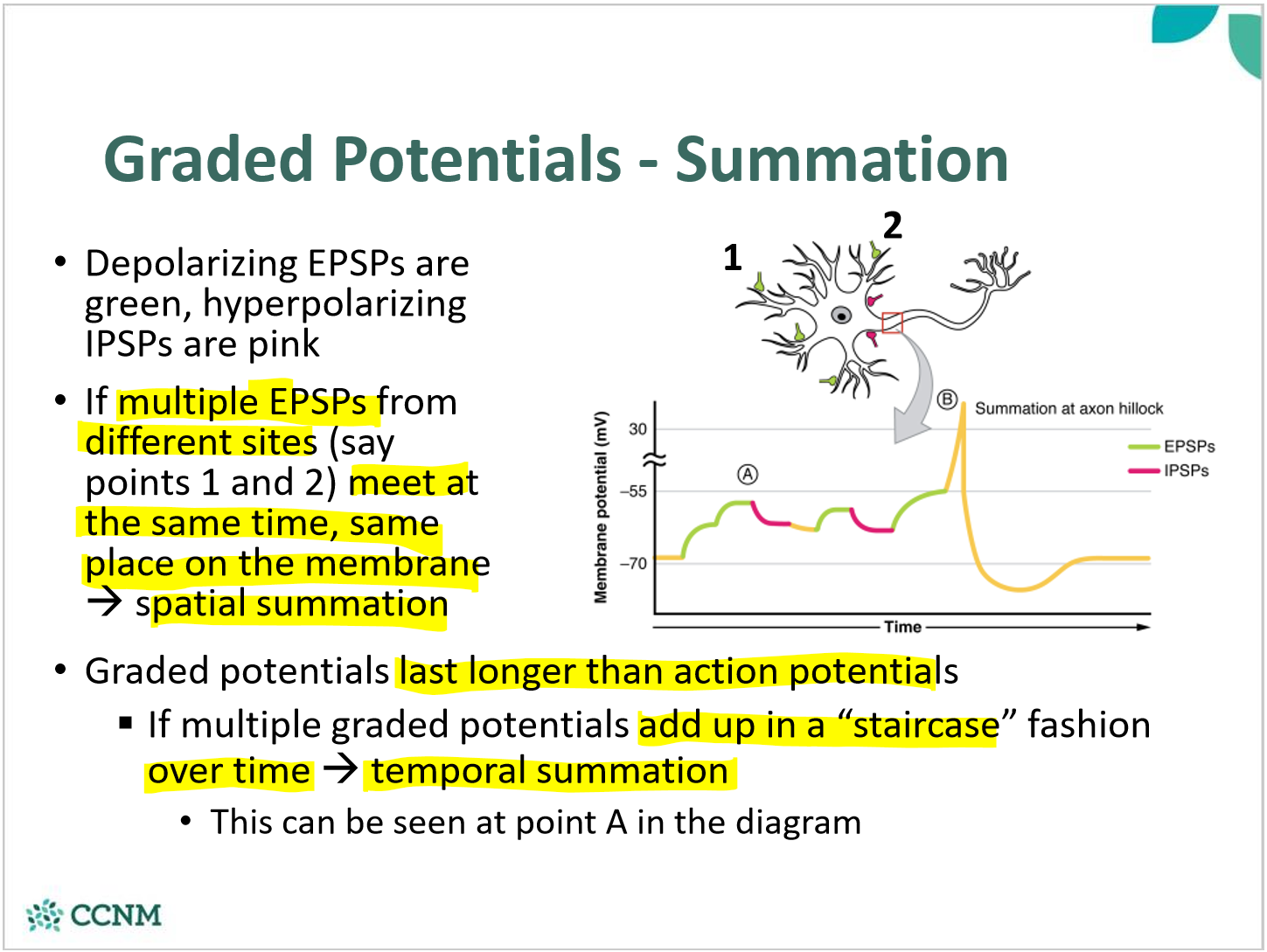
compare spatial and temporal summation of GPs
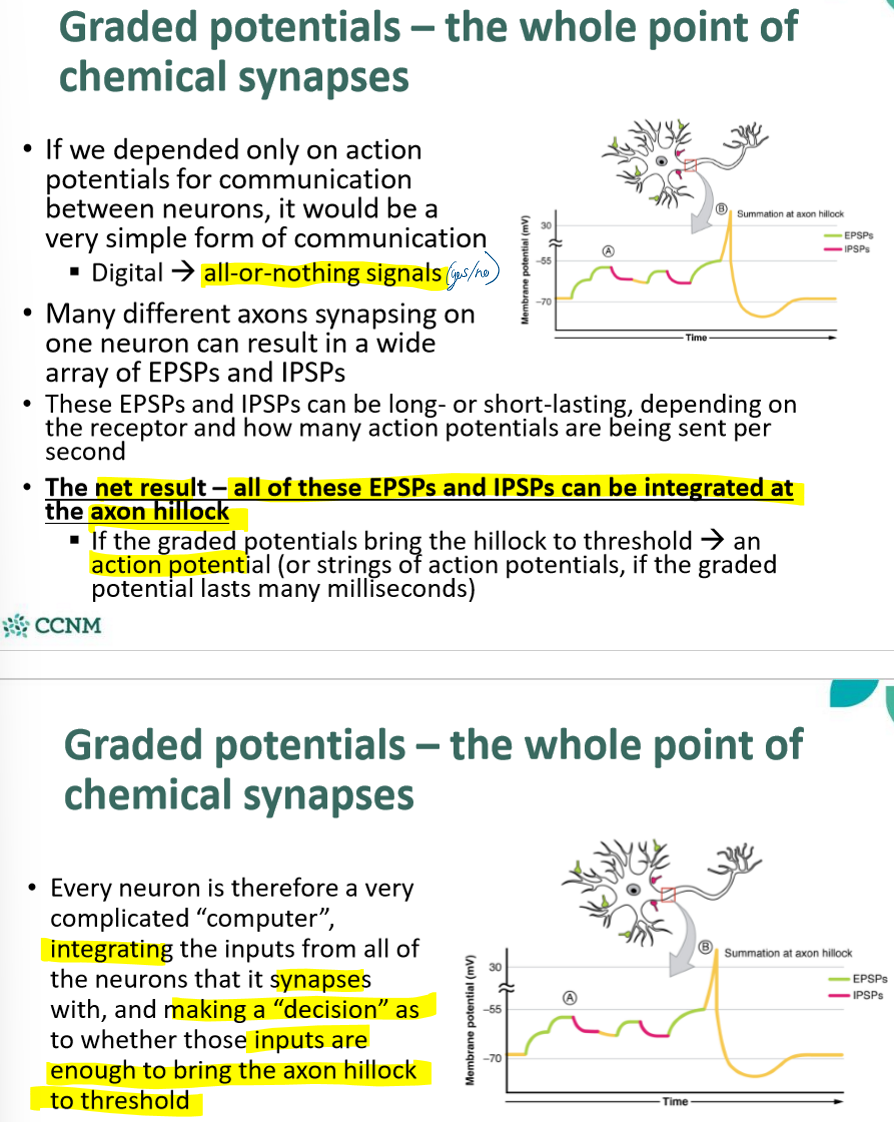
explain how neurons integrate signals
compare the origin of GPs vs APs

compare the types of channels of GPs vs APs

compare the amplitude/size of GPs vs APs

compare the duration of GPs vs APs

compare the polarity of GPs vs APs

compare the refractory period of GPs vs APs
