alkenes + addition polymerisation
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
what is an alkene?
an unsaturated hydrocarbon - C=C double bond is an area of high e- density
what is a polymer?
long chain molecule made from lots of small molecules (monomers) joined together
what is a monomer?
small molecules that join together to make polymers
what is addition polymerisation?
formation of long chain molecules from lots of small molecules joining together w/ no other products
draw the monomer structure of poly(ethene):

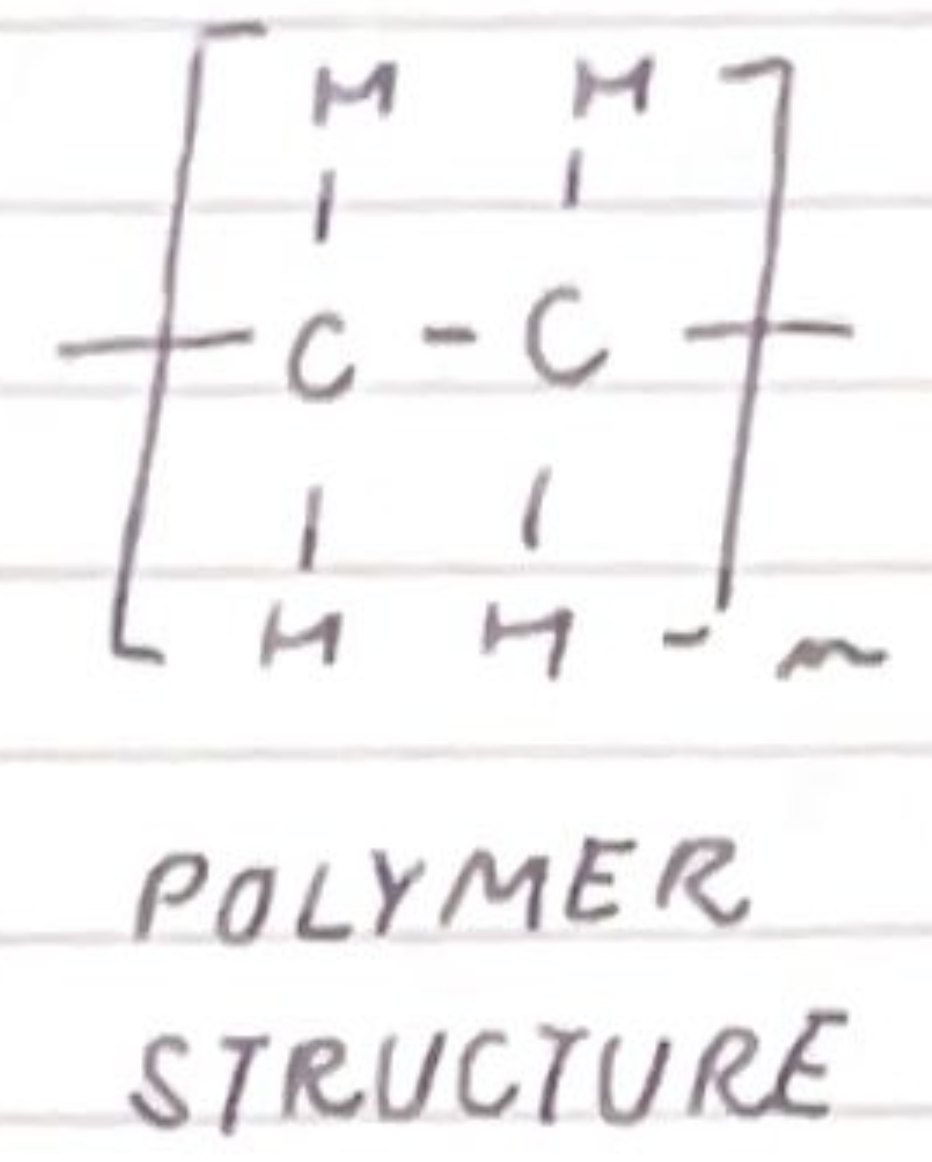
draw the polymer structure of poly(ethene):
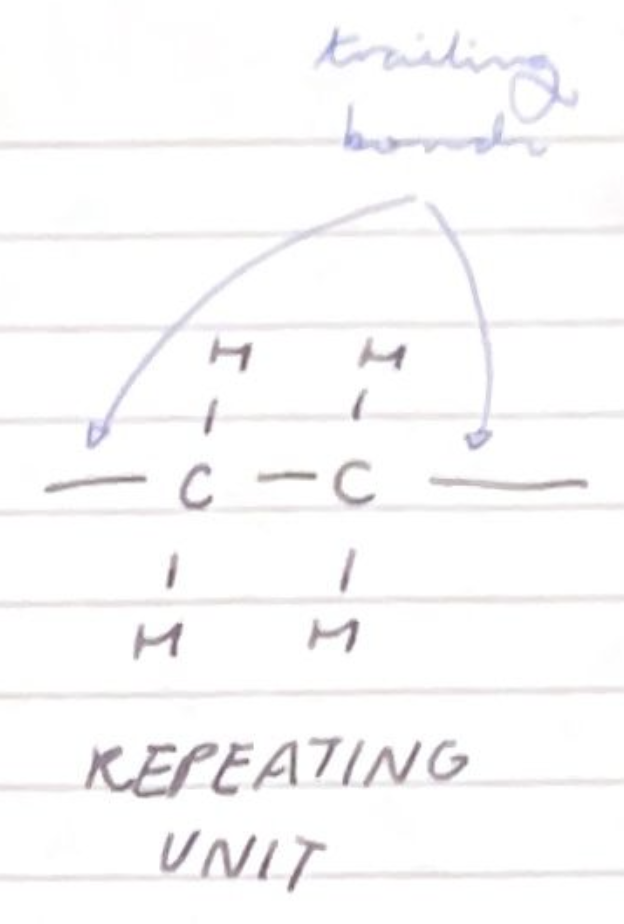
draw the repeating unit of poly(ethene) and name the bonds at either end of the repeating unit:
trailing bonds
how do we name addition polymers?
poly(name of alkene)
what are addition polymers formed from?
alkenes and substituted alkenes
describe the properties of addition polymers:
unreactive
chains usually non-polar so held together by VDWs
the longer the polymer chains are/the closer together the chains can get, the stronger the VDWs between the chains will be
polyalkenes made up of long, straight chains → strong and rigid
polyalkenes made up of short, branched chains → weaker and flexible
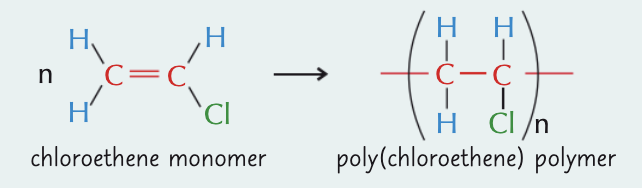
what is poly(chloroethene)/PVC and what can it be used for?
polymer of chloroethene
has long, closely packed polymer chains - hard, but brittle at room temp
rigid PVC - drainpipes and window frames
how can we modify PVC’s properties?
by adding a plasticiser - pushes polymer chains apart, reducing strength of VDWs
this means the polymer can slide around more, making it easier to bend
plasticised PVC - electric cable insulation, flooring tiles, clothes