1. Biological Molecules
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
What are monomers?
Monomers are the smaller units from which larger molecules are made.
What are polymers?
Polymers are molecules made from a large number of monomers joined together.
What are some examples of monomers?
- Monosaccharides
- Amino acids
- Nucleotides
What is a condensation reaction?
- Joins two molecules together
- Formation of a chemical bond
- Involves the elimination of a molecule of water
What is a hydrolysis reaction?
- Separates two molecules
- Breaks a chemical bond
- Involves the addition of a water molecule
What are 4 examples of condensation/hydrolysis reactions?
- Nucleotides <-> Polynucleotides (Nucleic Acids)
- Monosaccharides <-> Polysaccharides (Carbohydrates)
- Fatty acids + Glycerol <-> Lipids
- Amino acids <-> Polypeptides (Proteins)
What are carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are molecules which consist only of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen and they are long chains of sugar units called saccharides.
What are the 3 groups of carbohydrates?
- Monosaccharides
- Disaccharides
- Polysaccharides
What are monosaccharides?
Monosaccharides are the monomers from which larger carbohydrates are made.
What are the 3 common monosaccharides?
- Glucose (hexose sugar - 6 carbon atoms)
- Galactose
- Fructose
What is an isomer?
Same molecular formula but differently arranged atoms
What are the two isomers of glucose?
- α-glucose
- β-glucose
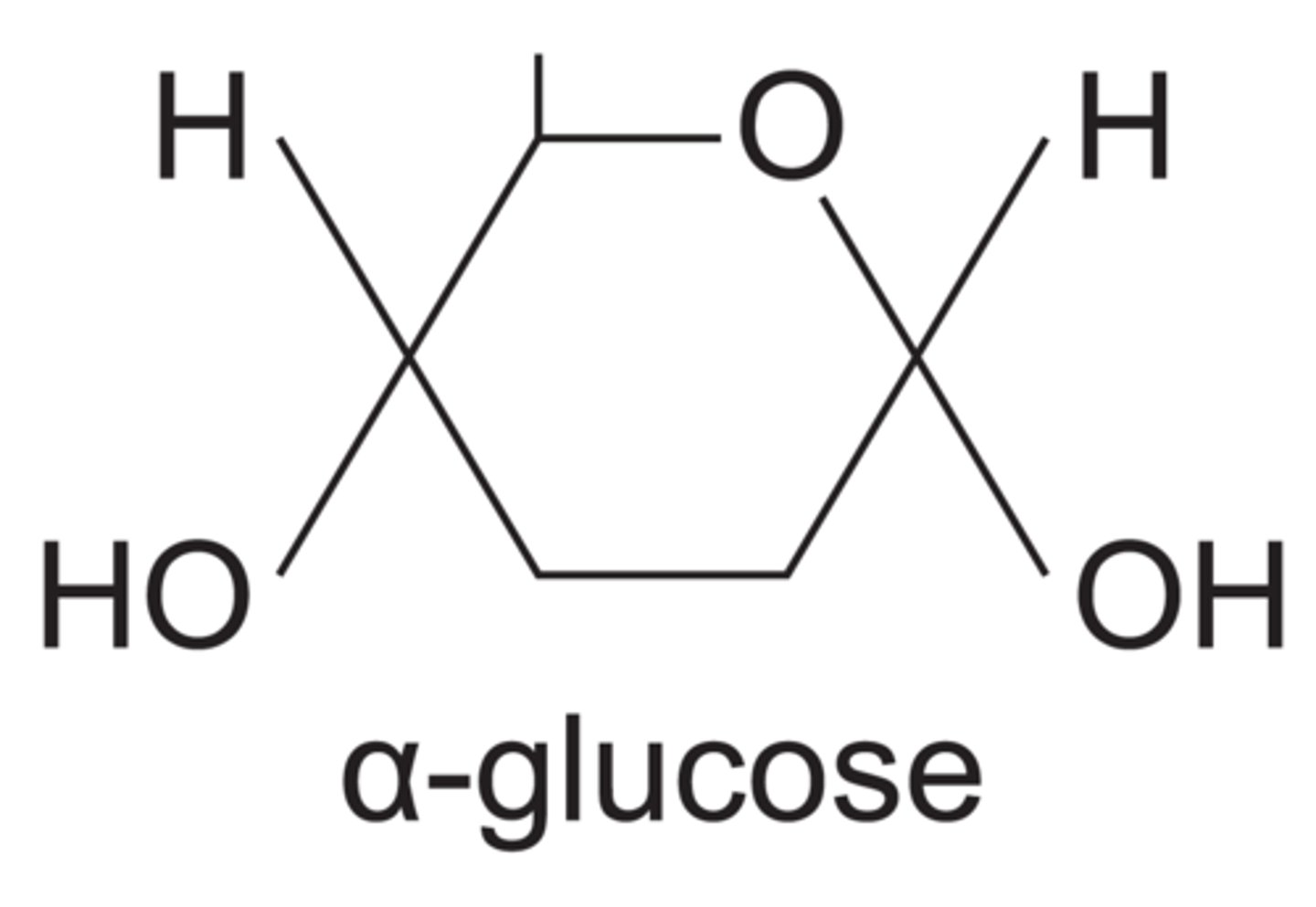
What is the structure of α-glucose?
What is the structure of β-glucose?
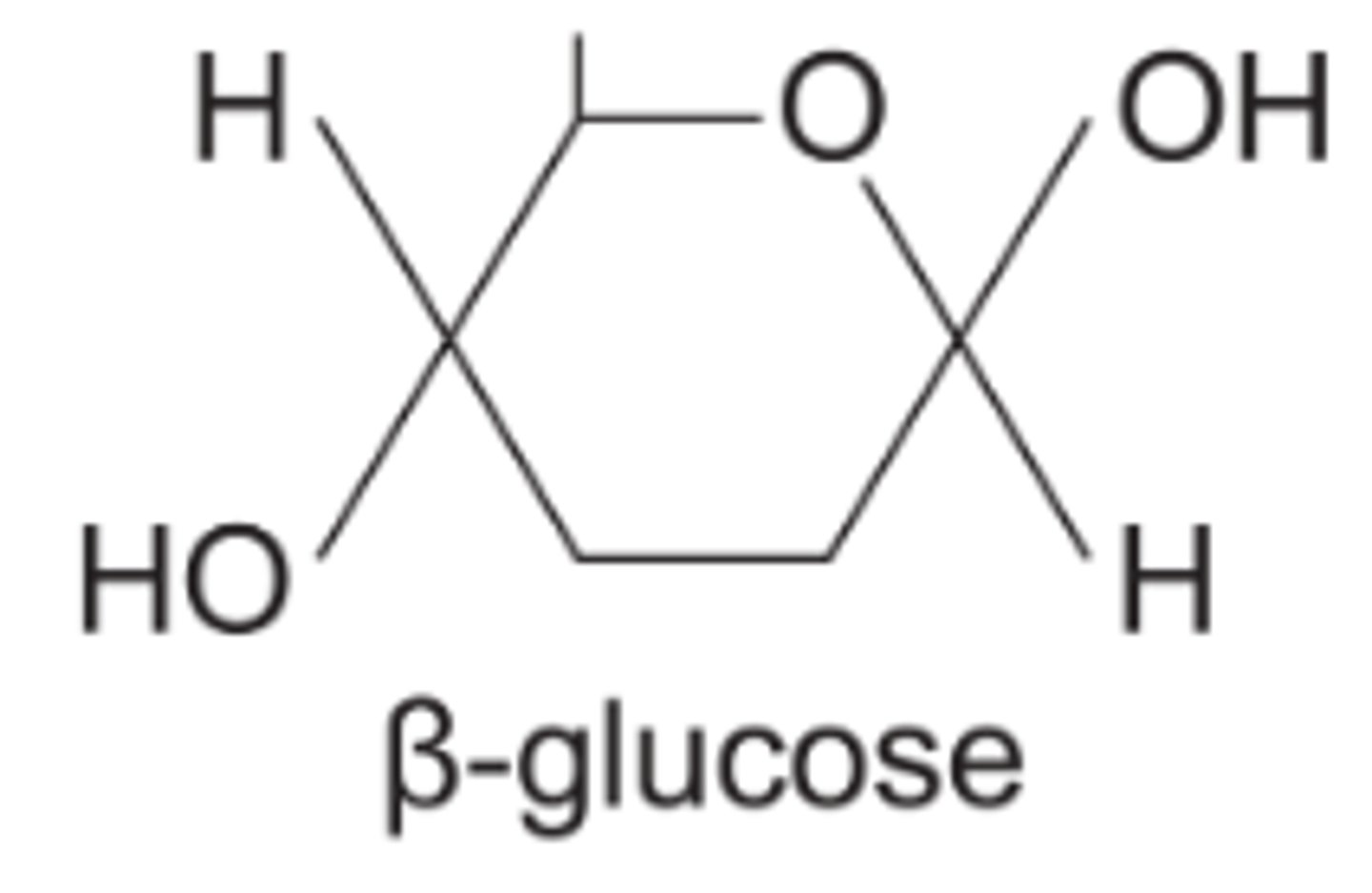
What is the difference in structure between α-glucose and β-glucose?
On the right, OH group is below C1 in a α-glucose but above C1 in a β-glucose.
What does a condensation reaction between two monosaccharides form?
A glycosidic bond
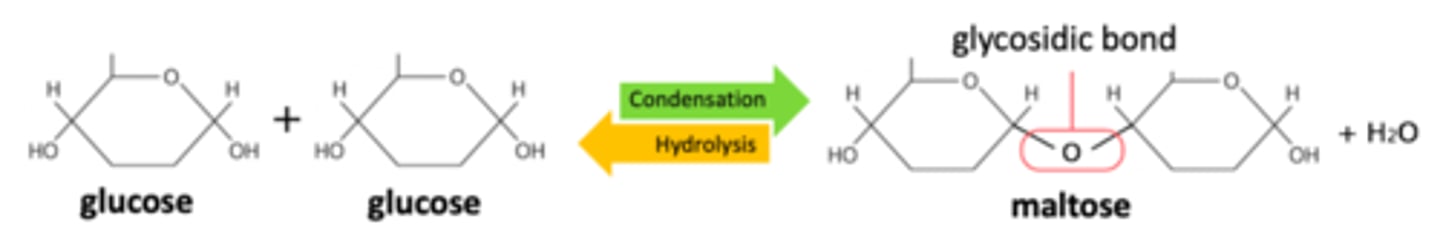
What are disaccharides?
Formed by the condensation of 2 monosaccharides
What are the 3 common disachharides and what are their monomers?
- Glucose + glucose = maltose
- Glucose + fructose = sucrose
- Glucose + galactose = lactose
What are polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides are formed by the condensation of many glucose units/monosaccharides
Why are monosaccharides soluble in water?
- Monosaccharides, including glucose, have a large number of OH groups - these are called hydroxyl groups
- Hydroxyl groups can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, so monosaccharides are soluble in water
What are the 3 common polysaccharides?
- Glycogen
- Starch
- Cellulose
What is ribose?
A pentose sugar - 5 carbon atoms
Why is glucose used in respiration?
- Glucose is produced in plant cells using light energy trapped during photsynthesis.
- This means that glucose is a store of chemical energy.
- The energy can be released during respiration.
Why is glucose extremely soluble in water?
- It contains a large number of hydroxyl groups.
- Hydroxyl groups are polar due to the small negative charge on the oxygen atom and the small positive charge on the hydrogen atom.
- This means that hydroxyl groups can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
Why do plant cells store glucose as starch?
- Due to glucose's extreme solubility, if a cell contains a large amount of dissolved glucose, then this can cause water to move into the cell by osmosis.
- To solve this problem, plant cells store glucose as starch.
What is the function of starch?
An energy store in plant cells
How is starch structured?
Consists of two molecules called amylose and amylopectin.
Describe the structure of amylose.
- A polymer of α-glucose molecules, which are joined by 1,4 glycosidic bonds.
- The amylose molecule then twists into a compact helix, with hydrogen bonds forming between glucose molecules along the chain.
- Unbranched
Describe the structure of amylopectin.
- A polymer of α-glucose, joined by 1,4 glycosidic bonds.
- Unlike amylose, amylopectin had a branch every 25-30 glucose molecules. A branch is another chain of α-glucose molecules, joined by 1,4 glycosidic bonds.
- The branch is connected to the main chain by a glycosidic bond, but the glycosidic bond is between carbon 1 and 6.
How does the structure of starch relate to its function?
- Tight helix - making starch compact and therefore it can store a large amount of glucose molecules for its size.
- Insoluble in water - does not cause water to enter the cell by osmosis.
- Large polysaccharides - molecule can't diffuse through the cell membrane and pass out of the cell.
How does a plant turn starch into glucose?
- When the cell needs glucose, enzymes are used to break the glycosidic bonds in starch. This is a hydrolysis reaction and requires water.
- The enzymes that break down starch act at the ends of the molecules.
- Because of this, the enzymes can break down starch rapidly.
What is the function of glycogen?
- Energy store in animals
- The major stores of glycogen are found in the liver and in muscle cells
How is glycogen structured?
- A polymer of α-glucose
- Most of the α-glucose molecukes are joined by 1,4 glycosidic bonds.
- However, glycogen also contains branches - the glucose molecules at the branch points are joined by 1,6 glycosidic bonds.
- Glycogen is more branched than amylopectin.
How does the structure of glycogen relate to its function?
- Large number of branches - lots of free ends, meaning enzymes can convert glycogen back to glucose very rapidly.
- Insoluble - does not draw water into cells by osmosis.
- Large molecule - cannot diffuse out of a cell
Why is it important that glycogen can be converted into glucose rapidly?
This is important as animals often have a high rate of respiration, and the energy needs of animals can change rapidly e.g. an animal may have to move quickly to escape from a predator, so the rate of respiration would increase, and glycogen in the animal's muscles could be rapidly converted to be used in respiration.
What is the function of cellulose?
Provides strength and structural support to plant cell walls
How is cellulose structured?
- Polymer of β-glucose
- Due to the hydroxyl being above carbon 1, if you want to form a glycosidic bond between carbons 1 and 4, the hydroxyl groups in point in different directions.
- When a molecule of cellulose is formed, every second β-glucose molecule is flipped, so that a glycosidic bond is formed between carbons 1 and 4.
- Unbranched polysaccharide
How does the structure of cellulose relate to its function?
- Cellulose forms a straight chain without any branches - allows cellulose molecules to get close together. Hydrogen bonds can now form between neighbouring chains. Because a huge number of hydrogen bonds form, this makes cellulose extremely strong. When cellulose chains group together, this is called a microfibril. Microfibrils then groupp together to form larger structures called macrofibrils. Macrofibrils group together to form a cellulose fibre, which form the plant cell wall.
- Cellulose cell wall is permeable to molecules - e.g. water, under normal conditions, plant cells contain a great deal of water. As water moves in by osmosis, the plant cell's contents push outwards against the cellulose cell wall. The strength of the cellulose cell wall means that it can resist the outwards pressure due to the cell contents, preventing the plant cell from bursting. Turgid plant cells help to give the plant its upright structure.
What are the reducing sugars?
- All monosaccharides
- Some disachharides e.g. maltose/lactose
What are the non-reducing sugars?
- No monosaccharides
- Some disachharides e.g. sucrose
What is the test for reducing sugars?
Benedict's test for reducing sugars
1. Add 3cm³ Benedict's reagent (blue) to 3cm³ sample (needs to be liquid to begin with)
2. Heat in boiling water bath for 5 minutes
3. Positive = green / yellow / brick-red precipitate (reducing sugar present)
Why does the test for reducing sugars work?
- If a reducing sugar is present, then this adds an electron the the copper 2+ ion. This now forms the copper 1+ ion, forming a red precipitate.
- If there is only a very small amount of reducing sugar, then only a very small amount of red precipitate forms. This causes the Benedict's solution to appear green.
- If more reducing sugar is present, then the colour turns yellow.
- A higher level of reducing sugar produces an orange colour.
- If a lot of reducing sugar is present, then we see a brick red colour.
Why is the Benedict's test semi-quantitative?
- This is because the Benedict's test only shows a narrow range of colour changes, and all humans perceive colours slightly differently.
- This means the Benedict's test is semi-quantitative
What is the test for non-reducing sugars?
First check to see if the solution also contains any reducing sugar. If it does, you will need to take that into account later.
1. First, take a small amount of the unknown solution and carry out the the Benedict's test, and note down any colour change that takes place.
2. Take a fresh boiling tube and add 3cm³ of the unknown solution.
3. Add 3cm³ of dilute hydrochloric acid (hydrolyse sugar into its constituent reducing sugars)
3. Heat in a boiling water bath for 5 minutes
4. Add 3cm³ of sodium hydrogencarbonate to neutralise the test tube as the Benedict's Reagent will not work in acidic conditions. pH paper is used to check that the solution is neutralised.
5. Add Benedict's reagent and heat again for 5 minutes
6. Non-reducing sugar present = green / yellow / orange / red precipitate
What are the only two circumstances where the test for non-reducing sugar works?
- If there is either no reducing sugar present or a small amount.
- This is because, if there is a large amount of reducing sugar in the first Benedict's test, even if there was a non-reducing sugar present, we would not be able to see a colour change beyond red.
What are reducing sugars?
Reducing sugars are sugars that can give away electrons to (reduce) other molecules.
What is Benedict's reagent also known as?
Copper II sulphate
How do you test for starch?
1. Place 3cm³ of food solution in a test tube
2. Add iodine dissolved in potassium iodide (orange/ brown) to solution and shake/stir
2. Blue-black colour = starch present
What are the first steps of all food tests?
1. In the first stage, grind the food with a small amount of distilled water in a mortar and pestle.
2. Once the food has been turned into a paste, add more distilled water and stir the mixture.
3. However, the mixture has solid food particles which could make the test results difficult to see. Therefore, you need to filter the mixture to remove these solid food particles.
- Tests are carried out on the filtrate.
How do you test for protein?
1. Place 3cm³ of food solution in a test tube.
2. Add 3cm³ of dilute sodium hydroxide solution and mix.
3. Add 10 drops of dilute copper (II) sulphate solution (blue) and mix again.
4. Purple/lilac - protein is present
What is biuret solution?
Biuret solution is a premixed solution of sodium hydroxide solution and copper (II) sulphate solution.
Why would the test for proteins not work on a solution of amino acids?
- The biuret test detects the presence of peptide bonds.
- Amino acids do not contain peptide bonds.
How is the test for lipids different to the other food tests?
- The food solution is not filtered.
- This is because lipids can stick to filter paper
- Instead, you would leave the food solution for a while to allow the particles to settle.
How do you test for lipids?
1. Add 3cm³ of food solution to a grease free test tube.
2. Add 3cm³ of ethanol and shake (to dissolve lipids)
3. Add 3cm³ of water and shake the solution.
4. White, cloudy emulsion - lipids are present
Clear - lipids are not present
Why is water a polar molecule?
The oxygen atom has a partially negative charge and the hydrogen atoms have a partially positive charge
How is water structured?
- A molecule of water contains one atom of oxygen chemically bonded (covalent) to two atoms of hydrogen.
What is a hydrogen bond?
- The opposite charges on the oxygen and hydrogen atoms mean that water molecules are attracted to each other.
- These forces of attraction are called hydrogen bonds.
- Hydrogen bonds are quite weak bonds, however even a small volume of water contains a large number of hydrogen bonds, so they have a large effect on the properties of water.
How are water molecules arranged in liquid water?
- They are not arranged neatly and are instead moving randomly.
- However hydrogen bonds are still present.
What are the 5 main properties of water?
- High specific heat capacity
- High latent heat of evaporation
- Cohesive
- Solvent
- Metabolite
Why does water have a high specific heat capacity?
- We have to put in a or take out a large amount of energy to change the temperature of water.
- Water is polar so it has many H bonds.
- When water is heated, the heat energy goes towards weakening or breaking the hydrogen bonds, rather than increasing the kinetic energy of the water molecules.
Why is it important in biology that water has a high specific heat capacity?
- It acts as a buffer against rapid temperature changes.
- This allows water to act as a habitat for aquatic organisms, because aquatic organisms would not be able to function if the temperature of water changed rapidly e.g. on cold or hot days
- Organisms mostly made of water so helps maintain a constant internal body temperature - important as temperature affects enzyme activity
Why is it important that ice is less dense than liquid water?
- Because it is less dense, it floats.
- Ice is a habitat for a number of organisms
- Ice also insulates the water below and prevents it from freezing, which means that organisms can continue to live in the water under the ice.
Why does water have a very high latent heat of vaporisation?
- It takes a large amount of heat energy to evaporate water.
- Water is polar so many H bonds form between water molecules
- These bonds can absorb a lot of energy before breaking, when water evaporates
Why is it important in biology for water to have a very high latent heat of vaporisation?
- Organisms can cool themselves without losing a great deal of water, making it an efficient cooling mechanism
- Helps organisms to maintain a constant body temperature
Why is water a solvent?
- Polar (has a slightly positive and negative ends)
- Can separate (dissolve) ionic compounds e.g. NaCl as +ve end attracted to -ve ion (Cl-) and negative end attracted to positive ion (Na+)
Why is it important in biology for water to be a solvent?
- Metabolic reactions occur faster in solution
Why is water cohesive?
- Polar so many H bonds form between water molecules
- So water molecules tend to stick together
Why is it important in biology for water to be cohesive?
- Cohesion allows long columns of water to travel in the xylem tubes, making it ideal as a transport medium in plants.
- Produces surface tension at an air-water surface so invertebrates can walk on water e.g. pond skaters
Why is water a metabolite in many metabolic reactions?
It is reactive
Why is it important in biology for water to be a metabolite?
- Water is a reactant in many different reactions e.g. hydrolysis and photosynthesis.
- Water is also produced in condensation reactions and aerobic respiration.
Where do inorganic ions occur?
- Occur in solution in the cytoplasm and body fluids of organisms
- Some in high concentrations and others in very low concentrations
What are the roles of a phosphate ion?
- PO43-
- Attached to other molecules as a phosphate group, for example:
- in DNA nucleotides, enabling nucleotides to join together forming phosphodiester bonds
- in ATP - bonds between these store / release energy
What are the roles of a hydrogen ion?
- H+
- Maintains pH levels in the body
- Too much H+ = acidic (low pH)
- Too little H+ = alkaline (high pH)
- Affects rate of enzyme-controlled reactions as can cause enzymes to denature
What are the roles of an iron ion?
- Fe2+
- Component of (haem group of) haemoglobin which is contained in red blood cells
- Transports oxygen around the body - oxygen temporarily binds to it, so it becomes Fe3+
What are the roles of a sodium ion?
- Na+
- Co transport of glucose and amino acids across cell membranes
- Involved in generating nerve impulses and muscle contraction
What are the 6 main functions of lipids in biology?
- A major source of energy in the human diet
- Energy store - e.g. adipose tissue in humans
- Insulate the body, reducing heat loss to the environment
- Adipose tissue is also found around vital organs e.g. kidneys and this helps to protect these organs from injury
- Waterproofing e.g. the oils which coat the feathers of aquatic birds
- Part of the structure of membranes, such as those which surround cells and mitochondria.
What are the two main types of lipids?
- Triglycerides
- Phospholipids
What is the general structure of a triglyceride?
1 molecule of glycerol and 3 molecules of fatty acid
How are fatty acid molecules structured?
- At the end, there is a carboxylic group
- The rest of the molecule consists of a long chain of carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen
What is the difference between saturated fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids?
- Saturated - contain only single covalent bonds between the carbon atoms.
- Unsaturated - contain at least one double covalent bond between the carbon atoms (monounsaturated or polyunsaturated).
How is a triglyceride formed?
- A glycerol molecule and a fatty acid chain can react to form an ester bond, and this process is called esterification. A molecule of water is also formed, meaning it is a condensation reaction.
- Two more fatty acid molecules react the same way with the same glycerol molecule.
How are lipids broken down in the human body?
- In the digestive system, lipase enzymes break the ester bonds, releasing the glycerol and fatty acid molecules.
- This reaction required 3 water molecules, and is an example of a hydrolysis reaction
How does the structure of triglycerides relate to its functions?
- They are non-polar molecules, meaning they are hydrophobic and therefore do not dissolve in water - why lipids are as waterproofing.
- High ratio of C-H bonds to C atoms in hydrocarbon tail
so release more energy than the same mass of carbohydrates
- Insoluble in water (clump together as droplets) so no effect on water potential of cell
How are phospholipids structured?
- 1 glycerol molecule bonded to 2 fatty acid molecules.
- The glycerol molecule is also bonded to phosphate.
How does the phosphate in a phospholipid affect its properties?
- The phosphate is negatively charged, meaning that this part of the molecule is polar.
- Because of this, the phosphate group is hydrophilic, meaning it is attracted to water molecules.
- This means that phospholipids contain both hydrophilic (head) and hydrophobic (tail) regions
How do phospholipids behave in water?
- The molecules position themselves so that the hydrophilic head groups can interact with the water molecules, whilst the hydrophobic tails cluster together, well away from water molecules.
- This is called a phospholipid bilayer.
Why are a phospholipids properties important?
It allows phospholipids to form the membranes that are found both around cells and within cells
What are amino acids?
Amino acids are the monomers from which proteins are made.
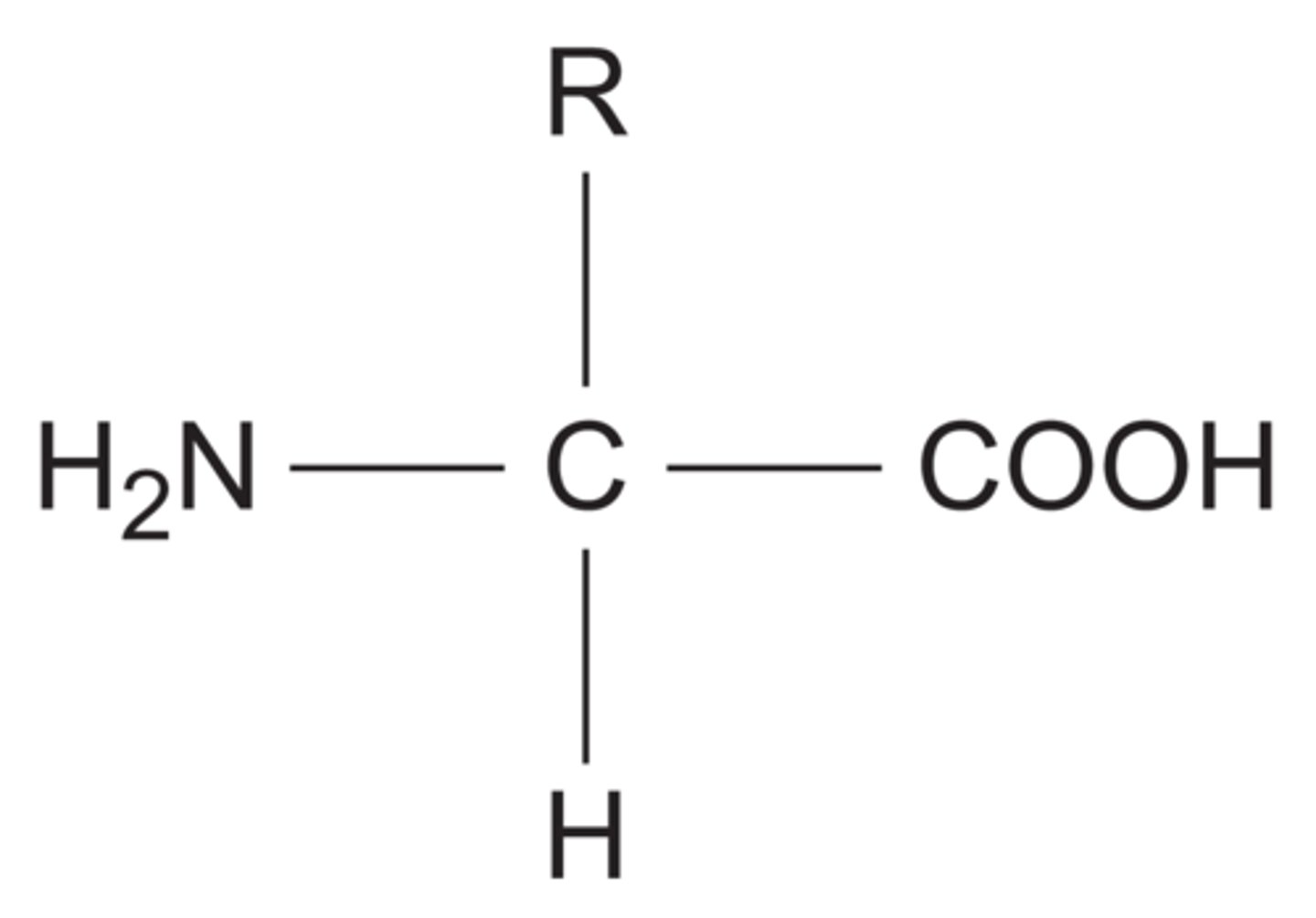
What is the general structure for amino acids?
- NH2 represents an amine group
- COOH represents a carboxyl group
- R represents a side chain.
How many amino acids are there?
- 20
- The twenty amino acids that are common in all organisms differ only in their side group (R)
What elements are present in proteins?
- Carbon
- Hydrogen
- Nitrogen
- Oxygen
- Some amino acids also contain the element sulfur
What does a condensation reaction between two amino acids form?
- A polypeptide and a molecule of water
- This reaction takes place in ribosomes, which is where proteins are synthesised in cells.
- The reaction is catalysed by a specific enzyme
What is the difference between dipeptides and polypeptides?
- Dipeptides are formed by the condensation of two amino acids.
- Polypeptides are formed by the condensation of many amino acids.
How do you break a polypeptide bond?
- By adding a molecule of water - this is called a hydrolysis reaction.
- This reaction is carried out by protease enzymes in the digestive system.
What is the difference between a polypeptide and a protein?
- In order to be classed as a protein, a polypeptide has to fold into a complex, 3D shape. Once the polypeptide has folded into the correct shape, it can then carry out its function, for example as an enzyme or a hormone.
- Many proteins actually consist of several different polypeptides, forming a large and complex molecule. (A functional protein may contain one or more polypeptides.)
- Proteins often contain other molecules helping them to carry out their function.
What are the four different levels of protein structure?
- Primary
- Secondary
- Tertiary
- Quaternary
What is the primary structure for a protein?
- Sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
- The primary structure of a polypeptide is determined by the DNA sequence of the gene which encodes that polypeptide.
Why is the primary structure for a protein important?
- It helps to determine the final 3D shape of the protein molecule, and the shape of a protein is critical for its function.
- Even changing a single amino acid in the primary structure can change the final shape of the protein, and this can prevent a protein from carrying out its function effectively.
What is the secondary structure for a protein?
- The hydrogen in the N-H has a slight positive charge whilst the oxygen in the C=O has a slight negative charge.
- Hydrogen bonding between amino acids (between carbonyl O of one and amino H of another)
• Causes polypeptide chain to fold into a repeating pattern e.g. alpha helix or beta pleated sheet
What is the relationship between primary and secondary structures of proteins?
- The type of secondary structure formed depends on the primary structure in that region.
- Certain amino acids tend to be found in alpha helices and others in beta pleated sheets