Image Receptors and Quality
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
History of X ray film
Kolls invented first films by using film that was cut into small pieces and wrapped in black paper
kodak was first film compant to develop prewrapped dental film in 1913
1920 kodak developed machine made film packets
Components of Film:
how many films does it have?
What feature? Why?
What protects film from light?
1 or two
raised dot
in mouth faces x ray tube, helps in mounting indicate where image goes in template
protective black paper
What is placed behind the film? Why? What is after that?
lead foil
protects film from receiving any seondary scatter radiation
(prevents fog)
Outer package wrapping that protects film from saliva and light
Secondary scatter radiation
radiation that spreads in diff directions from beam when that beam interacts with any substance, like body tisue
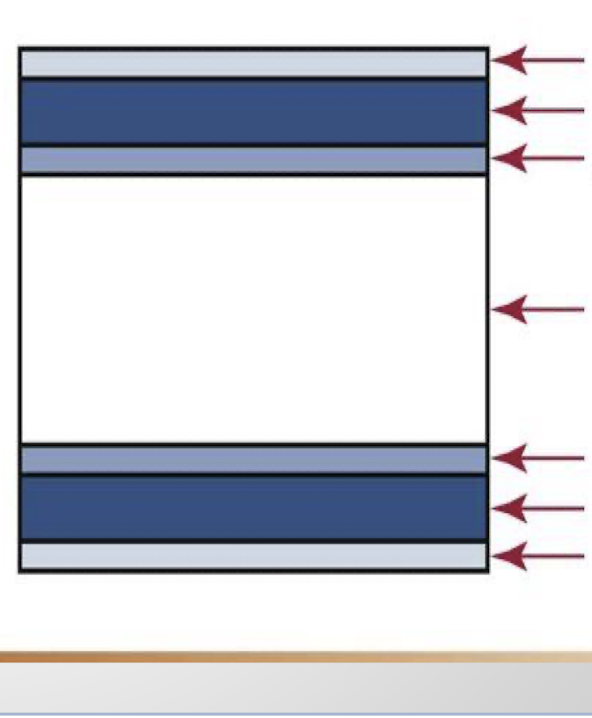
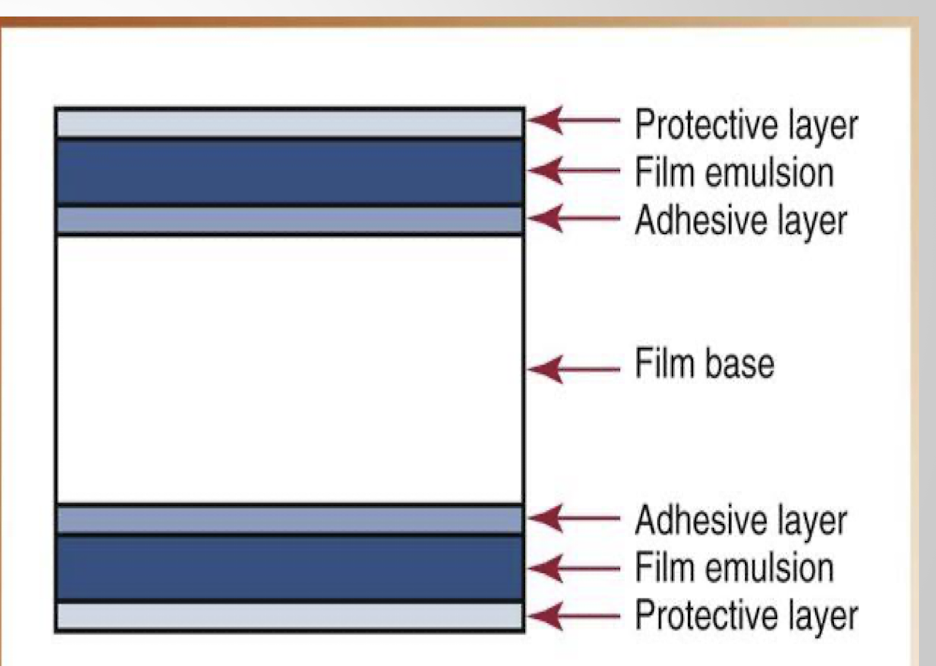
Definitions: name that component
Serves to attach emilsion to base
Attached to both sides of film by adhesive layer
Whats it made of and what do they do?
Provides strength and support
Protects emulsion from mishandling and processing damage
adhesive layer
Emulsion
gelatin and silver halide crystals: absorb radiation during exposures and stores energy in crystals
Creates the latent (invisible) image on exposed film
Film base
Protective layer
film processing
Converts latent image to visible image
preserves visible image so it says permanent
What are the requirements for film processing (4)
Darkroom
Chemicals
Developer solution
water
fixing solution
Films can be ___ processed or developed through?
manually (by hand), automatic
Darkroom requirements for film processing
correct lighting-safelight and white light
temp (70 degrees ideal) and humidity control (30-50%)
Increased temp = fog
Increased humidity = film doesnt dry
Decreased humidity: static electricity and film artifact
Film processing: requirments or film processing
Chemicals: developer solution
converst latent image to visible
reduces exposed crystals to black metallic silver
Softens emulsion during processing
Film processing: requirments or film processing
Chemicals: water
removes developer from film
Stops developing process
step is used when manually processing films
Film processing: requirments or film processing
Chemicals: fixing solution
removes unexposed silver halide crystals from emulsion
hardens emulsion
developed black metallic silver is fixed and preserved
Film fog”
darkening of images by sources other than radiation of primary beam to which film was exposed
grayness
destroys quality
Not caused by primary radiation
Causes of film fog (7)
visible light
improper safelight
outdated film
high developer temp
scatter/secondary radiation
improper storage (humidity + temp)
chemicals in processing
What to consider when acquiring digital systems (6)
Source of radiation (x ray unit itself)
Imaging receptors: either psp or sensors
software program
PSP plate readers (optimes at mUSOD)
Scanners and printers if you need to incorporate outside x rays
back up system
Two ways to obtain Digital X rays
Digital imaging receptors
indirect dental: photostimuable phosphor plates (PSP)
Direct digital: sensors
Indirect digital system
PSP plates
require the use of a laser to process latent image before converted back to visible image
middle step for processing = indirect
Two sided
Blue side = phosphor side: x rays hit these crystals to move to higher energy level capturing latent image
Back side: backing to reinforce strength
Direct digital system
Sensors:
immediate image:
white side = active and side of x ray on
Other side: cord that directly plugs into computer
What is the silver circle on PSP plate?
magnet
When you enter plate into processing machine: magnet first
How is the PSP image created?
Radiation to the PSP plate which writes latent image
visible wavelength laser reads image from PSP
creating and image requires illuminating the plate twice
creating an image requires the plate to be illuminated ?
twice
First illuminiation is emitting radiation to PSP which creates invisible latent image
When psp is put thru processor, a red light (second illumuniation source) reads the plate: displayed on computer monitor
indirect digital imaging due to middle or second processing step
What traps the x ray energy in the crystals?
How is this stored energy released?
How erased?
Photostimuable phosphor
stim by red laser and colleced in PSP reader and converted into digital image
X ray image is erased from plate by intense light source, returning all eelcctrons to orignal state and making plate ready for reuse
Direct digital: two types of sensors?
charge couple device CCD
Complementary MEtal Oxide semiconductors (CMOS)
CCD vs CMOS
CCD:
charge is transported across sillicon chip and read at one corner
tend to have higher quality and low noise due to more pixels
CMOS
each pixel can be read indivuadually due to multiple transitors
lower power
cheaper
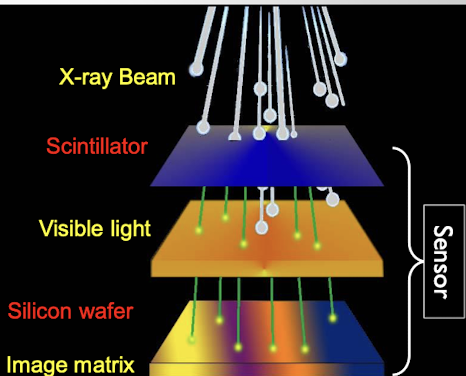
x ray beams reach scintillator
Scintillator absorbs charged particle radiation
Convert most x rays into visible light\
Light ineracts with silicone crystals and electrical charge created and formed in image matrix
stored charges removed electronically
conputer converts analog to digital to produce image
X rays have a wide range of?
at each pixel, the absorption of x rays produces a small?
energies and wavelength
voltage (electrical charge) which can flucuate (analog)
ADC
analog to diigital converter: converts analog voltage to digitral number proportional to magnitude of voltage
image matrix
rows and columns of squares known as pixels
Digital images have no ? What do they have?
physical form, exist as numbers on file
What is a pixel?
single picture element
Each pixel can only display limited number of ?
Number of gray levels depends on?
__ bits/pixel, or 65,536 gray levels
More pixels, = ?
HUman eye cannot distinguish more than ? under ideal
colors/grey levels
bit depth
16bits/pixel
better resolution and apperance
50 grey levesl
size of pixels will determine ?
spatial resolution of image:
smaller pixel, = more pixels needed for better quality
What allows us to see fine detail of image? what are units?
spatial resolution: line pair per mm
the smaller the pixels
the better visibility of smaller structures and bettter recored detail
Detector latitude
ability of imaging receptor to capture a range of x ray exposures
are sensors or PSP more sensitive?
Sensorys
for PSP plates, you have a larger range to ?
over or underexpose, high detector latitiude, but still want to use setting to avoid too light or dark
is there a point to going to higher side of green range
wont produce more detail and uncessary exposure
one basic property that affects radiographic quality
Photographic properties
Photographic properties
denstiy: amount of darkening of radiograph
Contrast: difference bween adjacent densities: black, white, grays on film
overerall, contribute to visual appearance of anatomy on radiograph
Radiographic density: controlling factors?
Controlling factors: MAS and distance
MA/time:"
milliamperes * seconds
determins quantity of x rays
longer = darker
dont mess with MAS - mess with time instead
2x the mas? density?
2x density as quantity is directly proportional to MAS
bite wings are used o assess
bone height and interproximal space
optimal density for eval of interprox space and bone height measurement
.32
To correct under or over exposure
30% rule: change of 30 is needed in mAs to demonstrate visible diff in density
along with mAs, the other controlling factor for density is?
distance
Intensity of radiation is inversely proportional to? (inverse square law)
square of the density
as you increase distance, you decrease density (beam divergence)
what helps maintain quality by standarizing distance between source and image receptor?
cone
Radiographic contrast is defined as ?
controlled by?
directly affected by?
difference between adjacent densities
kV
much tissues involved attenuate the beam as it enters the body
Fat and caries are ___
radiolucent
contrast is the __, controls the ?
standard for best image?
quality: force of emerging stream of x rays
60-70 kVp
15% rule
kV does influence density as secondary factor: increase kV by 15% = double mAS
a high kv image demonstrates
long scale contrast (more shades of gray)
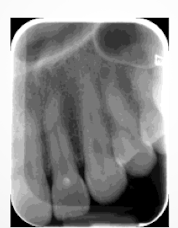
edges exposed = fogged white border ( light error)
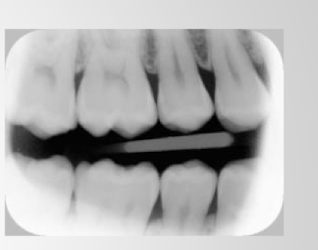
light exposure; go one by one
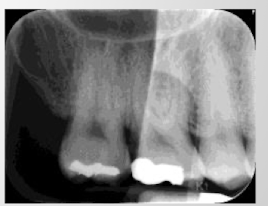
part way stuck in optime: exposed to light
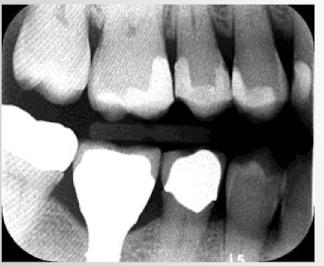
Quantum mottling: increase time of exposure
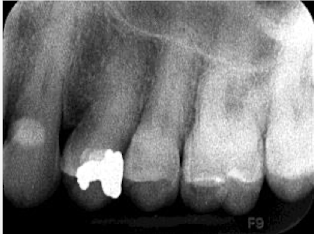
quantum mottling
if magnet doesnt impede anatomy when flipped backwards, do you still have to redo?
no
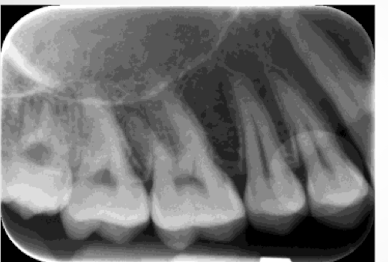
backwards placement of PSP
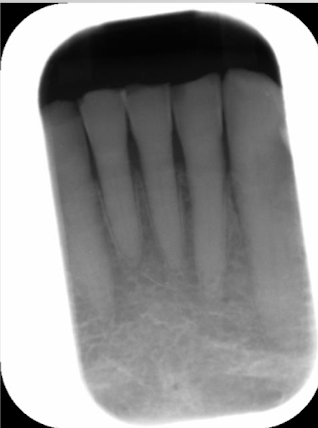
PSP plate put in processor on angle
dirt on PSP plate
patient glasses:
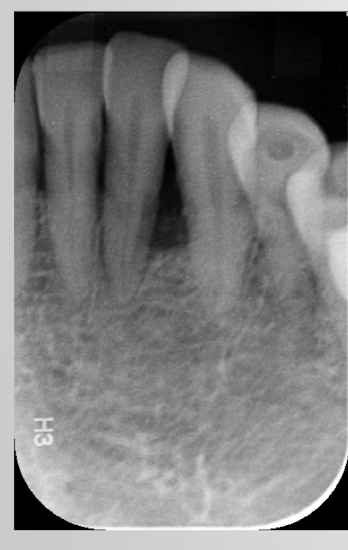
motion
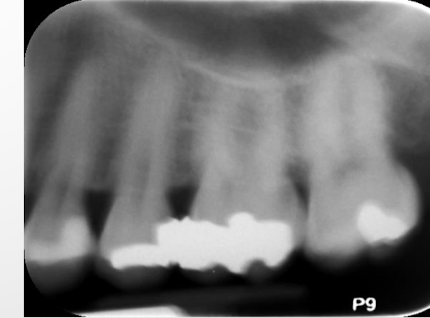
motion
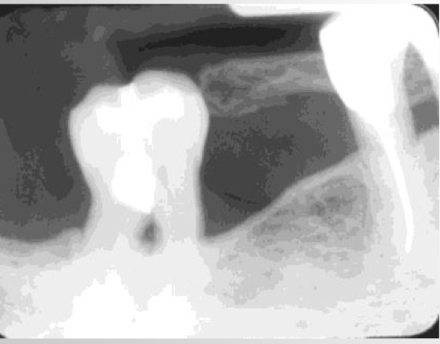
patient holding film
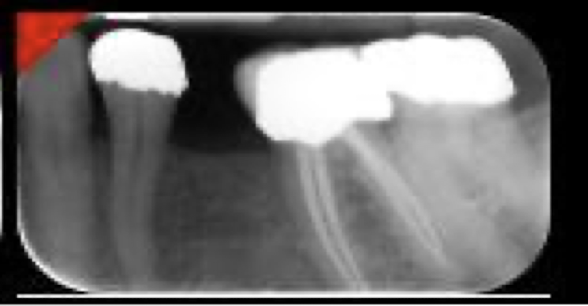
done on size 1 psp plate
what do you want to see in premolar pa
distal of canine, root apices of 1st, 2nd, premolar, 1st molar, 2-3 mm surrounding tissue
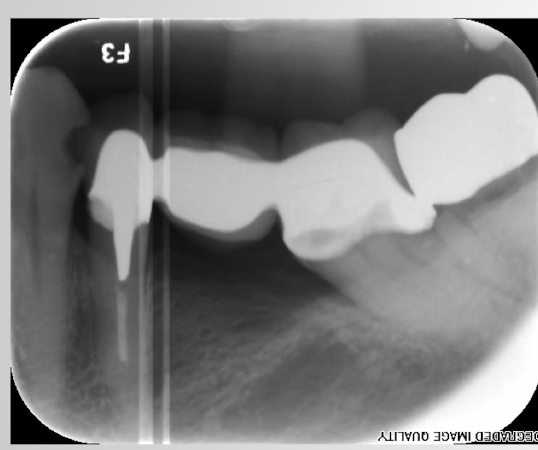
psp processing error
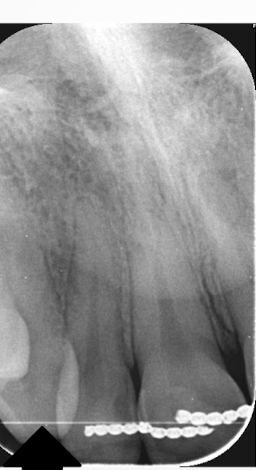
processing error
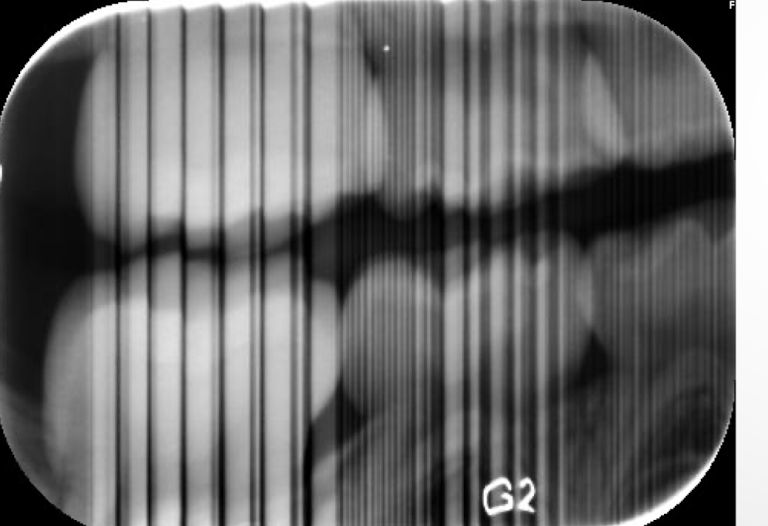
cardboard cover in wrapping PSP plates gets pulled into optiime processpr
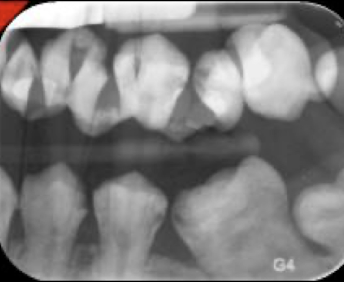
double exposure (same PSP plate twice)
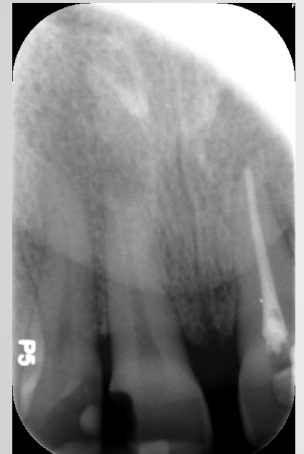
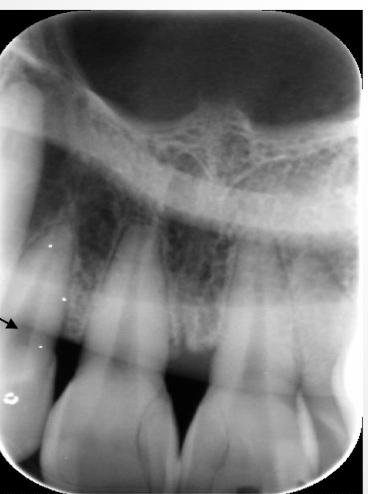
cone cut
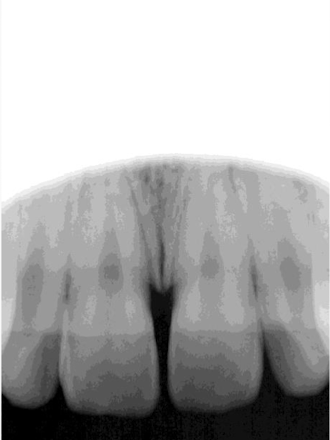
cone cut
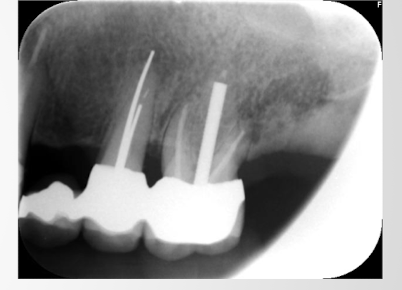
cone cut
cone cut error
cone not lined up to receptor: happens most common with bisecting angle technique as there is no ring for visual aid
thyroid collar
how?
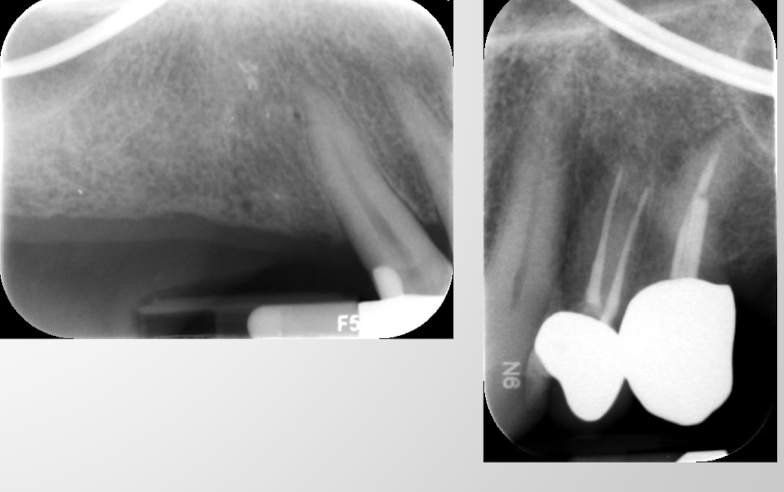
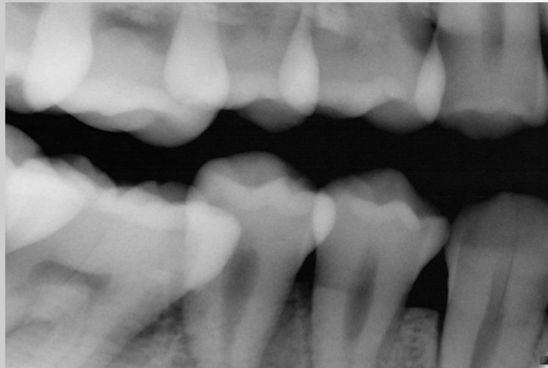
overlapping: incorrect horizontal angle
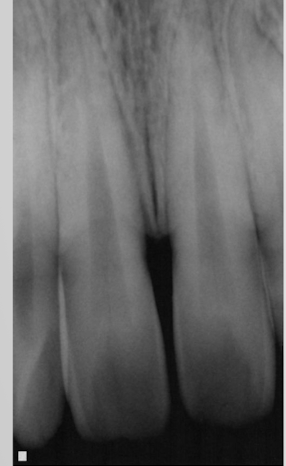
elongation: insufficent vertical tube angle: more common in biscecting angle
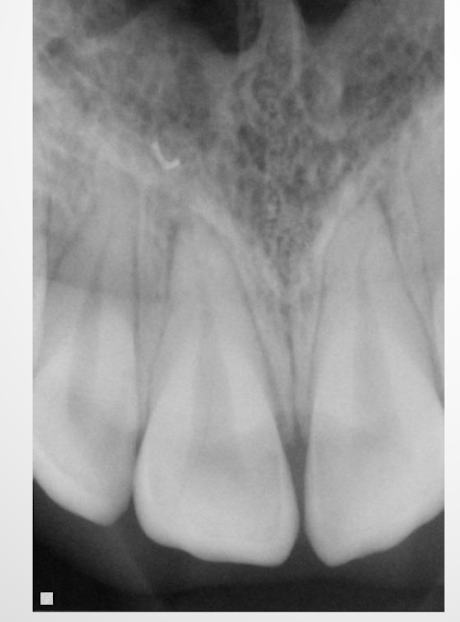
foreshortening: excessive vertical tube angle: decrease angle to fix
replace sensor
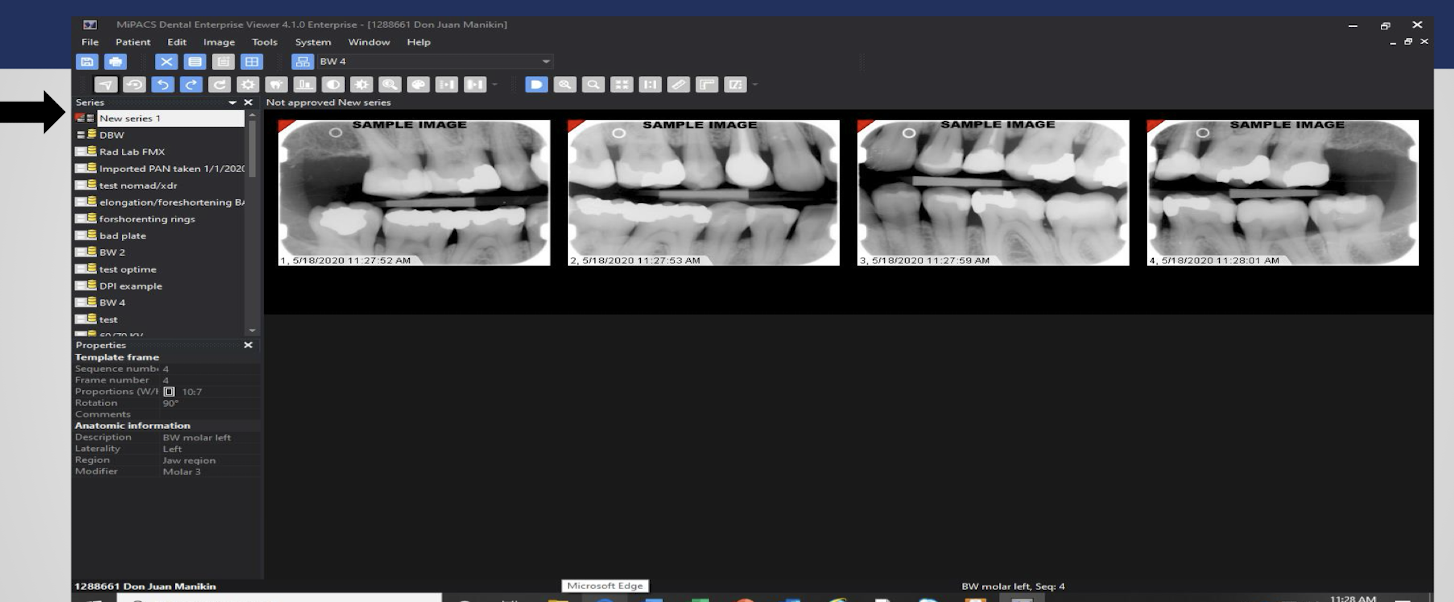
red triangle: series has not been approevs: additional images may still be added
international standard to transmit, store, retrieve, print, process, display medical imaging info
DICOM
dicom header
background: all image data
patinet ID and never be seperate
would contain data if image was altered
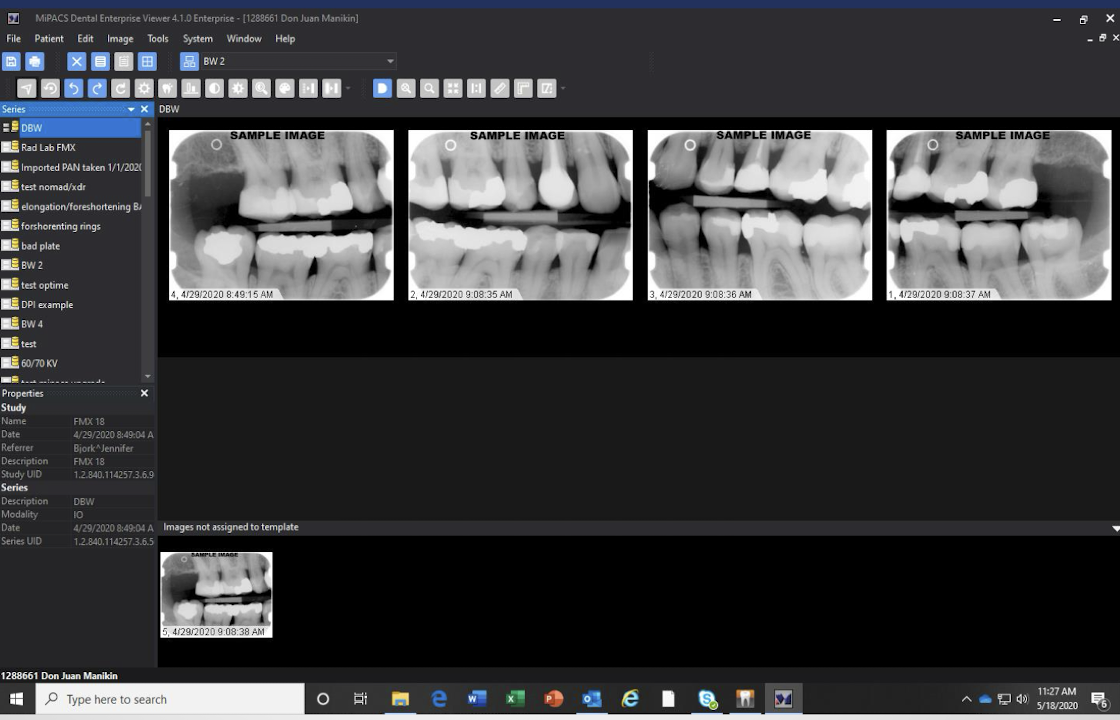
images have been saved and sent to DICOM server: yellow barrel
fidelity with which anatomic structure being examined is imaged
radio qualityq
how often testing x ray: how accurate, how much filtration?
how much digital?
3-4 years: visual charts, accuracy must be within 10%, 2 mm, 40-100 mR
D; 200, E: 150, FL 120
way to assure consistnt qualiuty: small graduated increase in thickness
stepwedge
PSP plates should be checked for scratches on a __ basis
monthly
CLEANED WITH cavi wipes
psp plates sould be cleaned with?
denatuerd alcohol
what side is active of sensor XDR
white: direct x ray towards
radiation safety plan submitted to state for what?
pans and CBCT
X
CRACKLING
test digital sensors and monitor __ for image degradation
annually: digital phantom
lowest exposure in which max line pair and number of holes can be cisualized
baseline quality assurance exposure : compare next year
what test pattern to use fo rcontrast and brightness setting of monitor?
SMPTE: society of motion picture and televesion engineers test pattern
also limitations in spactial resolution and aliasing display
in each corner; differentiate all lines of squares horizontally and vertically
5% at both ends visible = adequate
limitations of rectangualr colliamation (5)
revert to round when:
endodontic procedures
long roots
severe gag refkex
intraoral around dental dam
bisecting angle technique
target receptor distance of __
16”