Big Idea 7: Earth Systems and Patterns (Weather, Climate, and The Water Cycle)
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
What is the water cycle?
The water cycle is the process of water moving between Earth's bodies of water, land, and atmosphere through evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.
What would these items represent in a model of the water cycle: lamp, ice, layer of water, water drops forming near the ice, water dripping down the side of the tank?
The lamp would represent the Sun, ice would represent the cold temperatures in the atmosphere, the water layer at the bottom of a tank would represent an ocean or lake, water drops forming near the ice would represent condensation/clouds, and the water drips would represent precipitation.
Why is the ocean an important part of the water cycle?
The ocean makes up about ¾ of Earth's surface. It connects all of Earth's water through the processes of evaporation and precipitation.
What state of matter is water in the ocean?
Water in the ocean is liquid.
What state of matter is water vapor in the atmosphere?
Water vapor in the atmosphere is gas.
What state of matter is condensation in the clouds?
Condensation in the clouds is liquid.
What state of matter is rain?
Rain is liquid water.
What state of matter is snow?
Snow is frozen, solid water.
What state of matter is sleet?
Sleet is a mixture of liquid and solid water.
What state of matter is hail?
Hail is frozen, solid water.
What drives the water cycle?
The water cycle is driven by energy from the Sun.
What is evaporation?
Evaporation is a process caused by heat in which liquid water changes into water vapor (gas).
During evaporation, water changes from a ___ to a ___.
During evaporation, water changes from a LIQUID to a GAS.
What is condensation?
Condensation is a process caused by cooling in which water vapor (gas) changes back into liquid. Examples are clouds, water droplets on the side of a cold glass, dew.
During condensation, water changes from a ___ to a ___.
During condensation, water changes from a GAS to a LIQUID.
What is precipitation?
Precipitation is when water falls back down to Earth as either rain, hail, sleet, or snow.
What weather conditions might create rain?
Low pressure, high humidity, warm air temperature (above freezing), stratus or cumulonimbus clouds
What weather conditions might create hail?
Low pressure, high humidity, warm air temperature (above freezing), freezing temperatures in the clouds, cumulonimbus clouds, thunderstorms
What weather conditions might create snow?
Low pressure, high humidity, cold air temperature (below freezing), stratus or cumulonimbus clouds
What weather conditions might create sleet?
Low pressure, high humidity, warm air temperature (above freezing), freezing temperatures in the clouds, stratus or cumulonimbus clouds
What is weather?
Weather is the condition of the atmosphere at a particular place and time.
What conditions affect weather?
Air temperature, air pressure, humidity, wind speed and direction, and precipitation are conditions that affect weather.
What is air temperature?
Air temperature is the measure of heat in the air. It is measured by a thermometer.
How does cloud cover impact air temperature?
When the sky is cloudy, the Sun's rays are reflected off of the clouds back into space and the air temperature decreases.
What is air pressure?
Air pressure is the weight of air pressing down on Earth. It is measured by a barometer.
Low air pressure can signal ___ weather.
Low air pressure can signal BAD weather (cloudy, rainy, stormy).
High air pressure can signal ___ weather.
High air pressure can signal GOOD weather.
Air pressure _____ as the elevation _____.
Air pressure DECREASES as the elevation INCREASES.
You will likely see stormy weather during days when air pressure is ___.
You will likely see stormy weather during days when air pressure is LOW.
You will likely have clear skies and good weather on days when air pressure is ___.
You will likely have clear skies and good weather on days when air pressure is HIGH.
What is humidity?
Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. Higher humidity helps in the formation of clouds, dew, and fog and leads to precipitation (rain, snow, sleet, or hail). It is measured with a hygrometer.
Is there more humidity when the air is warmer or colder?
Warmer temperatures cause more evaporation and more water vapor (moisture) to be held in the air.
What conditions might create good weather?
High pressure, low humidity, no precipitation, cirrus or cumulus clouds
What is wind speed and direction?
Wind speed is how fast the wind is blowing. It is measured with an anemometer. Wind direction tells what direction the wind is blowing. It is measured with a weather vane.
What causes wind?
Wind is caused by the uneven heating of the Earth causing air to flow from high pressure to low pressure zones.
When hot air rises leaving space in an area, then...
...cold air will rush into that available space causing wind.
What are cirrus clouds?
Cirrus clouds are thin, wispy, feathery clouds found high in the sky. Cirrus clouds typically signify fair, pleasant weather. They can also signal a change in the weather.
What are cumulus clouds?
Cumulus clouds are puffy, white clouds. Cumulus clouds typically signify fair weather. But these clouds have the potential to grow into cumulonimbus.
What are cumulonimbus clouds?
Cumulonimbus clouds are tall, dark clouds. Cumulonimbus clouds typically signify thunderstorms and heavy precipitation.
What are stratus clouds?
Stratus clouds are low, gray, and flat. Stratus clouds can bring foggy weather and rain (if it's warm) or snow (if it's cold).
What are the weather conditions in a swamp or wetland?
Swamps and wetlands are typically warm with high humidity.
What are the weather conditions in a desert?
Deserts are very dry with low humidity and low precipitation. Temperatures during the day can be hot but get cool at night.
What are the weather conditions in a rainforest?
Rainforests are typically hot and humid with a large amount of precipitation.
What are the weather conditions on a mountain?
The higher the elevation, the cooler the temperature. Air pressure also decreases as you go up a mountain. A rain shadow desert is formed when one side of the mountain gets a lot of rain, and the other side almost none.
What are the weather conditions in a grassland?
Temperature, precipitation, and humidity vary by season in a grassland.
What are the weather conditions in the tundra?
The tundra is extremely cold and windy with little precipitation.
What is climate?
Climate describes the general weather conditions in an area over a period of time.
What are the three climate zones?
Polar, temperate, tropical
How does a large body of water like an ocean affect the climate of an area?
A large body of water makes the climate of that area more stable so there is less difference in the high and low temperatures. There is also higher humidity and more precipitation in the area.
How does elevation affect the climate of an area?
The higher the elevation, the colder the temperature.
The higher the latitude, the ___ the temperature of an area.
The higher the latitude, the COLDER the temperature of an area.
The lower the latitude, the ___ the temperature of an area.
The lower the latitude, the WARMER the temperature of an area.
Which climate zone has warm weather all year long?
The tropical zone has warm weather all year long.
Which climate zone is associated with mild or moderate temperatures?
The temperate zone is associated with mild or moderate temperatures.
Which climate zone has cold weather all year long?
The polar zone has cold temperatures all year long.
Which climate zone is associated with changing seasons?
Winter, spring, summer, fall -- the temperate zone has them all.
Where is the equator located? What is the climate like?
The equator is an imaginary line that runs around the middle of Earth. It is located at 0º latitude. The weather there is warm all year long.
Where are the polar zones located?
The polar climate zones are located around the north pole (90ºN) and the sound pole (90ºS).
Where are the temperate zones located?
The temperate zones are located between the polar and tropical zones (66.5ºN - 23.5ºN and 23.5ºS - 66.5ºS).
Where is the tropical zone located?
The tropical climate zone is located just above and below the equator (0º).
Does air temperature increase or decrease as latitude increases?
Air temperature INCREASES when latitude increases
Is moving from 0 degrees to 90 degrees N considered an increase in latitude?
YES. moving from 0 degrees to 90 degrees N IS considered an increase in latitude
Is moving from 0 degrees to 90 degrees S considered an increase in latitude?
YES. moving from 0 degrees to 90 degrees S IS considered an increase in latitude
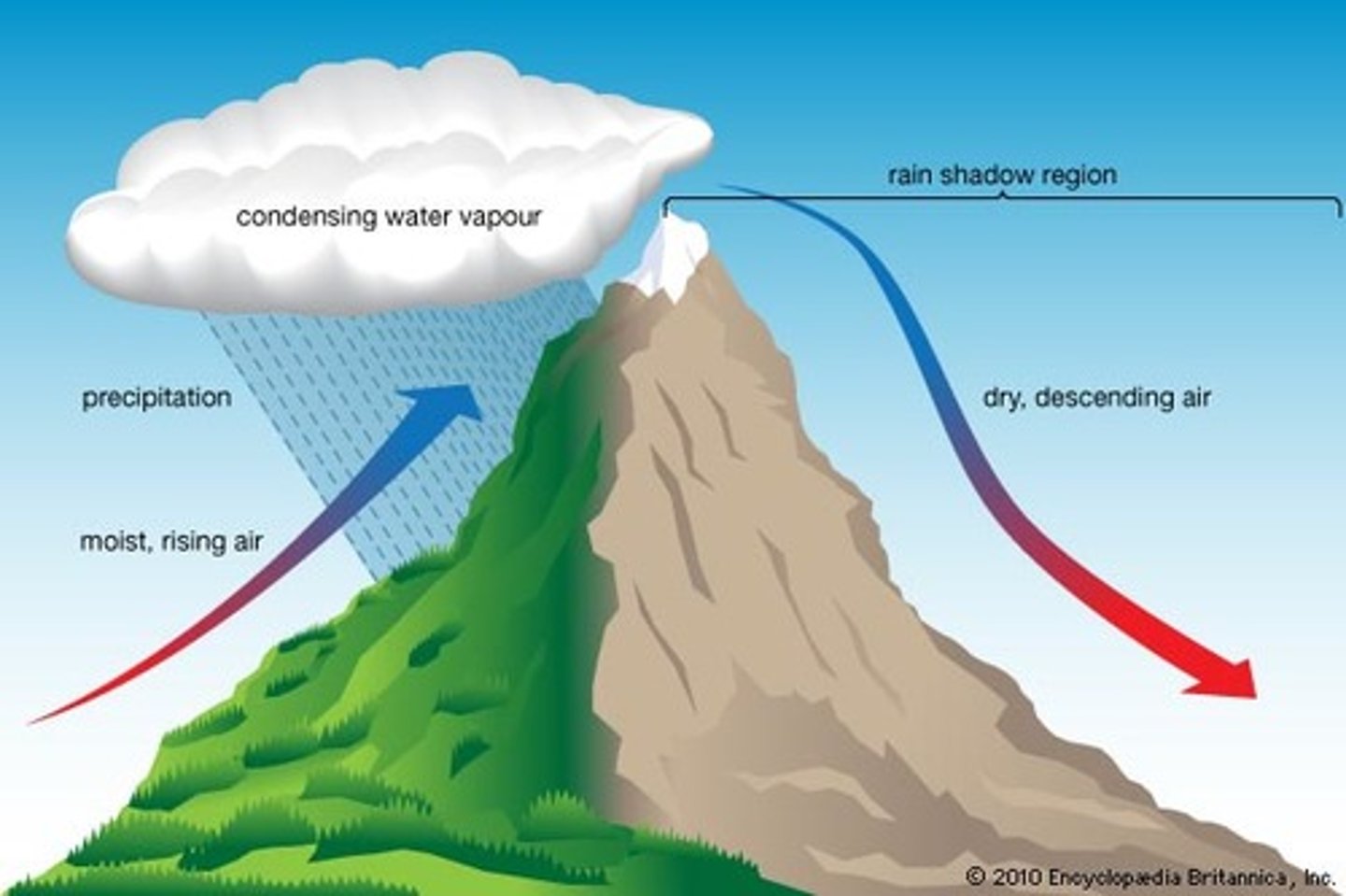
What is the rain shadow effect?
Precipitation falls on the windward side of a mountain range, resulting in lush vegetation & a warm, moist climate on one side, but a desert area on the leeward side.

What causes rain shadows?
mountains
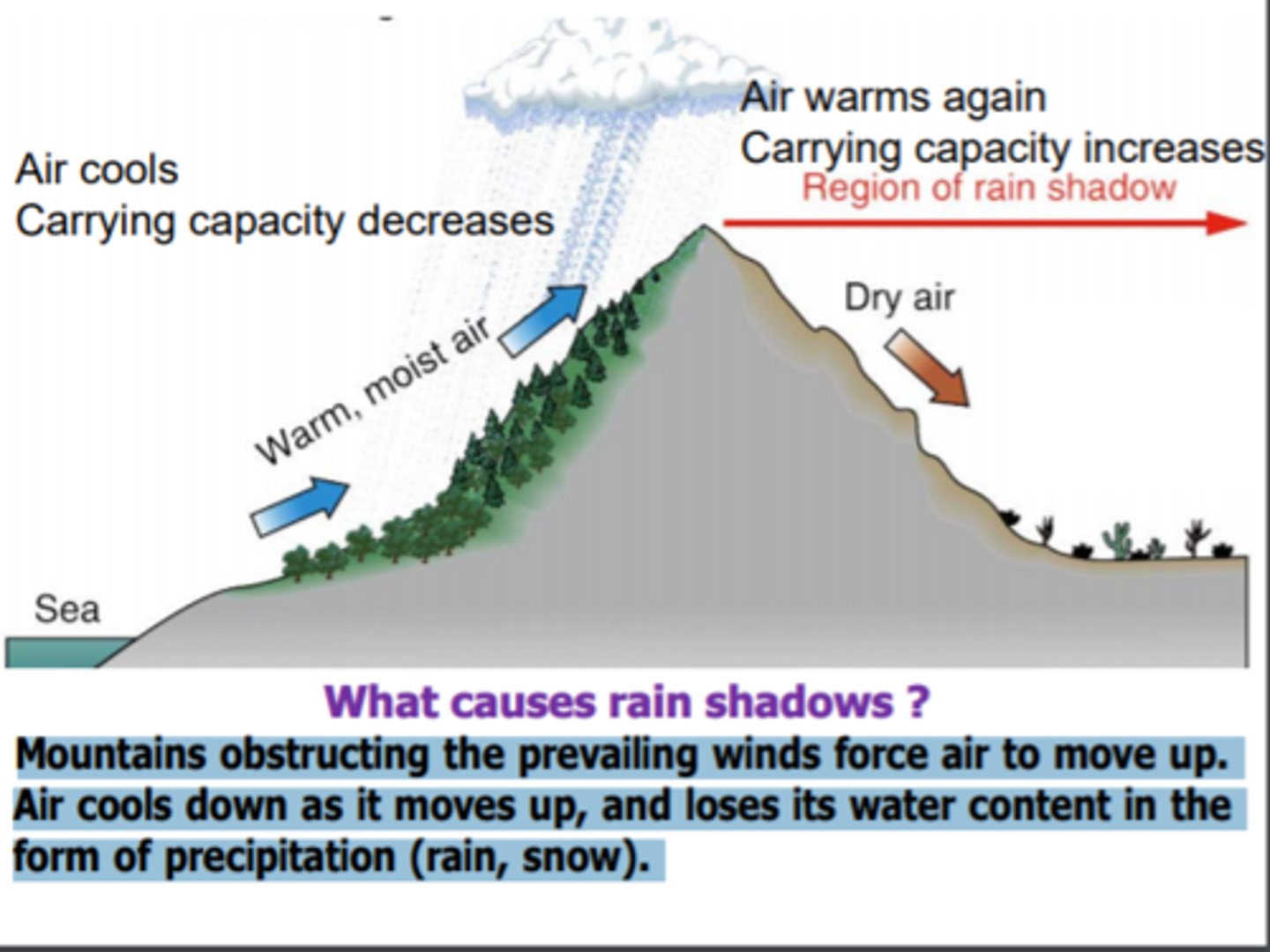
How do rain shadows form?
When rainfall has occurred over an upland area, the area on the lee side of the hills will receive less rain because the air descends, warms and becomes drier
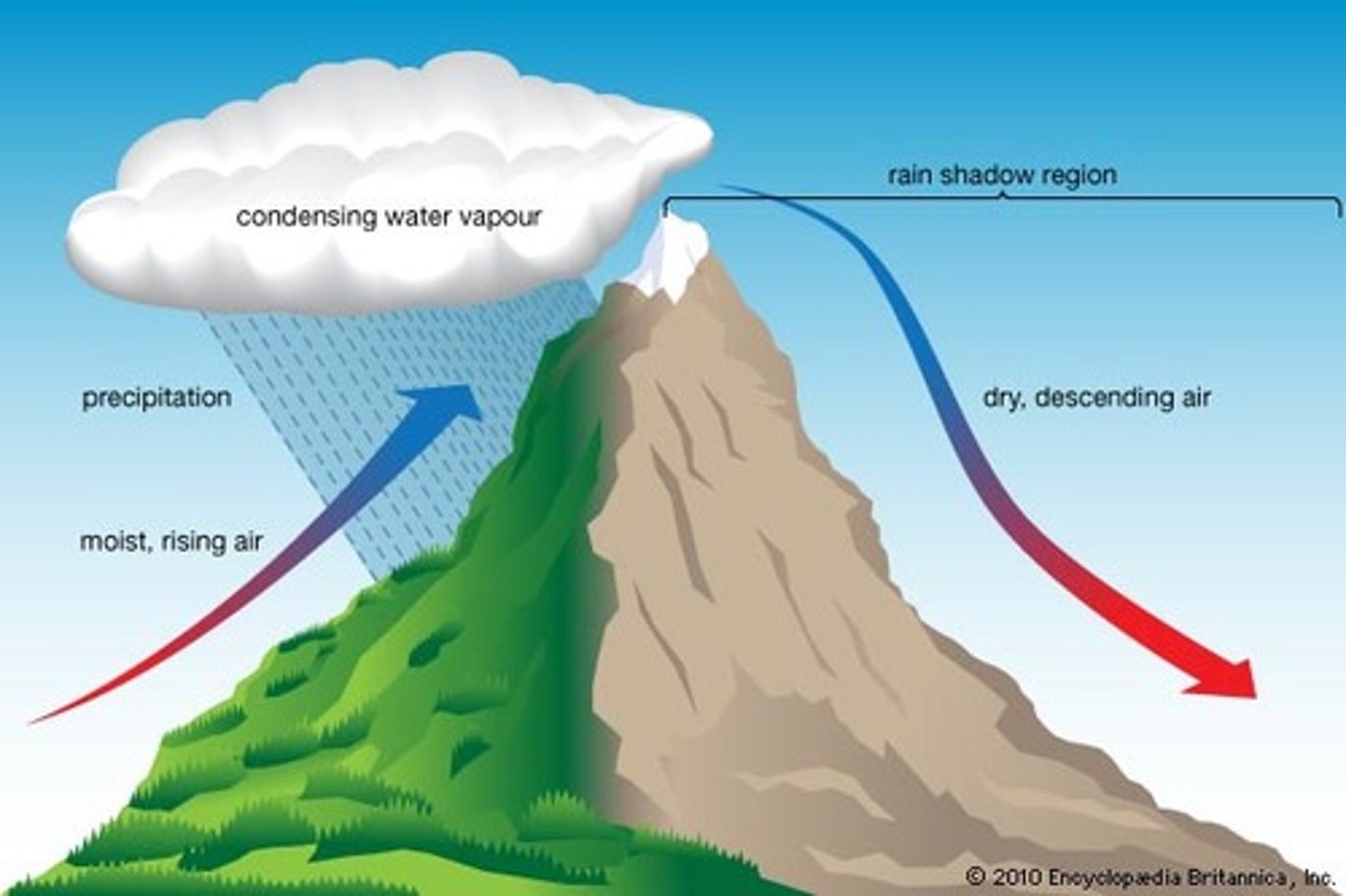
rain shadow
a region with dry conditions found on the leeward side of a mountain range as a result of humid winds from the ocean causing precipitation on the windward side