BIO 208 Laboratory Exercises for Week 7
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
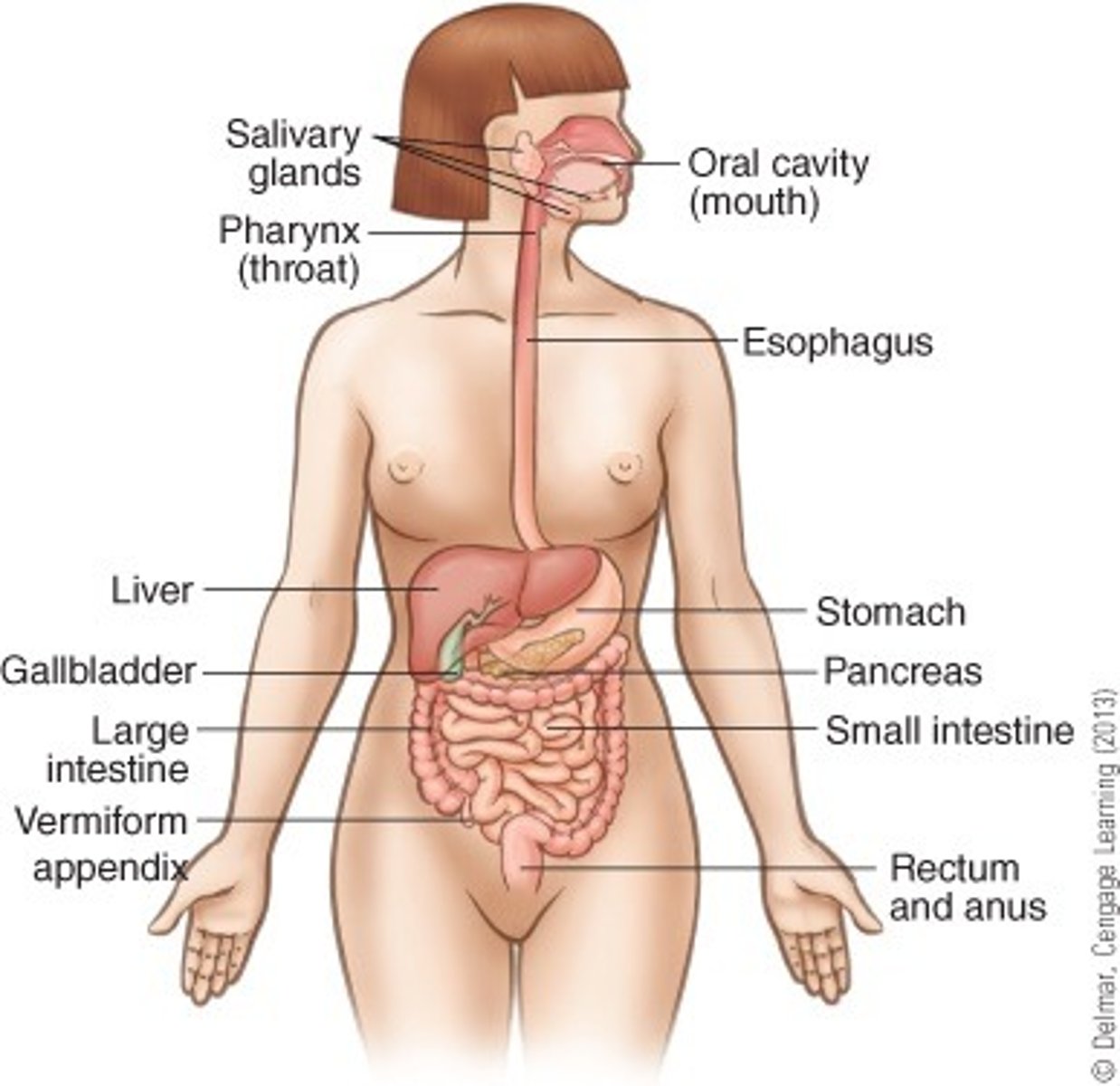
Identify the major organs of the digestive system:
- mouth
- salivary glands
- pharynx
- esophagus
- liver
- gallbladder
- stomach
- pancreas
- small intestine
- large intestine
- anus
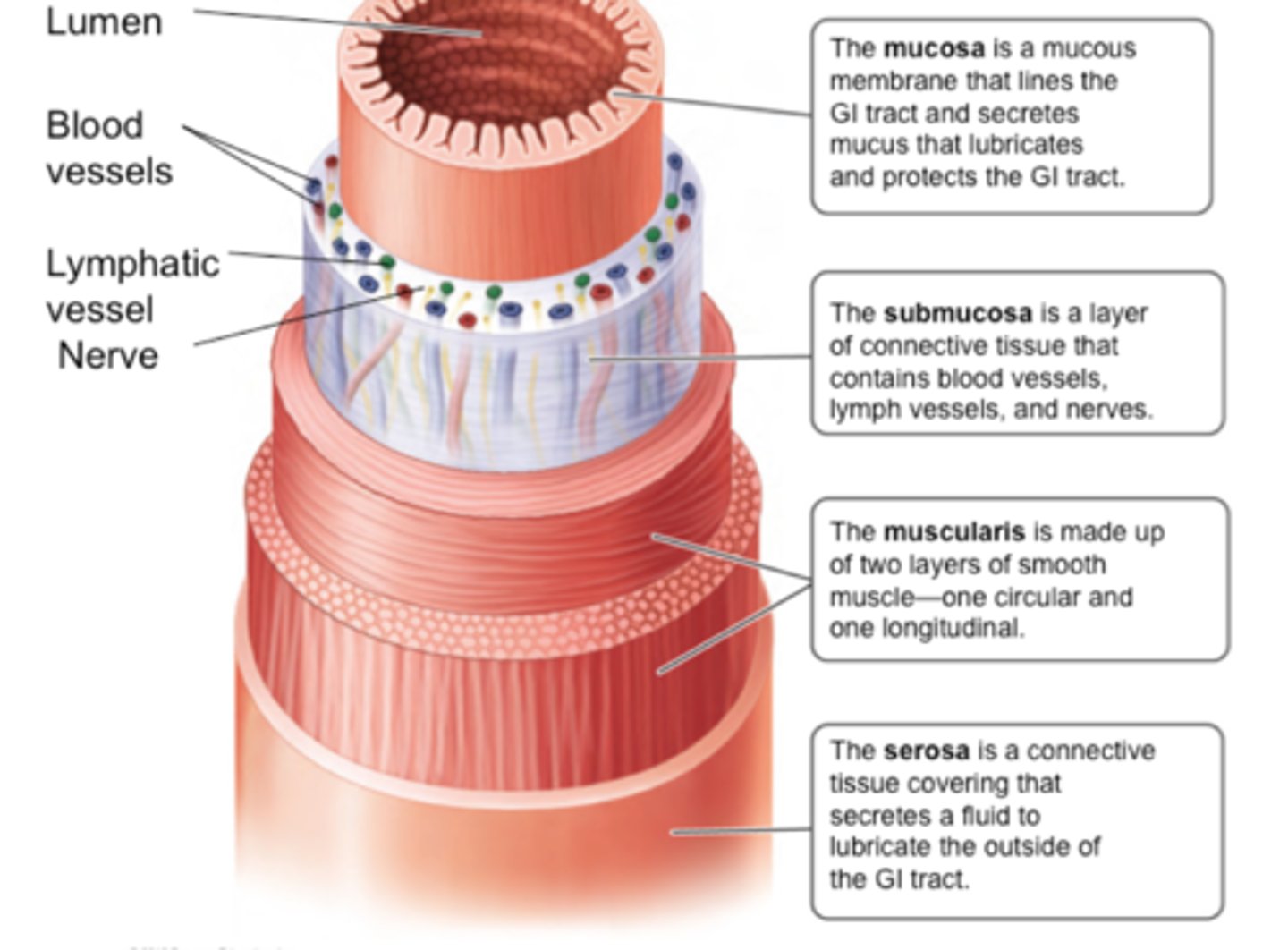
Identify the following layers of the GI tract:
- mucosa
- submucosa
- muscularis (muscular layer)
- serosa
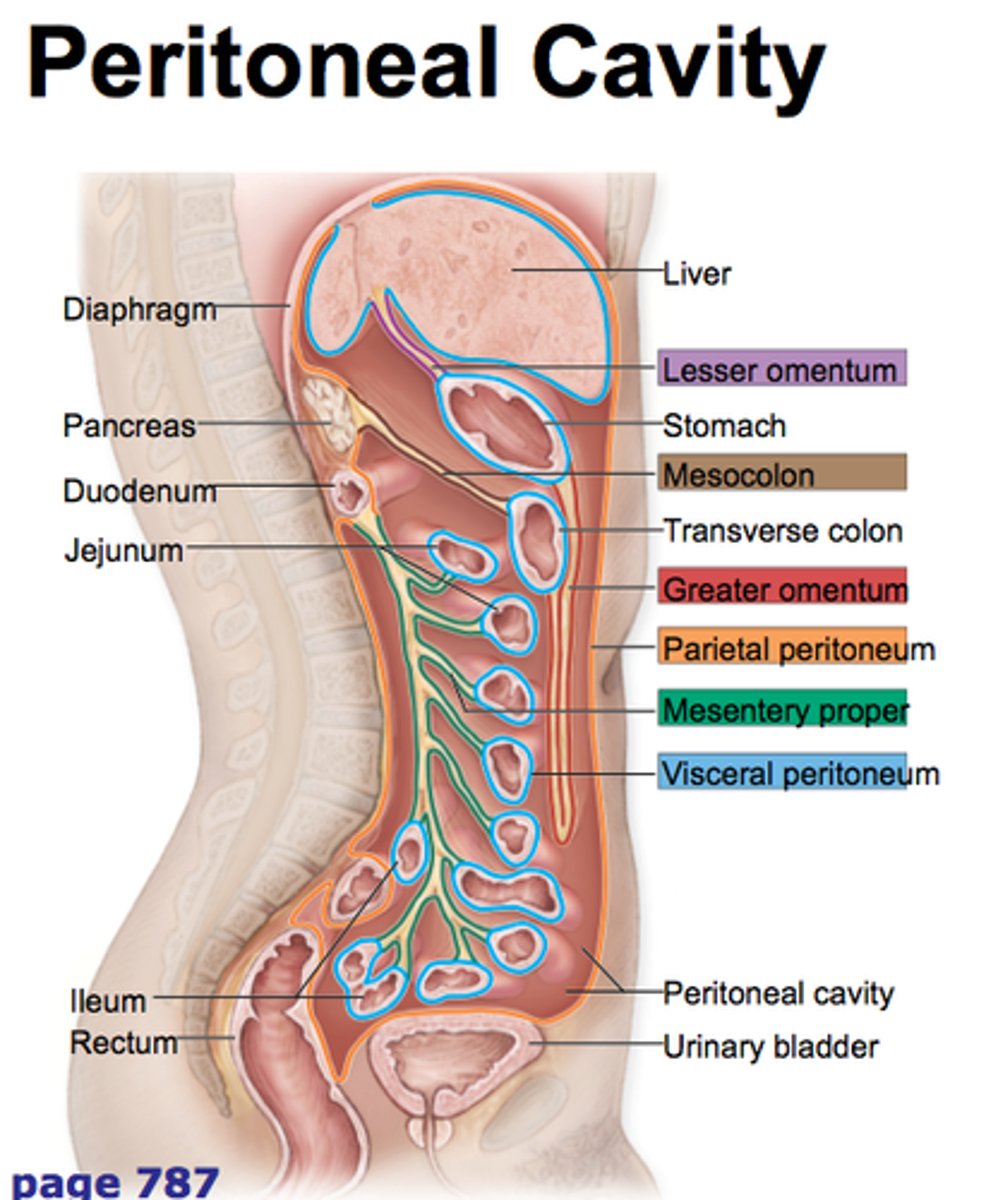
Identify the following structures of the peritoneal folds:
- lesser omentum
- mesocolon
- greater omentum
- parietal peritoneum
- mesentery
- visceral peritoneum
falciform ligament
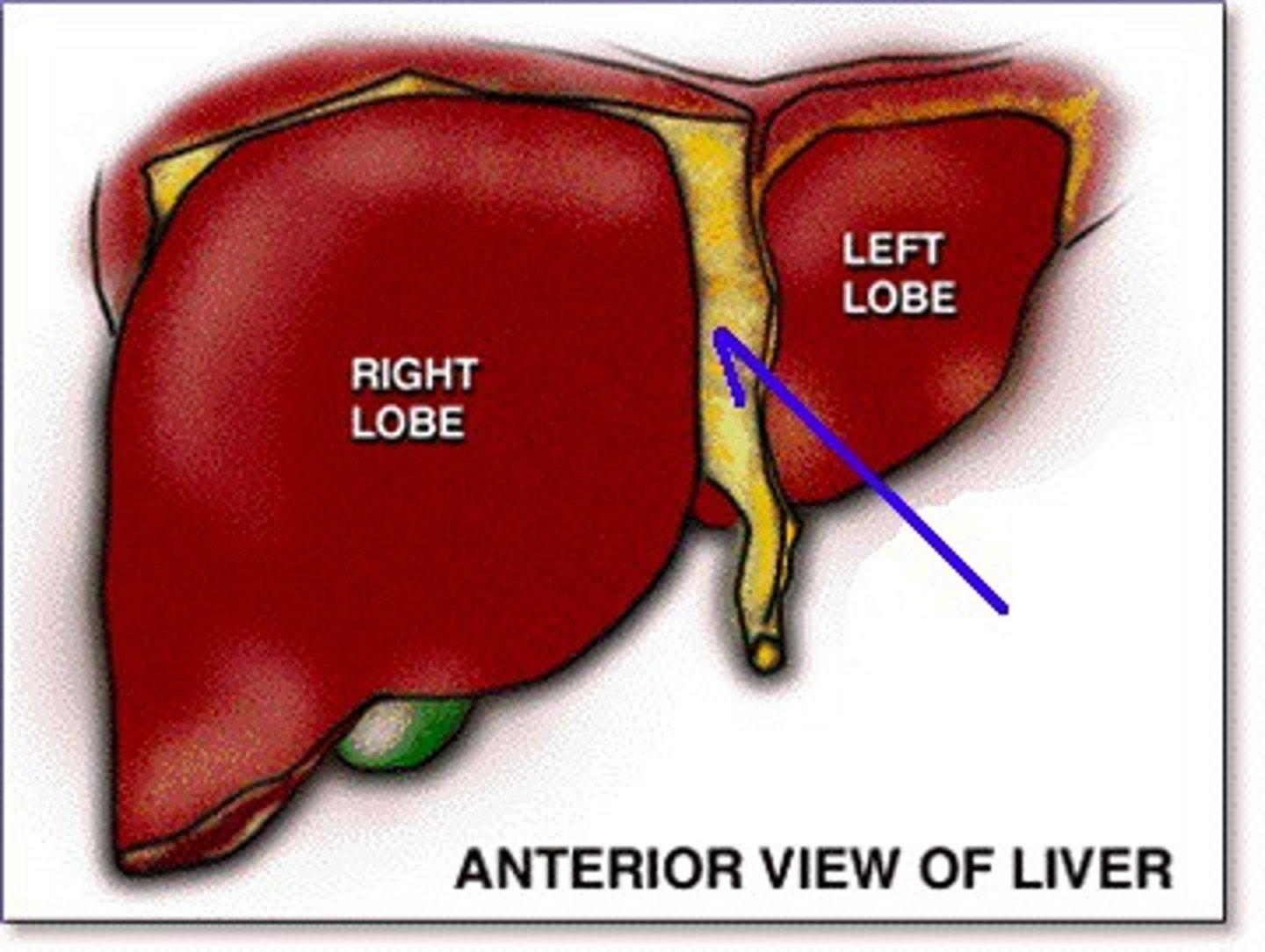
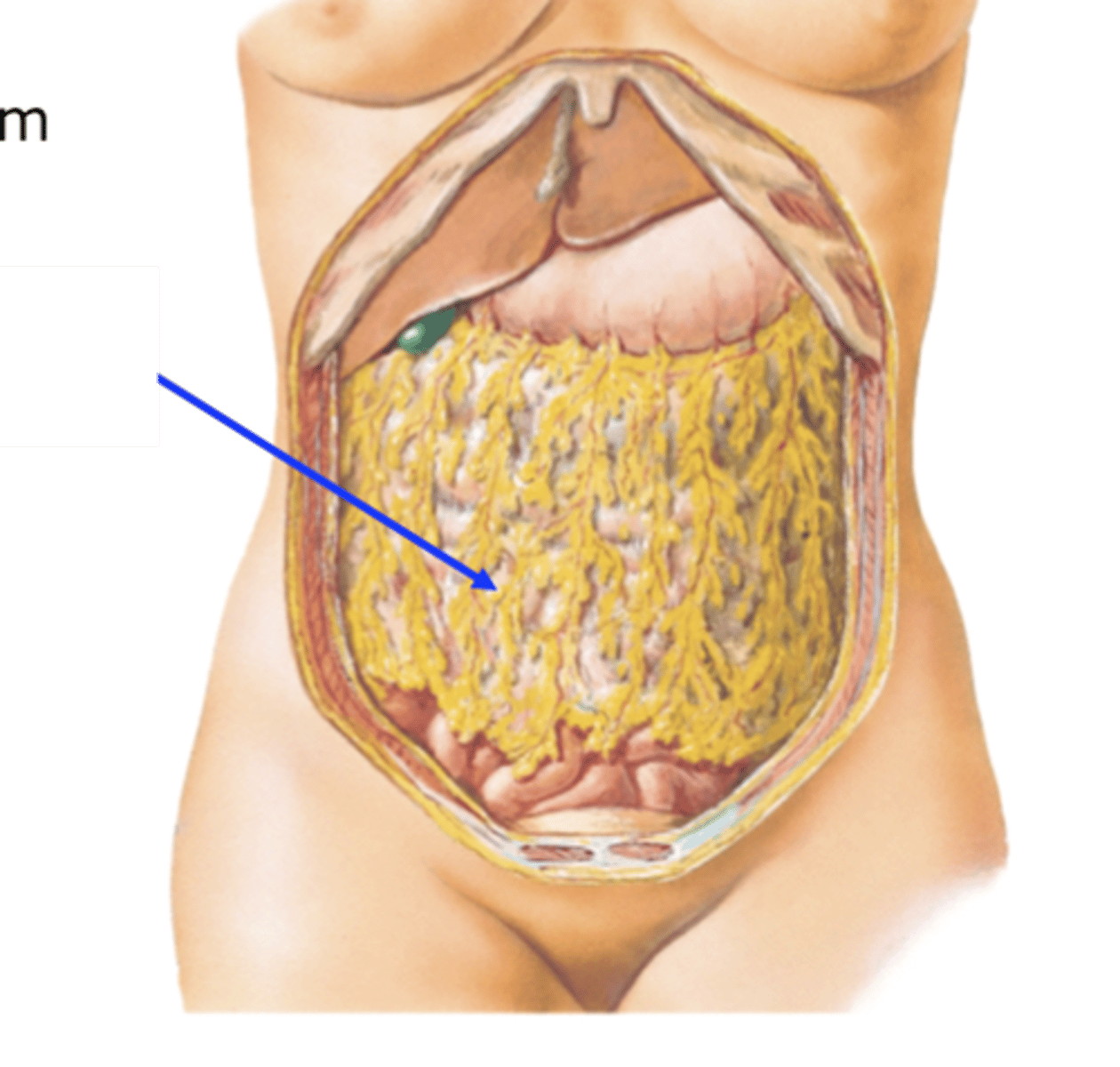
greater omentum
part of the peritoneum attached to the stomach and to the colon and covering the intestines
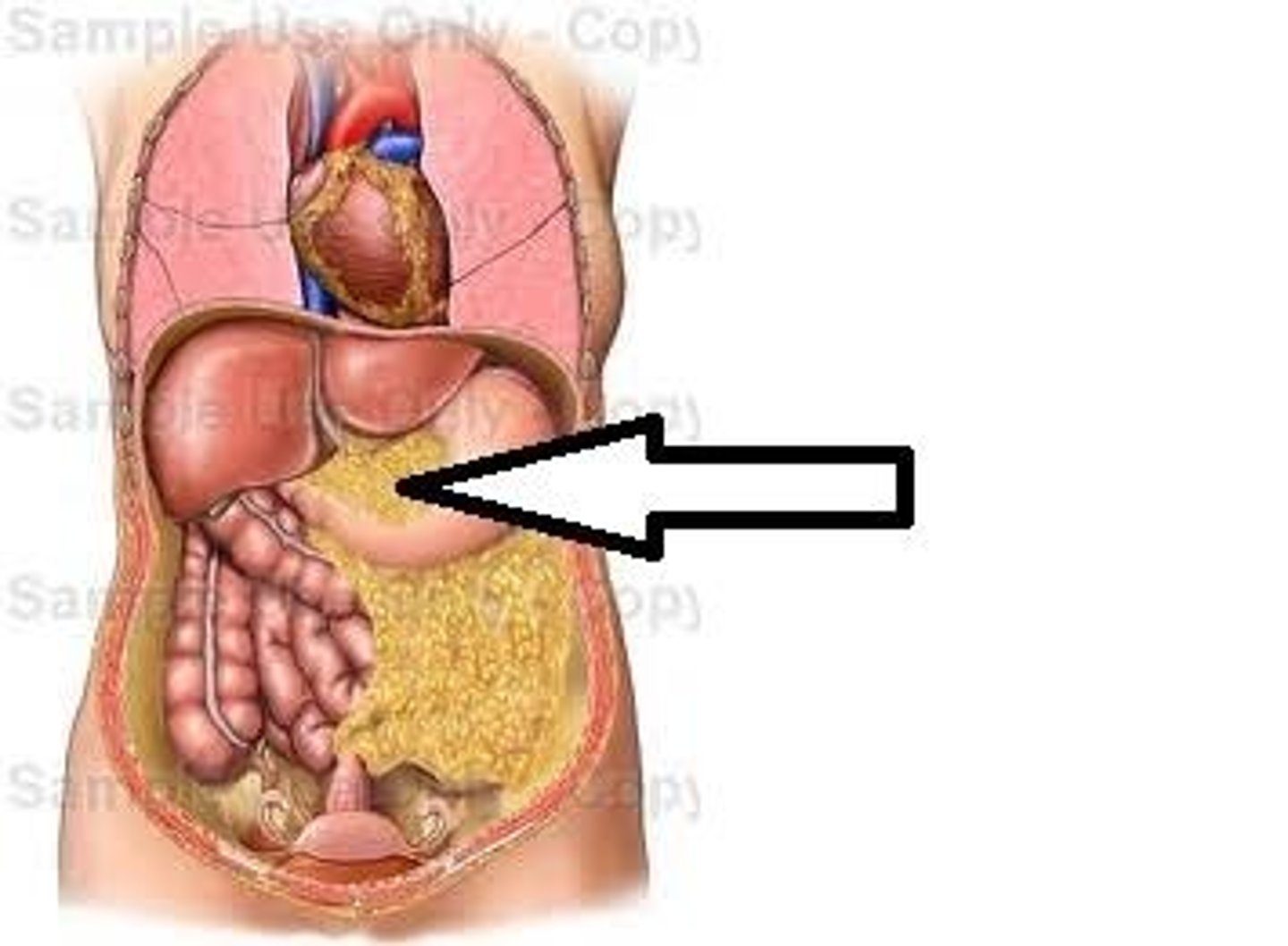
lesser omentum
attaches stomach to liver
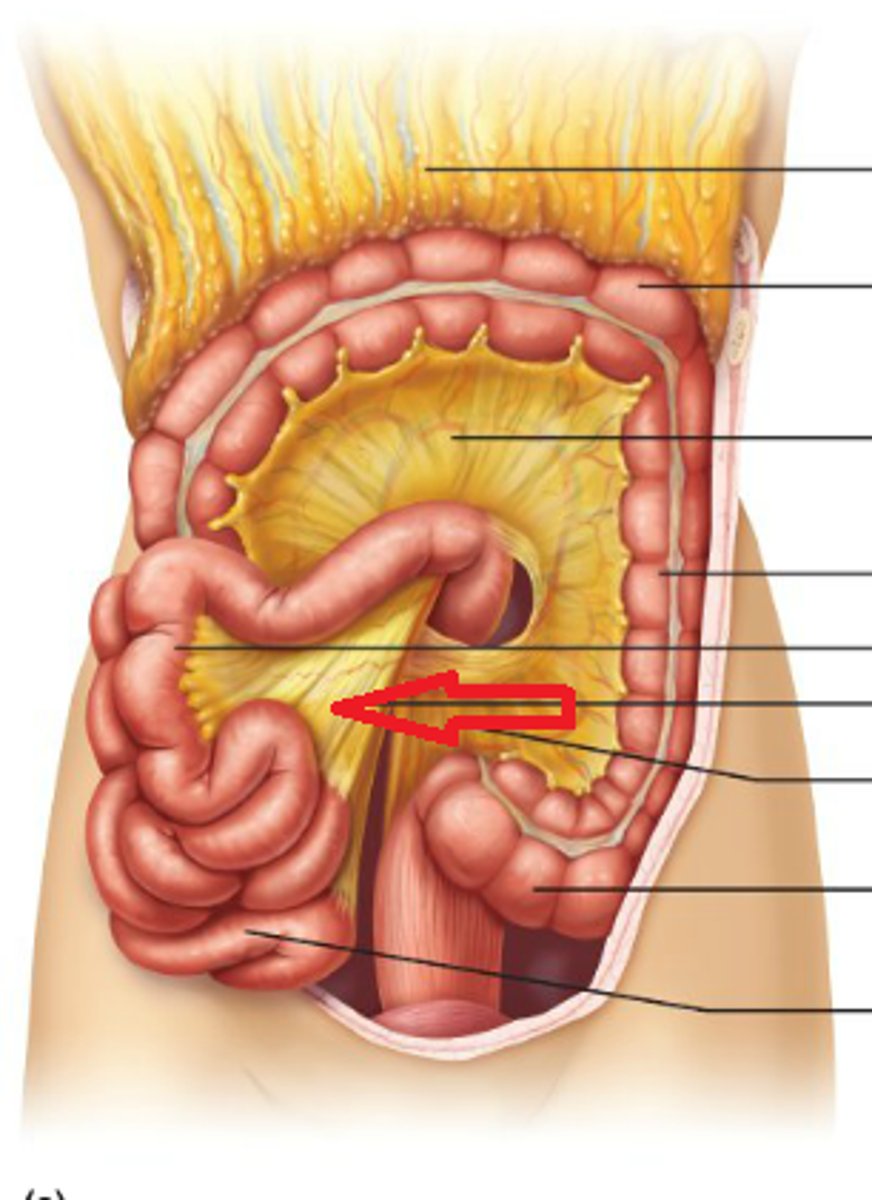
mesentery
a fused double layer of the parietal peritoneum that attaches parts of the intestine to the interior abdominal wall
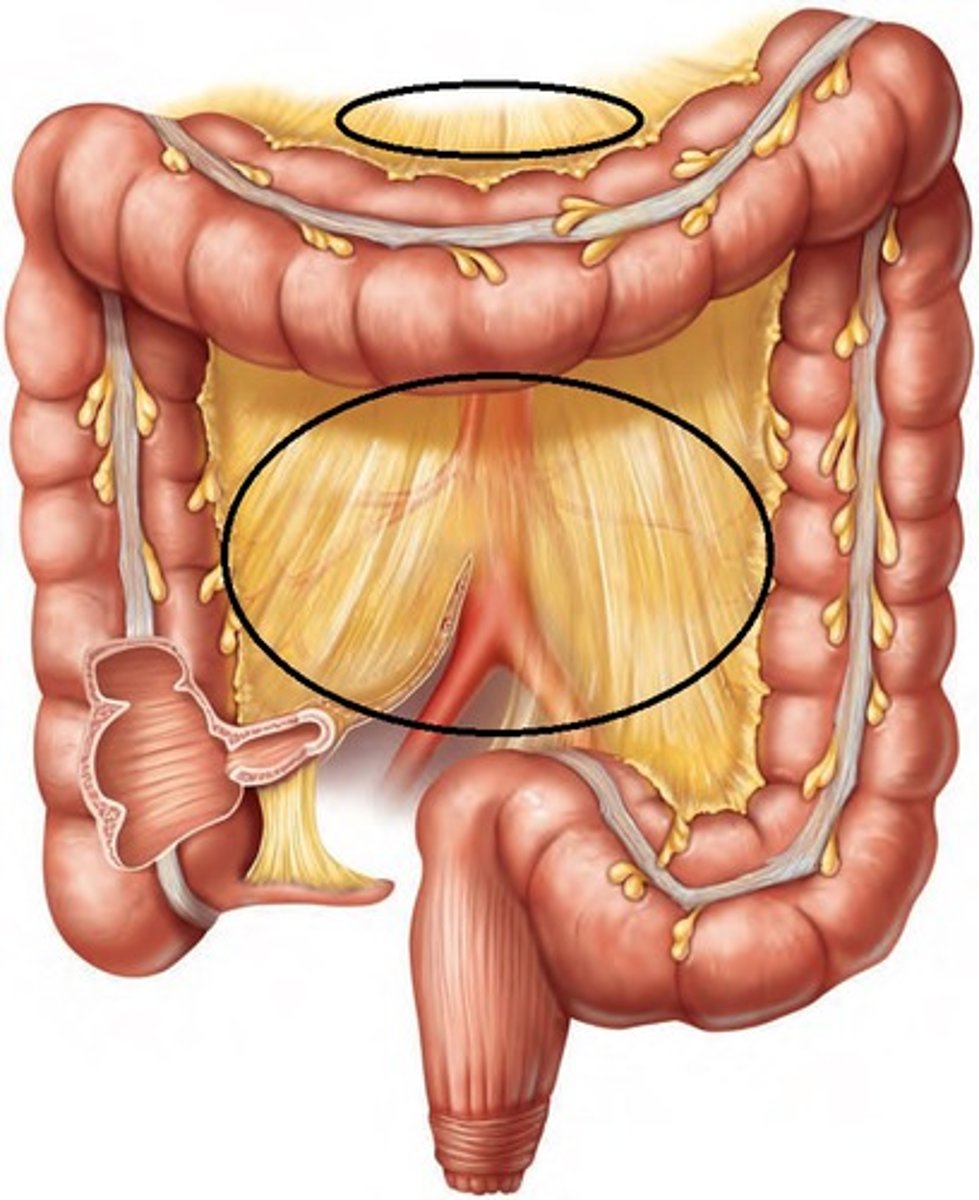
mesocolon
extension of the mesentery that anchors the colon to the posterior abdominal wall
parietal peritoneum
the outer layer of the peritoneum that lines the interior of the abdominal wall
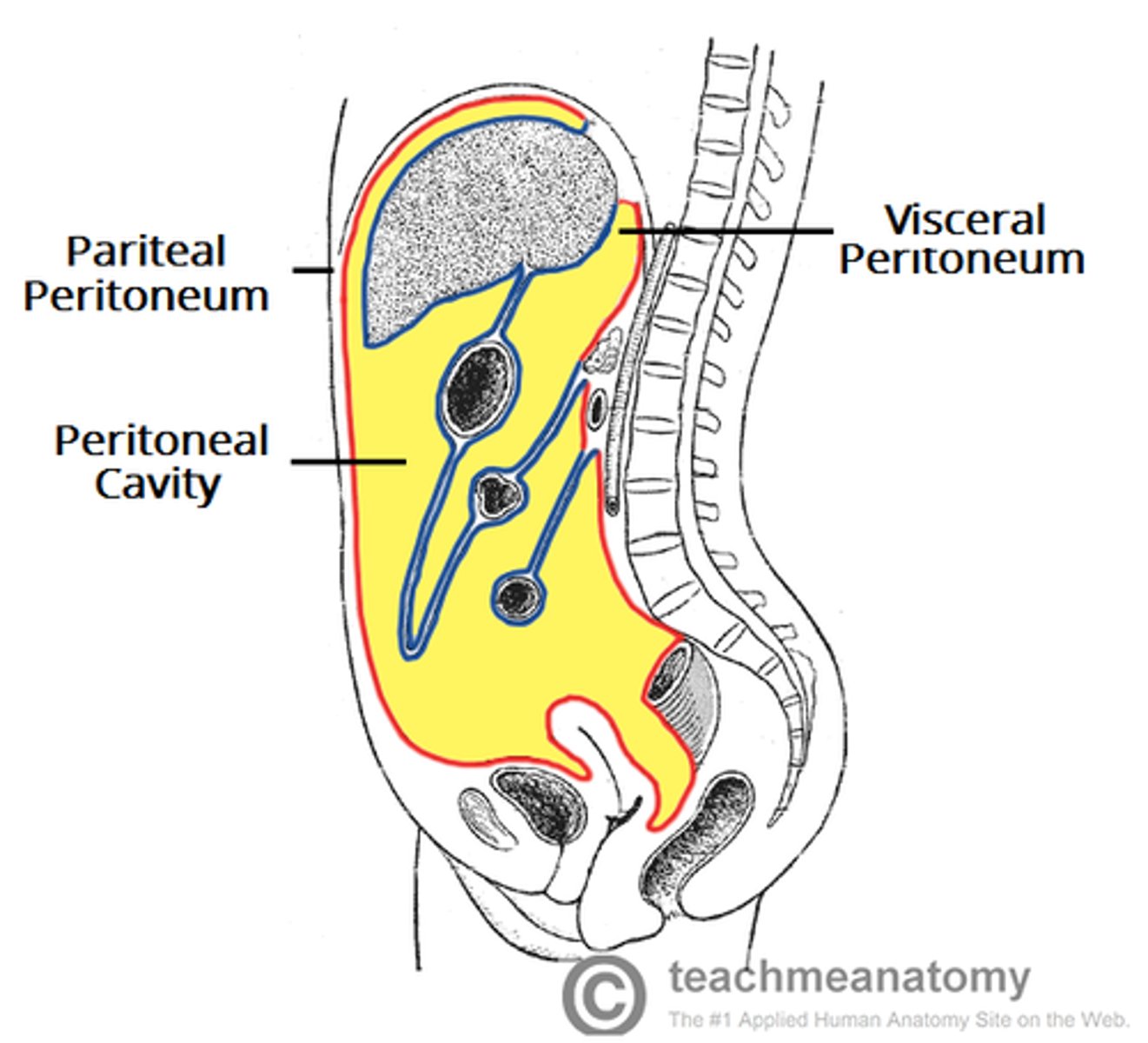
visceral peritoneum
the inner layer of the peritoneum that surrounds the organs of the abdominal cavity
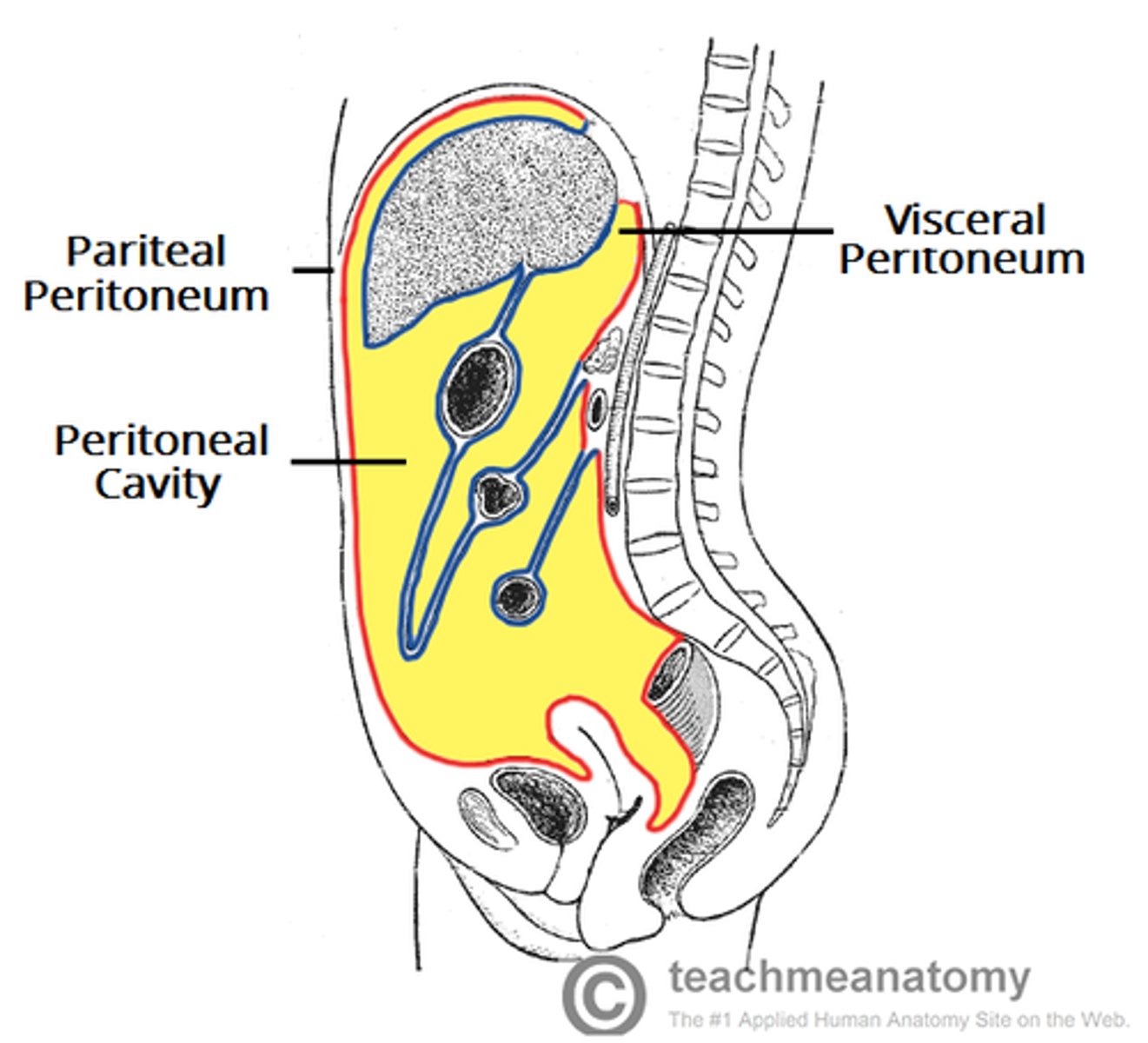
peritoneal cavity
space between the parietal and visceral peritoneum
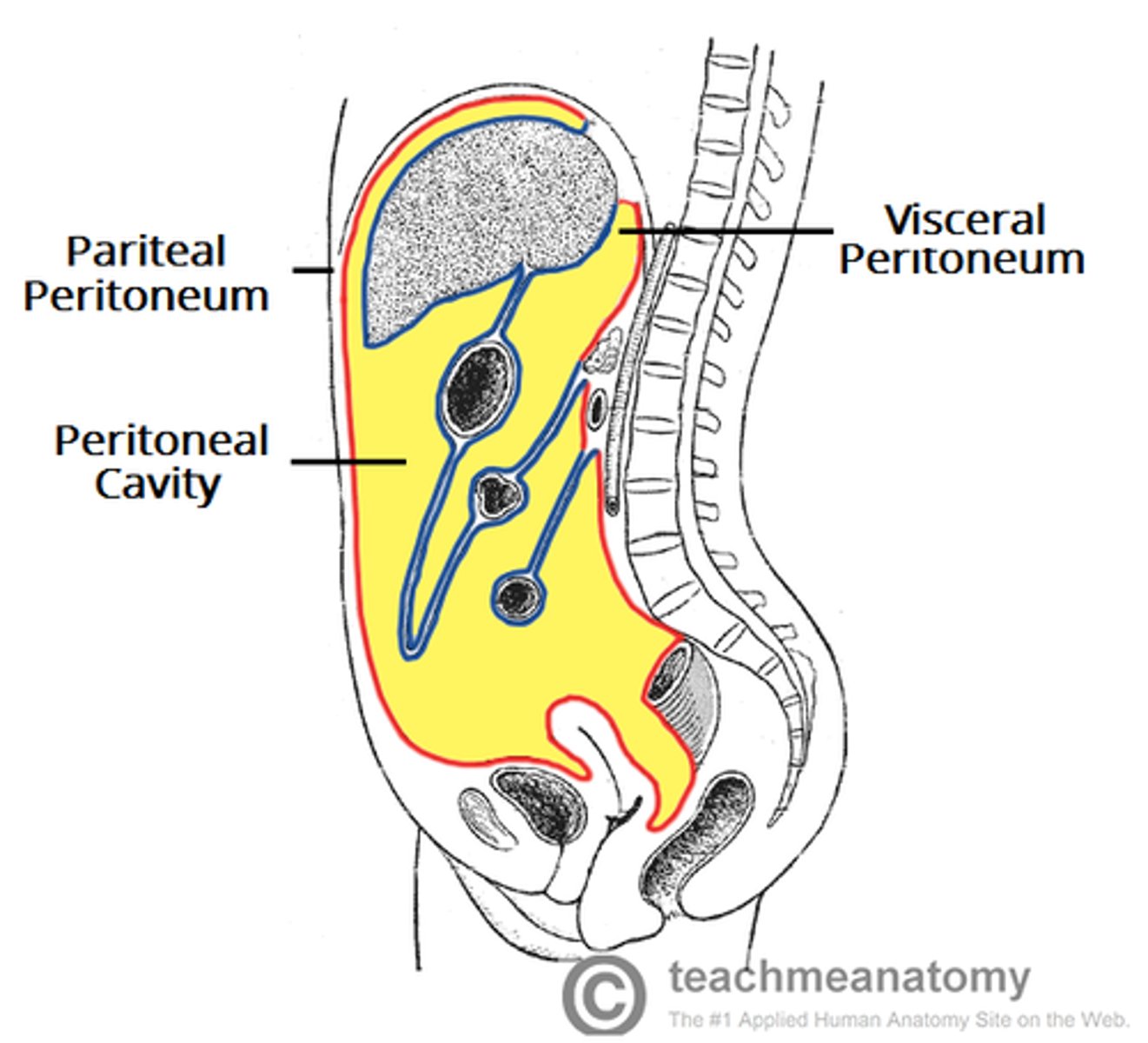
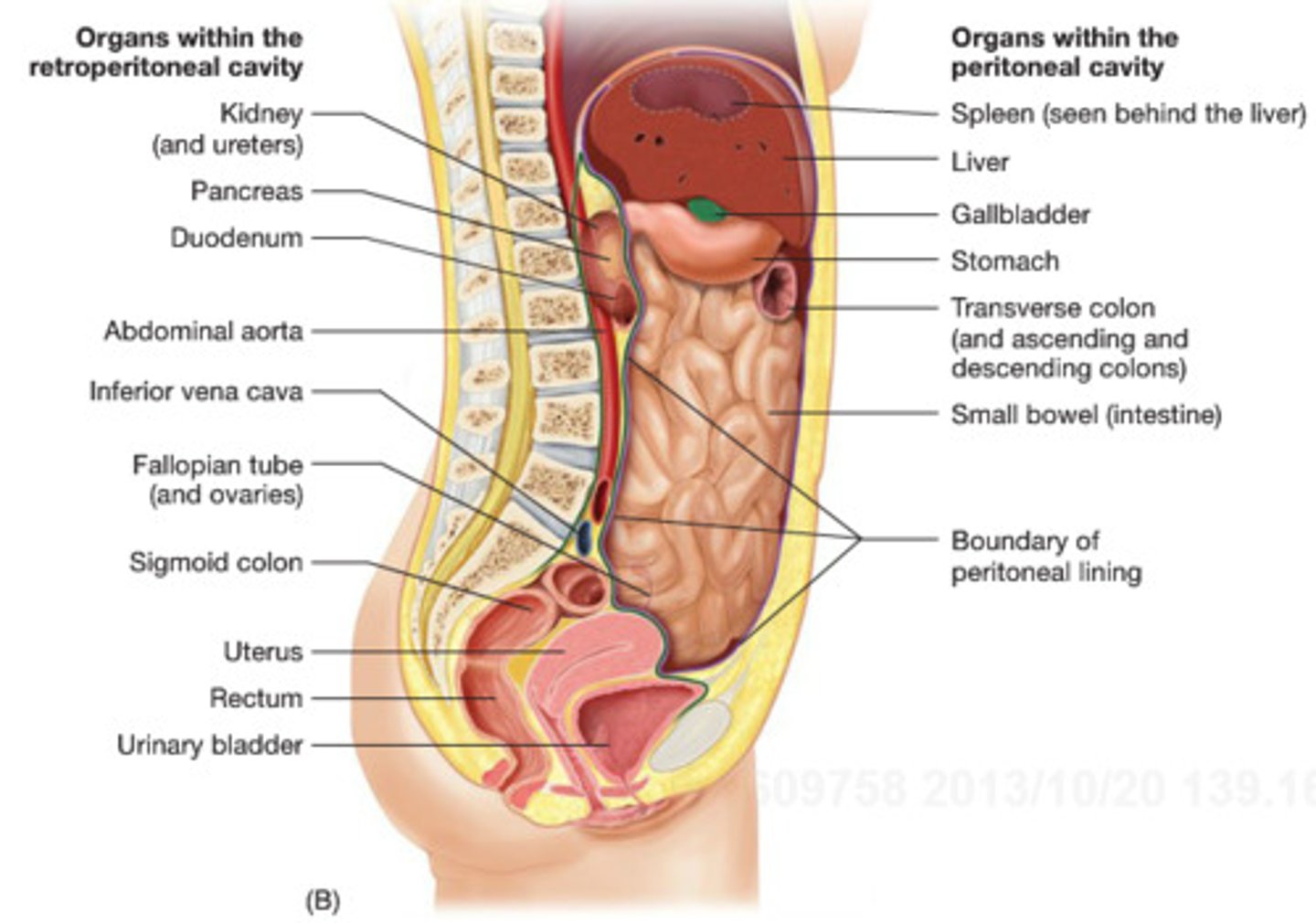
retroperitoneal organs
located outside, or posterior to, the peritoneum
includes most of pancreas, duodenum, and parts of large intestine
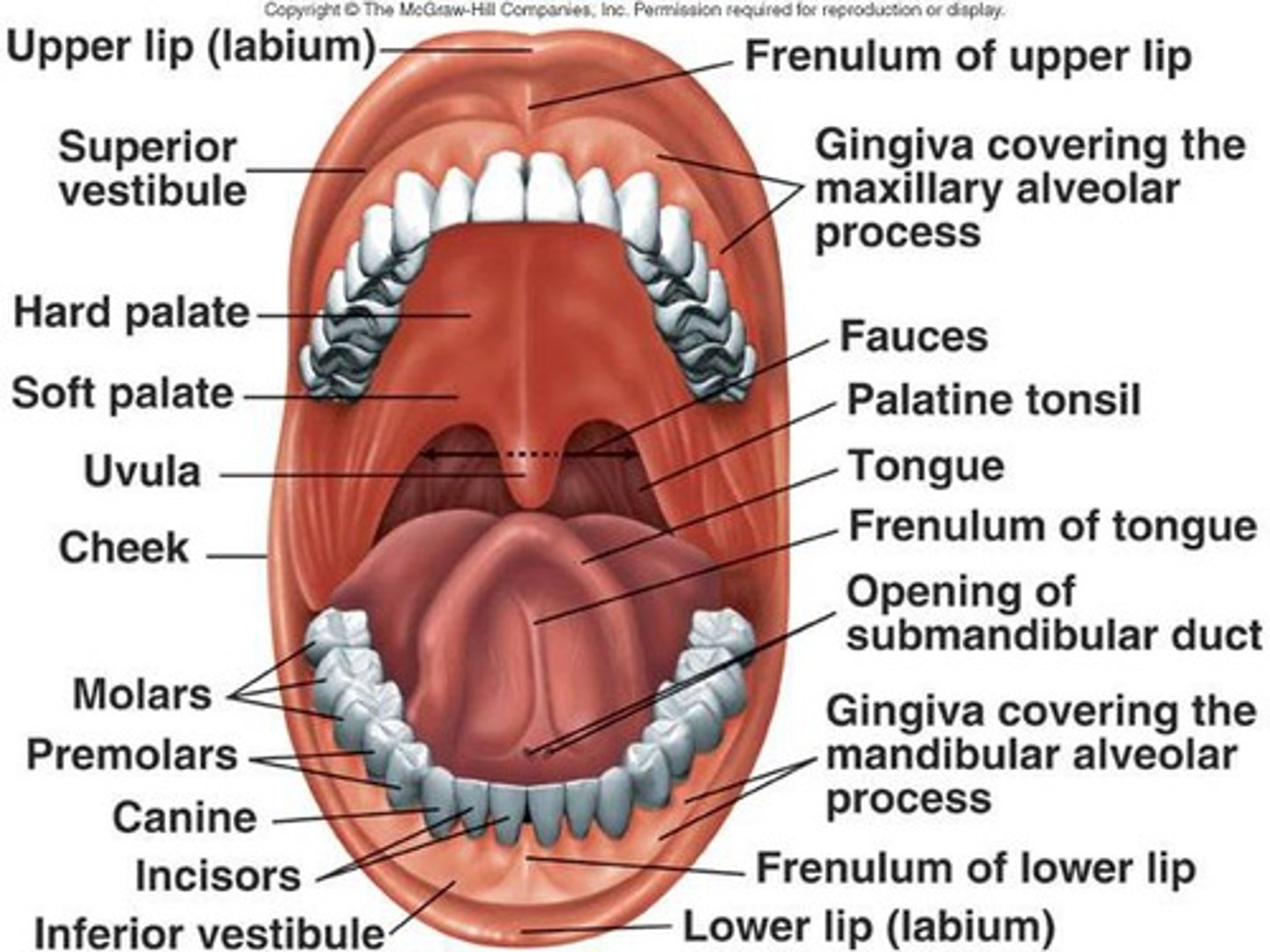
Identify the following structures of the oral cavity:
- cheek
- fauces
- gingivae
- hard palate
- soft palate
- inferior labial frenulum
- inferior lip
- superior lip
- palatine tonsil
- tongue
- uvula
- vestibule
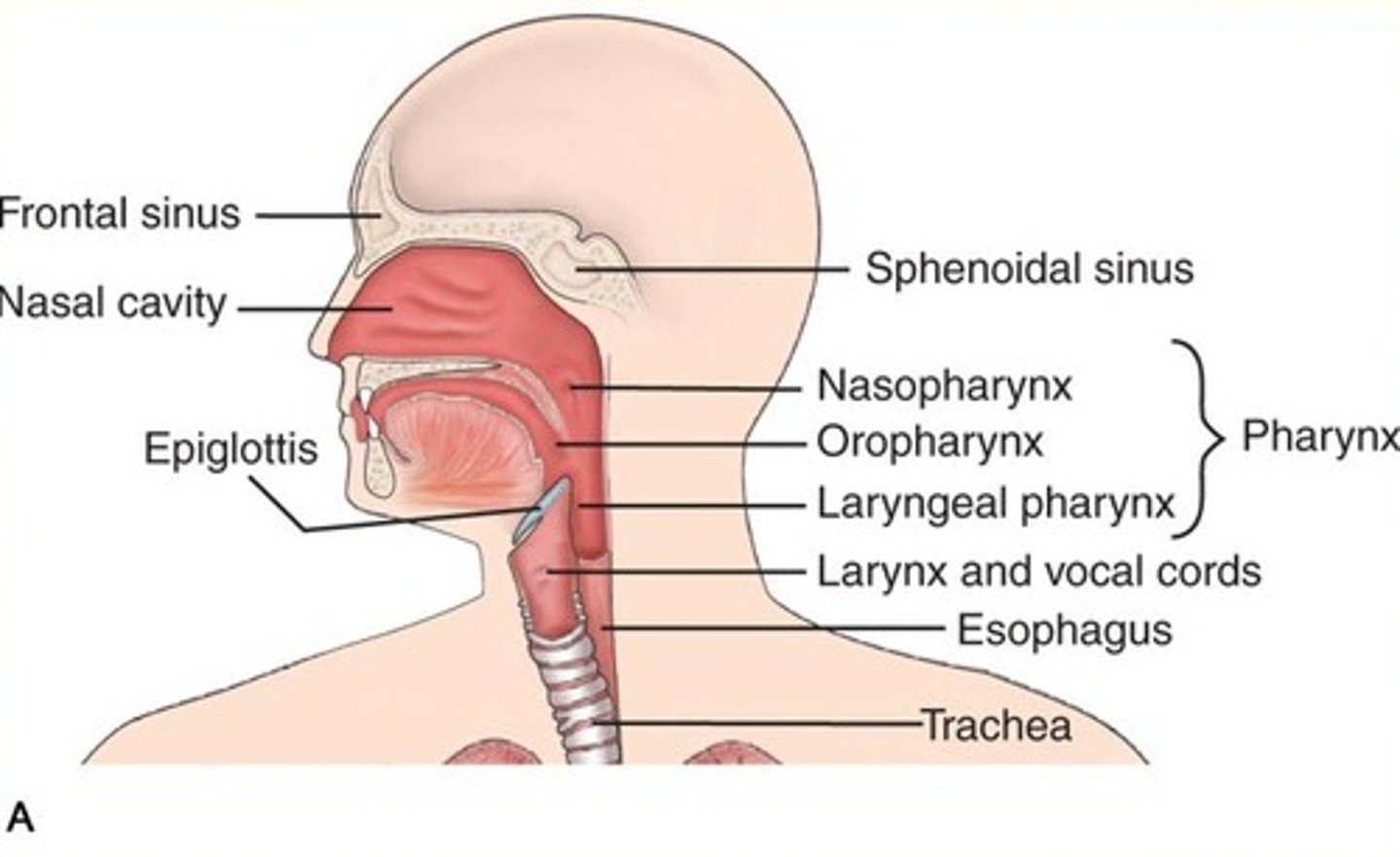
Identify the following structures of the pharynx:
- esophagus
- nasopharynx
- oropharynx
- laryngopharynx
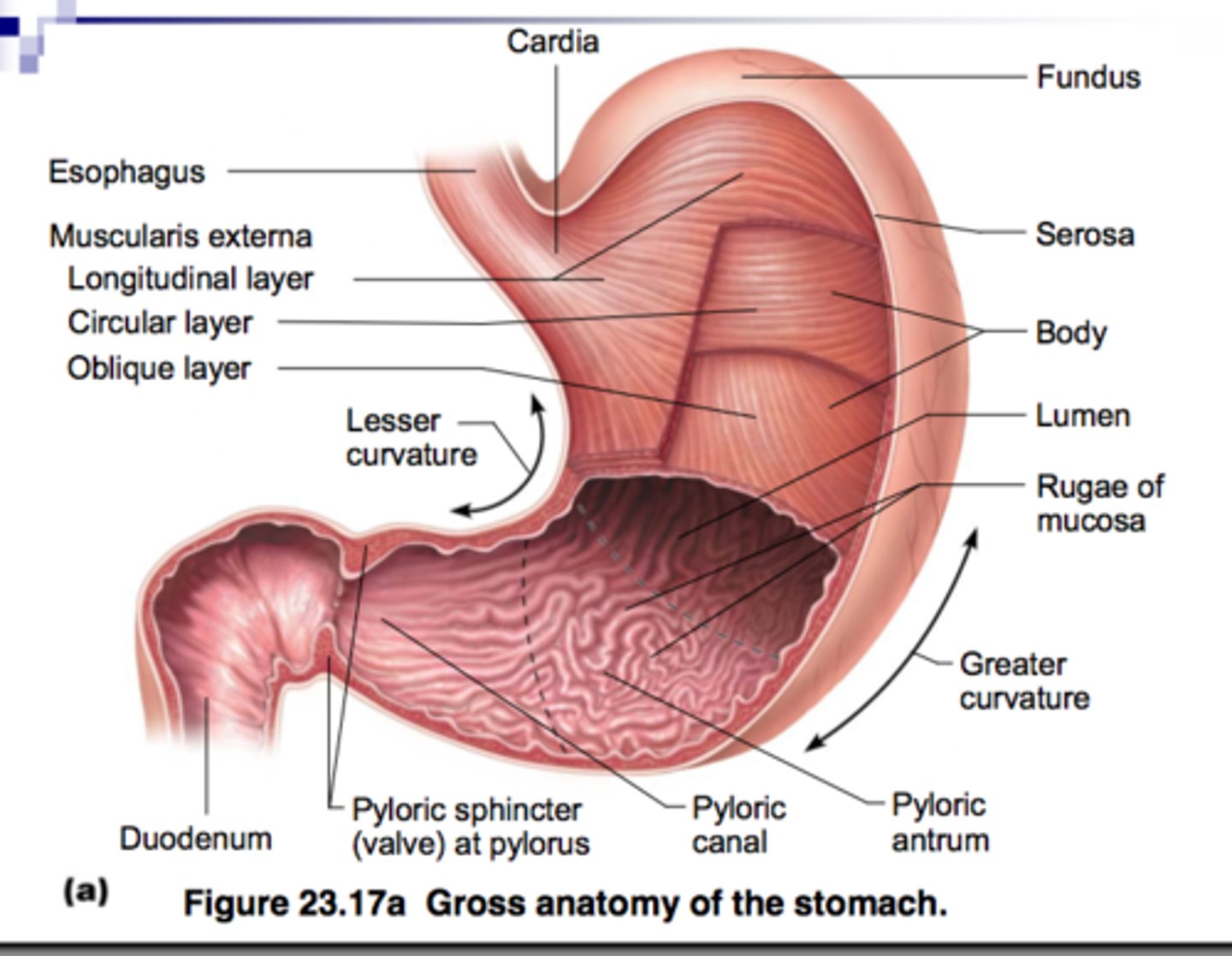
Identify the following structures of the stomach:
- lesser curvature
- body
- cardia
- lower esophageal sphincter
- fundus
- longitudinal muscle layer
- circular muscle layer
- oblique muscle layer
- greater curvature
- pyloric antrum
- pyloric canal
- pyloric sphincter
- pylorus
- gastric folds (rugae)
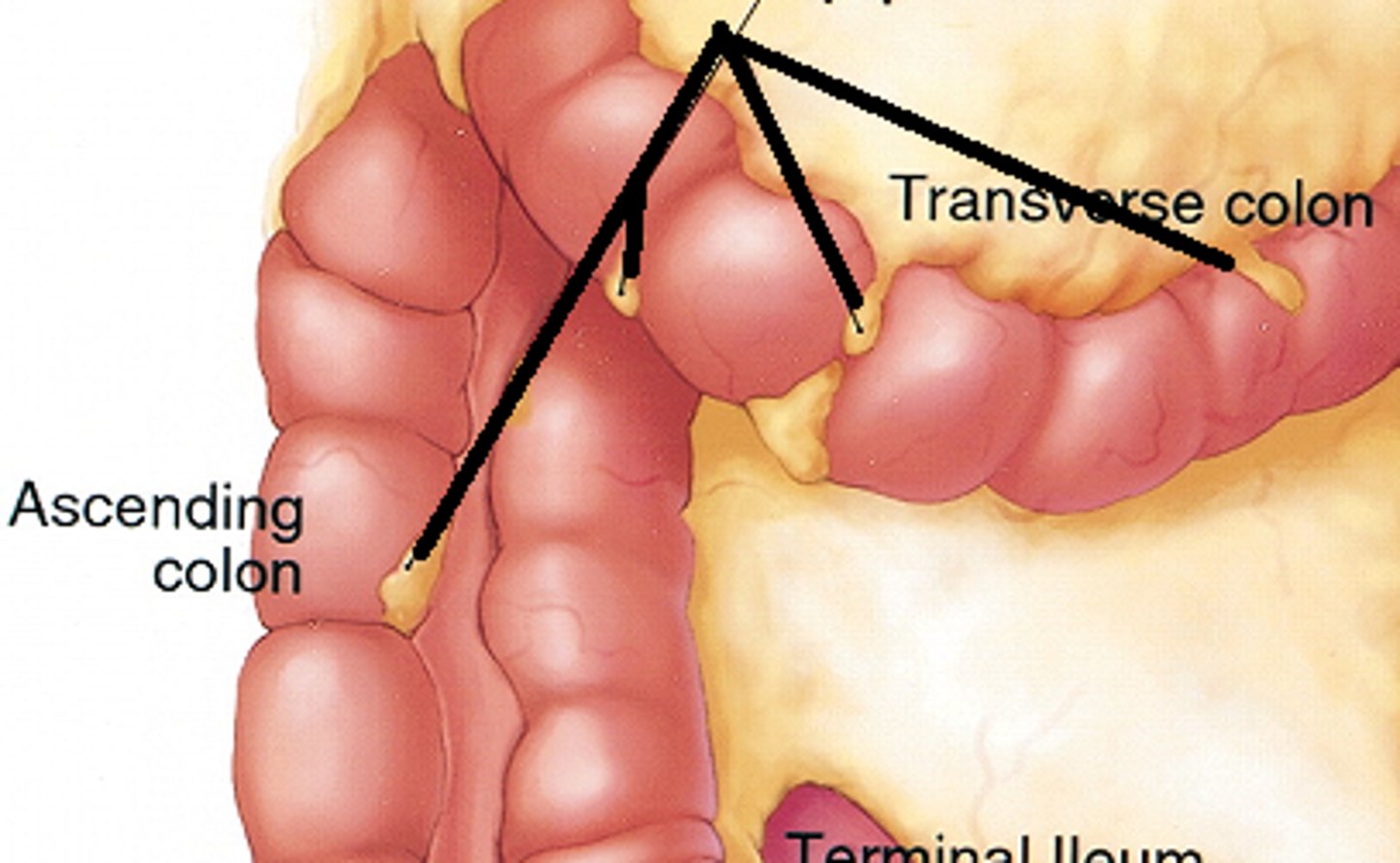
ascending colon
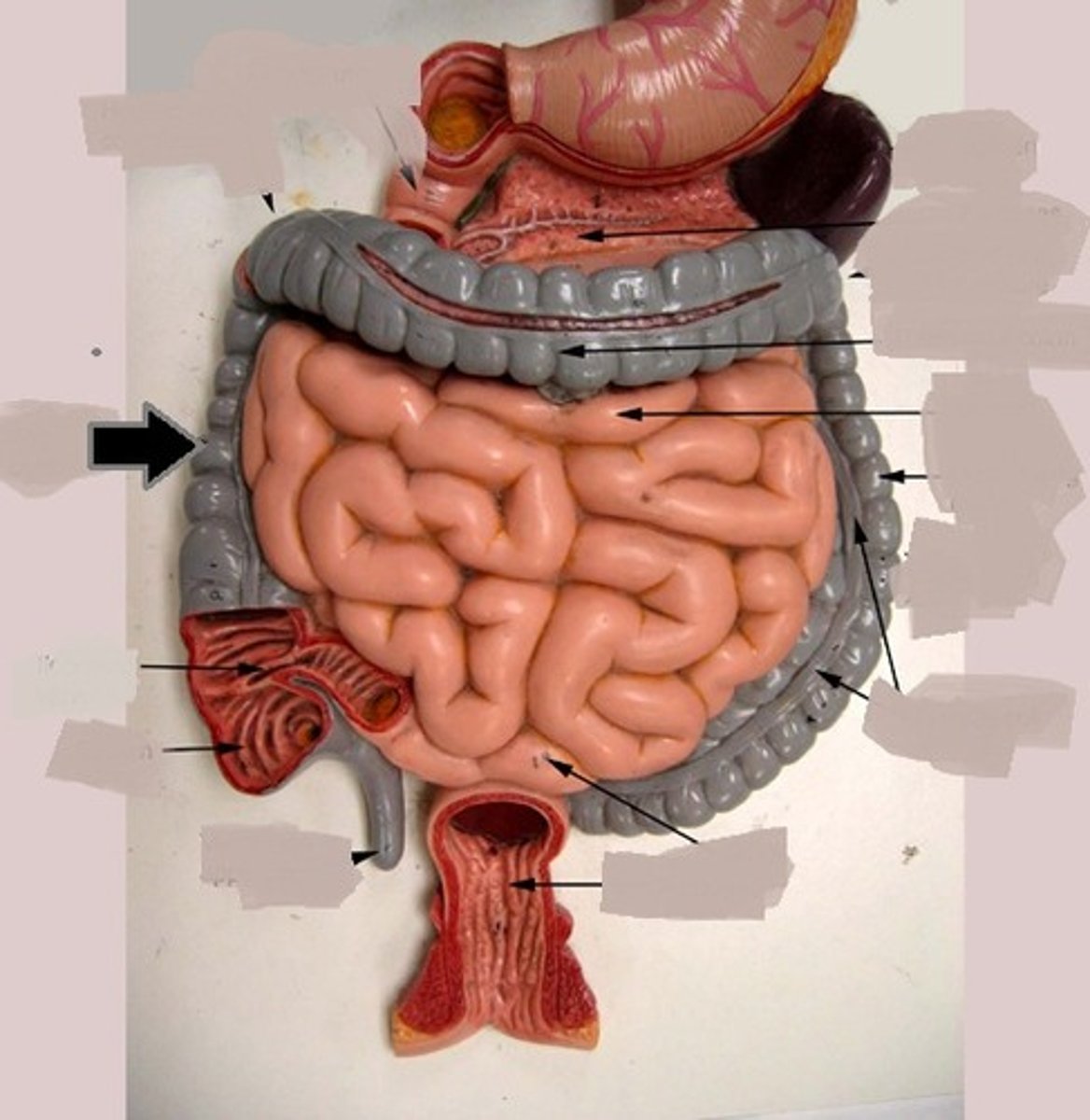
descending colon
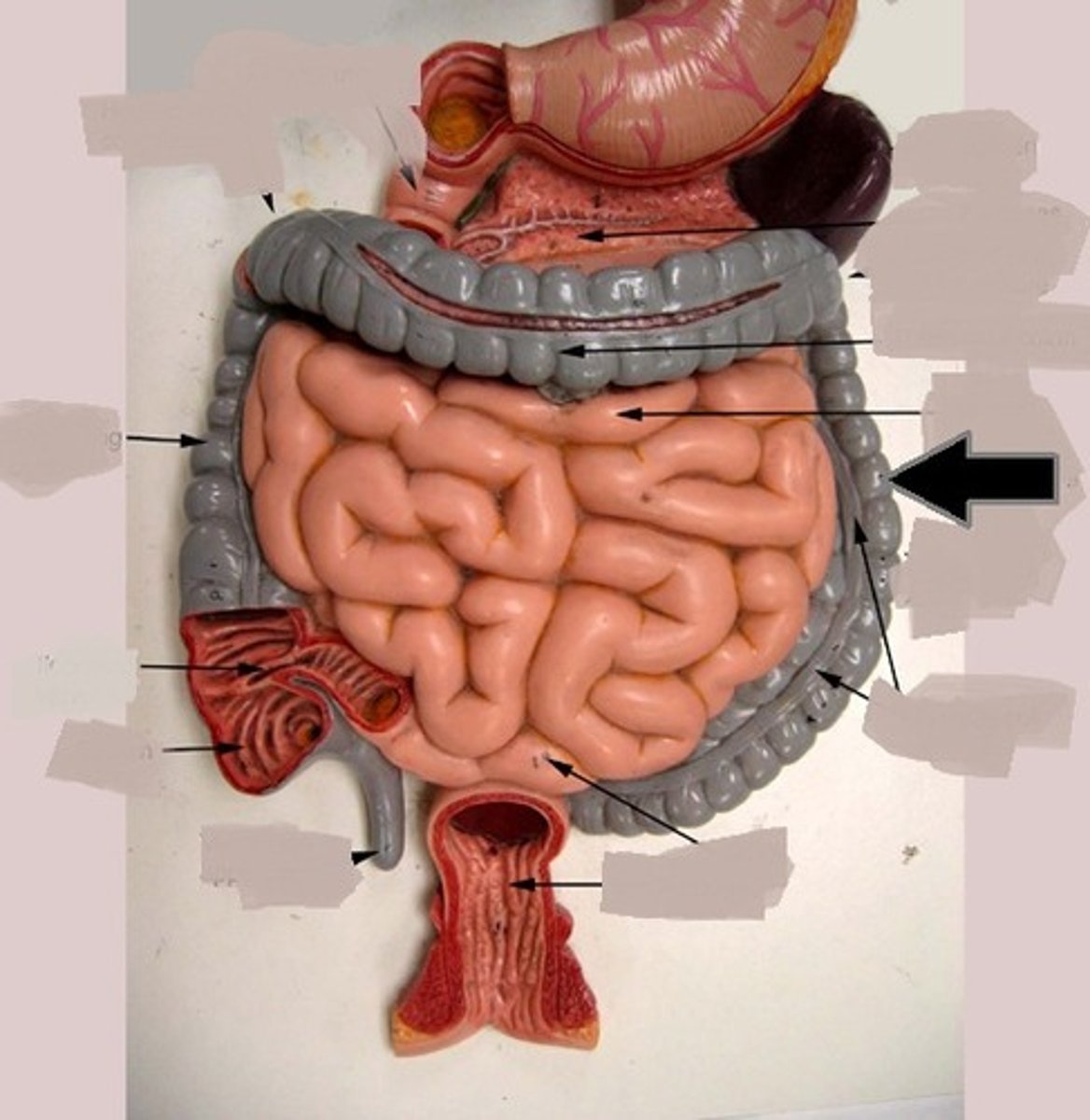
transverse colon
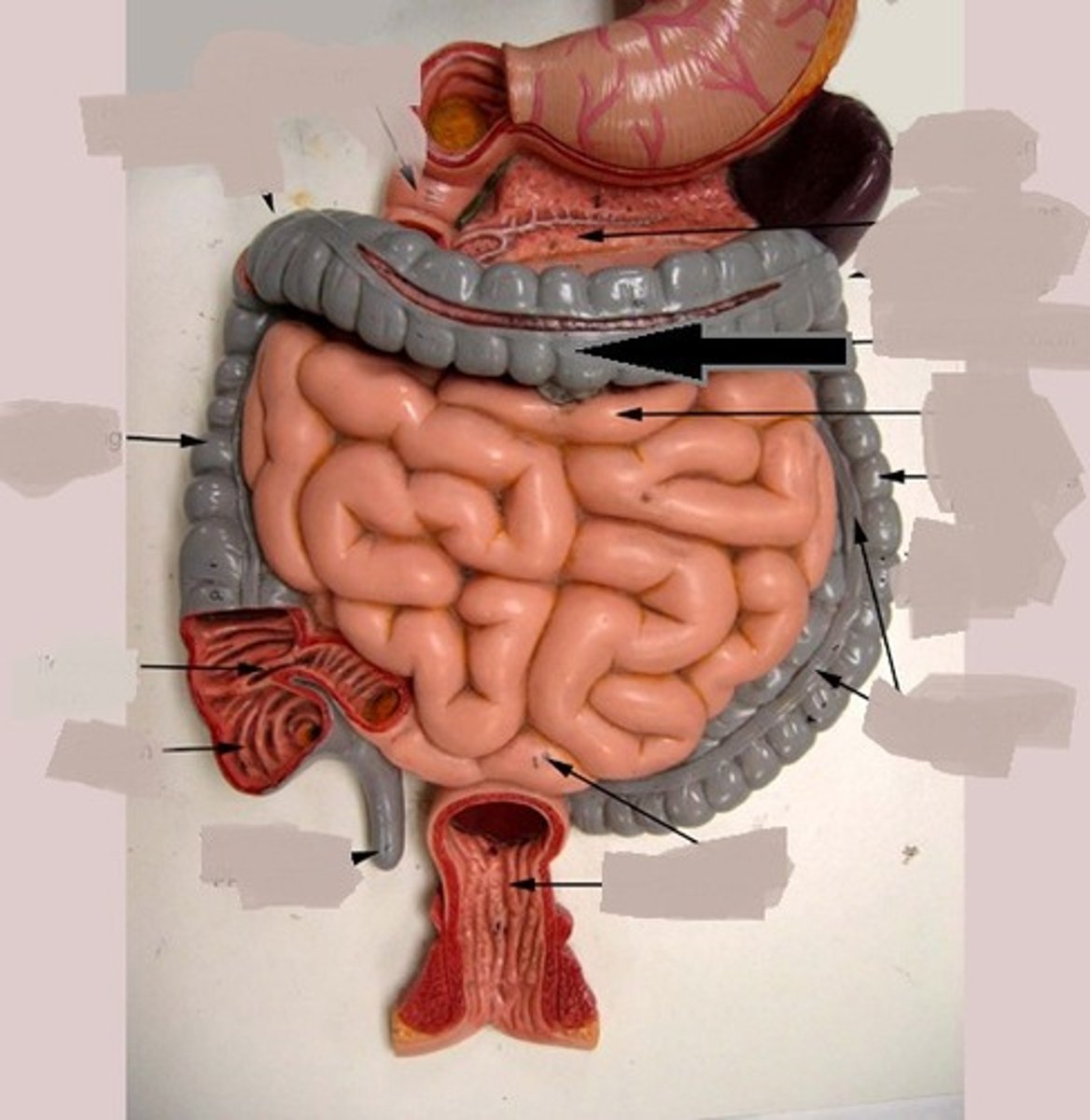
sigmoid colon
last segment of the colon
right before the anus
anal column
a longitudinal fold in the mucous membrane of the anal canal that contains a network of arteries and veins
appendix
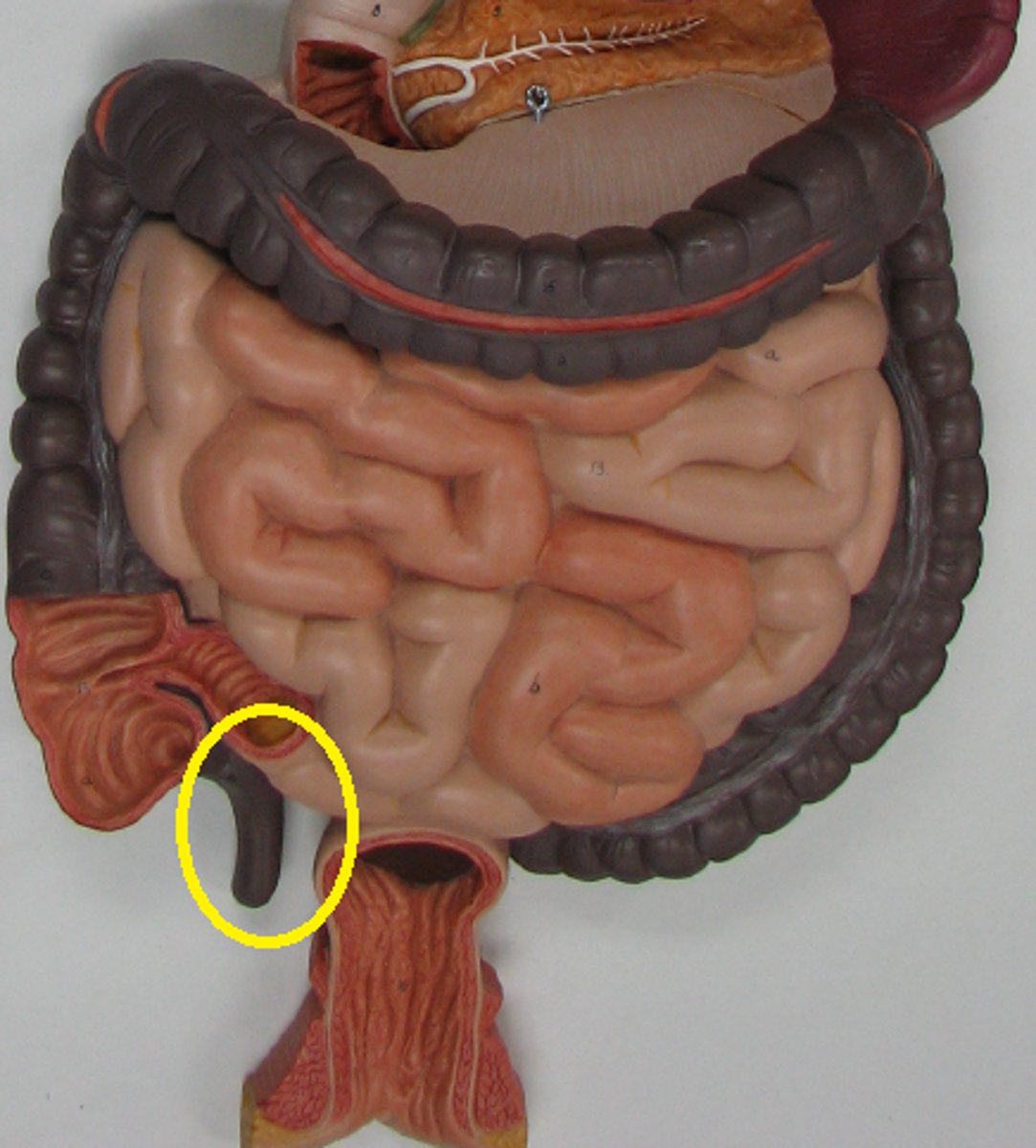
cecum
a pouch connected to the junction of the small and large intestines
external anal sphincter
skeletal muscle, voluntary
internal anal sphincter
smooth muscle, involuntary
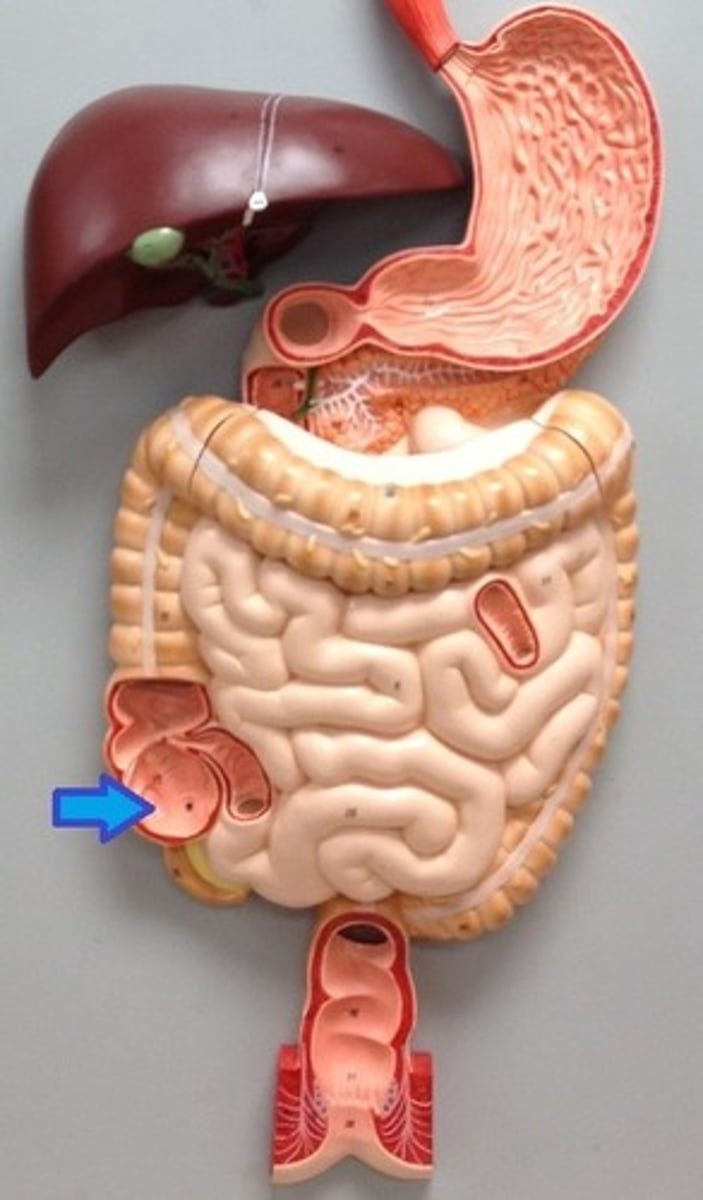
duodenum
first portion of the small intestine
shortest section
resembles the shape of a "C"
receives food through the pyloric sphincter
(A in this image)
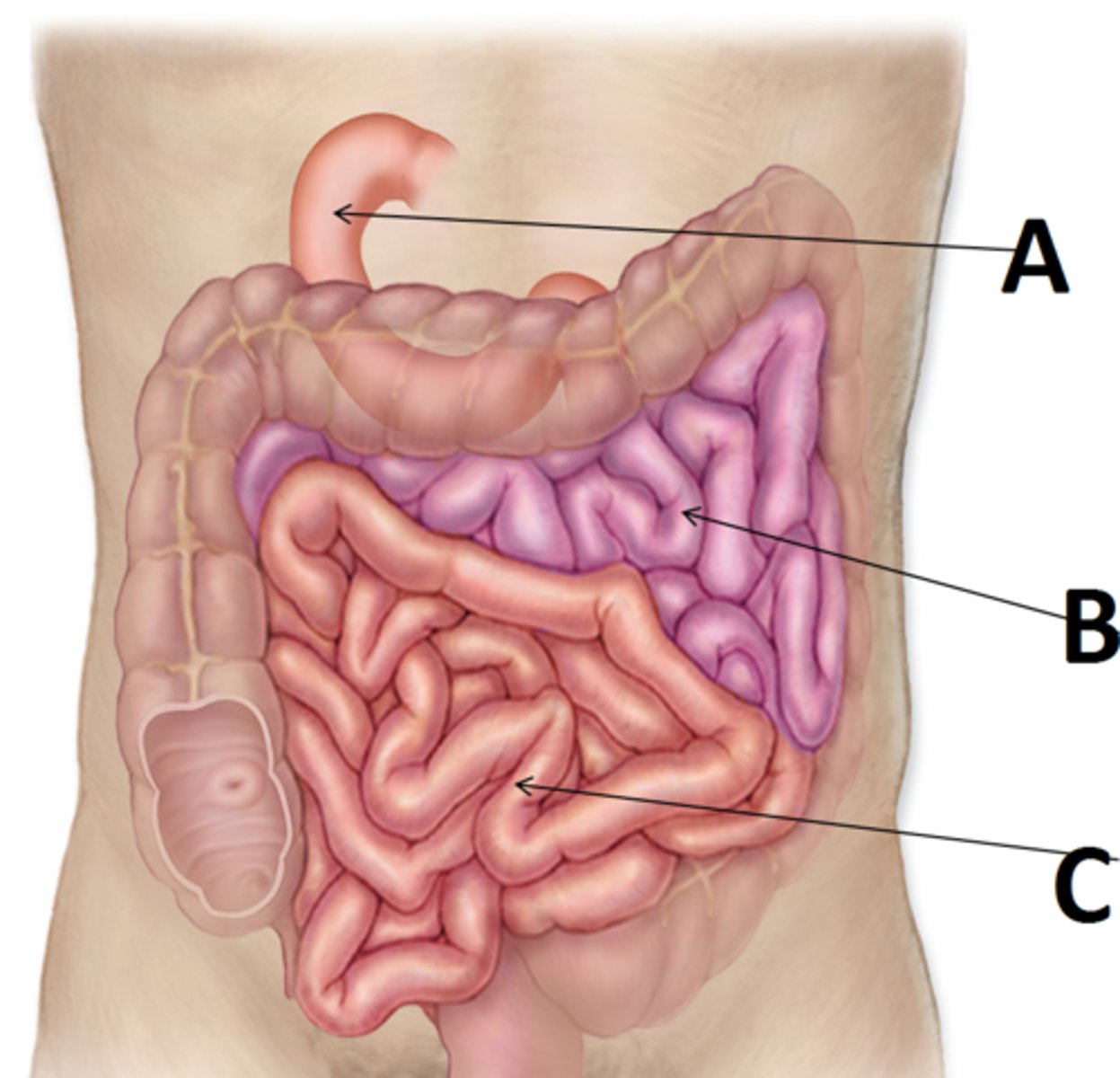
ileum
the last section of the small intestine
about 6 feet long
ends at the ileal orifice
(C in this image)
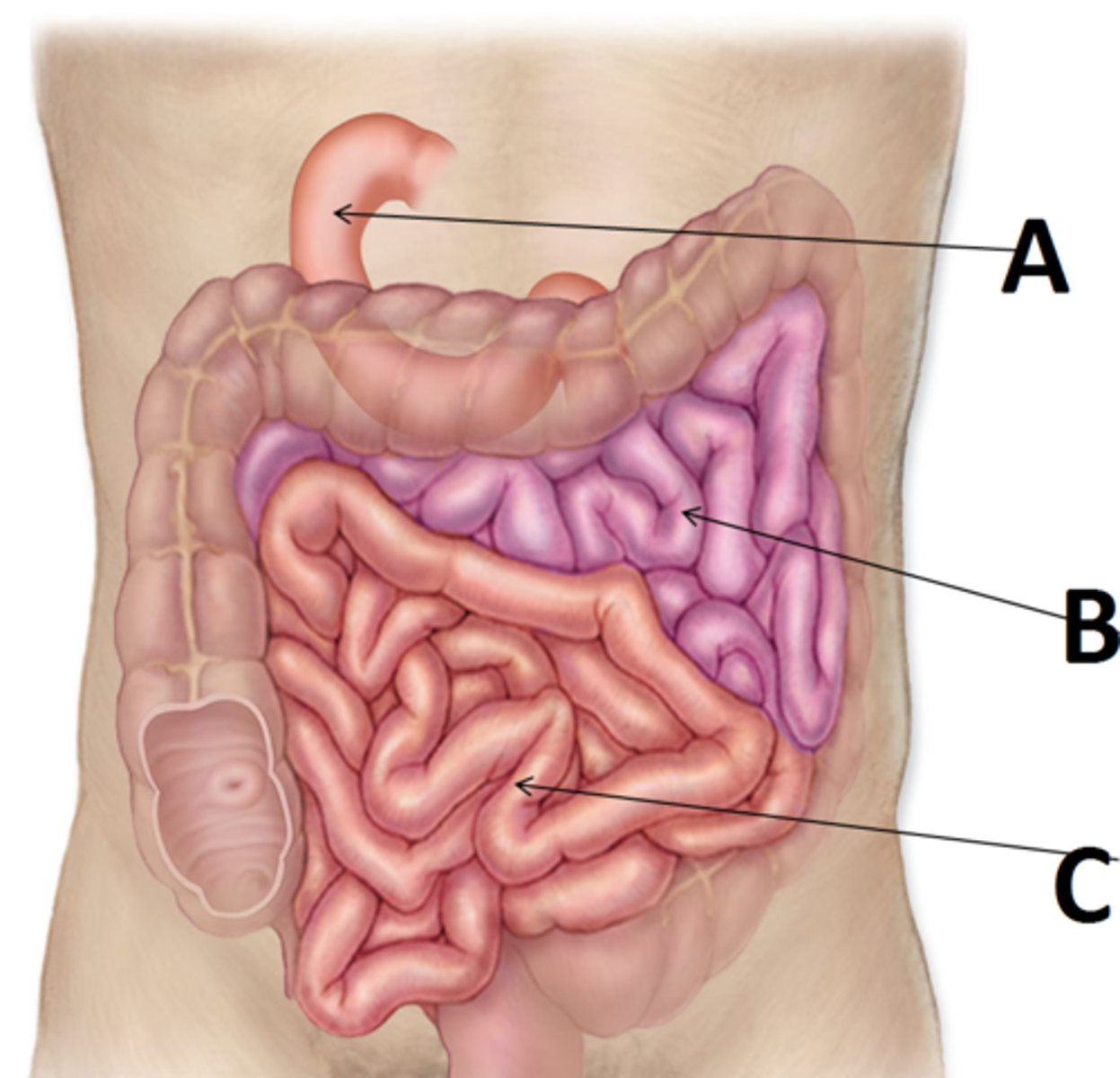
jejunum
middle section of the small intestine
3 feet long
thicker layer of smooth muscle
(B in this image)
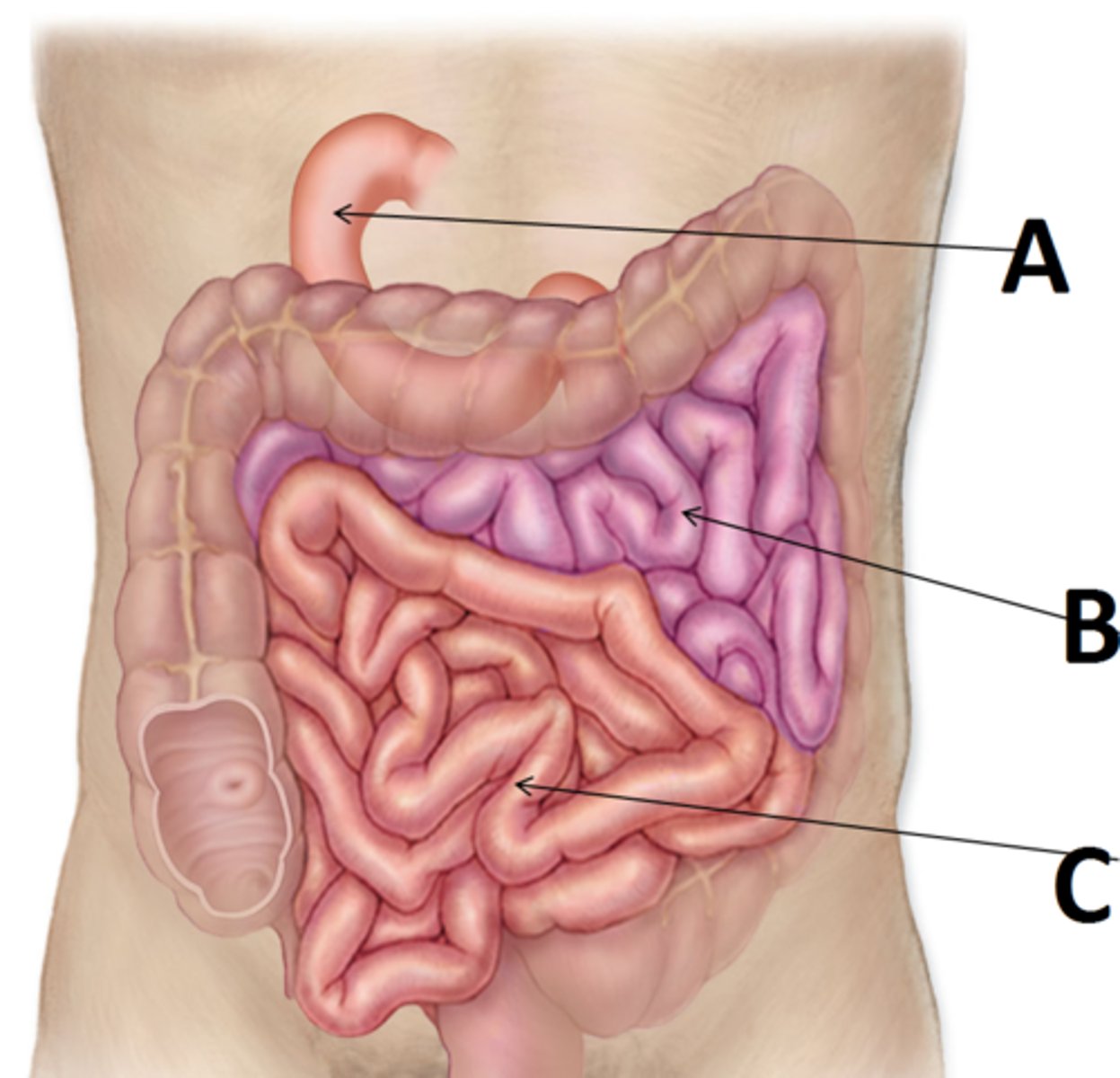
epiploic appendages
also called omental (fatty) appendages
fat-filled pouches of visceral peritoneum that hang from the teniae coli
haustra
pouches of the large intestine that allow expansion and elongation
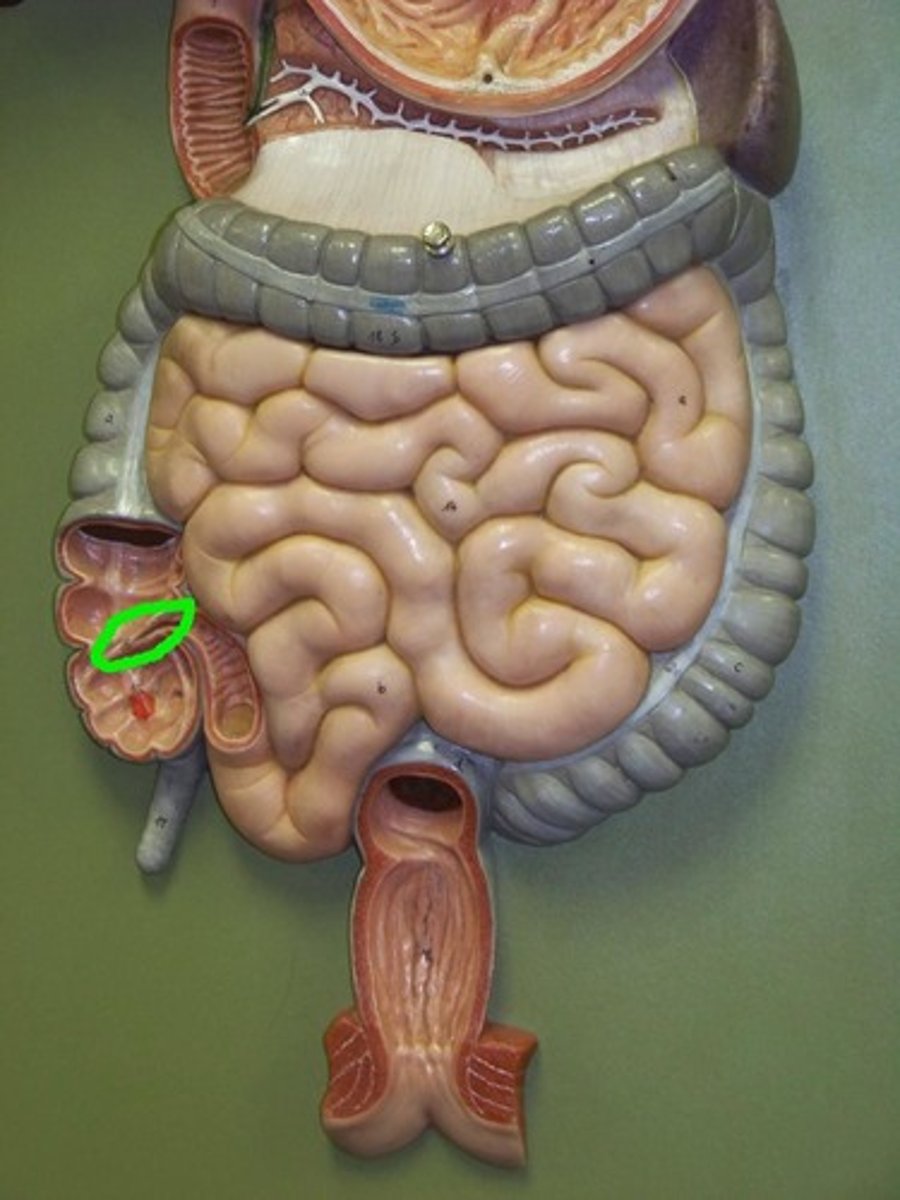
ileocecal sphincter
band of muscle that encircles the junction of ileum and cecum
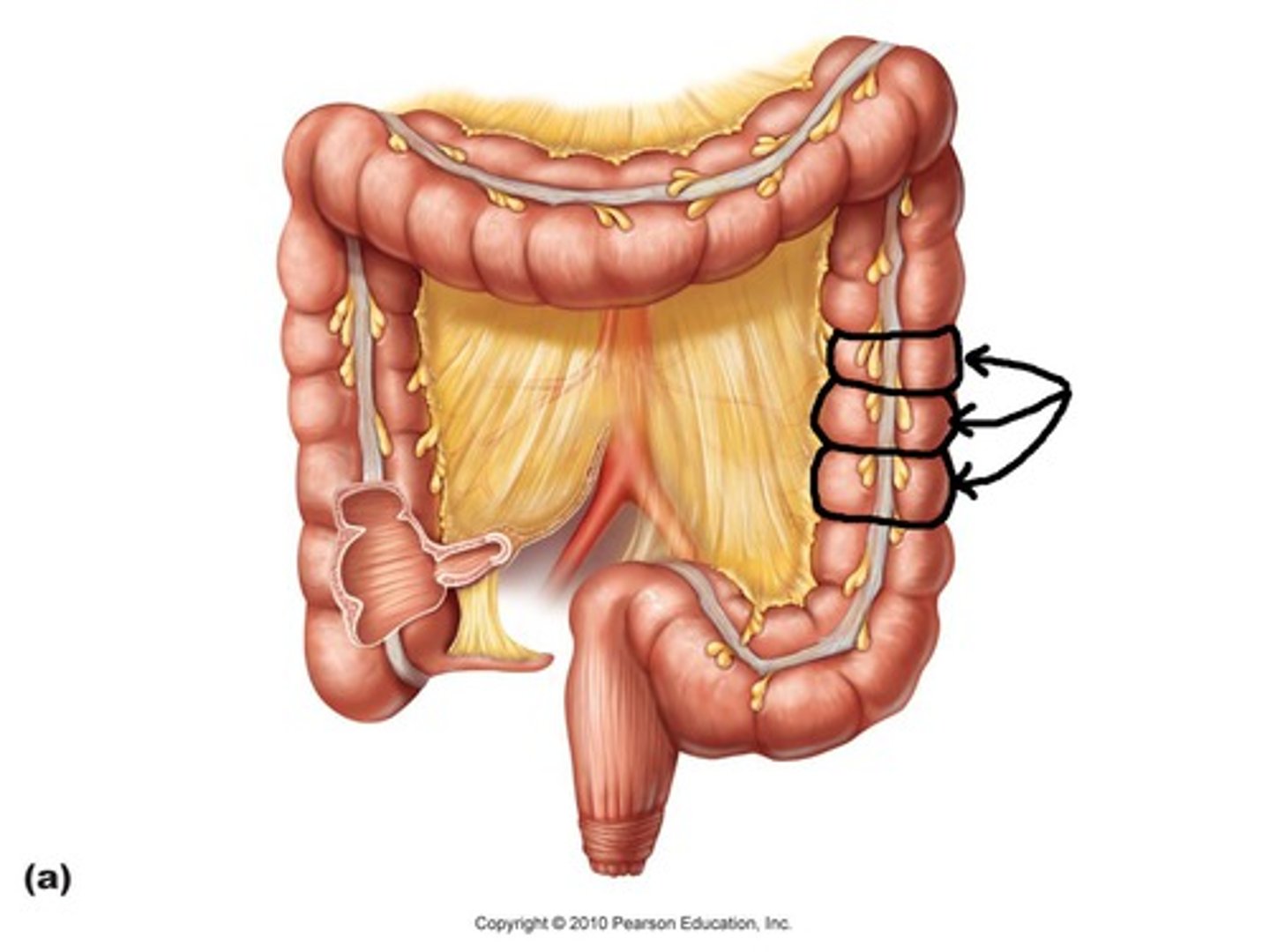
left colic flexure
point where the transverse colon curves below the inferior end of the spleen

right colic flexure
the right-angle turn that continues from the ascending colon
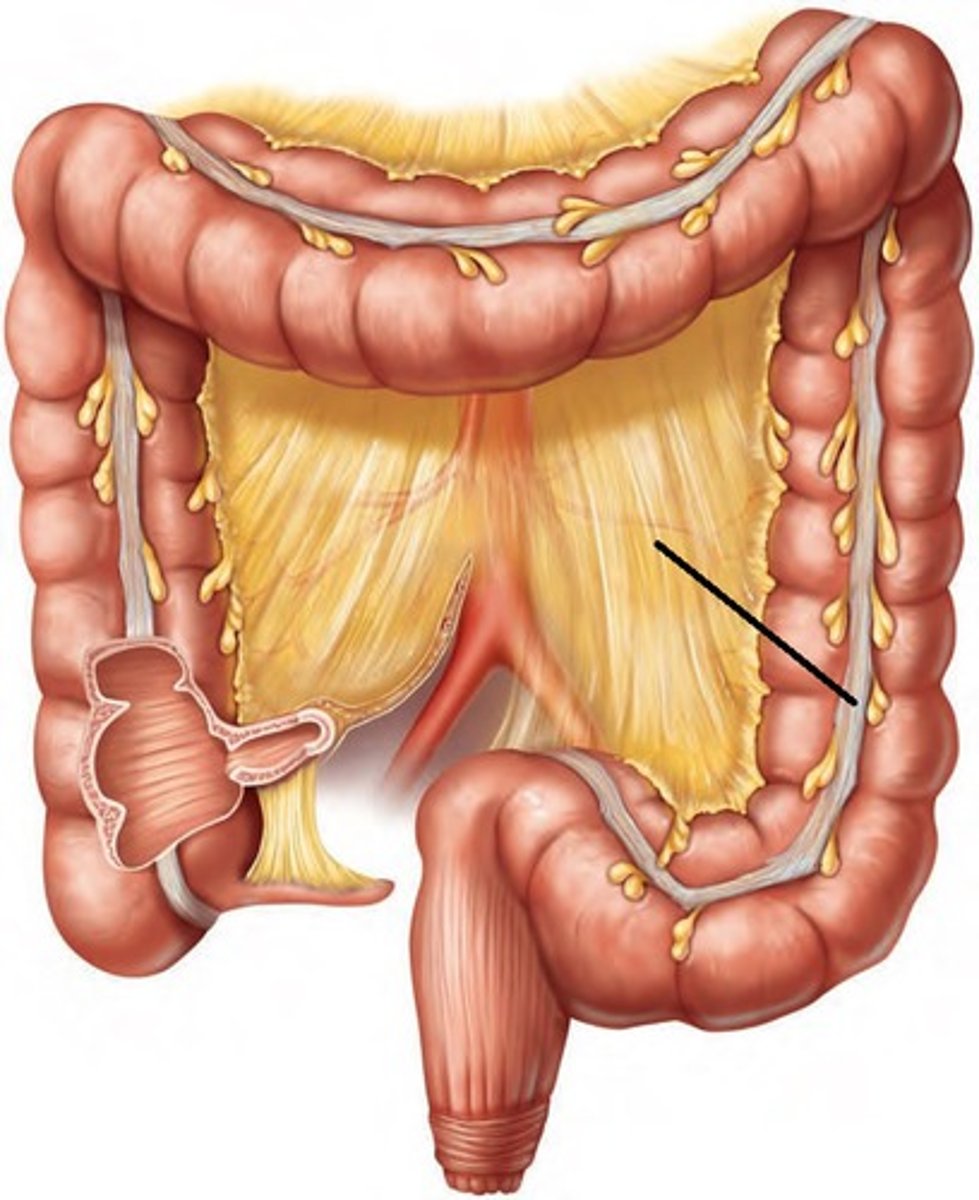
rectum
right after the sigmoid colon, before the anal canal
teniae coli
three separate bands of longitudinal smooth muscle in muscularis
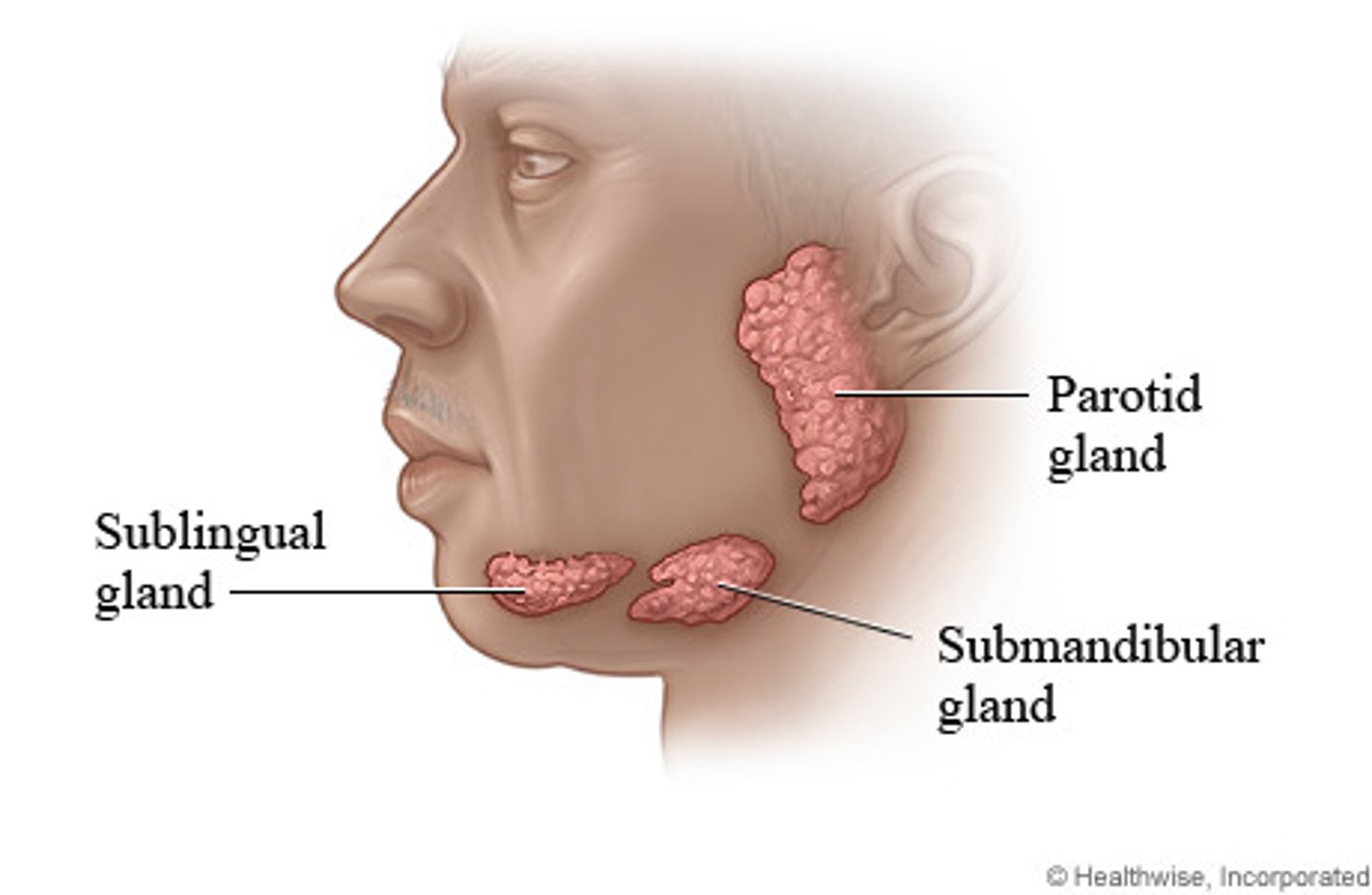
Identify the following glands of the mouth:
- parotid gland
- sublingual gland
- submandibular gland
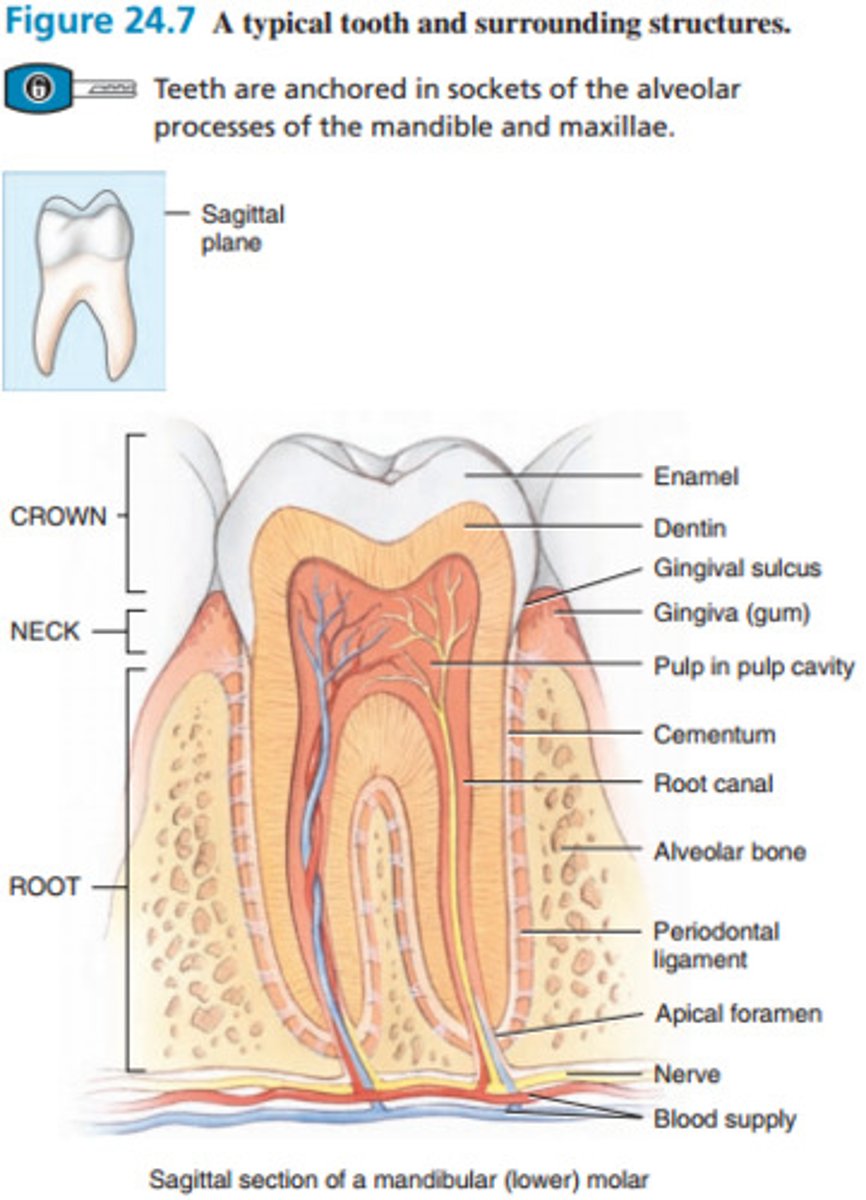
Identify the following structures of a tooth:
- apical foramen
- blood supply
- cementum
- crown
- dentin
- enamel
- gingiva
- neck
- nerve
- periodontal ligament
- pulp cavity with pulp
- root
- root canal
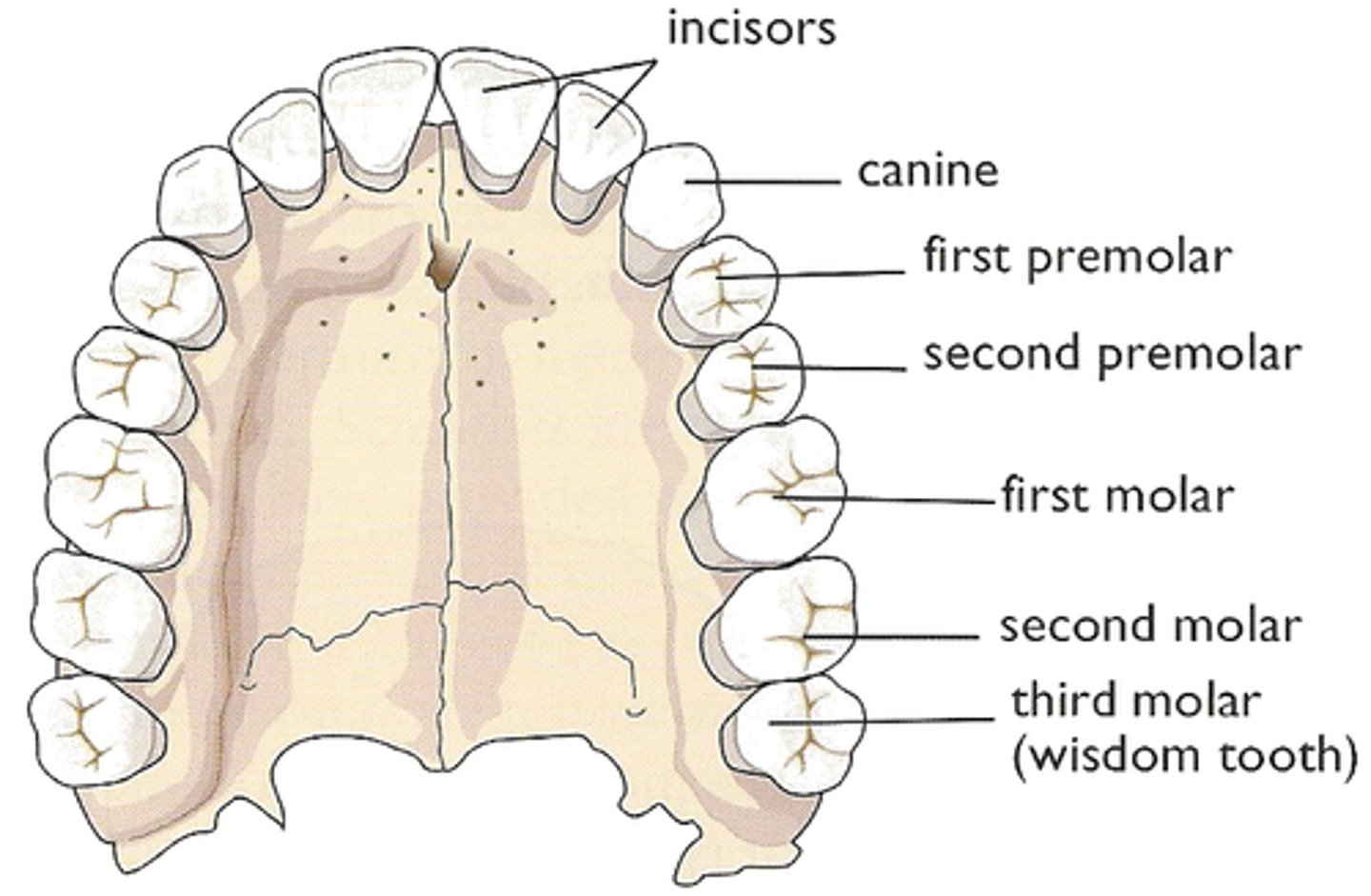
Identify the following teeth of the mouth:
- cuspids
- incisors
- molars
- premolars
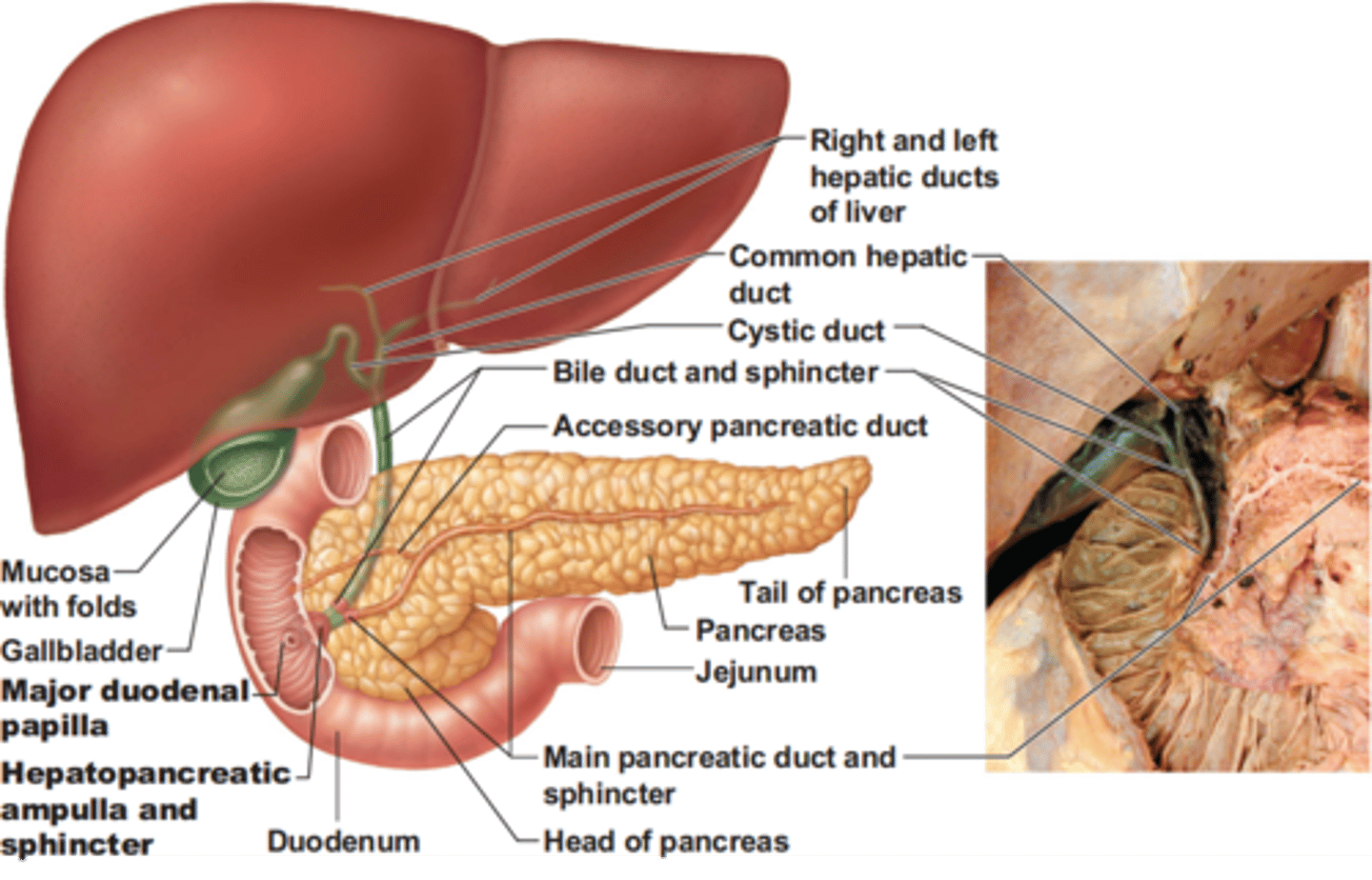
Identify the following structures of the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder:
- accessory pancreatic duct
- head of the pancreas
- body of the pancreas
- tail of the pancreas
- common bile duct
- common hepatic duct
- cystic duct
- duodenal papilla
- duodenum
- gallbladder
- hepatopancreatic ampulla
- jejunum
- left hepatic duct
- right hepatic duct
- left lobe of the liver
- right lobe of the liver
- pancreatic duct
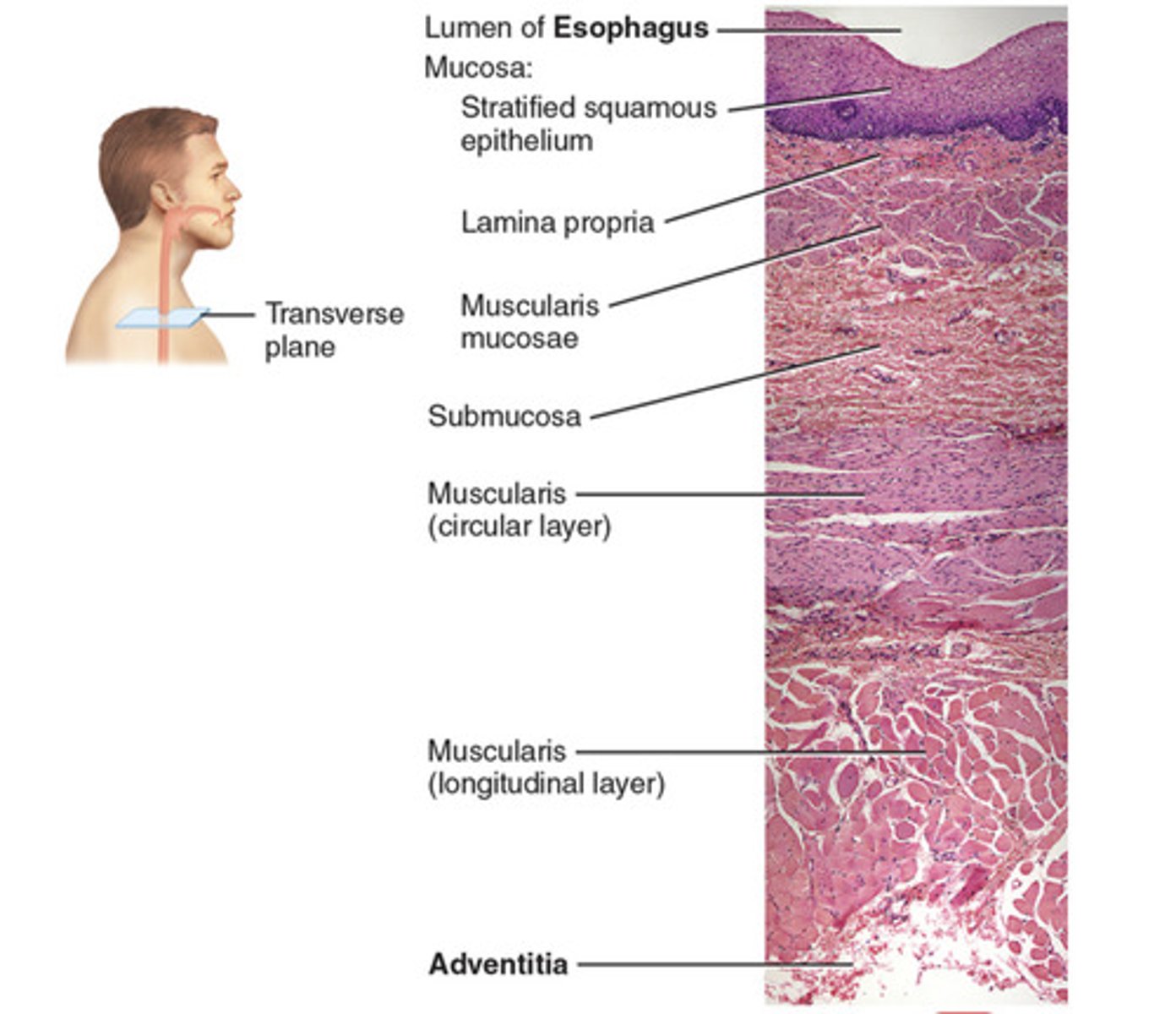
Identify the following structures on a histological image of the wall of the esophagus:
- stratified squamous epithelium
- lamina propria
- muscularis mucosae
- mucosa
- submucosa
- circular layer
- longitudinal layer
- adventitia
histology of serosa
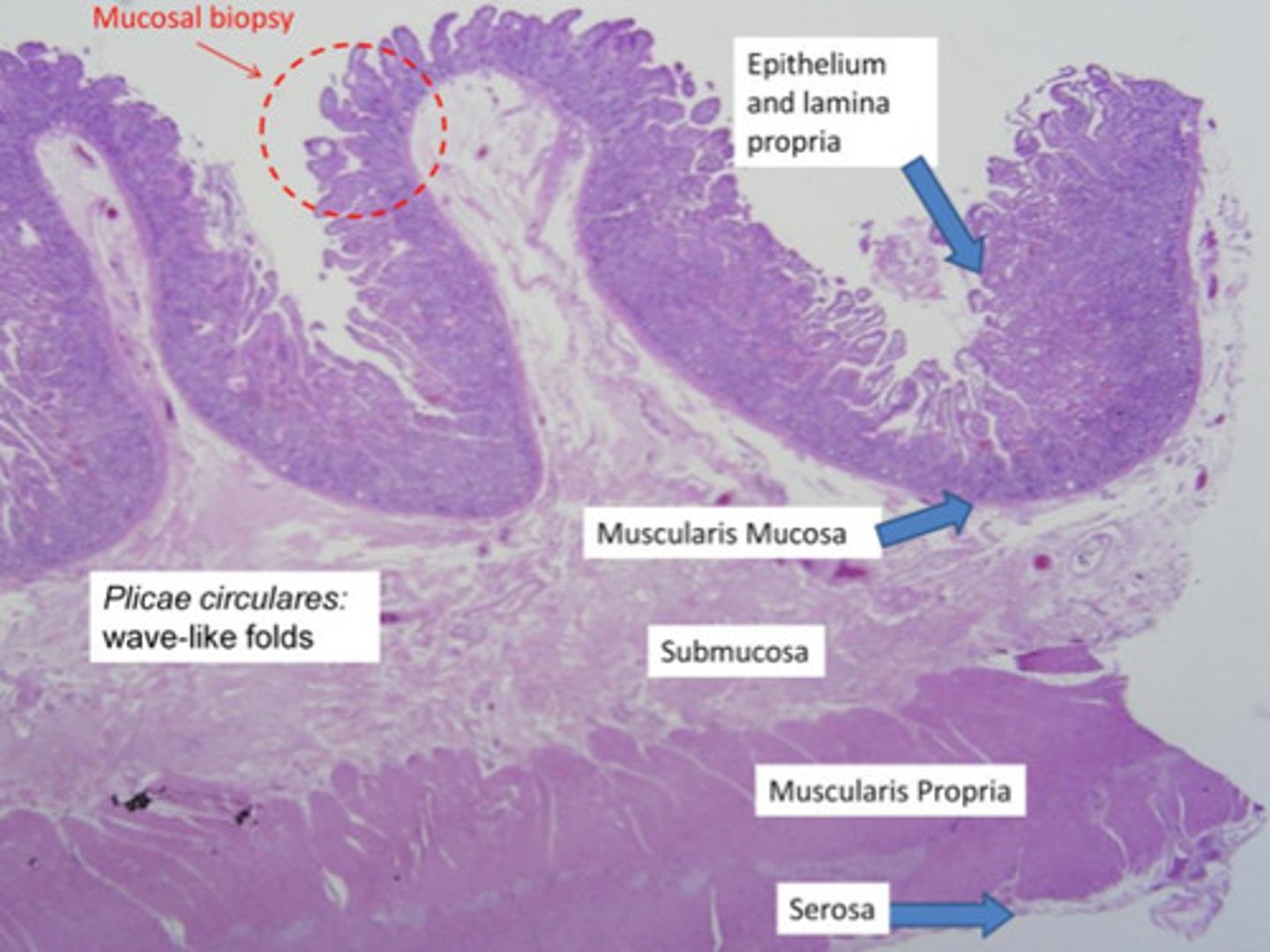
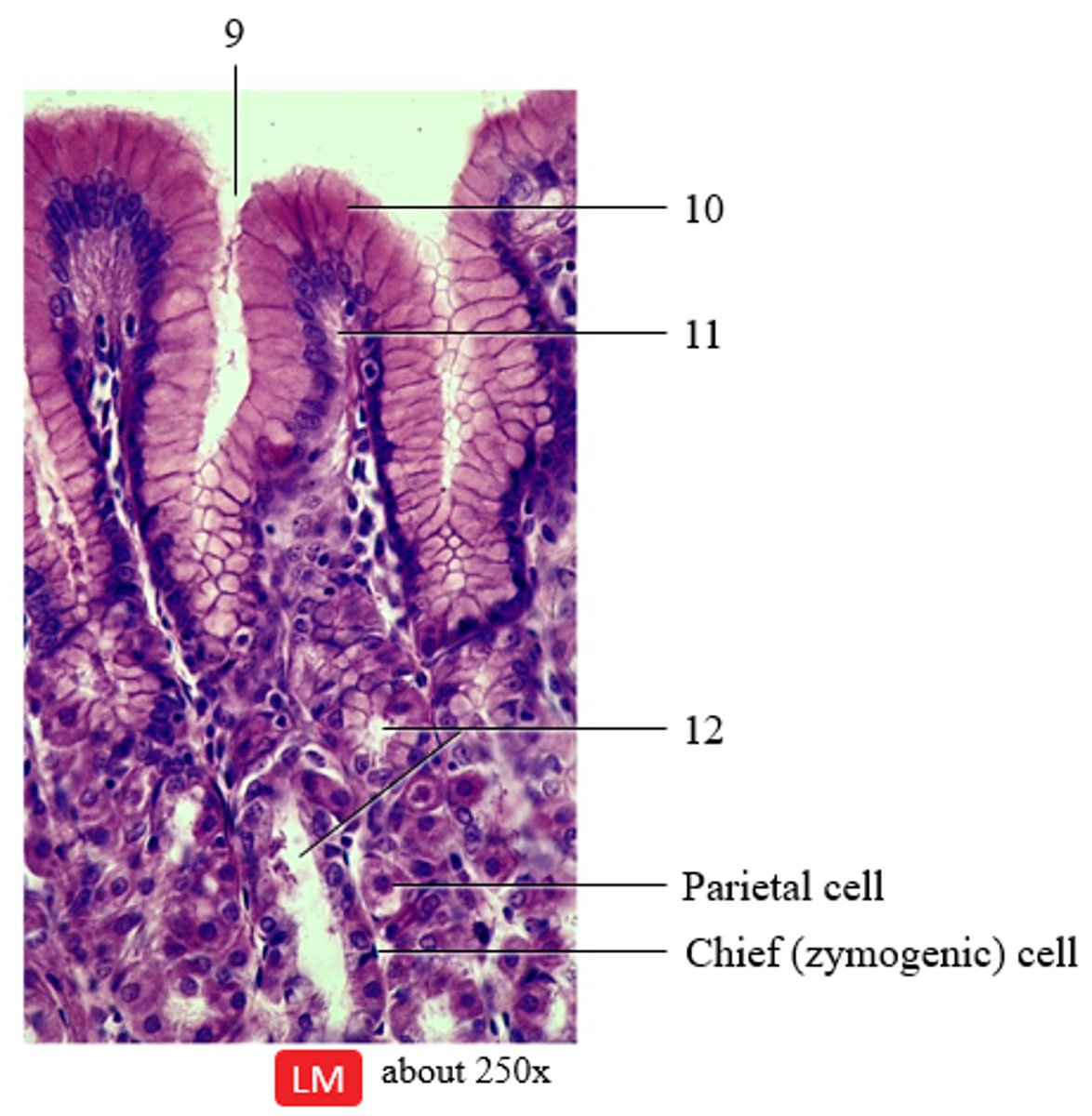
Identify the following structures on a histological image of the fundic mucosa of the stomach:
- gastric glands
- gastric pit
- lamina propria
- simple columnar epithelium
9 - gastric pit
10 - simple columnar epithelium
11 - lamina propria
12 - gastric glands
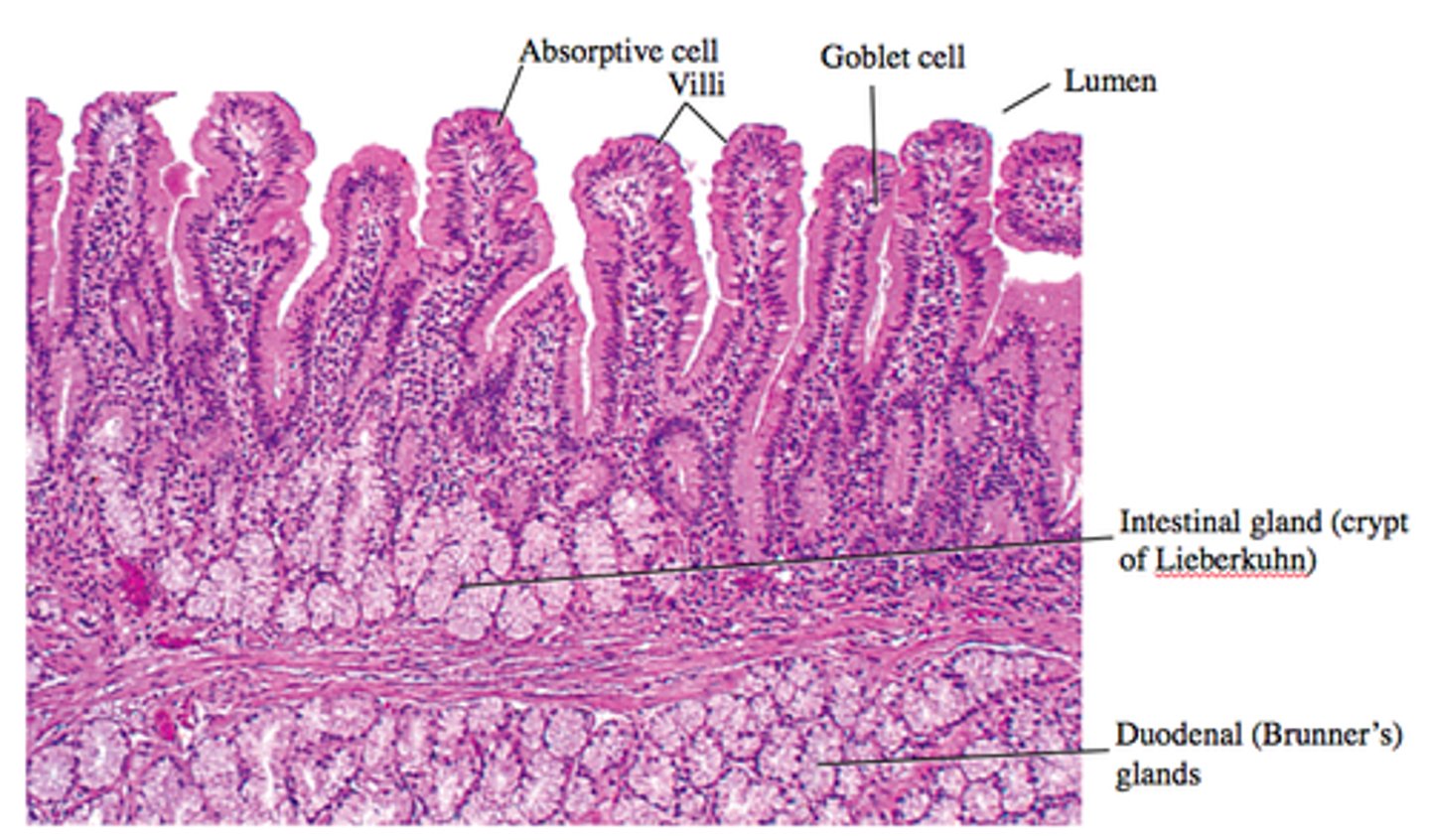
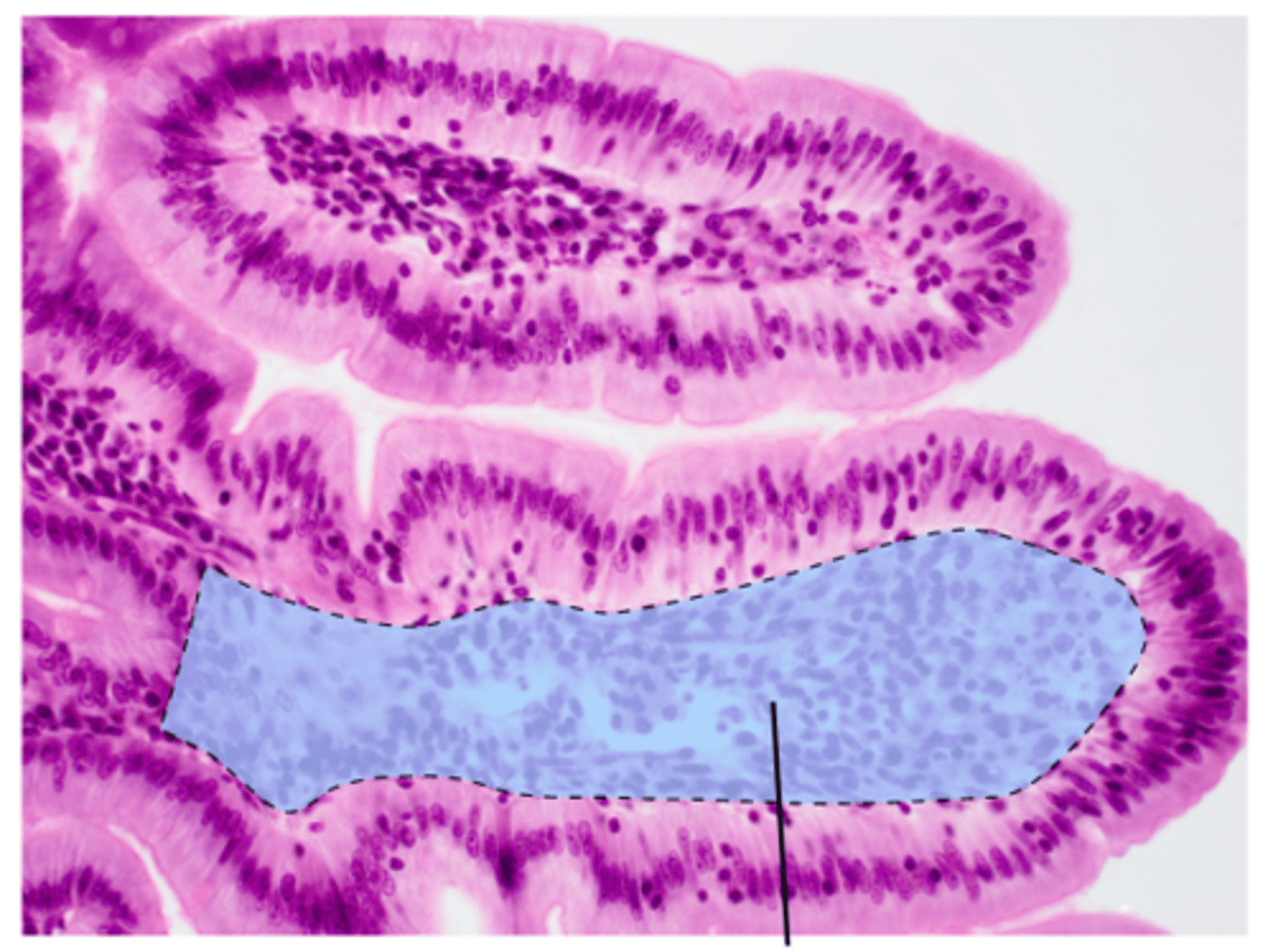
Identify the following structures on a histological image of the duodenum of the small intestine:
- simple columnar epithelium
- goblet cell
- villus
- intestinal gland
- duodenal gland
lamina propria of duodenum histology
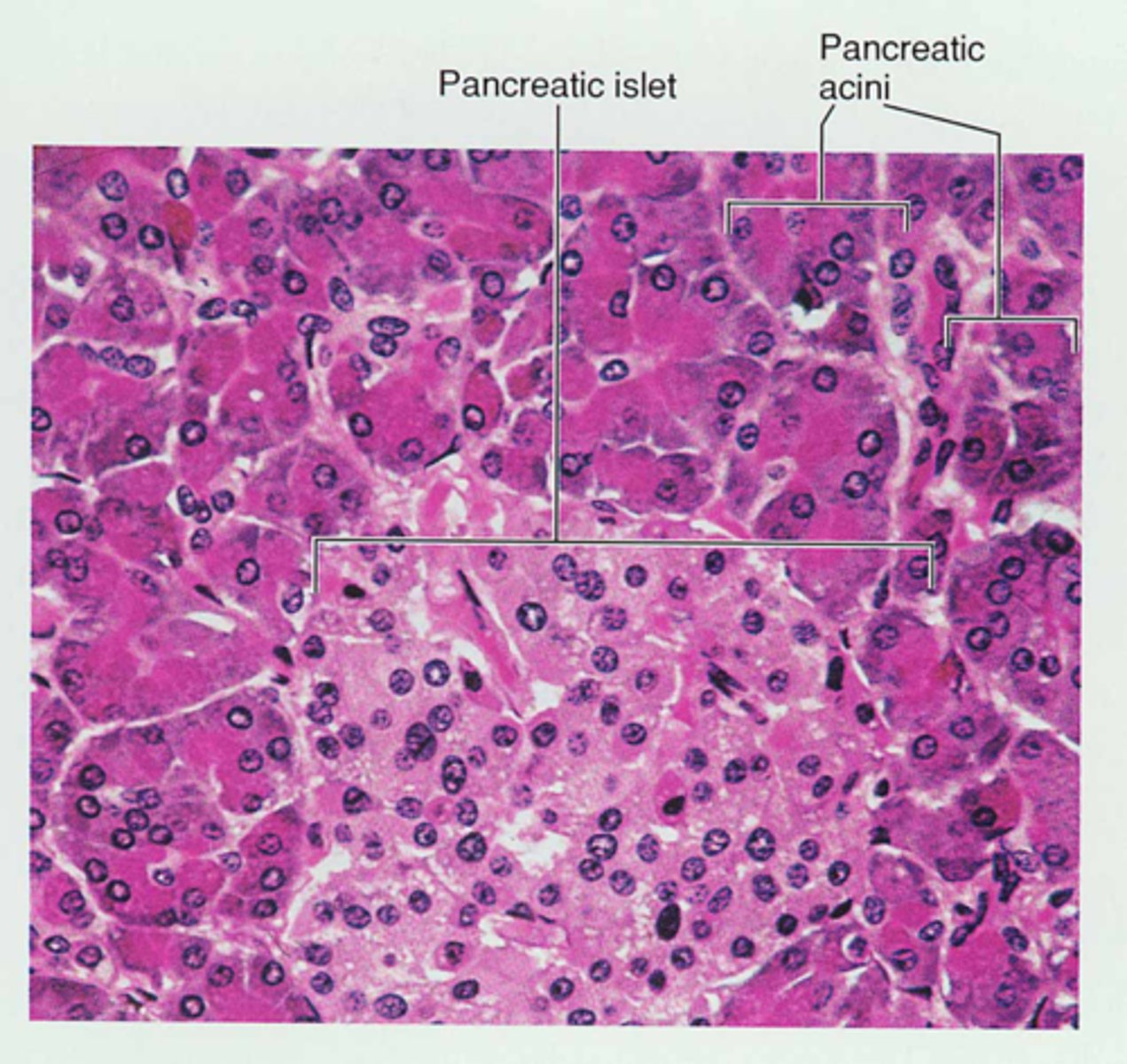
Histology of the pancreas:
- acini
- pancreatic islet (islet of Langerhans)
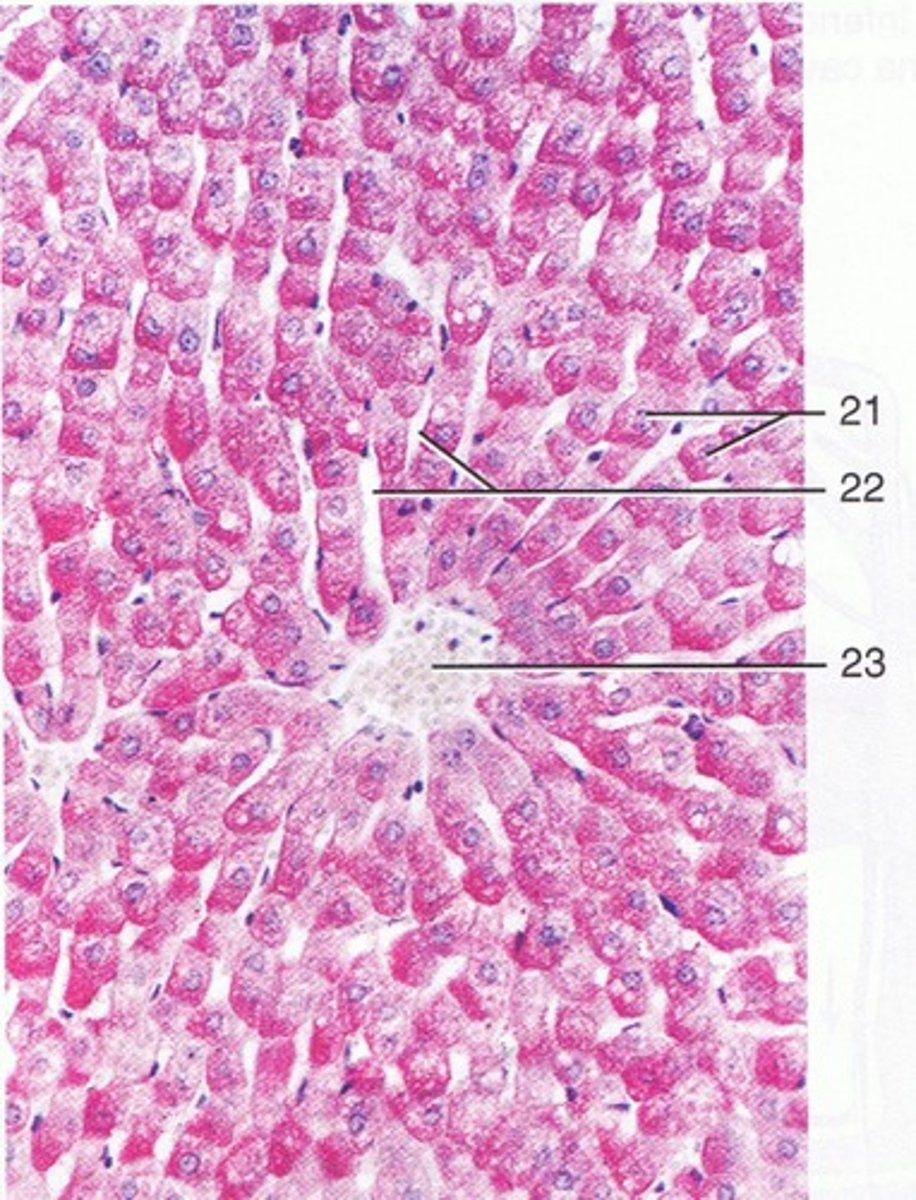
Identify the following structures of the histology of the liver:
- central vein
- hepatocytes
- hepatic sinusoid
21 - hepatocyte
22 - hepatic sinusoid
23 - central vein
Bile is stored in the _____.
gallbladder
During swallowing, the _____ prevents food and fluid from entering the nasopharynx.
soft palate
The esophagus function in:
propulsion