Pharm test 3
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
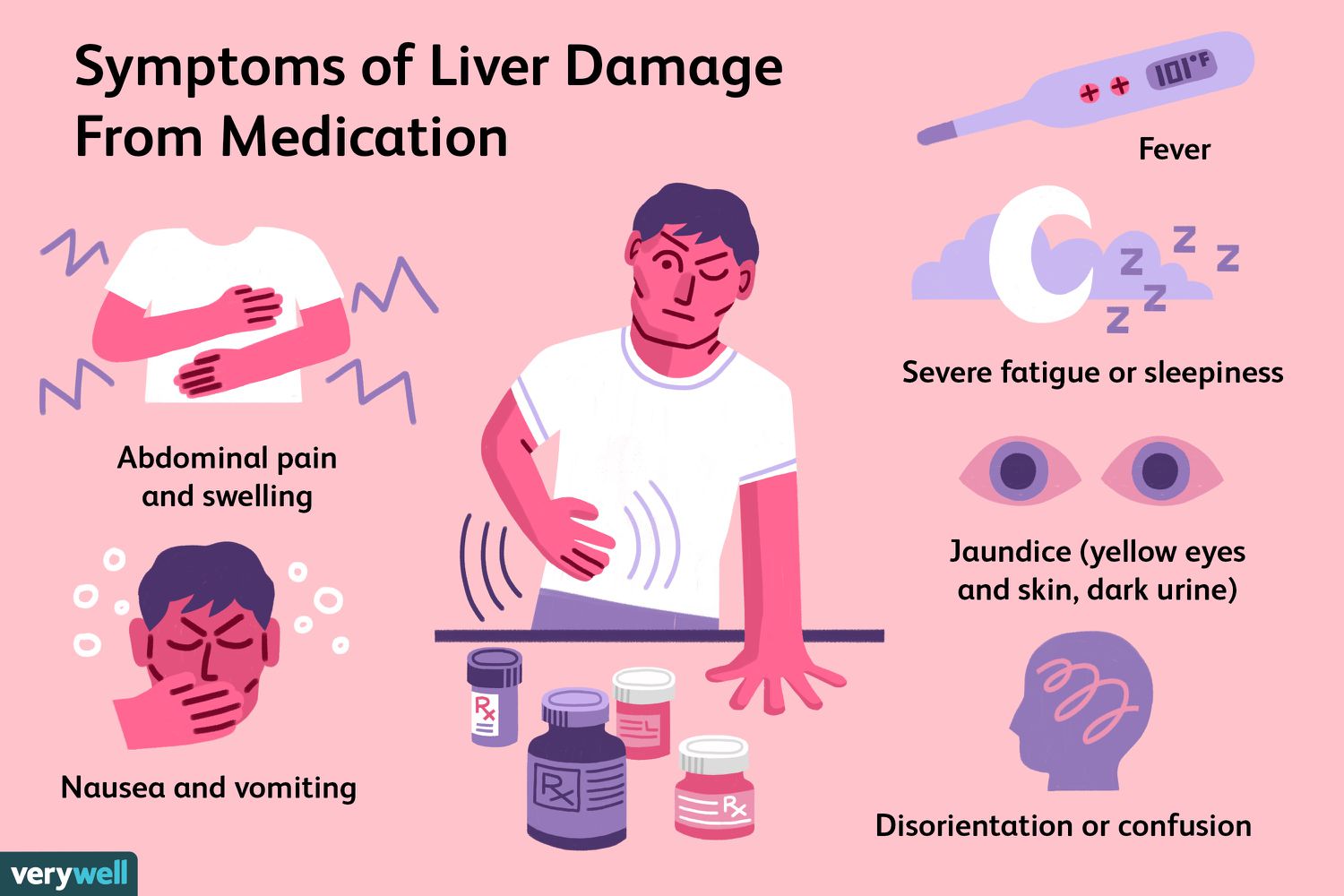
What is the number one concern with Tylenol
Liver damage
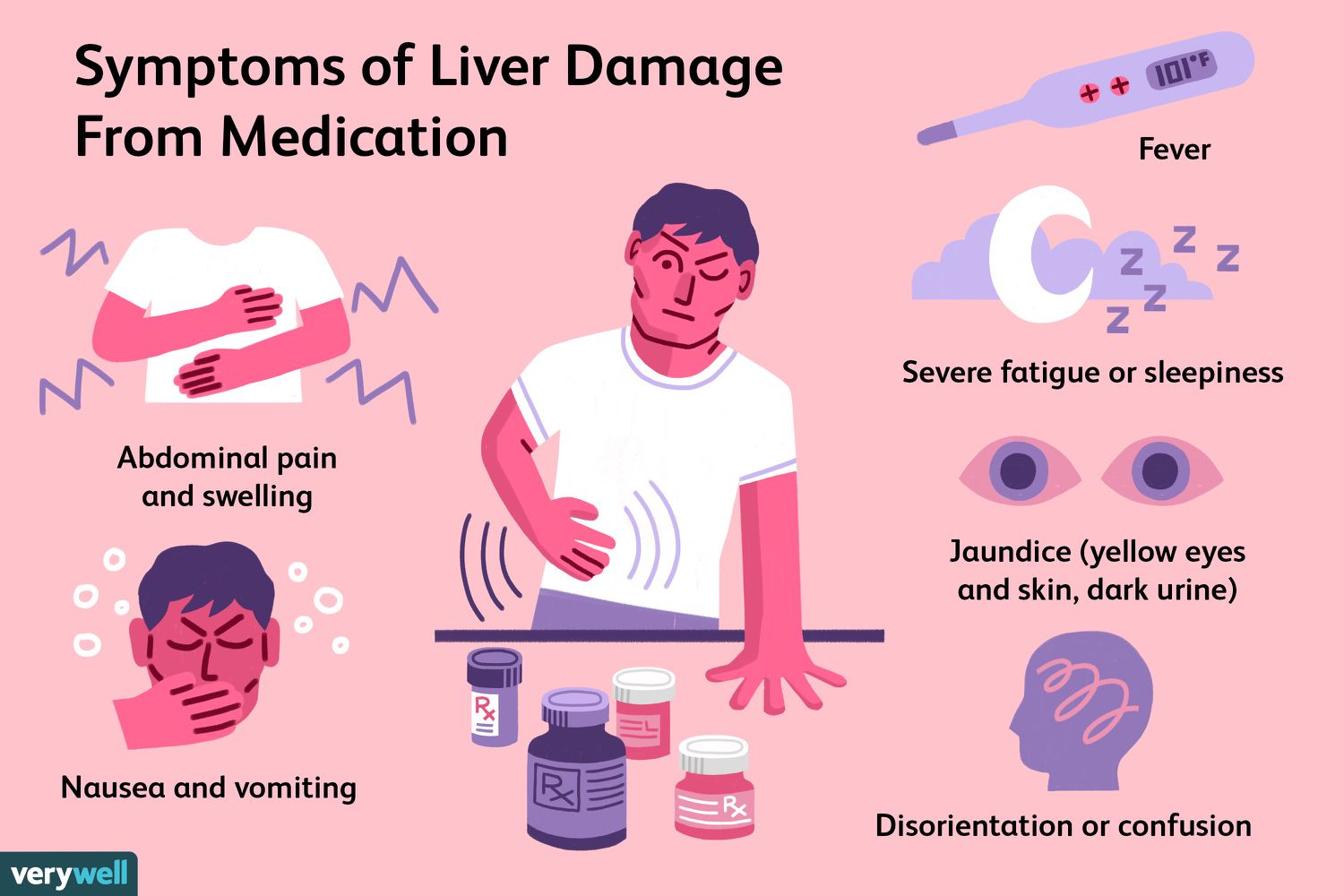
Early manifestations of liver damage
Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diaphoresis
Tylenol antidote
Acetylcysteine
First gen NSAIDs
Ibuprofen, aspirin, and ketorolac
Second gen NSAIDs
Celecoxib
What complications do first gen and second gen NSAIDs cause?
Potential GI bleed, nausea, vomiting, heart burn and abdominal pain
Caution use of NSAIDs
Smokers, alcohol abuse disorders, and peptic ulcers
Salicylism symptoms
tinnitus, nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis, and respiratory alkalosis
What does salicylism indicate?
Salicylism occurs before full toxicity of aspirin occurs
Symptoms of aspirin toxicity
Diaphoresis, dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, respiratory depression, high fever, acidosis and potential coma
What is an important precaution when administering any opioid?
Vital signs must be checked before and after administration
What type of insulin is Lispro?
Rapid acting, 10 mins
What is the peak duration for Lispro
1-3 hours
What type of insulin is "regular” insulin
Short acting, 30 mins
What type of insulin is NPH
Intermediate acting, 4 hours
What is the peak for NPH
4-12 hours
What is the peak for “regular” insulin
2.5-5 hours
What type of insulin is Glargine?
Long acting, 1 hour
What is the peak for Glargine?
Peakless
How should you store insulin
in a cool place, typically the refrigerator, and avoid freezing.
Sulfonylureas
Glipizide, glyburide, glimepride
Method of action for glipizide
Stimulates insulin secretion from the pancreas
Adverse effects of glipizide
Hepatotoxicity, hypoglycemia, blood dyscrasias and skin reactions
Biguanide, Metformin method of action
Decreases hepatoglucose production inhibiting glycogenesis and reduces insulin absorption in the intestine
What type of diabetes does Biguanide and Metformin
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Levothyroxine
Thyroid hormone replacement
Administration of Levothyroxine
Must be given 30-60 mins prior to food for max absorption
Iodine 131
Antithyroid, selectively destroys hyperactive thyroid
Iodine 131 drug interactions
Lithium Carbonate
Methimazole
Antithyroid, blocks synthesis of t3 and t4
Adverse effects of Methimazole
Hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, bone marrow suppression, lymph node enlargement, purpuric, and maculopapular rash
Mineralocorticoids
Maintain fluid and electrolyte balance in the body.
What do mineral corticosteroids treat
Renal insufficiency caused by hypopituitarism and Addison’s disease
Fludrocortisone
Affects fluid electrolyte balance causing sodium and water retention
Side effects of Fludrocortisone
Hypernatremia and hypokalemia
Glucocorticoids action
Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppression
Indications of glucocorticoids
Treats cancers, treat organ transplantation auto immune, allergies and shock
Why should not steroids be abruptly
Can cause renal insufficiency
Adverse effects of Estrogen
Hypertension, thrombophlebitis, hyperglycemia, and breakthrough bleeding
Drug interaction between Estrogen and Warfarin
Diminish anticoagulant effects
Drug interaction between Estrogen and Phenytoin
Inhibit metabolism of Phenytoin which can cause Phenytoin toxicity
Adverse effects of progestin
Amenorrhea, breakthrough bleeding, endometriosis and contraception