ib economics chapter 8
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/41
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
1
New cards
Circular Flow of Income
a flow of income in an economy where the value of output produced is equal to the total income generated in producing that output, which is equal to expenditures made to purchase the output
2
New cards
Circular Flow of Income Displays:
flows of goods and services and factors of production between firms and households and how national income or GDP is calculated
3
New cards
Factors of Circular Flow of Income
households, firms, leakages and injections
4
New cards
Explain Households within the Circular Flow of Income
supply domestic firms with needed factors of production, these factors are supplied by factor owners in return for a reward
5
New cards
Explain Firms within the Circular Flow of Income
produce goods and services and results in incomes being generated for factors of production
6
New cards
Explain Leakages from the Circular Flow of Income
as not all income will flow from households to businesses directly, some part of house hold income can be designated to savings ==(S)==, taxation ==(T)== and imports ==(M)==
7
New cards
Explain Injections from the Circular Flow of Income
in addition to investment, government spending ==(G)== or exports ==(X)== so boosting the circular flow of income leading to a multiplied expansion of output (e.g. investment expenditure ==(I)==)
8
New cards
Draw the Circular Flow of Income for a CLOSED ECONOMY
* Known as a closed 2 sector economy
\
* No international trade
\
* 2 sectors: households & firms
\
* No international trade
\
* 2 sectors: households & firms
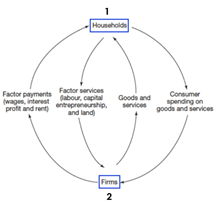
9
New cards
Draw the Circular Flow of Income for an OPEN ECONOMY
* Known as a closed 4 sector economy
\
* There is international trade
\
* 4 sectors: households & firms, government & international trade
\
* There is international trade
\
* 4 sectors: households & firms, government & international trade
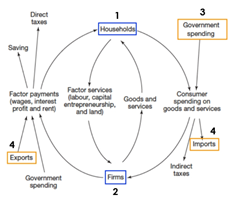
10
New cards
Circular Flow of Income in relation to Leakages and Injections
* Rate of injections=rate of withdrawels economy is at equilibrium
* Leakages > Injections, savings into financial market does not come back into the flow as investment, thus ⇩goods and services purchased, ⇩production and output by firms, ⇧unemployment and ⇩household income
* Leakages < Injections, the expenditure flow increases since injections are larger than leakages. Foreign consumers and demand for more goods and services ⇧exports, ⇧output and production by firms to meet increased demand, ⇩unemployment and ⇧household income
* Smaller the leakage, smaller the income flow (vice versa)
* Leakages > Injections, savings into financial market does not come back into the flow as investment, thus ⇩goods and services purchased, ⇩production and output by firms, ⇧unemployment and ⇩household income
* Leakages < Injections, the expenditure flow increases since injections are larger than leakages. Foreign consumers and demand for more goods and services ⇧exports, ⇧output and production by firms to meet increased demand, ⇩unemployment and ⇧household income
* Smaller the leakage, smaller the income flow (vice versa)
11
New cards
Measures of Economic Activity
1. National Income Accounting
2. GDP (most common)
12
New cards
National Income Accounting
the measurement of an economy’s national income and output as well as other measures of economic performance by specialised statistical services in every country. Deals with aggregate measures of outcome of economic activities.
13
New cards
GDP
a measure of the value of aggregate output of an economy, it is the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country during a given time period
* Measured through calculating: expenditure, income and output methods
\
* Value of output is equal to the income that is generates, meaning wages, rent, profit and interest
\
* It is assumed all incomes are spent and expenditure will equal income
* Measured through calculating: expenditure, income and output methods
\
* Value of output is equal to the income that is generates, meaning wages, rent, profit and interest
\
* It is assumed all incomes are spent and expenditure will equal income
14
New cards
3 Ways of Measuring GDP
1. Expenditure Method
2. Income Method
3. Output Method
15
New cards
Expenditure Method
adds up market value of all domestic expenditures make on final goods and services in a single year (final goods and services= a good or service purchased directly by the consumer). Total spending made up of: Consumption ==(C)==, Investment ==(I)==, Government Spending ==(G)== and Net Exports ==(X-M)==. \n Thus equation: ==AD= GDP= C + I + G + (X-M)==
16
New cards
Income Method
Measures the value of aggregate output of an economy, which adds up all income earned by factors of production in the course of providing goods and services within a country in a given time period. The value of an output produced is based on the costs involved in producing that output including wages, rent interest and profit. All payments are representative of income paid to factors of production.
17
New cards
Output Method
to measure the value of aggregate output of an economy, which calculates the value of all final goods and services produced in the country within a given time period. The sum of the value differs between the sales and revenue received and the cost of raw materials used
18
New cards
National Income Statistics
statistical data used to measure national income of an economy, consisting of factor payments or the sum of wages, interest rent plus profit and is often used interchangeably with the value of aggregate output. Measure economic growth through: ==total output= total income + total expenditure==
19
New cards
Types of National Income Statistics
1. GDP
2. GNI/GNP
20
New cards
GDP
market value of all final goods and services, produced by all residing within a domestic economy disregarding their nationality, during a specific period of time
21
New cards
Real GDP and Nominal GDP

22
New cards
GNI/GNP
==GDP+net income from abroad==, factors of production owned by a country’s citisins regardless of where the output is produced during a specific time period
23
New cards
Equation to compare Economic Performance Among Countries
GDP/(GNI per capita)= (GDP )/GNI÷total populationvv
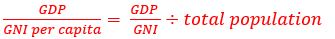
24
New cards
Real GDP as a measure of Standards of Living (SOL)
* As Real GDP ⇧, SOL⇩
\
* ⇧Real GDP doesn’t not always ⇧income, it may ⇩income due to worsening distribution of income
\
* Real GDP foes not reflect the true change of goods and services, therefore to assess SOL reviews change in types of products produced and ways they are produced
\
* ⇧Real GDP doesn’t not always ⇧income, it may ⇩income due to worsening distribution of income
\
* Real GDP foes not reflect the true change of goods and services, therefore to assess SOL reviews change in types of products produced and ways they are produced
25
New cards
GDP and GNI as a measure of SOL
* If SOL= level of economic and social wellbeing of an individual or household, it can be classified as quantitative and qualitative SOL
* Quantitative SOL- measured by GDPCapita
* Qualitative SOL- measured by factors like life expectancies, literacy rates, healthcare…
* Quantitative SOL- measured by GDPCapita
* Qualitative SOL- measured by factors like life expectancies, literacy rates, healthcare…
26
New cards
Limitations of GDP & GNI
1. Doesn’t consider non-marketed output- goods and services supplied for free prices that are economically insignificant (this would make GDP/GNI higher) e.g. growing own produce
\
2. Doesn’t consider informal markets- a market that is not taxed nor regulate by the government because they are unreported e.g. illegal- drugs and legal- street food stalls
\
3. Doesn’t consider social costs & negative externalities- social costs+private costs+external costs, external costs e.g. pollution or environment degradation. Social costs are also subjective, intangible and hard to calculate in monetary values
\
4. Doesn’t consider international price differences- goods and services sold at varying price worldwide which is significant because purchasing power is based on price in relation to income
\
5. Doesn’t consider number of hours worked & leisure- ⇩ in working hours= ⇧ leisure in leisure which increases standards of living
\
6. Doesn’t consider life factors- e.g. low crime rates, low pollution, low pollution, low sense of security and peace
\
7. Doesn’t consider type of goods and services produced- e.g. production of military weapons ⇩SOL but ⇧GDP
27
New cards
Green GDP
the measurement of GDP growth with the environmental consequences of that growth factored in
\
* Accounts for monetized loss of biodiversity and costs caused by climate change
* Measures how a country is prepared for sustainable economic development which preserves resources for future generations
\
* Accounts for monetized loss of biodiversity and costs caused by climate change
* Measures how a country is prepared for sustainable economic development which preserves resources for future generations
28
New cards
Calculating Green GDP
1. Method 1: Green GDP minus value of environmental degradation
\
2. Method 2: Green GDP minus value of environmental degradation minus costs of cleaning up negative externalities
29
New cards
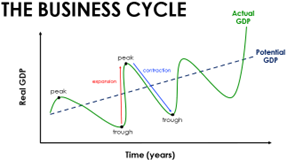
The Business Cycle
the fluctuation in growth of real output or real GDP, consisting of alternating periods of expansion and contraction

30
New cards
Expansions and Contractions within the Business Cycle
* Expansion indicates that the economy is growing in real terms
* Rise in GDP=increase in total output (and GDP growth)
\
* Economy contracts during recessions
* Fall in GDP= decrease in total output (and GDP growth)
* Rise in GDP=increase in total output (and GDP growth)
\
* Economy contracts during recessions
* Fall in GDP= decrease in total output (and GDP growth)
31
New cards
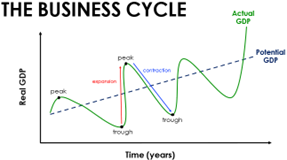
Stages of the Business Cycle
* Expansion= positive growth in real GDP and economy is growing, utilisation of resources aids the economy reaching maximum capacity and resources become scarce due to increase in the general price level (e.g. inflation)
\
* Peak= the economy has reached its maximum real GDP, when the economy transitions into the contraction phase; the economy is at maximum capacity or full employment of resources and the economy will experience inflation
\
* Contraction= negative growth in real GDP. If the contraction lasts more than 6 months, it is a recession. There will be a rise in unemployment of resources and the general price level will begin to fall
\
* Trough= the minimum real GDP when the economy transitions from the contraction phase to the expansion phase. Unemployment is high, spending is low and consumers and business possess pessimistic attitudes regarding the future economy resulting in more cautious behaviours
\
* Peak= the economy has reached its maximum real GDP, when the economy transitions into the contraction phase; the economy is at maximum capacity or full employment of resources and the economy will experience inflation
\
* Contraction= negative growth in real GDP. If the contraction lasts more than 6 months, it is a recession. There will be a rise in unemployment of resources and the general price level will begin to fall
\
* Trough= the minimum real GDP when the economy transitions from the contraction phase to the expansion phase. Unemployment is high, spending is low and consumers and business possess pessimistic attitudes regarding the future economy resulting in more cautious behaviours
32
New cards
Economic Growth
an increase in the national output of an economy over a period of time.
Economic growth= ⇧ national income and ⇧ GDP/GNI per capita
Economic growth= ⇧ national income and ⇧ GDP/GNI per capita
33
New cards
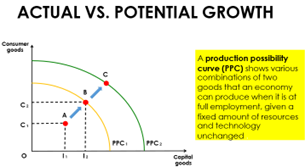
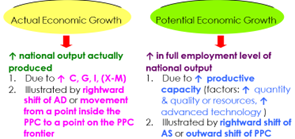
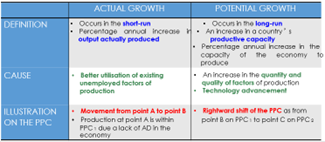
Two types of Economic Growth
1. Actual Economic Growth: GDP ⇩ because firms cut down on production as demand falls, thus ⇩ employment levels. Wage rates and price levels are assumed to be fixed as they are usually set by contracts and cannot be changed.
\
2. Potential Economic Growth: the level of GDP where there is full employment of resources. There can still be unemployment of labour known as the natural rate of unemployment
* Natural rate of employment (NAIRU): unemployment that occurs when the economy is producing as its potential or full employment level of output and is equal to the sum of structural, frictional plus seasonal unemployment
34
New cards
Equations of Actual and Potential Economic Growth
35
New cards
Evaluate Actual and Potential Economic Growth
36
New cards
GDP Gap
the difference between the actual output of an economy and the potential output of the economy
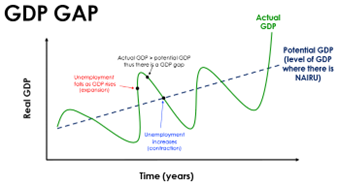
37
New cards
Inflationary Gap
a situation where real GDP > Potential GDP and unemployment is lower than NAIRU which arises when the AD curve intersects the SRAS curve at a higher level of real GDP than potential GDP
38
New cards
Deflationary Gap
a situation where real GDP < Potential GDP and unemployment is greater than NAIRU which arises when the AD curve intersects the SRAS curve at a lower level of real GDP than potential GDP (also referred to as recessionary gap)
39
New cards
Alternative Measures of Well-being
1. OECD Better Life Index
2. Happiness Index
3. Happy Planet Index
40
New cards
OECD Better Life Index
41
New cards
Happiness Index
42
New cards
Happy Planet Index