alcohols phenols and ethers
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
Phenols
Compounds formed when a hydrogen atom in an aromatic hydrocarbon is replaced by an -OH group.
Ethers
Compounds formed by substituting the hydrogen atom of the hydroxyl group of an alcohol or phenol by an alkyl or aryl group.
Mono-, Di-, Tri- or Polyhydric alcohols
Alcohols classified based on the number of hydroxyl groups they contain.
Allylic alcohols
Alcohols where the -OH group is attached to a sp3 hybridized carbon adjacent to a carbon-carbon double bond.
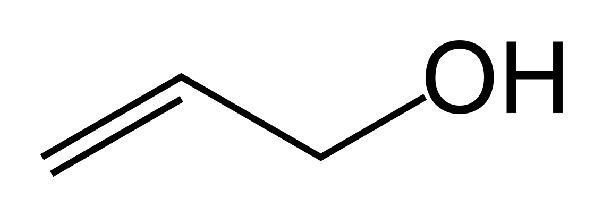
Vinylic alcohols
Alcohols where the -OH group is bonded to a carbon-carbon double bond.
Simple or symmetrical ethers
Ethers where the alkyl or aryl groups attached to the oxygen atom are the same.
Mixed or unsymmetrical ethers
Ethers where the two groups attached to the oxygen atom are different.
IUPAC system
The system of nomenclature used to name alcohols, phenols, and ethers based on the parent alkane or benzene ring and the position of substituents.
Common name
The name of an alcohol or phenol derived from the common name of the alkyl or aryl group and adding the word "alcohol" or "phenol" to it.
Cyclic alcohols
Alcohols with a hydroxyl group attached to a carbon atom in a cyclic structure.
Ortho, meta, and para
Terms used in the common names of substituted phenols to indicate the positions of substituents on the benzene ring.
Alcohols
Organic compounds that contain a hydroxyl (-OH) group attached to a carbon atom.
Phenols
Organic compounds that contain a hydroxyl (-OH) group attached to an aromatic ring.
Ethers
Organic compounds that contain an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups.
Common name
A name given to a compound based on traditional or common usage.
IUPAC name
A systematic name given to a compound according to the rules of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).
Dihydroxy derivatives
Compounds that have two hydroxyl (-OH) groups attached to a benzene ring.
Alkyl/aryl groups
Groups derived from hydrocarbons, either alkyl groups (containing only carbon and hydrogen) or aryl groups (containing a benzene ring).
Bond angle
The angle between two bonds in a molecule.
Acid catalysed hydration
The addition of water to an alkene in the presence of an acid catalyst to form an alcohol.
Hydroboration-oxidation
A reaction in which an alkene reacts with diborane (BH3)2 followed by oxidation to form an alcohol.
Catalytic hydrogenation
The addition of hydrogen to a compound in the presence of a catalyst to form an alcohol.
Reduction
A chemical reaction in which a compound gains electrons or hydrogen atoms.
Carboxylic acids
Organic compounds that contain a carboxyl (-COOH) group.
Esters
Organic compounds that are derived from carboxylic acids and alcohols.
Lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH4)
A strong reducing agent used to reduce carboxylic acids to alcohols.
Catalytic hydrogenation
The addition of hydrogen to a compound in the presence of a catalyst to form an alcohol.
Alcohols
Organic compounds that consist of an alkyl/aryl group and a hydroxyl group.
Phenols
Organic compounds that consist of an aromatic ring with a hydroxyl group attached.
Grignard reagents
Organic compounds that contain a carbon-metal bond, commonly used in the synthesis of alcohols.
Nucleophilic addition
A reaction in which a nucleophile attacks an electrophile, resulting in the formation of a new bond.
Carbonyl group
A functional group consisting of a carbon atom double bonded to an oxygen atom.
Adduct
A compound formed by the addition of two or more molecules.
Hydrolysis
A chemical reaction in which a compound reacts with water to form two or more new compounds.
Primary alcohol
An alcohol in which the hydroxyl group is attached to a carbon atom that is bonded to only one other carbon atom.
Secondary alcohol
An alcohol in which the hydroxyl group is attached to a carbon atom that is bonded to two other carbon atoms.
Tertiary alcohol
An alcohol in which the hydroxyl group is attached to a carbon atom that is bonded to three other carbon atoms.
IUPAC names
The systematic names given to organic compounds according to the rules of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry.
Catalytic reduction
A reaction in which a compound is reduced in the presence of a catalyst.
Hydration
A reaction in which water is added to a compound.
Sulphuric acid
A strong acid commonly used in chemical reactions.
Benzene derivatives
Organic compounds that are derived from benzene.
Haloarenes
Organic compounds that contain a halogen atom attached to an aromatic ring.
Sodium phenoxide
The sodium salt of phenol, formed by the reaction of phenol with sodium hydroxide.
Diazonium salts
Organic compounds that contain a diazonium group (-N2+).
Cumene
A hydrocarbon compound used in the production of phenol and acetone.
Intermolecular hydrogen bonding
The attraction between the hydrogen atom of one molecule and the electronegative atom of another molecule.
Van der Waals forces
Weak intermolecular forces that arise from temporary fluctuations in electron distribution.
Solubility
The ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent.
Hydrogen bonds
Strong intermolecular forces that occur between a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative atom and another electronegative atom.
Alkyl/aryl groups
Organic groups derived from alkanes or aromatic compounds.
Boiling points
The temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas.
Cleavage
The breaking of a chemical bond.
Electrophiles
Chemical species that accept an electron pair in a chemical reaction.
Protonated alcohols
Alcohols that have gained a proton.
Brönsted acids
Substances that can donate a proton to a base.
Electron-releasing group
A group that donates electron density to a molecule.
Alcohols
Organic compounds that contain a hydroxyl (-OH) group attached to a carbon atom.
Alkoxide
An ion formed by the reaction of an alcohol with a metal, in which the metal replaces the hydrogen atom of the hydroxyl group.
Proton donor
A substance that donates a proton (H+) in a chemical reaction, also known as a strong acid.
Phenols
Organic compounds that contain a hydroxyl (-OH) group directly attached to a benzene ring.
Acidity
The measure of how easily a substance donates a proton in a chemical reaction.
Ionisation
The process of forming ions by gaining or losing electrons.
Delocalisation
The spreading out of charge or electron density over multiple atoms or molecules.
pKa
The measure of the acidity of a compound, with lower values indicating stronger acids.
Esterification
The reaction between an alcohol or phenol and a carboxylic acid, acid chloride, or acid anhydride to form an ester.
Acetylation
The introduction of an acetyl group (CH3CO) into a compound.
Cleavage
The breaking of a chemical bond.
Dehydration
The removal of a molecule of water from a compound.
Alkenes
Unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain a carbon-carbon double bond.
Oxidation
A chemical reaction that involves the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state.
Dehydrogenation
A type of oxidation reaction that involves the loss of dihydrogen (H2) from a compound.
Strong oxidising agents
Substances like acidified potassium permanganate that are used to oxidize alcohols to carboxylic acids directly.
Acidified potassium permanganate
A strong oxidizing agent used to convert alcohols to carboxylic acids directly.
Aldehydes
Organic compounds that are formed when primary alcohols are oxidized, often using CrO3 as the oxidizing agent.
Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC)
A reagent used to oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes in good yield.
Chromic anhydride (CrO3)
An oxidizing agent used to convert secondary alcohols to ketones.