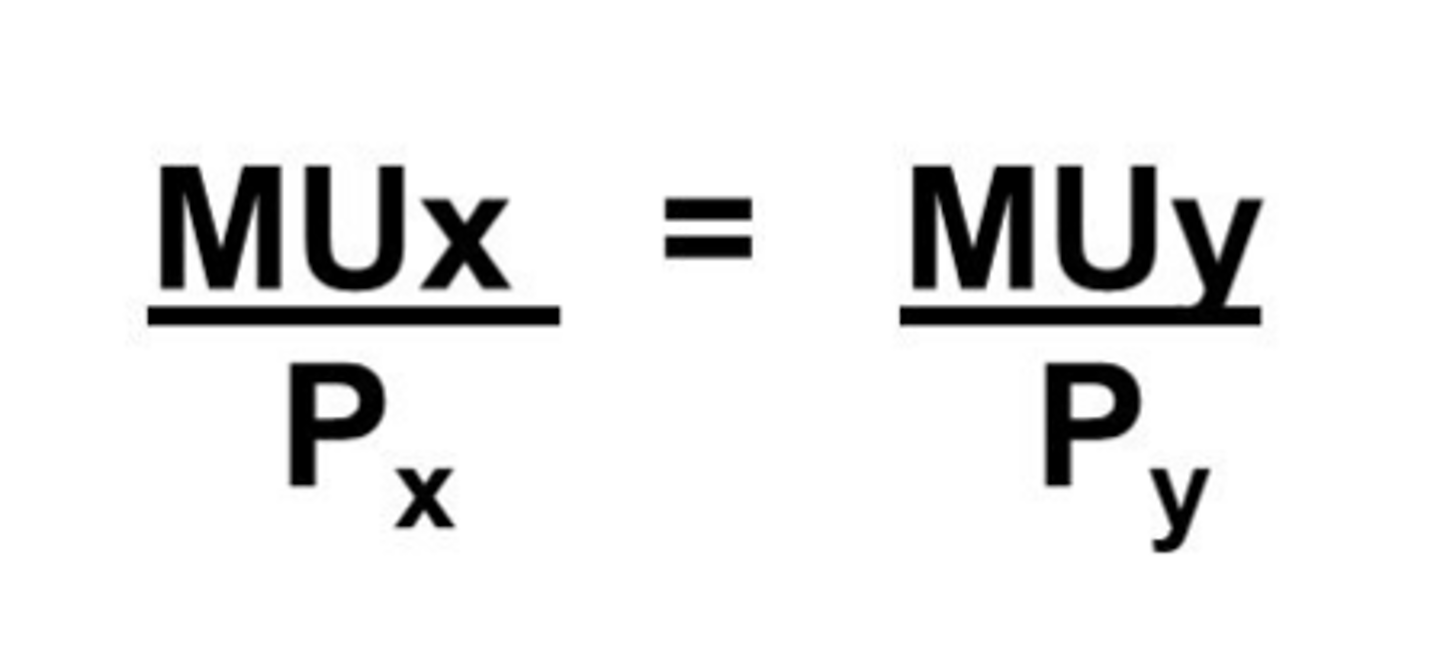Unit 1: Basic Economic Concepts
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Economics
The study of how people seek to satisfy their needs and wants by making choices

scarcity
Limited quantities of resources to meet unlimited wants

Microeconomics
the study of how households and firms make decisions and how they interact in markets

macroeconomics
the study of the economy as a whole, including topics such as inflation, unemployment, and economic growth
theoretical economics
economists use the scientific method to make generalizations and abstractions to develop theories
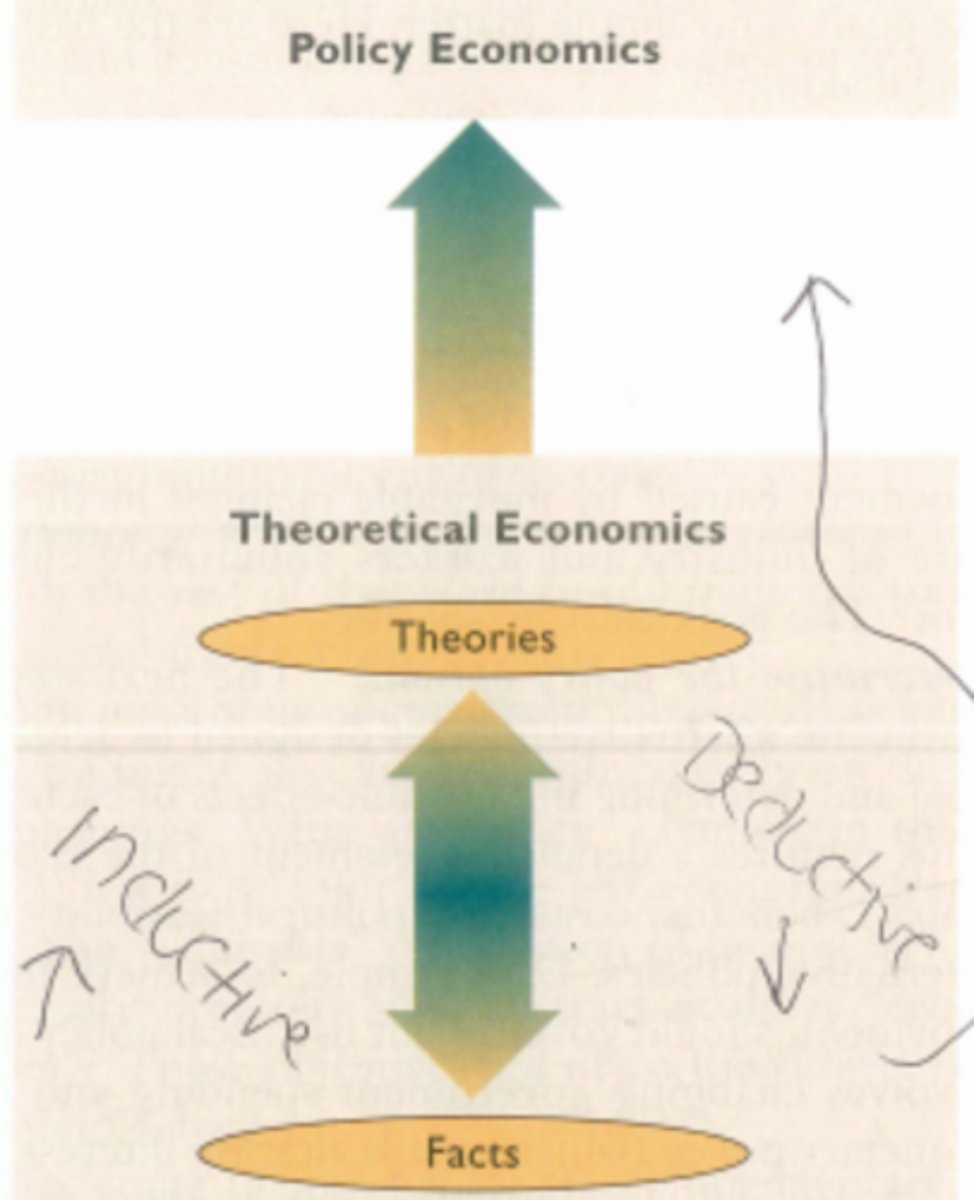
policy economics
Theories are applied to fix problems or meet economic goals

positive economics
the branch of economic analysis that describes the way the economy actually works; based on Facts

normative economics
The part of economics involving value judgments about what the economy should be like; focused on which economic goals and policies should be implemented; policy economics; What ought to be.

trade-off
all the alternatives that we sacrifice when we make a decision

marginal costs (MC)
the cost of producing one more unit of a good
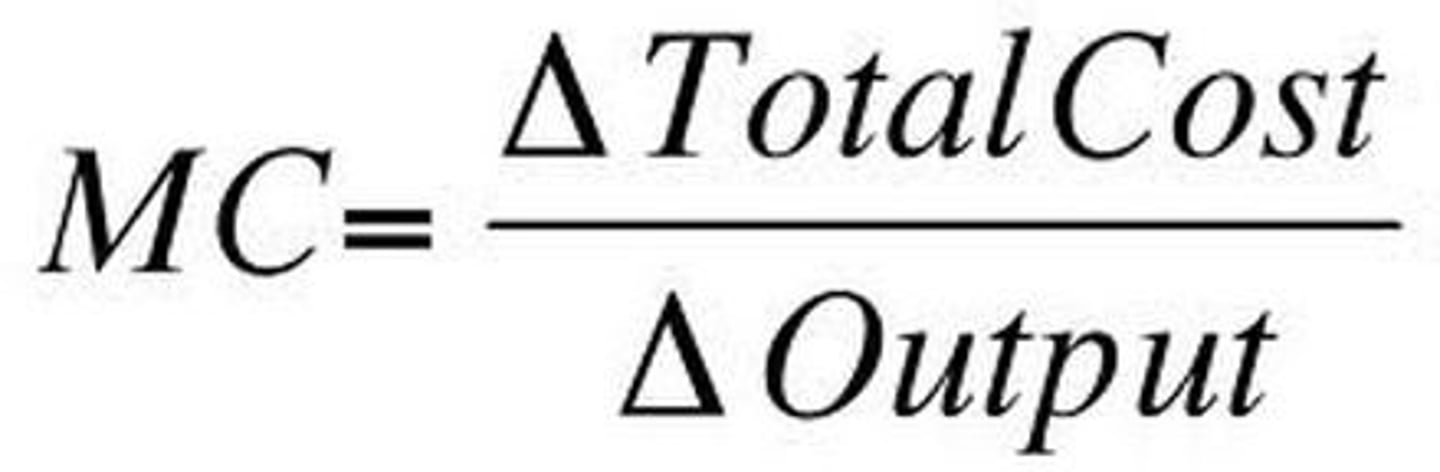
marginal benefit (MB)
The additional benefit received from the consumption of the next unit of a good or service

marginal analysis
analysis that involves comparing marginal benefits and marginal costs (Marginal = Additional)
opportunity cost
the most desirable alternative given up as the result of a decision

four factors of production
land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship
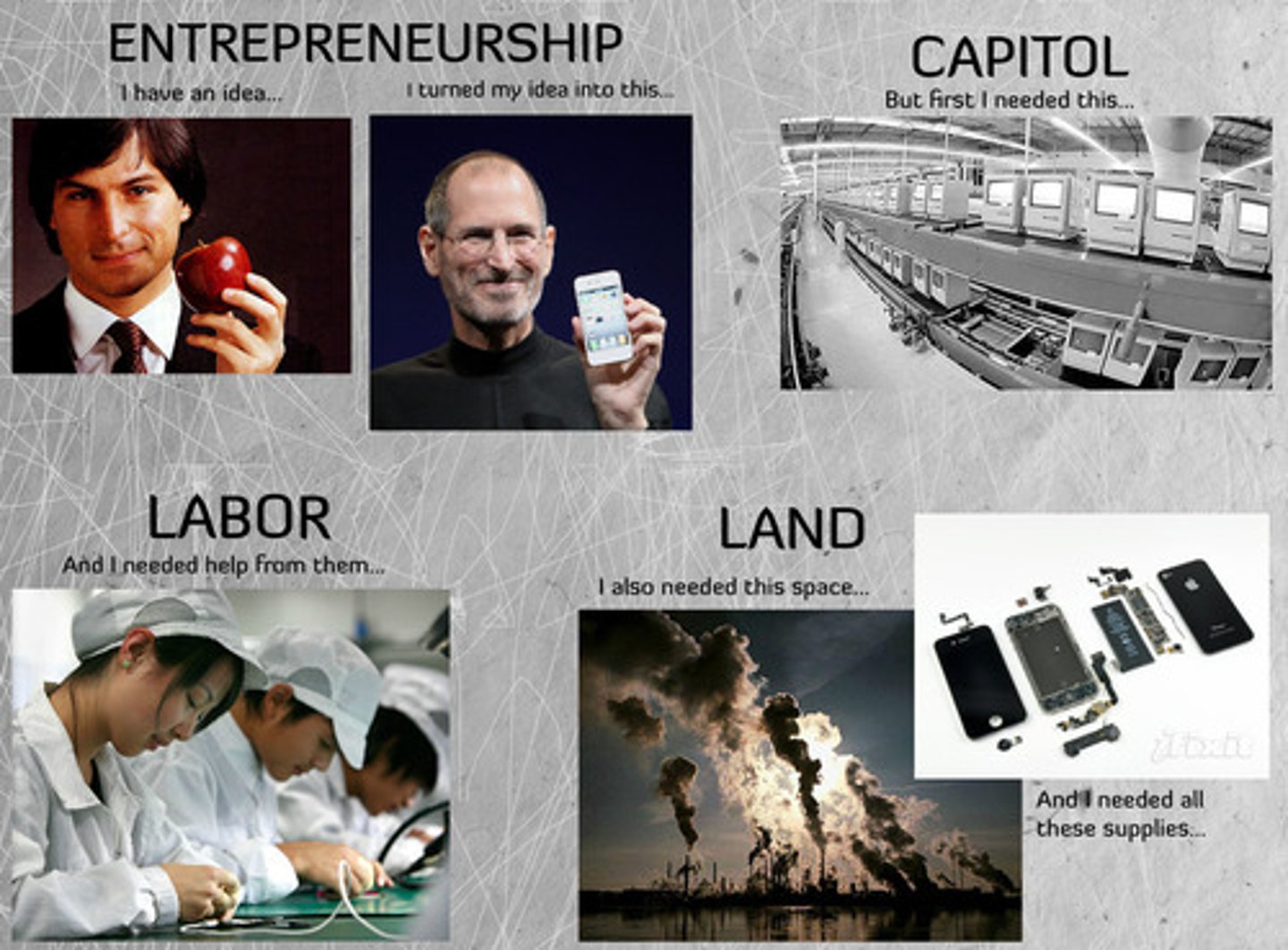
land
all natural resources used to produce goods and services (water, sun, plants, animals, etc)

labor
Human effort directed toward producing goods and services

physical capital
the human-made objects used to create other goods and services

human capital
the skills and knowledge gained by a worker through education and experience

Entrepreneurship
the process of starting, organizing, managing, and assuming the responsibility for a business

investment
the money spend by businesses to improve their production usually by increasing their capital

consumer goods
products and services that satisfy human wants directly

capital goods
Buildings, machines, technology, and tools needed to produce goods and services.

Productivity
The value of a particular product compared to the amount of labor needed to make it.

Three Economics Questions
What to produce? How to produce? For whom to produce?

economic system
the method used by a society to produce and distribute goods and services
command economy
An economic system in which the government controls a country's economy. aka: communism

free market economy
an economic system in which decisions on the three key economic questions are based on voluntary exchange in markets

mixed economy
An economy in which private enterprise exists in combination with a considerable amount of government regulation and promotion.

Laissez-faire economics
Theory that opposes government interference in economic affairs beyond what is necessary to protect life and property.

invisible hand
A phrase coined by Adam Smith to describe the process that turns self-directed gain into social and economic benefits for all

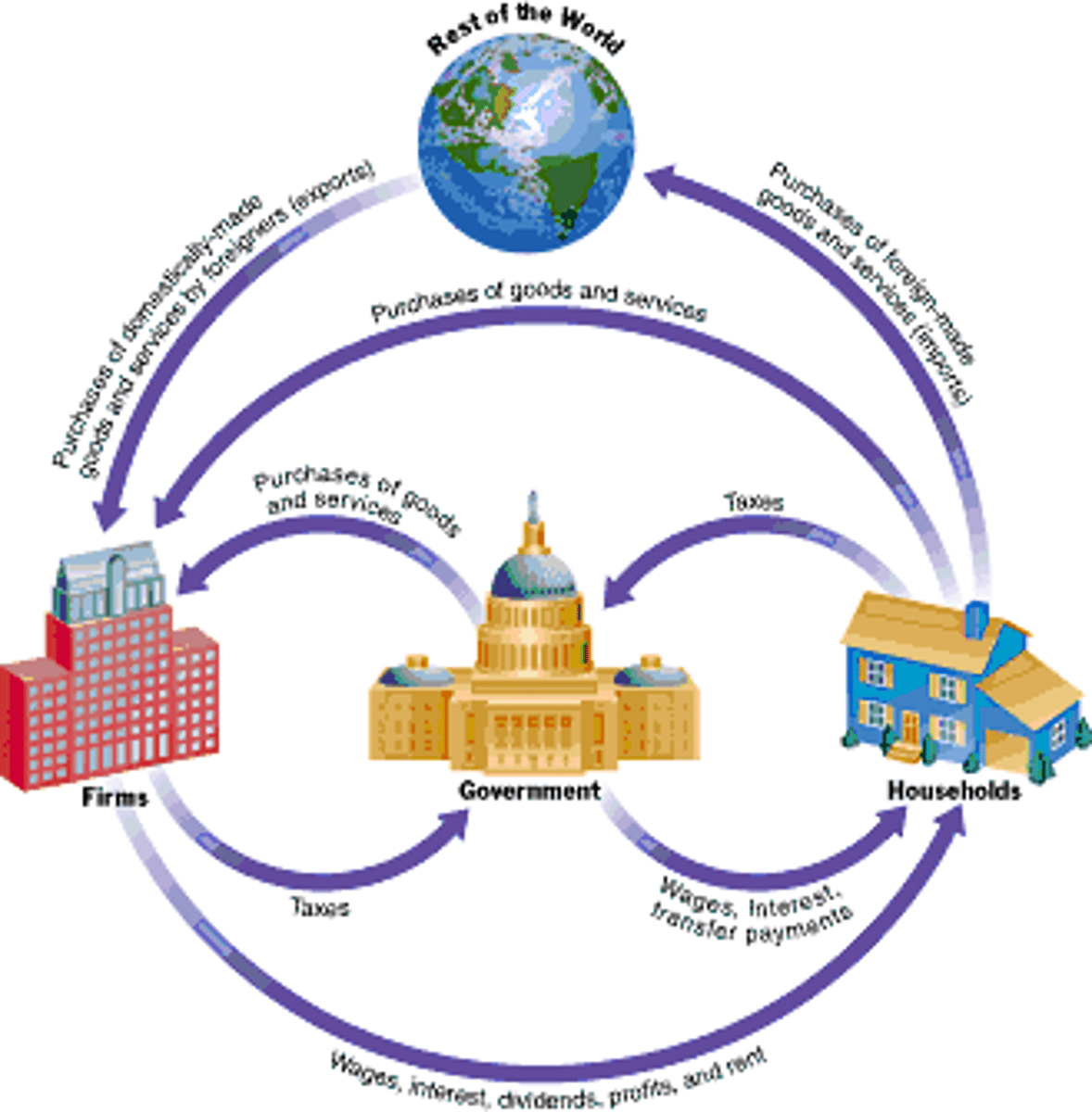
circular flow matrix
relationship between households, businesses, and the government
businesses supply products but demand resources
consumers supply resources but demand products
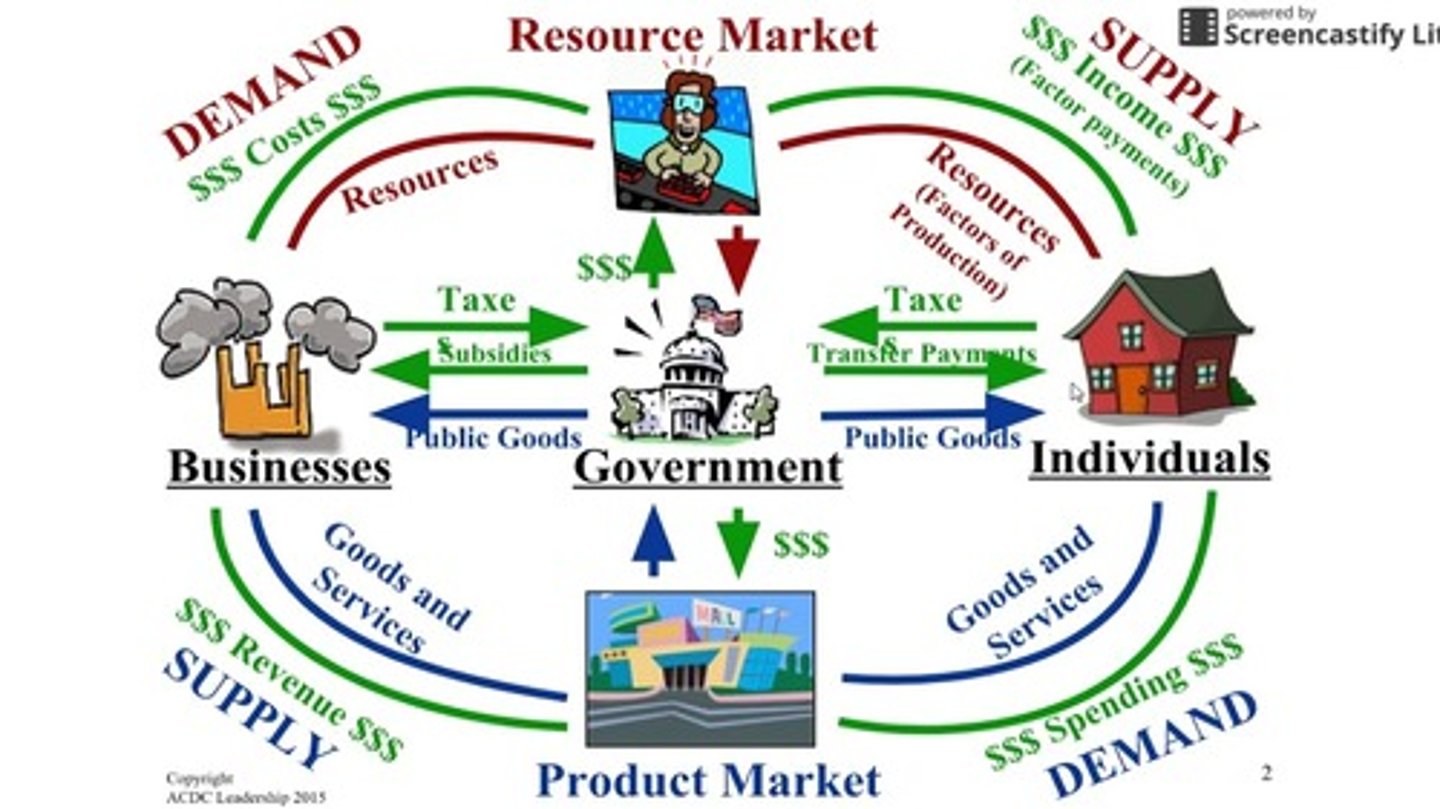
product market
the market in which households purchase the goods and services that firms produce

resource market
a market in which households sell and firms buy resources or the services of resources

private sector
the part of the national economy that is not under direct government control.

public sector
the part of an economy that is controlled by the government.

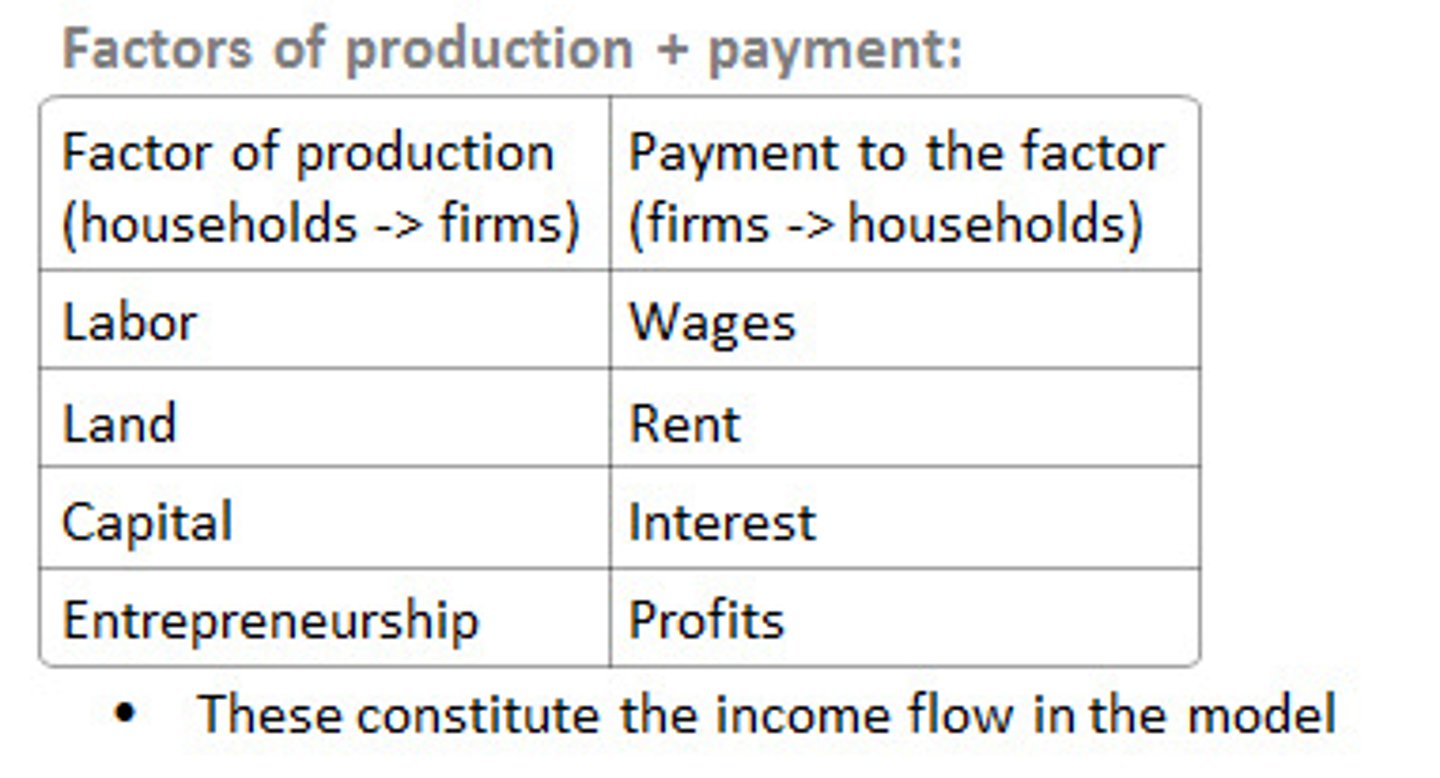
factor payments
payment for the factors of production, namely rent for land, wages for labor, interest for capital, and profit for entrepreneurship
transfer payments
Benefits given by the government directly to individuals. Transfer payments may be either cash transfers, such as Social Security payments and retirement payments to former government employees, or in-kind transfers, such as food stamps and low-interest loans for college education.

Subsidies
a sum of money granted by the government or a public body to assist an industry or business so that the price of a commodity or service may remain low or competitive.
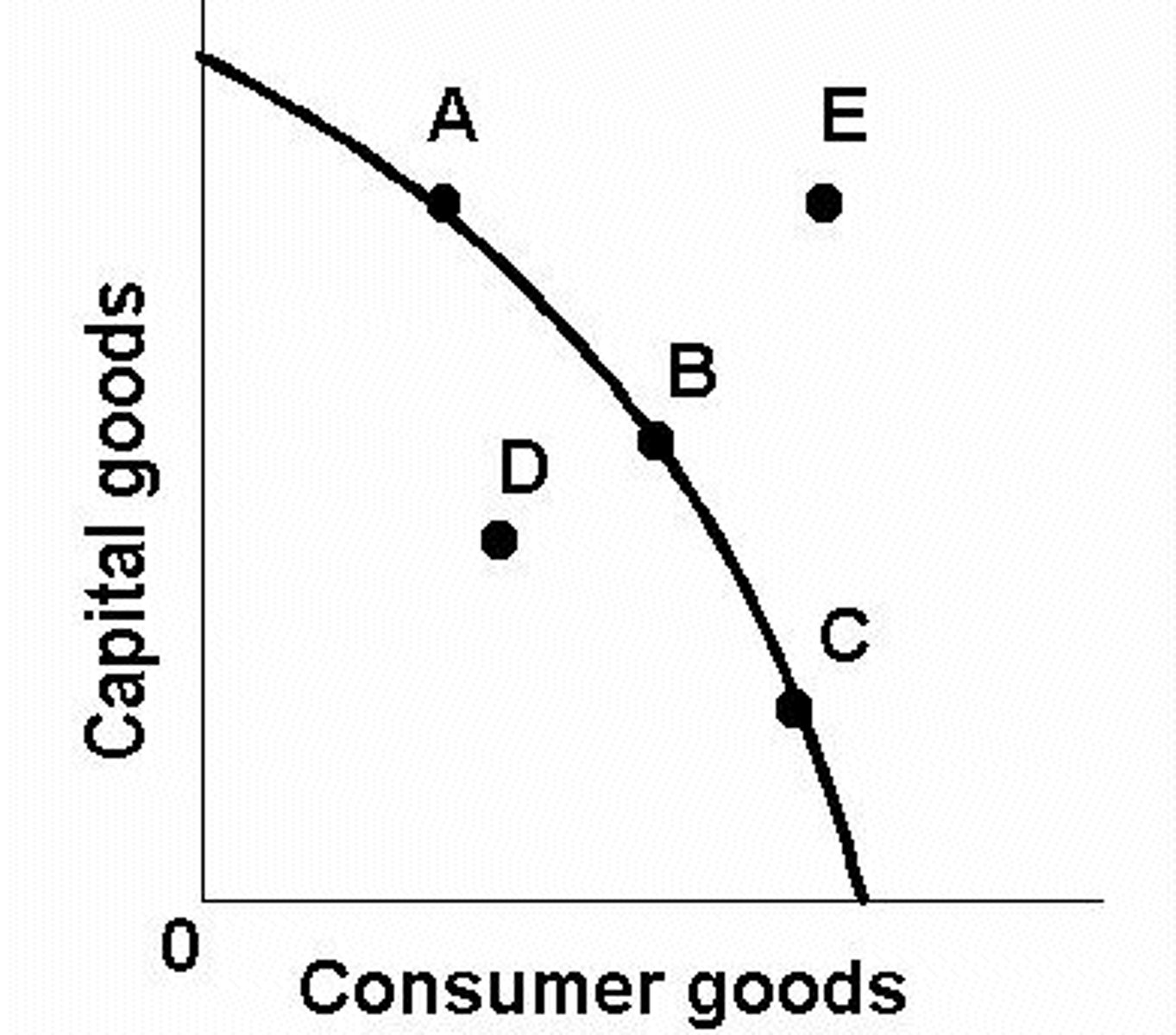
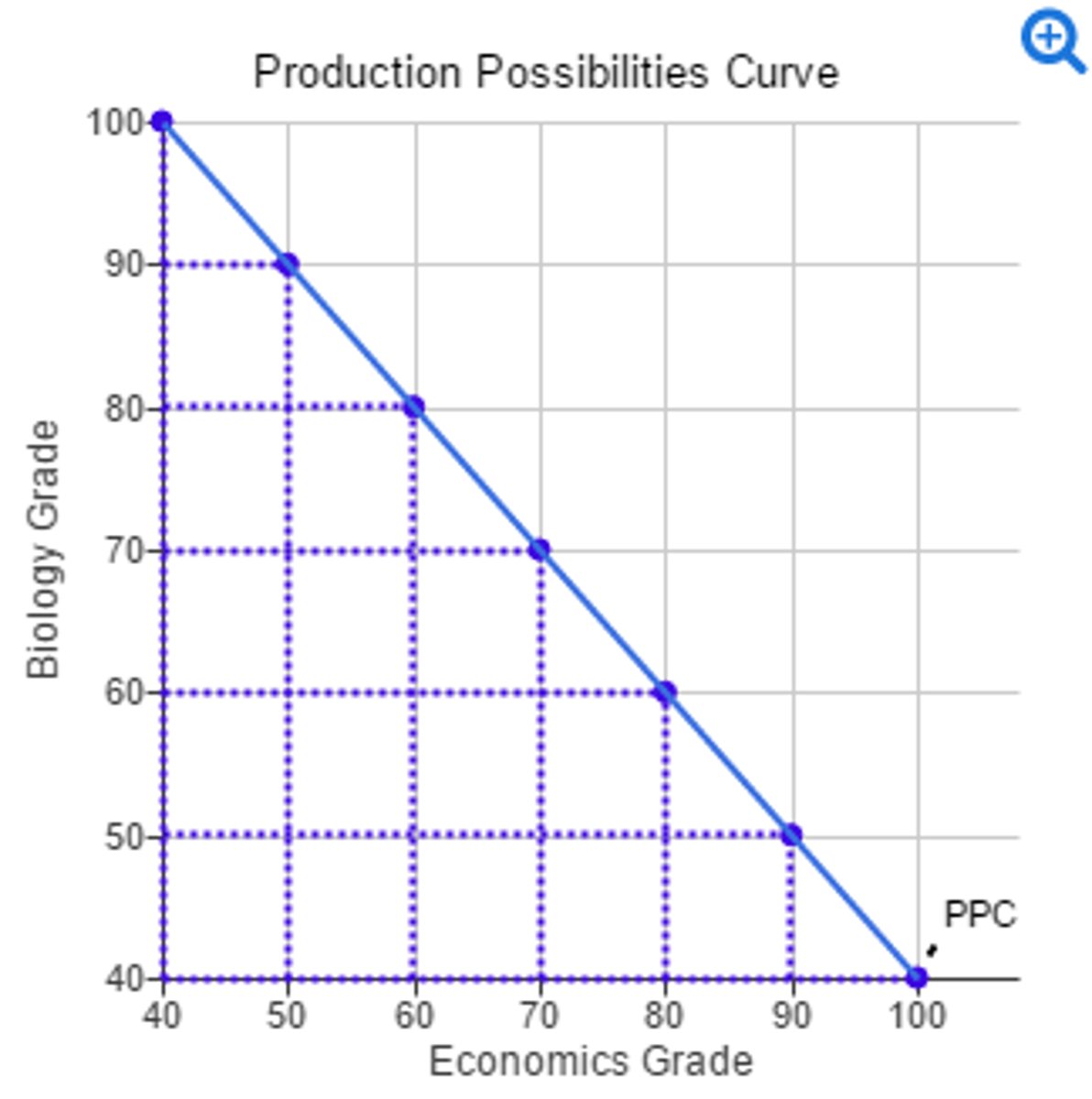
production possibilities curve
a graph that shows alternative ways to use an economy's productive resources
constant opportunity cost
Resources are easily adaptable for producing either good
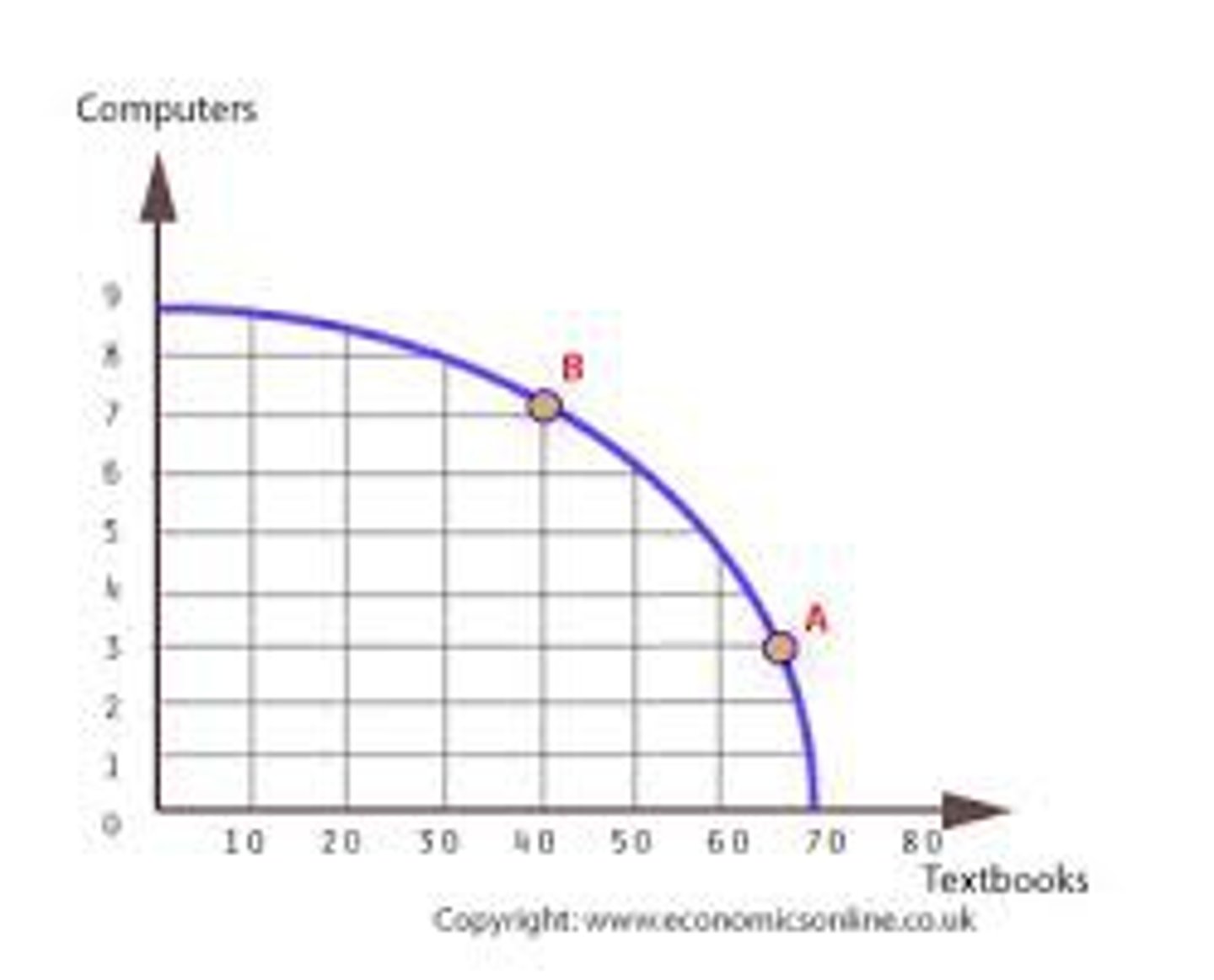
increasing opportunity cost
the opportunity cost of producing additional units of a good rises as society produces more of that good
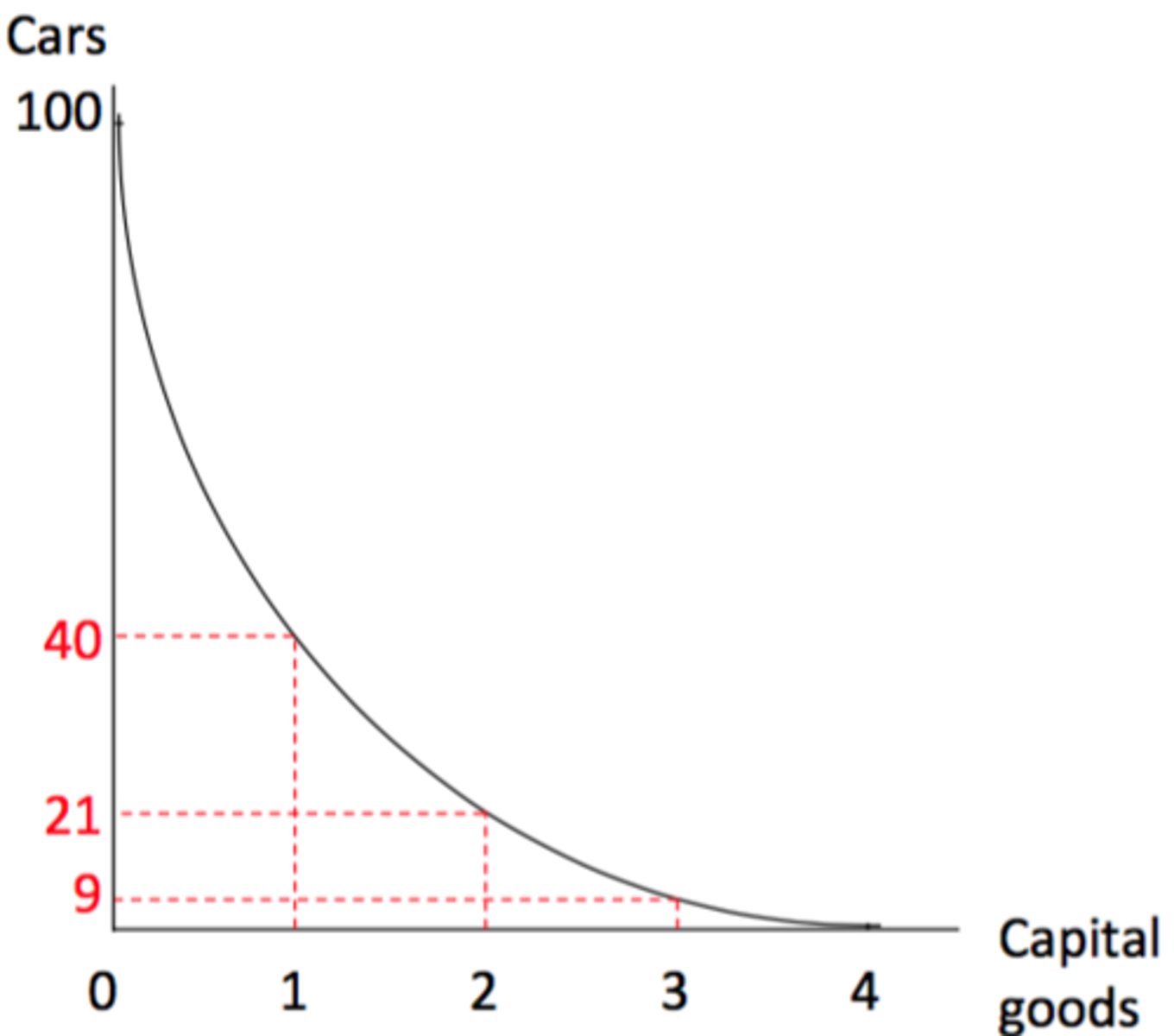
decreasing opportunity cost
having to give up an ever decreasing amount of one good to get additional units of another
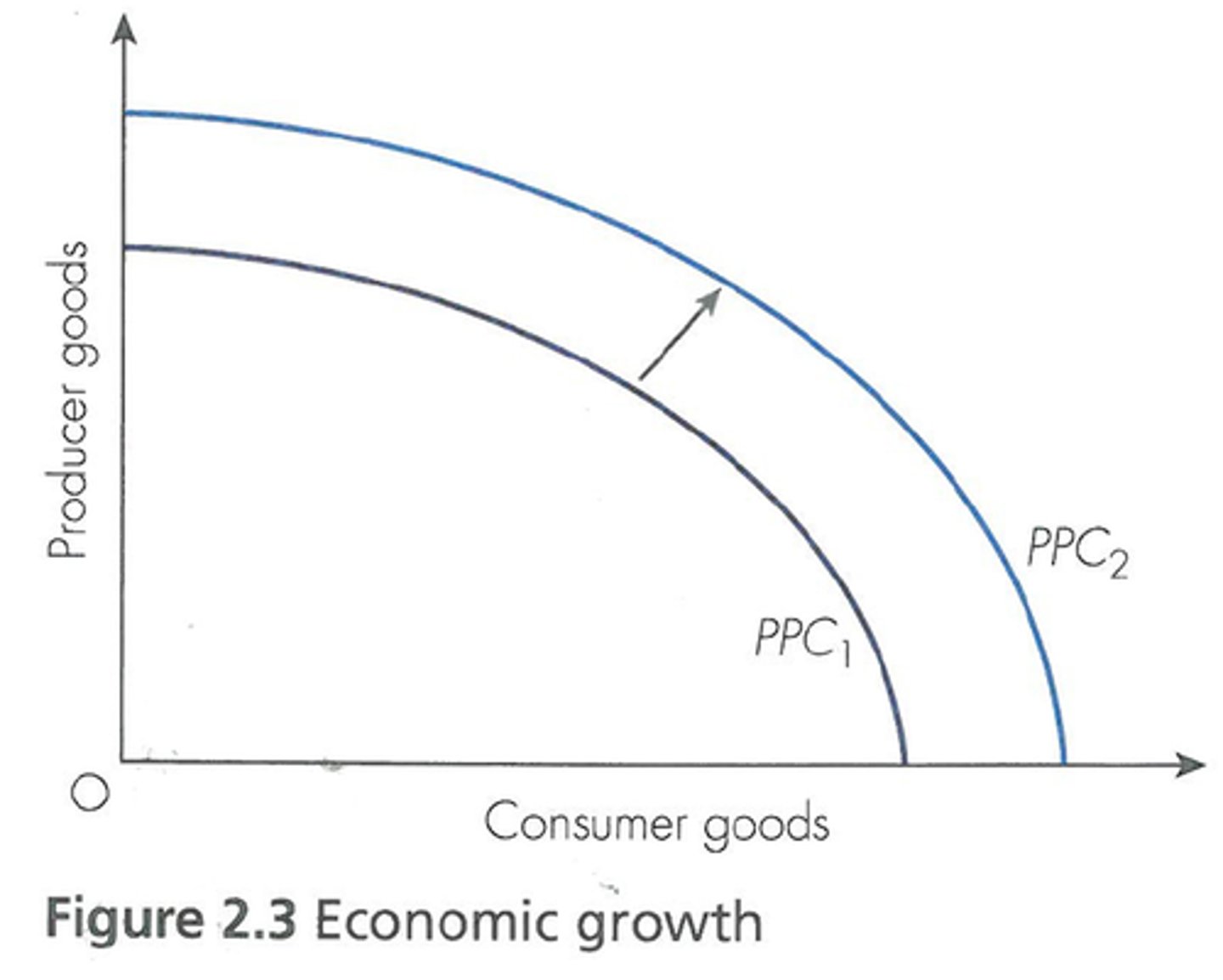
Three shifters of the PPC
1. change in resource quantity or quality
2. change in technology
3. change in trade
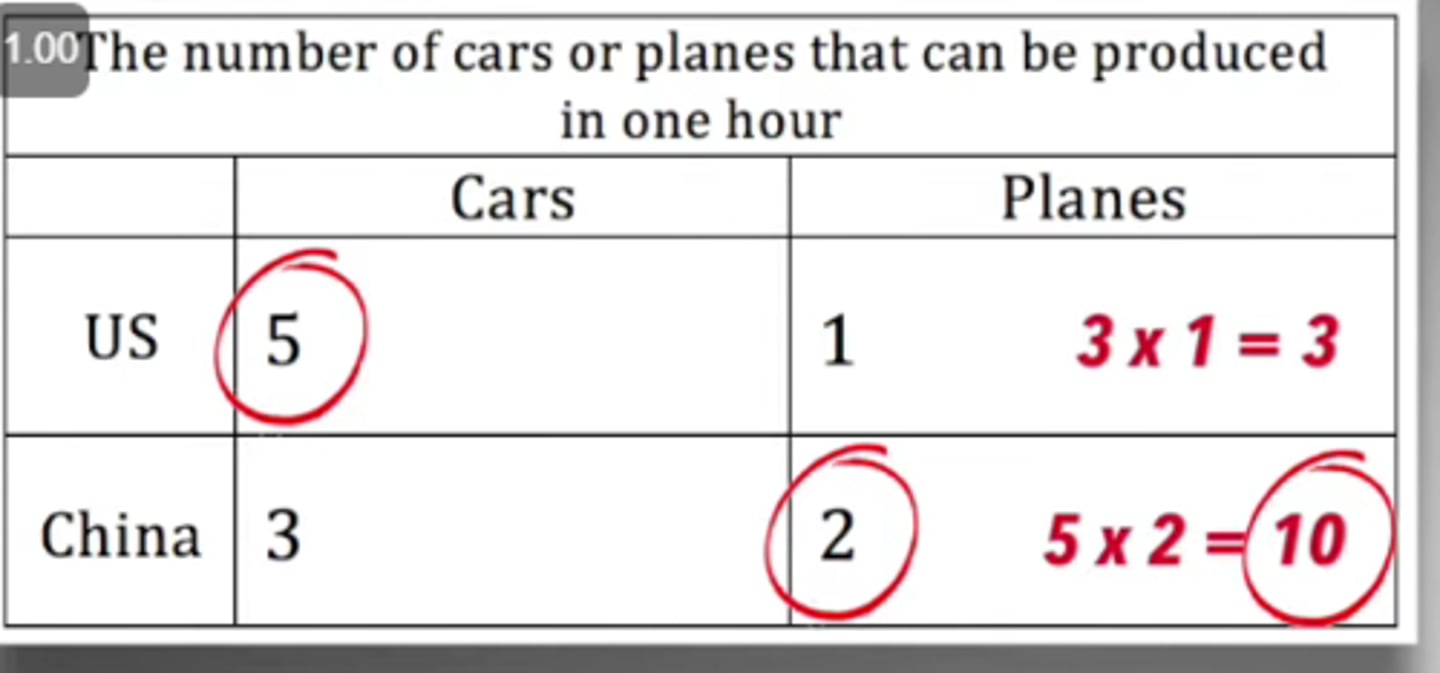
absolute advantage
the ability to produce a good using fewer inputs than another producer

comparative advantage
the ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another producer

terms of trade
the ratio at which a country can trade its exports for imports from other countries
output questions
OOO - Output: Other goes Over
input questions
IOU - Input: Other goes Under
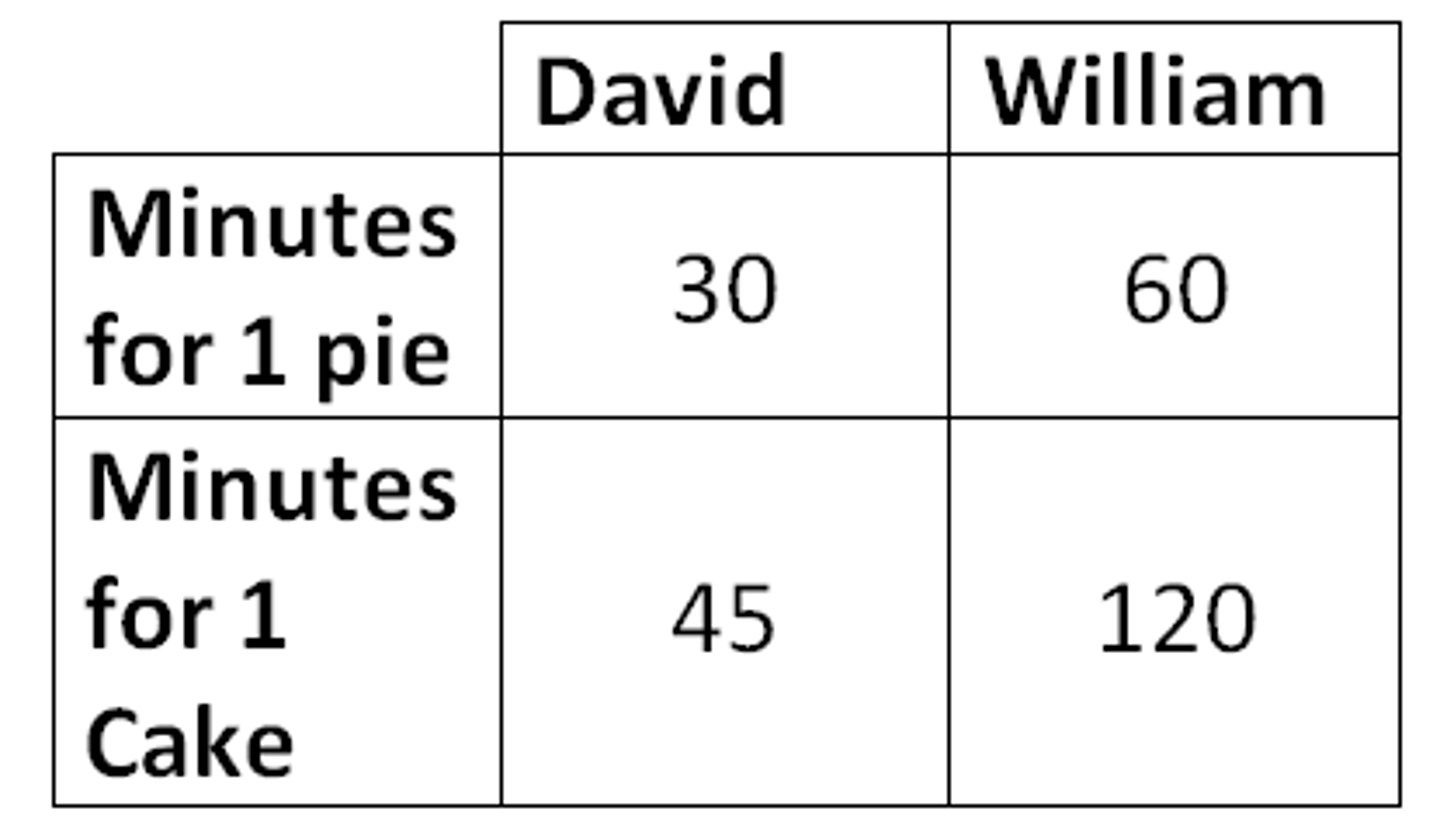
explicit costs
The actual payments a firm makes to its factors of production and other suppliers.

implicit costs
Indirect, non-purchased, or opportunity costs of resources provided by the entrepreneur

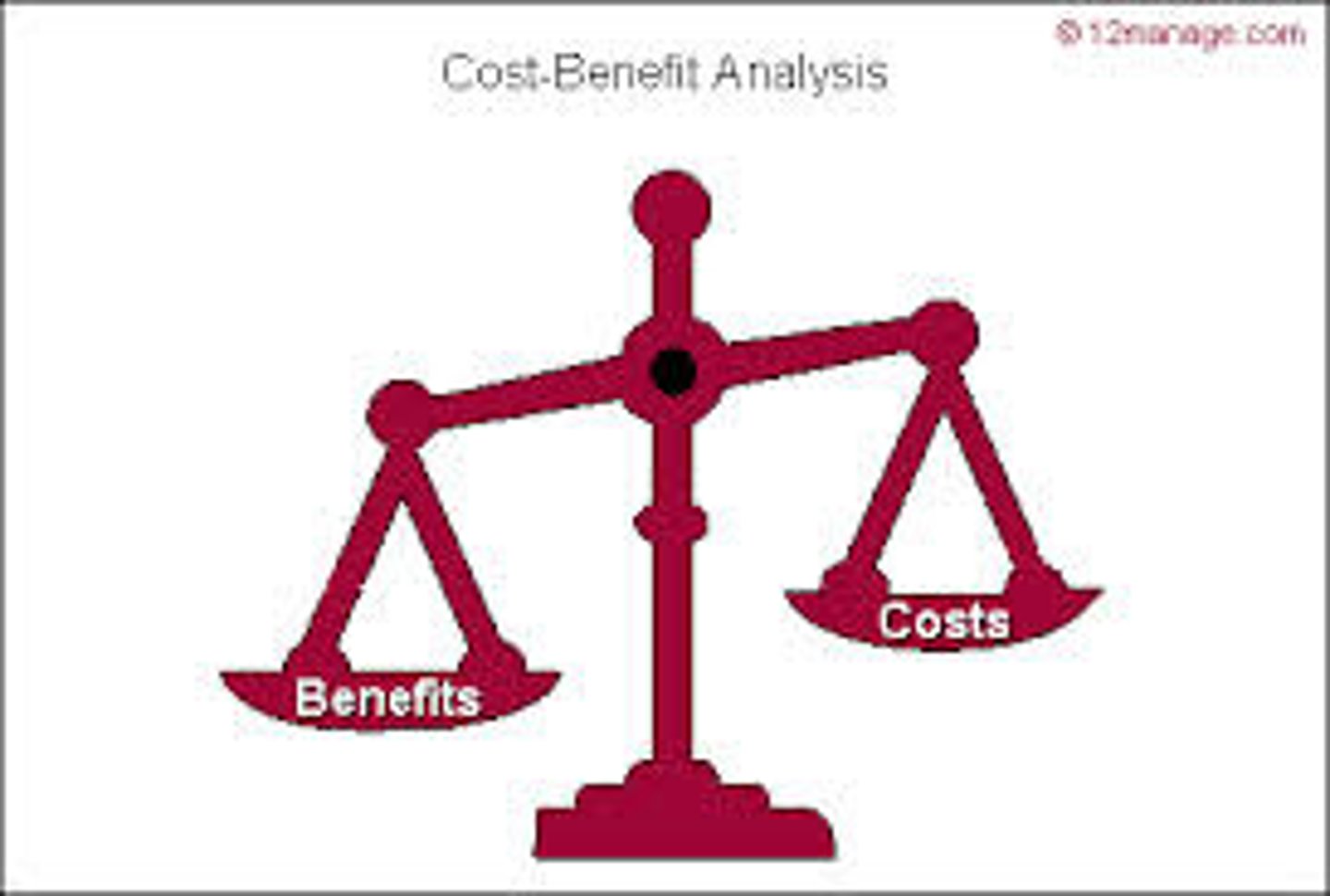
cost benefit analysis
a study that compares the costs and benefits to society of providing a public good

law of diminishing marginal utility
the principle that consumers experience diminishing additional satisfaction as they consume more of a good or service during a given period of time

marginal utility
an additional amount of satisfaction (Utility = Satisfaction)
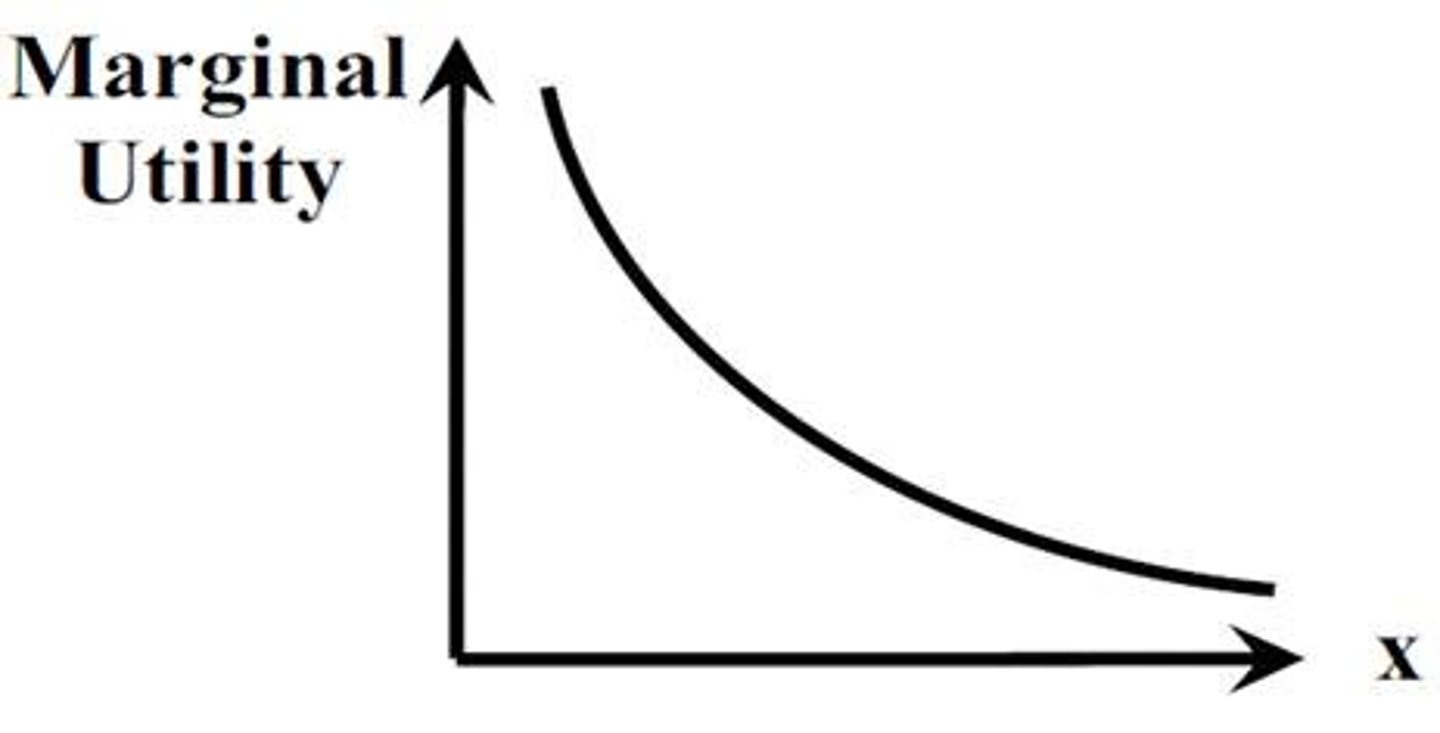
utility maximizing rule
The principle that to obtain the greatest utility, the consumer should allocate money income so that the last dollar spent on each good or service yields the same marginal utility.