AP psychology Unit 2 Flashcards
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
expressive aphasia
loss of the ability to speak
Receptive aphasia
loss of the ability to comprehend written and spoken language
CAT or CT
computerized image using X-rays passed through various angles of the brain —- Shows STRUCTURE
MRI
a magnetic field and pulses of radio waves cause the emission of faint radio frequency signals that depend upon the density of the tissue —- Shows STRUCTURE
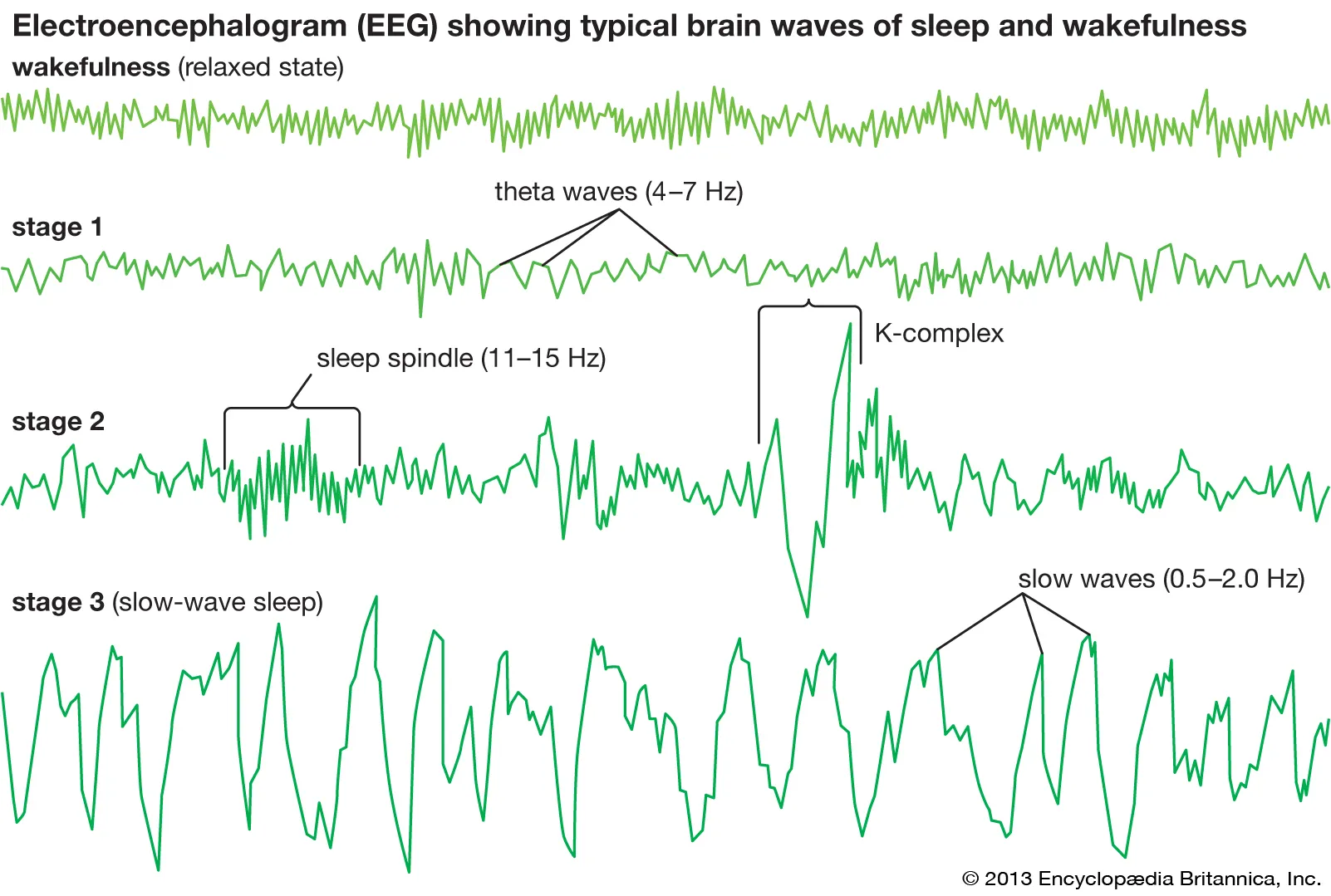
EEG
recording of the waves of electrical activity sweeping across brain’s surface.used to study brai during states of arousal such as sleeping dreaming—-DOES NOT PROVIDE STRUCTURE NOR FUNCTION
PET
produces color computer graphics.visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while brain performs a task—-FUCNTION
fMRI
measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. higher resolution that PET scanner.BOTH an STRUCTUREAL AND FUNCTIONAL
Parasympathetic stimulation
restoring digestive processes (salivation, peristalsis, enzyme secretion), returning pupils to normal pupil size, stimulating tear glands, and restoring normal bladder contractions.
Sympathetic stimulation
results in responses that help your body deal with stressful events including dilation of your pupils, release of glucose from your liver, dilation of bronchi, inhibition of digestive functions, acceleration of heart rate, secretion of adrenaline from your adrenal glands, acceleration of breathing rate, and inhibition of secretion of your tear glands.
reptilian brain
maintains homeostasis and instinctive behaviors, roughly corresponds to the brainstem, which includes the medulla, pons, and cerebellum.
old mammalian brain
roughly corresponds to the limbic system that includes the septum, hippocampus, amygdala, cingulate cortex, hypothalamus, and the thalamus, which are all important in controlling emotional behavior, some aspects of memory, and vision.
new mammalian brain
accounts for about 80 percent of brain volume and is associated with the higher functions of judgment, decision making, abstract thought, foresight, hindsight and insight, language, and computing, as well as sensation and perception.
convolutions
the surface of your cortex has peaks called gyri and valleys called sulci, which form convolutions that increase the surface area of your cortex.
Basal ganglia
regulates initiation of movements, balance, eye movements, and posture, and functions in processing of implicit memories.
Plasticity
if one region is damaged, the brain can reorganize to take over its function.
Glial cells
guide the growth of developing neurons, help provide nutrition for and get rid of wastes of neurons, and form an insulating sheath around neurons that speeds conduction.
cell body
contains cytoplasm and the nucleus, which directs synthesis of such substances as neurotransmitters.
Neurogenesis
the growth of new neurons, takes place throughout life.
acetylcholine ACH
causes contraction of skeletal muscles, helps regulate heart muscles and is involved in memory too little is causing Alzheimer’s disease
Dopamine
acts on areas of the brain to give you feelings of pleasure, satisfaction and motivation.too much Schizophrenia.lack parkinson’s disease-a brain disorder that causes unintended or uncontrollable movements, such as shaking, stiffness, and difficulty with balance and coordination
Glutamate
involved in information processing throughout the cortex and especially memory formation in hippocampus. both schizoprenia and alzhimer’s may involve glutamate receptors
seretonin
sexual activity, concentration, attentions, moods, emotion. lack - depression
endorphins
natural painkillers
GABA
inhibits firing of neurons.Benzodiazepine(valium) and anticonvulsant drugs increase activity of GABA. Huntigton’s disorder that causes nerve cells (neurons) in parts of the brain to gradually break down and die.
Norepinephrine/Noradrenaline
attentiveness, sleeping, dreaming, learning.
Agonists
may mimic a neurotransmitter and bind to its receptor site to produce the effect of the neurotransmitter.
Antagonists
block a receptor site, inhibiting the effect of the neurotransmitter or agonist.
afferent neurons
nerve fibers responsible for bringing sensory information from the outside world into the brain
efferent neurons
motor neurons, are the nerve fibers responsible for carrying signals from the brain to the peripheral nervous system in order to initiate an action. In other words, they are the neurons that tell your body to perform an action, such as removing your hand from a hot pan.
PINeal Gland
endocrine gland in brain that produces melatonin that helps regulate circadian rhythms and is associated with seasonal affective disorder.
Hypothalamus
produces hormones that stimulate (releasing factors) or inhibit secretion of hormones by the pituitary.
Pituitary Gland
promote secretion by other glands including TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone); ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone), which stimulates the adrenal glands; FSH (follicle stimulating hormone), which stimulates egg or sperm production; ADH (antidiuretic hormone) to help retain water in your body; and HGH (human growth hormone).
Thyroid Gland
endocrine gland in neck that produces thyroxine, which stimulates and maintains metabolic activities. lack results in mental retardation
Parathyroids
produce parathyroid hormone, which helps maintain calcium ion level in blood necessary for normal functioning of neurons.
Adrenal Glands
endocrine glands atop kidneys
Pancreas
gland near stomach that secretes the hormones insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar that fuels all behavioral processes.
Fraternal twins
are siblings that share about half of the same genes because they develop from two different fertilized eggs or zygotes; they are dizygotic twins.
Monozygotic twins
develop from the same fertilized egg or zygote
Turner syndrome
females with this syndrome have only one not 2 X sex chromosome (XO)=short,webbed neck,lack ovaries and fail to develop secondary sex characteristics at puberty.
Klinefelter’s syndrome
males with this syndrome arise from an XXY zygote=syndrome become evident ay puberty when male secondary sex characteristics fail to develop but breast tissue does. they tend to be passive
Down syndrome.
The presence of three copies of chromosome 21 results in the expression of Down syndrome.
Tay-Sachs syndrome
produces progressive loss of nervous function and death in a baby
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
results in severe, irreversible brain damage unless the baby is fed a special diet low in phenylalanine within 30 days of birth; the infant lacks an enzyme to process this amino acid, which can build up and poison cells of the nervous system.
Huntington’s disease
is an example of a dominant gene defect that involves degeneration of the nervous system.an inherited disorder that causes nerve cells (neurons) in parts of the brain to gradually break down and die.
Preconscious
is the level of consciousness that is outside of awareness but contains feelings and memories that you can easily bring into conscious awareness.
Nonconscious
is the level of consciousness devoted to processes completely inaccessible to conscious awareness, such as blood flow, filtering of blood by kidneys, secretion of hormones, and lower-level processing of sensations, such as detecting edges, estimating size and distance of objects, recognizing patterns, and so forth.
Reticular formation
Reticular formation and thalamus are involve in changes in wakefulness, arousal and attencion.
Hypnagogic state
you feel relaxed, fail to respond to outside stimuli, and begin the first stage of sleep, Non-REM-1.
Insomnia
is the inability to fall asleep and/or stay asleep.
Narcolepsy
is a condition in which an awake person suddenly and uncontrollably falls asleep, often directly into REM sleep.
Sleep apnea
is a sleep disorder characterized by temporary cessations of breathing that awaken the sufferer repeatedly during the night.