M3: LEC AND LAB 2: SEEDLESS-VASCULAR PLANTS
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What are protracheophytes?
extinct intermediary groups btwn NVPs and SVPs w dichotomous branching
How did the protracheophytes get a little bit taller and have branching compared to the NVPs who were smaller and had no branching?
1) parenchyma cells evolved into hydroid cells w some lignin (black dot)
2) A.M. switches from the base of the plant to the top in embryology
a) divides and creates the left and right branch
hydroid cells = elongated parenchyma cell
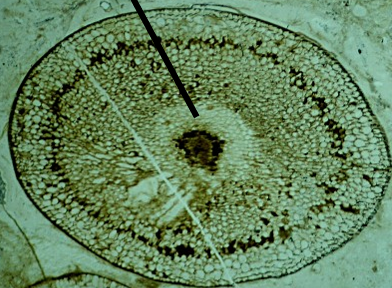
T/F - Protracheophytes have tracheids.
False - protrache- indicates they do not have tracheids
What did the hydroid cells with lignin evolved into? In what group?
In the protracheophytes, the hydroid cells with some lignin evolved into tracheids in SVPs.
T/F - protracheophytes led the movement of plants away from water.
False - the SVPs (tracheophytes) led the movement of plants away from water
Once SVPs arrived onto land, what happened?
1) an explosion of plants on barren land —> the land became green
2) O2 stabilized in the atmosphere
3) basis of terrestrial life
4) led the profound movement of plants away from water
How do we know about the evolutionary history of plants? What year?
Rhynie Chert, Scotland:
1) silica erupted and exploded from the volcanic hot springs
a) petrified the ecosystem from over 400 MYA
2) discovered the fossils of fungi, lichens, plants, and arthropods
What organism(s) are part of the Extinct Rhyniophytes?
Cooksonia
What are some characteristics (not listed on the cladogram) of Cooksonia?
1) terminal sporangia
2) lack leaves and roots
3) homosporous
Why is it a problem to have a terminal sporangia?
1) low spore count
2) high spore mortality
3) not using the surface area on the side of Cooksonia
Why is Cooksonia sporophyte dominant?
the tracheids evolved in the sporophytes
T/F - Lycophytes were the first SVPs.
False - Extinct Rhyniophytes were the 1st SVPs.
T/F - Cooksonia is hetersporous.
False - SVPs are homosporous, except for one organism.
Define microphylls.
leaves with one vascular strand
Define megaphylls.
leaves with branching veins
How did microphylls arise?
1) leave-like tissues grew out from the stem
2) lignin grew into the leave-like tissues
How did megaphylls arise?
1) the branches overlapped
2) the branches fused tgt
3) tissue formed btwn the fused branches
What is another group name for lycophytes?
club mosses
What is another group name of the monilophytes?
ferns
What did the two major SVP clades formed on land? What year?
tall trees; 360 MYA
Why did the SVP trees grow so large?
the evolution of megaphylls was a selection pressure for plants to grow bigger and develop secondary growth
What happened 425 MYA?
1) tracheids fossils from this time
2) SVPs began growing
What two giant SVP trees and animals were present during the Carboniferous era?
a) Lepidodendron
b) Giant Horsetails
c) giant winged insects
d) giant amphibians
During the Carboniferous era, what happened to the remains of the SVP trees?
the remains of the trees do not decay bc of limited O2 and become coal by heat and pressure
What kind of tissue did the Lepidodendron have?
Unifacial vascular cambium = 2° Xylem only
What caused the evolution of giant insects (scorpions and millipedes) during the Carboniferous era?
increased oxygen
What happen at the end of the Carboniferious era?
1) plant cooled
2) SVPs, progymnosperms, giant insects (milipedes and scorpions), and giant amphibians croaked/died — bc of external fert.
3) gymnosperms and reptiles thriving — bc of internal fert.
Why did the planet cool during the end of the Carboniferous era?
the giant megaphylls absorbed too much CO2 and stored it as wood
Why did these giant SVPs trees die off at the end of the Carboniferous era?
water rescinded and external fert. needed water
What organism(s) are part of lycophytes?
lycopodium and selaginella
What does a strobulis (ancestral cone) consist of?
1) sporangia
2) leaves clustered on the branch tips
in summary, the cones have sporophylls (microphylls w sporangia)
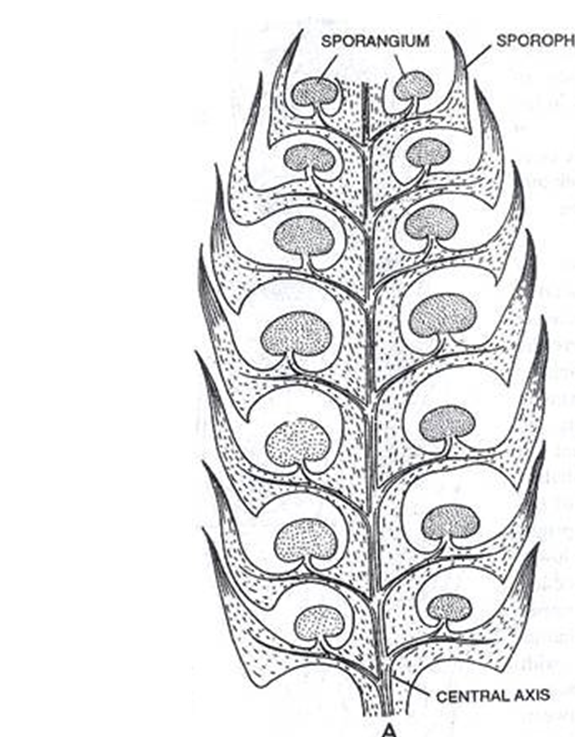
What is the significance of having a strobulis?
increased spore production
Compare the location of the sporangia in monilophytes vs rhyniophytes.
Monilophytes:
lateral sporangia
Rhyniophytes:
terminal sporangia
Define heterospory.
having 2 diff. types of spores (micro- and mega-)
Why is it important to have megaspores and microspores?
Megaspores:
make BIG gametophytes —> more food for the eggs
Microspores:
make small gametophytes —> better sperm dispersal
Why is heterospory important evolutionarily?
first step in making pollen and seeds in “higher” plants
Why is pollen and seeds important?
1) pollen protects the sperm
2) seed protects the egg
3) led to internal fertilization
4) “higher plants” live anywhere
Why do the megaphylls arise coil in true ferns?
the megaphylls arise from tangled rhizomes, so the coil protects them from damage
define fiddle heads.
megaphylls arise coiled
define sori.
clusters of sporangia on the backside of the leaf
What is the func of sori?
reproduction
What is the func of the annulus?
active spore dispersal:
1) folds back
2) spring forward to fling the spores
define indusium.
covering of the sori
What is the func of the indusium?
protects the sori
T/F - All true ferns have an indusium.
False - only some have it.
What are the 4 different types of indusium?
leave tissues folding, edges of the leaves folding, tips of the leaves folding, or naked sori
What are the characeristics of the true fern gametophyte?
heart-shaped, photosynthetic, and bisexual
What organism(s) are part of the simple fern?
whisk fern (psilotum) and equisetum (horsetail)
What organism(s) is part of the whisk fern?
psilotum
Why does the psilotum lack leaves and roots?
since they’re an epiphyte, they underwent a reversal evolution of megaphylls and roots.
epiphytes means plant growing on top of another plant
What does the psilotum consist of?
stem, sporangia on ednation

define ednation.
epidermal outgrowth
T/F - Whisk Fern have true leaves.
False - they have ednation which are not true leaves.
Why are ednations not leaves?
lack lignin
What is the func of silica walls?
anti-predation
Why does the horsetail feel rough?
has silica walls
What happens to the size of the gametophyte over time form the NVPs to the SVPs? Why?
the size of the gametophyte decreased bc SVPs move away from water — becoming sporophyte dominant
What selection pressure allowed the reduced megaphylls of the horsetails to have only one vein left?
the big, rigorous rhizomes grew underneath other plants and received sunlight while the other plants in the shade freeloaded off the plants that were photosynthesizing
What happens to the horsetail elaters when they are dry? How do you think this helps them travel thru the air?
they’re open, so the elaters are wing-like allowing the spores to fly in the air
What happens when the horsetail spore hits moist air as it is flying? How does this assist in spore landing in moist environment and germination?
the elaters wrap around the spore, stopping the flying spore, and landing the spore in wet land where external fert. can florish