Concepts of Biology Exam #2
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Speciation
The evolution of a new species, occurs when a population becomes reproductively isolated from other members of the species
Speciation requires what 2 things
Populations must separate from each other physically 2. Then populations become reproductively isolated
Allopatric speciation
occurs due to geographic/physical isolation
Sympatric speciation
occurs within the same geographic region
RIM
Prevent the flow of genetic material among populations, and preserve the genetic integrity of each species by preventing reproduction
Species
Group of organisms that can successfully interbreed and produce fertile offspring
Pre/Post Zygote
Pre: reduce the chance of zygote formation
Post: reduce the survival and reproduction of hybrid offspring
Forms of Isolation
Ecological Isolation, Behavioral Isolation, Temporal Isolation, Mechanical Isolation
Basic Structure of a Cell
Cell membrane, Cytoplasm, nucleus
Major cell components
Cell/Plasma membrane, nucleus, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum (smooth and rough), Golgi body, vesicles, mitochondria, chloroplasts (plants)
Extinction
The end of a lineage
Unicellular, multicellular, and colonial
Uni - single-cell organism, colonial - multiple cells working together doing the same thing, multi - multiple cells doing different functions
Organelles
Specialized structures with particular functions
What are cells?
The smallest unit at which all life processes can occur
Nucleus
The control center, most prominent organelle, contains DNA, has phospholipid bilayer
Cell Membrane
Provides structure, is the boundary between cell and external environment, and regulates what goes in and out of the cell
Phospholipids
An important component of cell membranes, amphipathic, forms a natural bilayer
Fluid Mosaic Model
Membranes are made of a variety of different molecules that can move around the membrane
Traits
Characteristics that are inherited
Membrane Functions
Diffusion, passive transport, active transport
Ribosomes
The little spots, help build proteins, lots of them
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Osmosis
The diffusion of water through a cell membrane
Passive/Active transport
Passive: High to low (no energy needed)
Active: Low to high (requires energy)
Vesicle mediated transport
Two forms that carry stuff in and out of the cell
Golgi Apparatus
Receives, processes, packages, and ships proteins and lipids, makes vesicles
E.R
Huge folded membranes, type determines presence or absence of ribosomes, has smooth or rough
Rough/Smooth ER
Rough: has ribosomes, helps process proteins
Smooth: does not have ribosomes, helps process lipids
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, converts molecules into ATP, double-membrane system, and has their own DNA
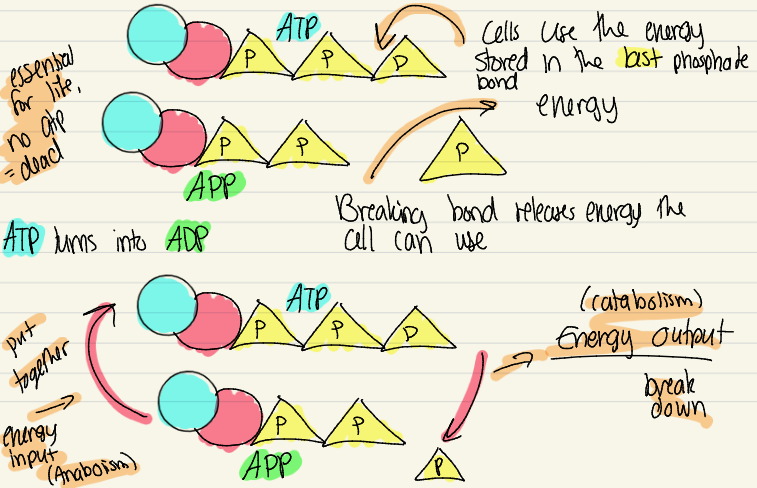
ATP
A special form of energy, essential for life
Chloroplasts
Site of photosynthesis, converts light energy to chemical energy
Energy
The capacity to do work (chemical, heat, radiant, electrical)
Vacuoles
Intracellular sacs, some are storage, some pump water out of a cell, many plant cells have a very large central vacuole
Pro vs. Eukaryotes
Pro: simple, no nucleus or organelles, small, bacteria
Eu: complex, nucleus and organelles, large
Laws of Thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed
Entropy tends to increase
Entropy
The state of disorder
Work
Any change in the state or motion of matter, most important work: survival and reproduction
Homeostasis
maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment despite the external environment
Fitness
The ability to survive and reproduce
Natural Selection
Organisms with certain traits are more likely to survive and reproduce than other organisms
Metabolism
The sum of all chemical activities within the individual
Metabolism = Catabolism + Anabolism
Anabolism
Processes that makes complex molecules from simple ones, amino acids into proteins
Catabolism
Processes that break down complex molecules into simple ones, release of energy
Endocytosis
moves stuff to the inside of the cell (encased in phospholipids)
Exocytosis
moves stuff outside of the cell (encased in phospholipids)
Photosynthesis
conversion of light energy into stored chemical energy of organic molecules
Respiration
conversion of energy from chemical bonds in nutrients to ATP energy
Respiration Equation
Glucose + Oxygen --> Carbon dioxide + water + ATP
Pigments
light absorbing molecules
Light Reactions
light excites electrons which are used to make ATP, oxygen is a waste product here,
Dark Reactions
Takes energy from ATP and stores it in a more stable sugar molecule
Glucose
A sugar
Anaerobic
Less efficient (only gives 2 ATP), produces a toxin
Aerobic
Glycolysis 2. The Citric Acid Cycle (Kerbs) 3. Electron Transport of Chemiosmosis
Glycolysis
Splits glucose, in process of generating a net ATP (lose 2, gain 4), happens outside the mitochondria
Citric Acid Cycle
Completes the breakdown of carbon molecules into CO2, makes some ATP, generates NADH, recycles used materials
Electron Transport Chain
Most important step, generates ATP from NADH, huge return of ATP (32 ATP per molecule), Oxygen removes waste to maintain diffusion
Matter
Anything with mass; takes up space
Gradualism
Slow changes
Punctuated Equilibrium
Change happens in quick spurts
Fluorescence
An electron emits a low-energy light wave and goes back to normal
Equation for Photosynthesis
Carbon Dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen
Phagocytosis
using endocytosis to eat food particles