Anatomy and physiology exam #1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:54 AM on 2/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
1
New cards
levels organization in order
\-Chemical level
\-cellular level
\-tissue level
\-organ level
\-organ system level
\-organismal level
\
\-cellular level
\-tissue level
\-organ level
\-organ system level
\-organismal level
\
2
New cards
Chemical level (levels of organization)
atoms, molecules & organelles: atoms combine to form molecules
3
New cards
cellular level (levels of organization)
single cell: cells are made up of molecules
4
New cards
tissue level (levels of organization)
group of similar cells: tissues consist of similar types of cells
5
New cards
organ level (levels of organization)
contain two or more types of tissues: organs are made up of different types of tissues
6
New cards
organ system levels (levels of organization)
organs that work closely together: different organs that work closely together
7
New cards
organismal level (levels of organization)
all organ systems combined to make the whole organism: human organism is made up of many organ system
8
New cards
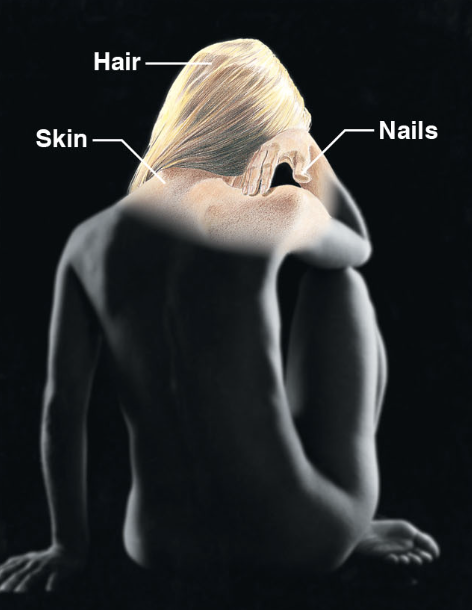
Integumentary system (body sys)
skin, hair and nail glands
protects deeper tissues from injury
protects deeper tissues from injury
9
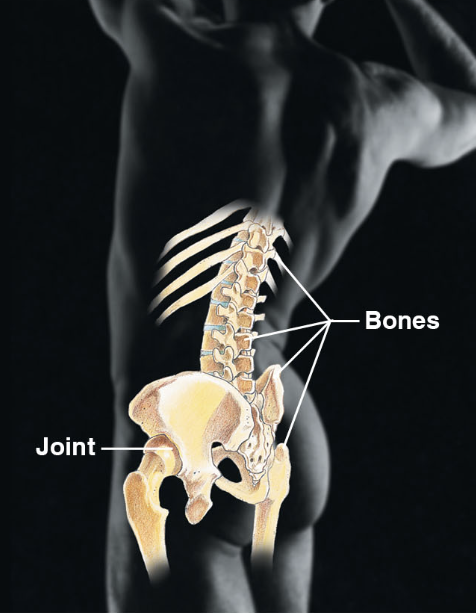
New cards
Skeletal system (body sys)
\-bones, cartilage, joints, ligaments and tendons
\-protects and supports organs
\-provides framework
\-blood cells are formed within bones
\-bones store minerals
\-protects and supports organs
\-provides framework
\-blood cells are formed within bones
\-bones store minerals
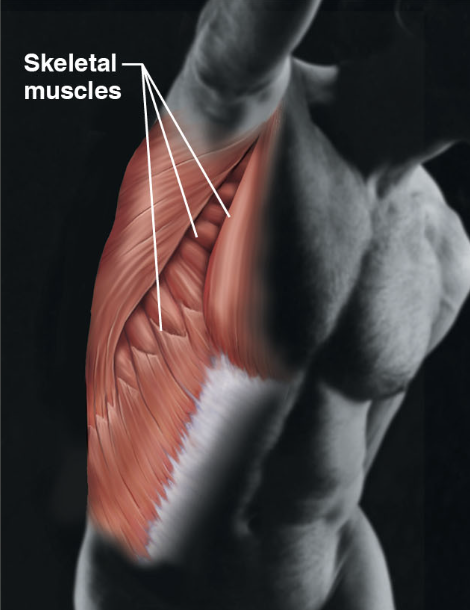
10
New cards
muscular system (body sys)
\-skeletal muscles
\-movement of the body
\-environment, locomotion, and facial expressions
\-maintain posture and produces heat
\-movement of the body
\-environment, locomotion, and facial expressions
\-maintain posture and produces heat
11
New cards
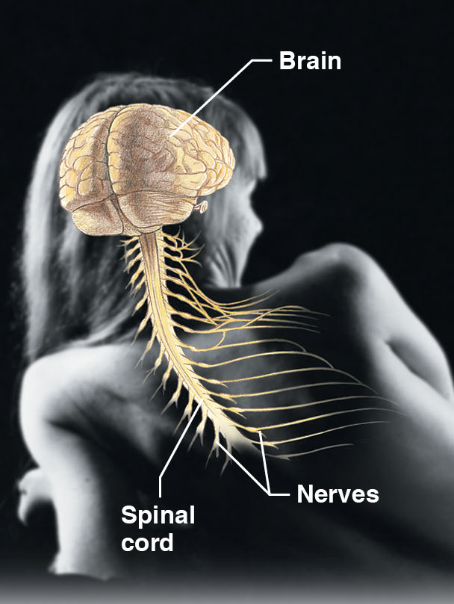
nervous system (body sys)
\-brain, spinal cord, and nerves
\-fast acting control sys
\-responds to internal and external changes by activating muscles and glands
\-fast acting control sys
\-responds to internal and external changes by activating muscles and glands
12
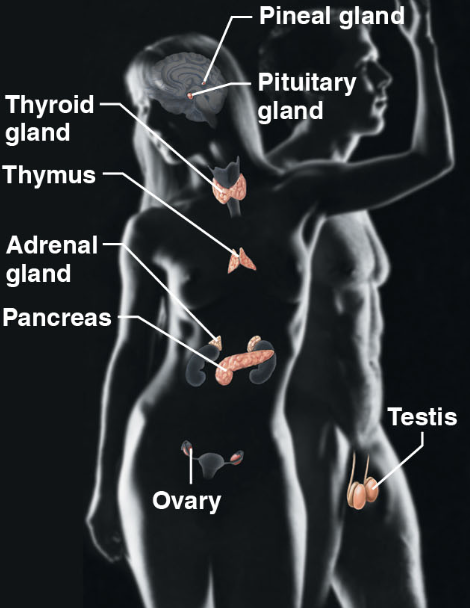
New cards
endocrine system(body sys)
\-Pineal glad, pituitary glad, testis, ovary, pancreas, adrenal gland, thyroid gland
\-responsible for secreting hormones that regulate growth, development and metabolism by body cells
\-responsible for secreting hormones that regulate growth, development and metabolism by body cells
13
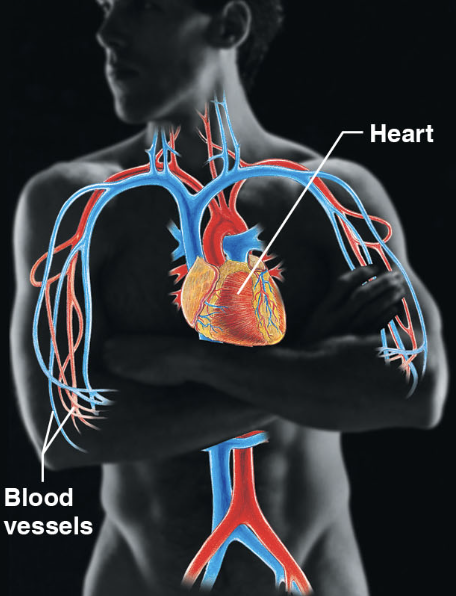
New cards
cardiovascular sys (body sys)
heart (pumps blood) and blood vessels (transport oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, waste etc.)
14
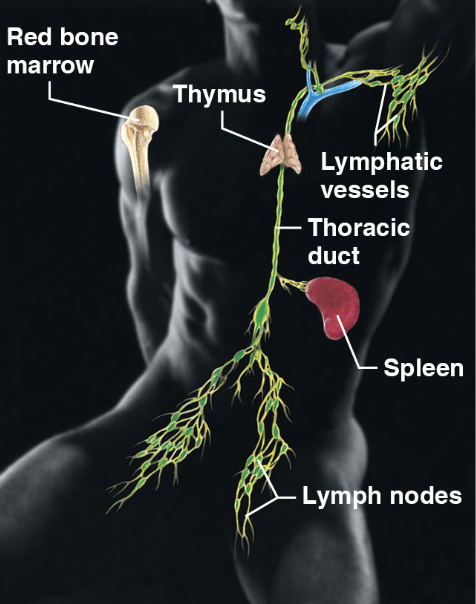
New cards
Lymphatic system/immunity (body sys)
\-red bone marrow, thymus, lymphatic vessels, thoracic duct, spleen, and lymph nodes
\-picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to blood
\-disposes of debris in lymphatic stream
\-houses white blood cells involved in immunity
\-picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to blood
\-disposes of debris in lymphatic stream
\-houses white blood cells involved in immunity
15
New cards
respiratory sys(body sys)
\-nasal cavity, pharynx, trachea, lung, bronchus
\-keeps blood supplied w/ oxygen and removes carbon dioxide
\-keeps blood supplied w/ oxygen and removes carbon dioxide
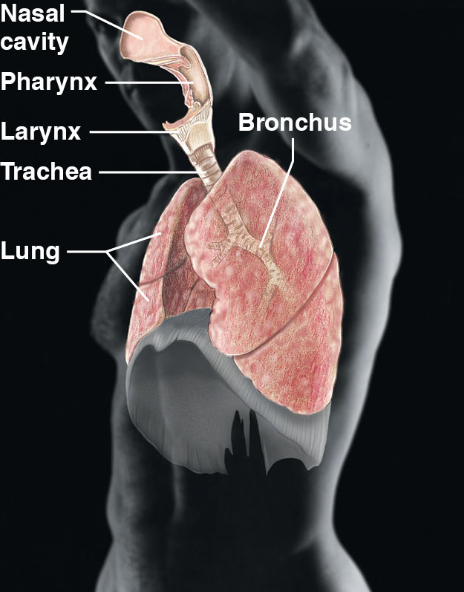
16
New cards
digestive sys (body sys)
\-oral cavity, esophagus, liver, small intestine, rectum, anus, large intestine.
\-breaks down into absorbable units, enter the blood for distribution into body cells.
\-breaks down into absorbable units, enter the blood for distribution into body cells.
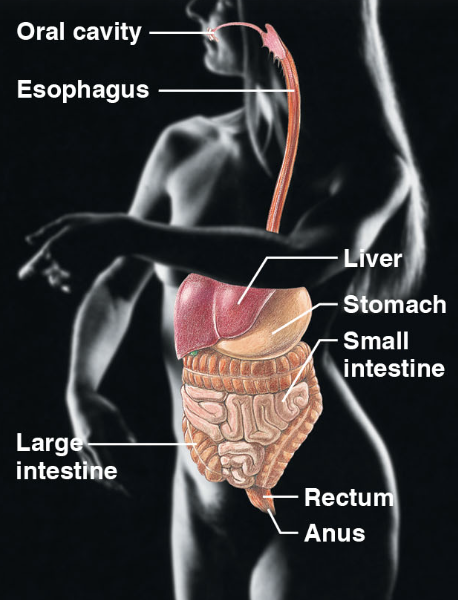
17
New cards
Urinary sys (body sys)
\-kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra
\-eliminates nitrogenous waste from the body
\-regulates water, electrolyte, and acid-base balance of the blood
\-eliminates nitrogenous waste from the body
\-regulates water, electrolyte, and acid-base balance of the blood
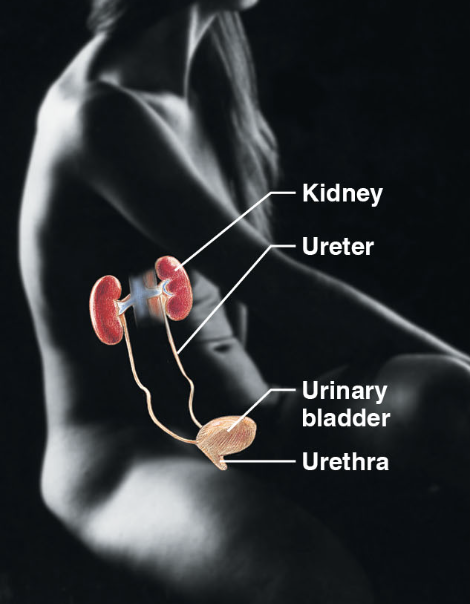
18
New cards
male reproductive sys (body sys)
\-prostate, penis, scrotum, ductus deferens
\-overall function of offspring
\-produce sperm and male sex hormone
\-overall function of offspring
\-produce sperm and male sex hormone
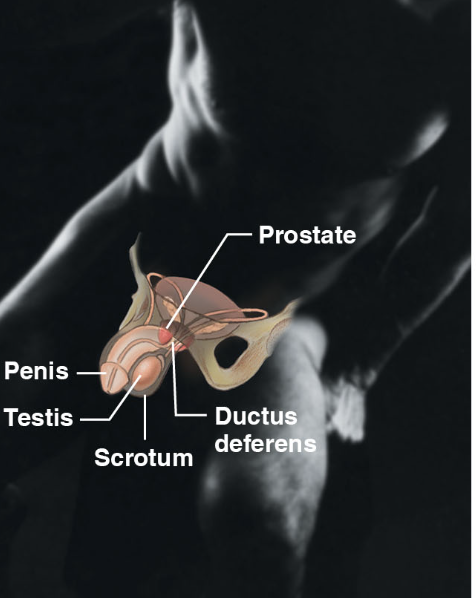
19
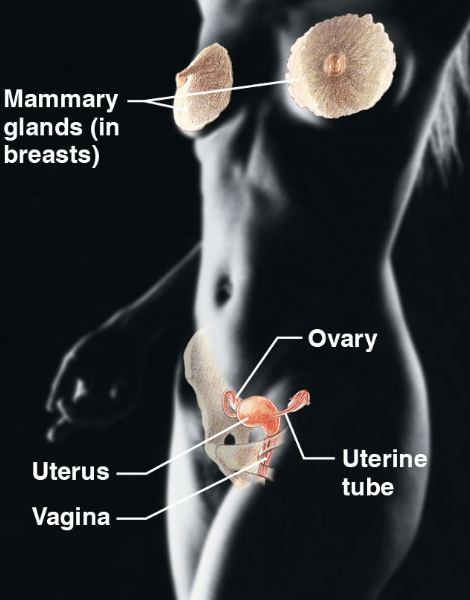
New cards
female reproductive sys (body sys)
\-mammary glands (in boobs), ovary, uterine tube, uterus, vagina.
\-overall production of offspring
\-ovaries produce eggs and female sex organs
\-overall production of offspring
\-ovaries produce eggs and female sex organs
20
New cards
understand interrelationships between organ systems
\-each of our body sys. is interconnected and dependent on each other.
\-our heart (cardiovascular sys) does not beat unless our brain (nervous sys) tells it to.
\-our skeletal sys are dependent on our digestive sys.
\-our heart (cardiovascular sys) does not beat unless our brain (nervous sys) tells it to.
\-our skeletal sys are dependent on our digestive sys.
21
New cards
survival needs
\-nutrients
\-oxygen and water
\-normal body temp
\-appropriate atmospheric temp
*too much or too little can be harmful and make cells unhappy*
\-oxygen and water
\-normal body temp
\-appropriate atmospheric temp
*too much or too little can be harmful and make cells unhappy*
22
New cards
homeostatic controls
\-body constantly monitored and regulated to maintain homeostasis
\*nervous = fast
\*endocrine sys = hormones and take time, mins, hours
3 components
1. receptor -where at
2. control center -alter/adjust
3. effector -change/tweak
\*nervous = fast
\*endocrine sys = hormones and take time, mins, hours
3 components
1. receptor -where at
2. control center -alter/adjust
3. effector -change/tweak
23
New cards
3 controls (homeostatic controls)
1. receptor (sensor)
1. monitors environment
2. responds to stimuli
2. control center
1. determines setpoint and which variable is maintained
2. receives input from receptor
3. determines appropriate response
3. effecter (comand)
1. receives output from control center
2. provides the means to respond
3. positive and negative feedback
1. positive: rare, amplify/increase stimulus. enhances original stimulus. ex: enhance of labor contractions by oxytocin
2. negative: most used feedback in body. reduces or shuts off original stimulus. ex: reg. body temp (nervous sys), reg of blood in glucose by insulin (endocrine sys)
24
New cards
homestasis
maintains of relatively stable internal conditions despite continuous changes in the environment. dynamic state of equilibrium readjusting as needed. maintained by contributions of organ sys.
25
New cards
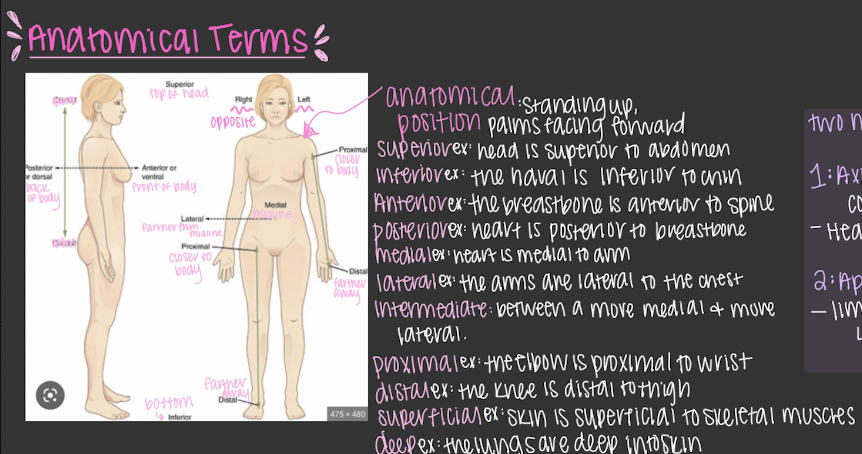
Anatomic terms
anatomical position:standing up, palms facing forward
\
two major divisions
1. axial: trunk, the center core region
2. appendicular: limbs > arms & legs
\
two major divisions
1. axial: trunk, the center core region
2. appendicular: limbs > arms & legs
26
New cards
Anterior/ventral
27
New cards
posterior/dorsal
28
New cards
Planes
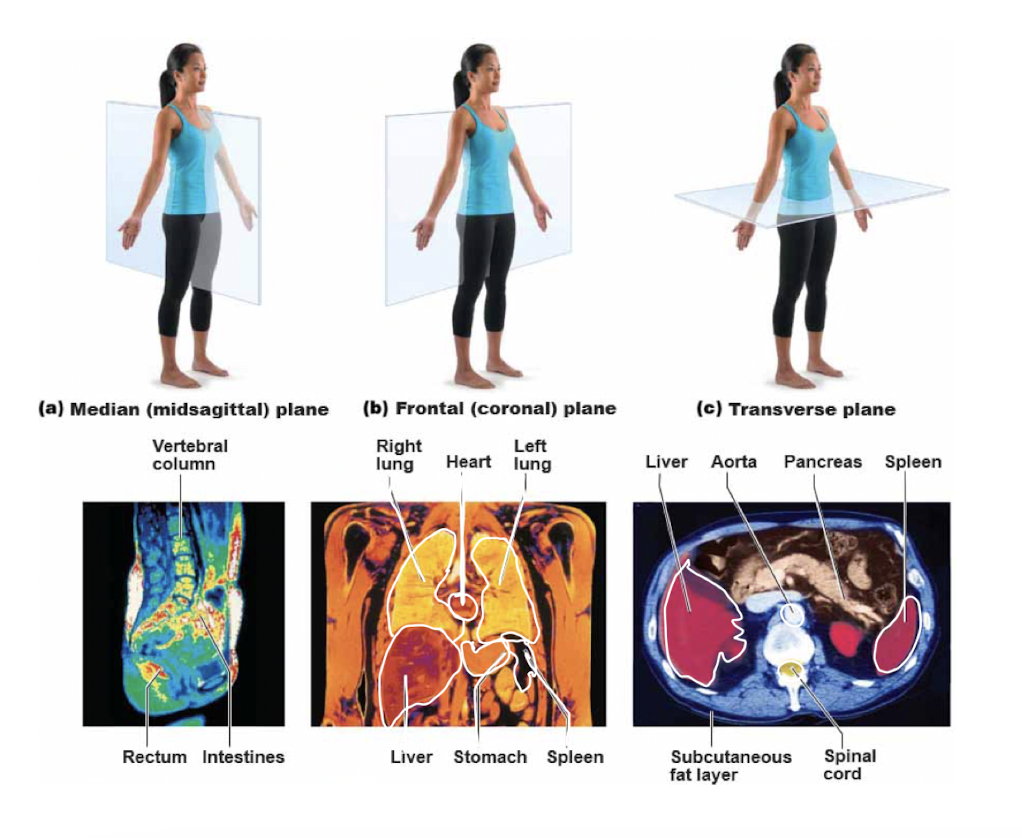
29
New cards
saginal
midline in body, “cut” in half
* midsagittal: median plane: perfectly on midline
* parasaginal: off centered. not on midline
* midsagittal: median plane: perfectly on midline
* parasaginal: off centered. not on midline
30
New cards
oblique section
cuts at angle other than 90 degrees to vertical plane
31
New cards
body cavities
* internal cavities closed to the environment
* provide different degrees of protection to organs w in them
* provide different degrees of protection to organs w in them
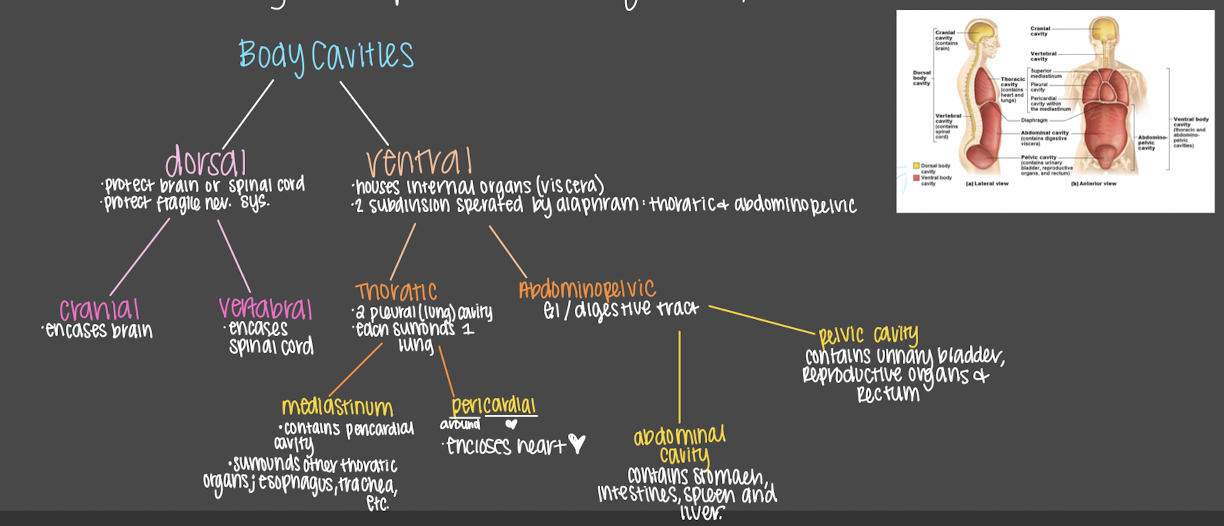
32
New cards
9 abdominal regions
1. **right hypochondriac region** (liver, gallbladder)
2. **right lumbar region** (ascending colon of the large intestine)
3. **right iliac** (**inguinal) region** (cecum, appendix)
\-
4. **epigastric region** (stomach)
5. **umbilical region** (small intestine, transverse colon of large intestine)
6. **hypogastric (pubic) region** (urinary bladder)
\-
7. **left hypochondriac region** (diaphragm, spleen)
8. **left lumbar region** (descending colon of the large intestine)
9. **left iliac (inguinal) region** (initial part of sigmoid colon)
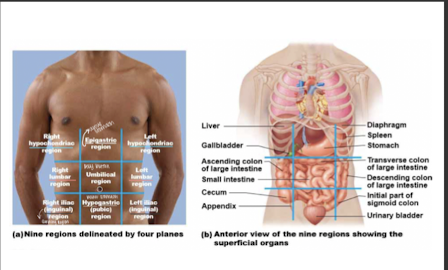
33
New cards
parietal v visceral
parietal: surrounds the abdomen and pelvis
visceral: wraps around abdominal organs
visceral: wraps around abdominal organs
34
New cards
key elements for biological processes and the human body
4 elements
1. oxygen
2. hydrogen
3. carbon
4. nitrogen
1. oxygen
2. hydrogen
3. carbon
4. nitrogen
35
New cards
subatomic particles
1. proton +
2. neutron (neutral)
3. electron -
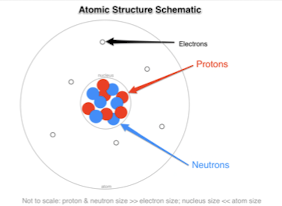
36
New cards
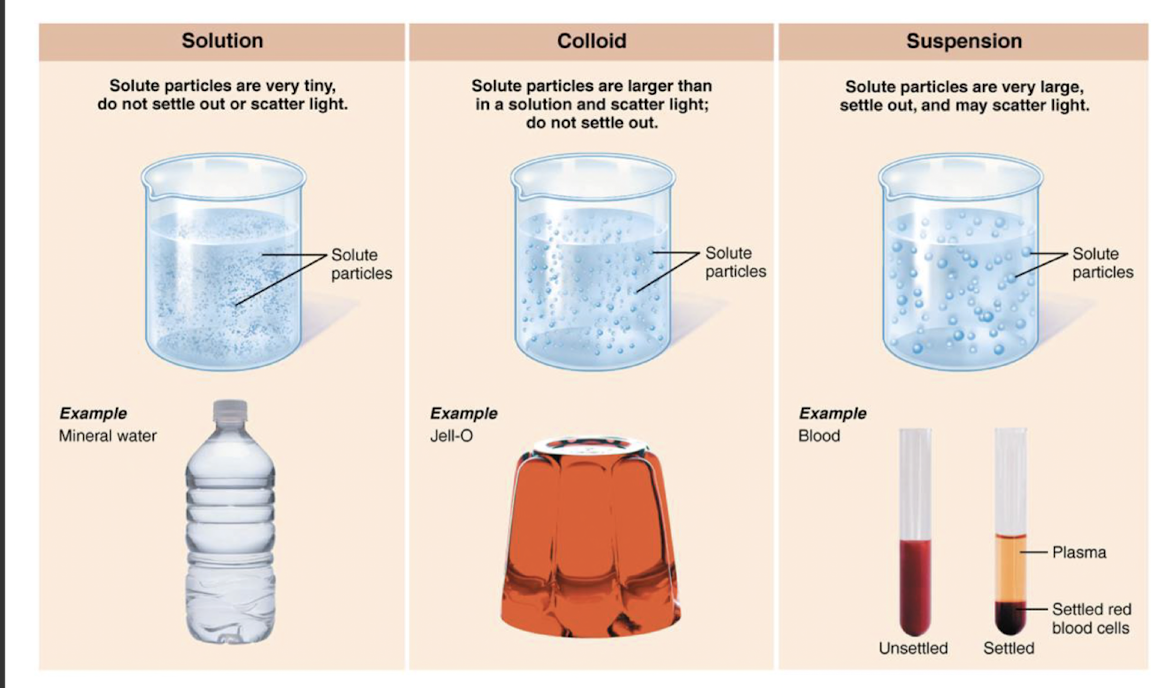
mixture v compound
1. mixture
* two or more components physically intermixed
* do not involve chemical bonding between components
* can be physically separated
2. compound
* specific molecule w/ 2 or more diff kinds of atoms bonded together ex: C6H12O6
* compounds separated by breaking chemical bonds
37
New cards
chemical bonds
chemical bonds: are “energy relationships” between electrons reaching atoms
Octet rule:
* atoms want 8 electrons in valence shell-driving force behind chemical reactions
* most atoms do not have full valence shells
* gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve stability.
Octet rule:
* atoms want 8 electrons in valence shell-driving force behind chemical reactions
* most atoms do not have full valence shells
* gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve stability.
38
New cards
3 major chem bonds
1. ionic bonds
2. covalent bonds
3. hydrogen bonds
39
New cards
ionic bond
* transfer of valence electrons from one atom to another resulting in ions
* anion (gains electrons - negative charge)
* cation (loses electrons + positive charge)
* attraction of opposite charges results in ionic bond
* anion (gains electrons - negative charge)
* cation (loses electrons + positive charge)
* attraction of opposite charges results in ionic bond
40
New cards
covalent bonds
* formed by sharing of 2 or more valence electrons between 2 atoms
* Share 2 elections=single bond
* Share 4 electrons=double bond
* Share 6 electrons= triple bond
* allows each atom to fill its valence shell at least part of the time
* 2 types of covalent bonds
* *nonpolar*: equal sharing of electrons between atoms > electrically balanced ex: CO2
* *polar*: unequally sharing of electrons between 2 atoms electrically unbalanced, polar molecules. ex: H2O
* Share 2 elections=single bond
* Share 4 electrons=double bond
* Share 6 electrons= triple bond
* allows each atom to fill its valence shell at least part of the time
* 2 types of covalent bonds
* *nonpolar*: equal sharing of electrons between atoms > electrically balanced ex: CO2
* *polar*: unequally sharing of electrons between 2 atoms electrically unbalanced, polar molecules. ex: H2O
41
New cards
hydrogen bonds
* attractive force between electropositive hydrogen of one molecule and electronegative atom of another molecule
* niot true bond, more of a weak magnetic attraction
* common between dipoles like: water
* niot true bond, more of a weak magnetic attraction
* common between dipoles like: water
42
New cards
molecular formula
Chemical formula that shows th enumber of different atoms present in a molecule. ex: CO2 > c 1 > o 2
43
New cards
chemical reactions
* chemical reactions occur when chemical bonds are formed, rearranged or broken > reactions written as symbols = chemical equations
* compounds are represented as molecular formulas ex: H2O or C6H12O6
* types: synthesis, decomposition, exchange
\
* compounds are represented as molecular formulas ex: H2O or C6H12O6
* types: synthesis, decomposition, exchange
\
44
New cards
Synthesis (chemical reactions)
* atom or molecules combing to form larger, more complex molecule
* used in anabolic (building) process
* A + B = AB
* used in anabolic (building) process
* A + B = AB
45
New cards
Decomposition (chemical reactions)
* breakdown or a molecule into smaller molecules or atoms
* involve catabolic (bond-breaking) reactions
* AB = A + B
* involve catabolic (bond-breaking) reactions
* AB = A + B
46
New cards
exchange (chemical reactions)
*displacement* reactions- involve both sythesis and decompostion
* AB + C = AC + B
* AB + CD = AD + CB
\
* AB + C = AC + B
* AB + CD = AD + CB
\
47
New cards
rate of chemical reactions
* chemical reaction speed can be affected by:
* temp: increase temp=increase rate
* concentration of reactions: increase concentration= increased rate
* particle size: smaller particles =increased rate
* CATALYSTS: increase reaction rate w/o being chemically changed or becoming part of the product
* *enzymes* are biological catalysts
* control metabolic processes
* temp: increase temp=increase rate
* concentration of reactions: increase concentration= increased rate
* particle size: smaller particles =increased rate
* CATALYSTS: increase reaction rate w/o being chemically changed or becoming part of the product
* *enzymes* are biological catalysts
* control metabolic processes
48
New cards
Water
* most abundant inorganic compound: 60-80% of cell volume
* special properties
* **high heat capacity:** can absorb and release heat w/ little temp changes
* **high heat vaporization:** evaporation requires a lot of heat
* useful cooing mechanism
* **polar solvent properties:** dissolves and dissociates ionic substances, body major transport
* **reactivity**
* **cushioning**
* special properties
* **high heat capacity:** can absorb and release heat w/ little temp changes
* **high heat vaporization:** evaporation requires a lot of heat
* useful cooing mechanism
* **polar solvent properties:** dissolves and dissociates ionic substances, body major transport
* **reactivity**
* **cushioning**
49
New cards
salts
* I**onic compounds:** dissociate into separate ions in water
* cations and anions (negatively charged)
* except for H+ and OH- ions
* also called electrolytes: can conduct electrical currents in solution
* important roles in body functions
* ex: sodium, potassium, calcium, iron
* ionic balance is key component of homeostasis
\
* cations and anions (negatively charged)
* except for H+ and OH- ions
* also called electrolytes: can conduct electrical currents in solution
* important roles in body functions
* ex: sodium, potassium, calcium, iron
* ionic balance is key component of homeostasis
\
50
New cards
Acids and bases
both = electrolytes- dissociate in water
51
New cards
acids
acids- proton donors
* release HYDROGEN ions (H+)
* no electrons
* ex: HC1 > H+ + C1 -
* important acids
* \`HC1: hydriodic acid
* HC2H3O2:acetic acid
* release HYDROGEN ions (H+)
* no electrons
* ex: HC1 > H+ + C1 -
* important acids
* \`HC1: hydriodic acid
* HC2H3O2:acetic acid
52
New cards
bases
bases-proton acceptors
* pick up H+ ions in solution
* ex: NaOH > Na ++ OH-
* releases a hydroxyl ion (OH-) when dissolved in water
Important bases
* bicarbonate (HCO3-) and Ammonia (NH3)
pH: acid base concentration
* pH scale- measurement oh hydrogen ion concentration. (H+) in a solution, the mor ehydrogen ions the more acidic the solution
* pH ranges from 0-14: one being really acidic
* pick up H+ ions in solution
* ex: NaOH > Na ++ OH-
* releases a hydroxyl ion (OH-) when dissolved in water
Important bases
* bicarbonate (HCO3-) and Ammonia (NH3)
pH: acid base concentration
* pH scale- measurement oh hydrogen ion concentration. (H+) in a solution, the mor ehydrogen ions the more acidic the solution
* pH ranges from 0-14: one being really acidic
53
New cards
pH scale
1. acidic solutions: high H+ but low pH range=0-6.99
2. Neutral solutions: equal H+ and OH- ions, all are pH 7
3. alkaline (base) solutions: low H+ but high pH: Range- 7.01-14
*neutralization reaction: acids and base mixed*
54
New cards
Buffers
Resist abrupt and large swings in pH
* can release or bind H+ as necessary
* convert strong acids or bases into weak ones
* ex: carbonic acid- bicarbonate sys (important buffer sys of blood)
* can release or bind H+ as necessary
* convert strong acids or bases into weak ones
* ex: carbonic acid- bicarbonate sys (important buffer sys of blood)
55
New cards
organic v inorganic
1. organic
* polymer= a chain of similar units (monomers)
* Dehydration synthesis= created bond; connects
* hydrolysis reaction= break bonds
2. inorganic compounds do not contain a carbon atom in them
56
New cards
lipids
C, H, O fewer then carbs +/- P
insoluble in water
insoluble in water
57
New cards
triglycerides *(lipids)*
* solid-fat’s, liquids and oils
* 3 fatty acid bonded to glycerol molecule
* functions: store energy, insulation, protection
* saturated fats
* all Cs linked via single covalent bonds, max # of Hs
* solid at room temp (ex: animal fats, butter)
* unsaturated fatty acids
* I + Cs linked by double bonds, liquid at room temp
* 3 fatty acid bonded to glycerol molecule
* functions: store energy, insulation, protection
* saturated fats
* all Cs linked via single covalent bonds, max # of Hs
* solid at room temp (ex: animal fats, butter)
* unsaturated fatty acids
* I + Cs linked by double bonds, liquid at room temp
58
New cards
phospholipids *(lipids)*
* modified triglycerides- glycerol + 2 fatty acids + P group
* “head” & “tail” w different properties
* head is polar & hydrophillic
* tails are nonpolar & hydrophobic
* important in cell membrane structure
\
* “head” & “tail” w different properties
* head is polar & hydrophillic
* tails are nonpolar & hydrophobic
* important in cell membrane structure
\
59
New cards
steroids *(lipids)*
* four interlocking rings
* most important steroid = cholesterol
* made by the liver in animal products (cheese, eggs, meat)
* plasma membrane structure
* most important steroid = cholesterol
* made by the liver in animal products (cheese, eggs, meat)
* plasma membrane structure
60
New cards
eicosanoids *(lipids)*
* derived from fatty acid in the cell membrane
* prostaglandins
* role in blood clotting, blood pressure, inflammation, and smooth muscle contractions
* blocked by NSAIDs (over counter drugs)
* prostaglandins
* role in blood clotting, blood pressure, inflammation, and smooth muscle contractions
* blocked by NSAIDs (over counter drugs)
61
New cards
carbohydrates
starches and sugars- C, H, O: 3 classes
62
New cards
monosaccharides *(carbohydrates)*
1 sugar
* absorbable, simplist carb > monomers
* ex: pentose sugars (ribose and deoxyribose) hexose sugars (glucose)
* absorbable, simplist carb > monomers
* ex: pentose sugars (ribose and deoxyribose) hexose sugars (glucose)
63
New cards
disaccharides *(carbohydrates)*
2 sugars
* to large to pass through cell membrane
* ex: sucrose, maltose, lactose
* formed by dehydration synthesis of two monosaccharides
* to large to pass through cell membrane
* ex: sucrose, maltose, lactose
* formed by dehydration synthesis of two monosaccharides
64
New cards
polysaccharides *(carbohydrates)*
3+ sugars
* polymers of monosaccharides, formed by dehydration synthesis of many monomers
* ex: starch: storage carb, plants
* ex: glycogen: storage carb, animals
* not absorbable
\
* polymers of monosaccharides, formed by dehydration synthesis of many monomers
* ex: starch: storage carb, plants
* ex: glycogen: storage carb, animals
* not absorbable
\
65
New cards
proteins
* 20-30% of cell mass
* variety of cell functions
* structural, chemical (enzymes), concentration (muscles), communication defense
* C, H, O, N and +/- S & P
* amino acid monomers connected by peptide bonds in polypeptide polymer
* four structural levels
*amino acids: linked by covalent bonds (peptide bonds, amine group (N), acid group (COH), H*
* variety of cell functions
* structural, chemical (enzymes), concentration (muscles), communication defense
* C, H, O, N and +/- S & P
* amino acid monomers connected by peptide bonds in polypeptide polymer
* four structural levels
*amino acids: linked by covalent bonds (peptide bonds, amine group (N), acid group (COH), H*
66
New cards
Protein structural level
1. primary: line of amino acids
2. Secondary: primarily amino acids interact
1. ALPHA HELIX- coil, spring-like
2. BETA PIEATED SHEETS- accordion ribbons
3. tertiary: secondary structures interact
4. quaternary: 2+ diff polypeptides interact
67
New cards
protein shapes
1. fibrous (structural) proteins
1. strand, water insoluble, stabe, mechanical, support and tensile strength
2. tertiary or quaternary structure (3-D)
3. ex: keratin, elastin, collagen
2. globular (functional) proteins
1. compact, spierical, water-soluble, and sensitive to environment
2. tertiary or quaternary structure (3-D)
3. specific function regions (activity sites)
4. ex: antibodies, hormones, enzymes.
68
New cards
enzymes actions
1. substrate binds to enzymes active site > forms enzyme substrate complex
2. substrate rearrangement > final product
3. product release from enzyme
69
New cards
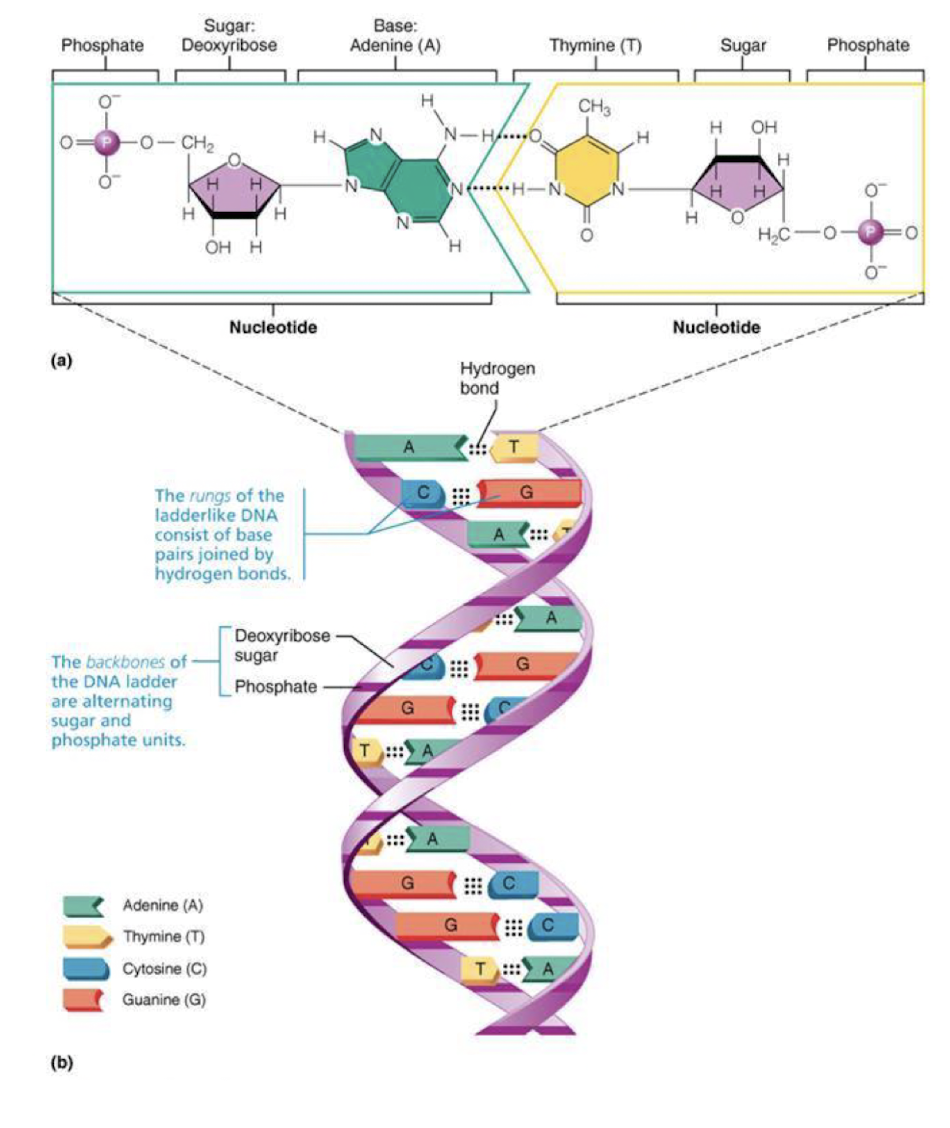
DNA
genetic blueprint for synthesis of all proteins
* double helix-in cell nucleus
* 4 nitrogen bases
* purines: adenine (A), guanine (G)
* Pyrimidines: Cytosine (C), thymine (T)
* specific nitrogen bonding pattern-complentary base pairing rules
*A pairs w T*
*G pairs w C*
* double helix-in cell nucleus
* 4 nitrogen bases
* purines: adenine (A), guanine (G)
* Pyrimidines: Cytosine (C), thymine (T)
* specific nitrogen bonding pattern-complentary base pairing rules
*A pairs w T*
*G pairs w C*
70
New cards
RNA
links DNA to protein synthesis
* differs from DNA
* singles stranded, active outside nucleus, ribose sugar, uracil instead or thymine
* 3 varieties of RNA
* messenger mRNA
* transfer tRNA
* ribosomal rRNA
\
* differs from DNA
* singles stranded, active outside nucleus, ribose sugar, uracil instead or thymine
* 3 varieties of RNA
* messenger mRNA
* transfer tRNA
* ribosomal rRNA
\
71
New cards
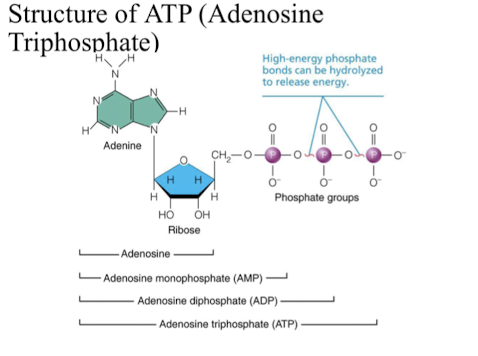
ATP
* chemical energy released when glucose is broken down is captured as ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
* directly powers chemical reactions in cells
* end phosphate group can be transferred to other compounds- use energy stored in phosphate bond to do worol
* loss of third phosphate group converts to ATP to ADP
* loss second phosphate group converts to ADP to AMp
* directly powers chemical reactions in cells
* end phosphate group can be transferred to other compounds- use energy stored in phosphate bond to do worol
* loss of third phosphate group converts to ATP to ADP
* loss second phosphate group converts to ADP to AMp
72
New cards
cell theory
* structural and functional unit of life
* cells can only come from other cells
* cant be created from nothing
\
* cells can only come from other cells
* cant be created from nothing
\
73
New cards
cells
1. plasma membrane: flexible outer boundary
2. cytoplasm: intracellular fluid containing organelles; everything in cell membrane
3. nucleus: DNA containing control center; “brain” of the cell
74
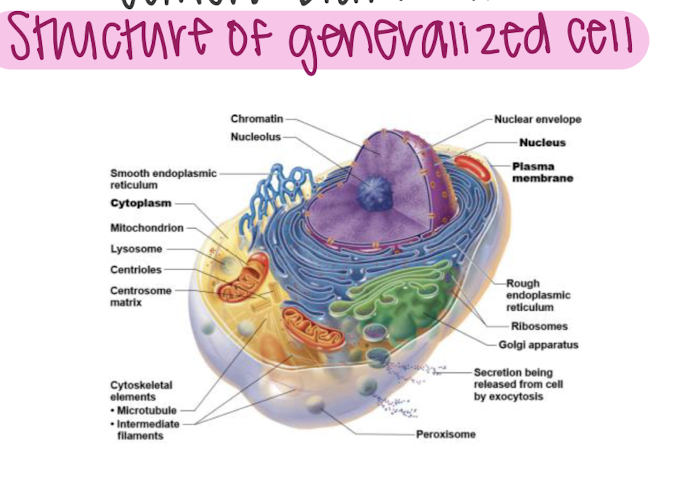
New cards
structure of generalized cell
75
New cards
cell diversity
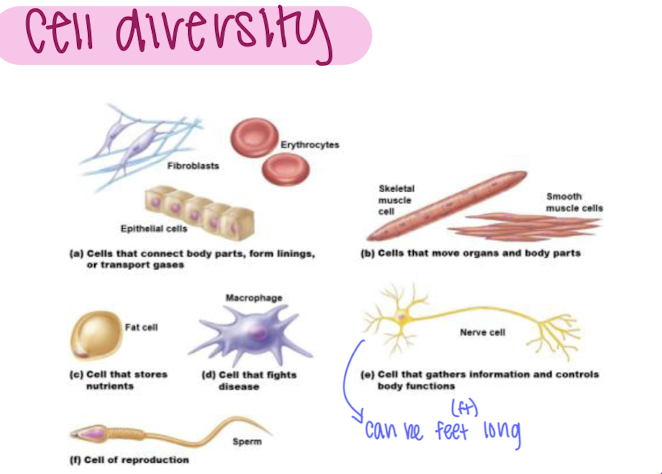
76
New cards
extracellular materials
outside the cell
* interstitial fluid
* blood plasma
* cerebrospinal fluid
* interstitial fluid
* blood plasma
* cerebrospinal fluid
77
New cards
Plasma membrane
barrier: intracellular v extracellular
lipid bilayer:
* phospholipids, glycoproteins, cholesterol
* proteins: embedded in the cell membrane
* integral: film attachment, transport, enzyme, receptor
* peripheral: loose attachment, enzyme, shape, change, connections
* fluid mosaic
Glycocalyx- CHOs (sugars) attached to proteins or lipids
* specific patter > cell recognition
*immune sys*
lipid bilayer:
* phospholipids, glycoproteins, cholesterol
* proteins: embedded in the cell membrane
* integral: film attachment, transport, enzyme, receptor
* peripheral: loose attachment, enzyme, shape, change, connections
* fluid mosaic
Glycocalyx- CHOs (sugars) attached to proteins or lipids
* specific patter > cell recognition
*immune sys*
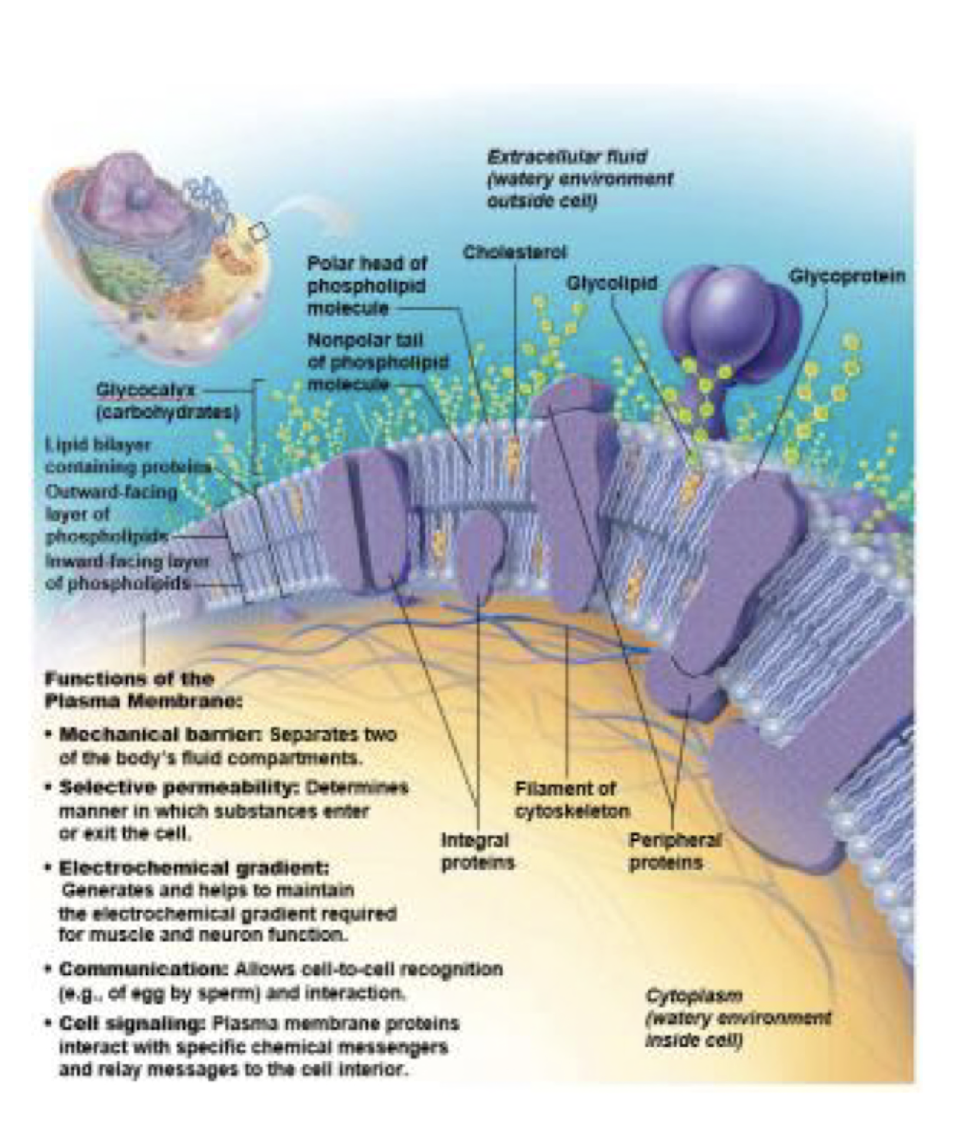
78
New cards
cell junctions
1. tight junctions: leak proof seal > like a ziplock bag
1. GIT, urinary sys
2. desmosomes: rivets or buttons, flexibility= doesn’t prevent leaking
1. skin, cardiac
3. gap junctions: proteins form tunnels, fast communication
1. cardiac, smooth muscle
79
New cards
passive v active transport
passive:
* no energy is required w concentration gradient
* types
* simple diffusion
* facilitated diffusion- carrier protein
* osmosis
* osmolarity: total concentration of solute particles
active:
* energy (ATP) required, against concentration gradient
* types
* active transport
* primary active trans. - ATP used to change protein shape (-Na+-K+ ATPase pump enzyme)
* secondary active trans. - ion gradient changes primary active trans. allow other substances to move
* Reticular trans. - macromolecules in vesicles- very long trans molecules
* endocytosis
* phagocytosis: cell eating
* pinocytosis: cell drinking
* receptor: mediated endocytosis-specific
* exocytosis: kicking something out of the cell
* no energy is required w concentration gradient
* types
* simple diffusion
* facilitated diffusion- carrier protein
* osmosis
* osmolarity: total concentration of solute particles
active:
* energy (ATP) required, against concentration gradient
* types
* active transport
* primary active trans. - ATP used to change protein shape (-Na+-K+ ATPase pump enzyme)
* secondary active trans. - ion gradient changes primary active trans. allow other substances to move
* Reticular trans. - macromolecules in vesicles- very long trans molecules
* endocytosis
* phagocytosis: cell eating
* pinocytosis: cell drinking
* receptor: mediated endocytosis-specific
* exocytosis: kicking something out of the cell
80
New cards
osmosis pressure changes
hydrostatic pressure:
* pressure of water inside cell, pushing on membrane
osmotic pressure:
* solutes/particles pulling on water (toward)
* the more solutes inside a cell, the higher the osmotic pressure
* pressure of water inside cell, pushing on membrane
osmotic pressure:
* solutes/particles pulling on water (toward)
* the more solutes inside a cell, the higher the osmotic pressure
81
New cards
osmosis
Tonicity: solution changes cell shape by from water volume shifts
1. isolotic soltuion: same osmolarity as inside the cell
1. no change- most IV liquids
2. hypertonic solution: higher osmolarity than inside cell
1. water flows out > shrinks the cell *crenation*
3. hypotonic solution: lower osmolarity than inside the cell
1. water flows into cell > cell swelling *cell burst>lysing/lysis*
1. isolotic soltuion: same osmolarity as inside the cell
1. no change- most IV liquids
2. hypertonic solution: higher osmolarity than inside cell
1. water flows out > shrinks the cell *crenation*
3. hypotonic solution: lower osmolarity than inside the cell
1. water flows into cell > cell swelling *cell burst>lysing/lysis*
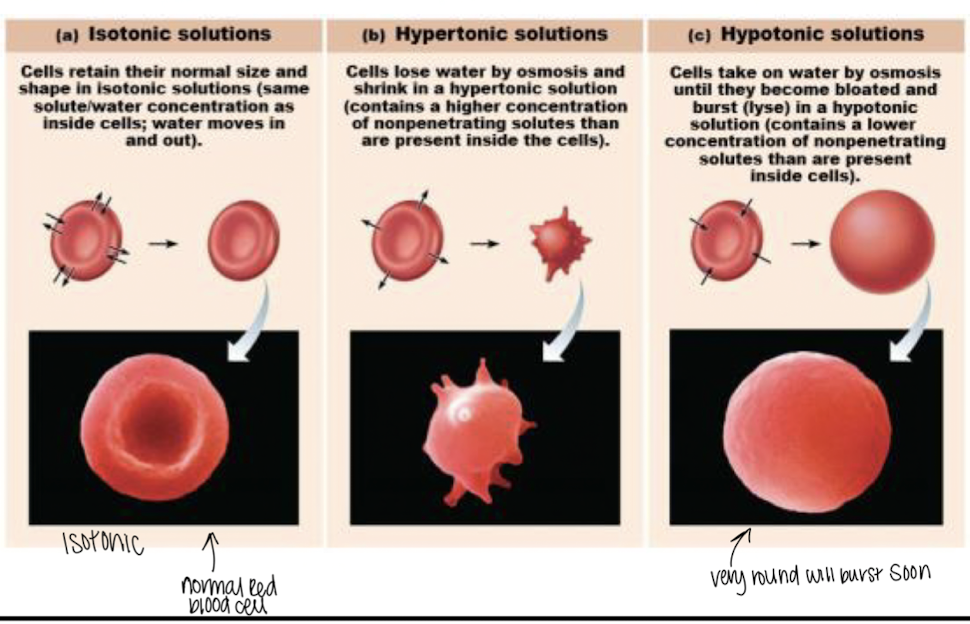
82
New cards
membrane potential
resting membrane potential (RMP) - electrical potential energy produced by charged particles moving across the plasma membrane
* the voltage at the membrane surface
* voltage= difference in electrical charge between 2 points: outer and inner surface of cell membrane
* rest of cells & extracellular fluid are neutral
* membrane voltages-range of -50 to -100 mV
Na+ -K+ ATPase Pump: sodium-potassium pump
* 3 Na+ pumped OUT of the cell
* 2 K+ brought INTO the cell
* cellular Na+ concentration is relatively consistent
* Na+ leaks channels
* myocytes & neurons > open gated channels allowing Na+ & K+ move quickly
* the voltage at the membrane surface
* voltage= difference in electrical charge between 2 points: outer and inner surface of cell membrane
* rest of cells & extracellular fluid are neutral
* membrane voltages-range of -50 to -100 mV
Na+ -K+ ATPase Pump: sodium-potassium pump
* 3 Na+ pumped OUT of the cell
* 2 K+ brought INTO the cell
* cellular Na+ concentration is relatively consistent
* Na+ leaks channels
* myocytes & neurons > open gated channels allowing Na+ & K+ move quickly
83
New cards
the cell
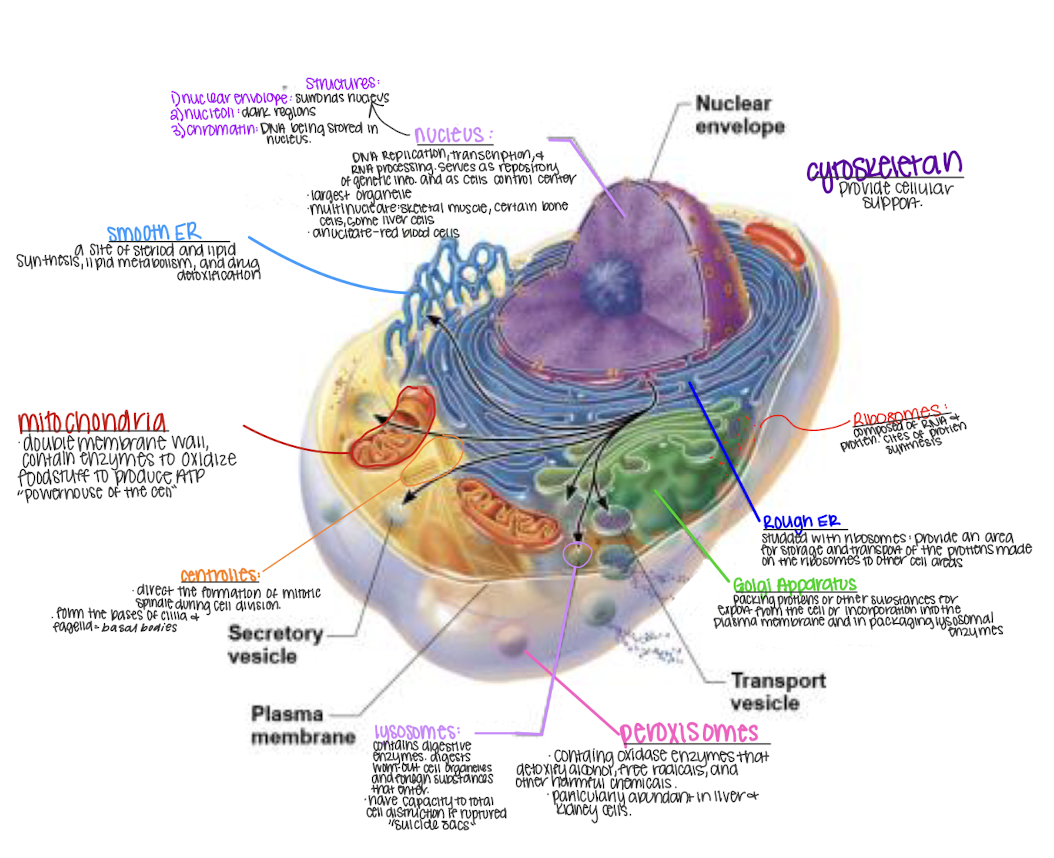
84
New cards
cell cycle: leads to cell division
* series of changes a cell undergoes from formation unit reproduces
* major periods:
* interphase: cell grows and usual activities
* prepares for cell division, uncondensed chromatin
* subphases
* G1 (gap 1) vigorous growth & metabolism
* S (synthesis) DNA replicates occurs
* G2 (gap 2) preparation for division
* cell division: mitosis > 2 daughter cells
* 4 stages of mitosis
* prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
* major periods:
* interphase: cell grows and usual activities
* prepares for cell division, uncondensed chromatin
* subphases
* G1 (gap 1) vigorous growth & metabolism
* S (synthesis) DNA replicates occurs
* G2 (gap 2) preparation for division
* cell division: mitosis > 2 daughter cells
* 4 stages of mitosis
* prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
85
New cards
Prophase (1) *(4 stages of mitosis )*
1) prophase:
* __***early prophase***__: chromatin condenses > chromosomes, two copies (sister chromatids) held together by a centromere.
* __***late prophase***__: nuclear envelope breaks. microtubules attach to centromeres and pull chromosomes to the center of the cell
* __***early prophase***__: chromatin condenses > chromosomes, two copies (sister chromatids) held together by a centromere.
* __***late prophase***__: nuclear envelope breaks. microtubules attach to centromeres and pull chromosomes to the center of the cell
86
New cards
metaphase (2) (*4 stages of mitosis )*
centromeres of chromosomes aligned at cells equator
87
New cards
Anaphase (3) (*4 stages of mitosis )*
centromeres of chromosomes split simultaneously > each sister chromatin is separate now. chromosomes pulled toward their pulls by mtor proteins of kinetochores
88
New cards
Telophase (4) (*4 stages of mitosis )*
begins when chromosome movement stops. chromosomes unciol > chromatin. nuclear membranes form around chromatin. nucleoli reappear, spindle, disappears.
* __***cytokinesis:***__
* when telophase is wrapping up and begins during late anaphase, a ring of actin microfilaments contract > from cleavage furrow. two daughter cells pinched apart.
* __***cytokinesis:***__
* when telophase is wrapping up and begins during late anaphase, a ring of actin microfilaments contract > from cleavage furrow. two daughter cells pinched apart.
89
New cards
protein synthesis
DNA holds code for protein synthesis: directs amino acids in polypeptide. gene-segment of DNA that holds code for polypeptide. determined in oder of (A, G, T, C): ex: GGC codes for amino acid proline
* role of RNA > linking DNA to proteins, formed in nucleus
* two steps
* __***transcription***__: dna information coded in mRNA
* __***translation***__: mRNA decoded to assemble polypeptides
DNA ------------------→ RNA--------------→ Protein
transcription translation
* role of RNA > linking DNA to proteins, formed in nucleus
* two steps
* __***transcription***__: dna information coded in mRNA
* __***translation***__: mRNA decoded to assemble polypeptides
DNA ------------------→ RNA--------------→ Protein
transcription translation
90
New cards
transcritpion __*(protein synthesis)*__
1. initiation: get started. RNA polymerase separates DNA strands
2. Elongation: majority of time, bring in nucleotide
3. Termination: end of gene
\
91
New cards
translation __*(protein synthesis)*__
Language or nucleic acids (base sequence) is translated into the language of proteins (amino acid seq.)
* invlove: mRNA, tRNA, Ribosomes, +/- rough ER
* invlove: mRNA, tRNA, Ribosomes, +/- rough ER
92
New cards
Tissues
group of cells similar in structure & appearance that perform common of related function
93
New cards
histology
study of tissues
94
New cards
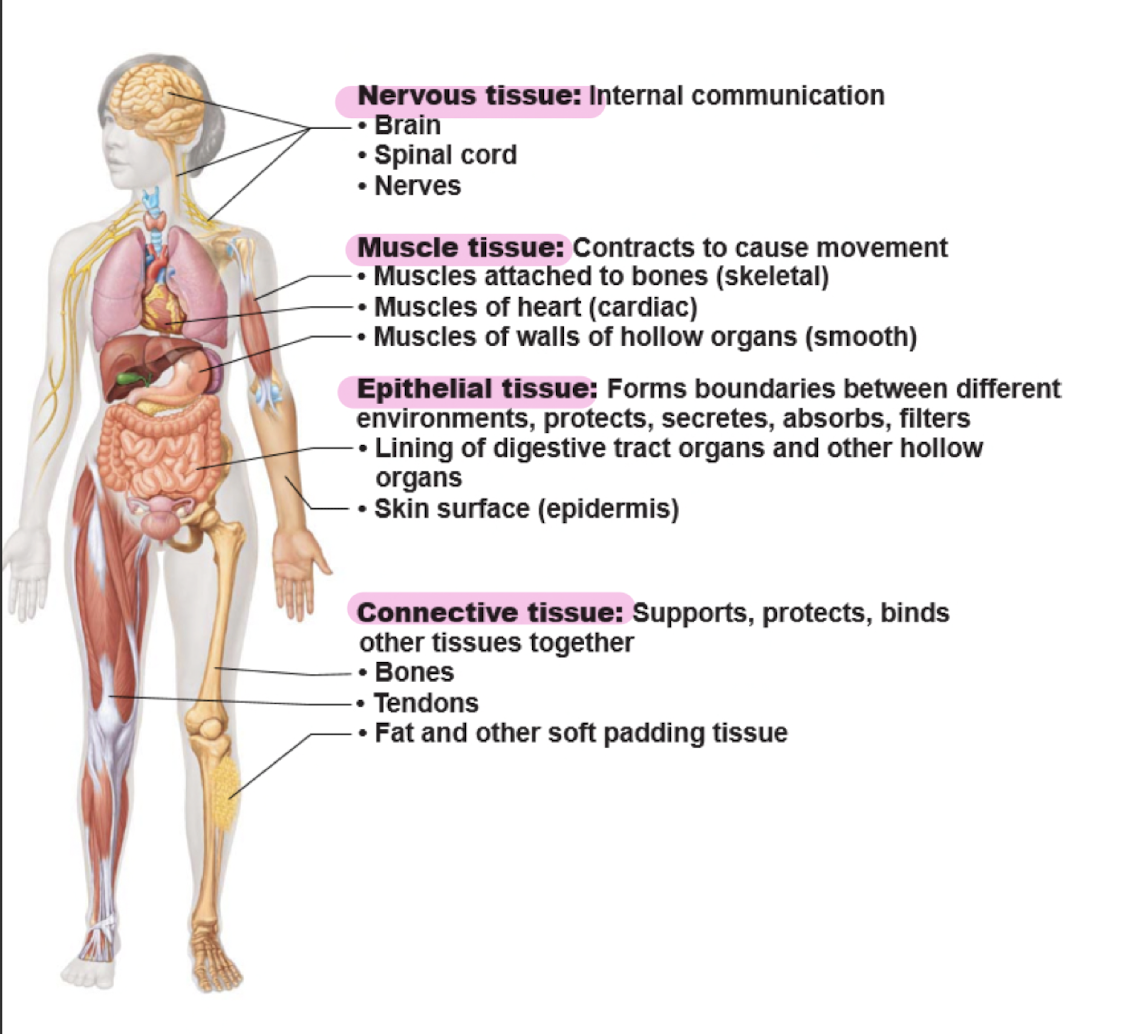
four basic types of tissues
1. epithelial
2. connective
3. muscle
4. nervous
95
New cards
5 distinguishing characteristics of tissues
1. polarity: apical (top) & basal (bottom) surface
2. specialized contracts: tight junctions, desomeones
3. supported by connective tissues: basement membrane
4. avascular (poop blood supply) but innervated
5. regeneration: undergoes mitosis easily
96
New cards
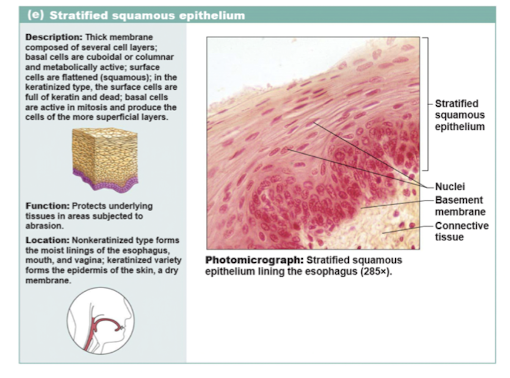
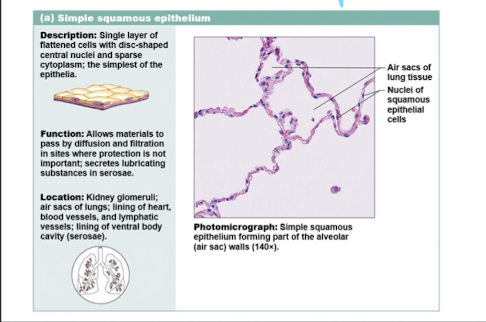
simple squamous epithelium
97
New cards
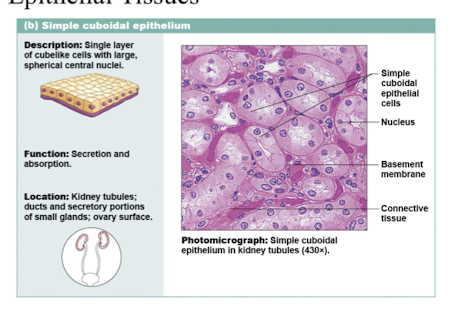
simple combodial epithelium
98
New cards
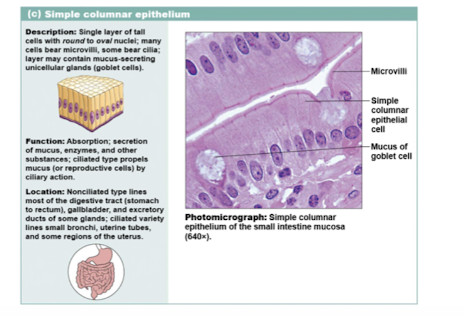
simple columnar epithelium
99
New cards
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
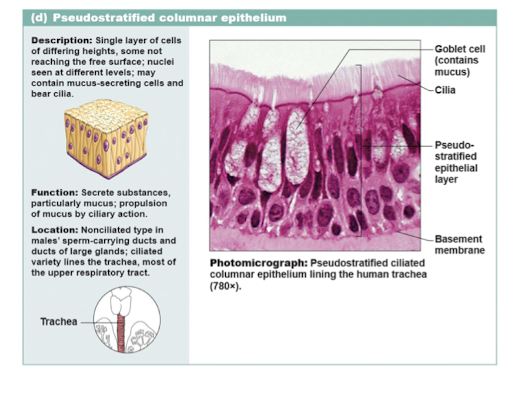
100
New cards
stratified squamous epithelium