week 5: Interventions for cognitive functioning in pediatrics
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Importance of Cognition in OT
•Identify Cognitive Deficits to Establish Baseline
•Identify Cognitive Demands in Environment & in Occupations
•Develop intervention to improve cognitive performance for Occupation
Cognitive functioning affects occupational performance.
Preschool
Progression of ADL & IADL involvement among Children
Home
Morning Routine
Clean up
Prepare cold snack
Make Bed
Outside
Library visit
Community Events
Playground
Controlling Temper/ Impulsive behaviors
Progression of ADL & IADL involvement among Children
middle childhood
Home
Prepare Simple Meals
Take care of Space & needs
Put away Groceries
Completion of homework
Outside
Asist with grocery shopping
Participate in after school programs, community center activities
Follow schedule
Progression of ADL & IADL involvement among Children
younger adolescence
Home
Plan and prepare Simple hot & cold meals
Use of communication devices
Babysit
Manage Medications
Outside
Use public Transportation Independently
Volunteer
Emerging Safety Awareness
Progression of ADL & IADL involvement among Children
older adolescents
Home
Operate kitchen appliances
Home repairs
Outside
Driving
Works Part time
Volunteer
College Readiness
Factors Impacting Cognitive Development
•Sensory
•Psychological
•Physiological
•Environmental
Comorbidities
•Children with DCD →
•Autism →
•Traumatic brain injuries→
•Acquired Brain injury/Genetic Conditions→
•Intellectual disabilities →
•ADHD →
•Down Syndrome →
•Oppositional Defiant Disorder
components of cognition
Memory:
•Short
•Long
•Working
Attention:
•Selective
•Sustained
•Divided
Orientation:
•Alertness
•Arousal
Perception:
•Discrimination of senses
Thought:
•Content
Cognition defined:
“The Child’s ability to acquire and use information in order to adapt to environmental demands.”
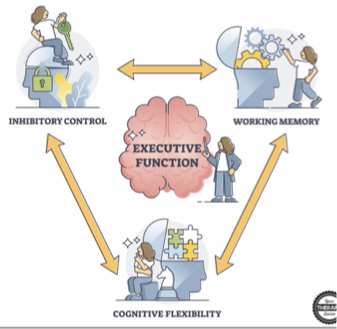
Higher Level Components of Cognition: Executive Functioning
•Working Memory
•Inhibitory Control
•Cognitive Flexibility
•Planning and Organization
•Self Regulation
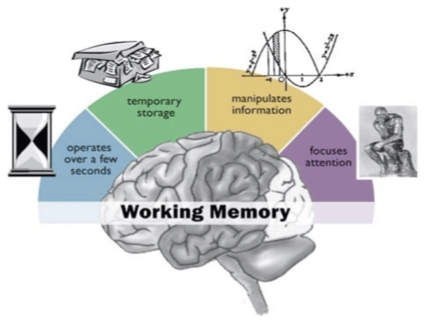
Working Memory
■The ability to hold, update and manipulate information
■Deficits
–Difficulty to remember steps to complete a project
– difficulty following schedule (give 3 step direction)
TBI, ADHD
Inhibitory Control
The ability to inhibit, resist, or not act on impulse
The ability to STOP one’s own behavior at the appropriate time
Deficits:
Intrusiveness
lack of personal safety
ADHD, OCD, ODD
Cognitive Flexibility
The ability to change plans or actions as the circumstances demand
Switching or alternating attention and changing focus
Deficits:
Rigid thinking
Perseverative behaviors
Behavioral/emotional outburst
Plan:
Ability to manage current and future-oriented task demands in context
Anticipation of future events
ability to set goals to meet them,
Develop appropriate steps ahead of time to carry out task or activity
Organization:
Memory component (how one learns and retrieves information) and bringing order to information
Identifying critical steps/groups of information to follow a plan and execute tasks
Deficits: planning and organization
Easily overwhelmed by increased information
Impacts overall learning of content managing assignments
Self Regulation
The ability to control emotions/actions so that goals can be achieved and tasks completed.
EF within the emotional realm
Deficits:
lability (frequent mood changes)
explosiveness (tantrums)

Executive Skills involving Thinking (cognition)
Working Memory |
Planning/prioritization |
Organization |
Time Management |
Metacognition |
Executive Skills involving doing (behavior)
Response Inhibition |
Emotional control |
Sustained attention |
Task initiation |
Goal-directed persistence |
Flexibility |
Method of Cognitive Assessment
•Observation
•Interview
•Occupational History
•Standardized tests
Patient Reported Outcome
Performance based test
•Environmental Assessment
Dynamic occupational therapy cognitive assessment for children
Ages 6-12
Measures cognition and learning potential
Child kitchen task assessment (CKTA)
Ages 8-12
Examines EF through performance
Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function (BRIEF-2)
Ages 5-18
Parent/Client Questionnaire
DO- EAT
Ages 5-8
Measures performance on 3 tasks
Making a sandwich
Making chocolate milk
Fill out certificate of outstanding performance for self
Weekly calendar planning activity
12-17
Measures EF by entering appointments and errands in a weekly schedule
Why use Cognitive Approaches?
Performance Based approach to assist the child in identifying, developing, & utilizing cognitive strategies to increase occupational performance:
•Motivation
•Generalization
•Facilitate Lifelong Development
Cognitive Rehabilitation Models: Dynamic Model of Cognition
Based on Dynamic Systems theory (individual, task and environment)
Integrates info. on learning from cognitive & educational psych with OT practice (Ex. Vygotsky, Bandura)
Discovery learning (construct knowledge from past experiences and direct experiences)
Metacognition
Cognitive and occupational performance change based on personal as well as task and environmental factors
The ability to effectively use strategies learned depends on personal factors & external factors
Provides broad view of cognition and therefore supports multiple intervention approaches
Improve self awareness, modify external factors
Emphasis on Ability to apply cognitive strategies & be self directed in improving performance vs completing the task itself
Guidelines for Cognitive Intervention
Design environment rich with opportunities to practice EF & cognitive skills
Complex and progressive to facilitate cog. Challenge
Variability in practice
Intensity and frequency of practice is important
Support child’s development of self-awareness at all stages of intervention
Wean external supports when appropriate
Prompt hierarchy (ex. CKTA)
Help family and others involved to have reasonable expectations
Simple directions; Environmental Set up
Education on Arousal & SP

Cognitive Rehabilitation Models: remedial: MAIN DIFF
Main focus is on retraining and restoring impaired areas of cognition
Targets core components such as memory, attention, EF, etc. that cause the deficit
Cognitive Rehabilitation Models: Adaptive/functional: MAIN DIFF
•Main focus is on facilitating functional participation despite cognitive deficits
•Main goal is to adapt the environment/task to individual’s abilities
Cognitive Rehabilitation Models: Remedial/Restorative
Emphasis on evaluating & restoring impaired cognitive skills
Follow hierarchy (higher cortical skills vs. lower level skills)
No evidence that practice of cognitive components in isolation will generalize to task requiring these skills
Connect to Occupation
Examples:
Cognitive computer-based training programs,
Remedial: focused on specific cognitive components

Remedial Cognitive Intervention: Attention & Working Memory
Divided Attention
Visual Scanning (Driving)
Following Directions
Sequencing
example: Goal: Carlos will prepare 2 cold snacks/meals (sandwich, cereal, fruit), gathering then putting away all needed materials, independently for 3 sessions to demonstrate age-appropriate meal preparation.

Cognitive Rehabilitation Models: Adaptive/Functional Models
Emphasizes the ability to successfully perform everyday tasks and routines by building on the person’s assets and/or residual skills
•Indirect Approach:
Caregiver Education
Environmental Modifications
•Domain Specific Strategies:
External Sensory &Environmental
Mental of Self Verbalization Strategies
Task Modification & Specification Strategies
Domain Specific Strategies: Mental & Verbalization
Role Script: A pattern of words to help guide a sequence of actions
“Stab, Slice, Saw”
goal: Carlos will utilize a knife and fork to cut tough foods with min verbal cues for 75% of relevant opportunities

Domain Specific Strategies: Task Modification for Task Completion
Stimuli Reduction: Reading Bar

Organization: Restructure for Logic
Pacing Strategies: Assist with Timing: Tapping foot, humming, timer

Attention to Doing: Relevant Cue

Task Modifications– Organization & Planning
Task Simplification


organization:

Task Specification: Place Backpack Here

Cognitive Intervention For Organization
Verbalization: Self Questioning:

Indirect Education:

Task Modification:

goal example: Per parent report, Carlos will be prepared when time to leave for school (books in backpack, have lunch, etc.) with the use of a checklist or visual reminder for 3/5 days of the school week.
Cognitive Rehabilitation Models: Cognitive Strategies
CO-OP (Cognitive Orientation to Daily Occupational Performance Approach)
External control
visual checklist
Internal control
Self awareness training
E.g. Zones, video modeling, self-talk, etc.
Problem Solving Strategies

Cognitive Intervention - Time Management
Goal: Per parent report, Iris will demonstrate improved time management and attention to complete all steps of her morning routine with min VC to redirect attention to task 3/5 days per week

Cognitive Intervention: Cognitive Flexibility & Self Regulation
Group Intervention (Speech and Social Work)
Peer Dyads
Cognitive Strategy ->Zones of Regulation

Teletherapy Ideas
Meal Preparation
Scavenger Hunts!
Planning An Obstacle Course
Visual Schedules
Online Boardgames
Battleship
Chess
Connect 4
Puzzles
Dice games

Executive Function Intervention: Collaboration with Speech Therapists
Auditory Processing
Ex Lennox Gastaut syndrome
Safety
Receptive Understanding
Ex. Yes/No Questions
Wh Questions
Spatial Concepts
Aphasia
Expressive Speech
Gestalt Language Processer
Ex. It's a red car!”
Use of Communication Device
Executive Function Intervention: Collaboration with Speech Therapists
nova chat

Applications to Support EF
Applications to Google Keep
Google Read and Write
Sticky Notes
Day board Site Blocker
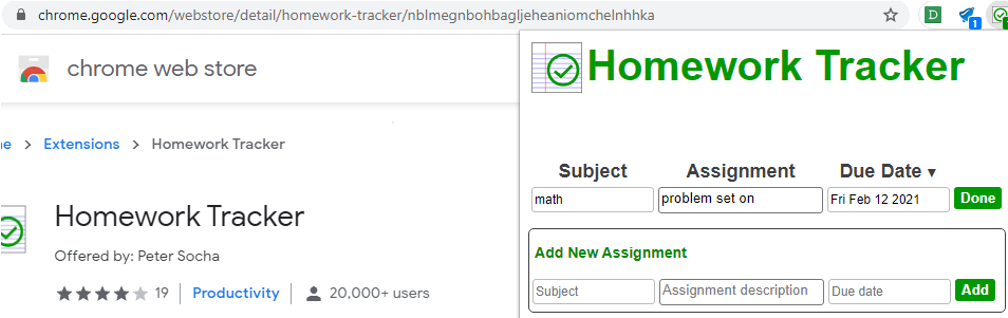
To Do list
Homework Tracker
Sometimes in school setting you may need to advocate for extensions to be allowed on laptop to promote school organization, plannings, attention etc.