Biology - Control of Gene Expression
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
1
New cards
the overall process of genetic information flowing from genes to proteins; genotype to phenotype:
gene expression
2
New cards
Scientists say that the gene has been expressed when:
it is transcribed and its product has been synthesized
3
New cards
in prokaryotes genes are turned on and off by what?
environmental factors
4
New cards
if all genes were turned on at the same time what would occur?
metabolic disorder
5
New cards
True or False: bacterium have multiple DNA molecules
False
6
New cards
a group of genes with related functions in a prokaryote:
operon
7
New cards
an operon is made up of what?
structural genes and a promoter region
8
New cards
genes that code for the protein product on the operon:
structural genes
9
New cards
genes that promote the movement of RNA polymerase onto the structural genes:
promoter genes
10
New cards
the promoter area is made up of which two things?
promoter gene and operator gene
11
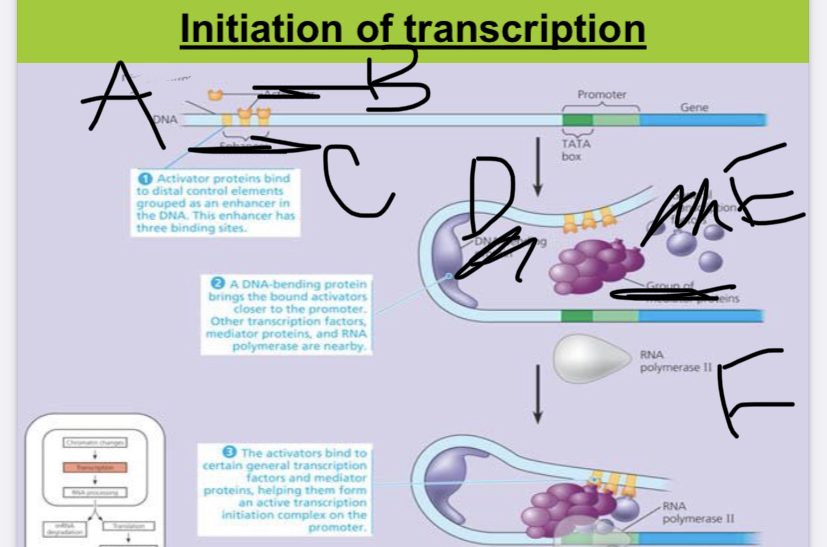
New cards
a region of the DNA that acts as an on-off switch for an operon:
operator
12
New cards
this part of the operon is located somewhere else on the DNA:
regulator
13
New cards
what does the regulator gene produce?
repressor proteins
14
New cards
in *trp* operon, how is the operon turned off?
when a large amount of tryptophan accumulates, one molecule binds to the repressor. then the repressor binds to the operator, turning it off.
15
New cards
when is the *lac* operon turned “off”?
when there is no lactose in the cell’s enviornment
16
New cards
Cancer results from:
mutations in genes that control cell division
17
New cards
How can viruses cause cancer?
They carry cancer-causing genes that are inserted into a host cell, making it cancerous
18
New cards
an altered version of a gene found in normal cells:
oncogene
19
New cards
mutations can change a ______ into a oncogene:
proto-oncogene
20
New cards
what are proto-oncogenes?
normal genes that promote cell division and have the potential to become an oncogene
21
New cards
what are the three kinds of changes in somatic cell DNA that can produce oncogene?
mutation in the gene, an error in DNA replication, movement of gene
22
New cards
result of mutations within genes:
hyperactive growth-stimulating protein in normal amount
23
New cards
result of an error in DNA replication:
normal growth-stimulating protein in excess
24
New cards
result of gene moving from its normal location:
normal growth-stimulating protein in excess
25
New cards
these proteins stimulate cell division:
growth factors
26
New cards
genes whose products inhibit cell division are called:
tumor supressor genes
27
New cards
when there is a mutation in the tumor-suppressor gene, what happens?
cell division is uncontrolled, resulting in cancer
28
New cards
colon cancer steps:
increased cell divison, growth of benign tumor, growth of malignant tumor
29
New cards
what is needed to produce a full-fledged cancer cell?
four or more somatic mutations
30
New cards
which gene puts women at a high risk of breast cancer?
a gene on chromosome 17 called BRCA1
31
New cards
what are some carcinogens?
asbestos, X-rays, UV rays, cigarette smoking, vaping, chewing tobacco
32
New cards
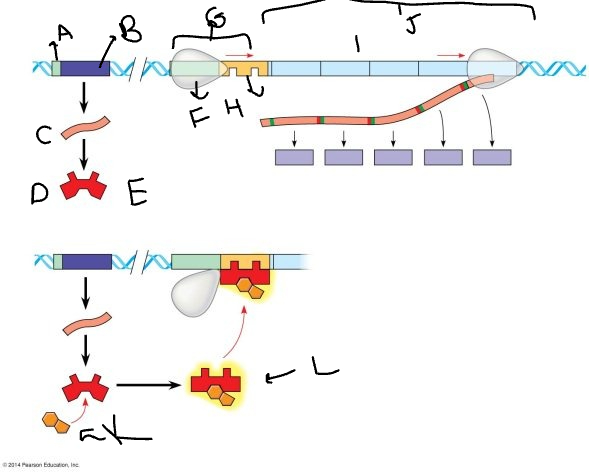
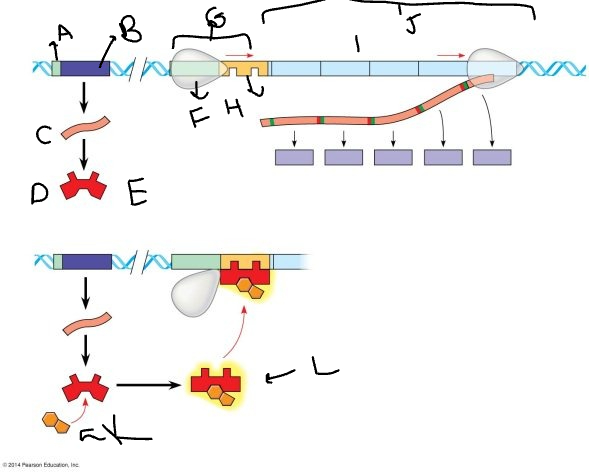
A:
promoter
33
New cards
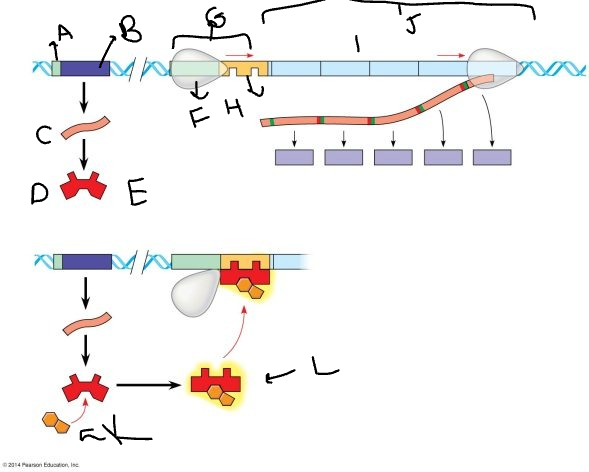
B:
regulatory gene
34
New cards
C:
mRNA
35
New cards
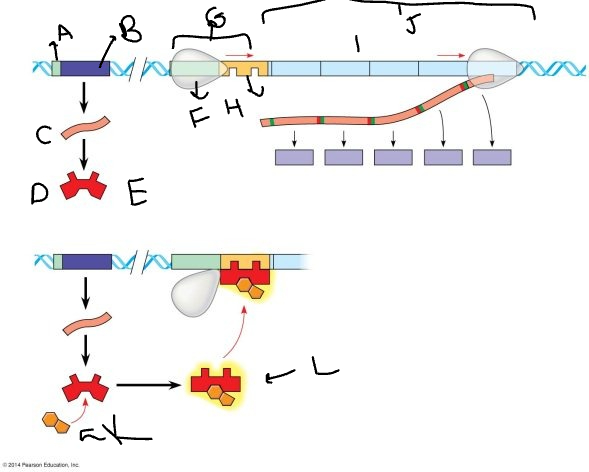
D:
protein
36
New cards
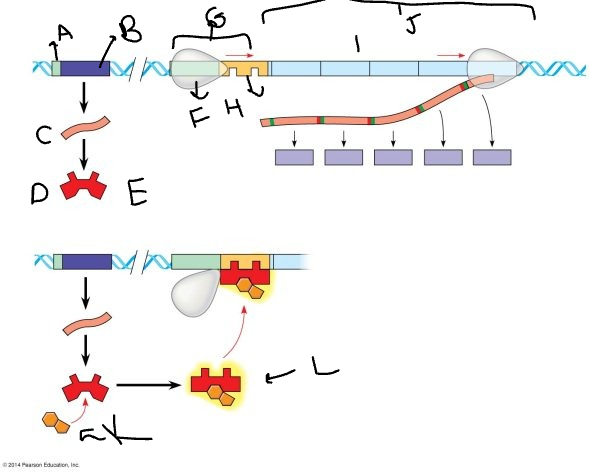
E:
inactive repressor
37
New cards
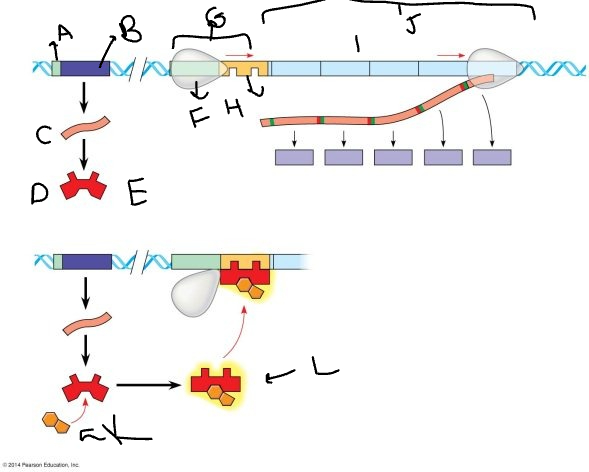
F:
RNA polymerase
38
New cards
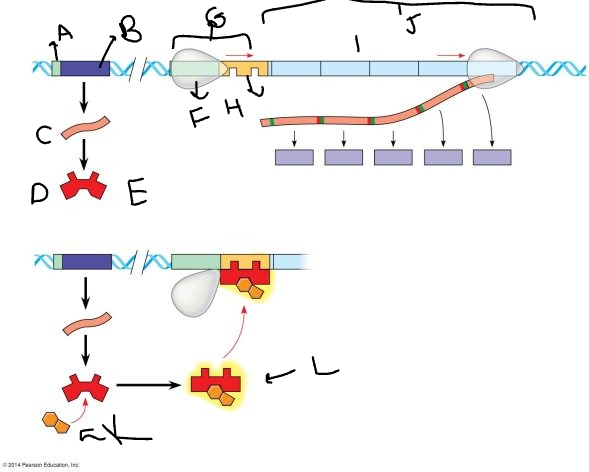
G:
promoter region
39
New cards
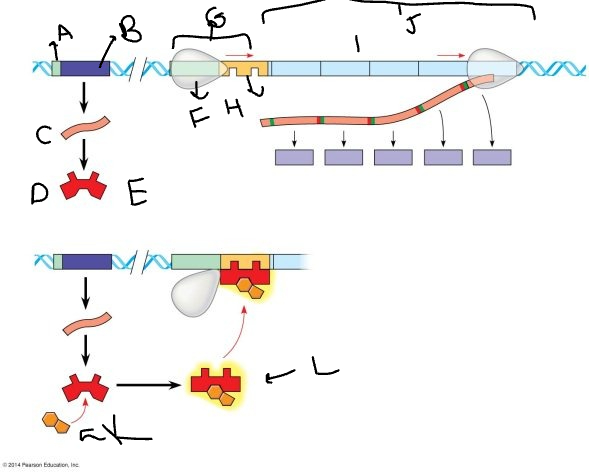
H:
operator
40
New cards
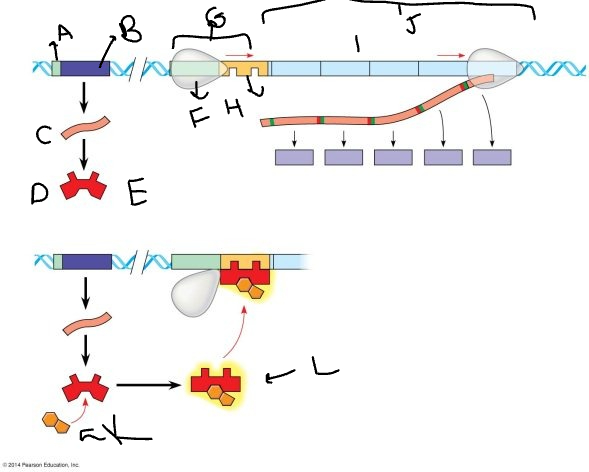
I:
genes
41
New cards
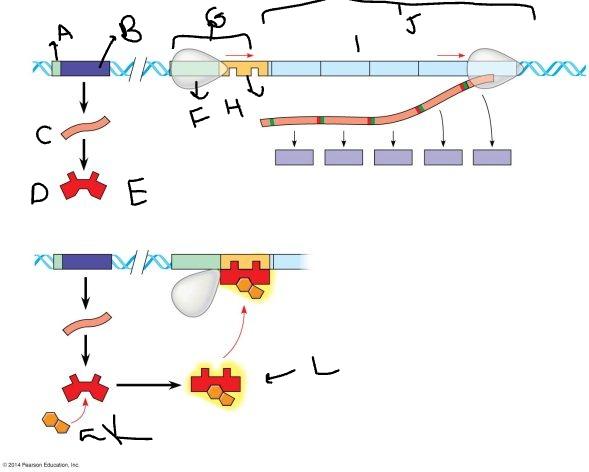
J:
*trp* operon
42
New cards
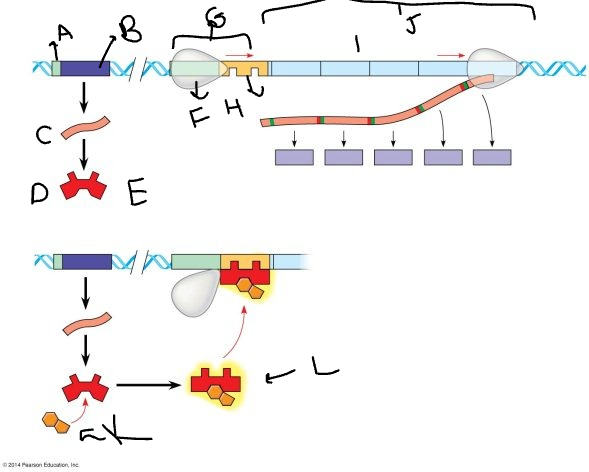
K
tryptophan molecule
43
New cards
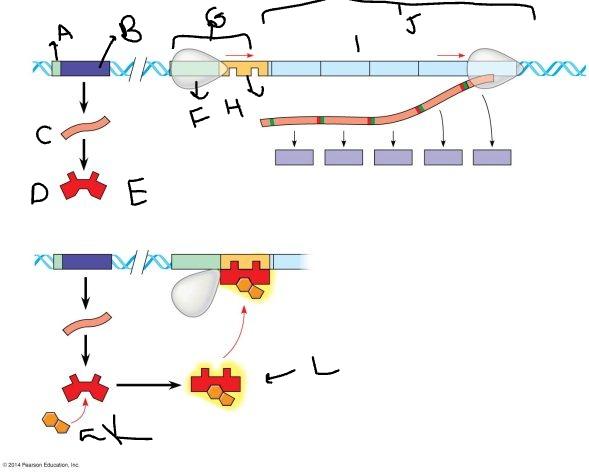
L:
active repressor
44
New cards
eukaryote cells are _______ according to the functions they perform:
differentiated
45
New cards
eukaryotic genes are turned on or off depending on:
the stage of development or environment factors
46
New cards
what did F. C. Steward find?
differentiated carrot cells could grow into adult cells that were identical to the parent plant
47
New cards
cells with the potential to grow into any cell:
totipotent
48
New cards
DNA is a single chromosome is how long?
4 centimeters long
49
New cards
DNA and histones proteins make up:
nucleosomes
50
New cards
each nucleosome consists of what?
a DNA segment and eight histone molecules
51
New cards
DNA packing prevents gene expression by:
prevening transcription proteins from accessing DNA
52
New cards
to initiate transcription, this must happen:
RNA polymerase must bind to the promoter region adjacent to a gene
53
New cards
what assists RNA polymerase in attaching to the promoter region?
transcription factors
54
New cards
RNA polymerase and transcription factors form a:
transcription initiation complex
55
New cards
these assist the transcription initation complex:
enhancers
56
New cards
these transcription factors bind to enhancer regions away from the gene:
activators
57
New cards
in order to bring the activators close to the gene, what has to occur?
the DNA bends due to a DNA-bending protein
58
New cards
RNA processing includes:
RNA splicing, addition of cap and tail
59
New cards
in the fruit fly, the differences between male and female are due to:
alternative RNA splicing
60
New cards
human RNA can be spliced in how many different ways?
7
61
New cards
how do the location of the cap and tail change the expression of the RNA?
changes the length
62
New cards
how is passage of mRNA through the nuclear envelope controlled?
molecules attached to pre mRNA prevent its passage into the cytoplasm until RNA processing is complete.
63
New cards
these molecules prevent translation if other molecules are not available:
inhibitory proteins
64
New cards
these molecules bind to sequences at the 5’ end of the mRNA, preventing the attachment of ribosomes:
regulatory proteins
65
New cards
enzymes in the cytoplasm attack this part of the mRNA molecule first:
poly-A tail
66
New cards
name three ways that proteins are modified to become functional:
cut into two or more chains, more molecules are attached, protein is transported to specific locations
67
New cards
how is insulin activated?
it is cut
68
New cards
what does breaking down proteins allow the cell to do?
this allows the cell to adjust the kinds and amount of proteins in response to changes in the enviornment
69
New cards
nuclear transplantation:
replacing the nucleus of an egg cell or a zygote with the nucleus of an adult somatic cell
70
New cards
early embryo is also called:
blastocyst
71
New cards
two kinds of cloning:
reproductive cloning and therapeutic cloning
72
New cards
describe reproductive cloning:
cloning of nonhuman mammals to create a genetically identical animal
73
New cards
how is cloning used in agriculture?
scientists are cloning farm animals with a desired set of characteristics. by cloning pigs with a certain set of genes, this allows them to provide organs for human transplant.
74
New cards
therapeutic cloning
cloning in which an embryo is produced, which produces embryonic stem cells. these stem cells can become any kind of differentiated cell
75
New cards
after fertilization of a fruit fly egg, what occurs?
different concentrations of proteins produced by the dividing cells determine polarity, which is the top, bottom, anterior, and posterior regions
76
New cards
what do the different concentrations of proteins during fruit fly fertilization activate?
they activate specific embryonic genes for segmentation
77
New cards
general regions of head, thorax, and abdomen are established by:
gap genes
78
New cards
specific formation of each body segment is established by:
pair rule genes
79
New cards
formation of body parts is established by:
homeotic genes
80
New cards
where are homeotic genes found:
in clusters on chromsomes
81
New cards
homeotic genes encode these proteins:
transcription factors
82
New cards
common sequence of 180 base pairs that codes for 60 amino acids found in the homeotic genes:
homeobox
83
New cards
what do the hox genes produce?
they code for a part in the homeotic transcription factors. this region can bind to a promoter, which turns a gene on and off
84
New cards
fruit flies scientific name
drosophila
85
New cards
growth of legs on the head instead of antennae:
antennapedia mutation
86
New cards
what are the stages of fruit fly development?
egg, larva, pupa, adult
87
New cards
define “gap” gene
Gap genes are a class of genes involved in the early development of an embryo. They are responsible for dividing the embryo into broad regions along the anterior-posterior axis. Gap genes are expressed in broad domains that overlap with one another, and their expression patterns help to establish the initial spatial coordinates of the embryo. Mutations in gap genes can lead to severe developmental defects.
88
New cards
define pair rule gene
Pair rule genes are a class of genes that are involved in the segmentation of the developing embryo in animals. They are responsible for dividing the embryo into a series of segments, each of which will give rise to a specific body part. Pair rule genes are activated in a striped pattern along the anterior-posterior axis of the embryo, and their expression is regulated by the maternal and gap genes. Mutations in pair rule genes can lead to defects in segmentation and patterning of the embryo.
89
New cards
Why is it likely that ancestors of fruit flies had 2 pair of wings? What gene causes them to have only one pair of wings?
It is likely that the ancestors of fruit flies had 2 pairs of wings because other insects, such as dragonflies and mayflies, also have 2 pairs. Evolution could have activated the gene responsible for one pair of wings, which is called Ultrabithorax (Ubx).
90
New cards
What are hox genes? What might occur if a hox gene mutated?
Hox genes are a group of genes that control the body plan of an embryo along the head-tail axis. They play a crucial role in determining the identity and positioning of body segments during development. If a hox gene mutates, it can cause developmental abnormalities, such as the formation of extra or missing body parts, or the transformation of one body part into another.
91
New cards
kruppul mutant flies description:
these flies are missing their thoracic segments
92
New cards
fushi tarazu mutant flies description:
missing every other segment
93
New cards
Ubx mutant flies description
extra pair of wings
94
New cards
Antp mutant flies description:
legs form where the antennae should be
95
New cards
What will happen to an embryo that doesn't have BICOID protein?
the embryo will develop without any anterior structures and will die
96
New cards
What will happen if BICOID is overexpressed?
the embryo will develop more anterior structures and less posterior structures, and eventually die
97
New cards
what kind of gene is HAIRY?
pair-rule gene
98
New cards
what kind of gene is EYELESS
homeotic gene
99
New cards
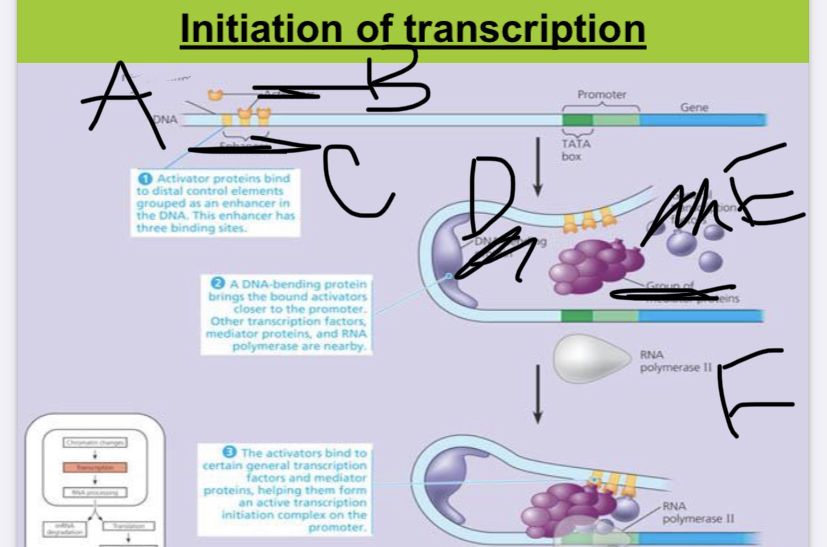
A:
distal control element
100
New cards
B:
activators