Photosynthesis Quiz
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Producers
capture sunlight and energy and use it to make organic molecules (food) from inorganic raw materials
They use some food for their own energy and body structures.
Provide food either indirectly or directly for consumes
Consumers
they get their own energy from building materials from producers
Decomposers
break down dead producers and consumer
Release inorganic molecules back into the environment
These molecules are later reused by producers
Photosynthesis
is the process where sunlight is captured to convert into chemical energy
Importance of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is important because its energy that is made is useful for living things.
Light dependent reactions:
they require light energy in order to occur.
Light-independent reactions:
these reactions are able to occur with the absence of light however they still require the energy that is captured from sunlight during light dependent reactions.
Calvin cycle
this is the second stage of photosynthesis where it uses energy from ATP and NADPH to convert CO2 into glucose or any other organic molecules.
LIGHT-DEPENDENT REACTIONS: (explain this process in your own words)
Light energy is captured by pigment molecules, mainly chlorophyll, within the thylakoids of chloroplasts. This energy is used to make (NADPH) also known as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate.
ETC: In this process a water molecule is split. The ETC transfers a high energy electron to NADP+ to make a proton a gradient across a membrane. When the water molecule is split oxygen is released into the environment. The energy that is being stored in the gradient is used to create ATP.
ATP Synthesis: the energy that is released from the flow of electrons is used to convert ADP into ATP. This process is called chemiosmosis.
Water Splitting: in order to refill the electrons lost in the chain, a water molecule is split in a process called photolysis. During this
Oxygen is released into the environment
(H+) protons are piling up within the thylakoid lumen
LIGHT-INDEPENDENT REACTIONS (AKA CALVIN CYCLE (explain this process):
Location: The Calvin Cycle occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast.
In the calvin cycle it uses the energy from ATP and the energy from electrons that are being carried by NADPH in order to convert CO2 from the environment as glucose. This is a process called carbon fixation. (it will first convert it into a 3 carbon molecule known as PGA)
The calvin cycle uses the energy from ATP and NADPH to build simple sugars and other organic molecules.
Carbohydrates aren't just used to build up simple sugars but they’re also important for the function and growth of the plant.
With the help of carbohydrates photosynthesis is able to use that to create other types of molecules.
Examples: Lipids: these are fats and oils that are used to store energy and for cell membrane building. (fatty acids: used for energy storage and insulation)
Proteins: they are important for building tissues and other functions in plants. (alanine: involved in protein structure and metabolisms, glutamate: used in creating proteins).
Carbs: starch: used for long term energy storage, cellulose: found in plant cells wells which provides strength and rigidity and sucrose: used for transporting sugars throughout the plant.
General equation of photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2. This means that the reactants, six carbon dioxide molecules and six water molecules, are converted by light energy captured by chlorophyll (implied by the arrow) into a sugar molecule and six oxygen molecules, the products.

THE ROLE OF ATP IN PHOTOSYNTHESIS:
ATP is the energy currency of the cell
It stored energy in the form of chemical bonds
When the bonds are broken energy is released and is used to allow chemical reactions in the cell occur
ATP is produced during the light dependent reactions its then later used in the Calvin Cycle to convert CO2 into glucose
In summary the role of ATP in photosynthesis is to store and release energy and to build organic compounds from carbon dioxide.
ROLE OF NADPH IN PHOTOSYNTHESIS:
NADPH is produced during the light dependent reactions and then it is used during the Calvin cycle to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
NADPH donates an electron to the Calvin cycle which reduces carbon dioxide in order to create it into other organic molecules like glucose
In summary, the purpose of NADPH is to donate electrons during the Calvin cycle; this allows the cell to reduce carbon dioxide and to be incorporated into other organic molecules.
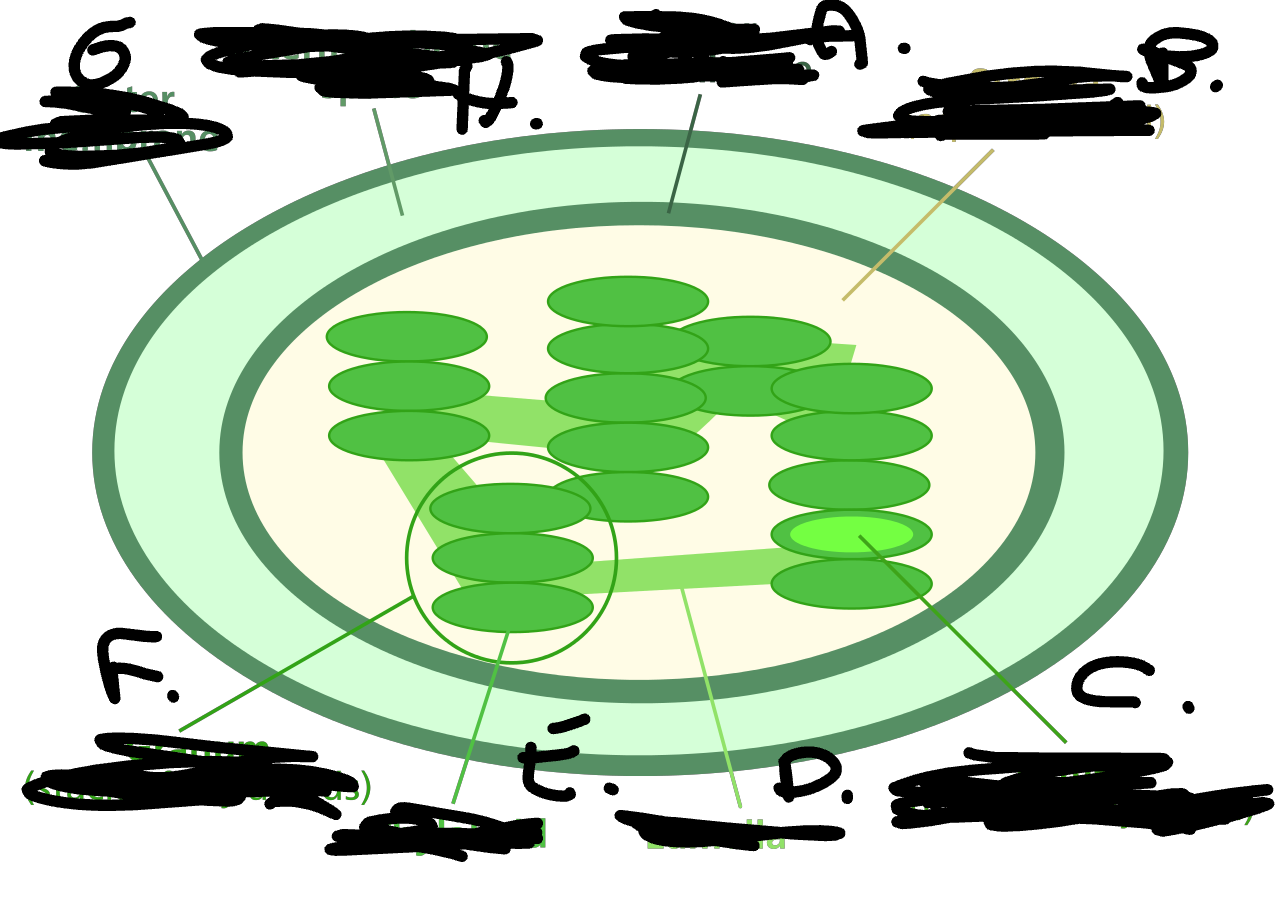
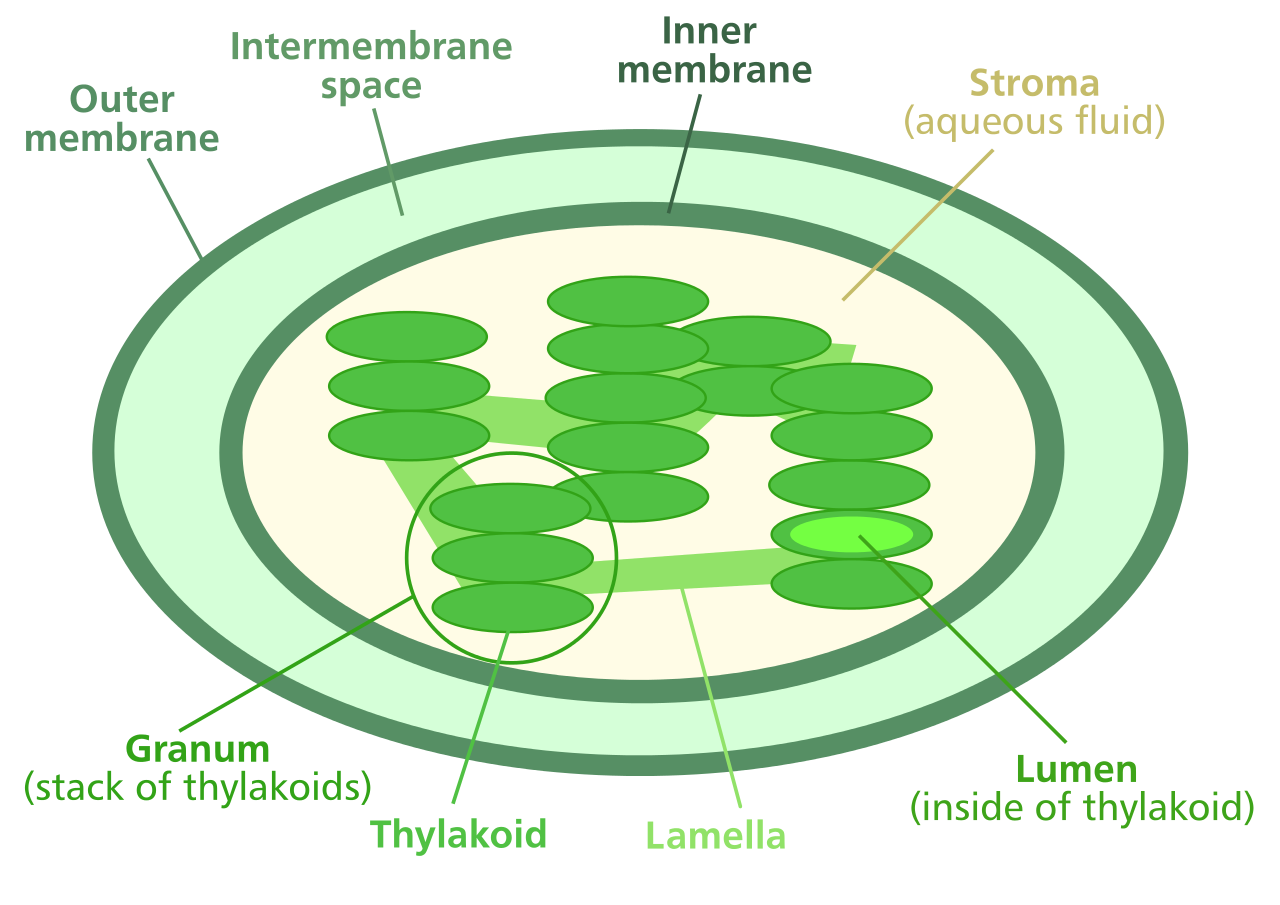
A. Inner Membrane
B. Stroma
C.Lumen
D.Lamella
E. Thylakoid
F.Granum
G.Outer membrane
H. Intermembrane space
Fluorescence
is the emission (release) of light of a longer wavelength (lower energy) than the absorbed light.
Two important points about pigment molecules and light (explain)
Firstyly, photosynthesis begins with sunlight which is made up of tiny packets of energy called photons. When a photon hits the pigment molecule the pigment molecule will absorb the energy from the photon. This absorbed light energy will make an electron “excited.” Before the lights hit the electron the electron is a low energy state. However the absorbed light energy boosts the electron to a higher energy level. (not all light can excite electron in plant pigments only specific wavelengths of light (like blue and red)
Secondly, the energy level of the absorbed photon must be equal to the energy difference between the ground state and excited state of the electron. If it's not equal the photon won't be able to be absorbed by the pigment.
There are three possible outcomes for the excited electron in the pigment molecule. This can depend on the environment that the pigment molecules are in as well as any other molecules that are present.
First outcome, the excited electron will return back to its ground state (low energy level). The energy that is being released is thermal energy or fluorescence. The molecule can lose a small amount of this energy through vibrations or collisions with other molecules. This lost energy is released as heat (thermal energy). Once it loses some energy the electron returns back to its ground state once it returns to its ground state the molecule emits a new photon. This photon has lower energy compared to the original absorbed photon because the molecule lost some of its energy as heat.
Second outcome, the excited electron is now going to be transferred to the next pigment molecule. Now that it's transferred to the next pigment molecule the high electron in this pigment molecule is excited however the original electron in the first pigment molecule is back to its ground state. In order for this to happen the two molecules must be very close to one another and aligned precisely.
Third outcome, the excited electron can be transferred to an electron acceptor molecule. (one of the most important steps in photosynthesis)
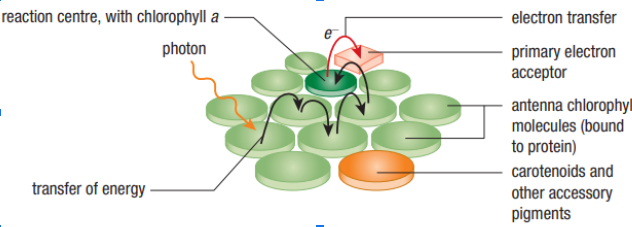
Antenna complex:
group of proteins and pigment molecules that are embedded within the thylakoid membrane of plants and other organisms. It's then able to capture that energy and transfer it to chlorophyll a molecules in the reaction center.
Reaction center:
is the central and most important pigment that is responsible for converting light energy into chemical energy.
Absorption spectrum:
its a visual representation of how much light a pigment absorbs at different wavelengths.
Action spectrum:
it shows the overall rate of photosynthesis at each wavelength.
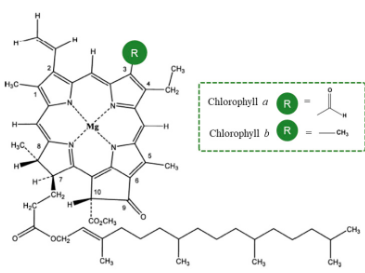
The most dominant chlorophylls are
chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b
structure of chlorophyll
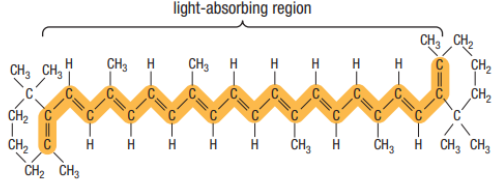
Carotenoid strutcure
During photosynthesis chlorophyll a becomes…
oxidized and donates an electron to a primary electron acceptor.
Both carotenoids and chlorophyll b are
able to absorb light energy from sun just like chlorophyll a however they can’t directly use this energy for photosynthesis themselves.
accessory pigments
they capture the light energy and then transfer it to chlorophyll a molecules in order to use that energy for the process.
structure of a leaf in depth
There are three process that contribute to the proton gradient in photosynthesis
Plastoquinone: Plastoquinone shuttles electrons between PS2 and PS1. During this it will pick up electrons from the stroma and release them into the thylakoid lumen.
Water splitting: the splitting of water in PS2 releases protons into the lumen.
NADPH formation: since the electrons are being used up from the stroma to reduce NADP+ to NADPH a proton is also being used for each electron. This will decrease the concentration of protons in the stroma and increase it instead in the lumen.
Photorespiration
this is where an enzyme which is responsible for fixing CO2 will accidentally grab O2 instead of CO2
why is photorespiration less efficient
this is because it uses the energy (ATP) that could’ve been used to make sugars. It also causes plants to grow slower and produce fewer fruits and seeds.
Bundle sheats
bundle sheaths are separated by mesophyll cells that separates them from air spaces in the leaf. This separation prevents RuBP from O2 which will reduce the rate of photorespiration. It contains RuBP
C4 cycle
In this cycle CO2 combines with PEP to make oxaloacetate this will be then reduced to malate by electrons that were transferred from NADPH
Malate
released out of the bundle sheaths
Chloroplasts
this is the organelle that carries out photosynthesis
it absorbs blue light and red light
it reflects green light this why plants appear green
mesophyll cells
captures CO2 from the environment.