waves
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
what is a transverse wave
a wave where vibrations occur perpendicular to the direction the wave is traveling
eg electromagnetic waves, water waves
What is a longitudinal wave?
a wave where vibrations happen parallel to the direction the wave is traveling eg. sound waves
define amplitude
maximum distance between the peak or trough of a wave and it’s equilibrium point
define wavelength
the distance from one point ona. wave to the same point on the next wave
define frequency
number of waves per second
measured in hertz Hz
define the period of a wave
time taken to complete one wave cycle
the equation for wave speed
wave speed = frequency x wavelength
equation for wave frequency
frequency = 1/time period
What properties do all waves have in common?
they can be reflected and refracted
transfer energy
similarities between a transverse and a longitudinal wave
all transfer energy
can be reflected and refracted
differences between a transverse and a longitudinal wave
transverse waves vibrate at right angles to the direction of travel
longitudinal waves vibrate in the same direction as the direction of travel
what is the doppler effect?
the change in frequency and wavelength caused by relative movement of the source of wave or observer
explain why the sound of a loud object moving away from a person at a constant speed decreases in pitch
- Due to the Doppler effect
- Wavefronts emitted at constant frequency by object
- Wavefronts arrive at person further apart than when they were emitted
- Distance between wavefronts is the wavelength
- Wavelength increasing
- Wave speed = frequency × wavelength
- Speed of waves is constant
- As speed is constant and wavelength has increased, frequency must decrease
- Decrease in frequency = decrease in pitch
- e.g. when an ambulance drives past the siren decreases in pitch
Give an example of the Doppler effect in light waves
- Light from distant planets looks red (red-shifted)
- Because planets are moving away from Earth
- wavelength increases and therefore moves to the red part of visible light spectrum
What do all EM waves have in common?
All transverse waves
- All transfer energy
- All travel at the same speed (speed of light) in a vacuum
- Can be reflected, refracted and diffracted
How are x-rays and gamma rays similar?
Both short wavelength EM waves
- Carry lots of energy per second
How do x-rays and gamma rays differ?
- X-rays are made when electrons moving at high speeds are stopped
- Gamma rays are released from unstable nuclei
- Gamma is more penetrative
- Gamma has shorter wavelength
What is the difference between the wavelength of a radio wave and the wavelength of a gamma wave?
The wavelength of a radio wave is the longest, whereas a gamma wave’s the shortest
What is the difference between the frequency of a radio wave and the frequency of a gamma wave?
Radio waves have the lowest frequency, but gamma waves have the highest frequency
What is the difference between the energy of a radio wave and the energy of a gamma wave?
radio waves have the lowest energy but gamma waves have the highest energy
Describe the differences between red and violet light.
Red light have a longer wavelength, but violet light has a shorter wavelength.
Red light have a lower frequency but violet light has a higher wavelength
Red light emits lower energy, violet light emits higher energy
Which EM wave can cause internal heating of body tissue
Microwave
Which EM wave causes burns
Infrared radiation
Which EM wave can cause skin cancer and blindness
UV
How can exposure to UV rays be reduced
Wear sunglasses
Cover skin with clothes or sunscreen
Stay in the shade
What are the dangers of X-rays and gamma rays
ionising radiation
mutation leading to cancer
How can exposure to gamma rays be reduced
Wear protective lead clothing
Describe the properties of light waves.
Transverse waves
- Vibrations occur perpendicular to the direction the wave is travelling
- Transfer energy
- Can be reflected, refracted, diffracted
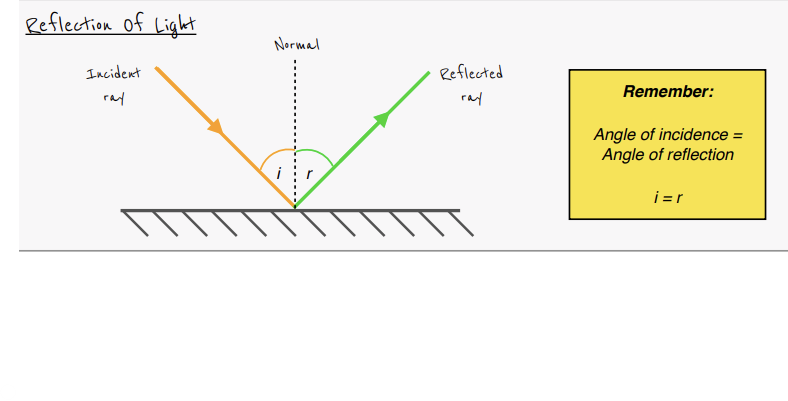
What is a normal line?
A line drawn perpendicular to the mirror
What is the angle of incidence
Angle between the normal and the incident ray
What is the angle of reflection?
Angle between the normal and the light ray reflecting off the mirror
What is the law of reflection?
- Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection
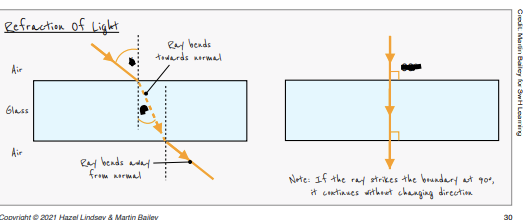
What is refraction?
A change in direction of waves when they travel across a boundary from one medium to another
Caused by a change in the wave’s speed.
Describe how a light ray changes direction when it enters and leaves a glass block
Bends towards the normal as it enters the block
Bends away from the normal as it leaves the block
what is the refractive index
- The extent to which light is refracted when it enters a medium
- More dense medium = greater refractive index = greater refraction of light
Give the equation linking refractive index (n), angle of incidence and angle of refraction
n= sin i / sin r
What happens when light passes from air to glass (i.e from less dense to more dense medium)?
- Light ray slows down
- Angle of refraction less than angle of incidence
- ray bends towards normal
describe an experiment to determine the refractive index of a glass block.
- Use light box to produce beam of light
- Use a ruler, pencil and paper to trace path of light
- Use protractor to measure angle of incidence and angle of refraction
- Repeat for different angles of incidence
- Repeat the same angles of incidence at least three times
- Use n = sin i / sin r to calculate average value of n
- Plot a graph of sin i against sin r
- Calculate n from gradient
define critical angle
- Angle of incidence beyond which rays of light are totally internally reflected
Define total internal reflection (TIR)
- When the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle
- All light is reflected, none is refracted
give the equation linking the critical angle with the refractive index
sin c = 1/n
State the conditions required for total internal reflection to happen
- Medium must be from more dense to less dense
- Angle of incidence > critical angle
Explain the relationship between refractive index and critical angle
- Larger refractive index means smaller critical angle
- Total internal reflection occurs when angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle
- Total internal reflection more likely to occur when refractive index is larger
how to optical fibres work?
- Total internal reflection
- Core of fibre made out of glass with high refractive index
- Cladding is made out of glass with lower refractive index
- Light entering core is at an angle greater than the critical angle so light is reflected
give examples of the use of optical fibres
- Endoscope - used in keyhole surgery
- Communication - more information sent per second compared to old copper wiring
Describe the properties of sound waves
- Longitudinal waves
- Transfer energy
- Can be reflected, refracted and diffracted
Describe how a sound wave moves through the air
- Vibration of air molecules
- Longitudinal wave
- Regions of compression and rarefaction
- Directions of vibration and propagation are parallel