Civics Grade 10
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Civics
The study of the rights citizens of countries have as well as the responsibilities they need to uphold.
Citizenship
a legal status and relation between an individual and a country, granting specific rights and duties.
The Divine Right of Kings
The belief that the king/queen of a country was chosen by God, and can do no wrong. This meant the ruler could do whatever they wanted because everyone believed God chose them.
The Magna Carta
A document stating laws and rights given to citizens, putting into place the law that every person has the right to a trial, and everyone no matter their status has to follow the law.
History of Democracy
A form of government which depends on the will of the people. The word democracy comes from the Greek words "demos", meaning people, and "kratos" meaning power; so democracy is "power of the people"
Indirect Democracy
A form of democracy in which citizens vote for representatives who make decisions on our behalf.
Direct Democracy
A form of government in which people vote on policies and laws directly.
Propaganda
Information like facts, rumours, half-truths, or lies used to promote a political cause and influence public opinion.
Rights and Responsibilities
Rights are freedoms we have that are protected by our laws, while responsibilities are duties or things that we should do, to be a good citizen
Presidential Democracy
This is where the head of government (president) is elected independently by the people or through an electoral college.
Parliamentary Democracy
This is where the head of government (prime minister) is responsible to and elected by the legislature or parliament
Monarch
a ruler king or queen) who rules a country usually by inheritance right, for their entire life.
Totalitarian
A system of government that is based on the total control over a country, and its citizens rights, beliefs, and opinions. This is normally done by censorship and propaganda. E.g. Nazi Germany and North Korea
Dictatorship
A government where only one person is the leader and makes all the rules and decisions without input from others. E.g. Hitler in Nazi Germany
Oligarchy
This is a form of government in which a small group of people who are normally rich, privileged and honoured, have power over a country and make all the decisions. E.g. South Africa during apartheid.
Theocracy
This is a system of government where a religious leader like a priest leads a country and is believed to be a god or chosen by god. E.g. The Pope rules Vatican City
Anarchy
A condition of lawlessness or political disorder when there’s an absence of governmental authority. E.g. The Coupe in Trinidad 1990
Absolute and Constitutional Monarchy
A system of government where the ultimate authority to run the state is in the hands of a king, dictator, or monarch who rules by a system like the divine right.
vs
A system of government where a king or queen serves as head of state, but their power is limited by a constitution and a legislature, meaning they don't rule absolutely
Revolution
A forcible overthrow of a government, in favour of a new system. E.g The French Revolution
Republic
a country where the leader is their elected representatives, and which has an elected president rather than a monarch. E.g. The Republic of Trinidad and Tobago
Municipal Government
The government in charge of a specific area or city and things like, libraries, snow removal, garbage collection, water and transportation. The leader of a municipal government is a Mayor
Provincial Government
The government in charge of their specific province or territory, and things like education, health care, natural resources, and licences. The leader of a provincial government is a Premier.
Federal Government
The government in charge of the nation's laws and things in their country like military, international relations, immigration, money and postal service. The leader of a federal government is a President or Prime Minister.
Mayor
The leader of the Municipal Government
Premier
The leader of the Provincial Government
Prime Minister/President
The leader of the Federal Government
3 Branches of the Federal Government
Legislative, Executive, and Judicial
Legislative Branch
The legislative branch is the part of the government responsible for making laws. In this branch, you can find the House of Commons, Senate, and the King/Queen.
Executive Branch
The executive branch consists of the President/Prime Minister, and his Cabinet (Ministers & MP’s). This branch is responsible for enforcing the laws of the land.
Judicial Branch
The judicial branch, which includes the Supreme Court, is in charge of deciding the meaning of laws and whether a law follows the rules of the Constitution.
How a law is created
House of Commons/Lower House
Anyone can propose a new law(bill) to the House of Commons
MPs (Members of Parliament) will review the bill with the Speaker of the House (leader) and decide to either veto it or pass it to the Senate.
Senate/Upper House
The Senate consists of senators chosen by the leader and can stay until their 75
Once again, the bill will be debated by the senators, and if it’s not vetoed, it will be passed on to the King/Queen.
King/Queen
The bill will be reviewed by the Governor General, a representative of the King/Queen
If the bill is not vetoed, it will be given the Royal Assent and turned into a law.
Bill
A draft of a proposed law presented to parliament for discussion
Royal Assent
Title given to a bill when its been passed and turned into a law by the King/Queen
Veto
The rejection of a decision or proposal of a new law.
Amendment
A change or addition made to a bill proposal.
Name and explain Lady Justice’s symbols
Blindfold - represents that everyone has a right to be treated fairly and have justice granted, no matter their status, background, or appearance.
Scale - symbolizes the equality of all and the weighing of evidence, arguments and facts before reaching a verdict
Sword - represents the enforcement of justice and the power of the law. It also shows the justice system protects people and their rights.
Book of Law - represents the legal knowledge, and the written laws are the foundation and core of the entire justice system
Toga - symbolizes the history of the law since in ancient Greece philosophers commonly wore these robes, symbolizing intelligence and wisdom in the law
3 Pillars of Justice
Fundamental Freedoms – Basic rights like free speech, religion, and privacy that protect individuals.
The Rule of Law – Laws apply equally to everyone, ensuring fairness and accountability.
The Common Good – Justice serves society as a whole, promoting peace, stability, and well-being.
Attempted 1990 Coup
The Jamaat al Muslimeen attempted to overthrow the government of Trinidad and Tobago on Friday, 27 July 1990. Over six days, Jamaat al Muslimeen, a radical extremist Islamist group led my Abu Bakr, held hostages (including Prime Minister A. N. R. Robinson) at the Red House and the headquarters of Trinidad and Tobago Television (TTT). 24 people were killed and A.N.R Robinson was shot in the lower right leg. On 1 August, they surrendered and were charged with treason, but were released shortly after.
First past the post system
A system where the first electoral party in an election to reach a certain amount of votes or cross a line/post of votes is the winner. E.g. horse racing
Manifesto
A written statement declaring intentions and aims to bring change to the world, issued especially before an election by a political party or candidate.
Constituency
A group of voters in a specific area who elect a representative to a legislative body, like Parliament or a local council.
Local vs National Elections in Trinidad
Elections within a city or town to select office-holders in local government, such as mayors and councillors.
vs
Elections where citizens of an entire country vote for their representatives in government, typically at the federal level.
Federal Elections
These are Country-wide and elect Members of Parliament (MPs) to the House of Commons. The political party with the most MPs forms the federal government (led by the Prime Minister).
Provincial Elections
These are Province-wide and elects the premier and the leading party forms the provincial government
Municipal Elections
These are City/Town-wide and elect a Mayor and City Councillors. There are no political parties, so most candidates run independently.
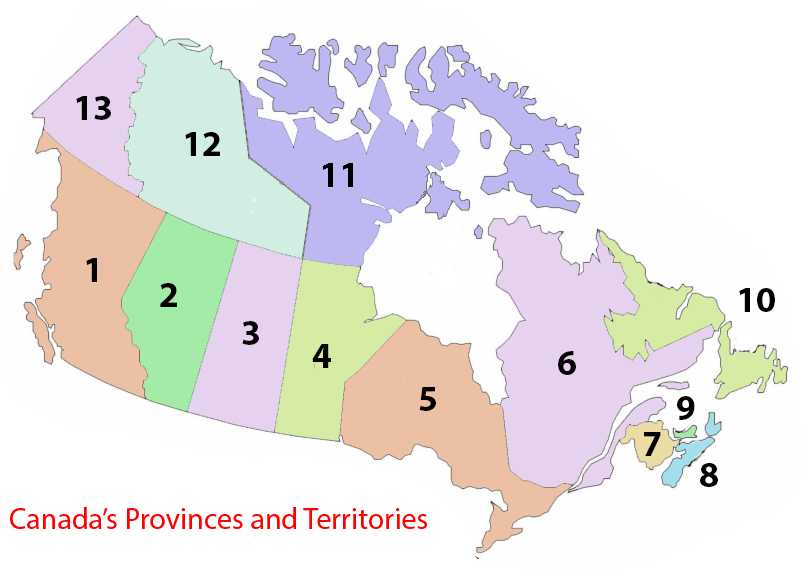
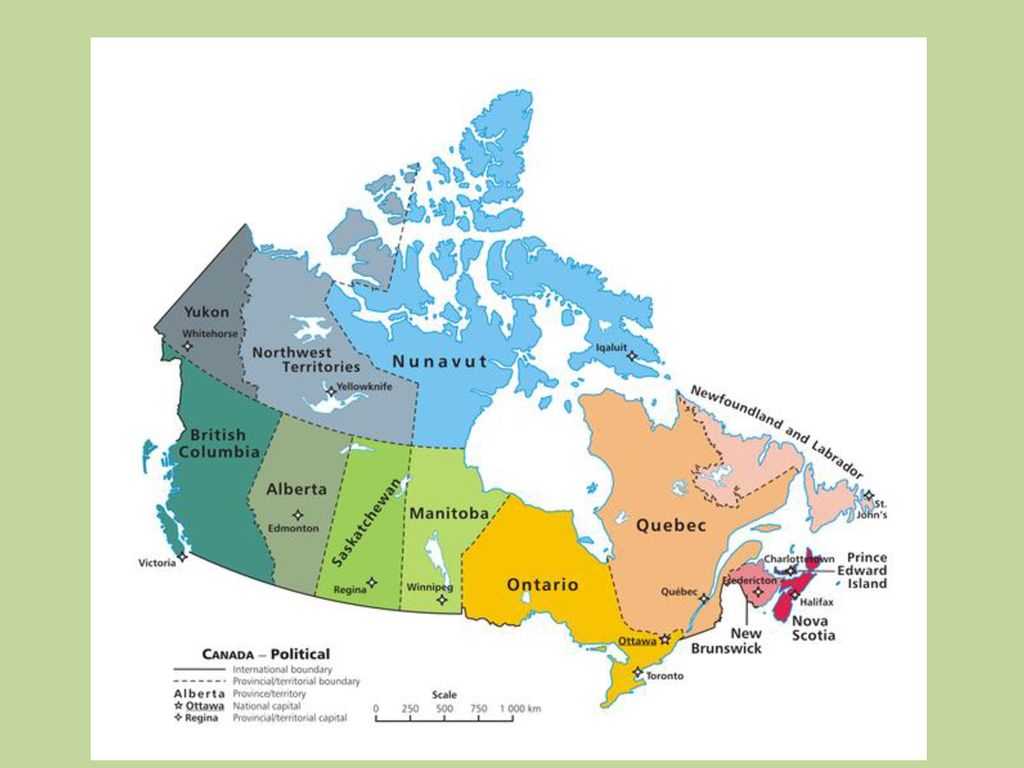
Name all the provinces and territories of Canada
If you were running for president, what issues would you fix?
Long cafeteria lines waste students’ break time.
Solution: Add an extra register and staff member to speed up service.
A single highway in Diego Martin causes heavy congestion and long commutes.
Solution: Build 2–3 additional highways and improve public transportation.
The justice system is slow and ineffective.
Solution: Implement crime prevention programs and use technology to speed up court cases.
Many public schools lack proper learning conditions.
Solution: Provide air conditioning, necessary supplies, and advanced technology.
Poor road conditions cause accidents.
Solution: Use Pitch Lake resources to repair unsafe roads and enforce traffic laws for safer roads.