27: Cartilage & Bone
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
Cartilage
Bone
What two things make up firm CT?
Diffusion
How do avascular cartilage receive nutrients?
Hyaline cartilage
Elastic cartilage
Fibrocartilage
What are the three type of cartilage
hyaline cartilage
most prevalent type of cartilage:
hyaline cartilage
identify the cartilage:
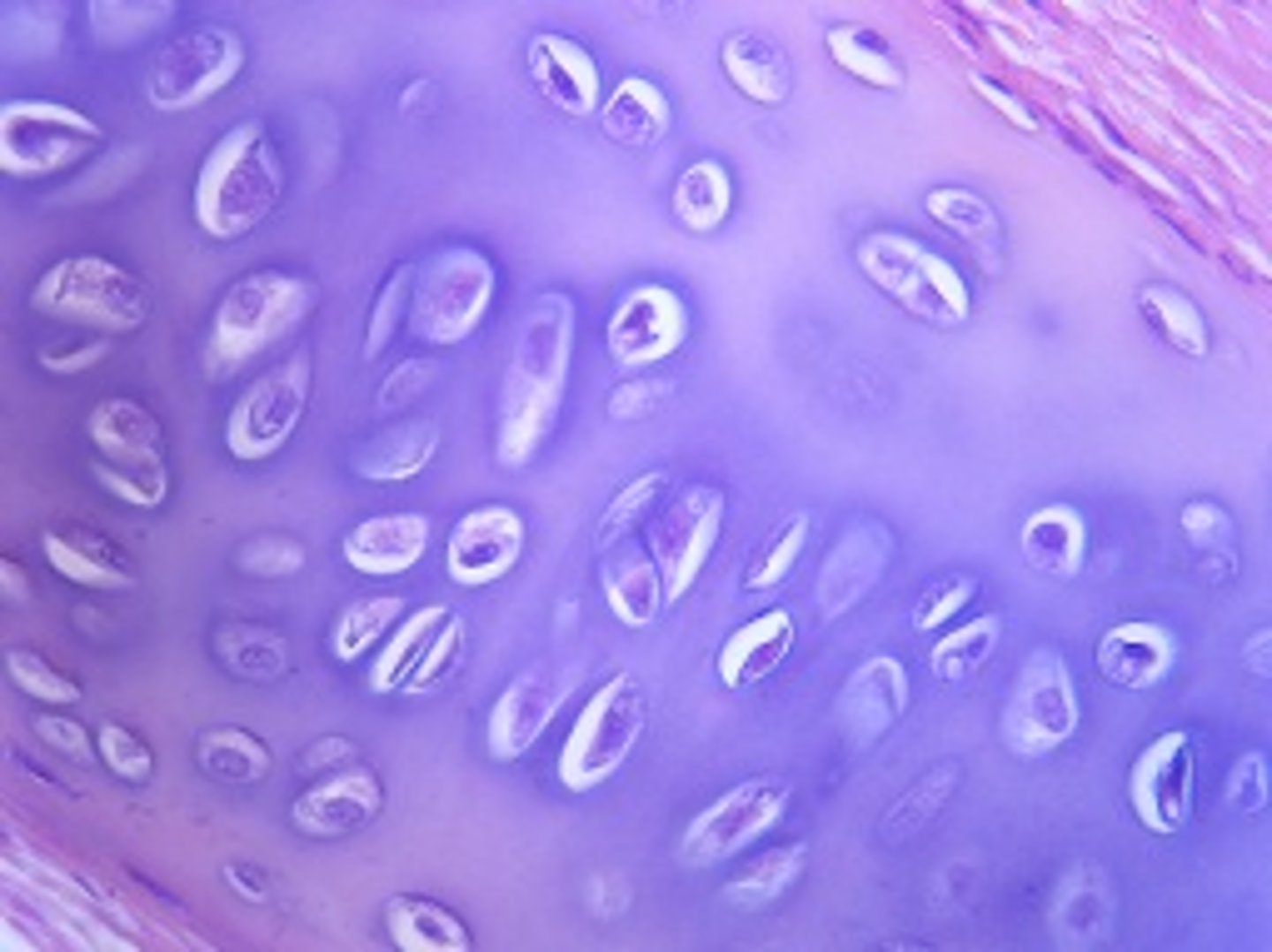
hyaline cartilage
identify the cartilage:
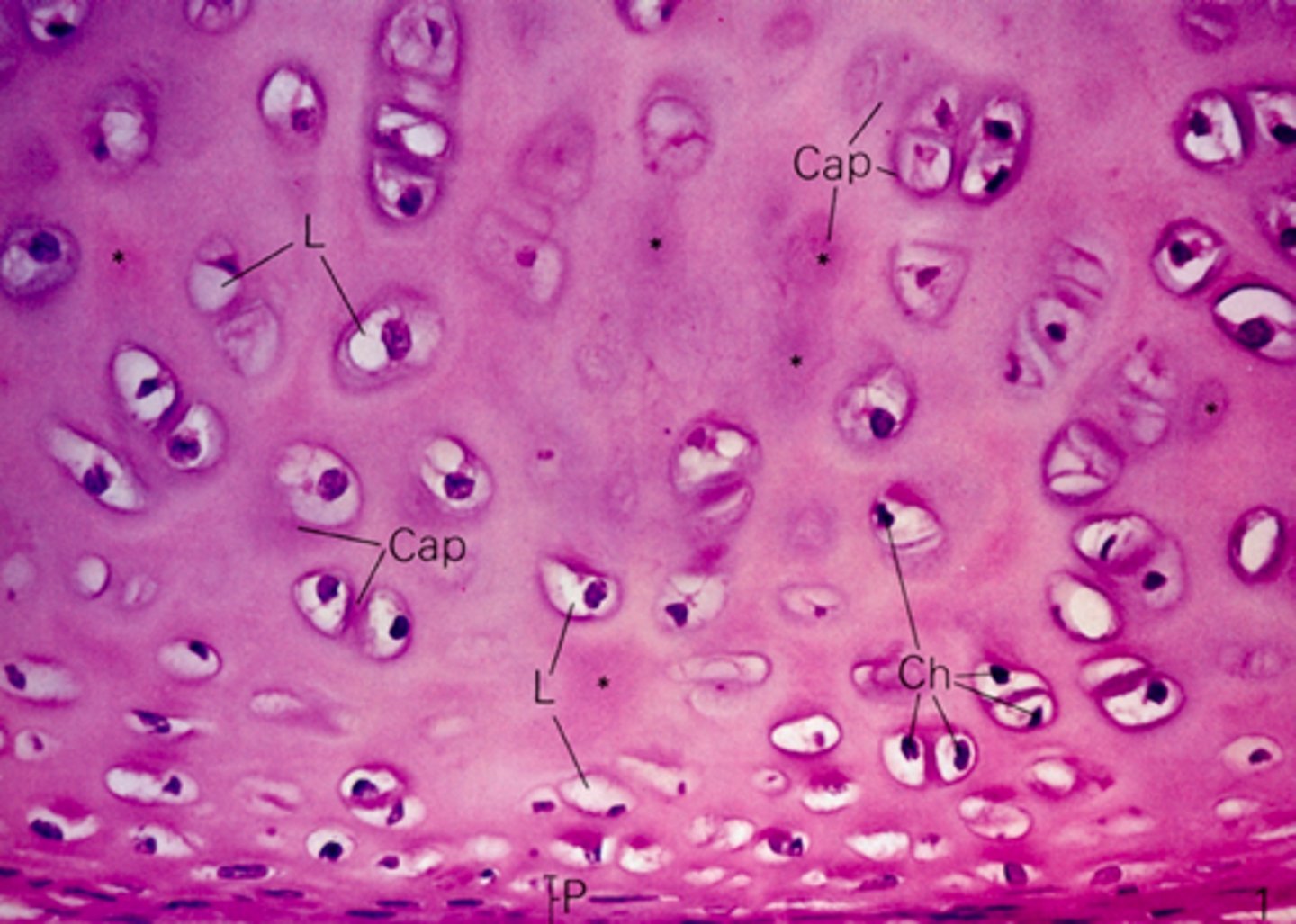
hyaline cartilage
identify the cartilage:
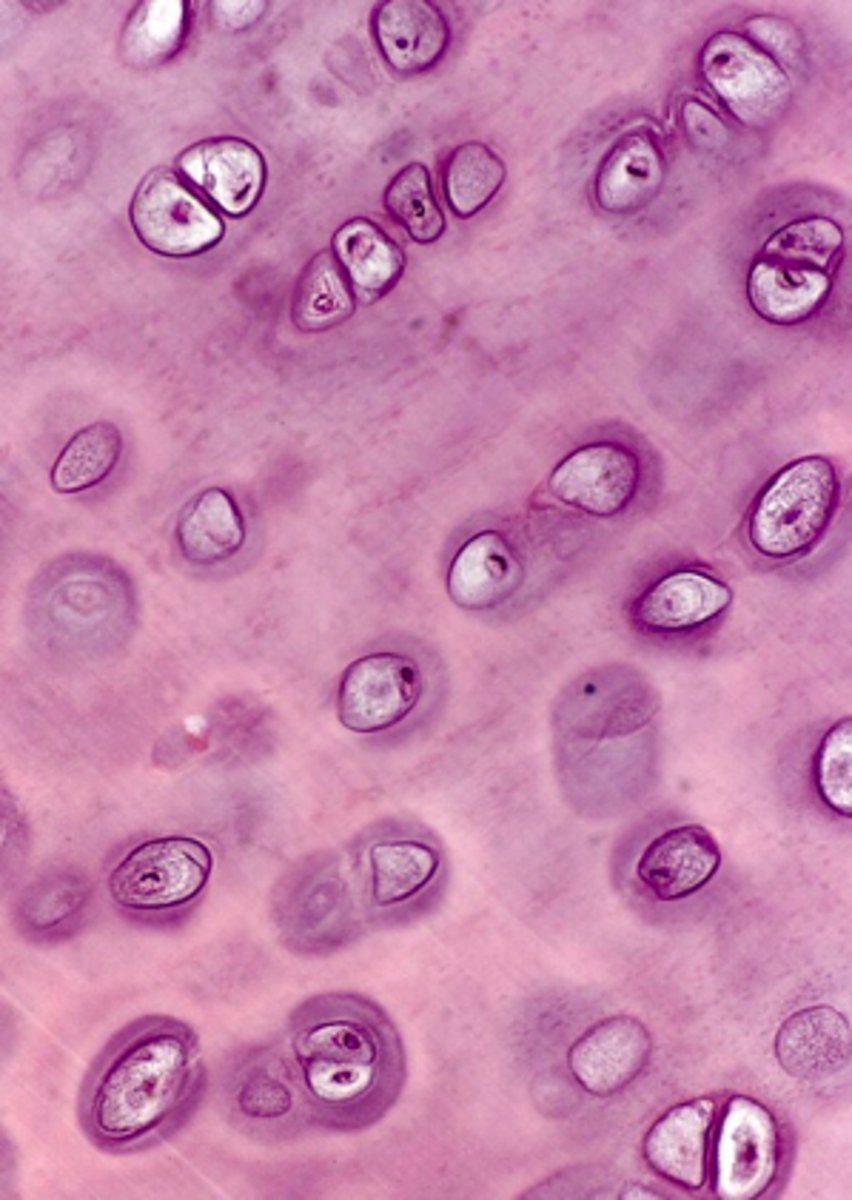
hyaline cartilage
identify the cartilage:
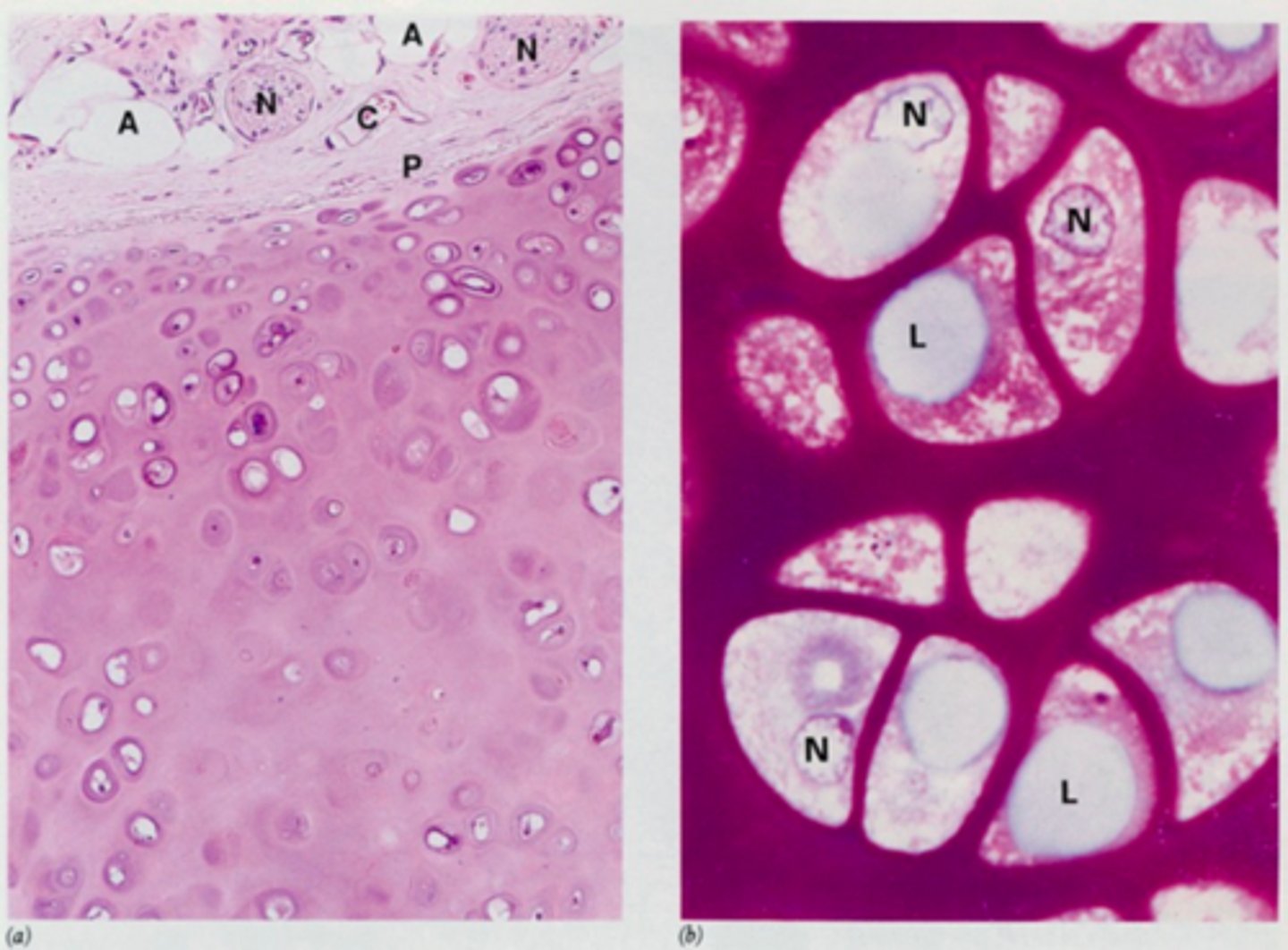
hyaline cartilage
what type of cartilage is located at all articular joint surfaces?
Hyaline cartilage
what type of cartilage is located in the respiratory system?
hyaline cartilage
what type of cartilage is found in fetuses?
hyaline cartilage
what type of cartilage are costal ribs made of?
elastic cartilage
-similar to hyaline but also contains elastic fibers
elastic cartilage
what type of cartilage is found in the external ear?
elastic cartilage
what type of cartilage is the Eustachian tube made of?
elastic cartilage
what type of cartilage is the Layrnx (epiglottis) made of?
fibrocartilage
what type of cartilage are the vertebral discs (IVD) made of?
fibrocartilage
-hydrated (resists compression) but also contains collagen I so also high in tensile strength
fibrocartilage
what type of cartilage do the temporomandibular joints contain?
fibrocartilage
what type of cartilage does the pubic symphysis contain?
Fibrocartilage
What type of cartilage is the meniscus made of?
false
t/f: all cartilage has its own vacsular supply
true
t/f: all cartilage is aneural
type II collagen
what type of collagen is abundant in all cartilages?
Hyaline cartilage
What cartilage has the following functions:
Resist compression
Cushioning
Hyaline cartilage
What cartilage has collagen II and aggrecan in it's matrix?
Elastic cartilage
What type of cartilage has the following function:
Flexible support
Elastic cartilage
What type of cartilage has collagen II, aggrecan, and elastic fibers?
Fibrocartilage
What type of cartilage has the following function:
Resist compression
Resist shearing forces
Fibrocartilage
What type of cartilage has collagen II, collagen I, versican, and aggrecan?
Hyaline cartilage (except for articular cartilage)
Elastic cartilage
What type of cartilage has a presence of perichondrium
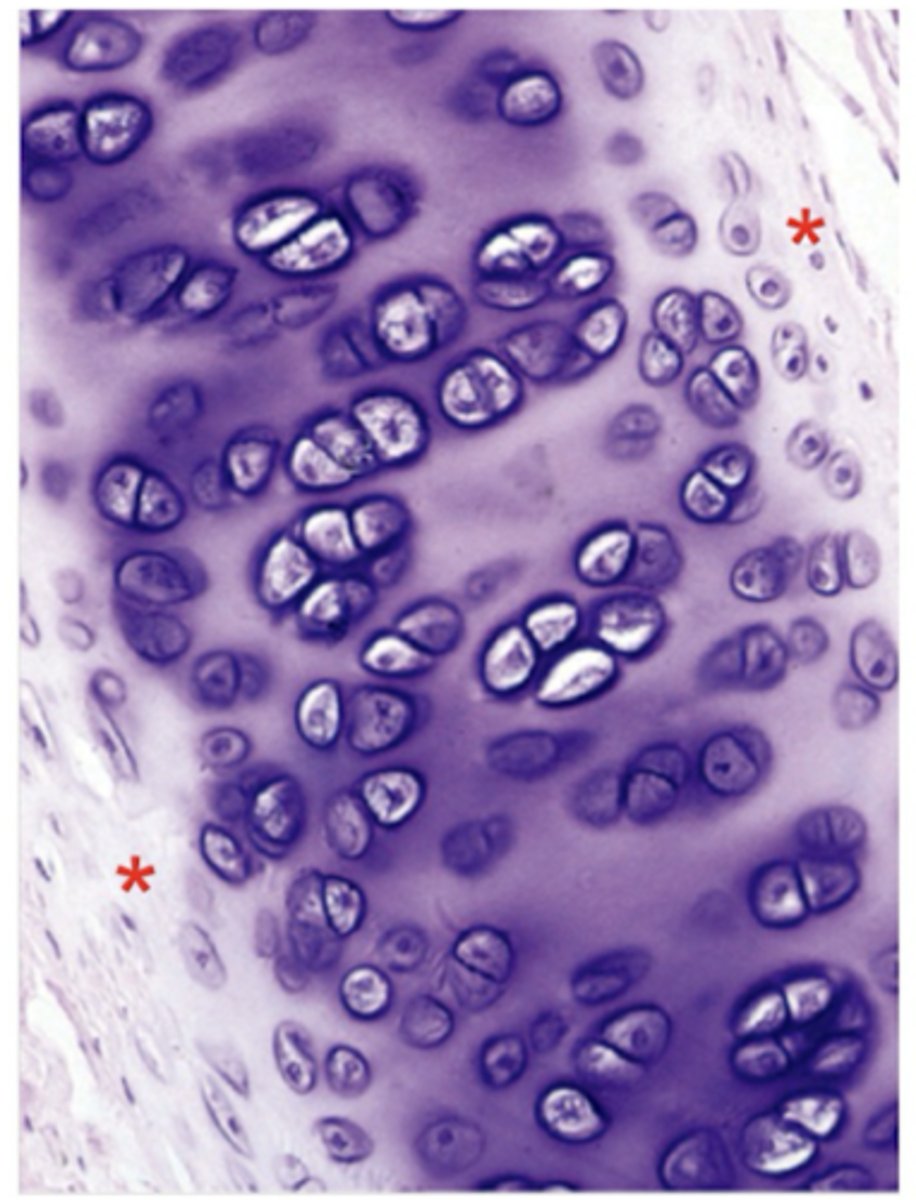
isogenous groups
identify the pink box:
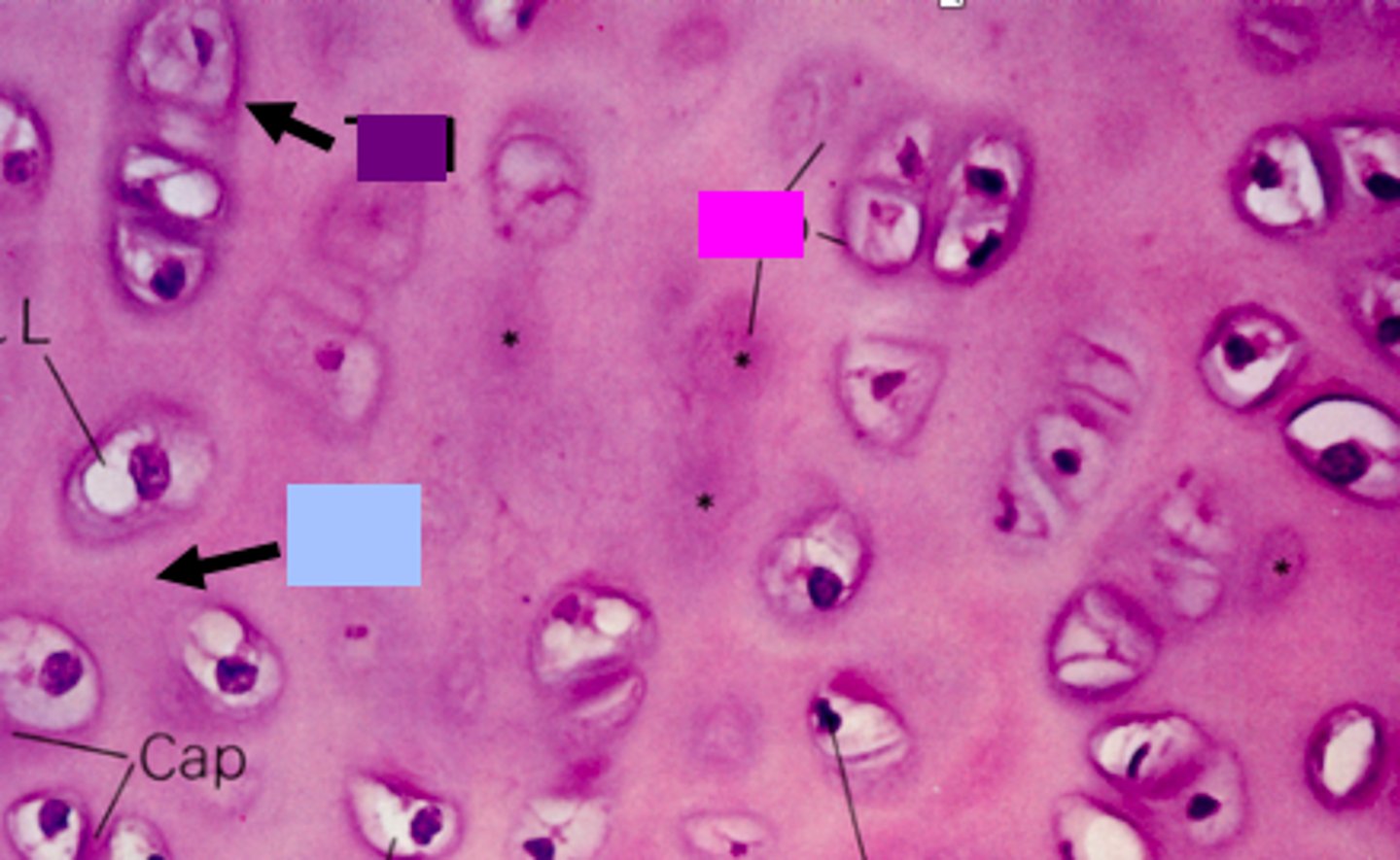
Descendants from a single cell
What is an isogenous group?
interterritorial matrix
identify the blue box:
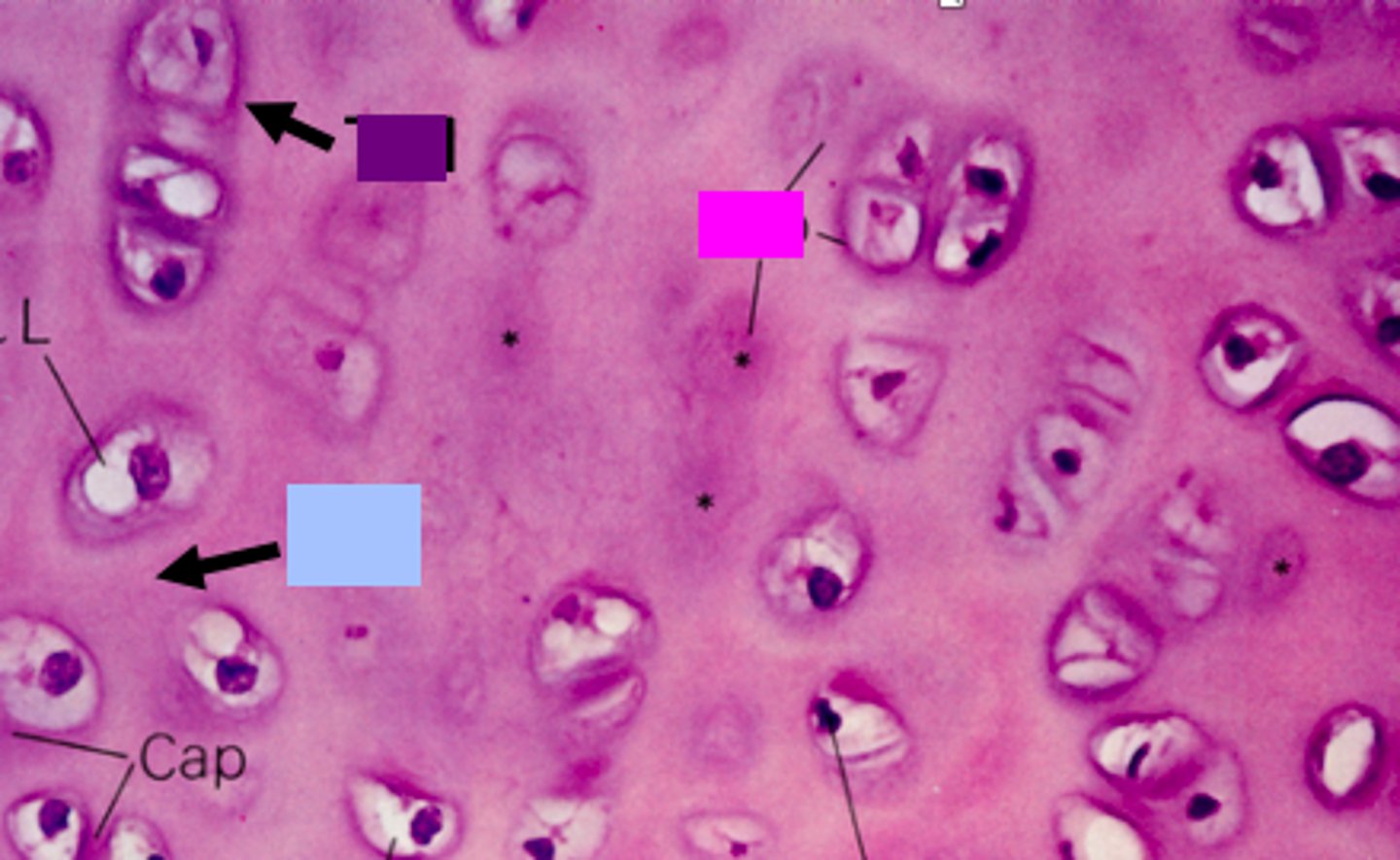
territorial matrix
identify the purple box:
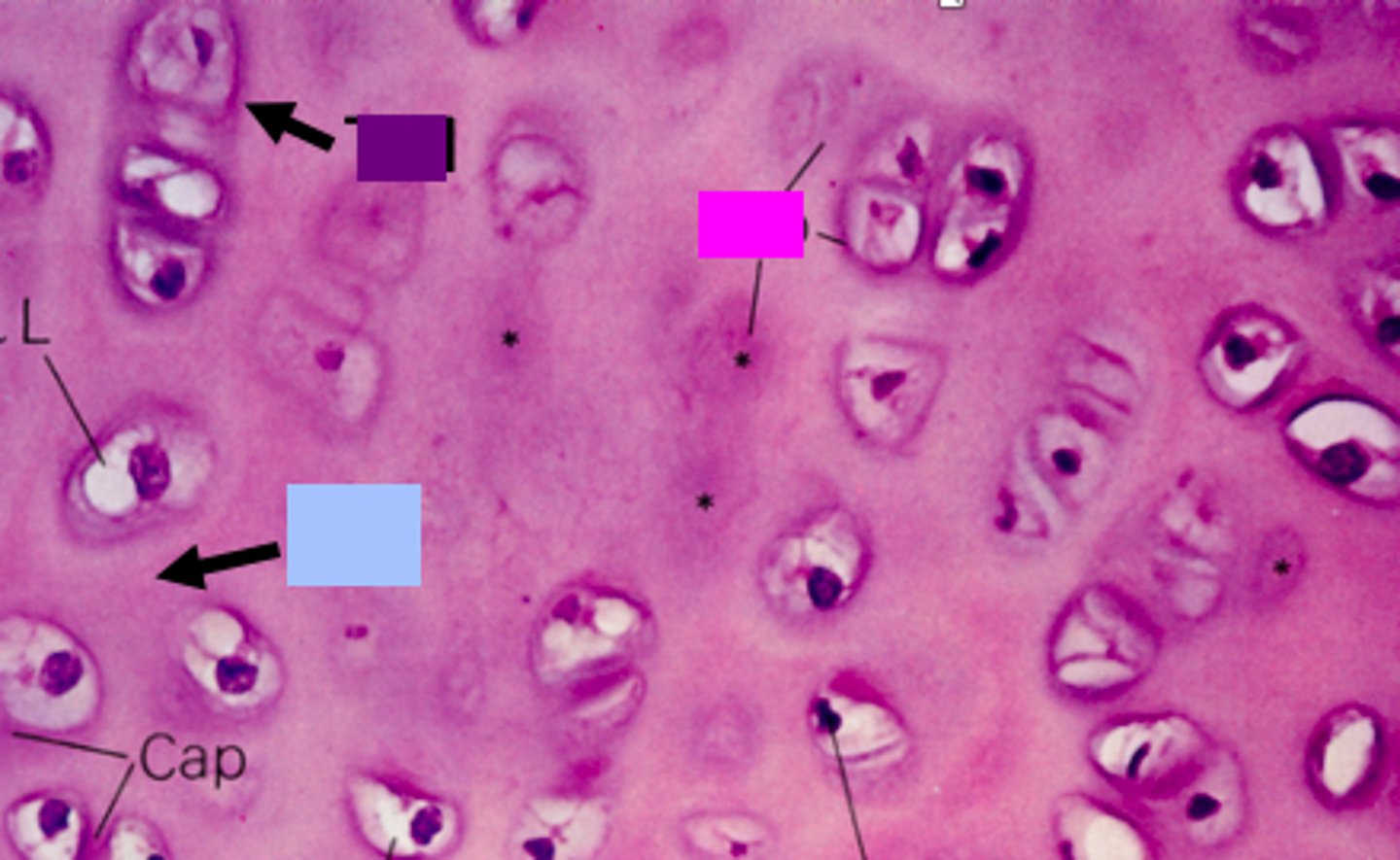
Basophilic
Territorial matrix (TM) has strong __________ staining
Perichondrium (collagen- I rich)
What does the P stand for?
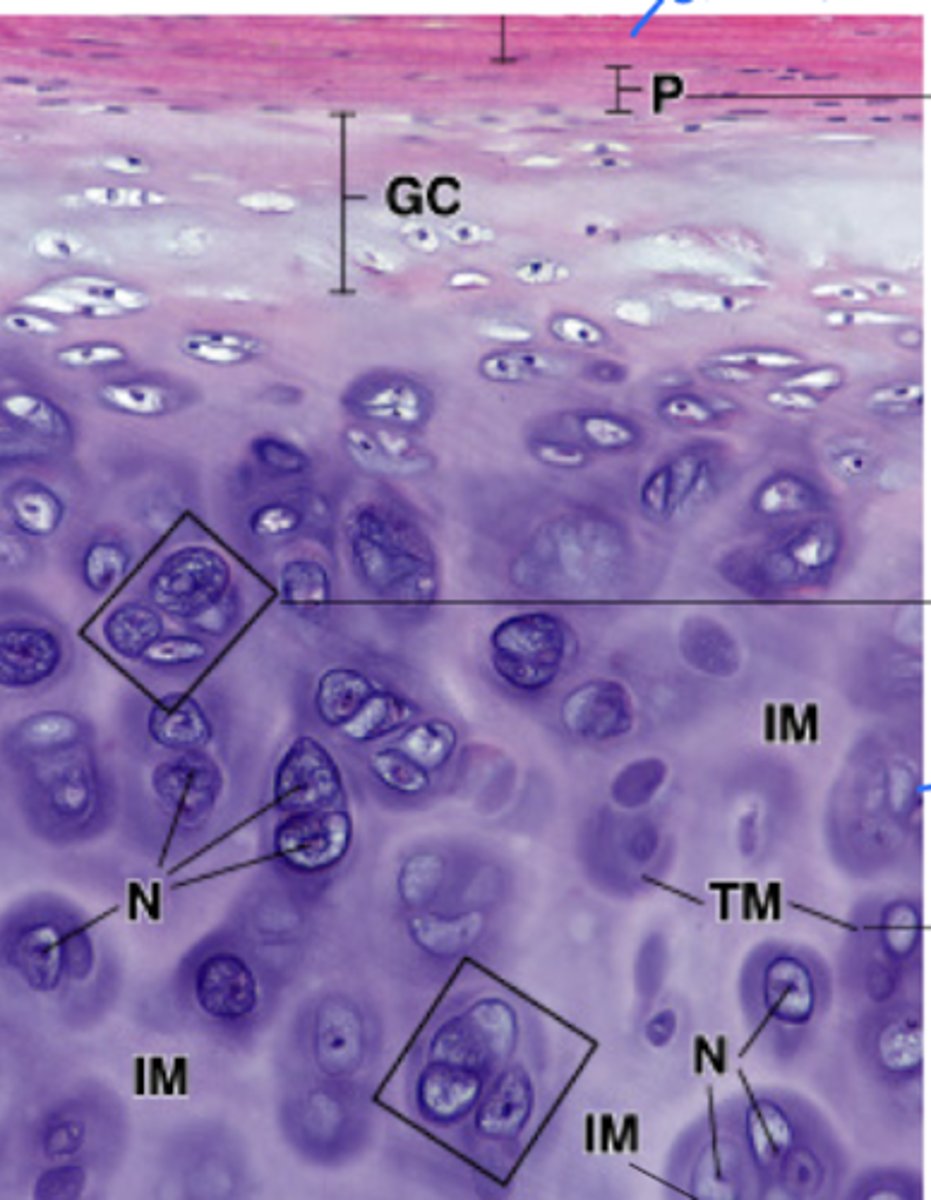
Territorial matrix
What does the TM stand for?
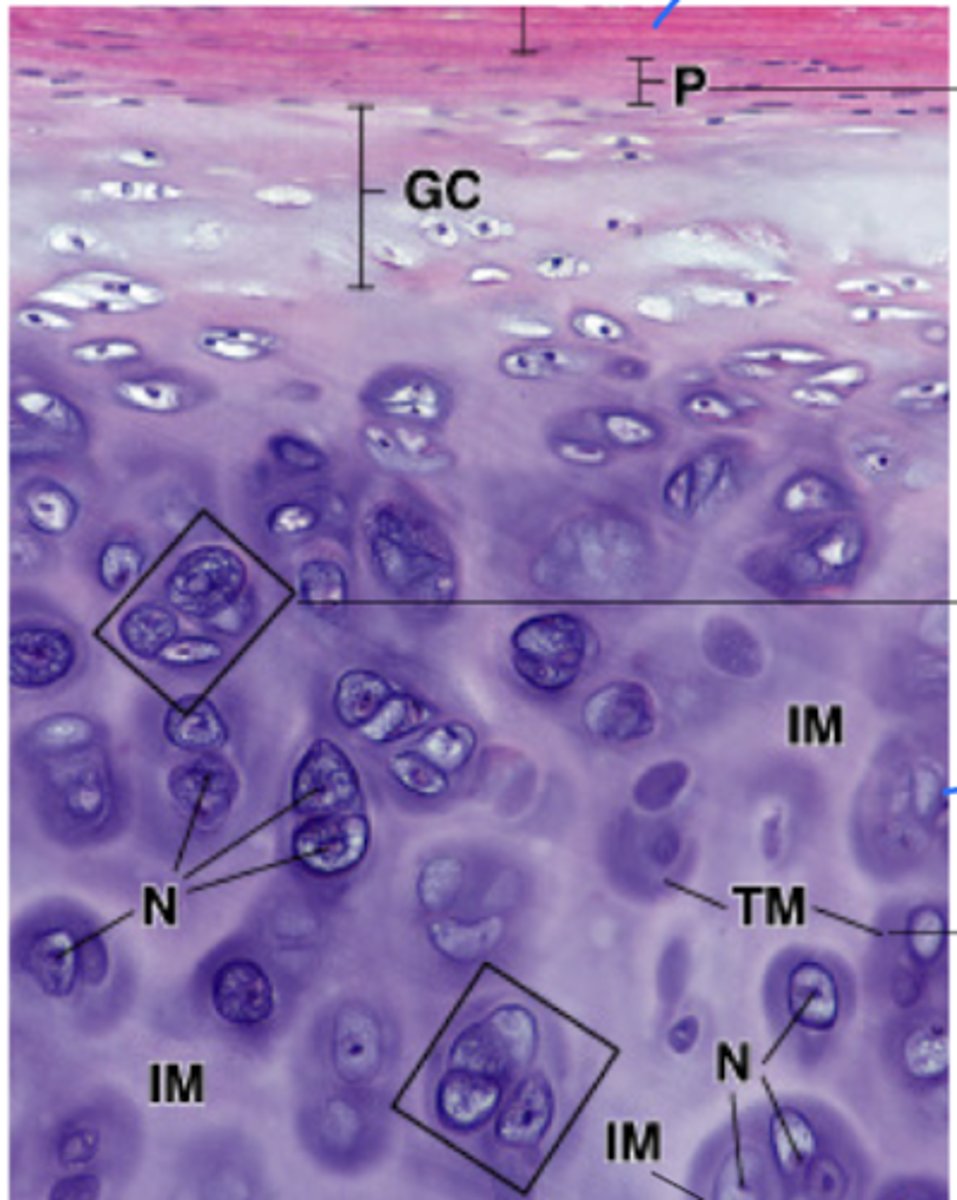
Interterritorial matrix
What does the IM stand for?
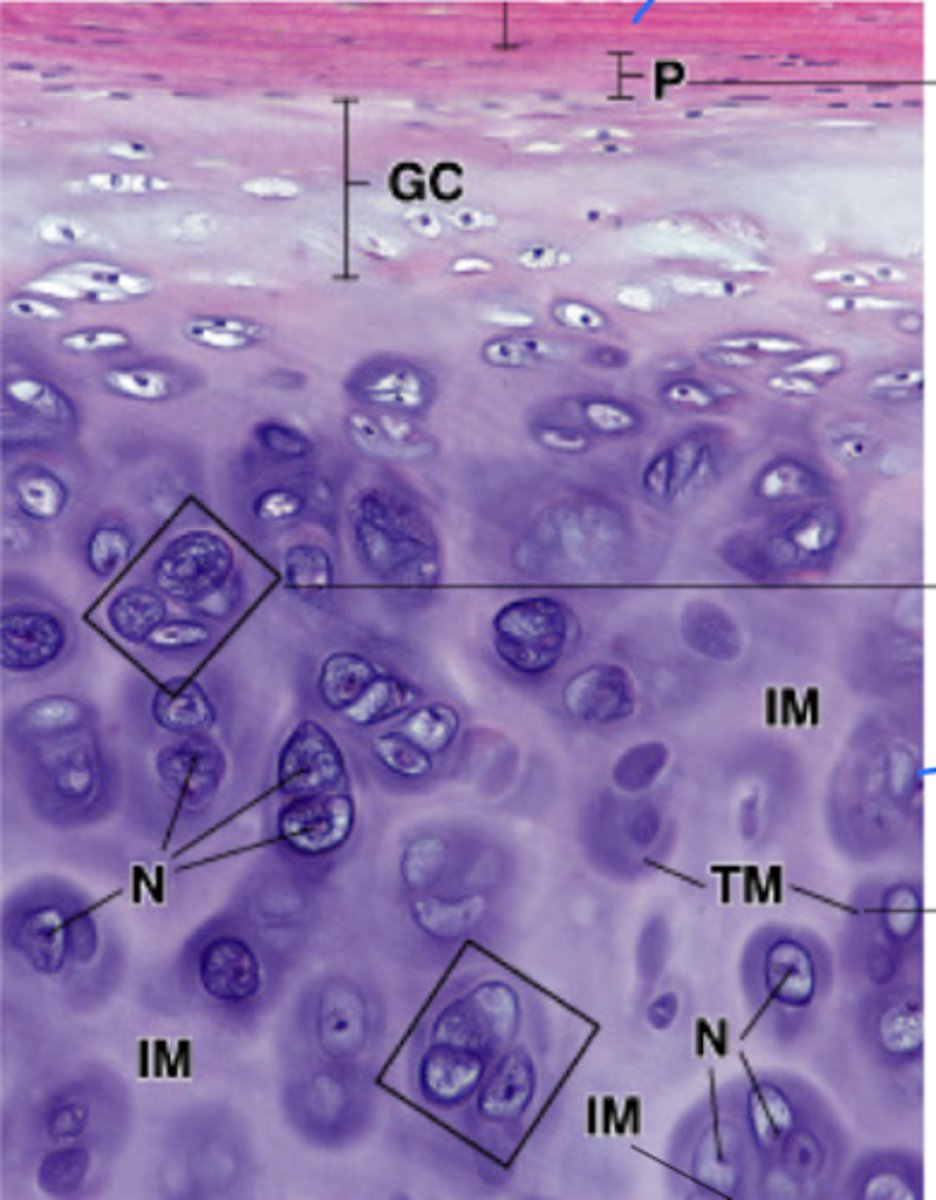
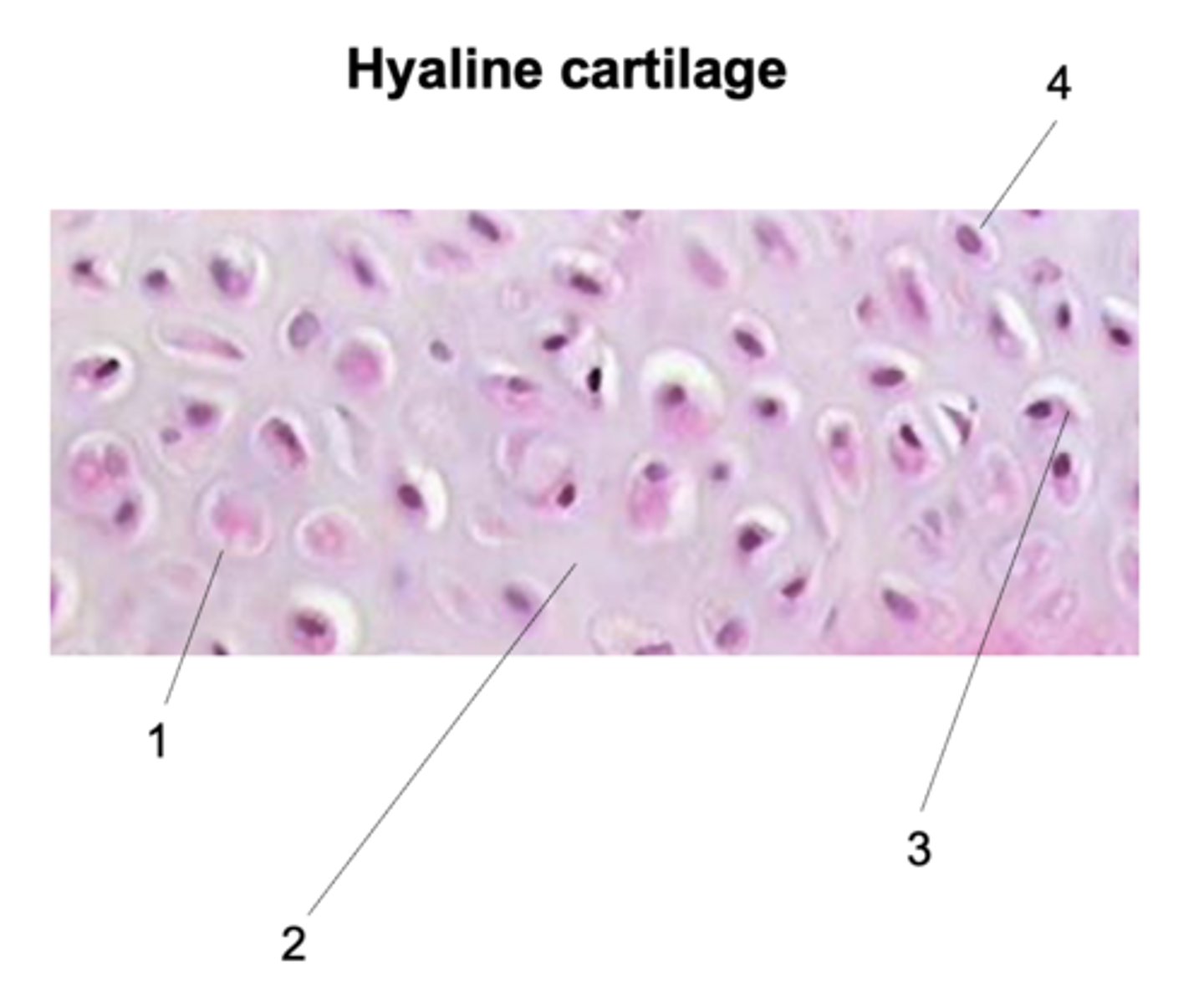
Chondrocyte
What does #1 point to?
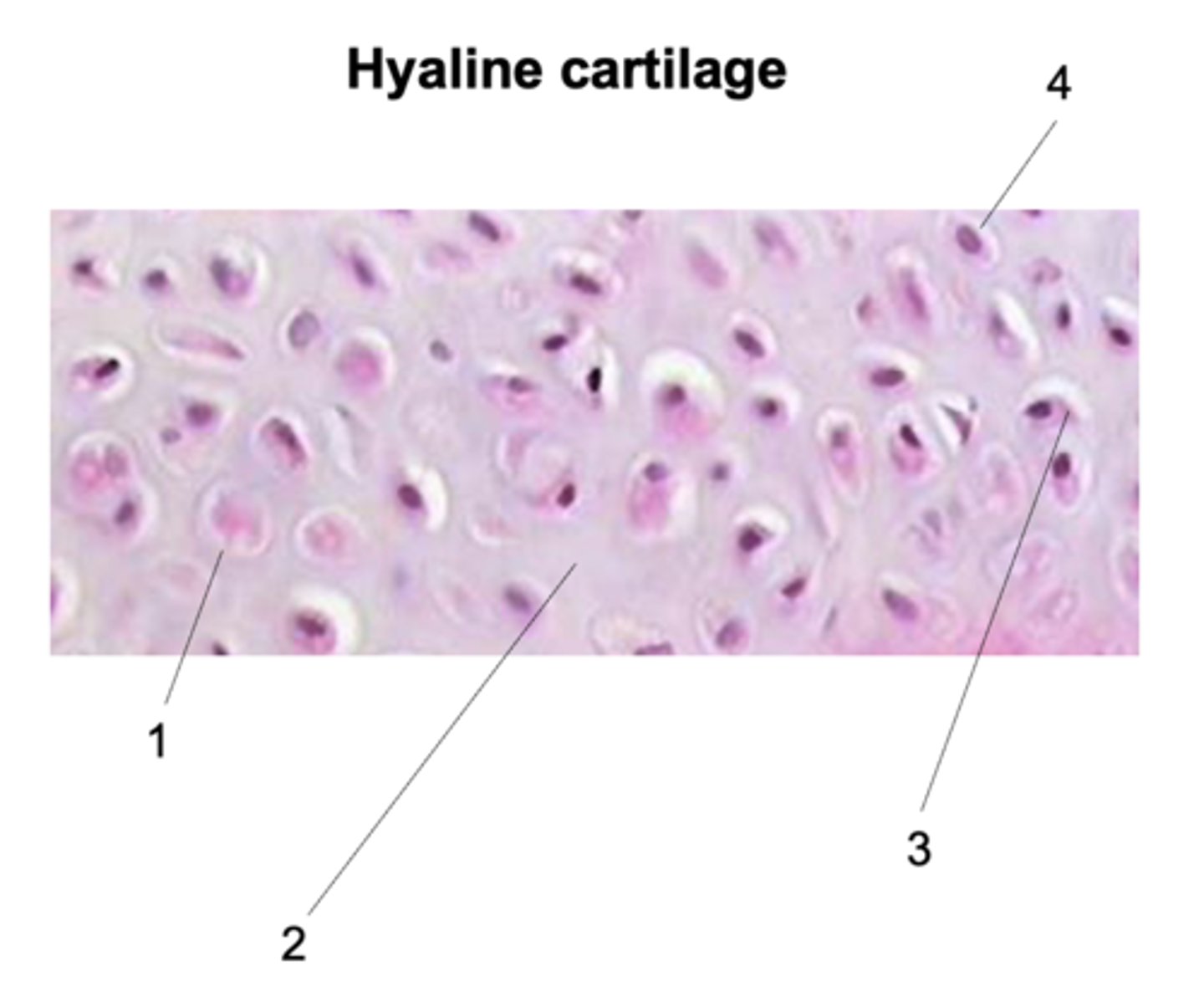
Extracellular matrix (ECM)
What does #2 point to?
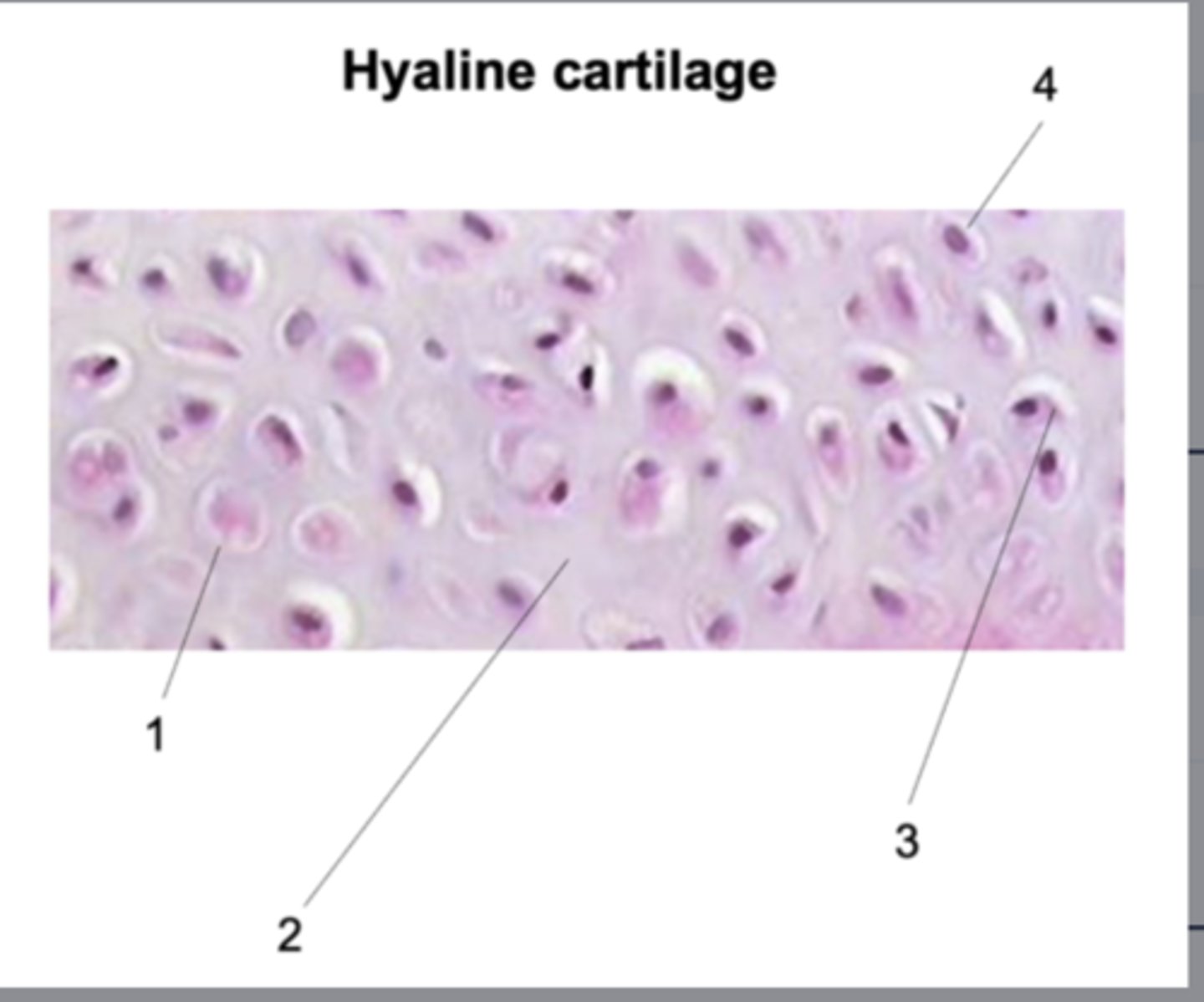
Lacuna
What does #3 point to?
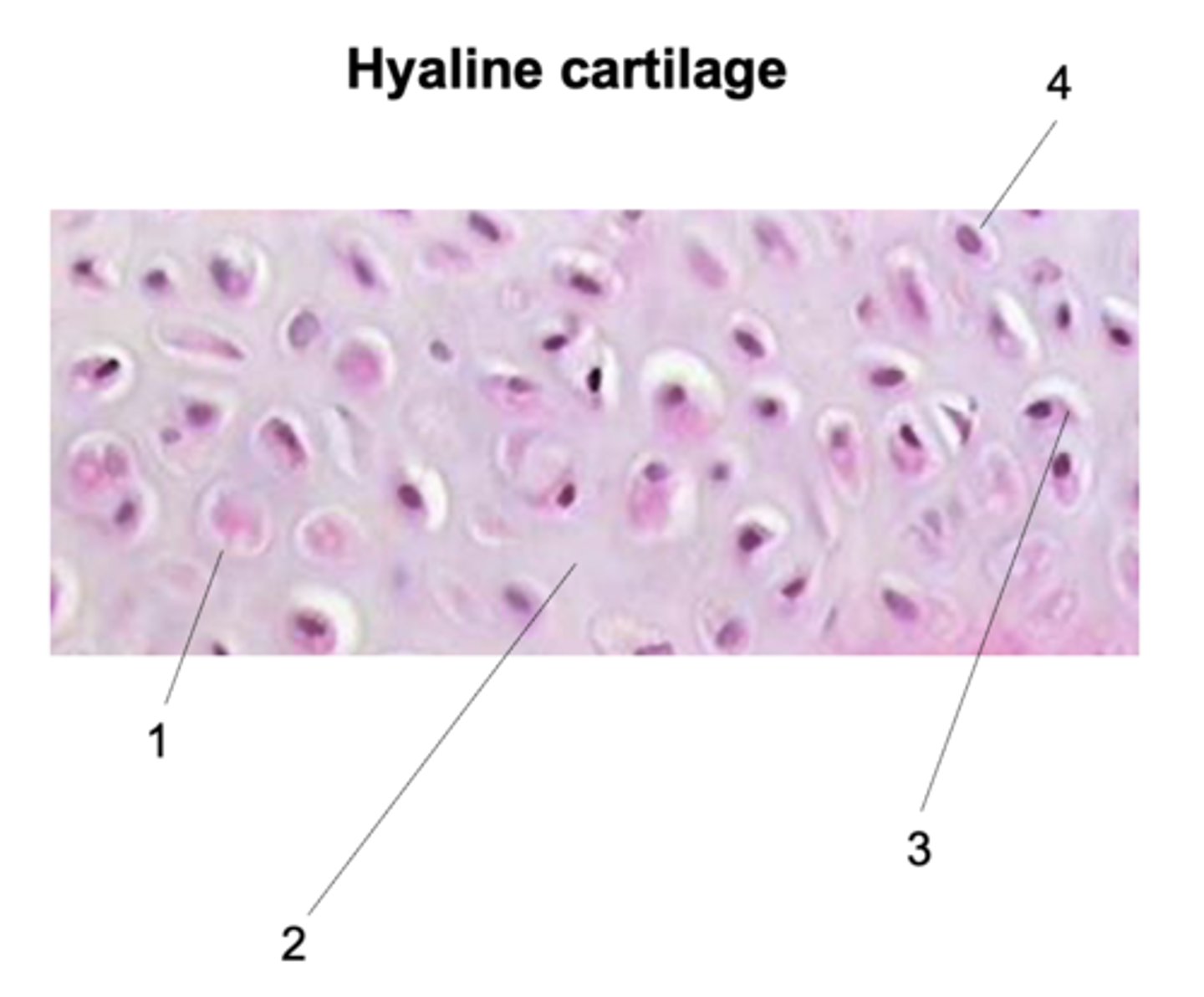
Nucleus
What does #4 point to?
true
t/f: all cartilage experiences both appositional and interstitial growth
Appositional growth
What type of growth is from the perichondrium, forms at surface and increases in girth?
Interstitial growth
What type of growth are there cell divisions within the matrix resulting in increases in length and girth?
lacuna
chondrocytes are located in the _______
Lacuna
A chondrocyte fully occupies the _________, closely attaching the ECM
osteoarthritis
degradation of hyaline cartilage at articular surfaces caused by wear and tear:
rheumatoid arthritis
degradation of hyaline cartilage and inflamed synovium due to autoimmunity
osteoarthritis
identify the cartilage disease:
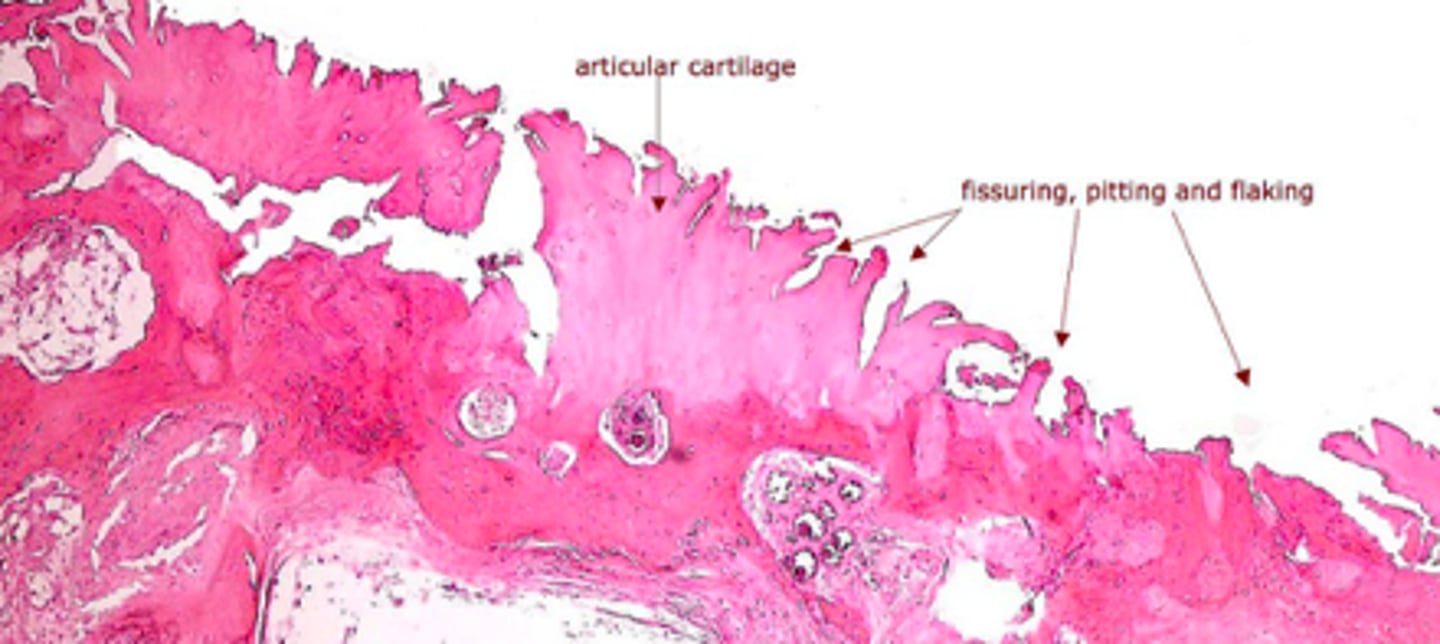
rheumatoid arthritis
identify the cartilage disease:
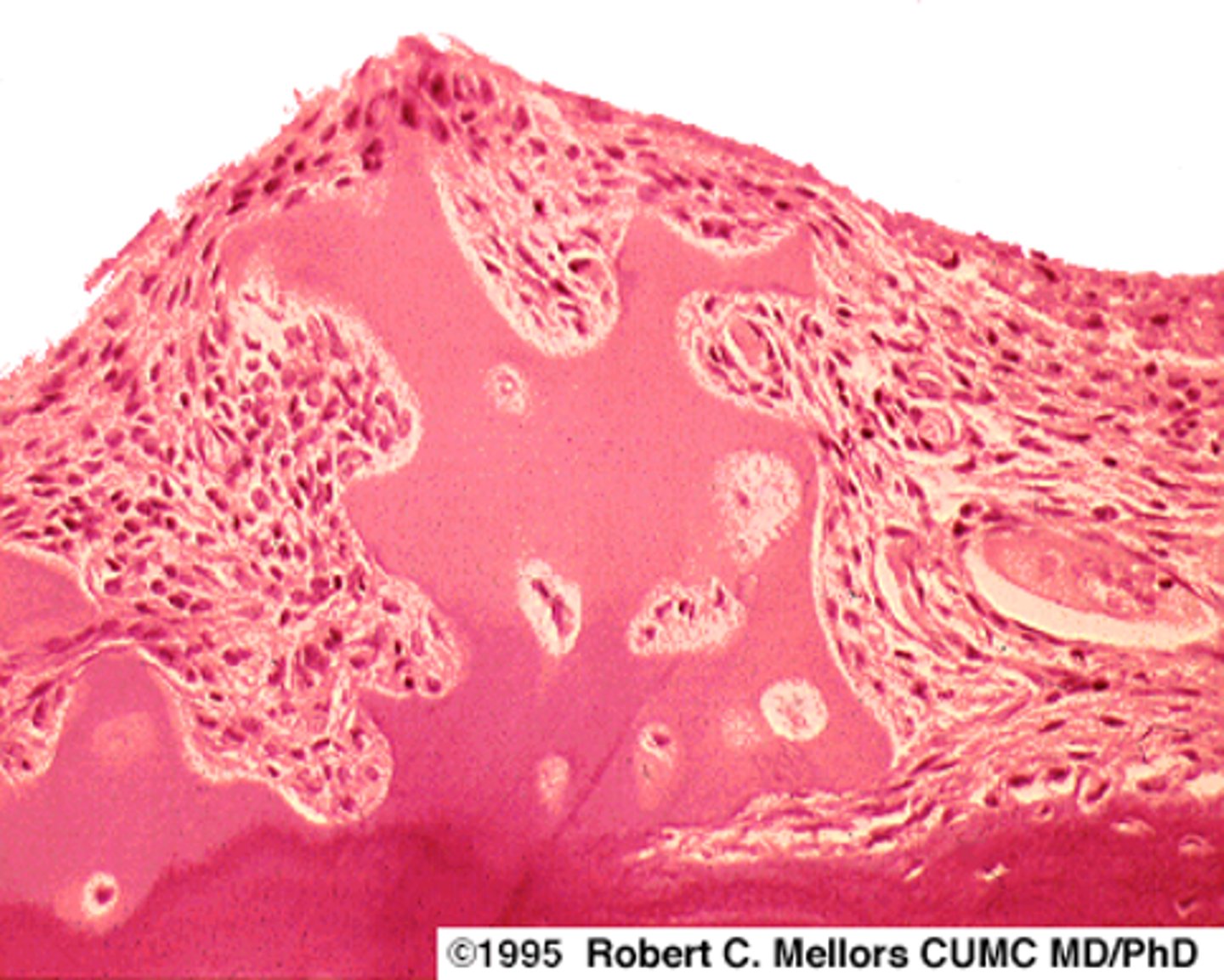
elastic cartilage
identify the cartilage:
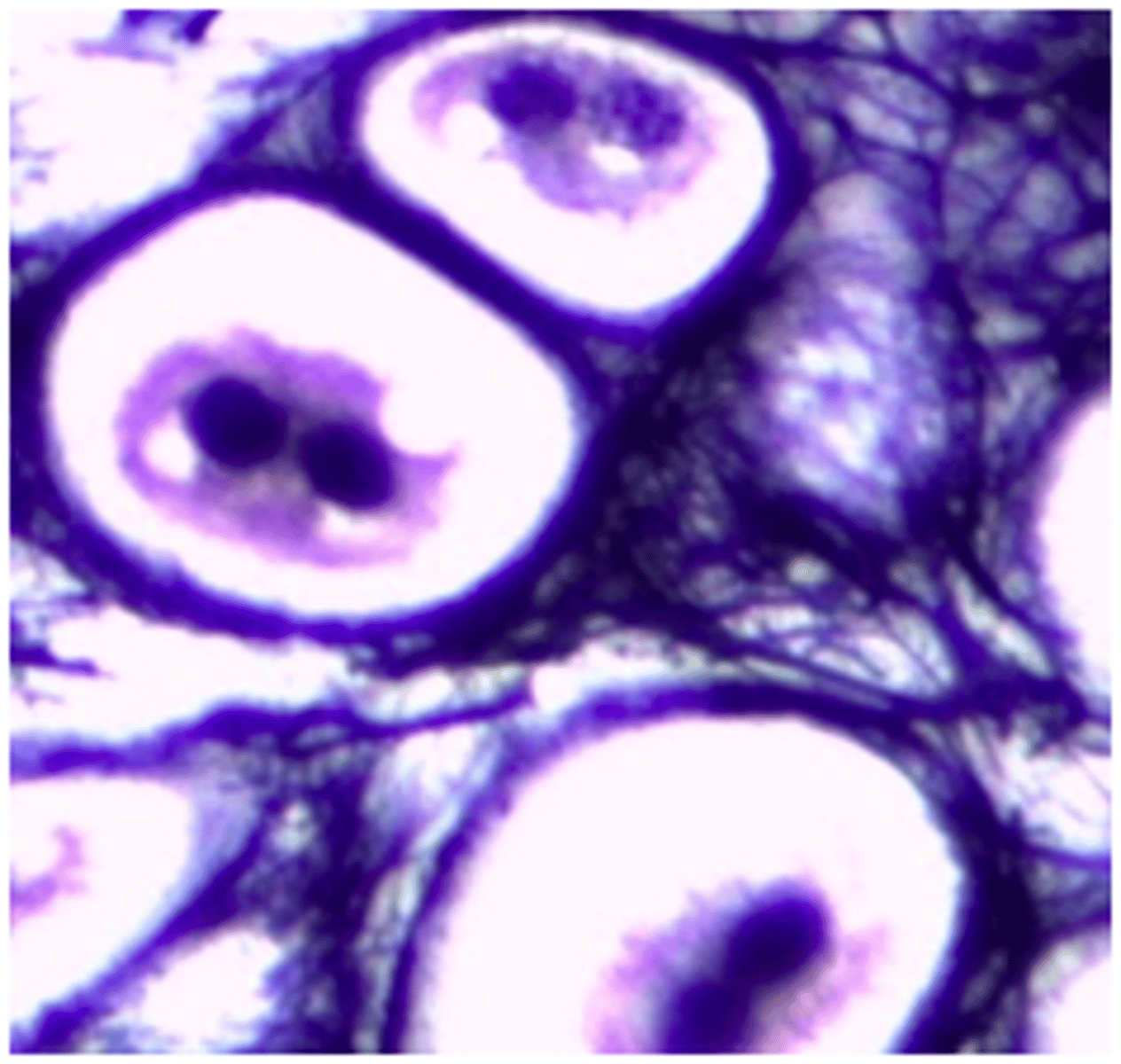
elastic cartilage
identify the cartilage:
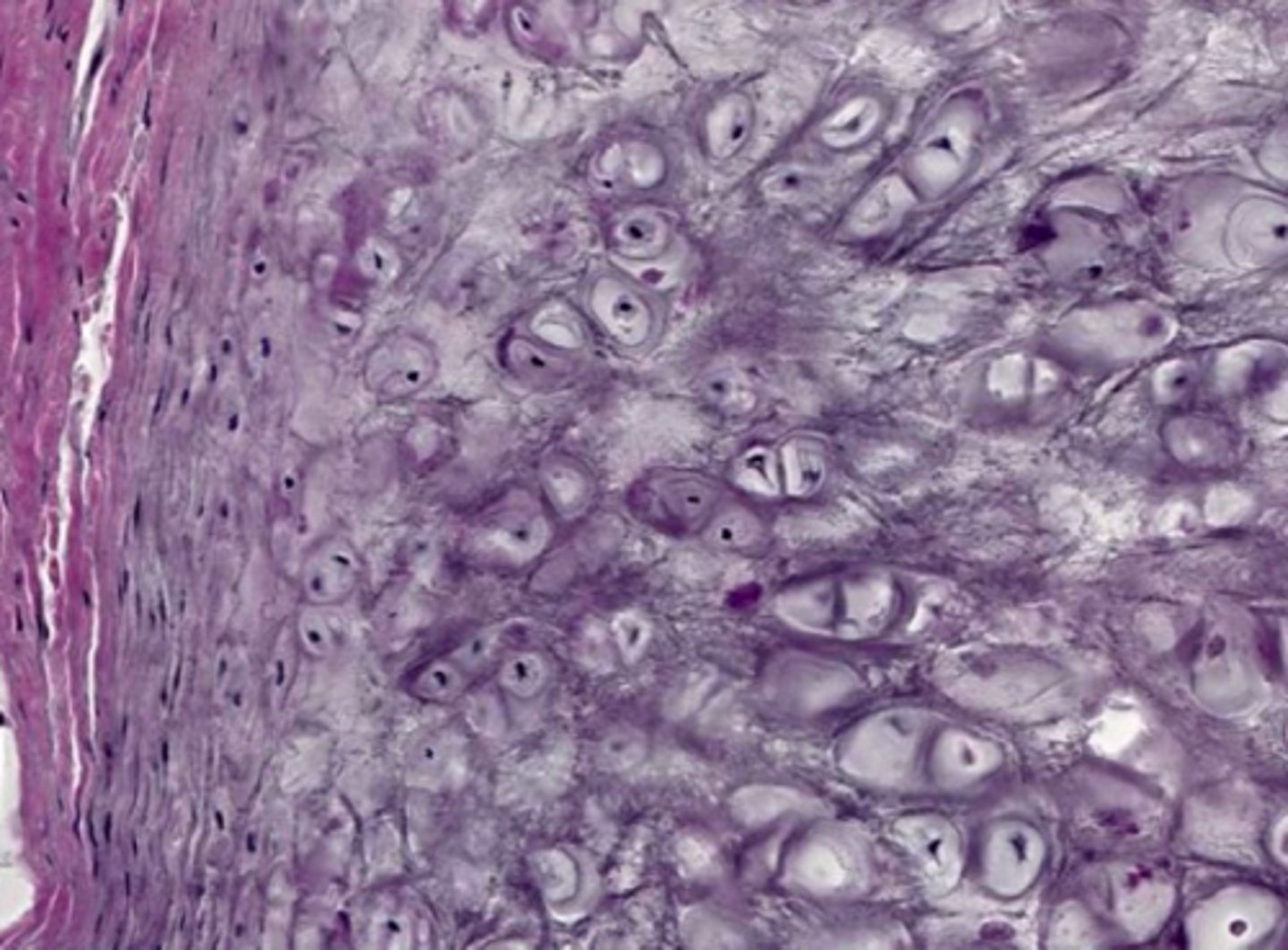
elastic cartilage
identify the cartilage:
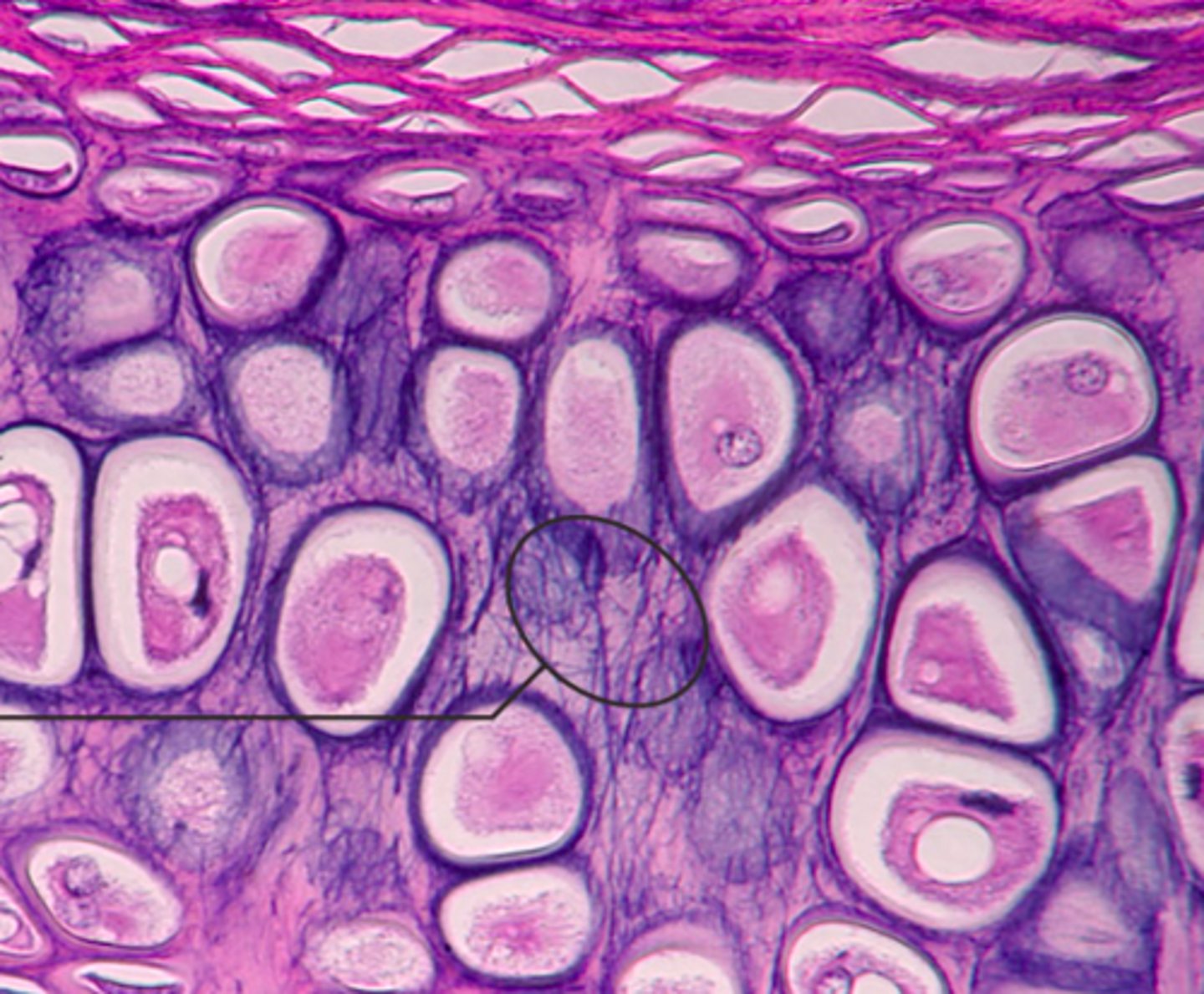
Elastic cartilage
Identify the cartilge
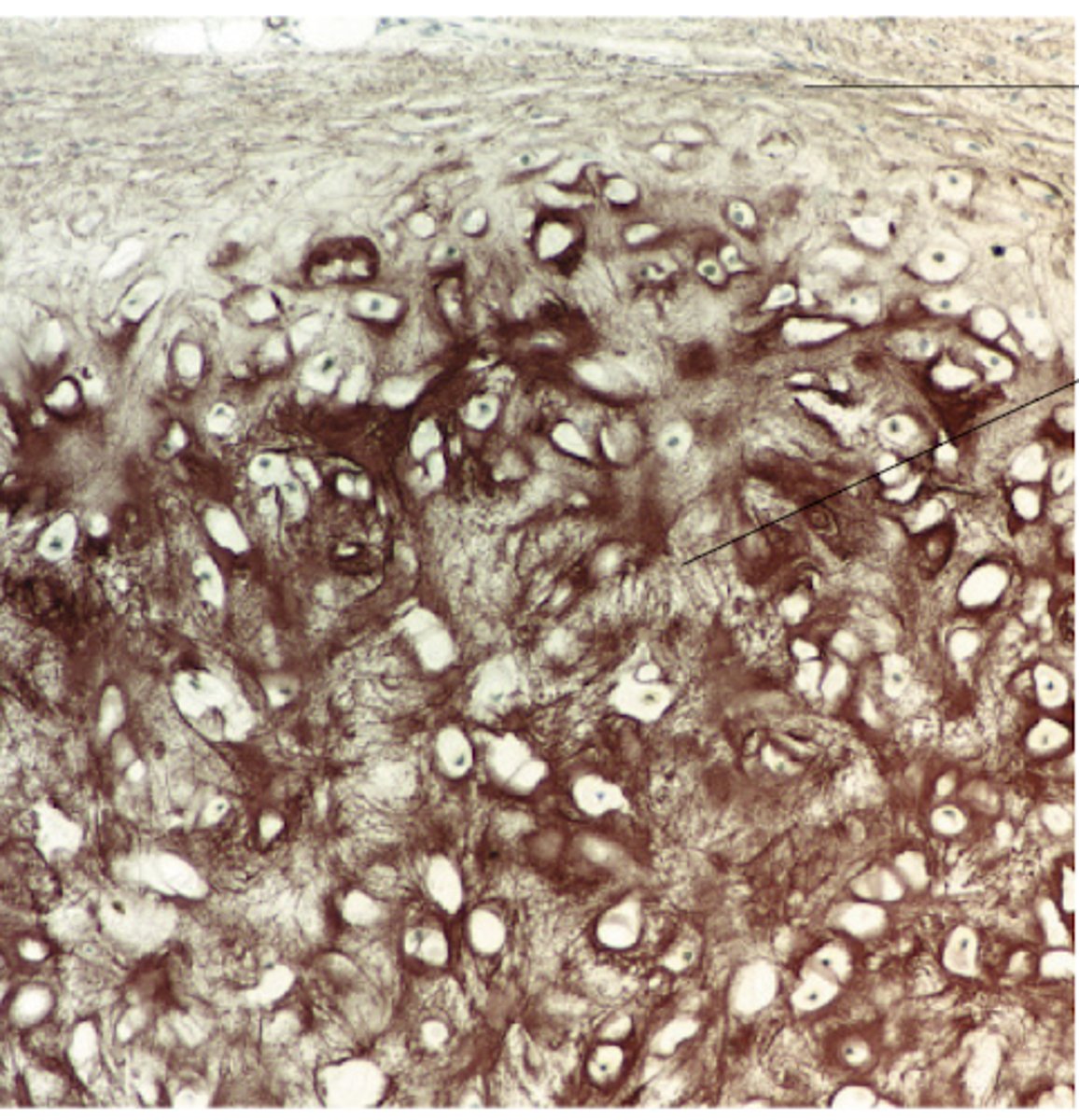
fibrocartilage
which type of cartilage does NOT have perichondrium?
Dense CT (has col I)
Hyaline cartilage (has col II)
Fibrocartilage is a combination of what?
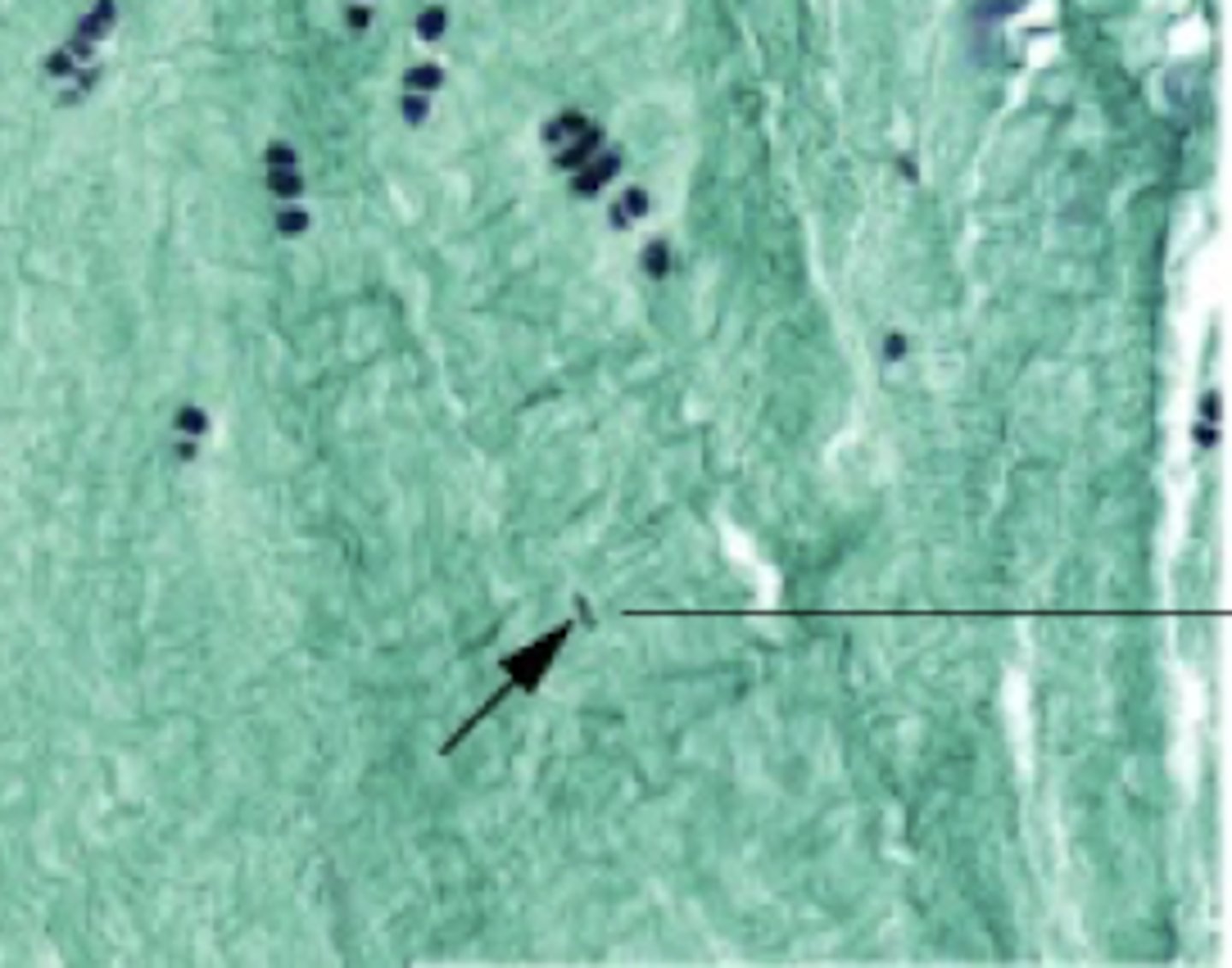
Nucleus of a fibroblast cell
What does the arrow point to?
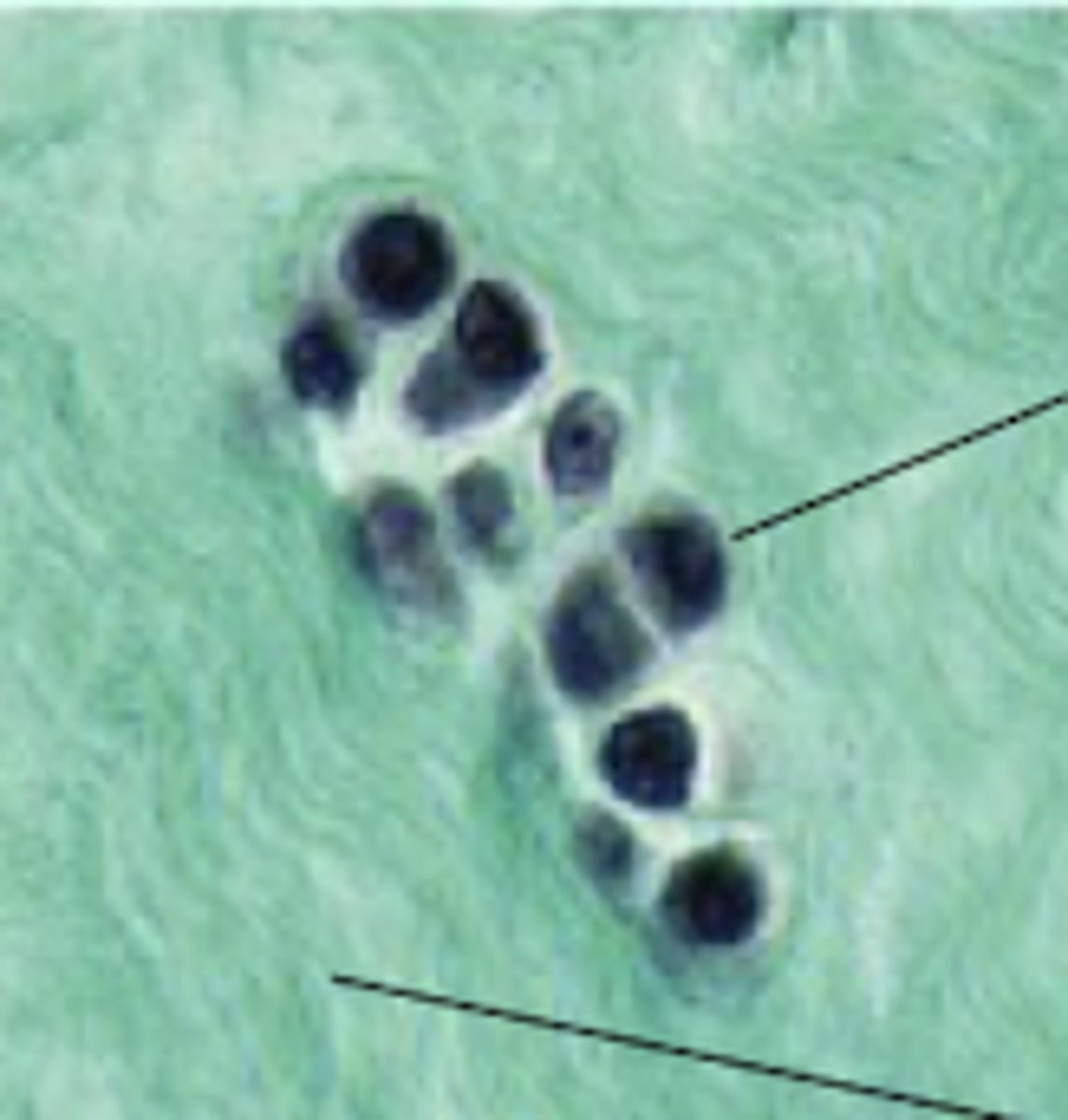
Isogenous group of chondrocytes
What would this be called in a fibrocartilage?
Collagen fibers in fibrocartilage
What is stained green?
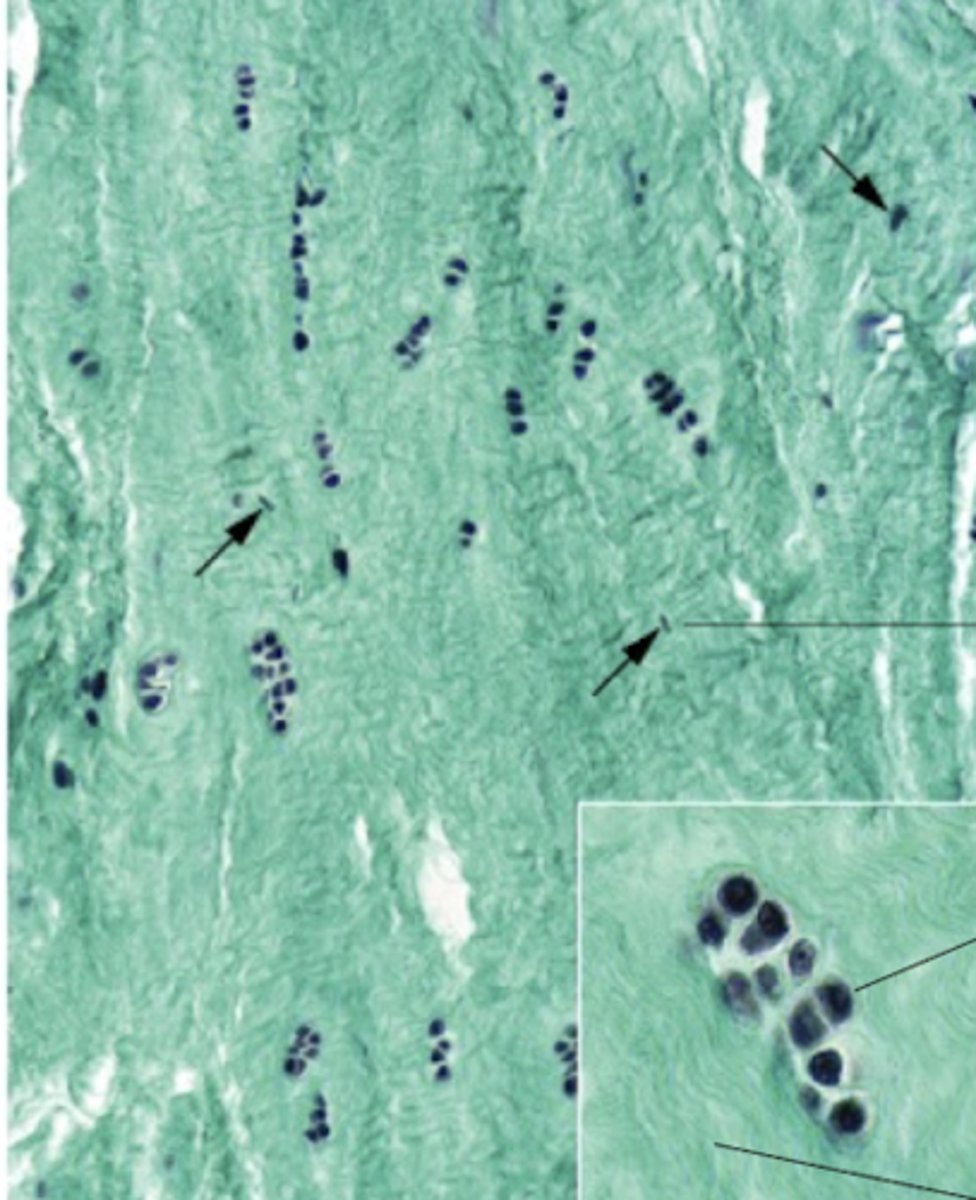
fibroblasts
additionally to chondroblasts, what cells do fibrocartilage have that elastic and hyaline not have?
fibrocartilage
identify the cartilage:
Negative (basophilic)
What type of charges do proteoglycans have?
Positive (eosinophilic)
What type of charges do collagen have?
GAG
Aggrecan = aggrecan core protein + _______
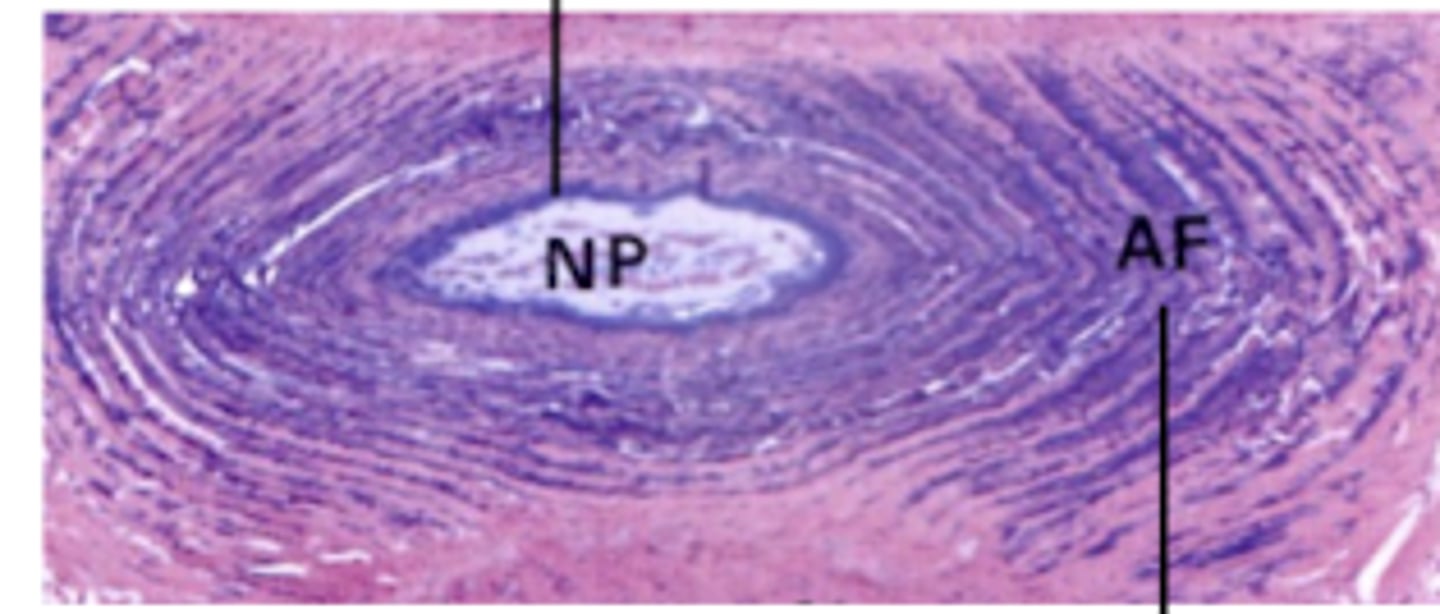
Nucleus pulposus
What does the NP stand for?
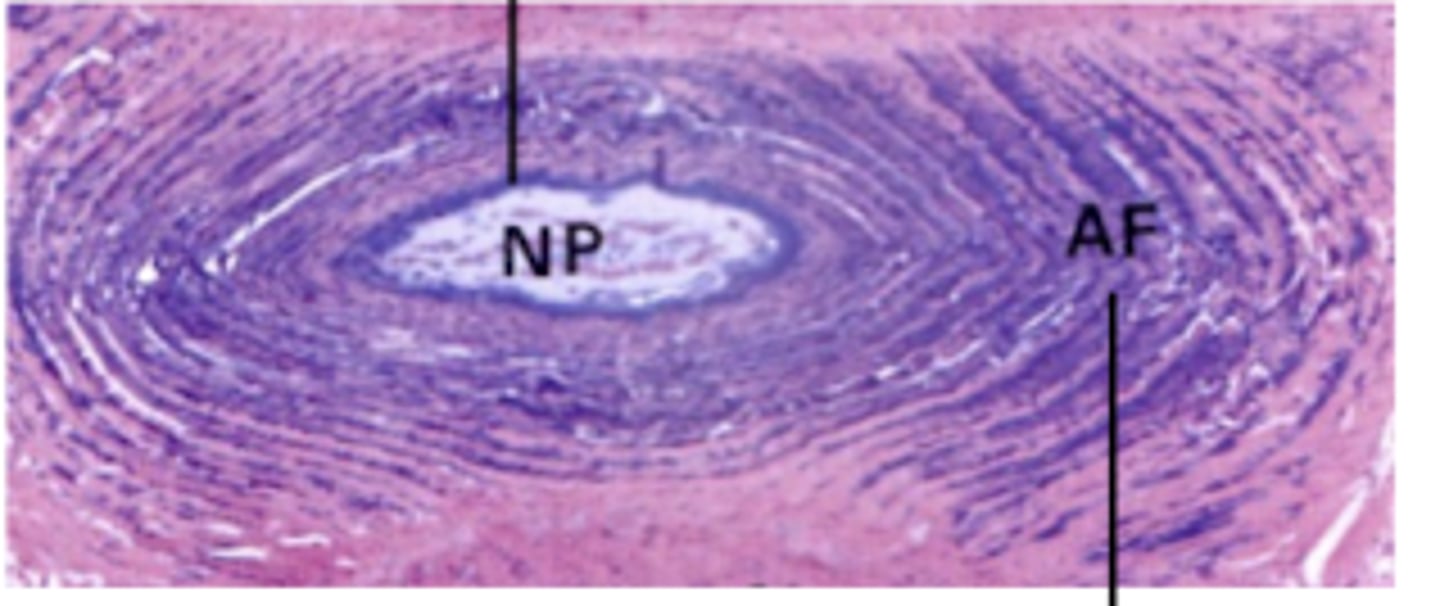
Anulus fibrosus
What does the AF stand for?
Herniated disc
What is it when a portion of the nucleus pulposus protrudes into the intervertebral foramen, pressing on one of the spinal nerves in the process
Synovial joint
What type of joint is shown?
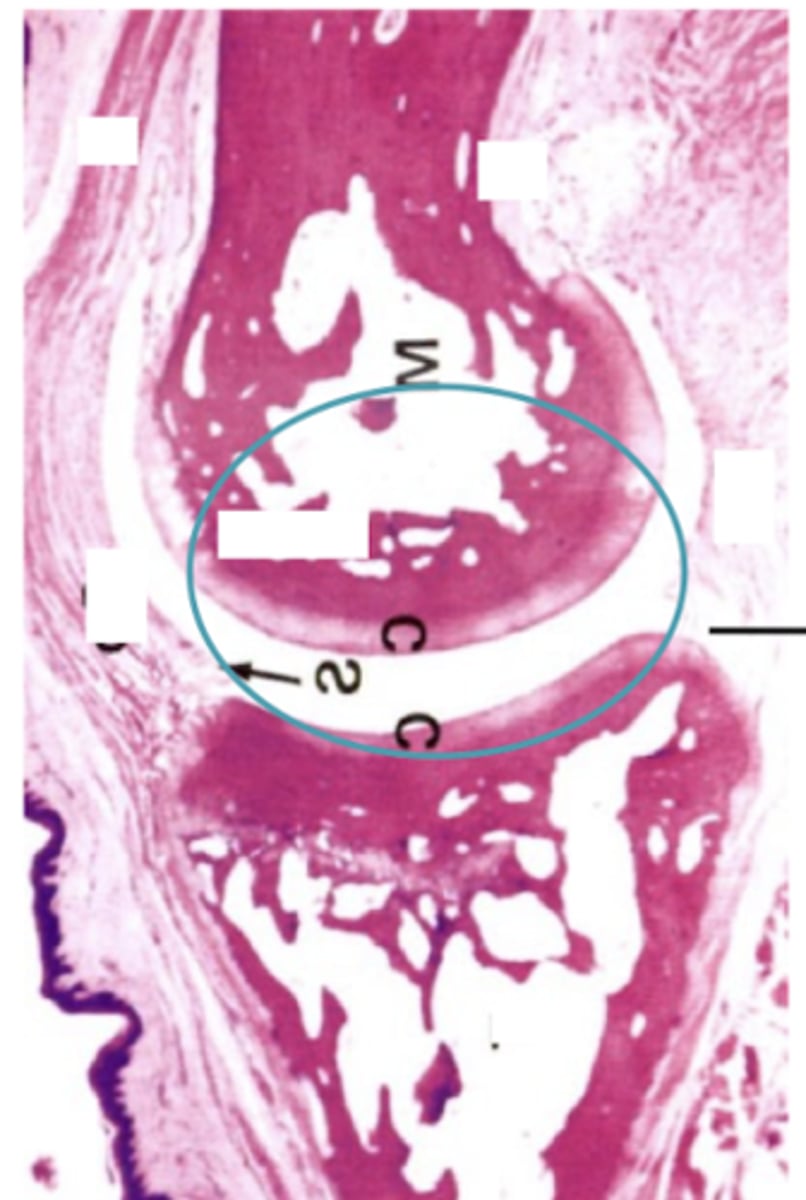
Articular cartilage (no perichondrium)
What type of cartilage is shown?
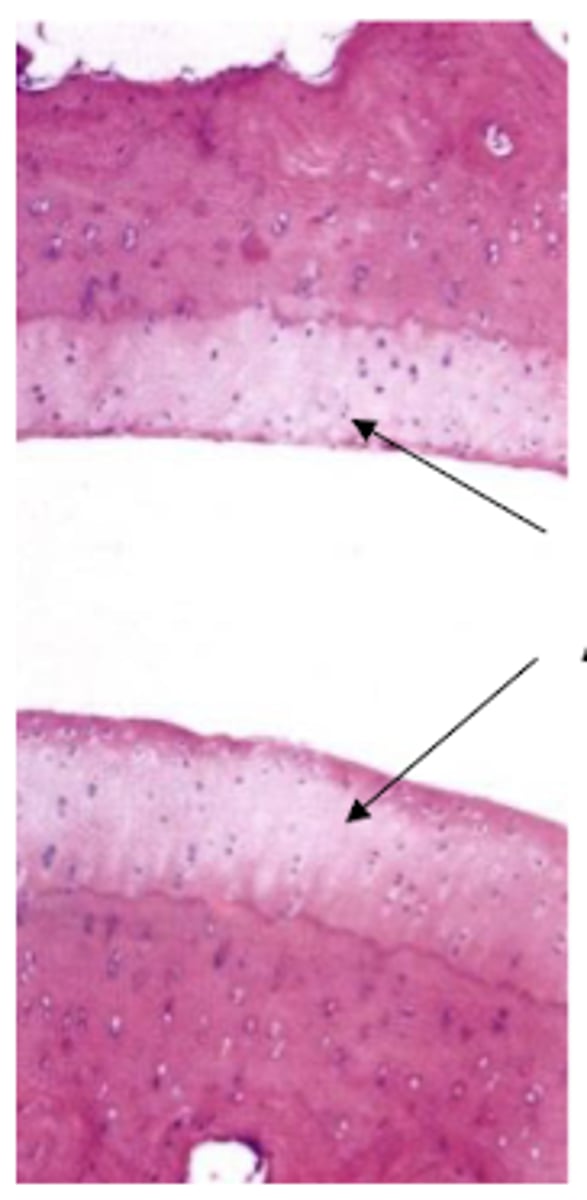
Articular cartilage
Arthritis is caused by degradation of what type of cartilage?
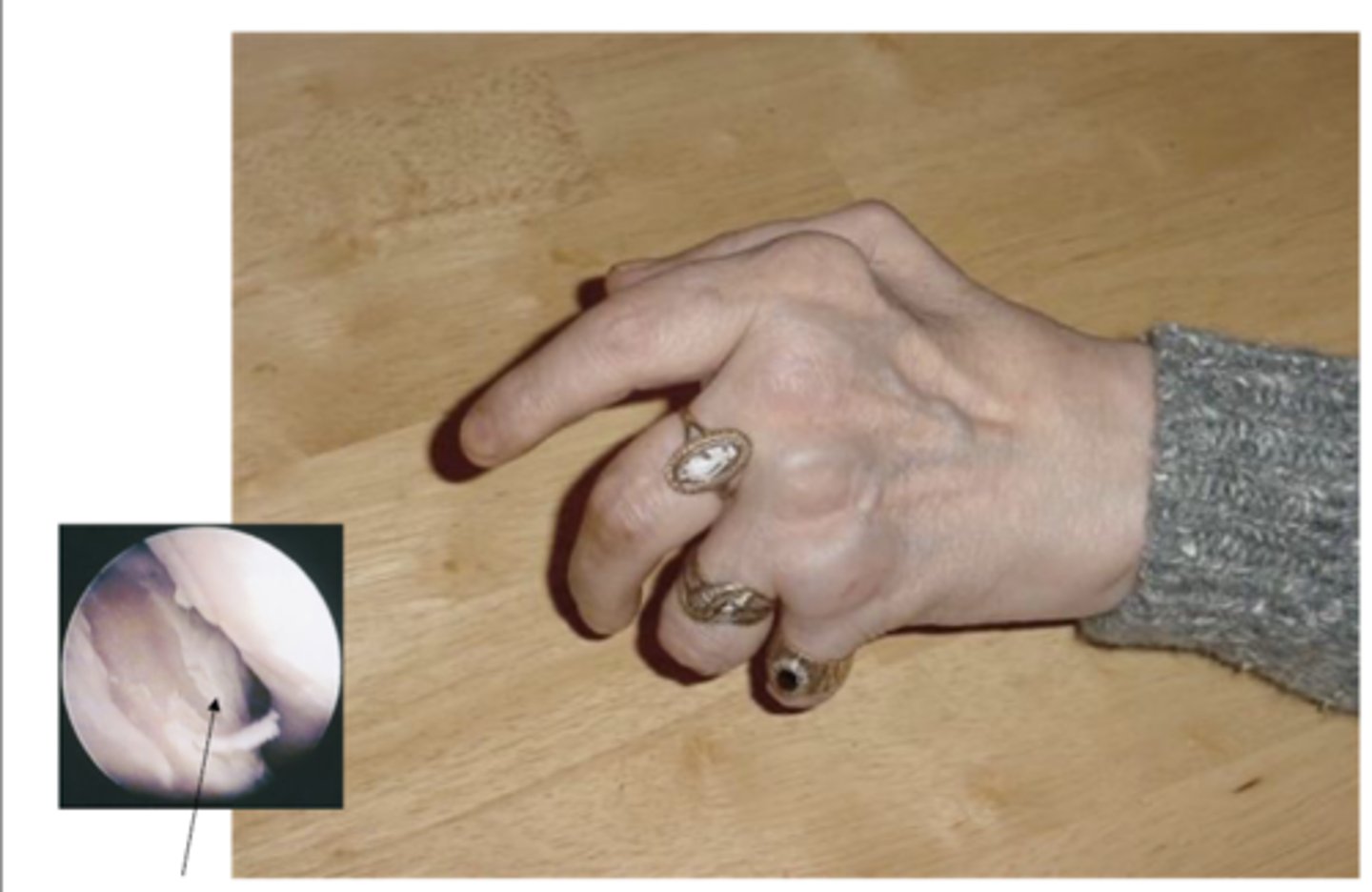
connective tissue
What type of tissue is bone?
Mineralized
is the extracellular matrix of bone mineralized or not mineralized?
Bone
What has the following function:
Support
Calcium and phosphate storage
Fibers: Collagen I
Ground substance: Proteoglycan
What makes up the organic extracellular matrix of bones?
Hydroxyapatite Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2
What makes up the inorganic extracellular matrix of bones?
Appositional
What type of growth are bones?
woven bone
-immature bone
-disorderly arrangement of collagen
True
T/F: Bones have vascular blood supply
compact
spongy
two types of lamellar bone are:
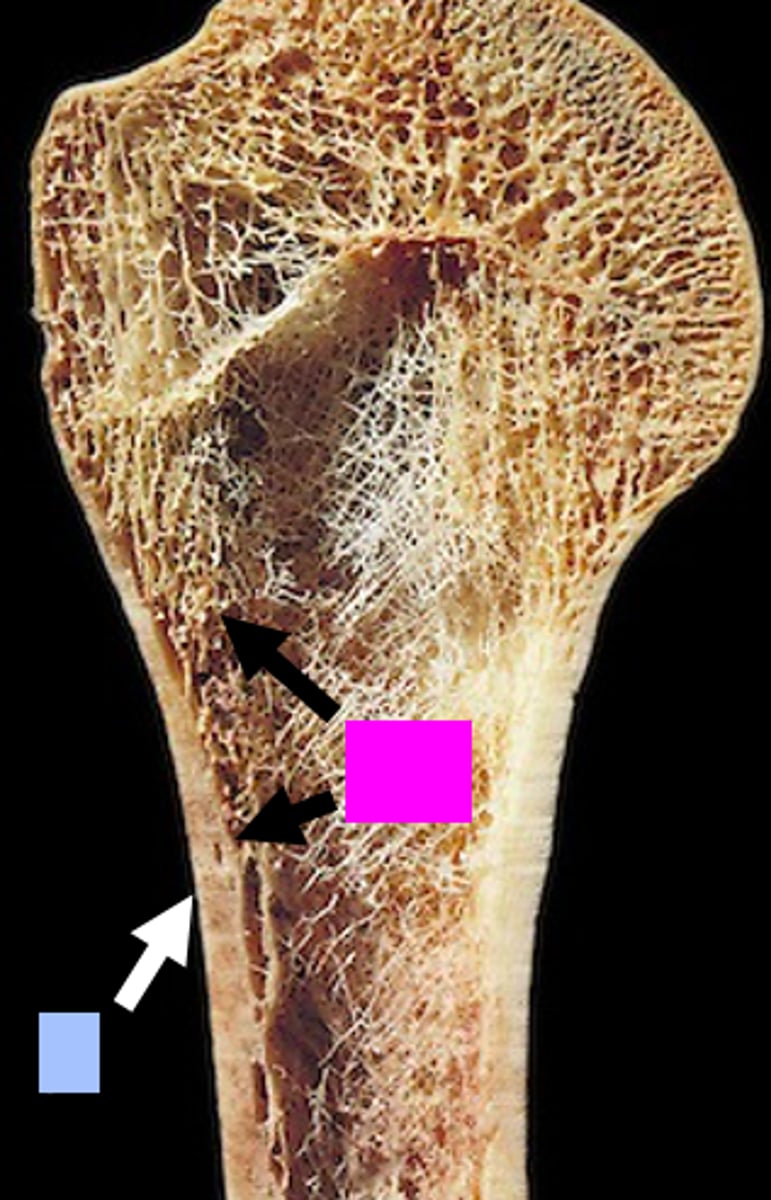
periosteum
identify the blue box:
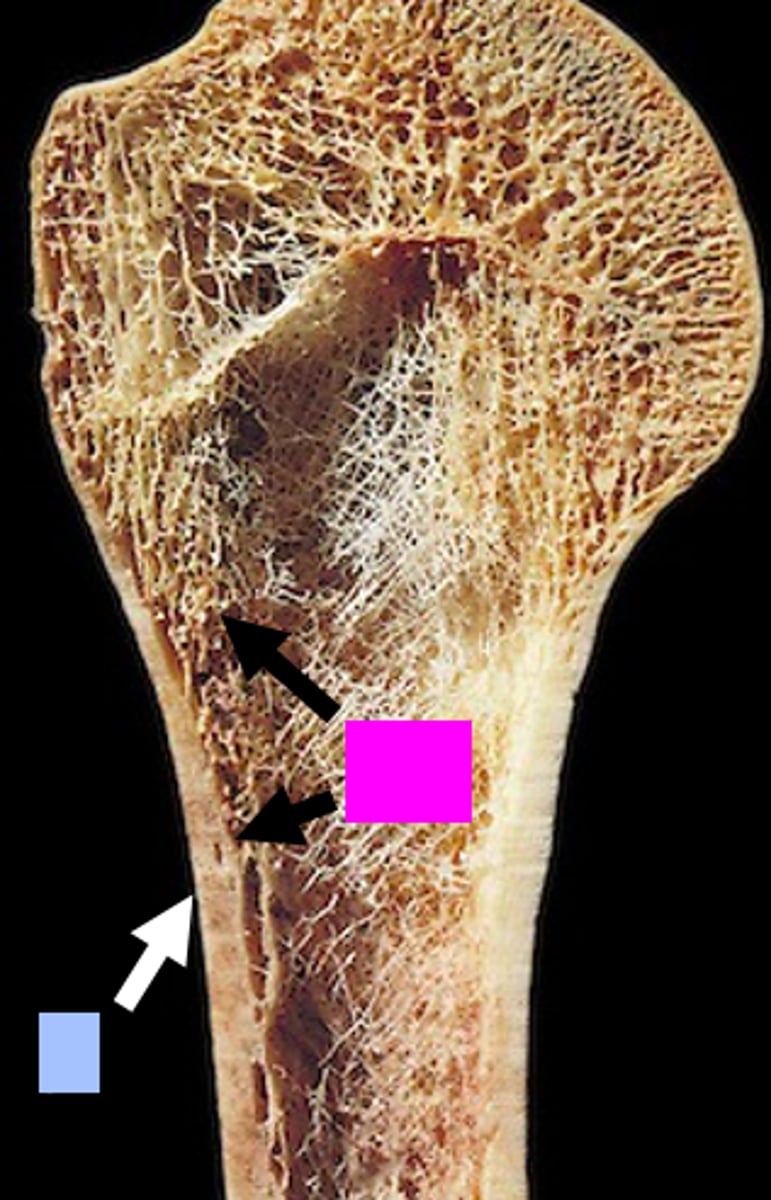
endosteum
identify the purple box:
Epiphysis
What is shown at #1?
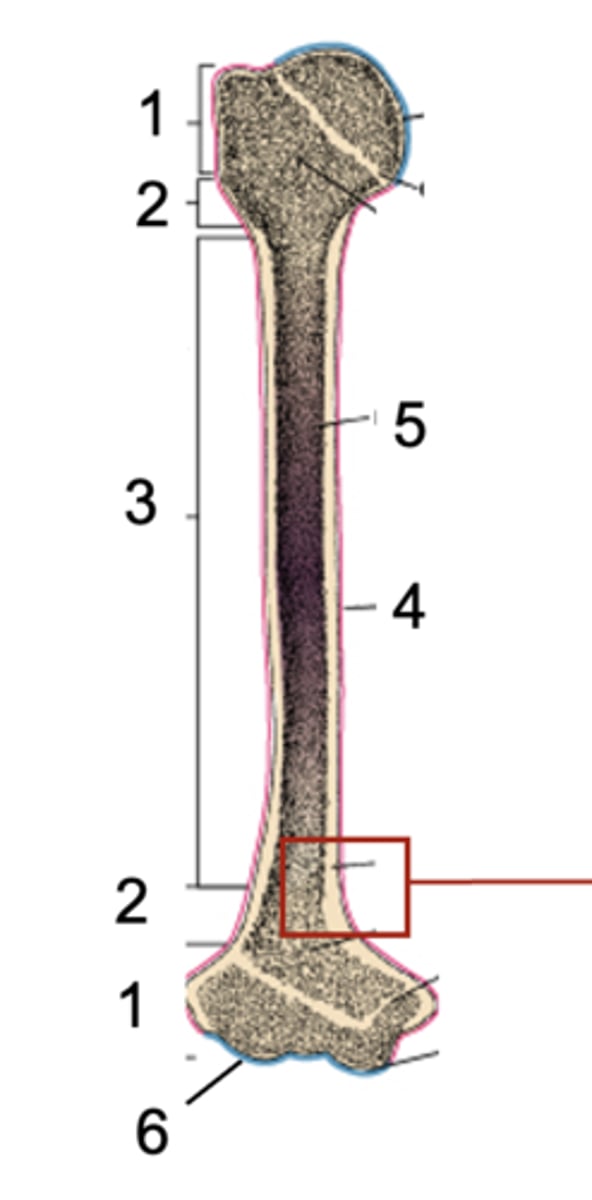
Metaphysis
What is shown at #2?
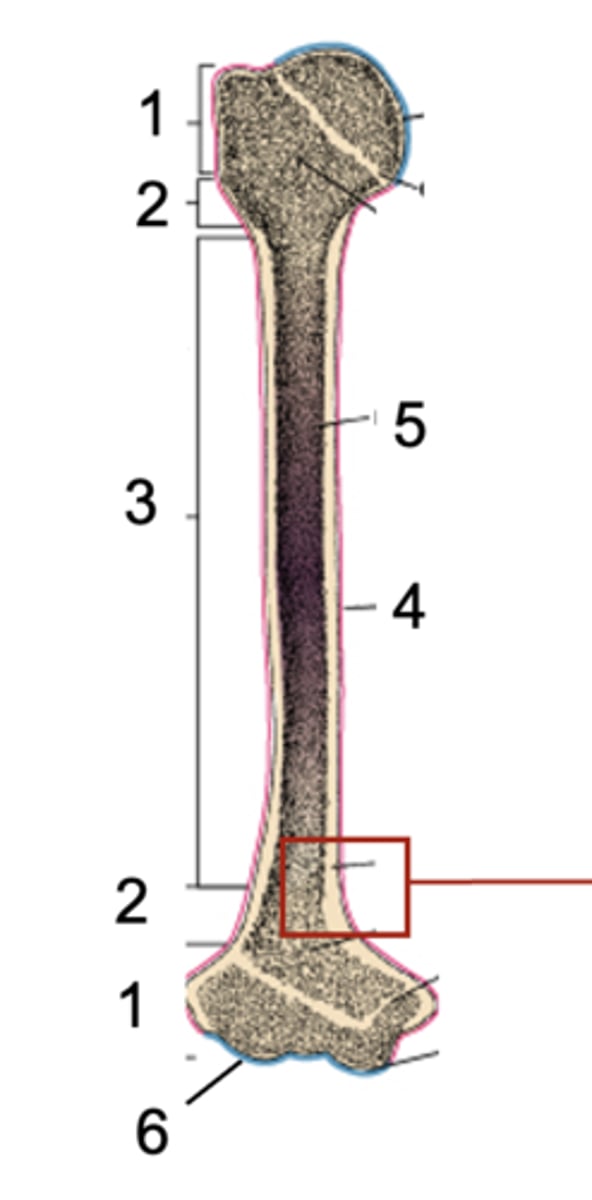
Diaphysis
What is shown at #3?
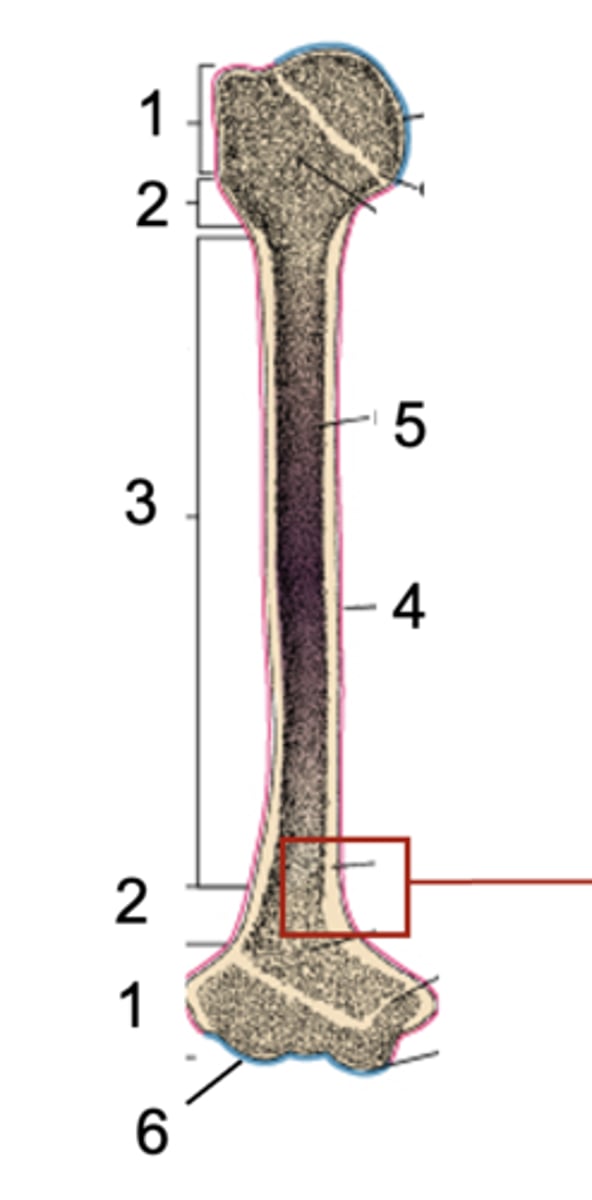
Periosteum
What is shown at #4 (red)?
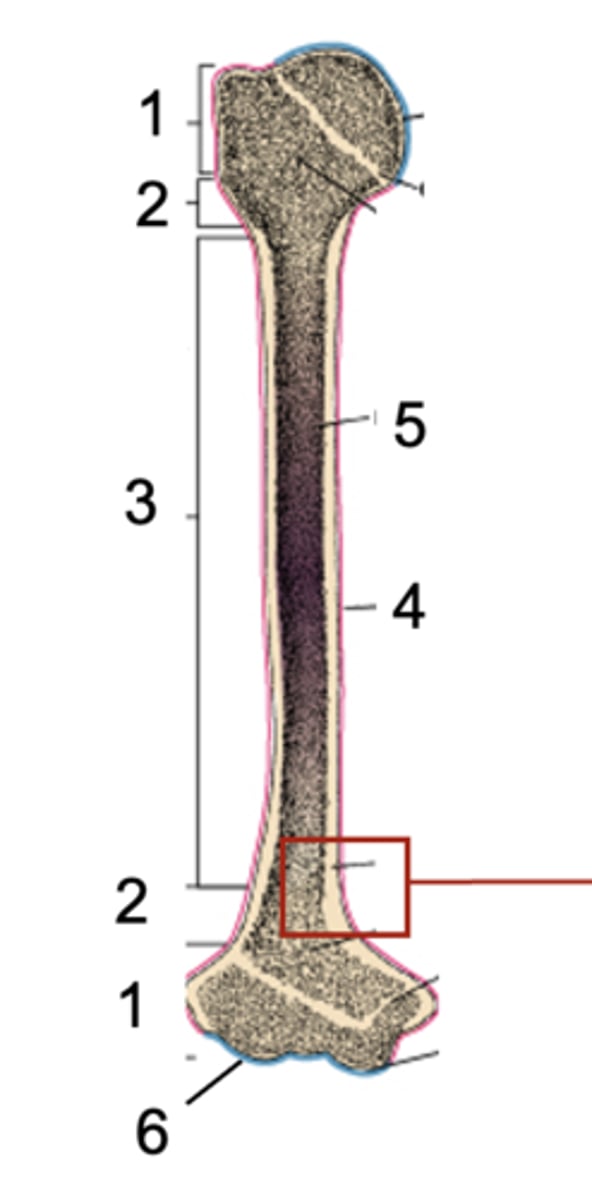
Bone marrow
What is shown at #5?
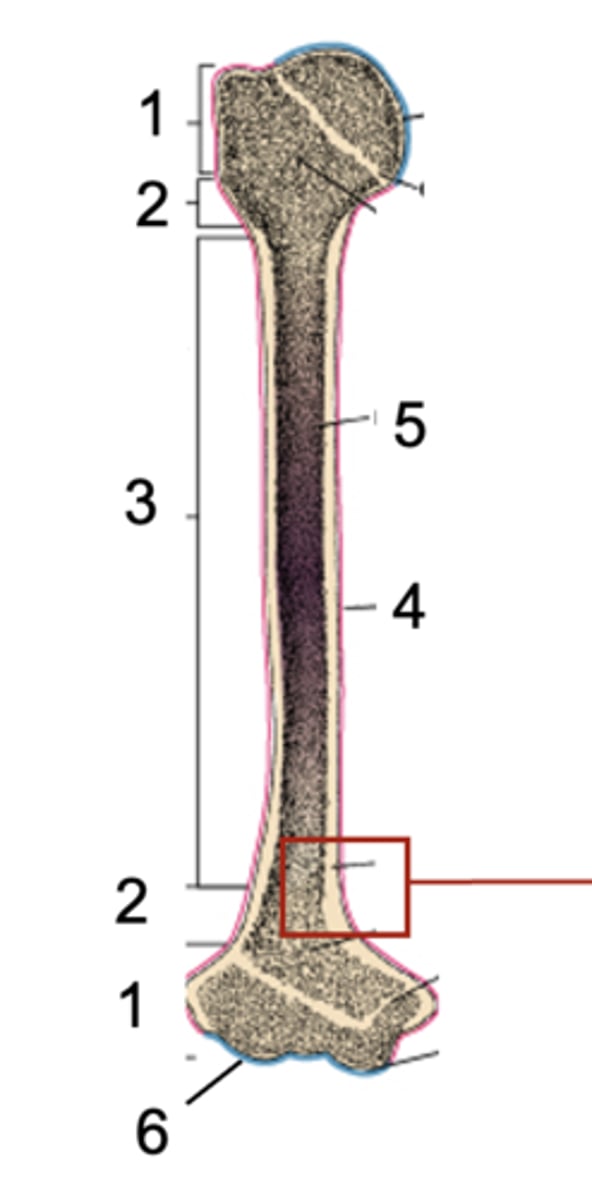
Articular cartilage
What is shown at #6 (blue)?
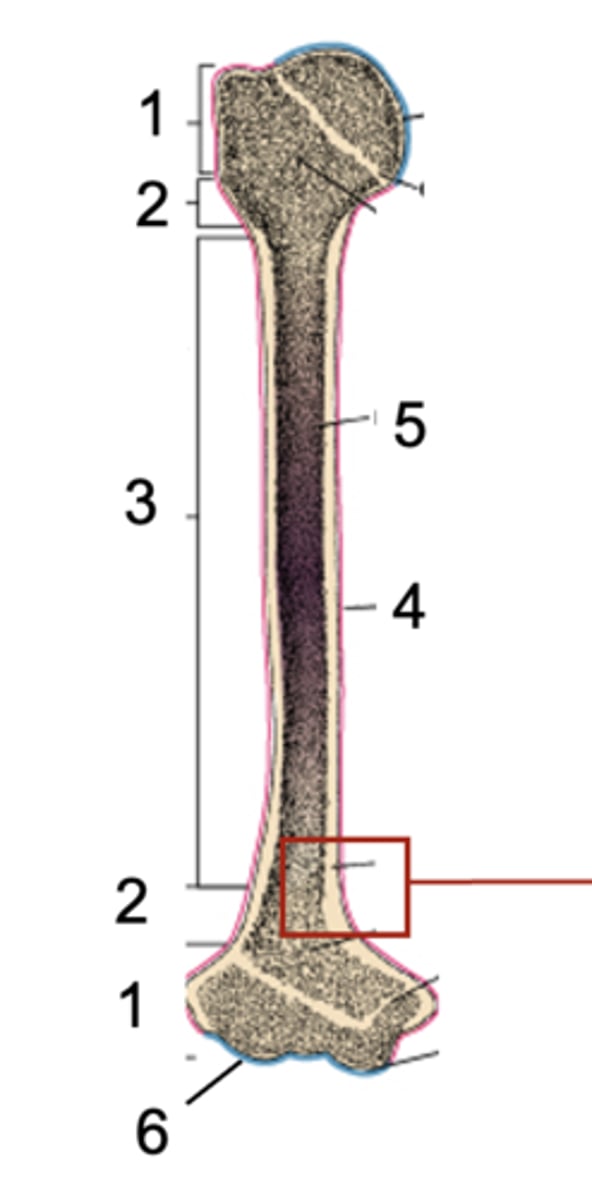
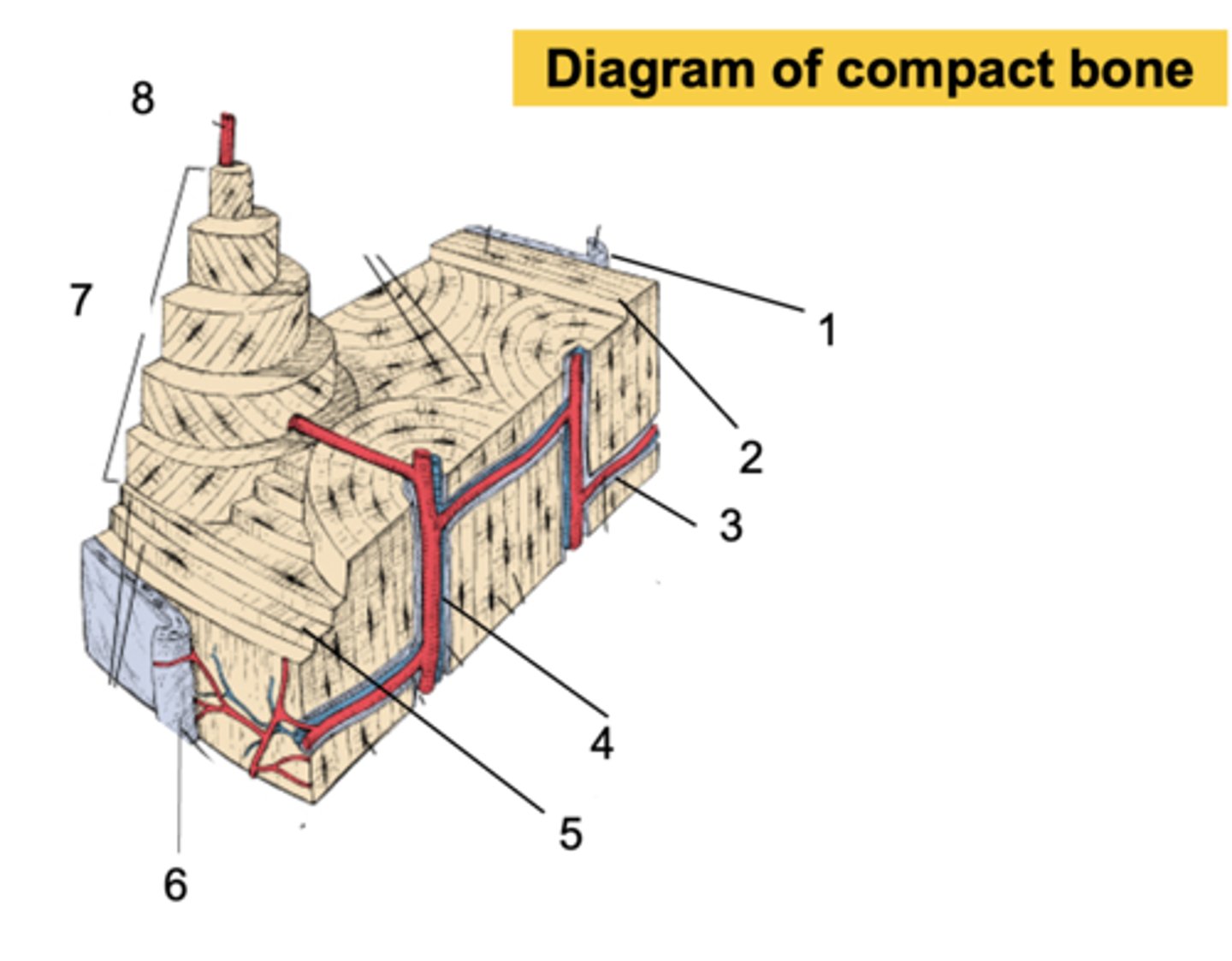
compact bone
what type of lamellar bone has:
-Haversian systems
-concentric lamellae
Spongy bone
What type of bone is formed first?
Spongy bone
What type of bone has a lamellated matrix?
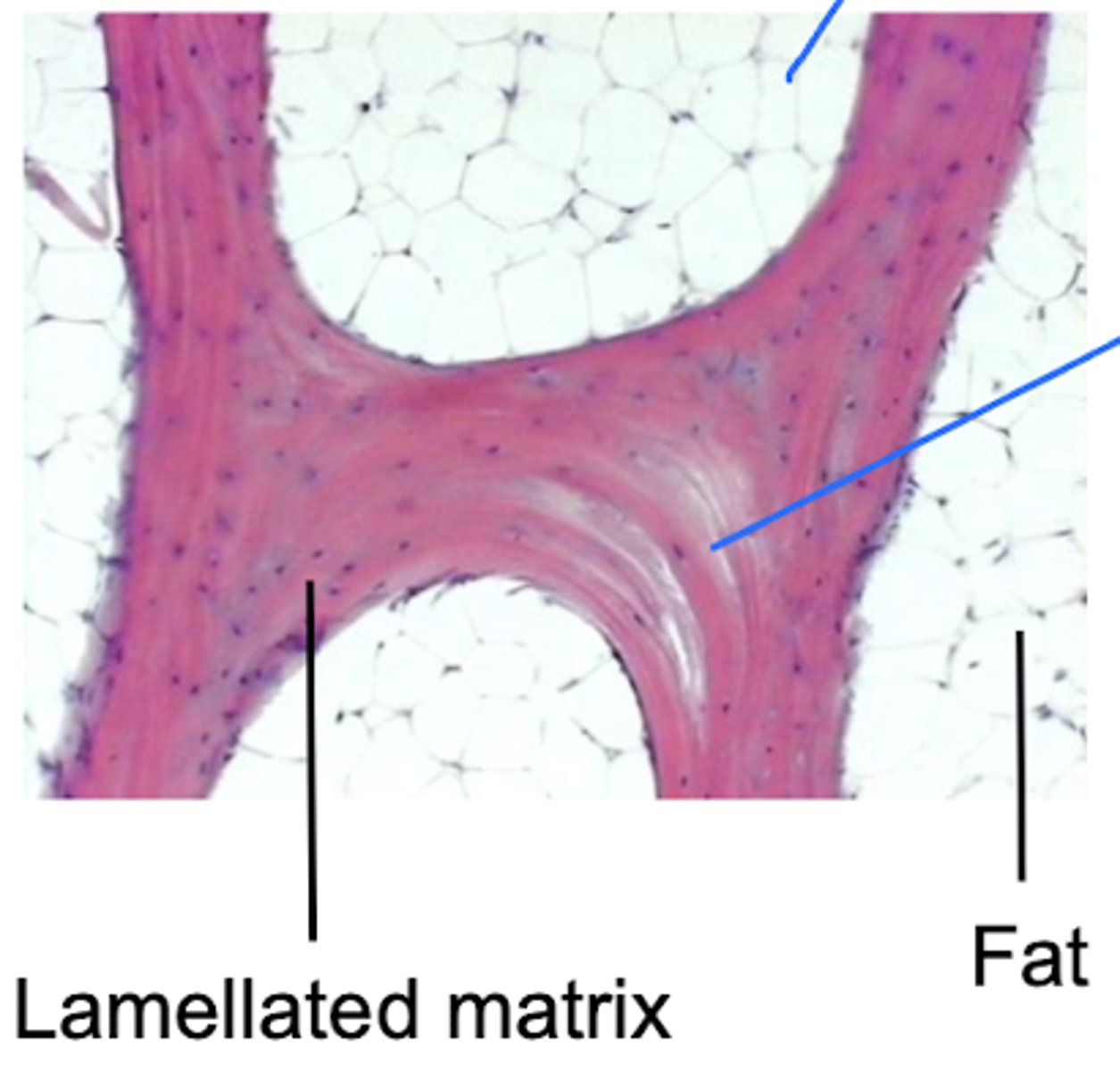
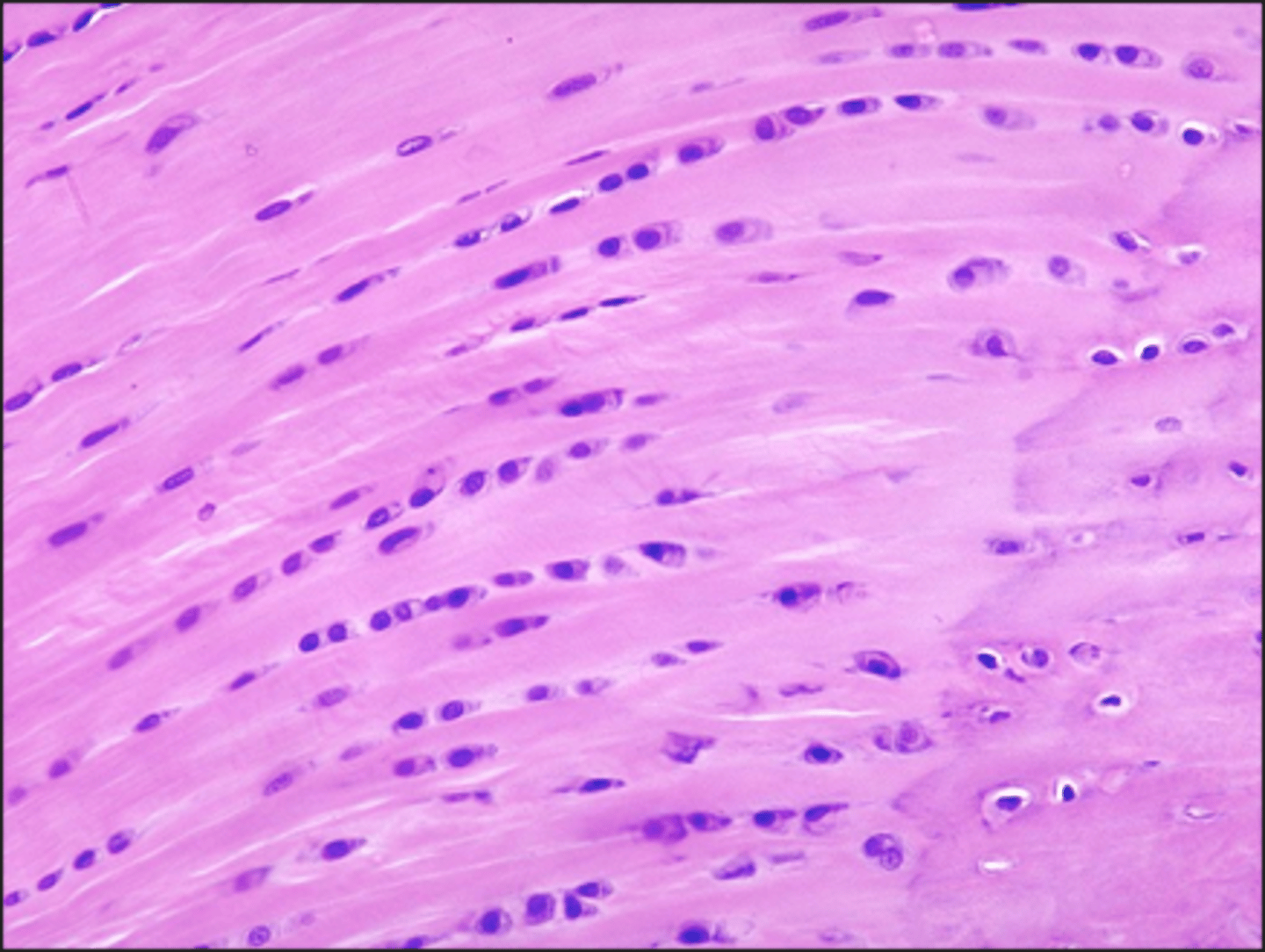
Hyaline cartilage
Identify this tissue
Osteons
Mature compact bone is composed of __________
Volkmann's canal (or transverse canal)
What connects osteons inside and outside the bone?
Haversian canal
What is the center of an osteon called?
Endosteum
What is shown at #1?
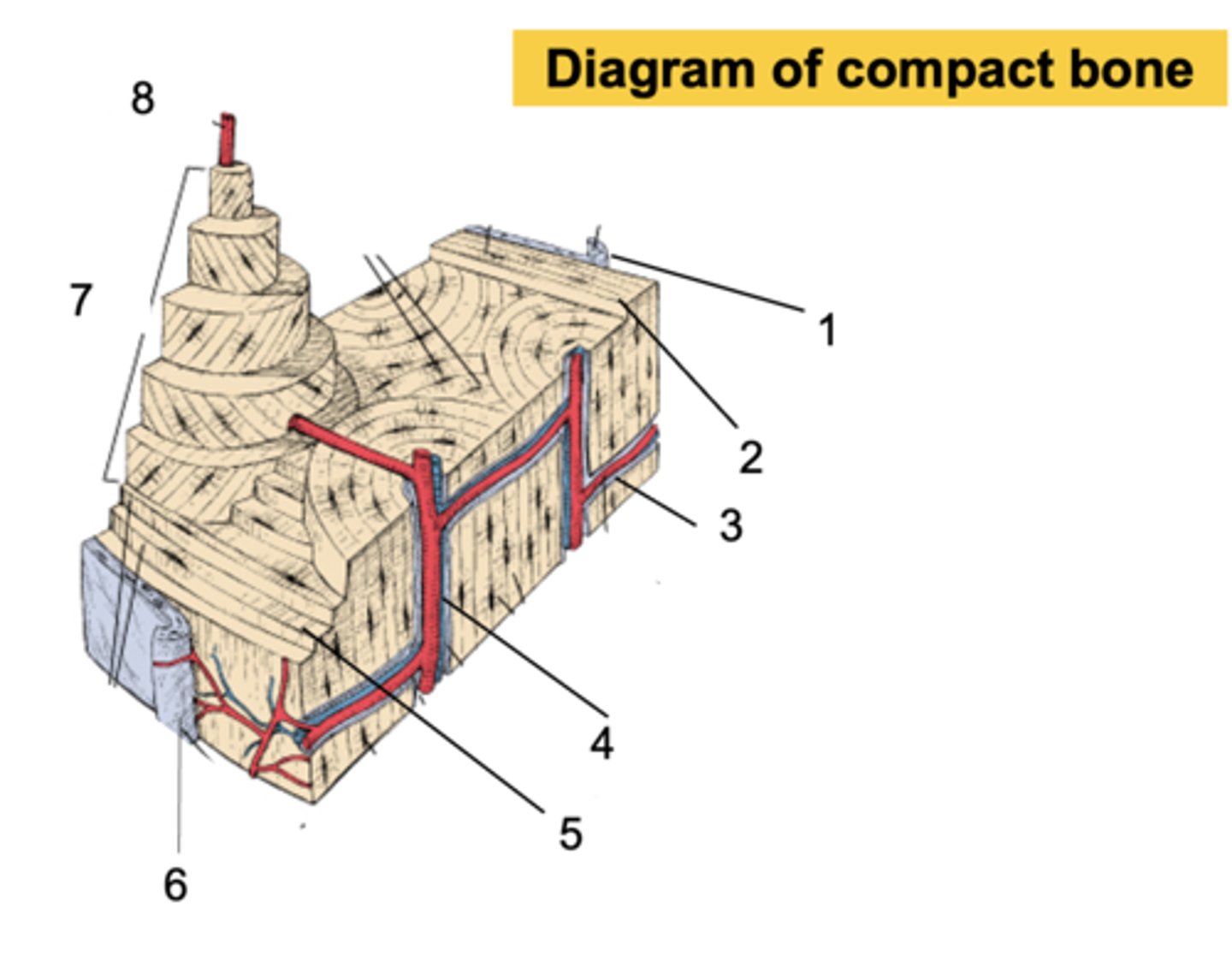
Inner circumferential lamella
What is shown at #2?
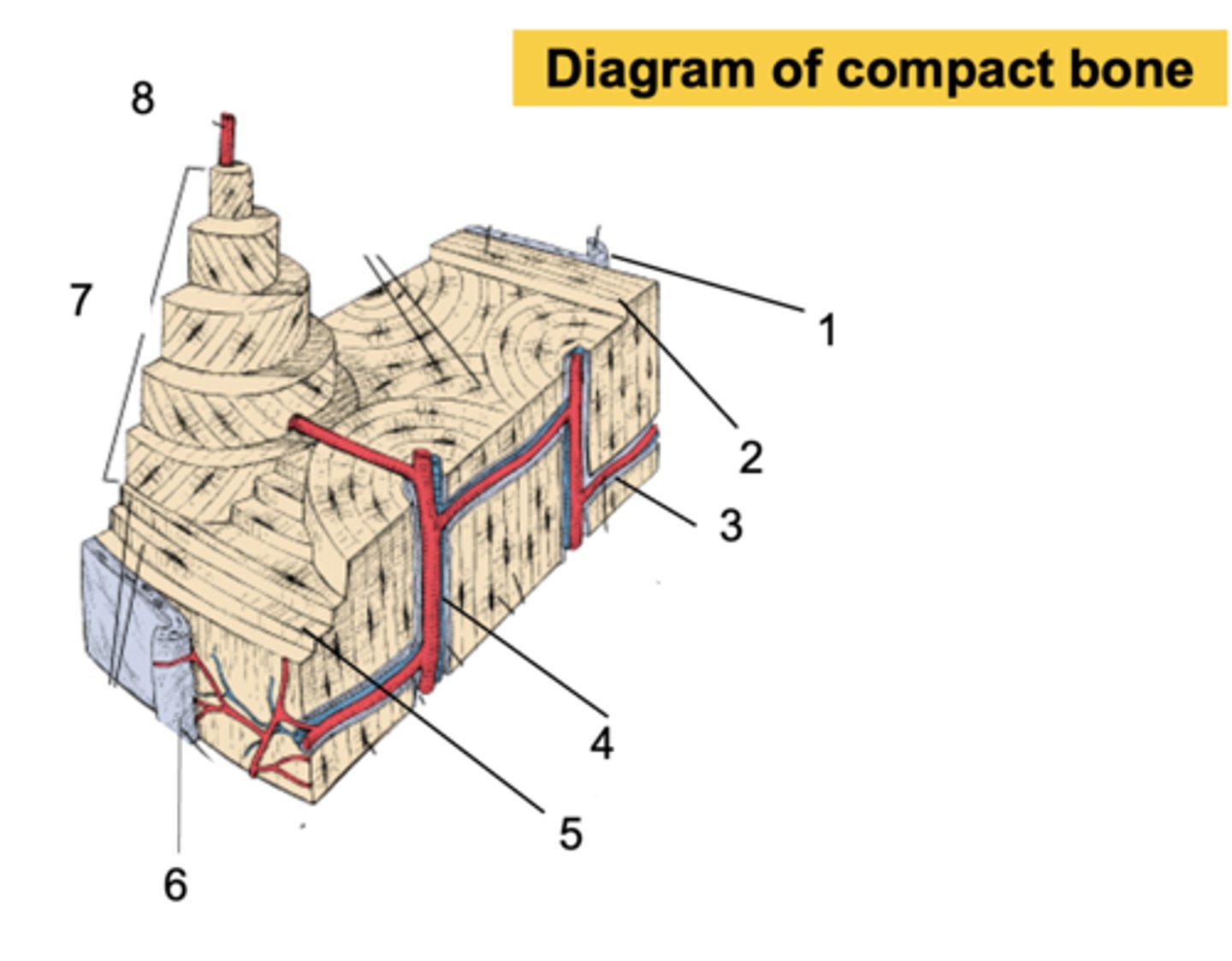
Volkmann's canal
What is shown at #3?
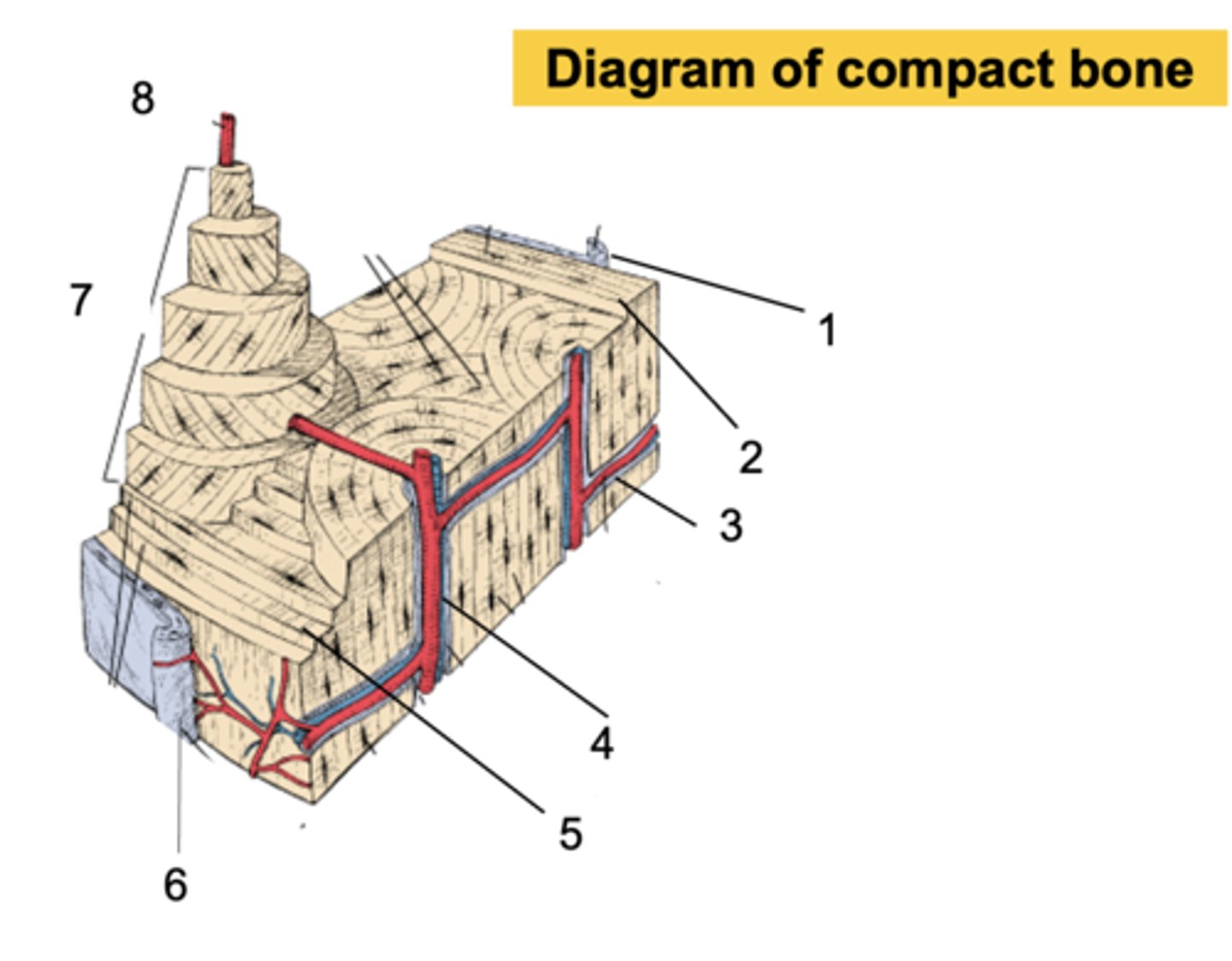
Haversian canal
What is shown at #4?