Week 4 Anatomy 2025 sem 1
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
What is a synapse?
Where an axon meets a neuron
What characteristic do excitatory synapses have?
Dendrites
What characteristics do inhibitory synapses have?
Cell bodies
What is white mater?
Myelinated brain matter
What is grey matter? Give examples
Unmyelinated neuronal cell bodies such as the cortex, basal ganglia, diencephalon nuclei and brainstem nuclei
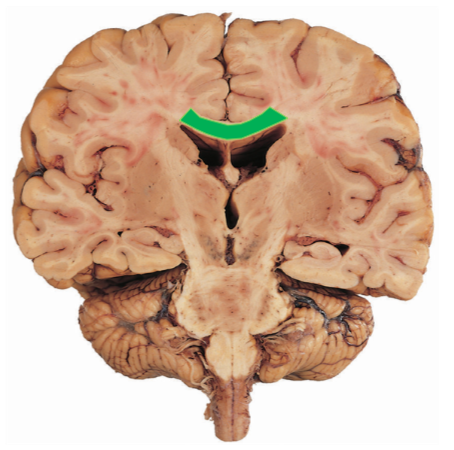
What is this bridge that connects the two hemispheres of the cerebrum?
Corpus callosum
What is this structure?
Cerebrum
What does white matter contain?
Axons
Commisural fibres
Association fibres
Projection fibres
What fibres to the external capsule contain and what are they responsible for?
Corticocortal fibres responsible for connecting the cerebral cortex areas within the same hemisphere.
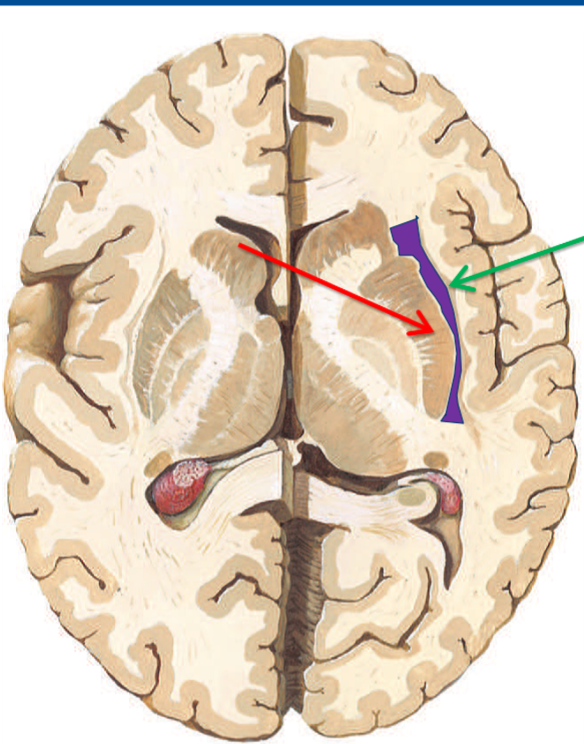
What structure is highlighted purple?
External capsule
What are the two structures the external capsule runs lateral to?
Lentiform nucleus
Claustrum
What is the corona radiata and what is its role?
Multiple broad fan shaped tracts interconnecting the cerebral cortex with the thalamus
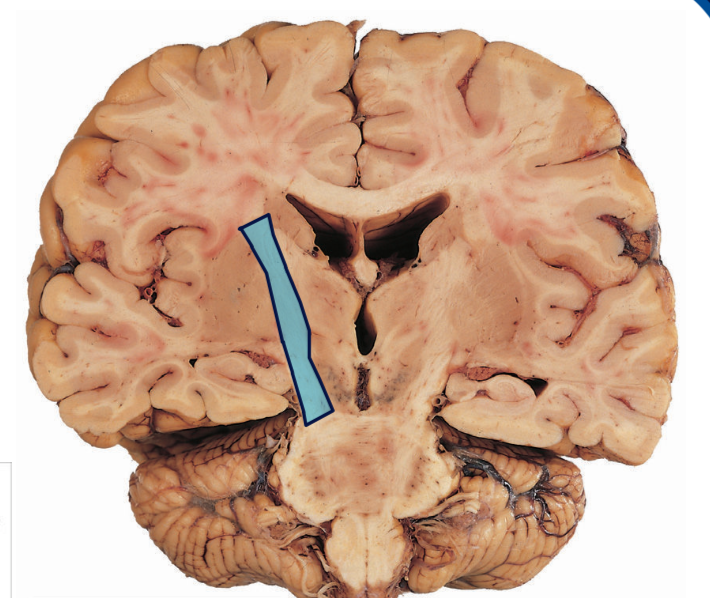
What structure is highlighted blue?
Internal capsule
What does the internal capsule consists of?
Largest collection of projection fibres within the cerebrum
What are the two projection fibre pathways in the internal capsule?
Afferent sensory to pariteal lobe
Efferent motor from frontal lobe
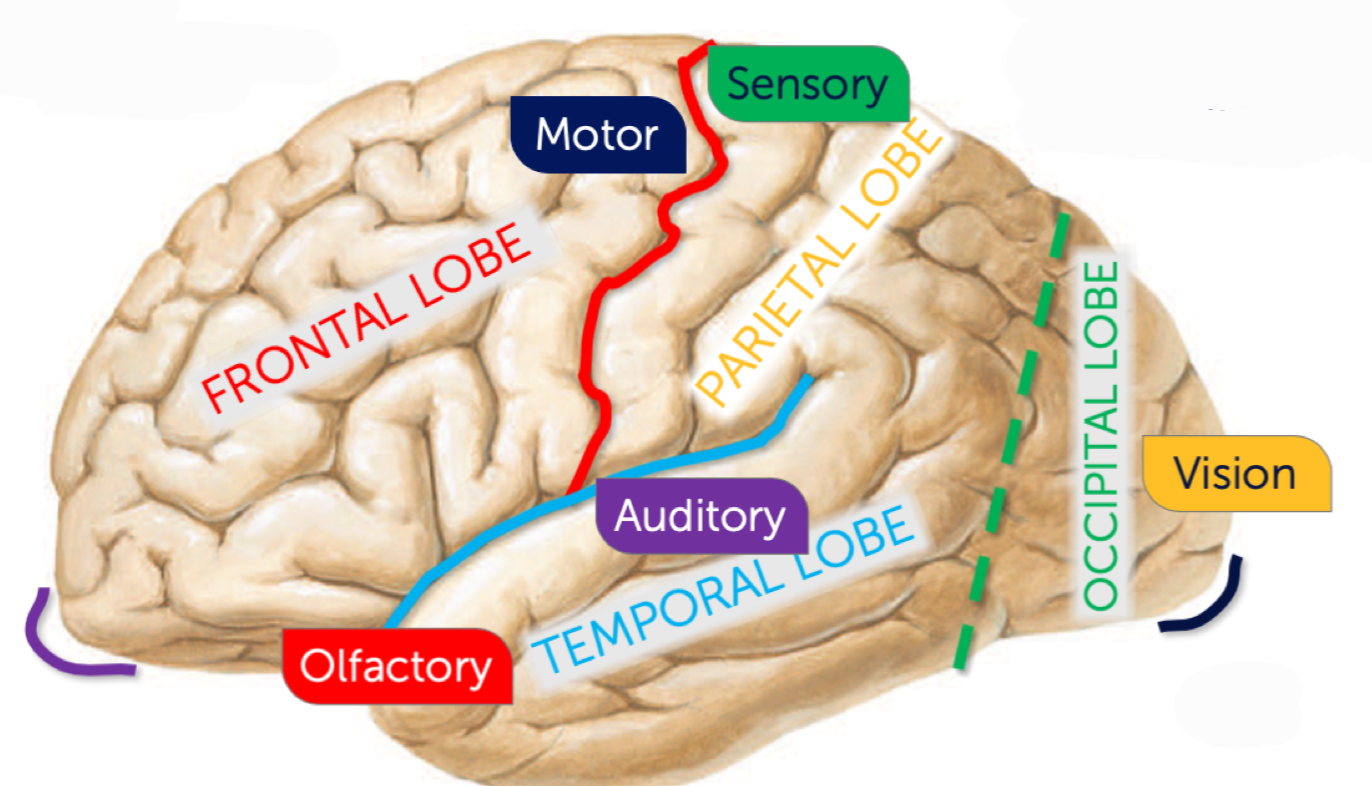
What sulcus is highlighted red?
Central sulcus
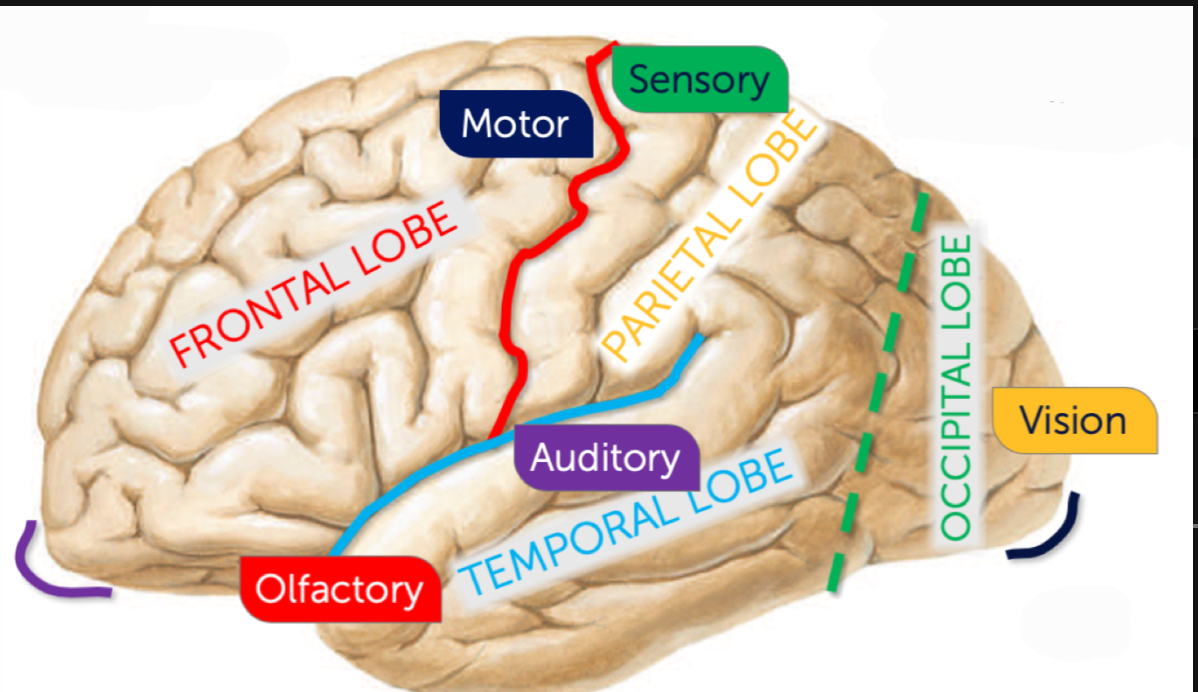
What sulcus is highlighted green?
Parieot-occipital sulcus
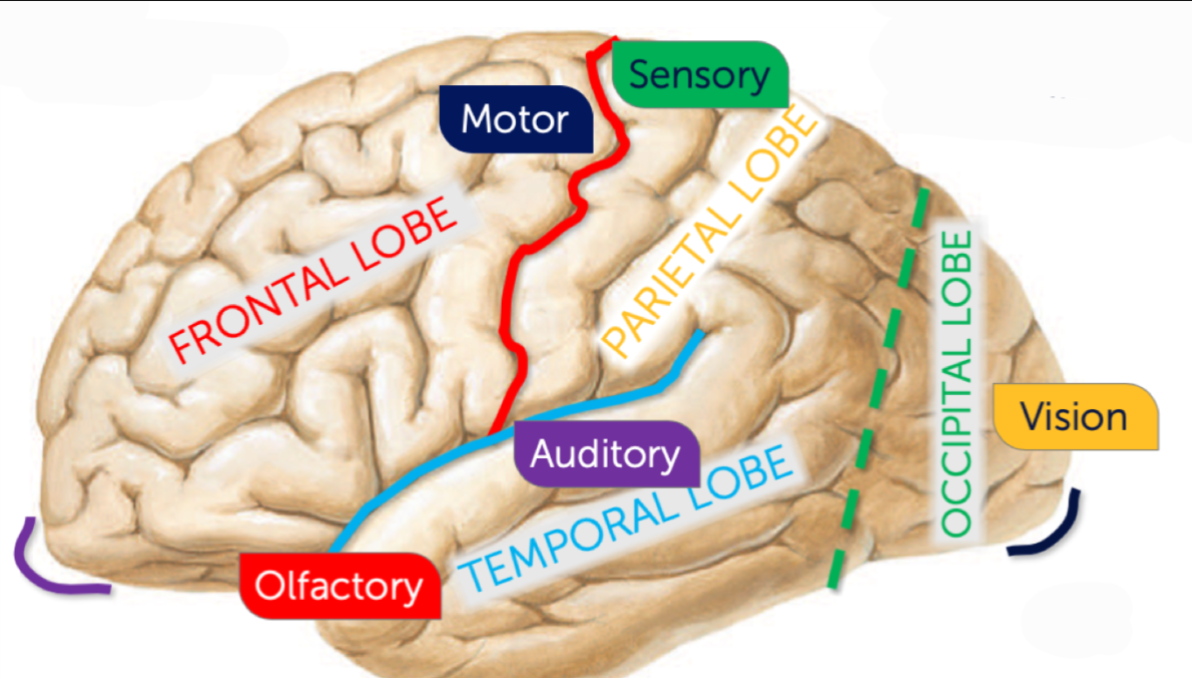
What sulcus is highlighted black?
Occipital pole
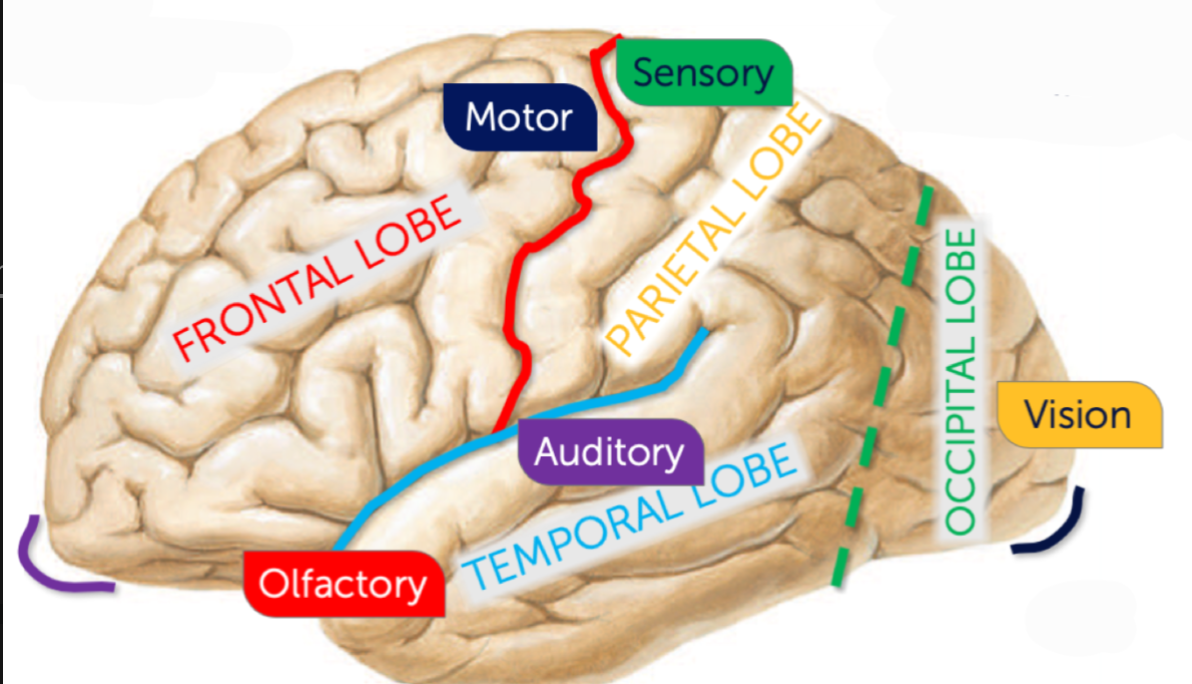
What sulcus is highlighted purple?
Frontal pole
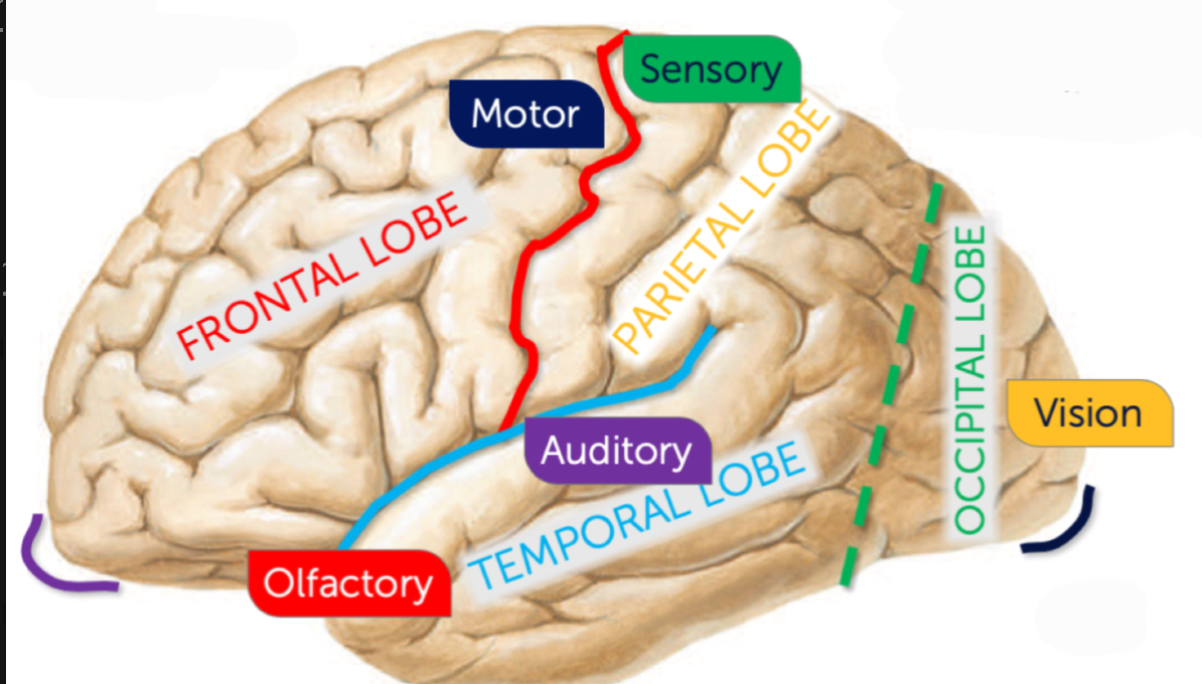
What sulcus is highlighted blue?
Lateral sulcus (fissure)
What forms the lateral wall, roof and floor surrounding the diencephalon?
Lateral wall - Thalamus
Roof - Lateral ventricles
Floor - Hypothalamus
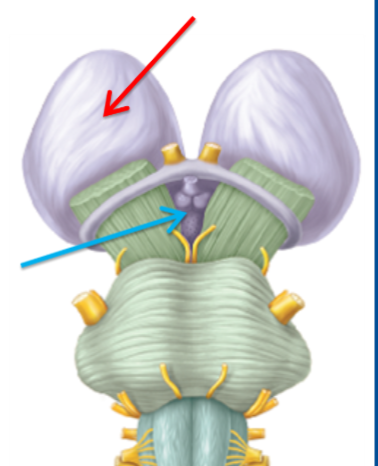
What structure is highlighted red?
Diencephalon
What is the role of the diencephalon?
Is a gateway, processing and relaying:
Sensory inputs (including sensory gating),
Motor coordination signals from the cerebellum and basal ganglia,
Inputs from the hypothalamus and mammillary bodies.
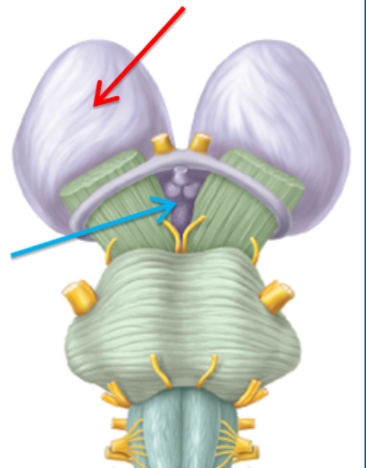
What structure is highlighted blue?
Hypothalamus
What is the role of the hypothalamus?
Connection to the pituitary gland allows it to regulate the body’s hormonal functions and maintain homeostasis
What is the basal ganglia and what is it responsible for?
Clusters of deep grey matter that help regulate skeletal muscle movement by controlling the speed, range, and coordination of motion, playing a key role in movement planning beyond the spinal level.
What are the three parts of the basalt ganglia?
Corpus stratum
Substance Niagara
Subthalamic nucleus
What are the two parts of the Corpus stratum?
Lentiform and caudate nucleus
What are the two parters of the Lentiform nucleus?
Putamen and globus pallidus
What is corpus tritium involved in?
Muscle tone and movements
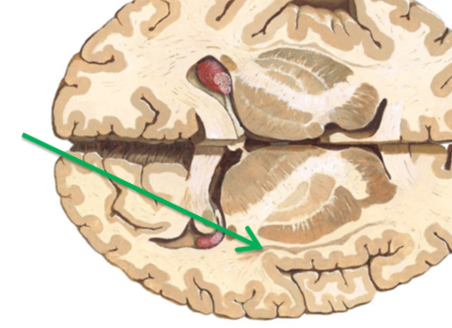
What is this structure what is located between (this fucking thing apparently has no known purpose)?
Claustrum between external capsule and insula
What is the role of the subthalemic nucleus?
Modulating movement
What is the role of nucleus accumbens?
Linked to reward, motivation and gratification and plays a role in addictive behaviours
What is the substania innomiata associated with?
Alzheimers disease as this is where a large loss of neurons are observable
What is the substania Niagara’s purpose?
Contains dopermagenic neurons crucial for movement control and is the most affected by Parkinson’s disease
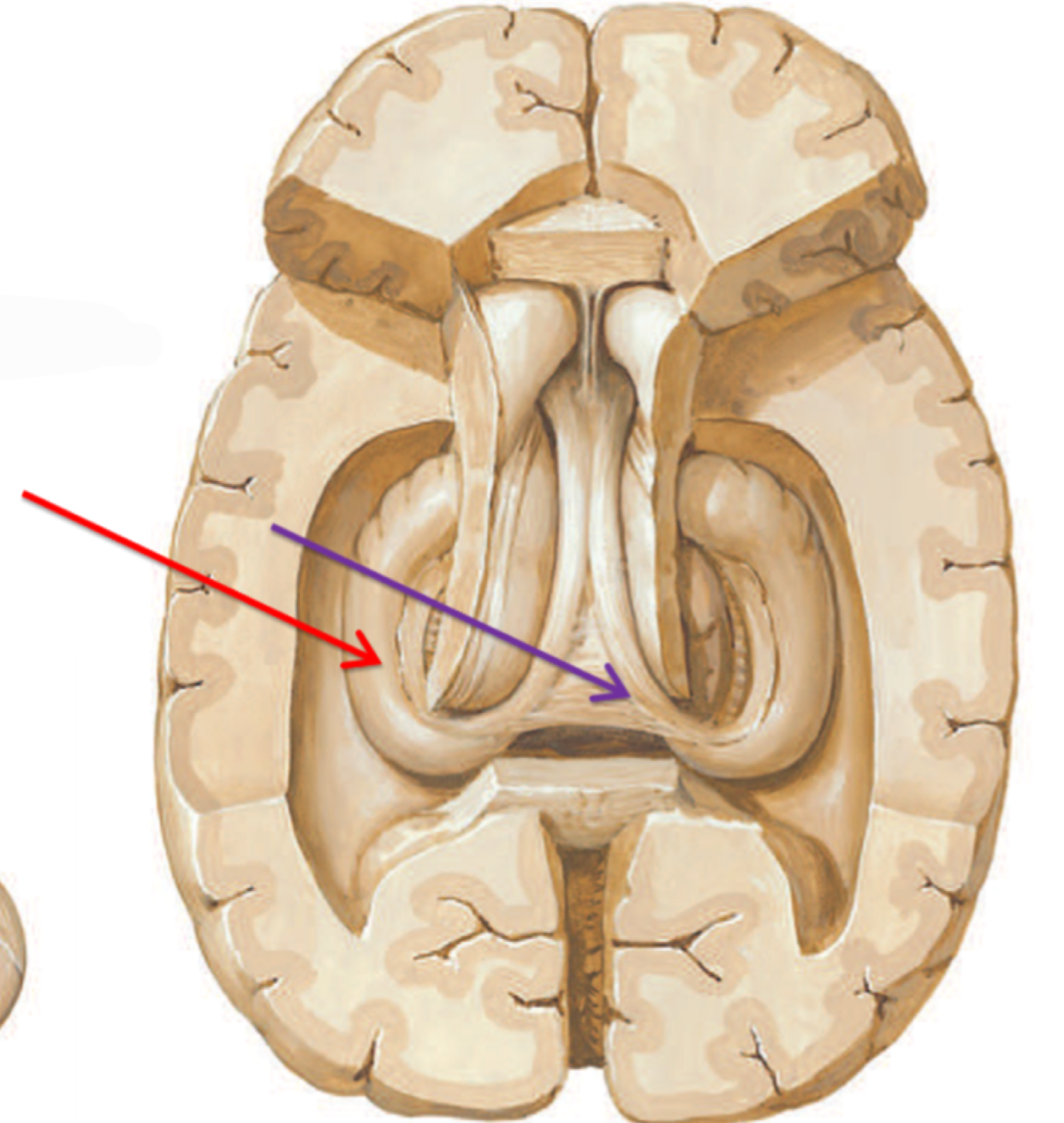
What structure is highlighted in red?
Hippocampus
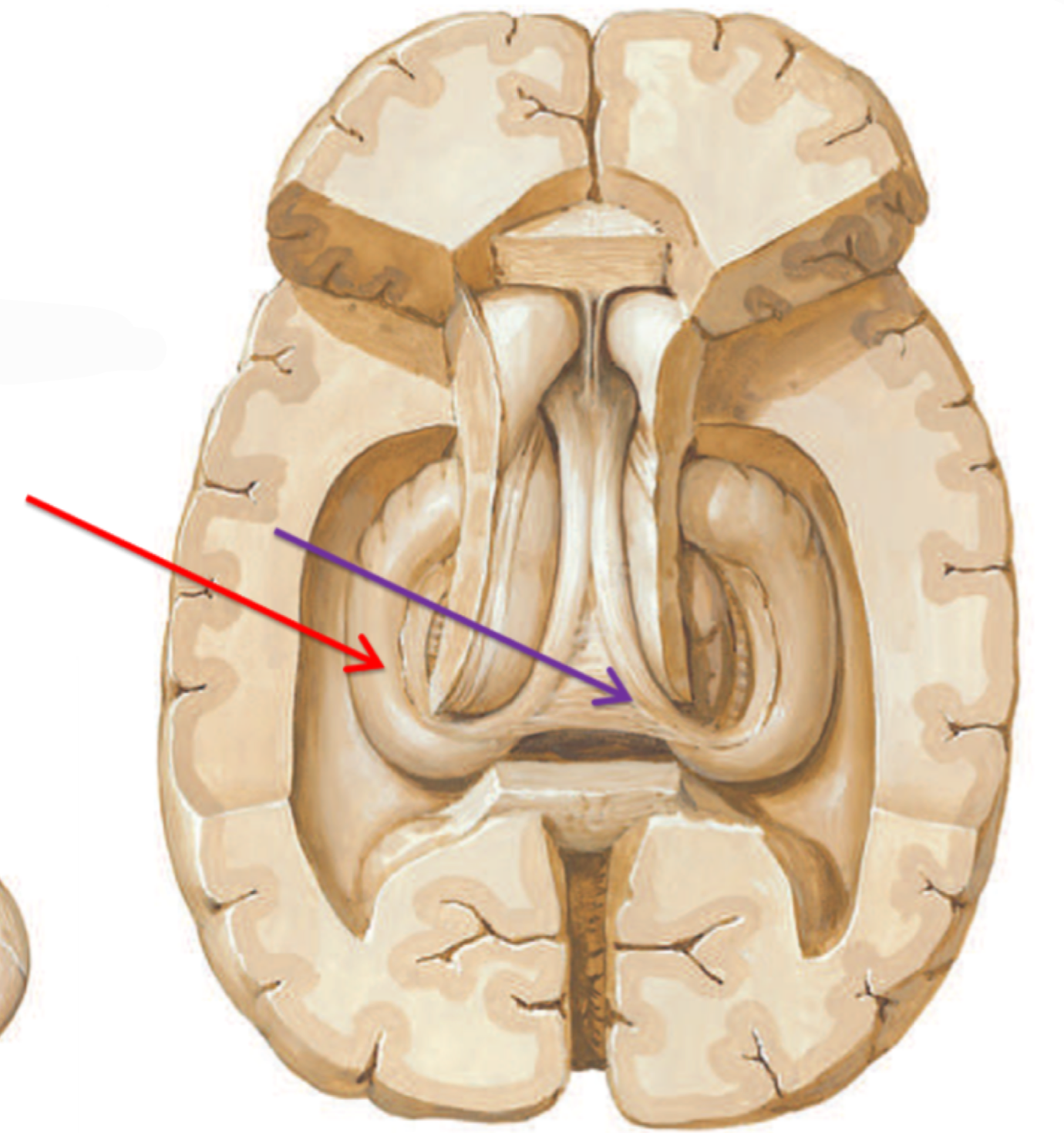
What structure is highlighted in purple?
Fornix
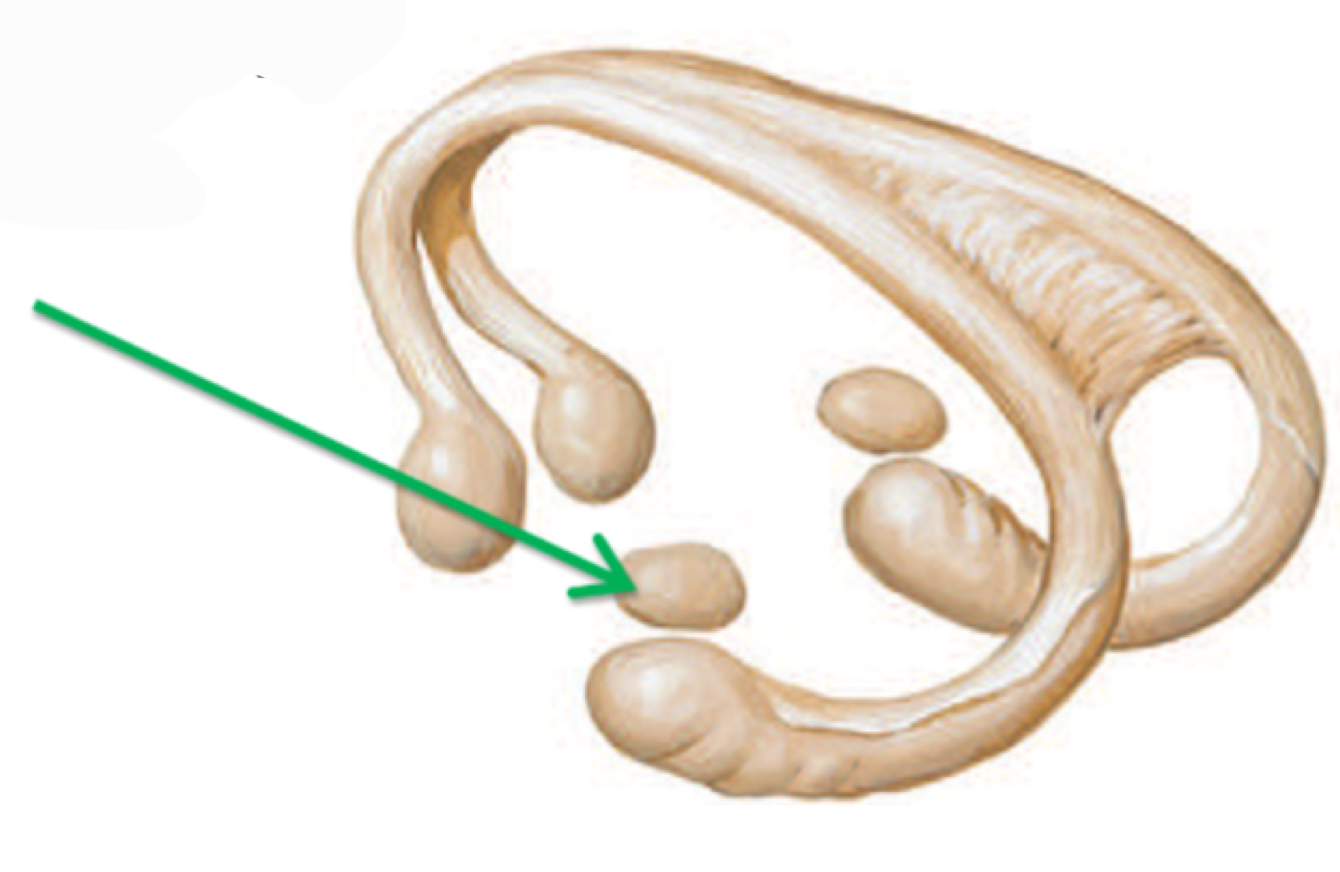
What structure is this?
Amygdaloid body
What are the there parts of the limbic system covered this module?
Hippocampus, Fornix, Amygdaloid body
What is the limbic system?
A group of small, connected brain parts around the corpus callosum and diencephalon
What are the main functions of the limbic system?
Memory, emotion, behaviour, and smell (olfaction)
Is the limbic system well-defined in function?
No, its functions are not sharply defined
Name 6 key structures in the limbic system.
Hippocampus, amygdala, cingulate gyrus, Fornix, mammillary bodies and anterior thalamic nuclei
Which limbic structure is linked to memory formation?
The hippocampus
Which structure in the limbic system is linked to emotion, especially fear?
The amygdala
Which structure connects limbic parts and carries signals?
The fornix
What cranial nerves does the cranial nerve nuclei house?
CN III and IV
What does the midbrain cavity contain?
Cerebral aquaduct
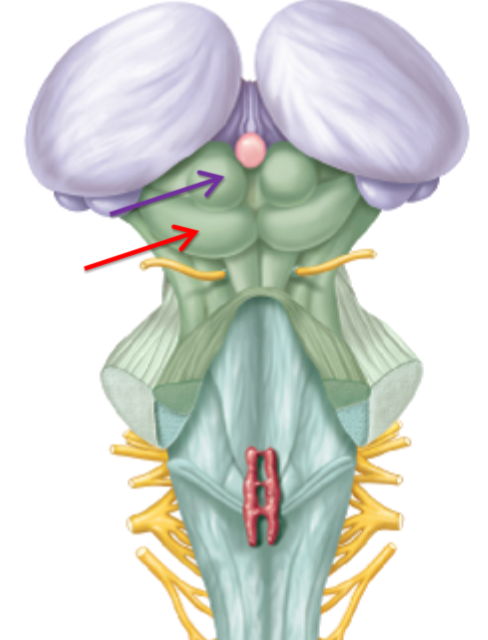
What structure is this what is it responsible for? (purple)
Superior colliculi responsible for visual reflex
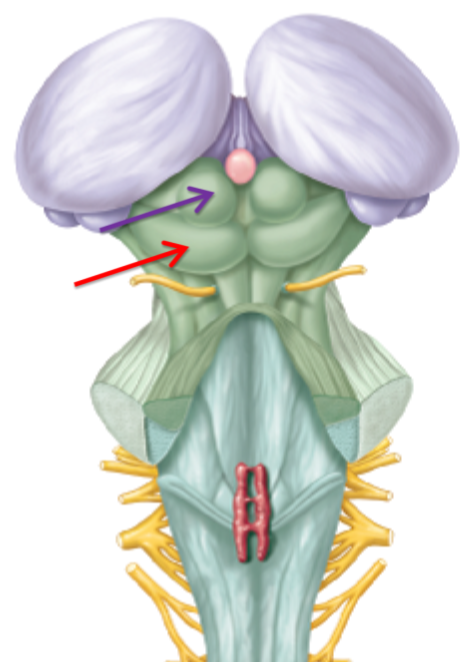
What structure is this what is it responsible for? (red)
Inferior colliculi responsible auditory reflex
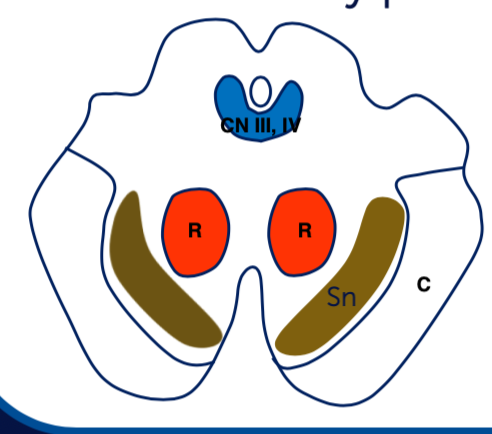
What is structure C? What is responsible for?
Corticospinal pathway which is a major motor pathway
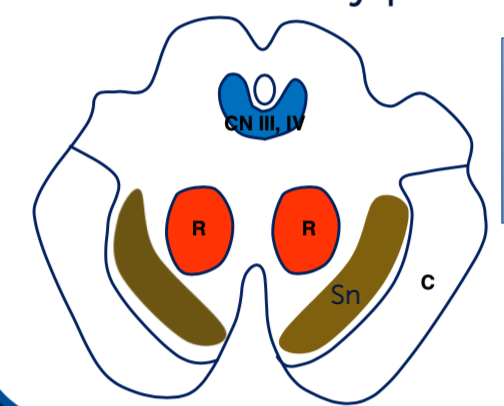
What is structure Sn? What is responsible for?
Substantia nigra involved in movement control and regulation of dopamine.
What is cranial nerve III?
Occulomotor nerve responsible for the ability to move and block your eyes
What cranial nerve IV?
Trochlear nerve responsible for controlling superior oblique eye muscle movement.
What does the pons cavity contain?
Fourth ventricle
What is reticular formation the the pons responsible for?
Includes vital centres for autonomic functions (e.g. respiration)
What cranial nerve nuclei are held in the pons?
CN V - CN VIII
What is the main function of the Trigeminal nerve (CN V)?
Facial sensations, taste, and jaw movements
What are the three branches of the Trigeminal nerve?
Ophthalmic (V₁), Maxillary (V₂), Mandibular (V₃)
What does the Abducent nerve (CN VI) control?
Eye movement
What is the role of the Facial nerve (CN VII)?
Facial expressions and sense of taste
What is the function of the Vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)?
Hearing and balance
What are the cranial nerves medulla?
CN IX - XII
What is the role Olives (Olivary nuclei)?
Involved in motor learning and coordination
What do the pyramids in the medulla contain?
Contain the corticospinal tracts (motor pathways)
What do the cavity in medulla contain?
Continuation of the fourth ventricle into the spinal canal
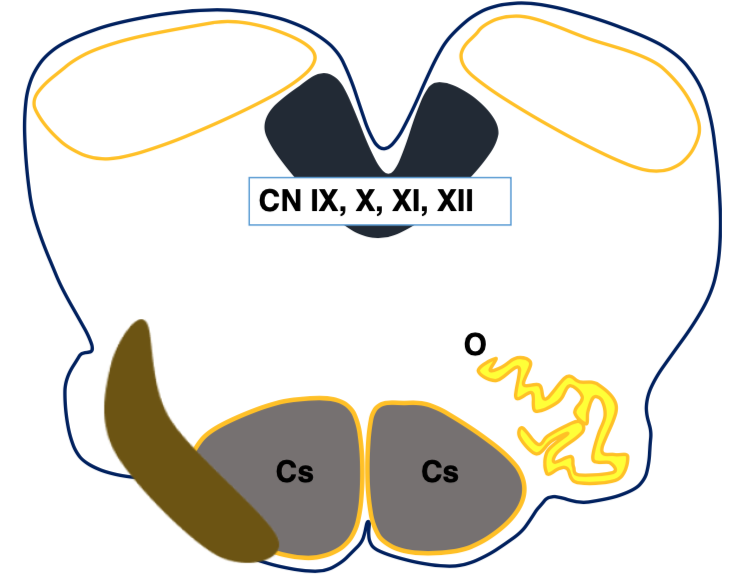
What is structure Cs and O?
Cs- Corticospinal tract
O- Olivary nucleus
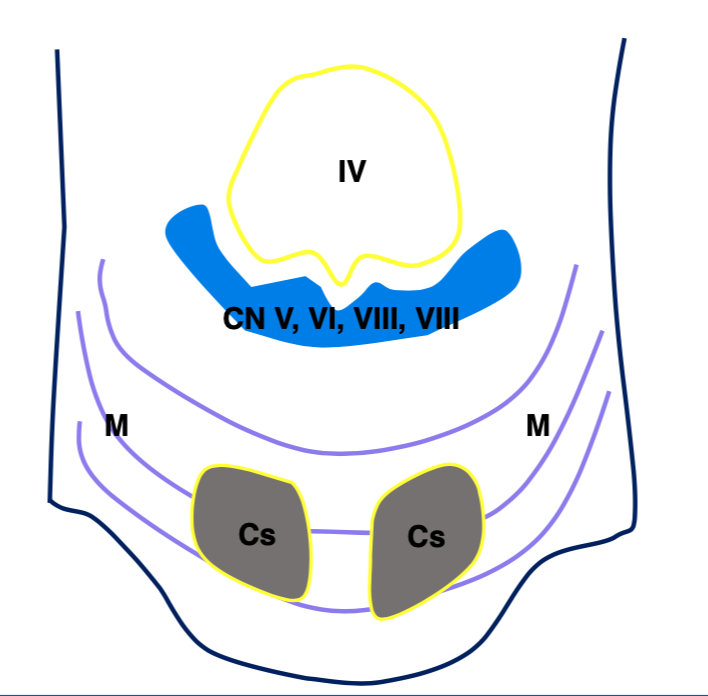
What is structure M?
Middle cerebellar peduncle
What cranial nerves are held in the medulla?
CN IX - XII
What does the Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) control?
Taste and swallowing
What is the function of the Vagus nerve (CN X)?
Regulates digestion and heart rate
What does the Spinal Accessory nerve (CN XI) control?
Shoulder and neck muscle movement
What does the Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) control?
Tongue movement