Lens & Sclera
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
vascularization of the lens
avascular
where is the lens located
in the posterior chamber between the vitreous and iris
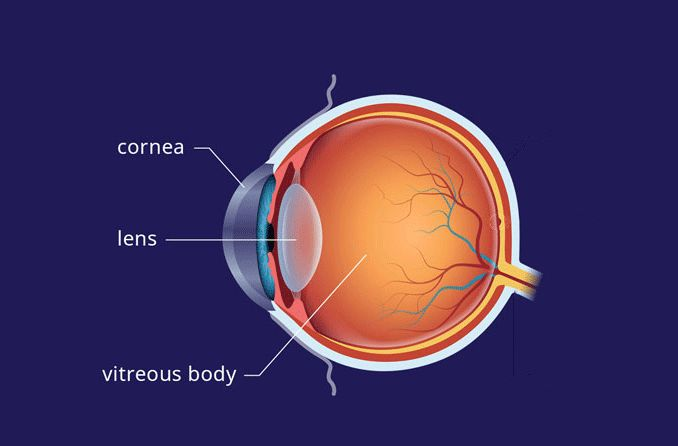
main function of the lens
light transmission and focusing light onto the retina
refractive power of lens
20 D (1/3 of refractive power of the eye)
the (anterior/posterior) lens is steeper
posterior
the lens is (more/less) acidic than the surrounding aqueous humor and blood plasma
more acidic
the lens is (spherical/aspherical) and becomes (flatter/steeper) towards the periphery
aspherical
flatter
what attaches the posterior lens surface to the anterior vitreous
ring-shaped hyaloid capsular ligament
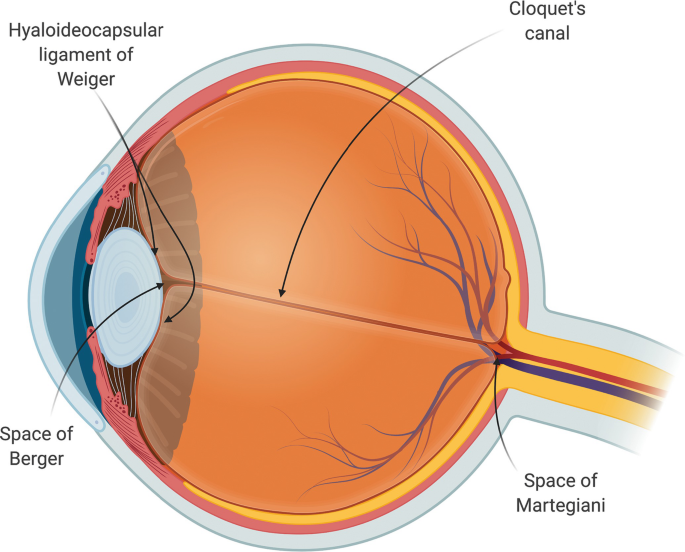
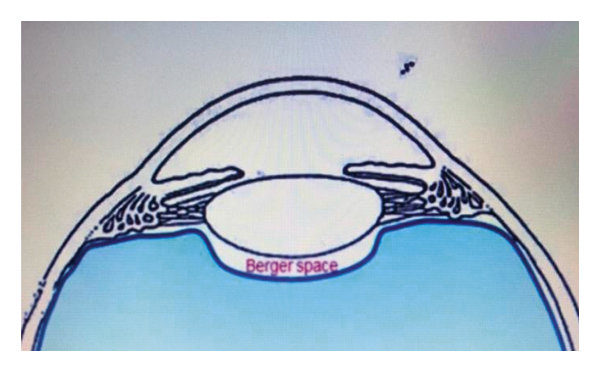
retrolental space of Berger
potential space between posterior pole of lens and anterior vitreous
what 2 characteristics of the lens help reduce spherical aberration
peripheral flattening
gradient index of refraction
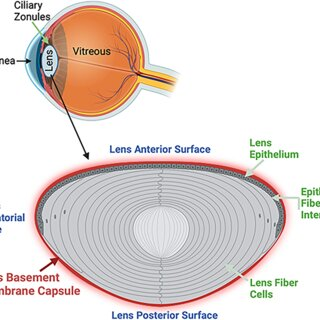
3 main parts of lens
lens capsule, lens epithelium, lens cortex
BM of the lens
lens capsule
location of lens capsule and how it is made
surrounds the entire lens
secreted by the anterior lens epithelium
where is the lens capsule the thinnest and thickest
thinnest at the posterior pole
thickest in a circle around the anterior pole
what is the lens capsule composed of
type 4 collagen fibers and GAGs
function of lens capsule
barrier against large molecules entering the lens
anterior lens capsule is the attachment point for lens zonules that extend from the non-pigmented ciliary epithelium
lens epithelium histology
single layer of cuboidal epithelial cells adjacent to anterior lens capsule
where is there no lens epithelium and why
no posterior lens epithelium
posterior epithelium was used to form primary lens fibers during embryological development
what are the junctions of lens epithelium cells
maculae occludens and gap junctions
function of lens epithelial cells
secrete lens fibers and lens capsule
main site of lens metabolism
germinal zone
zone anterior to the lens equator that contains mitotic epithelial cells that become secondary lens fibers
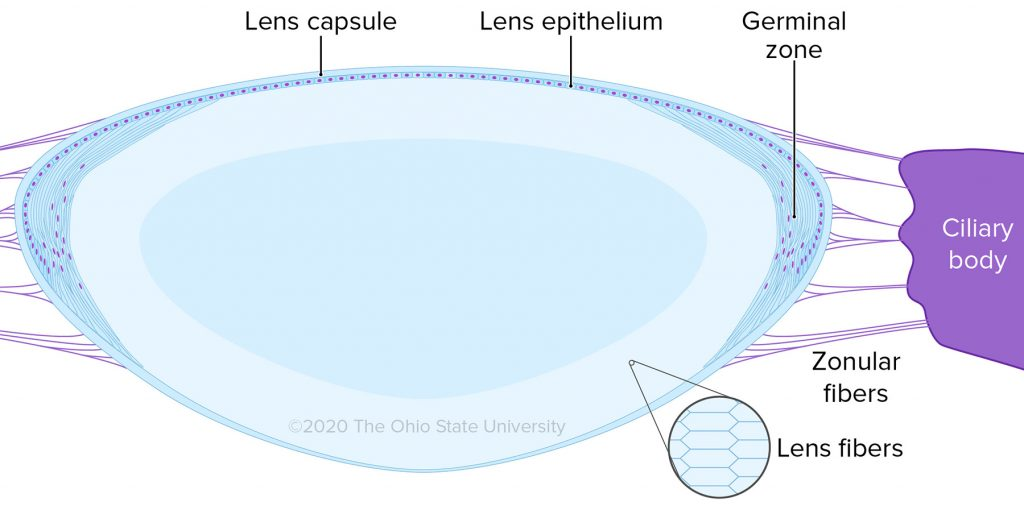
where are secondary lens fibers produced and when
germinal zone
production of lens fibers is continuous throughout life
composition of lens cortex
65-70% water, 30-35% protein, 1% other
what makes up most (85-90%) of lens proteins
water soluble alpha, beta, and gamma crystallins tightly packed within the cytoplasm of lens fiber cells
__________ crystallins act as ___________ by helping other crystallins recover from injury
alpha crystallins act as molecular chaperones by helping other crystallins (beta & gamma) recover from injury
what causes structural damage to crystallins & lens fibers
UV exposure and oxidation
role of alpha crystallins in the lens cortex
prevent degradation of lens fibers and loss of transparency by acting as molecular chaperones and helping beta & gamma crystallins recover from injury
what creates a gradient of refraction throughout the lens
variable crystallin concentration
where is the index of refraction highest in the lens
higher in the nucleus than the anterior lens
index of refraction of aqueous and vitreous
1.336
how are lens fibers organized and why
joined together by multiple interlocking mechanisms
allows lens fibers to easily slide past one another during lens movement
other names for lens zonules
zonules of zinn, suspensatory ligaments
what produces lens zonules
basement membrane of the non-pigmented ciliary epithelium in the pars plana and pars plicata
what are zonules composed of
microfibrils that have fibrillin and ECM
zonules (HAVE/DO NOT HAVE) true elastic fibers
do not have
primary lens zonules
attach right to lens capsule in pre and post equatorial regions of the lens
secondary lens zonules
connect primary lens zonules to one another or to non-pigmented ciliary epithelium of the pars plana
tension zonules
connect primary lens zonules to the valleys between the ciliary processes of the pars plicata
function of the sclera
forms posterior 5/6 of the protective CT coat of the eye (other 1/6 is cornea)
helps maintain globe shape and protect intraocular structures
what is the point of attachment for the EOMs
sclera
thickest area of the sclera
1 mm at the posterior pole
thinnest area of the sclera
0.3 mm under the recti tendon insertions
weakest area of the sclera
lamina cribrosa (within the ON)
what is the vascularization of the sclera
sclera is avascular
where does sclera get blood supply
sclera gets minimal blood supply from the episcleral vessels, choroidal vessels, and branches of the LPCAs
what innervates the sclera
sclera is minimally innervated by LPCNs and SPCNs
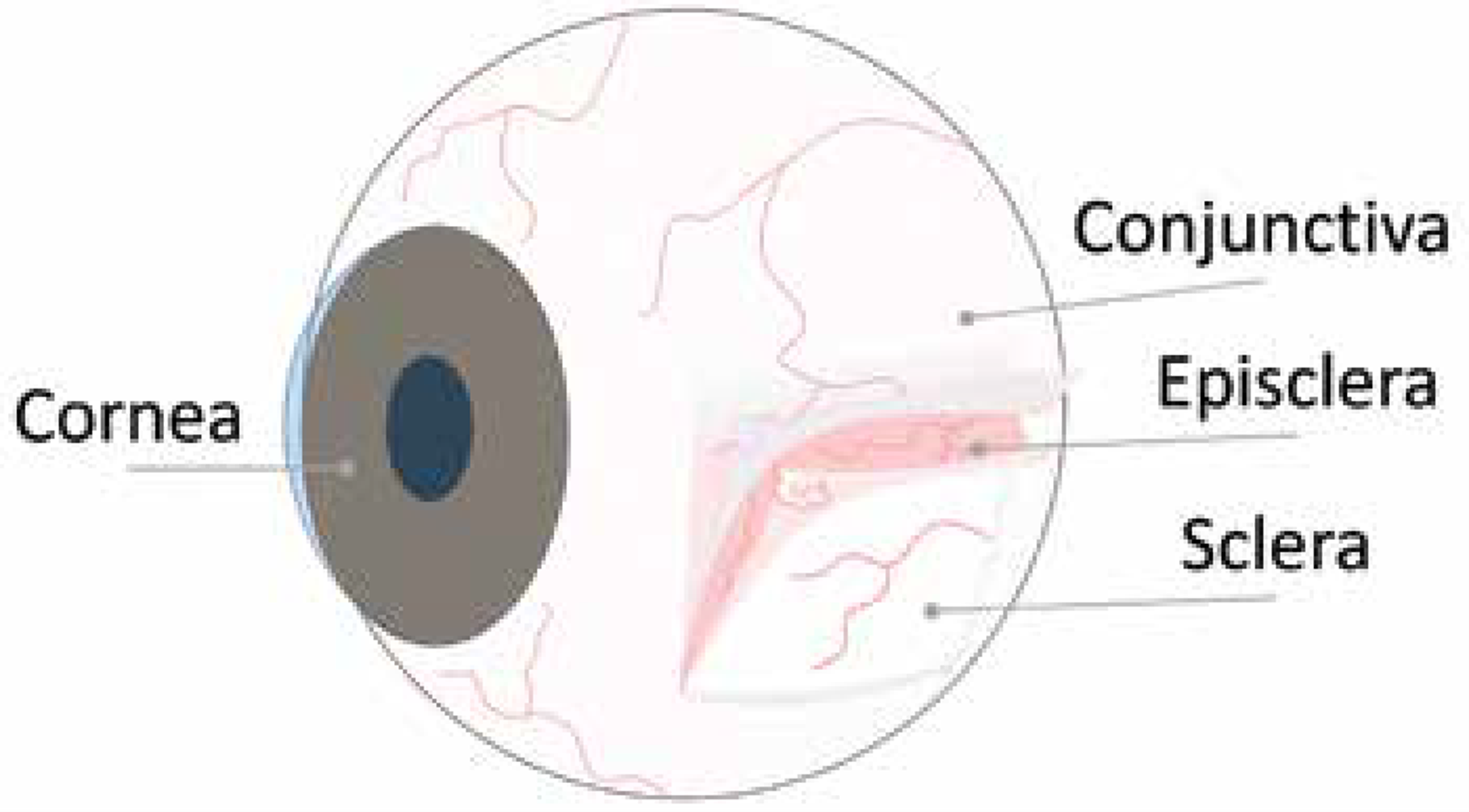
layers of the sclera
episclera, sclera proper, lamina fusca
episclera
loose CT with a capillary network that surrounds the cornea
ciliary flush definition and cause
circumlimbal injection of the episclera
inflammation of the CB or iris causes inflammation of the anterior ciliary arteries that innervate the episclera
where are the 2 networks of the ACAs
anterior conjunctiva
episclera
sclera proper
thick, dense, avascular CT continuous with corneal stroma
what is the sclera proper composed of
irregular collagen bundles, ground substance
collagen composition of sclera
irregular collagen bundles that provide strength but no transparency
composition of the sclera compared to the stroma
both have collagen bundles but stromal collagen is organized and evenly spaced (transparent) while scleral collagen is irregular and strong but opaque
both sclera and stroma have ground substance, but sclera has less fibroblasts and GAGs that stroma
episclera vs sclera proper
episclera: loose CT, highly vascular
sclera proper: dense CT, avascular
lamina fusca
innermost layer of sclera adjacent to choroid
lamina fusca composition
elastin fibers and melanocytes
conditions associated with blue sclera
ehlers-danlos syndrome
osteogenesis imperfecta
why does sclera have blue tint in infants
underlying uveal pigment is visible through thinner sclera
why does sclera become yellow in elderly
lipids become trapped in dense irregular CT over time
can signify liver disease
other name for tenon’s capsule
fascia bulbi
tenon’s capsule
thin transparent CT layer that covers the episclera
begins 2 mm behind limbus and encircles the rest of the globe
separates globe from surrounding adipose tissue
what layers surround and fuse with tenon’s capsule
episclera behind it
conjunctival submucosa in front of it
what perforates tenon’s capsule
tenon’s is perforated posteriorly by ON, ciliary vessels, ciliary nerves, and tendons of 4 recti muscles
anterior scleral foramen
area occupied by cornea (no sclera) 11.7 mm in diameter
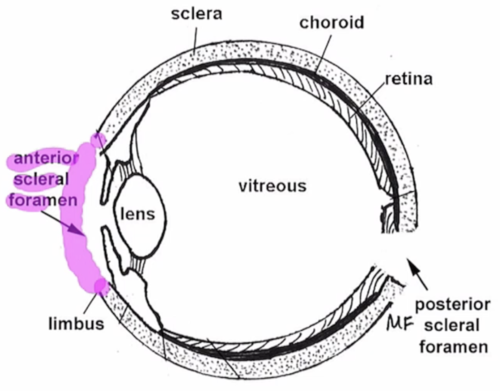
posterior scleral foramen
area where ON enters eye
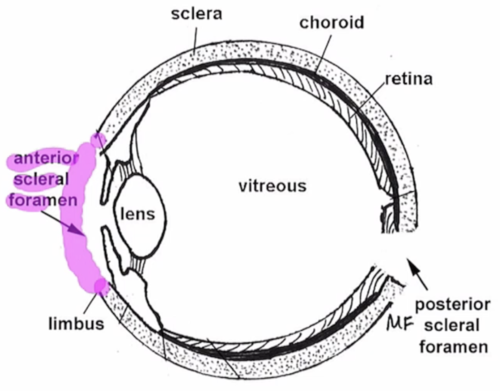
what is the lamina cribrosa composed of
scleral collagen and elastin fibers that associate with axon bundles and astrocytes in the ON
why is the ON in the lamina cribrosa most likely to be damaged by high IOP
the lamina is the weakest part of the sclera
3 emissaria (networks for veins, arteries, nerves) in the sclera
anterior emissaria, middle emissaria, posterior emissaria
anterior emissaria vessels and nerves
deep and intrascleral venous plexi, anterior ciliary arteries, episcleral artery branches, aqueous veins of ascher, LPCNs
deep and intrascleral venous plexi
travel through sclera to connect with ciliary vein and ciliary body
anterior ciliary arteries
travel through sclera to provide blood to anterior structures of the eye
episcleral arteries
travel through sclera to reach the AC angle
aqueous veins of ascher
travel through sclera to drain aqueous humor from Schlemm’s canal
LPCNs
form axenfeld loops in sclera
travel through sclera to innervate anterior structures of the eye
middle emissaria
vessels near equator traveling through sclera
what vessels travel through the middle emissaria of the sclera
vortex veins to drain the choroid
posterior emissaria
vessels that travel through the sclera near the ON
what vessel channels run through the posterior emissaria
LPCAs, SPCAs, LPCNs, SPCNs
how thick is the sclera at the posterior pole
1 mm (thickest point)
how thick is the sclera at the recti insertions
0.3 mm (thinnest points)
do the recti and obliques insert anterior or posterior to the equator
recti: anterior
obliques: posterior
index of refraction at the center of the lens
1.41
where are most lens zonules produced and where do they attach
produced at pars plana
attach to anterior mid-periphery of lens
in lens development, does anterior or posterior lens form first
posterior
why are posterior cells primary in lens development
they are first ones to act and first ones to form a lens nucleus
why does lens growth happen throughout life
anterior lens epithelium divides throughout life
where does nuclear sclerosis start
embryonic nucleus
why does embryonic nucleus have highest index of refraction
has the most crystallins
what generates the juvenile and adult nucleus
anterior lens epithelium
what generates the embryonic nucleus
posterior lens epithelium
what drugs can cause blue sclera
tetracyclines, minocyclines, topical steroids
what inflammatory eye disease can cause blue sclera
scleritis (2nd to inflammation)
which lens nucleus is demarcated by lens sutures
fetal