Chapter 2 - Basic Economic Questions, Production, and Trade
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Economic systems
These are the ways a country organizes its economy
Market economy
Systems in which private individuals and firms own most of the resources, with prices as the principal mechanism for communicating information.
Planned economy
Systems in which most of the productive resources are owned by the government, and most economic decisions are made by central governments.
Mixed economy
A mix of both market and planned economies, with government regulations and an extended role for government
Trade
Is the exchange of goods and services between individuals or countries.
Absolute Advantage
Exists when one country can produce more of a good than another country using the same amount of resources.
Comparative Advantage
Exists when one country has a lower opportunity cost of producing a good than another country.
Specialization
Occurs when countries or individuals focus on producing the goods or services for which they have a comparative advantage.
Gains from Trade/Specialization in Trade
Countries gain by specializing in producing goods in which they have a comparative advantage.
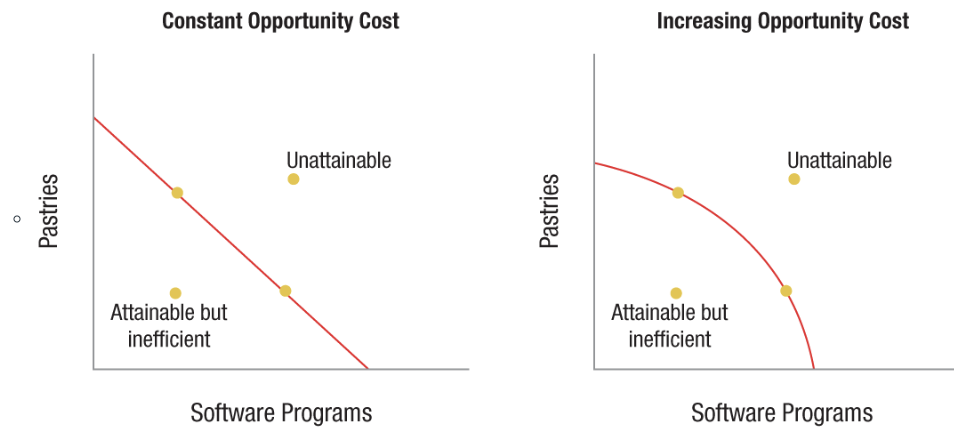
Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)
A PPF shows the different combinations of goods a fully employed economy can produce, given its available resources and current technology.
Points on a PPF graph
Points inside the PPF are also attainable, but are an inefficient use of resources.
Points on the PPF are attainable and represent efficient use of resources.
Points outside the PPF are unattainable given the current level of resources and technology.
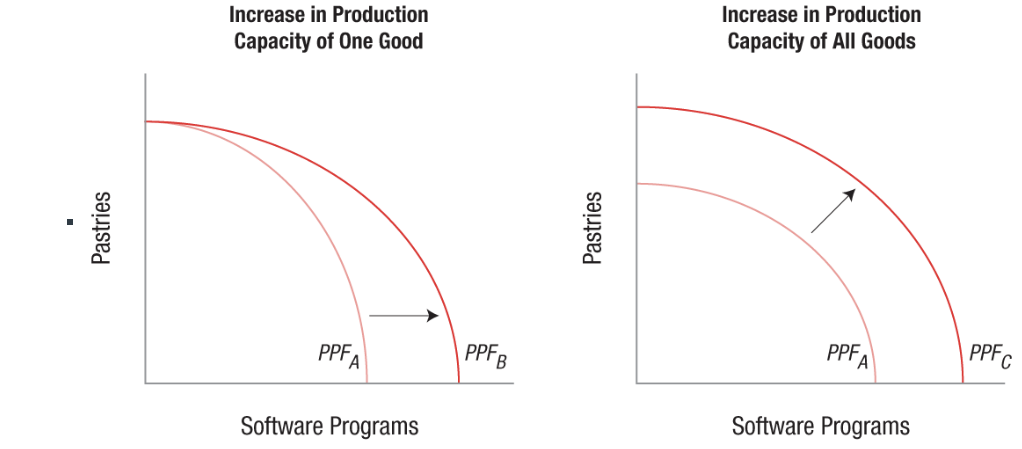
Economic Growth and the PPF
Economic growth can be seen as an outward shift of the PPF. Economic growth results from:
Capital accumulation
Expanding resources
Improving technologies
Increasing labor and human capital
Factors of Production
Are the resources used to create goods and services.
Consists of:
Land
Labor
Capital
Entrepreneurial Ability
Land
Includes land and natural resources.
Labor
Includes the mental and physical talents of people.
Capital
Includes all manufactured products used to produce other goods and services.
Entrepreneurial Ability
Entrepreneurs combine land, labor, and capital to produce goods and services. They take on the risks associated with running a business.