6B: Cleft Lip and Palate
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Craniofacial abnormality
An abnormality of the face and/or head
Abnormal growth patterns in soft tissue and bones
Cleft
Abnormal opening in an anatomical structure
Due to disruption in embryological (prenatal) development
Usually follows normal embryological fusion lines
Cleft lip and/or palate
Craniofacial anomaly/abnormality
Congenital malformation involving head and face
What is a cleft?
Elongated opening, resulting from failure of parts of mouth to fuse or merge
All structures present but may be under-developed
Occurs in utero during 1st trimester of pregnancy (1st 12 weeks)
Interferes with basic biological functioning and communication
At risk for problems with aesthetics, feeding, speech, resonance and hearing
Facial Embryology
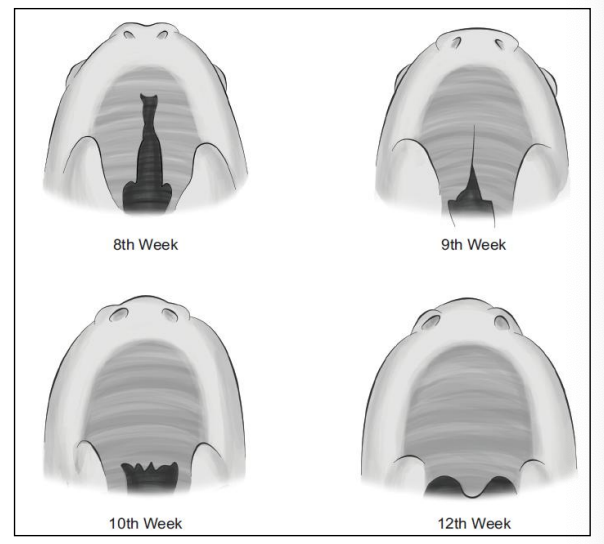
Development of face/ anterior aspects of mouth occurs during embryonic period (5-8 weeks gestation)
In normal development, facial tissues and bones grow toward midline and lips fuse together

Palatal Embryology
8-12 weeks gestation: Lip and palate meet at midline and develop from front (lip) to back (uvula)
Lips fuse ~week 6 and soft palate fuses by week 12
Degree of clefting related to amount of embryonic damage to lip and palate
shows on ultrasound
Cleft lip occurance type
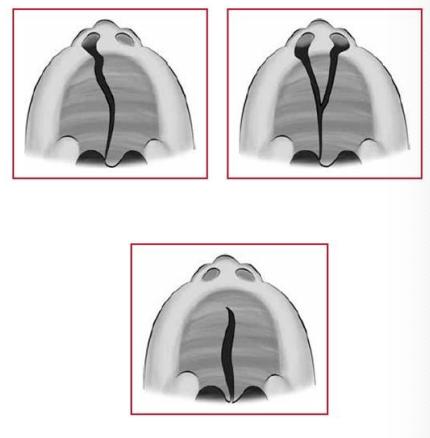
Cleft of lip and palate = 50%
Cleft of lip = 25%
Cleft of palate = 25%
Characteristics of cleft lip and palate
occurs in one of every 750 live births
Varies according to racial group (most common in first nation and asian populations)
Varies according to sex
2:1 males to females have cleft of lip with or without cleft palate
2:1 females to males have isolated cleft palate
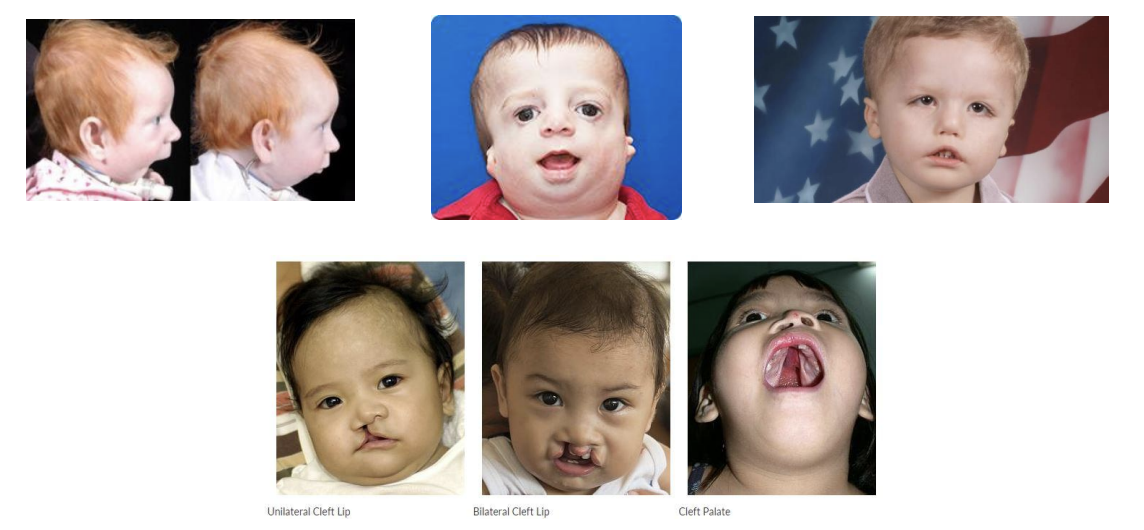
Cleft Lip types
Unilateral cleft lip (1 side of face, usually left)
Bilateral cleft lip (2 sides of face)
Complete cleft lip (runs right up into nose)
Incomplete cleft lip (does not go into nose)
Microform cleft
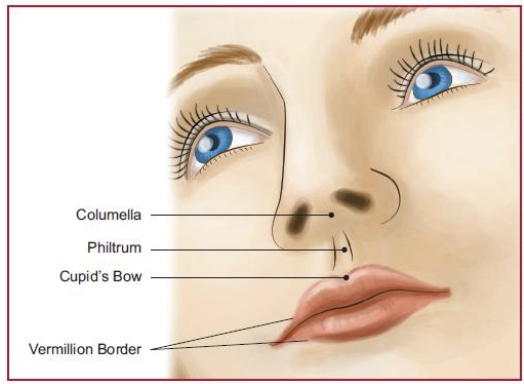
Small indentation in vermillion (mini)
characteristics…
Involves vermilion of upper lip and can extend to nostril
Can have flattened nose, flaring nostril
Columella short, misaligned
Most commonly left unilateral
If bilateral, usually also a cleft palate (*Isolated cleft of lip is rare)
Cleft Palate
Complete cleft palate
Involves both hard and soft palate
Extends through to uvula
Incomplete cleft palate
Cleft of soft palate and uvula only
Hard palate fully developed
Submucous cleft palate
Cleft of muscular region of the soft palate
Thin layer of mucosal tissue covers cleft
Signs
Bifid uvula
Notch in hard palate
effects uvula function. in speech (hyponasality)
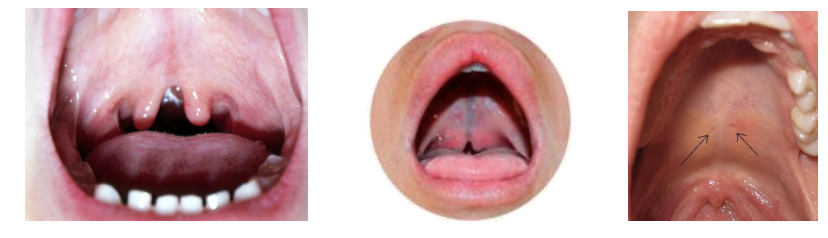
Isolated Cleft Palate
Can occur with or without cleft lip
Unilateral complete cleft of lip and palate
Extends from external portion of upper lip through the hard and soft palate
Bilateral cleft of lip and palate
Most severe because of lack of tissue
Isolated cleft palate frequently associated with syndromes
What causes cleft lip and/ or palate
Multifactorial causation
Majority due to combined genetic and environmental factors
Known etiologies
Chromosomal and genetic disorders
E.g., Pierre-Robin sequence, velocardiofacial syndrome
Family history
Environmental factors that increase risk of CL/P
Teratogens in utero,
e.g., Nicotine, alcohol, dilantin, thalidomide, viruses, x-rays
Maternal nutritional deficiencies
Risk higher among teen pregnancies and those with increased parental age (both parents > 35)
Team management
Individuals with CL/P often demonstrate multiple complex issues, including
early feeding and nutritional problems
dentofacial and orthodontic abnormalities
hearing loss
speech and resonance issues
aesthetic issues
*Requires cooperation among many professionals
Typical Team composition
Audiology
Genetics
Orthodontist
Otolaryngology
Pediatrician
Pediatric dentist
Psychology/social work
Speech-language pathology
Surgery
Assessment
Feeding
Dentition
Hearing
Communication
Feeding
CL/P can impact infant’s ability to suck and swallow
Ability to squeeze nipple with lips between tongue and alveolar ridge
Ability to maintain suction during swallowing
May require obturator (prothstetic palette)
Dentition
May have missing or malformed teeth
Particularly when cleft affects alveolar ridge
Maxillary retrusion common (25%)
Orthognatic surgery
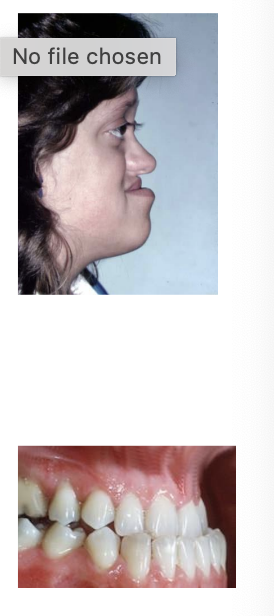
Hearing
At risk for middle ear infection due to Eustachian tube dysfunction (habitually open instead of closed)
Screen hearing every 3-6 months
Pressure Equalization (PE) tubes if necessary
Communication
*About 50% will require speech-language therapy
a) History
b) Oral mechanism evaluation (OME)
c) Voice/resonance
d) Articulation
Communication Assessment: History
Surgery/surgeries
Nasal regurgitation
Swallowing difficulties
Milestones
Parent concerns and priorities
VPI clinic
Team
Communication Assessment: OME
Examine structures and functions of the face, ears, nose, lips, tongue, alveolus, hard/soft palates, uvula, tonsils, pharynx
Examine dentition and occlusion
Communication Assessment: Voice and Resonance
Difficulty regulating airflow through the nasal cavity
Ability to regulate air flowing through nasal cavity during speech production aka resonance
Cleft palate leads to velopharyngeal insufficiency (VPI), which leads to hypernasal speech
Assessing nasal speech
Mirror below nose (gets foggy after saying a non-nasal word)
Listening & rating
Endoscope
Measuring nasal airflow with a nasometer
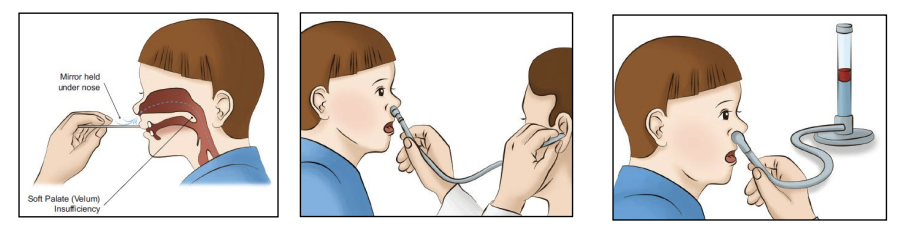
Communication assessment: Articulation
Due to VPI, consonants normally produced in oral cavity now influenced by nasal cavity
Surgery can often help
Persistent problems can include
Nasal emission
Stop consonants (/p, t, k, b, d, g/)
Fricative consonants (/s, z, f, v, th, sh/)
Compensatory articulation errors
Glottal stop
Pharyngeal, lateral fricatives

Typical treatment timeline
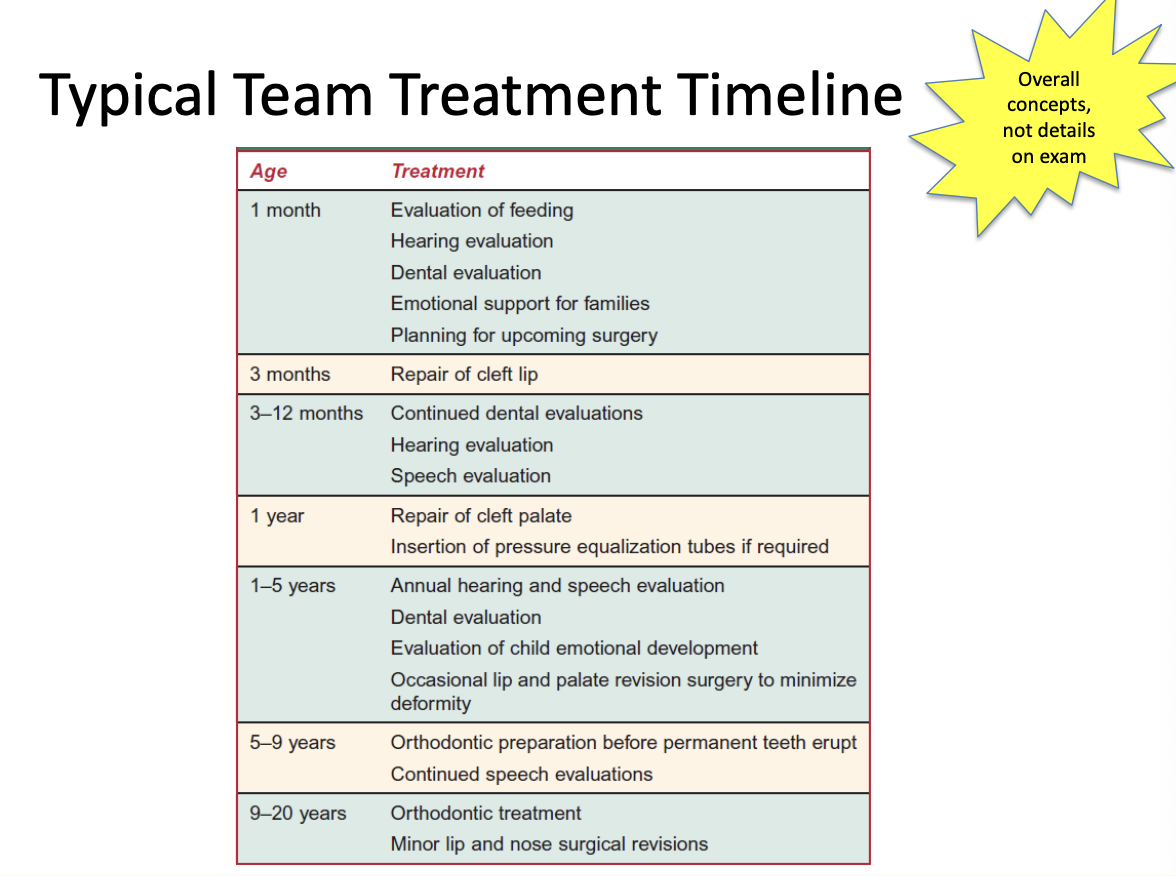
Treatment: Surgery
Decisions about repair based on facial growth, speech development, and psychological impact
Structural repair of lip and palate
Pharyngeal flap or sphincter pharyngoplasty to support VP function
Lip repaired at 3 months (feeding)
Palate repaired 9-15 months (speech)
Treatment: Dental
Orthodontics for malocclusions
Prosthodontics,
e.g., obturator, speech bulb (pushes velum up higher), palatal lift
Treatment: Hearing
Preventative or therapeutic insertion of myringotomy tubes for otitis media
Treatment: Speech-Langauge Therapy
<10% have a communication disorder following surgical repair of cleft
Major focus typically on reducing hypernasal resonance
Articulation goals may include differentiation between oral/nasal sounds, reduction of glottal stops, etc.
Methods
Traditional articulation therapy approach
Visual feedback via electropalatography
Treatment: Psychology
Psychosocial issues
Teasing/bullying – education/counselling
Issues with education
May result in behavioural problems, depression, and anxiety