Musculoskeletal Systems (Study for Musculoskeletal Exam)
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
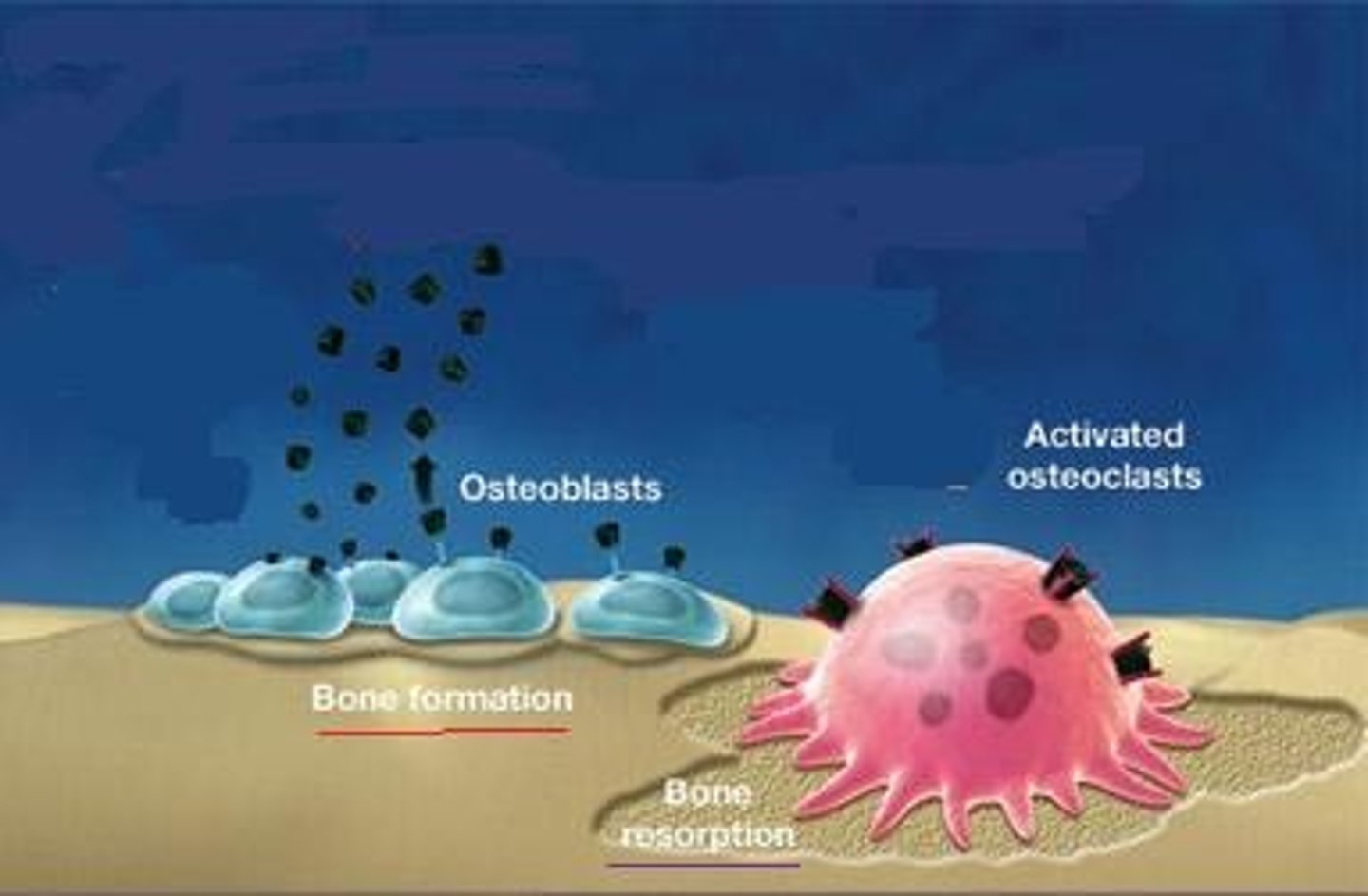
osteoclasts
large bone cells that resorb or break down bone matrix during bone modeling
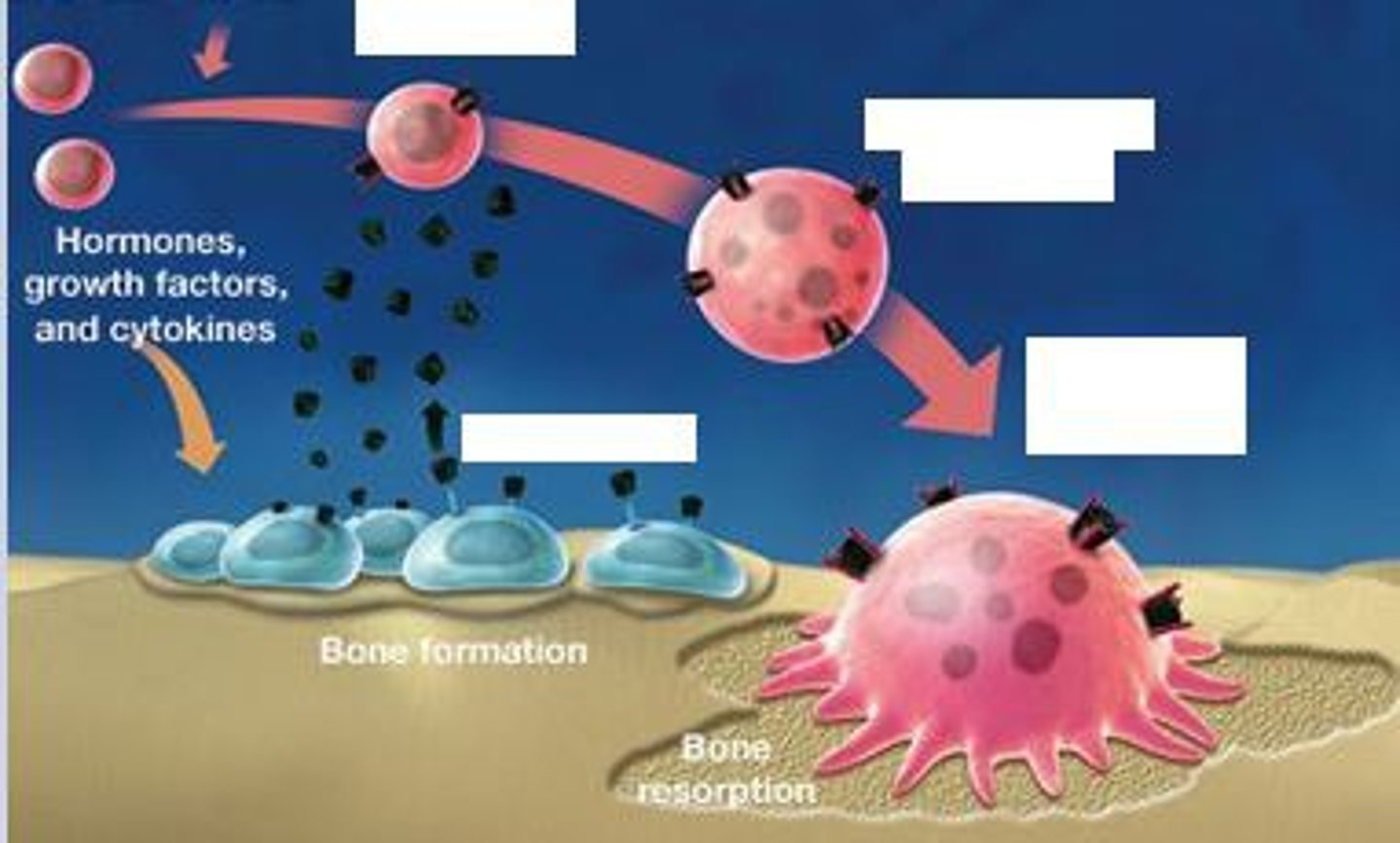
osteoblasts
bone building cells that build and fill bone with osteoid during bone modeling
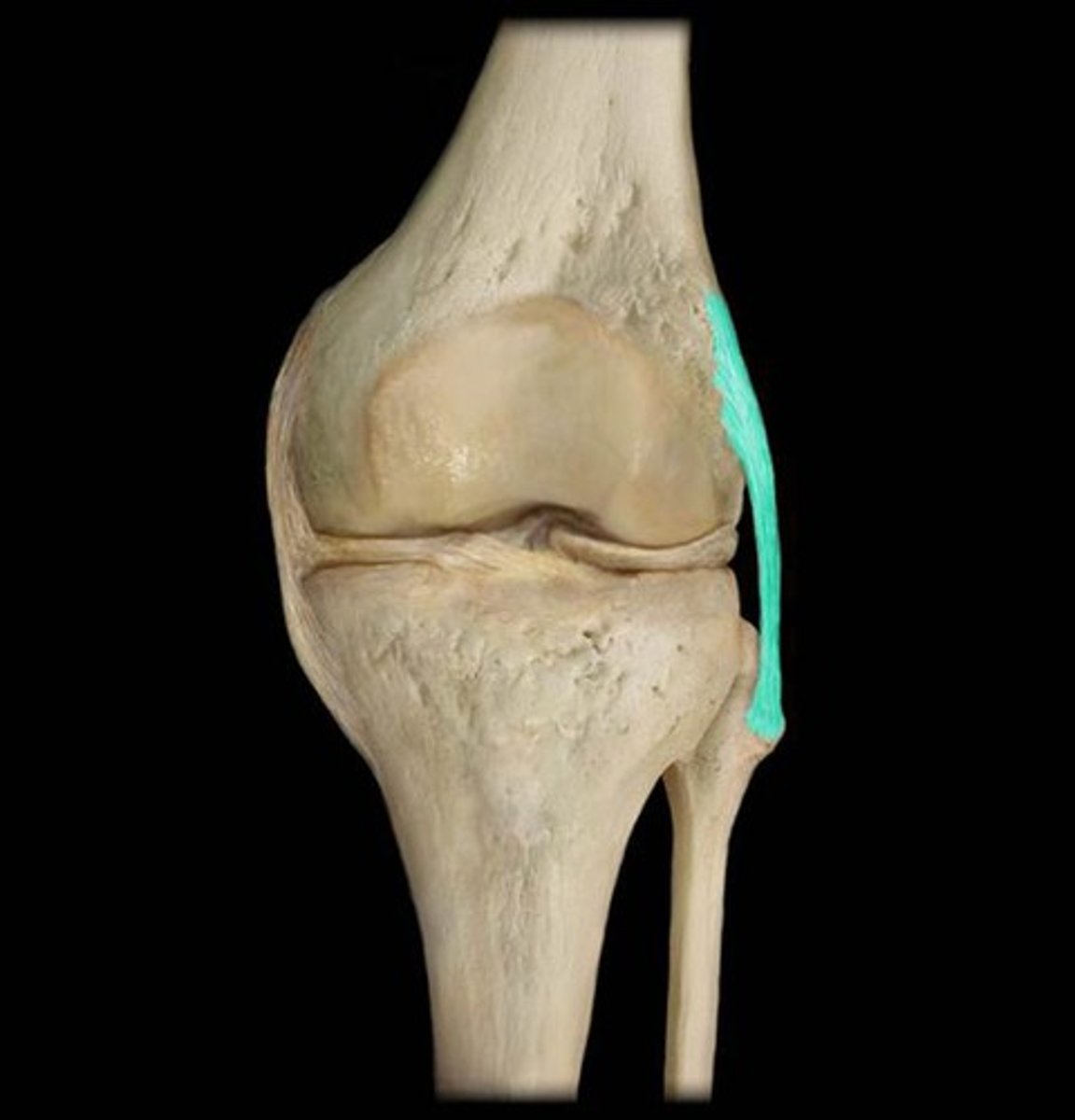
ligaments
fibrous bands that connect bones and bones/cartilages
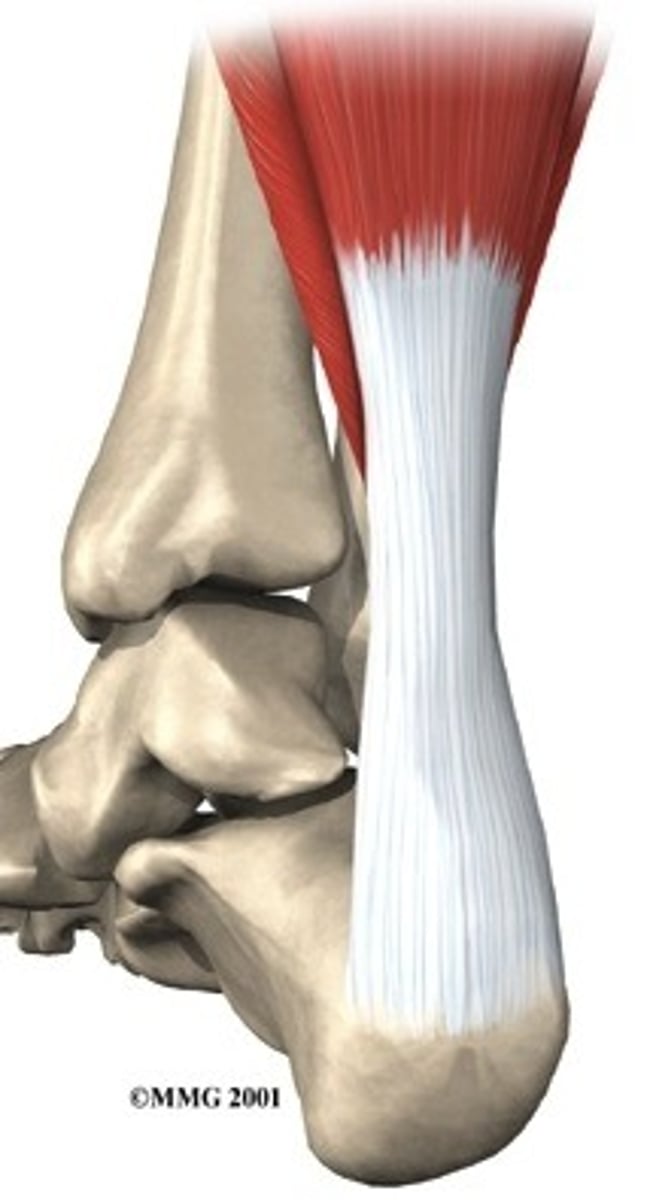
tendon
fibrous bands that connect bones to muscles
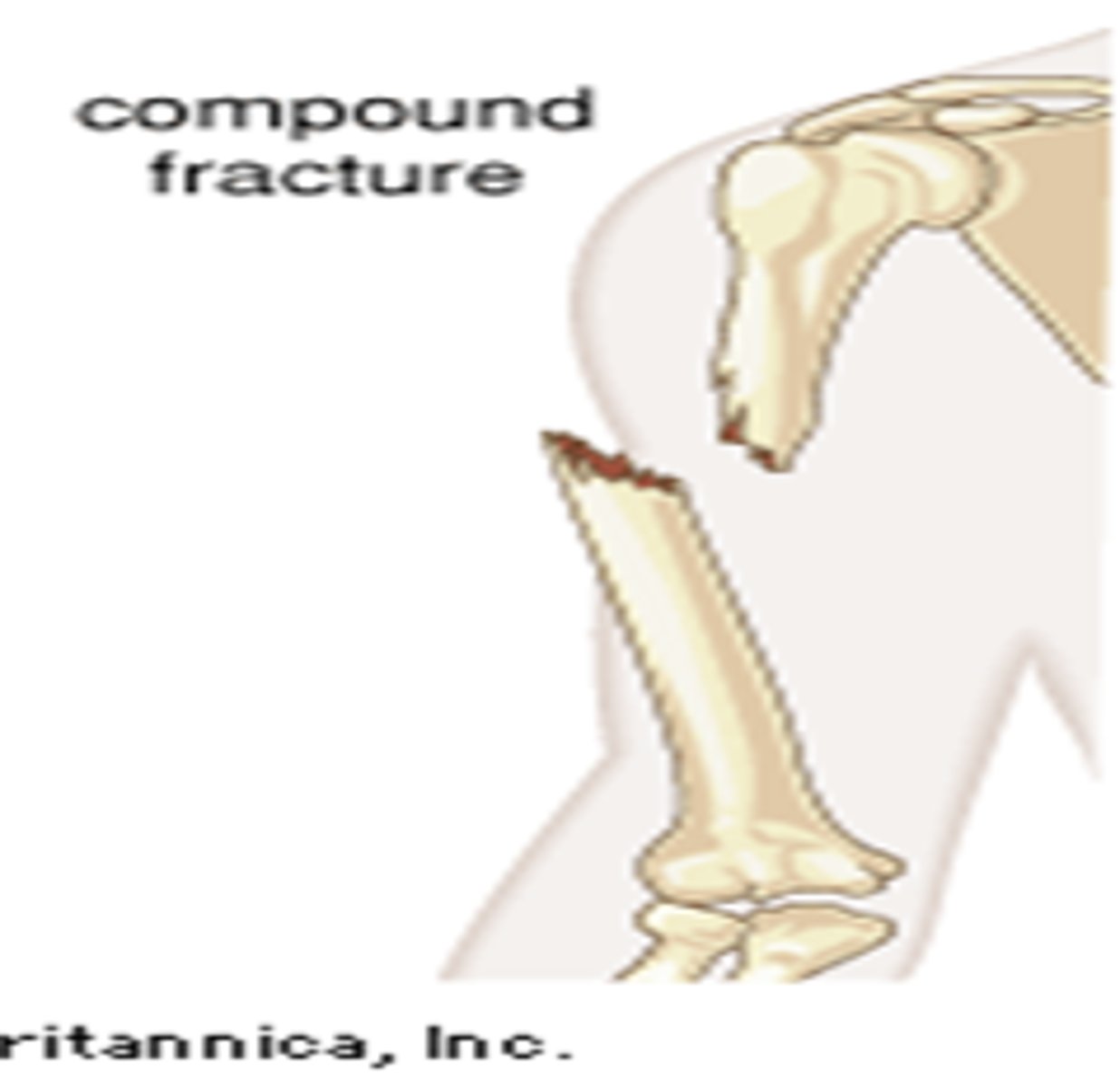
compound
type of fracture in which the broken bone penetrates the skin and is exposed to the outside of the body; also called open fracture
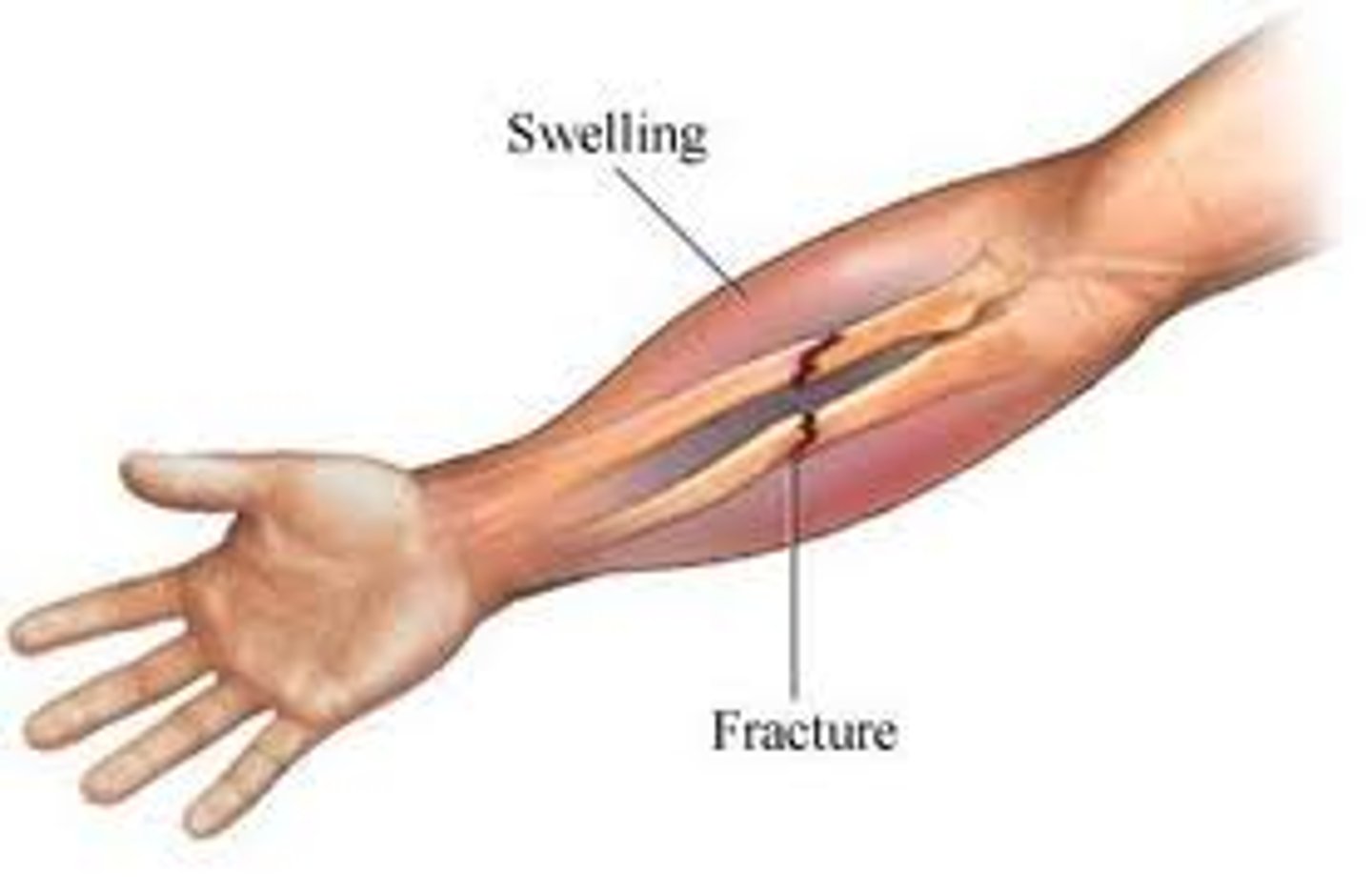
simple
type of fracture where the bone does not penetrate the skin; also called closed
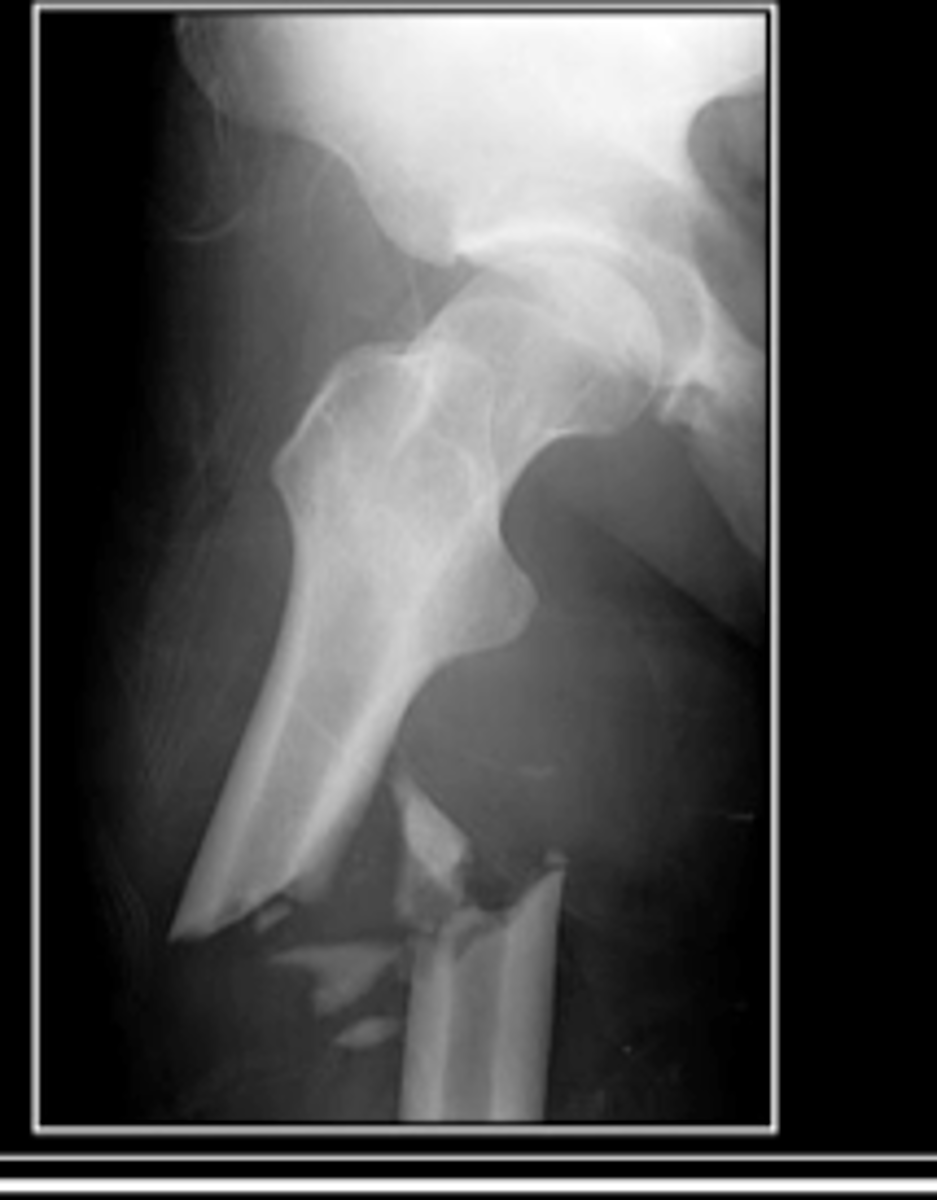
comminuted
type of fracture where bone breaks into many fragments
greenstick
a slight fracture in a bone that appears as a slight fissure or hairline in an x-ray; usually the simplest type of fracture to reset and splint; often seen in children due to high cartilage matrix of the bones
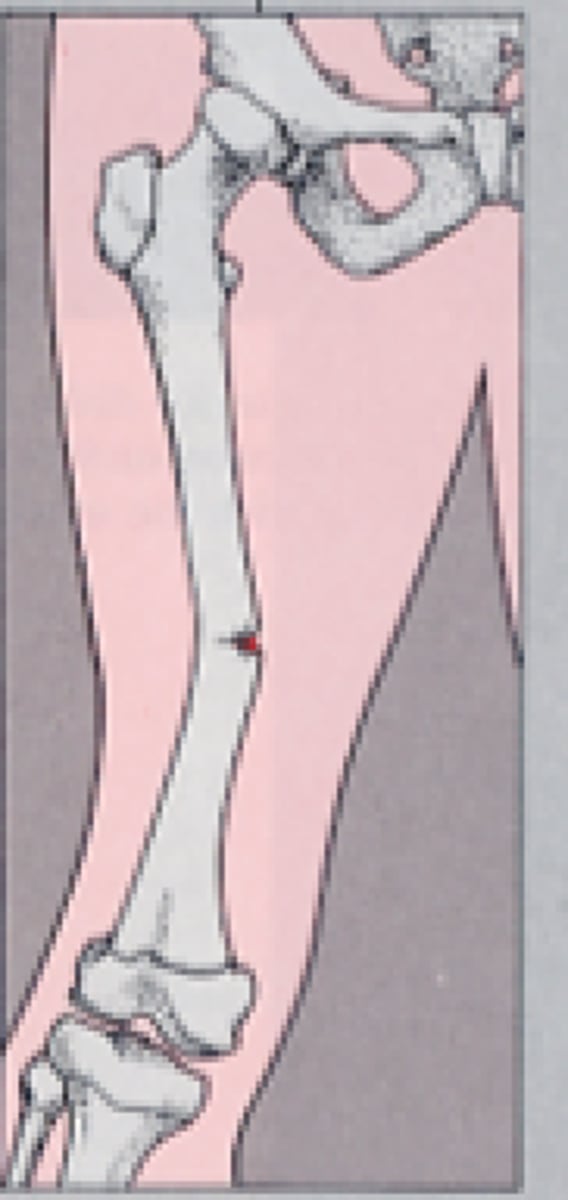
impacted
fracture (usually seen in long bones) where broken bone ends are forced into each other
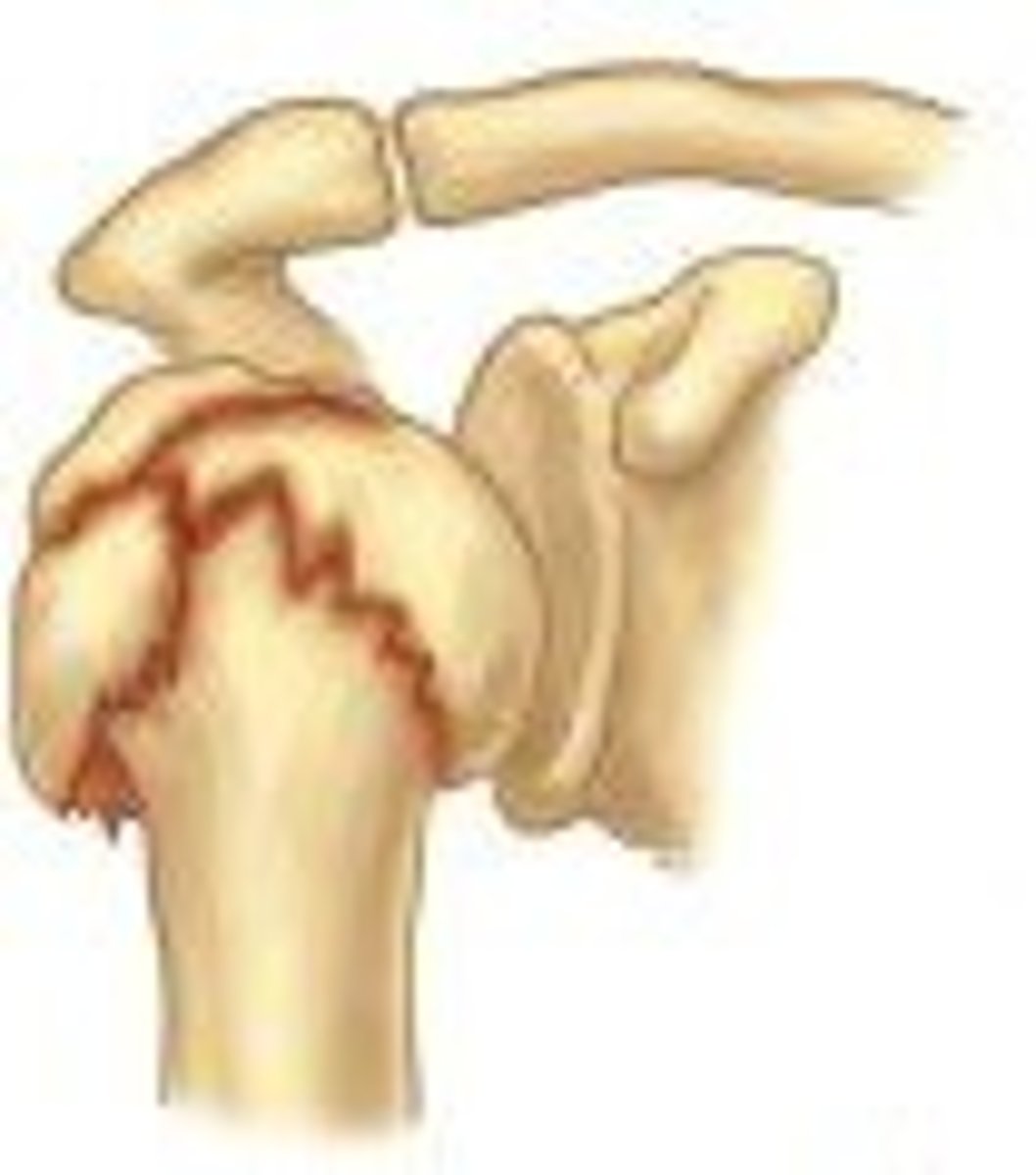
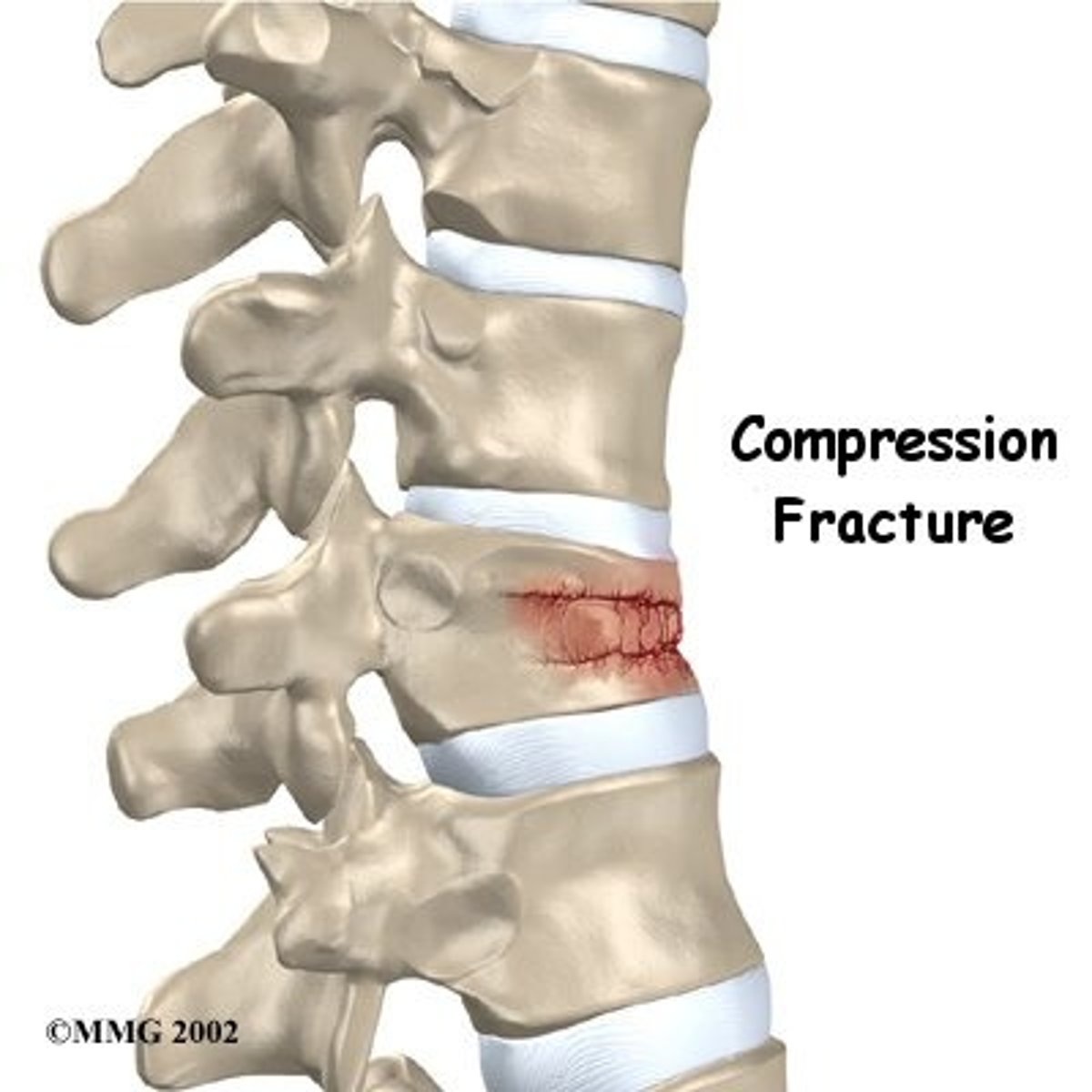
compression
type of impact fracture that occurs (usually in short or irregular bones) when the bone is pressed together (compressed) on itself
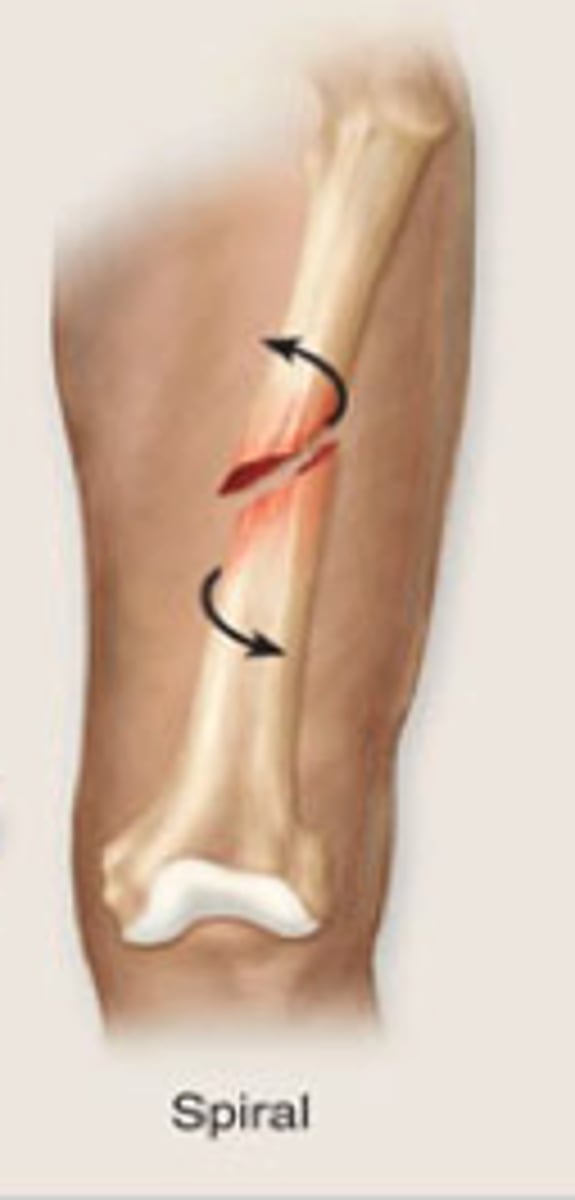
spiral
a fracture in which the bone has been twisted apart
long
bones that are longer than they are wide with heads at each end
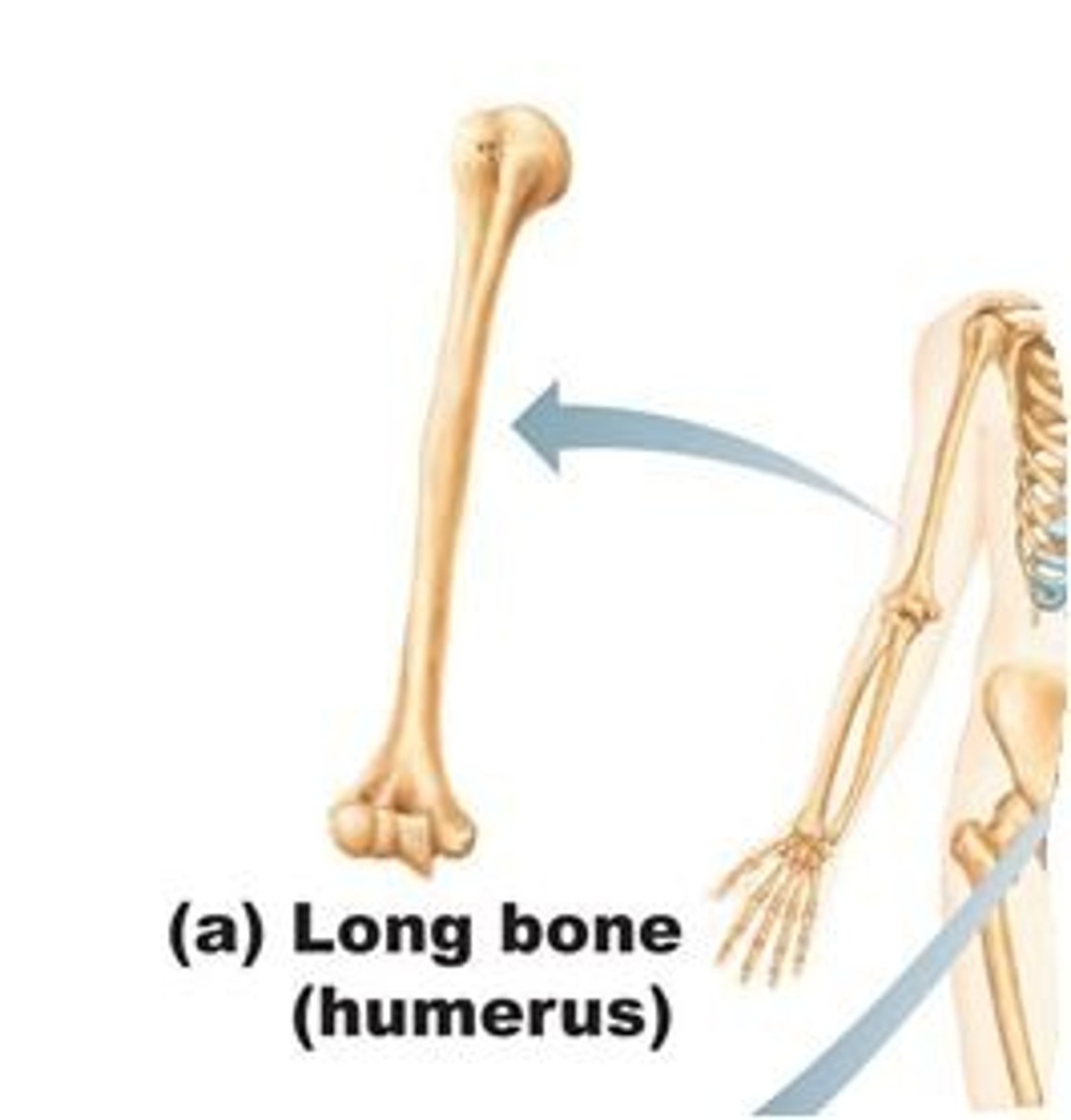
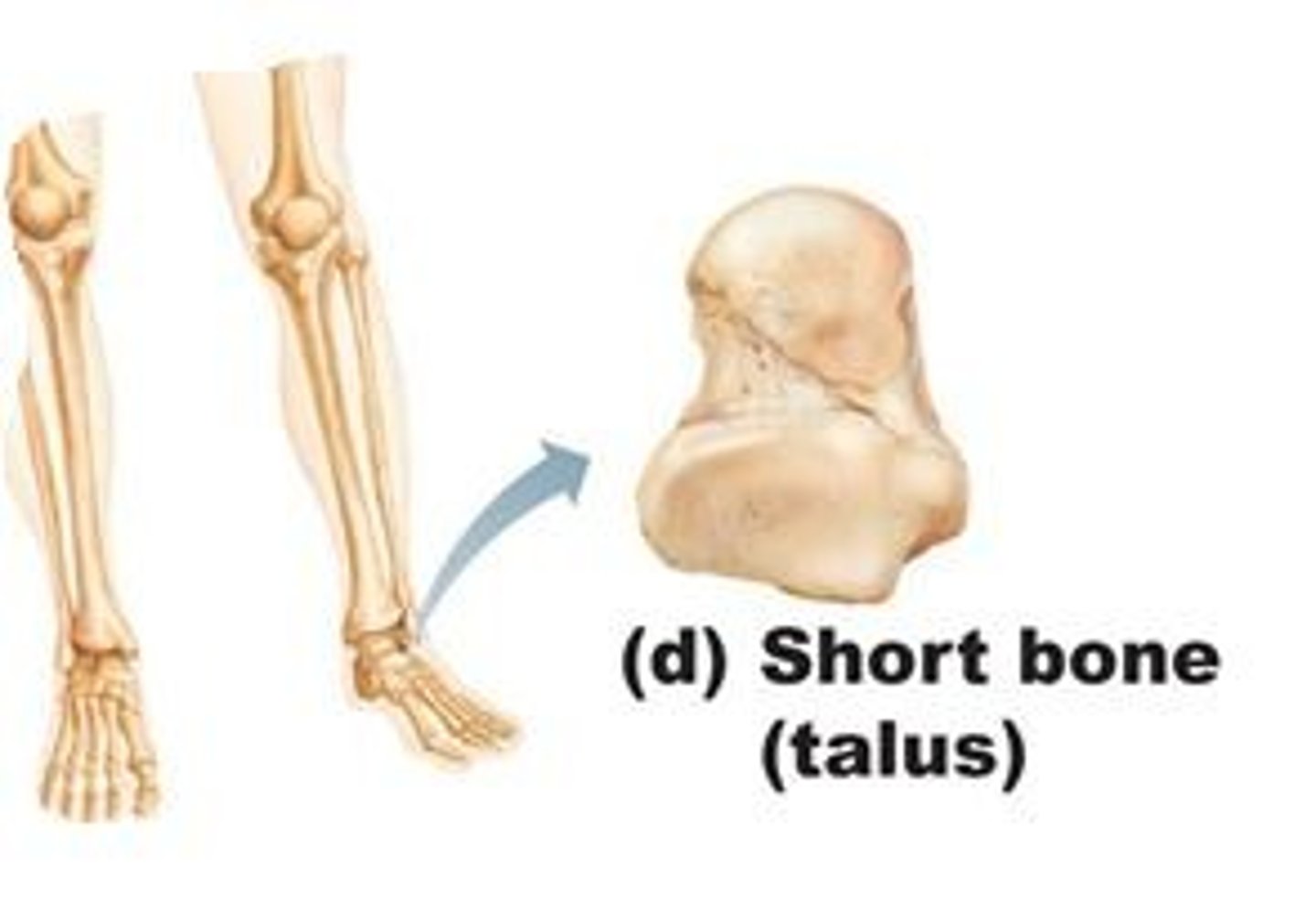
short
bones with a square-like shape; mostly spongy bone; ex, carpals and tarsals
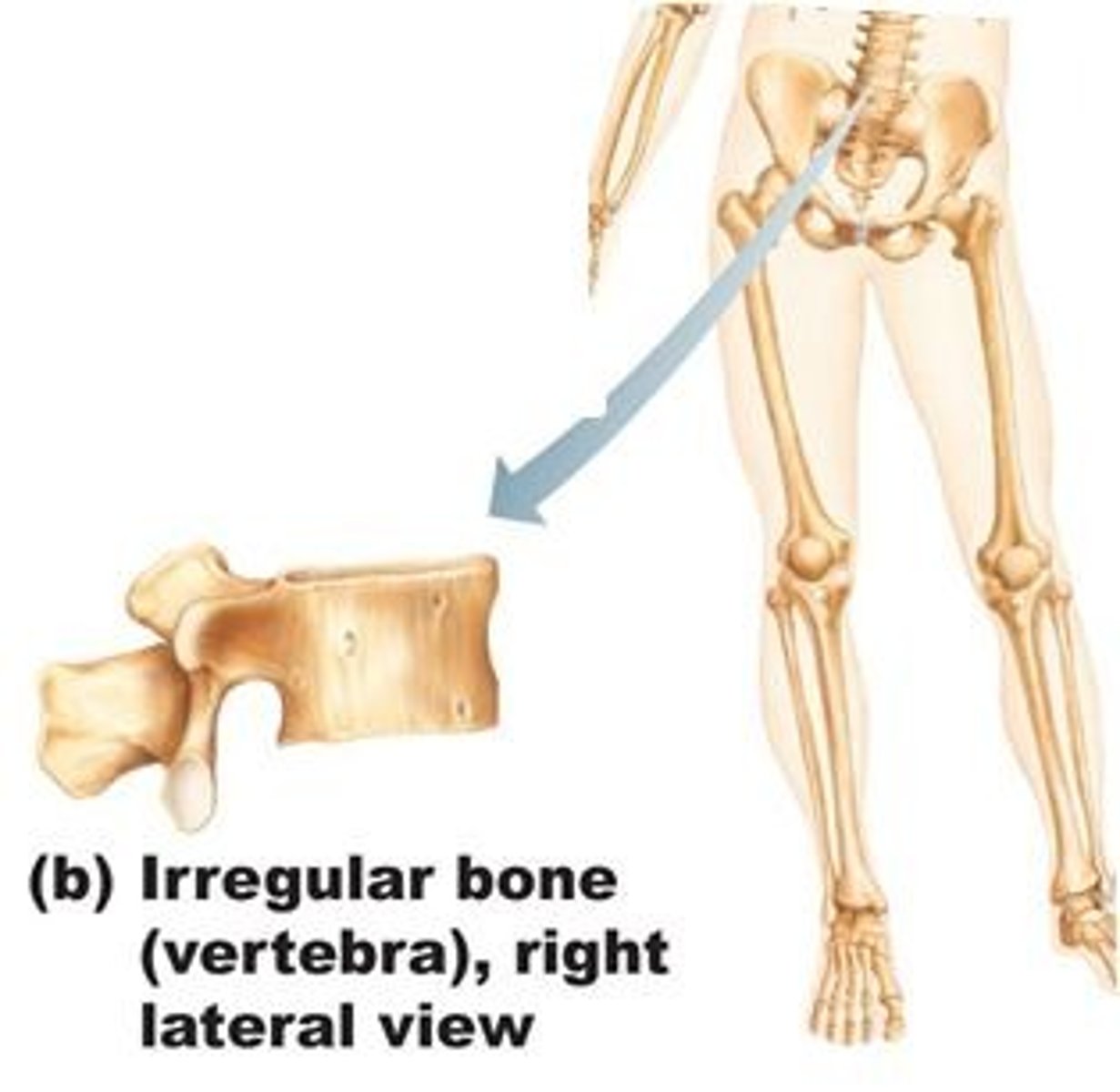
irregular
Bones with complicated shapes (e.x., vertebrae and hip bones)
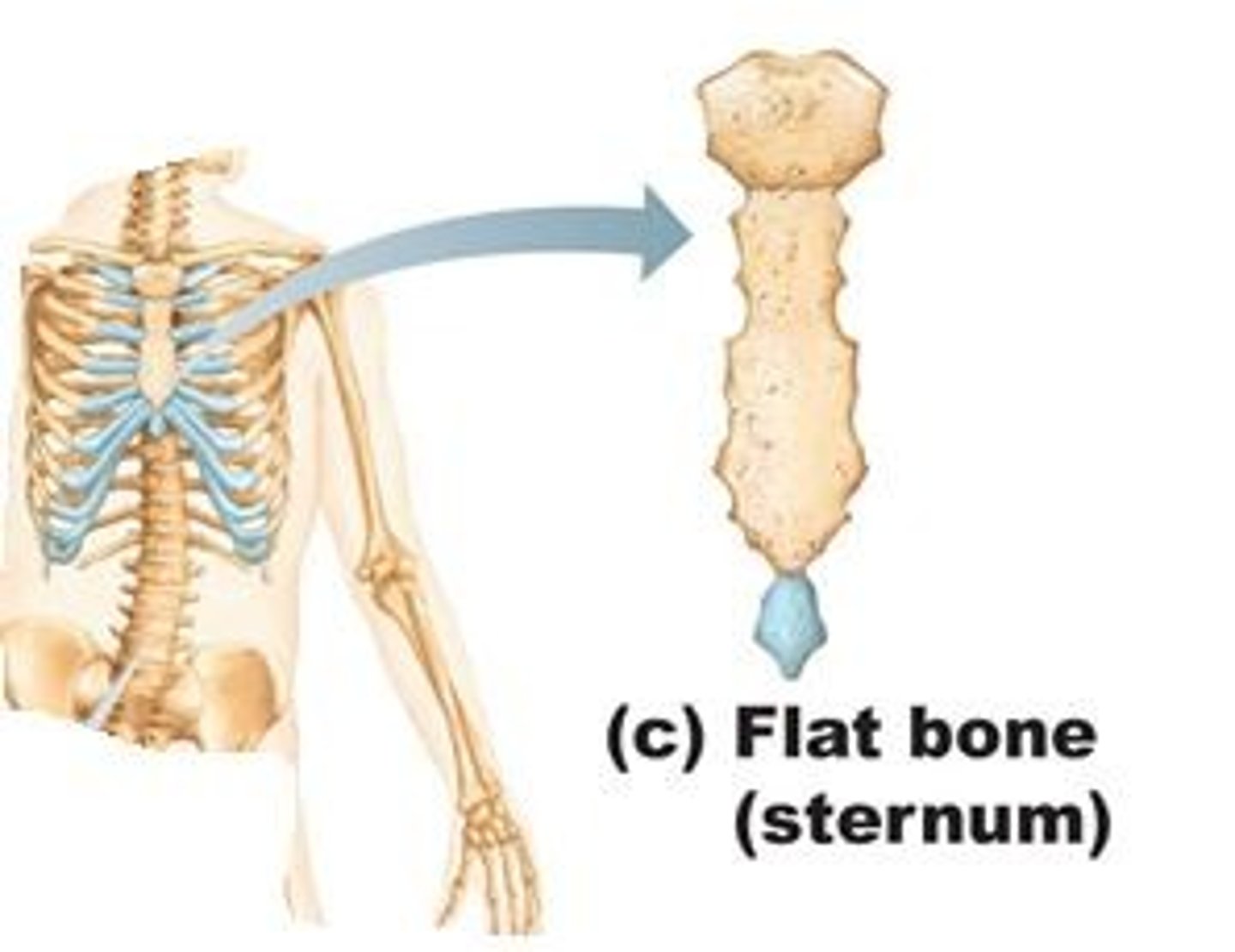
flat
A type of bone with a thin flattened shape. Examples include the scapula, ribs, and pelvic bones.
joint
A place in the body where two bones come together
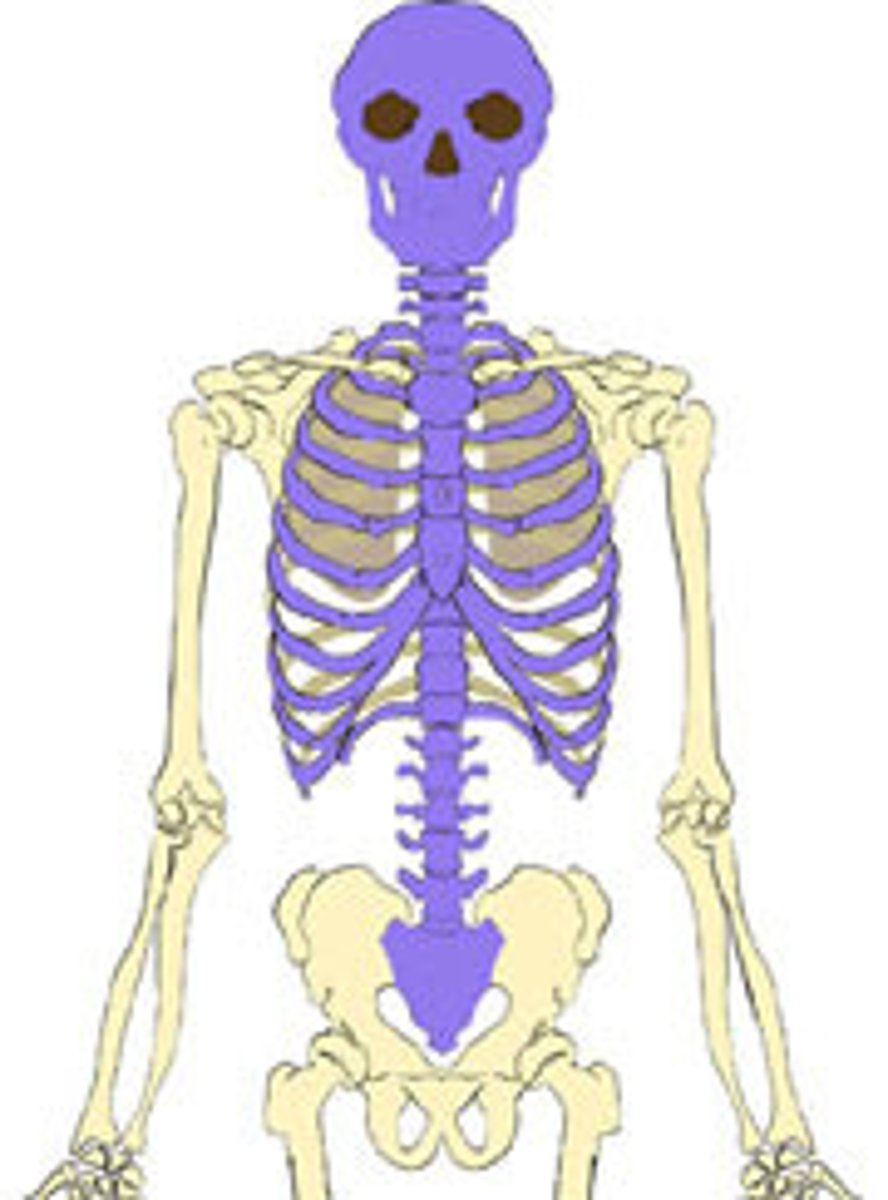
axial
Portion of the skeletal system that consists of the skull, rib cage, and vertebral column
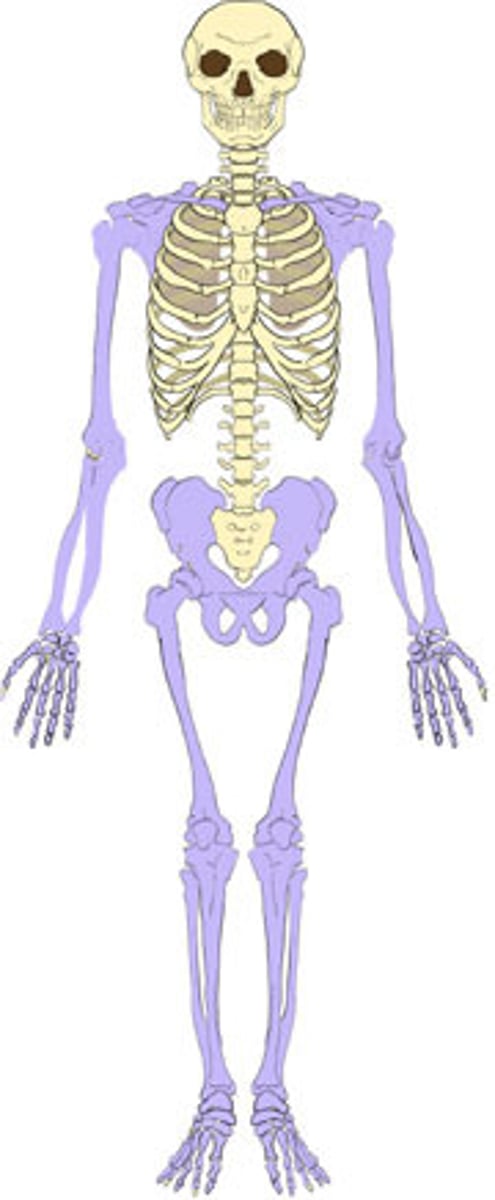
appendicular
Bones of the limbs and limb girdles that are attached to the axial skeleton
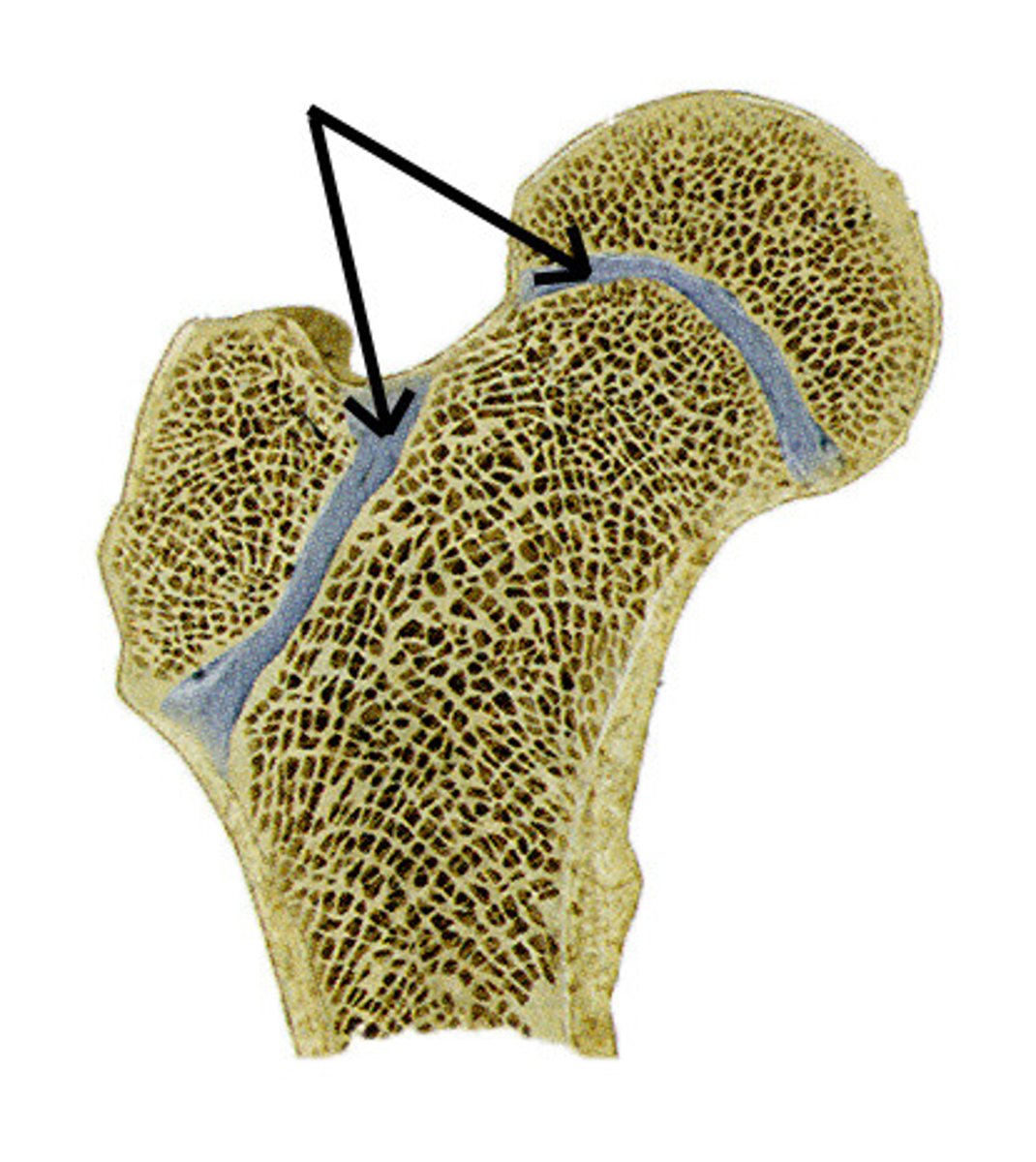
epiphyseal plate
growth plate; visible line or scar indicates that bone finished growing/lengthening
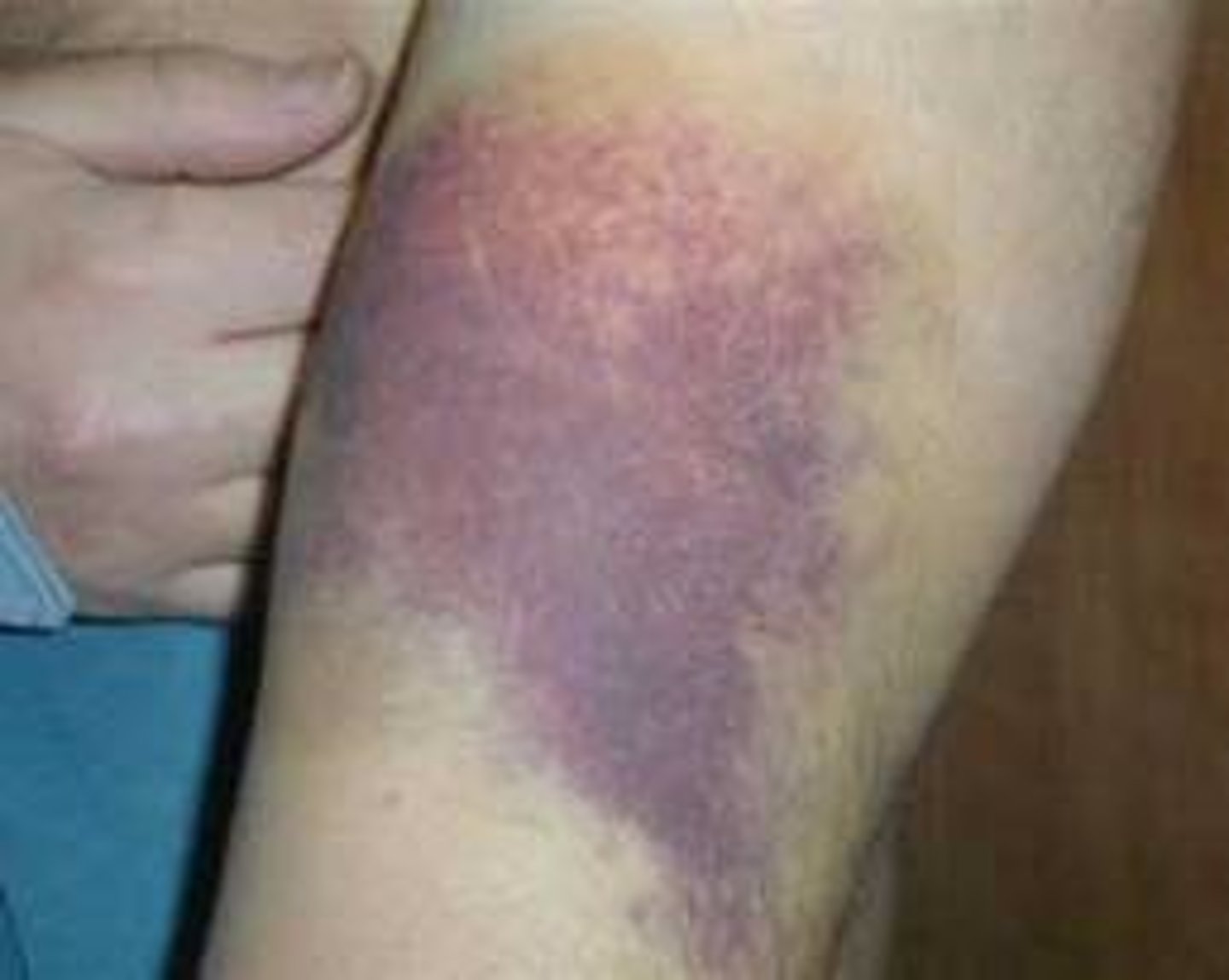
hematoma
1st step in healing a broken bone: an elevated, localized collection of blood trapped under the skin that usually results from trauma
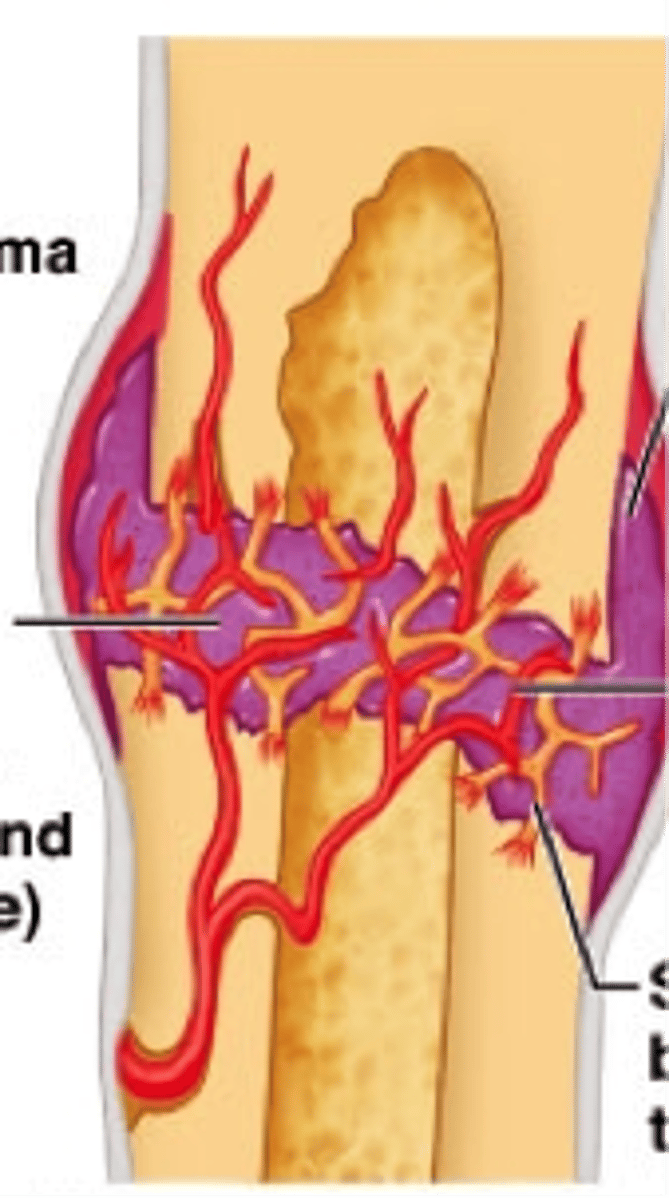
fibrocartilage callus
2nd step in healing a broken bone:
connective tissue forms scaffolding to close the gap
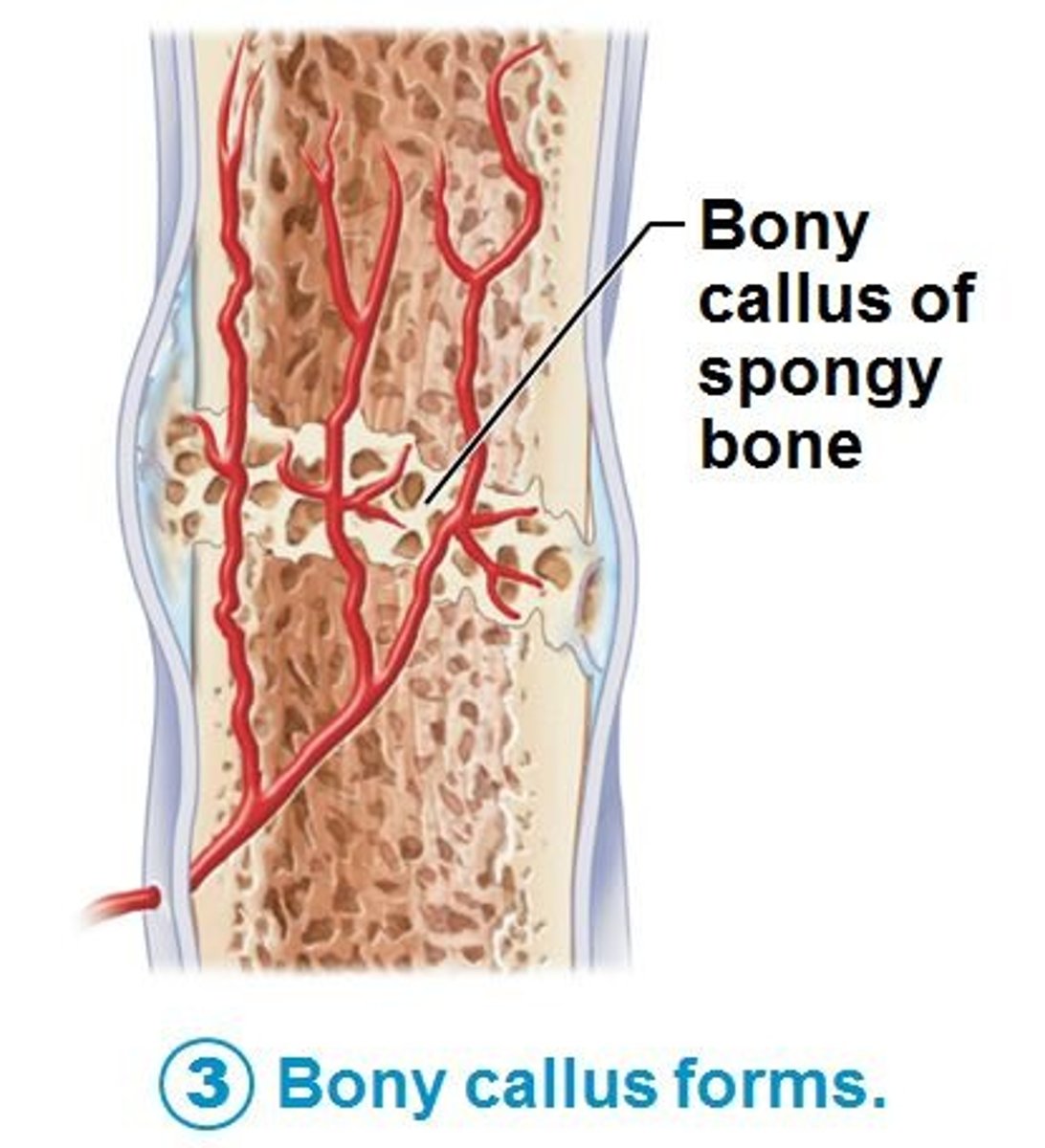
bony callus
3rd step in healing a broken bone: osteoblasts fill spongy bone with osteoid to create compact bone patch
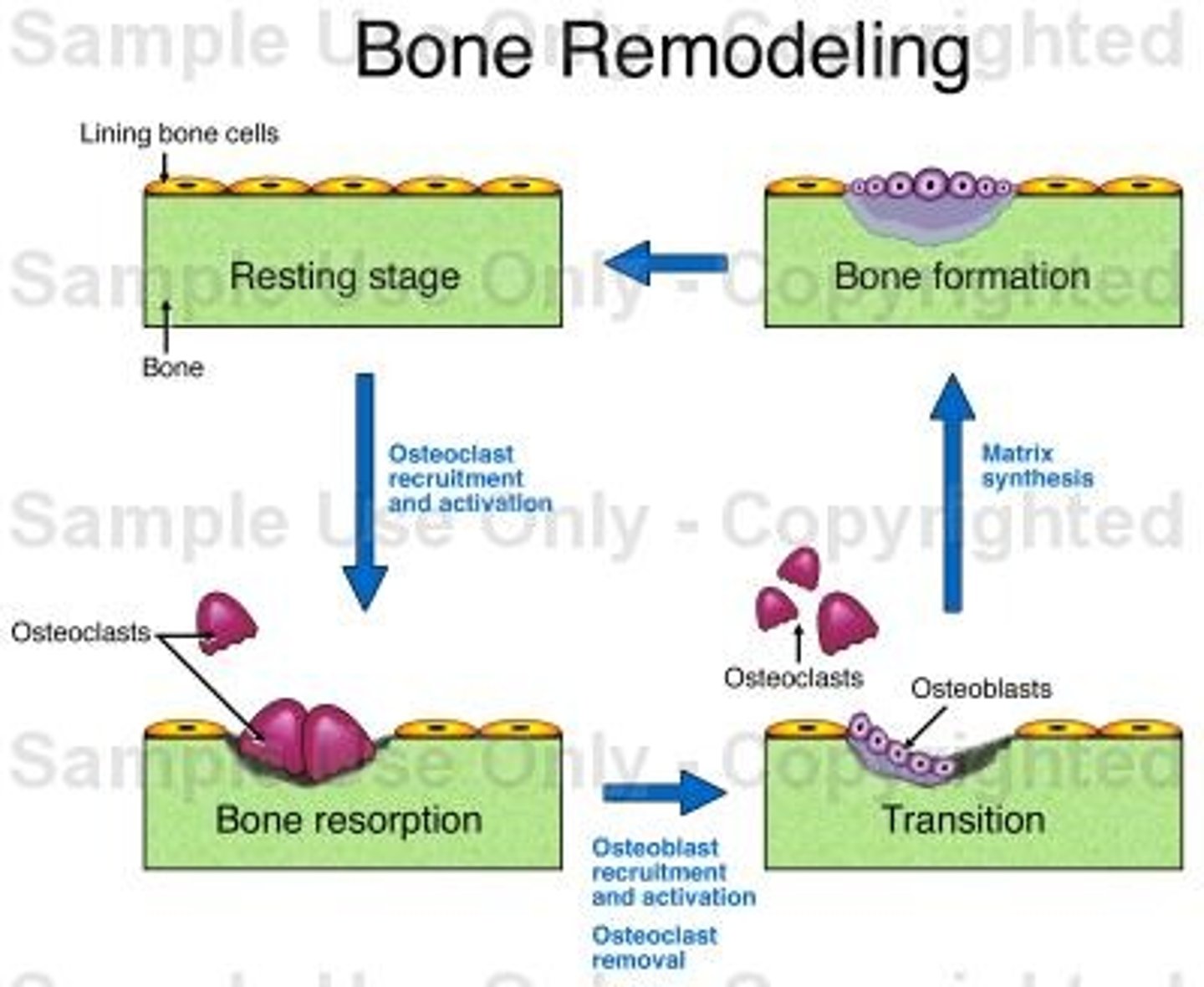
bone remodeling
4th (last) step in healing a broken bone: osteoclasts & osteoblasts reshape the bony callus formation
fibrous
a joint that connect bones without allowing any movement (like suture joints)
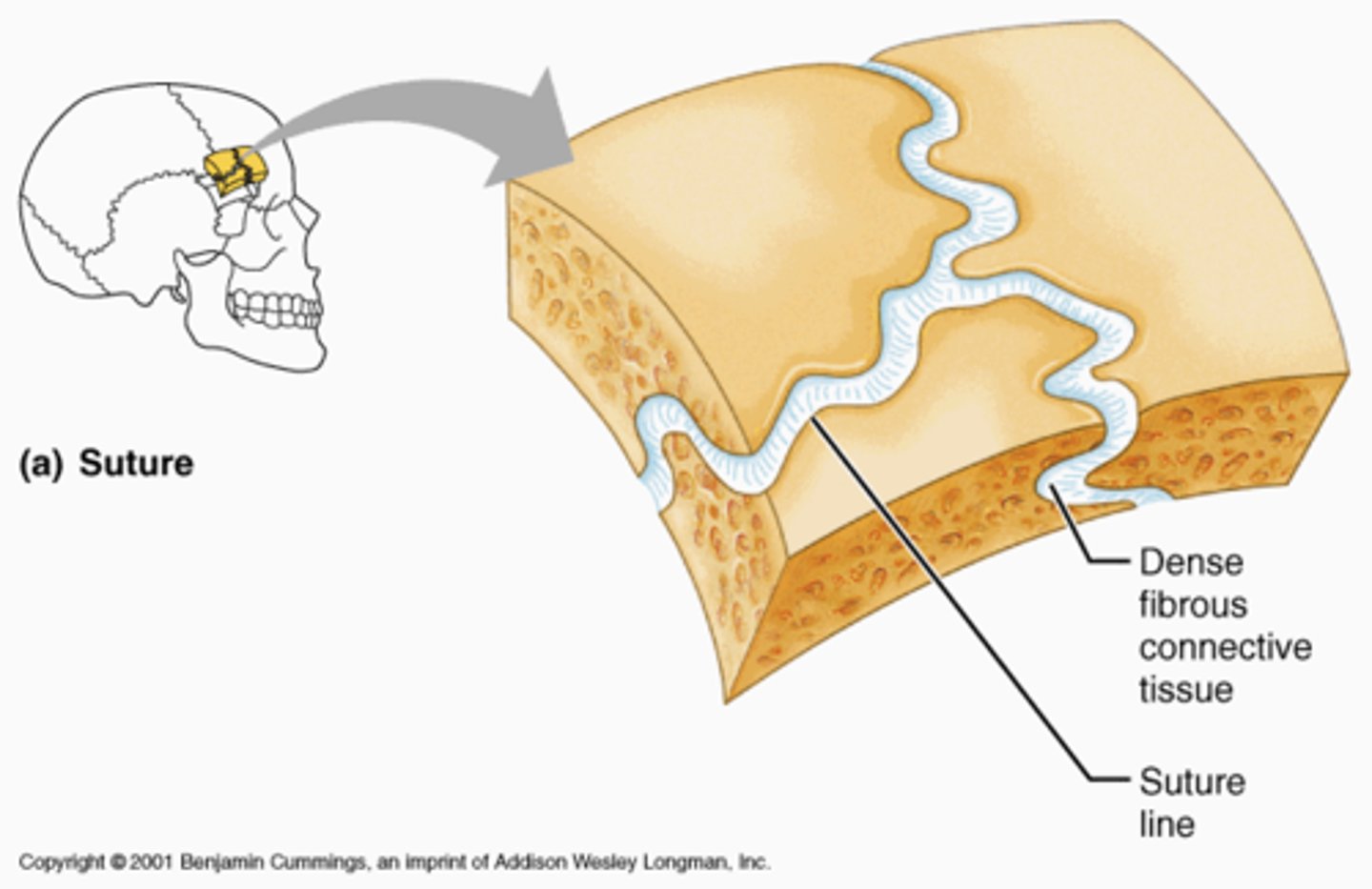
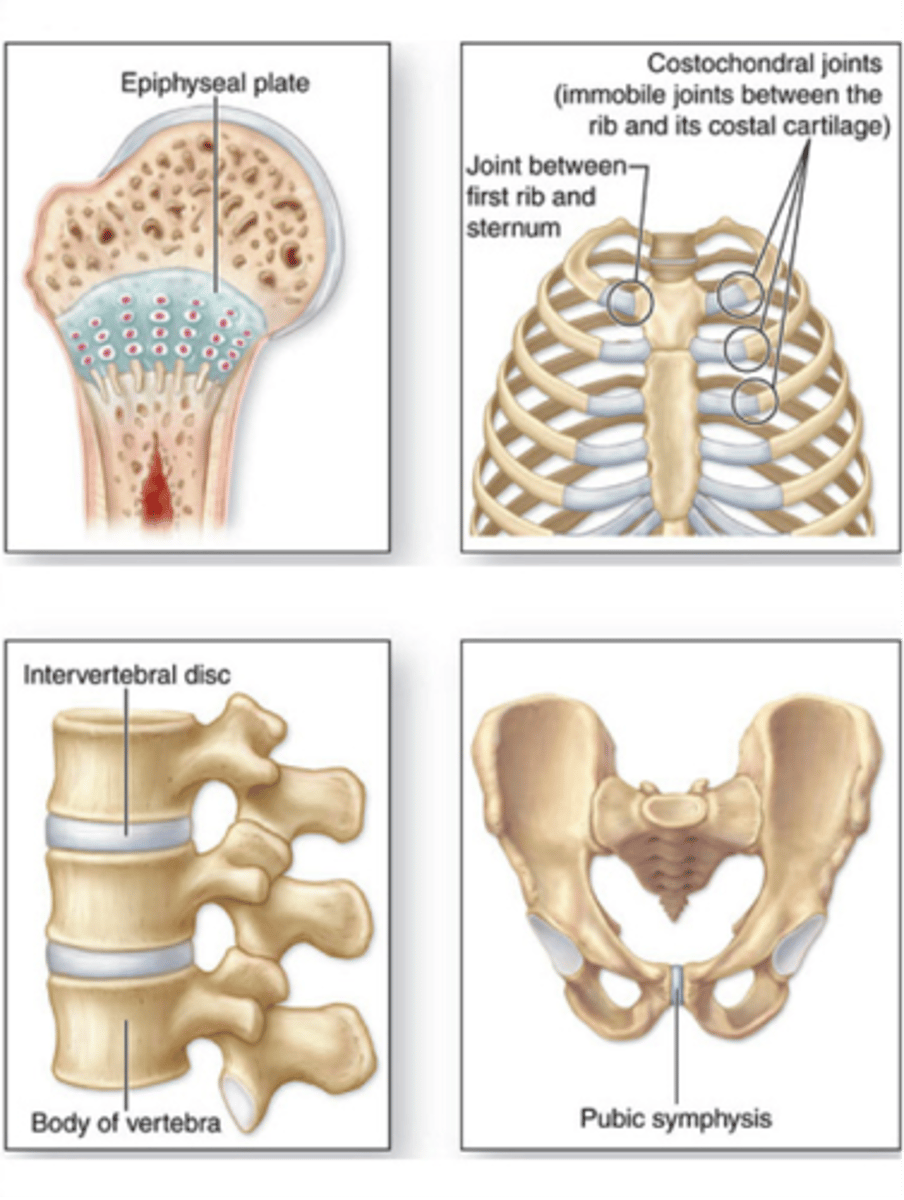
cartilaginous
a joint with limited movement where the bones are connected with cartilage
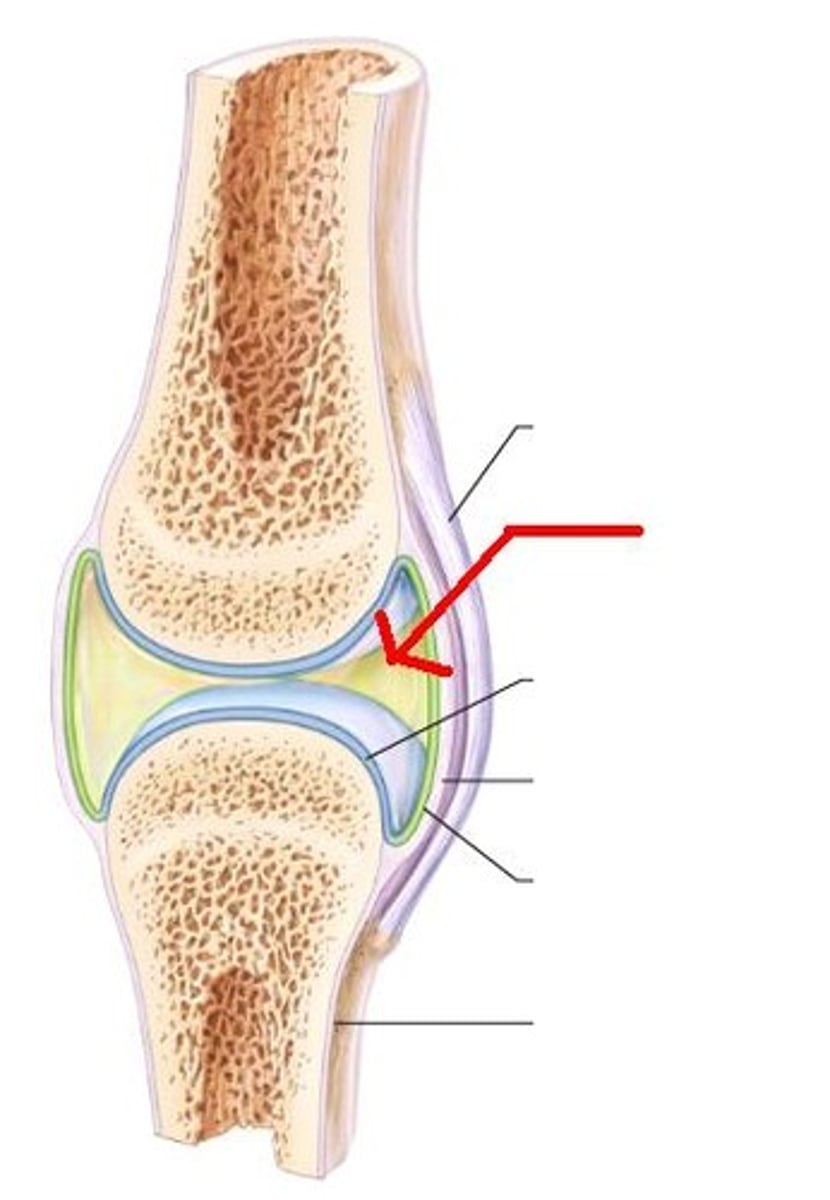
synovial
freely movable joint containing a cavity filled with synovial fluid
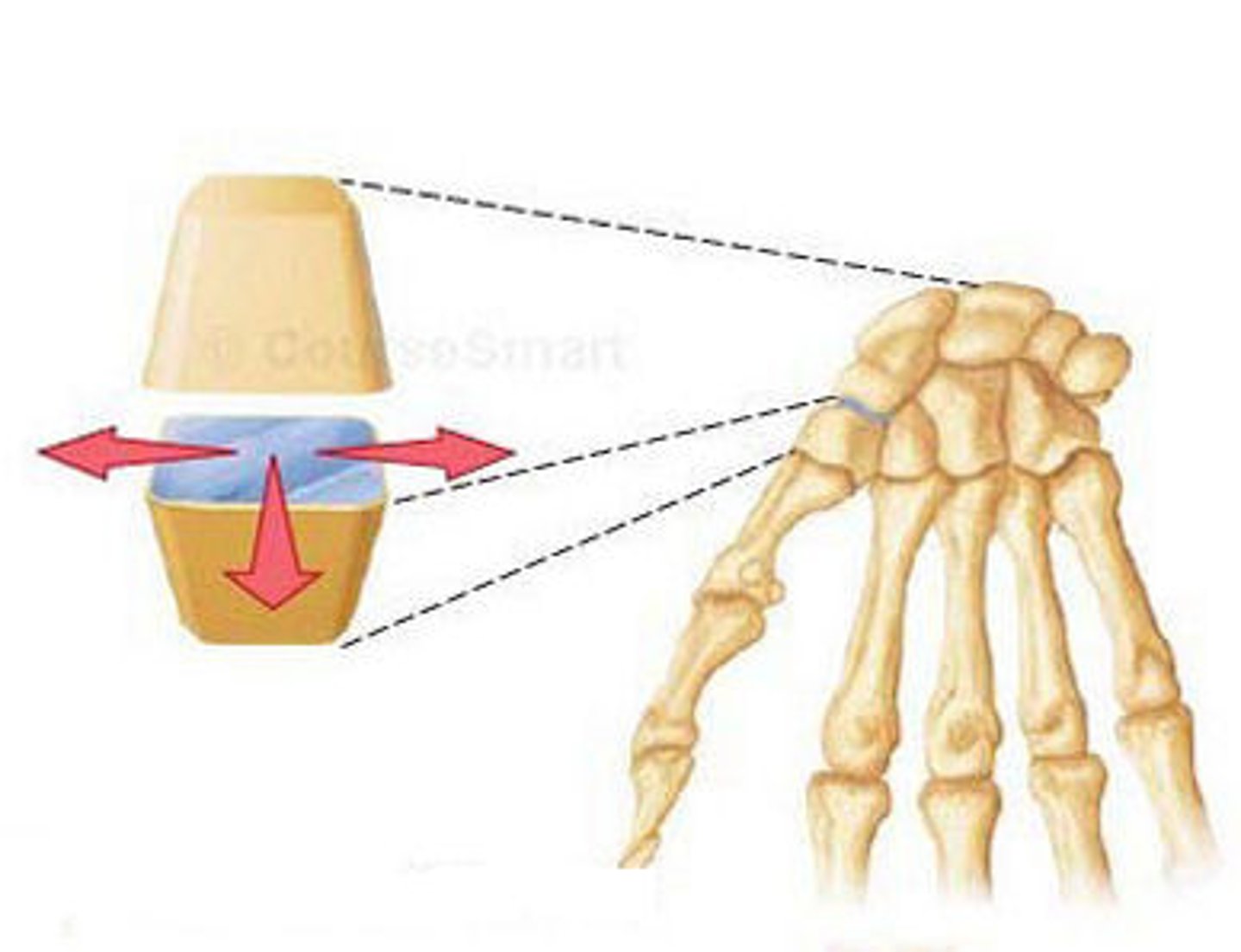
plane
joint that allows only short slipping or gliding movements; i.e. carpals
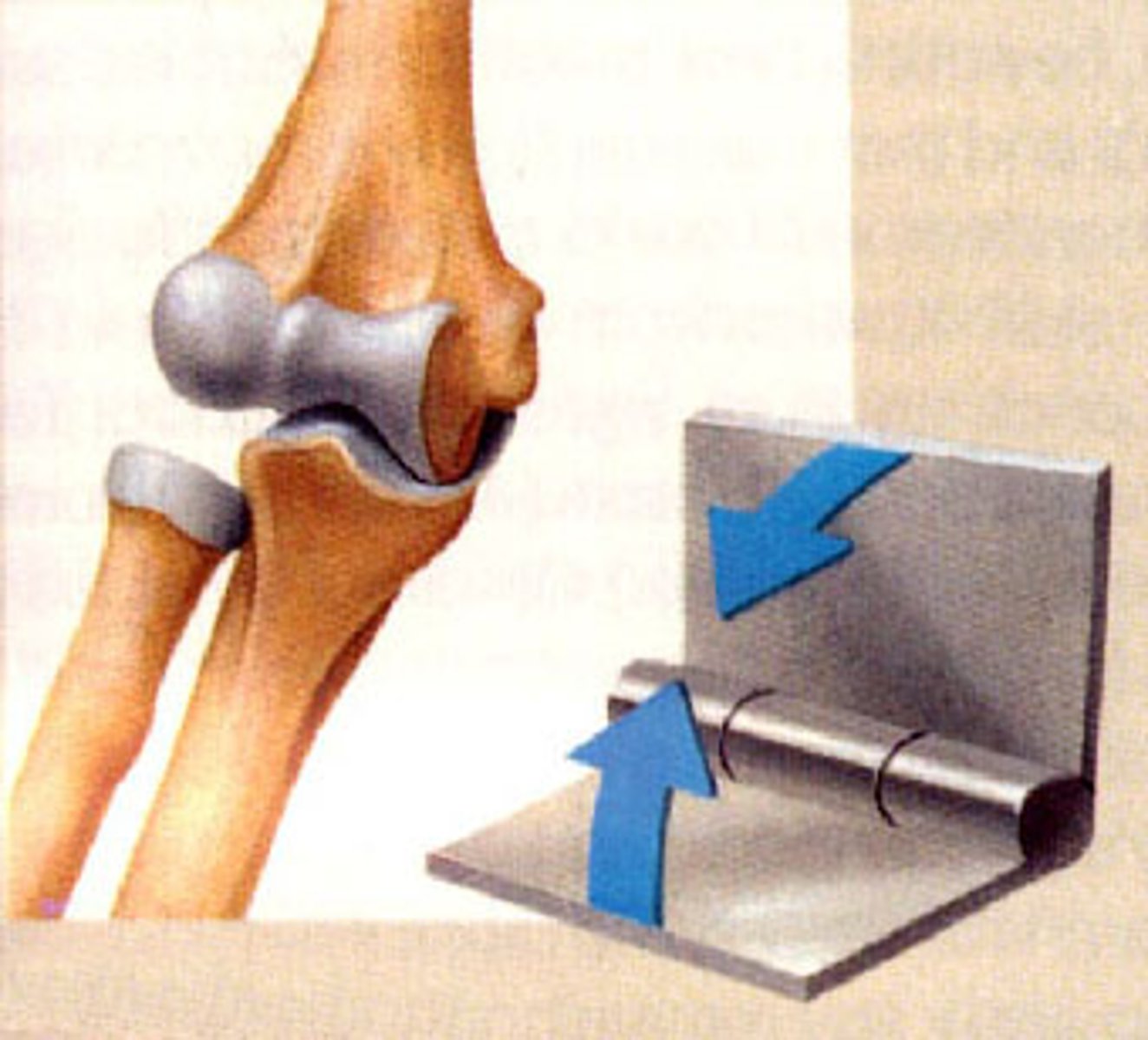
hinge
synovial joint between bones (as at the elbow, knee, or finger) that permits forward and back swinging motion in only one plane
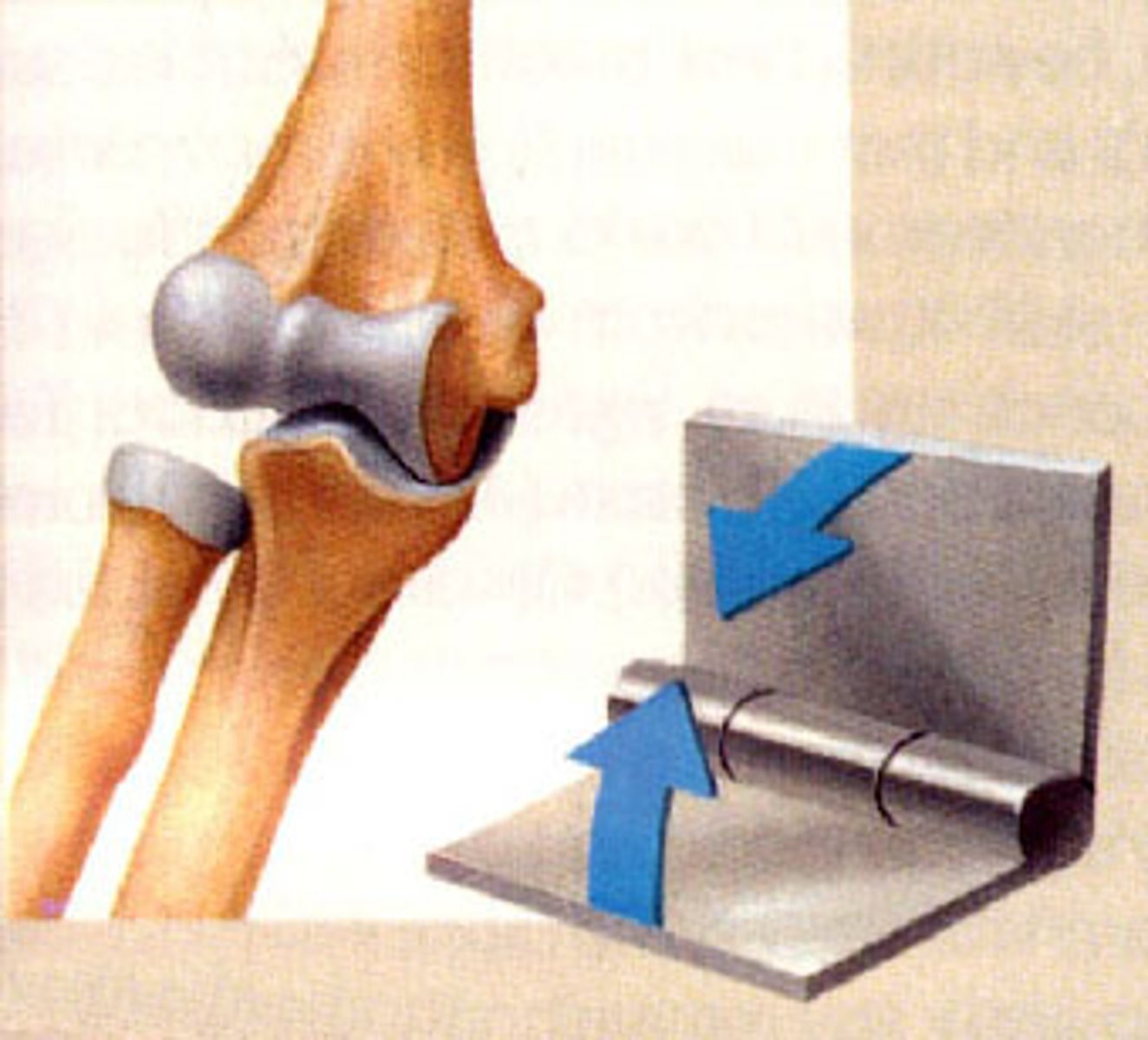
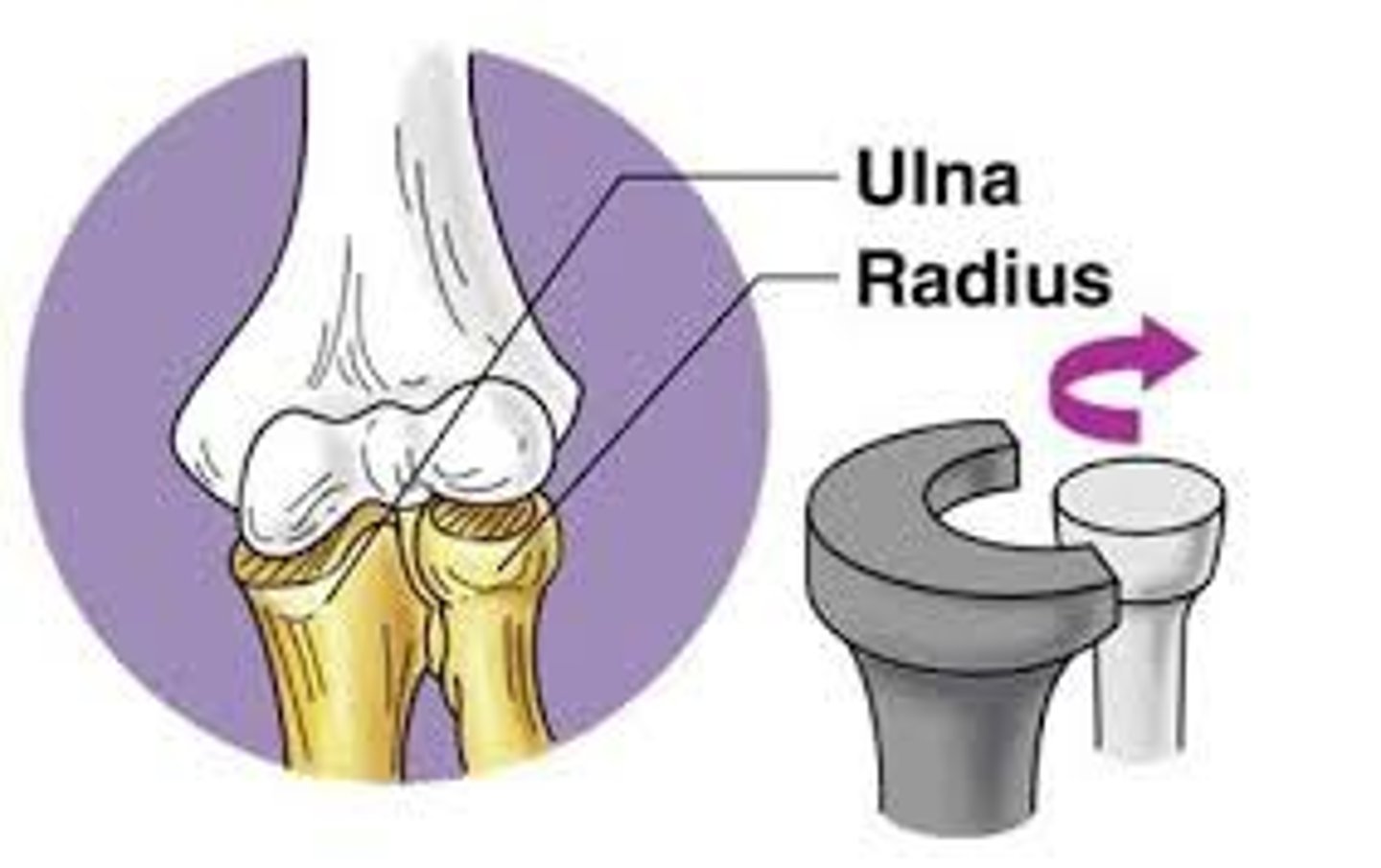
pivot
joint that allows a bone to rotate around an axis; i.e. connection between radius and ulna
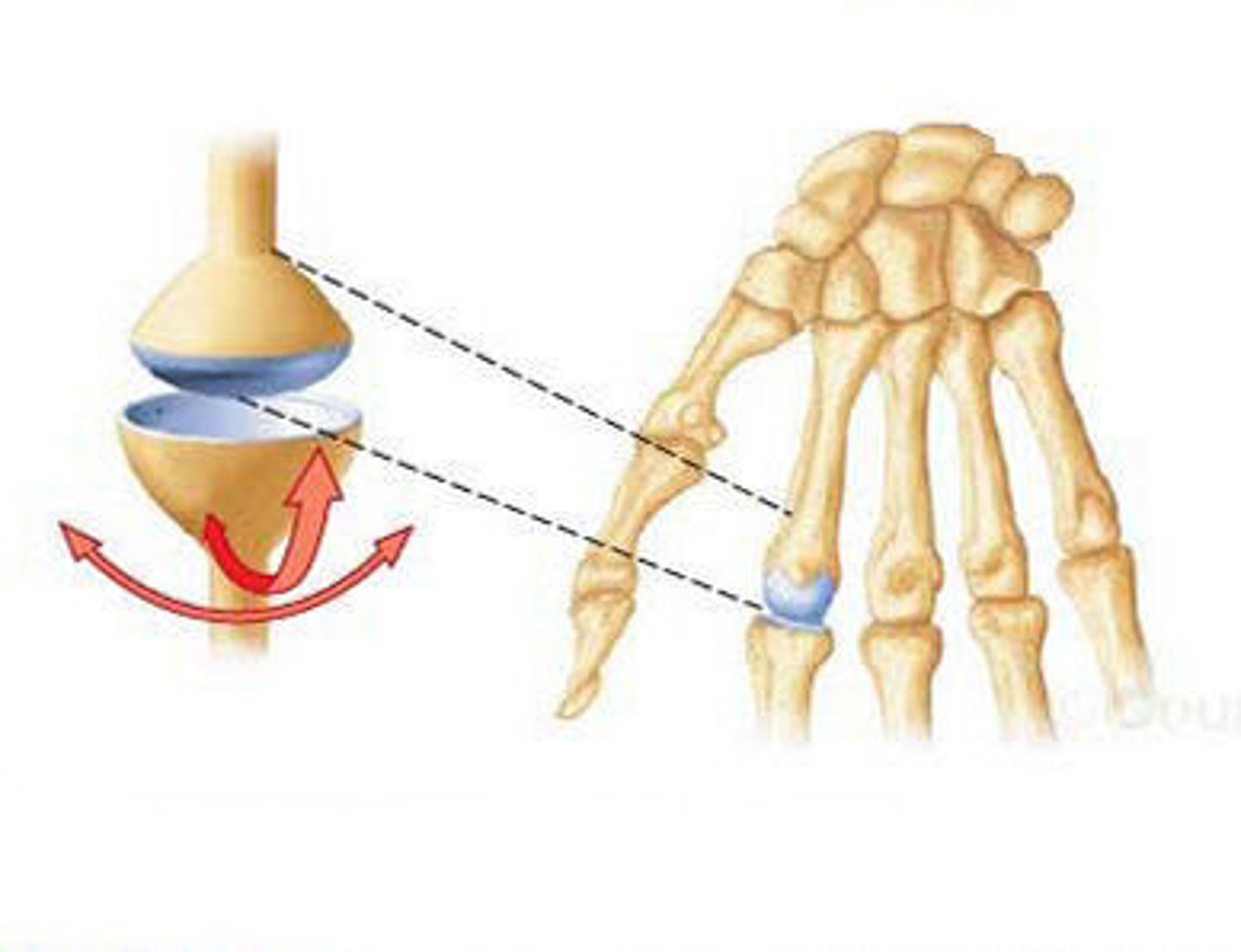
condyloid
synovial joint containing a bone with an oval-shaped projection that fits into hollow oval cavity; allows for all movement except rotation
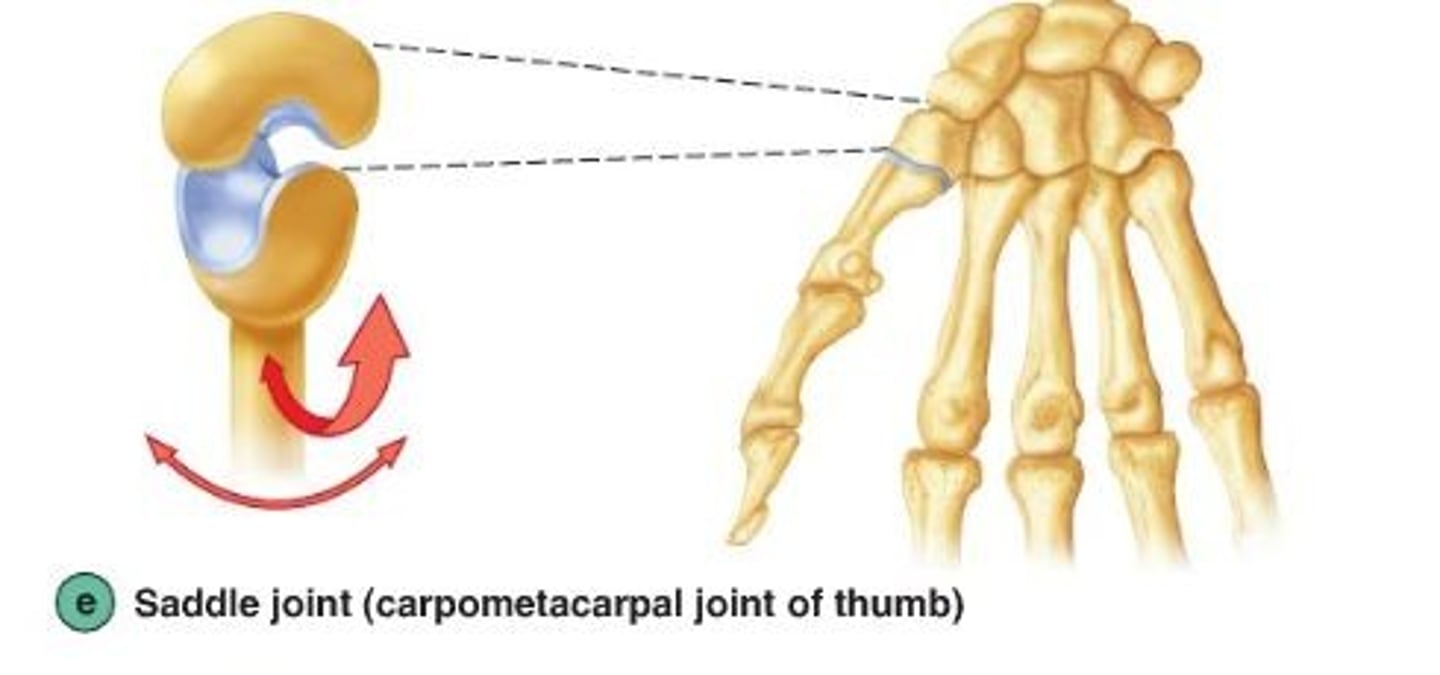
saddle
type of synovial joint found at the base of each thumb; allows grasping and rotation
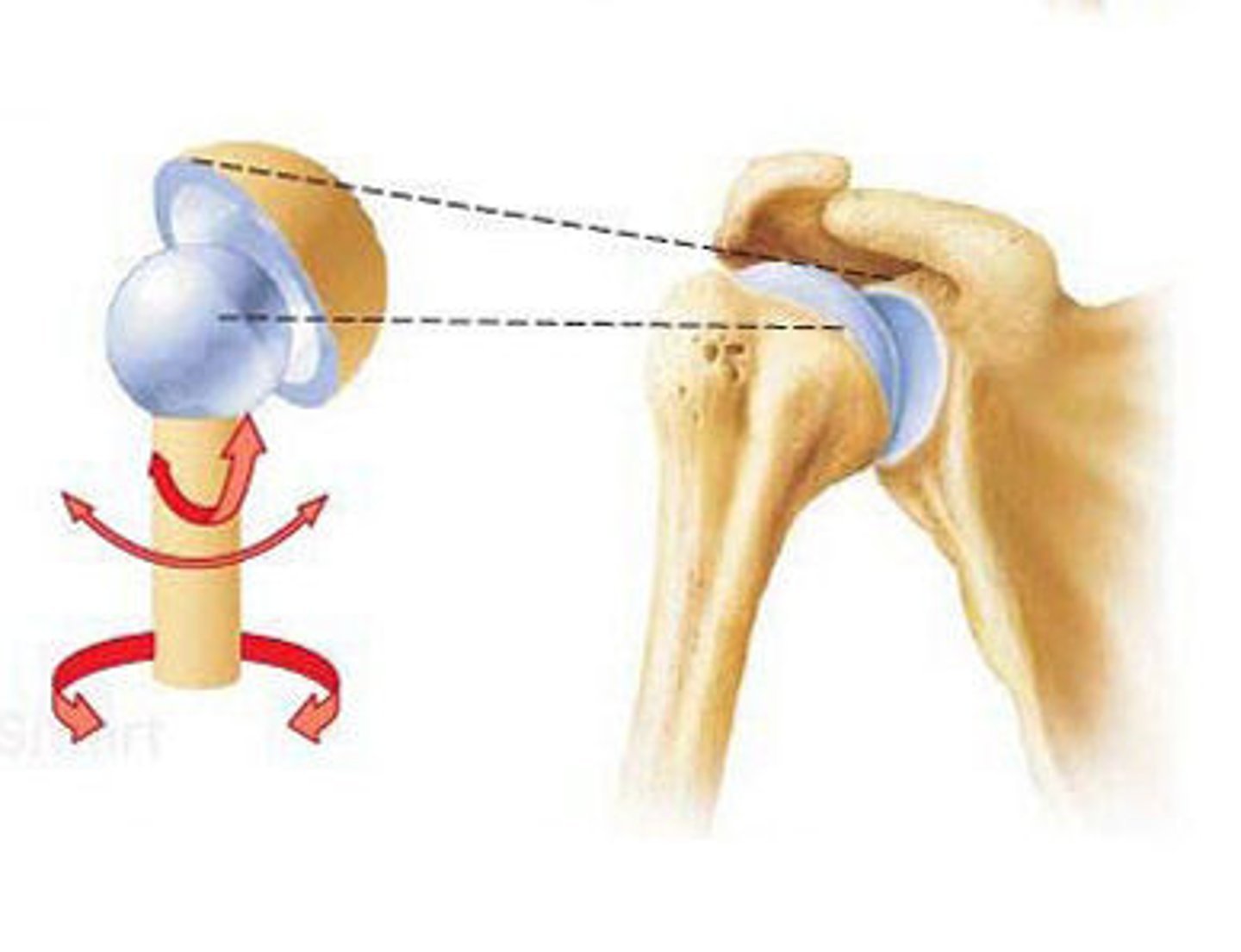
ball and socket
synovial joint containing a bone with a spherical head that fits into a round socket in another bone; i.e. shoulder & hip
4-6 seconds
initial available stores of FREE ATP are depleted in ___________
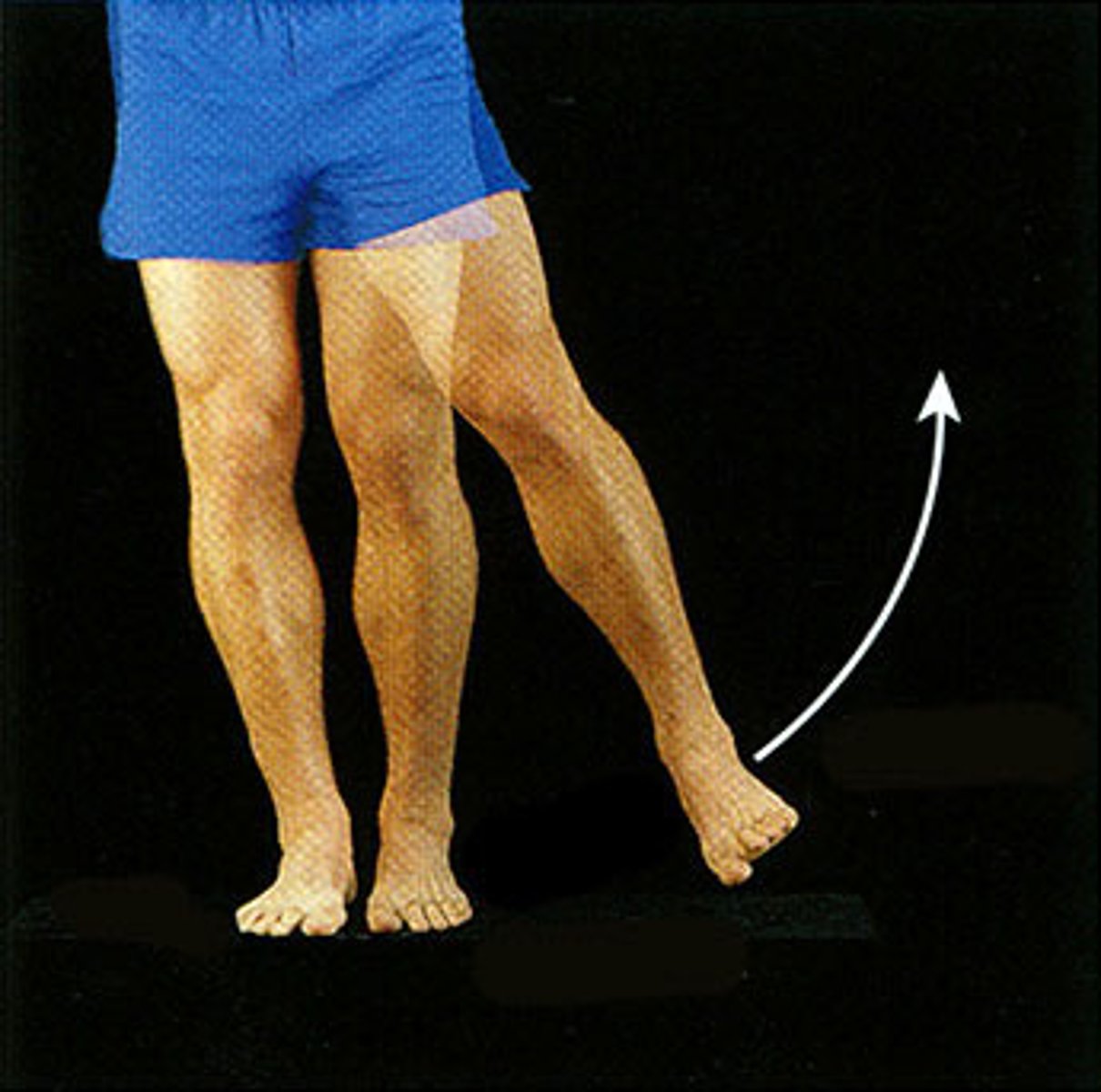
abduction
the motion of moving your arms/legs/fingers AWAY from one's body
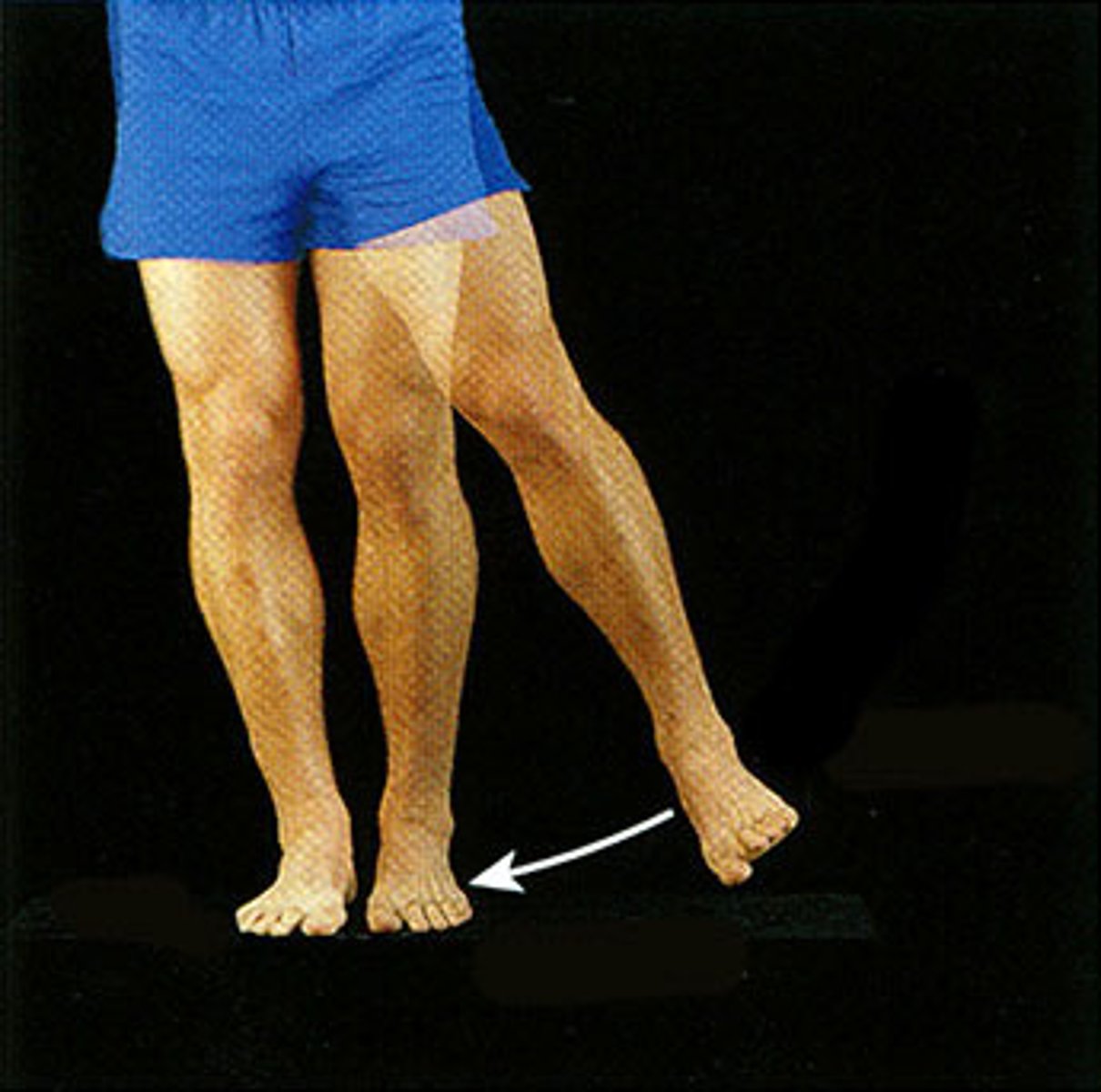
adduction
the motion of moving your arms/legs/fingers TOWARDS the midline of one's body
aerobic
Respiration that requires oxygen - as long as oxygen & food are present, this reaction produces unlimited amounts of ATP

anaerobic
energy production that does not require oxygen - also known as fermentation - produces considerably less ATP than aerobic respiration - produces lactic acid as a byproduct

antagonist
muscle within a group of muscles that opposes the primary movement; ie. When bending the elbow, the triceps brachii opposes the biceps' movement by doing the opposite of bending; straightening.

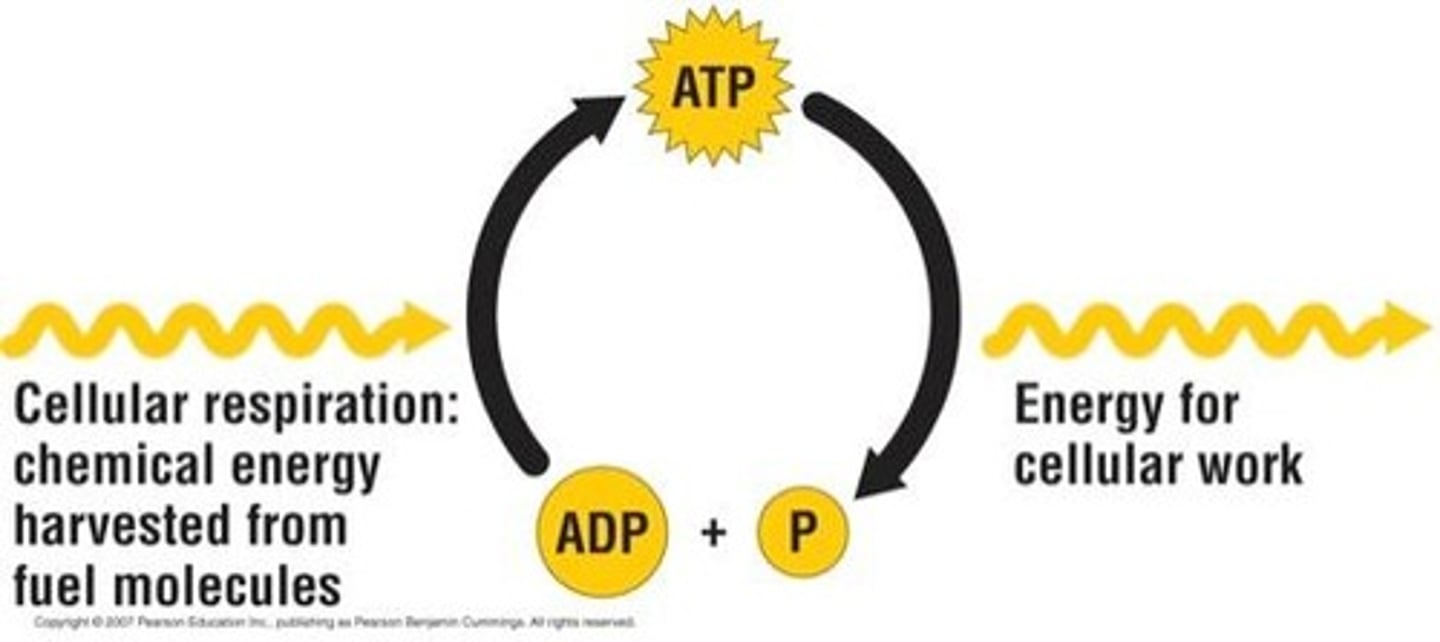
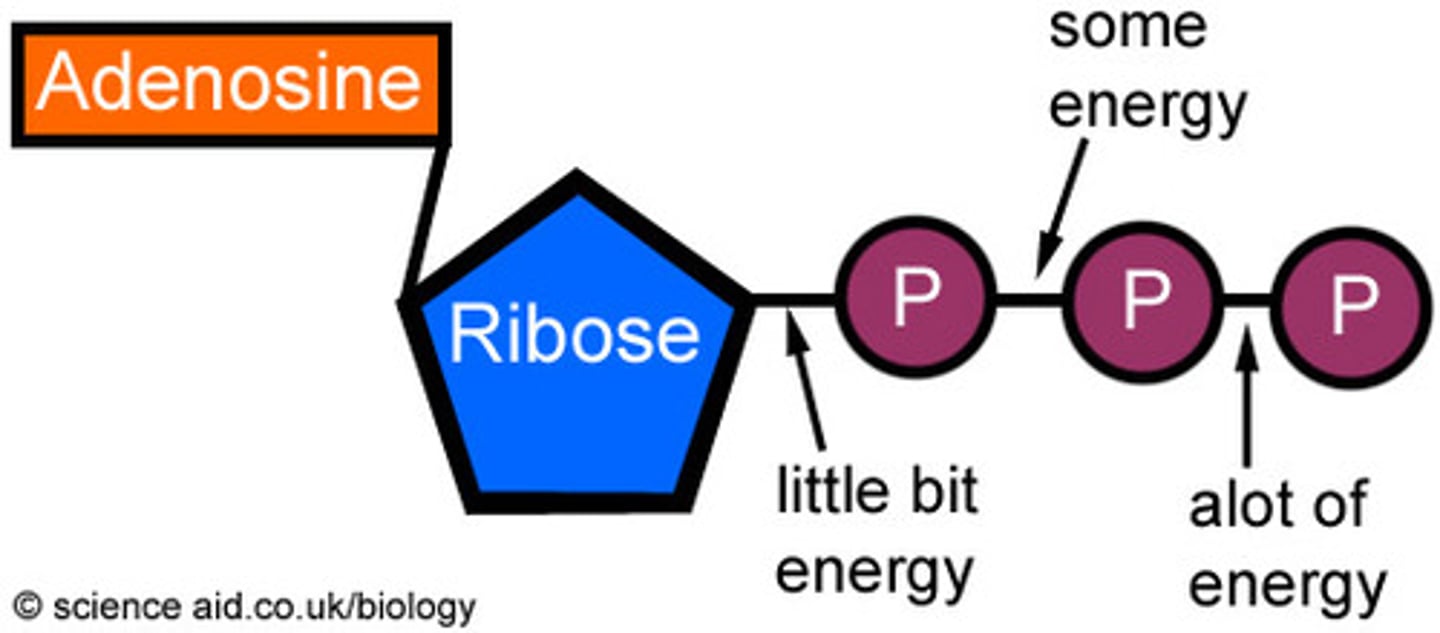
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work; food is converted into this energy so our bodies can use it as fuel
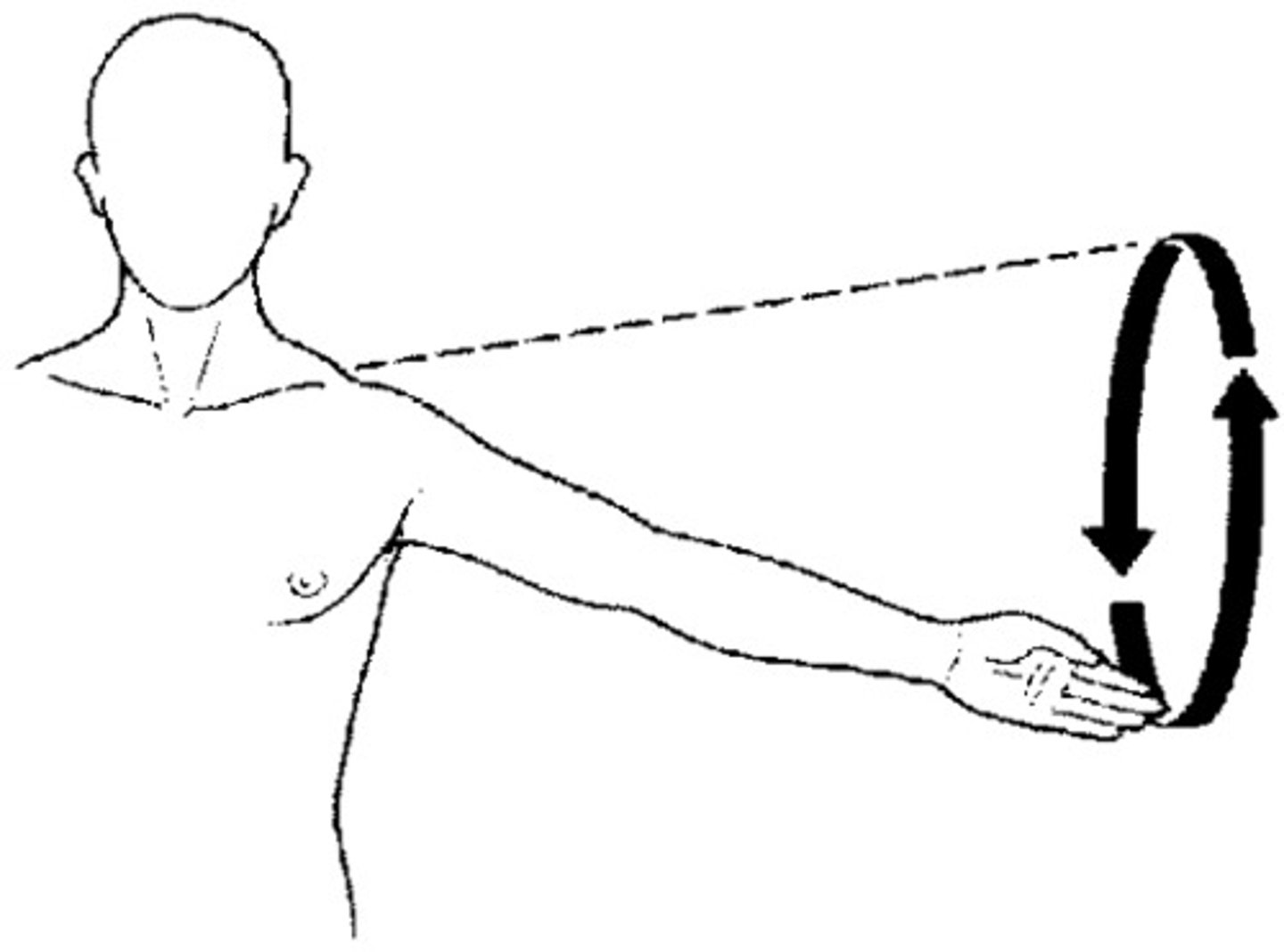
circumduction
the circular movement at the distal end of a limb
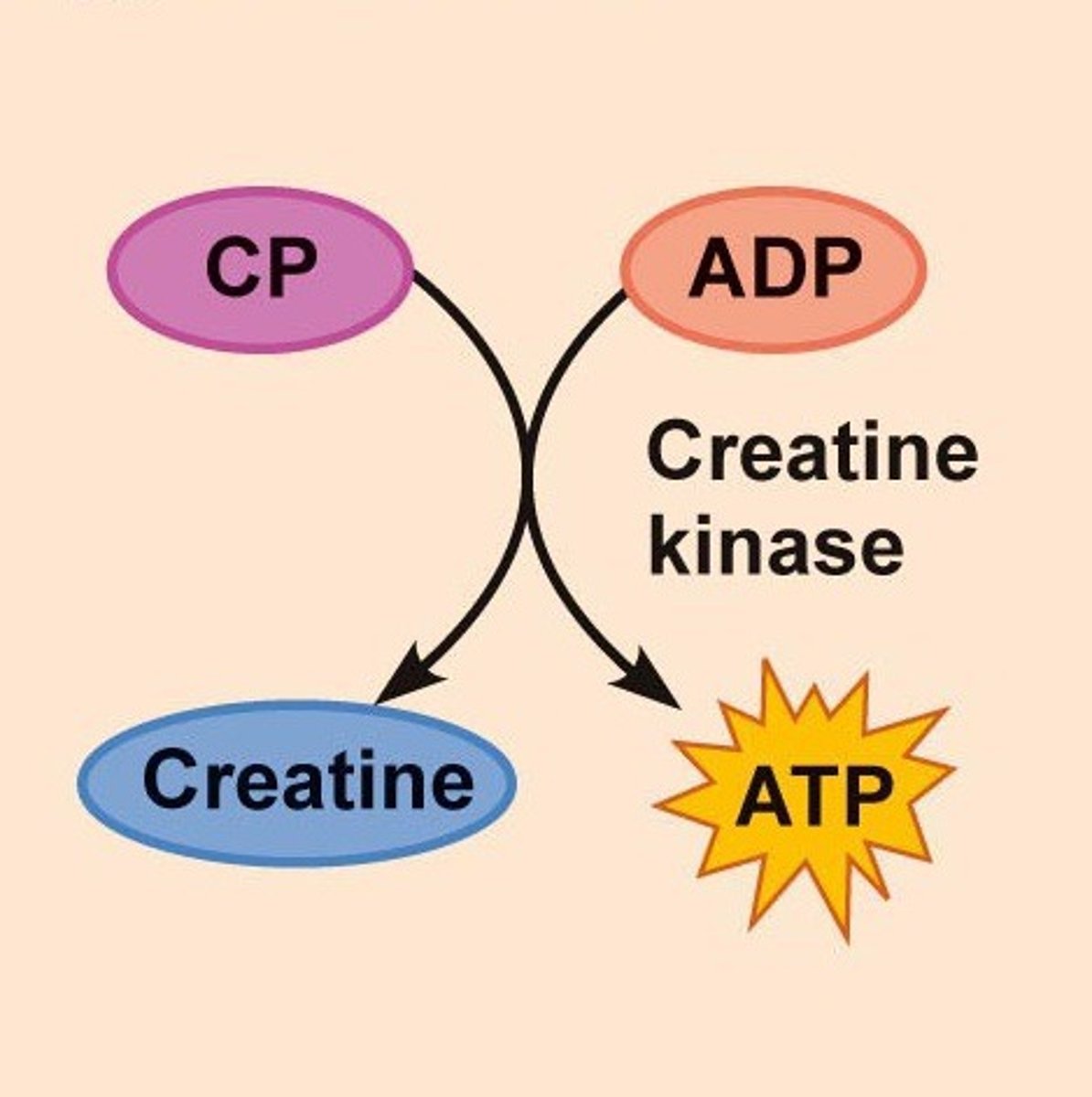
Creatine phosphate
a naturally occurring chemical in the body that functions by storing energy that will be transferred to ADP to re-synthesize ATP as needed. You have about 20 seconds worth of this stored molecule.
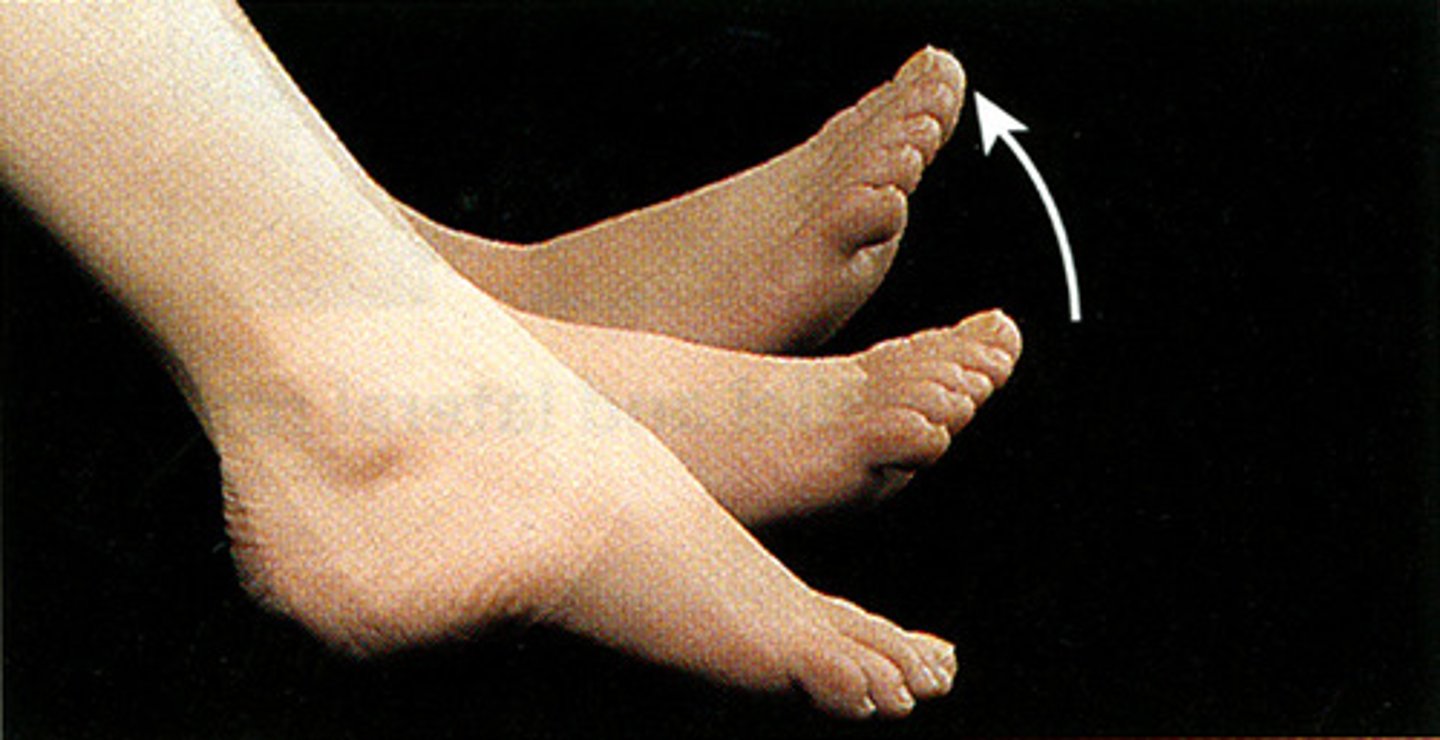
dorsiflexion
bending of the foot or the toes upward
eversion
foot turned outward so you can see the outside/ side of ankle- causes a knock-kneed walking stance
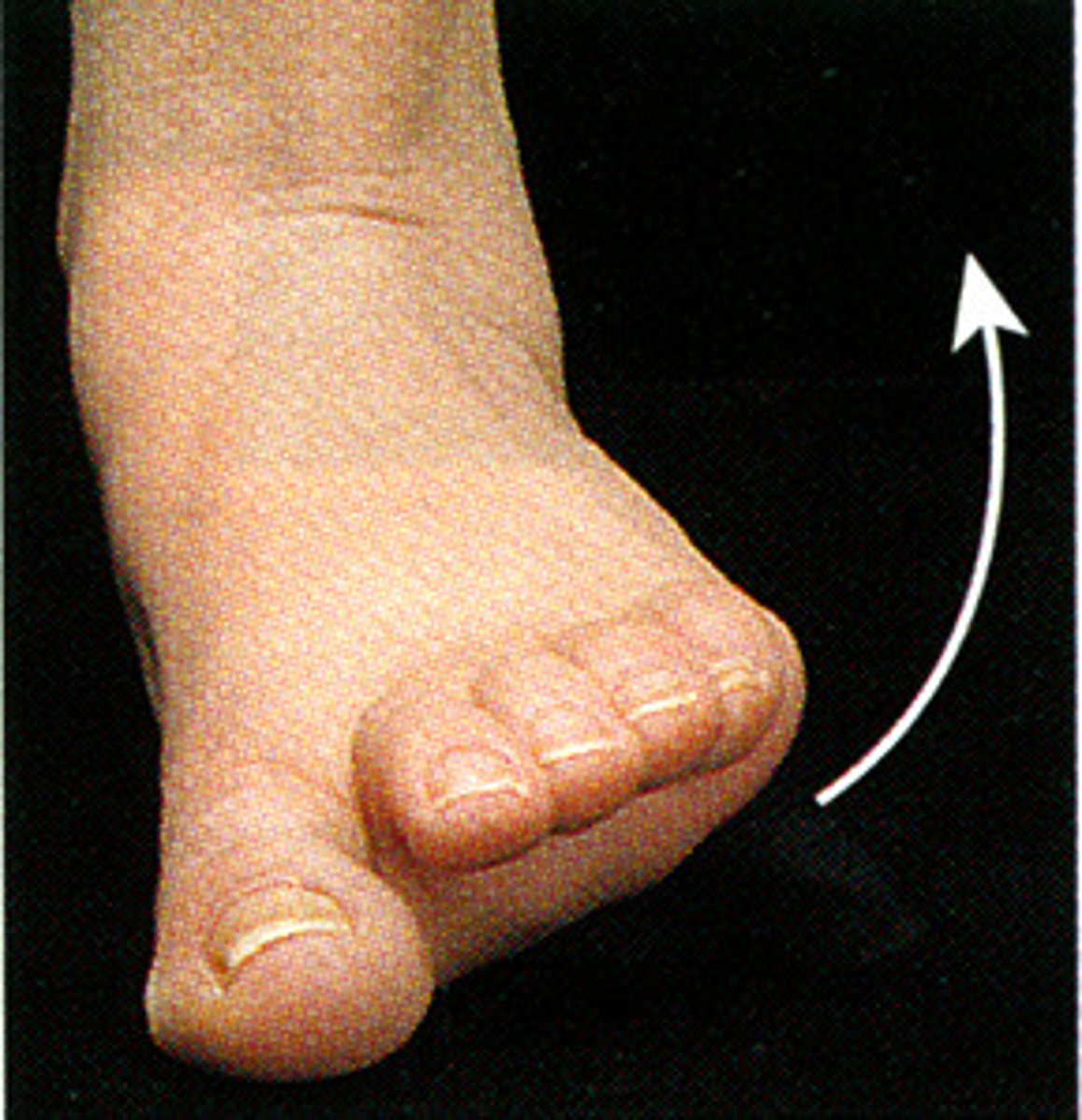
extension
straightening at the joint so that the angle between the bones is increased
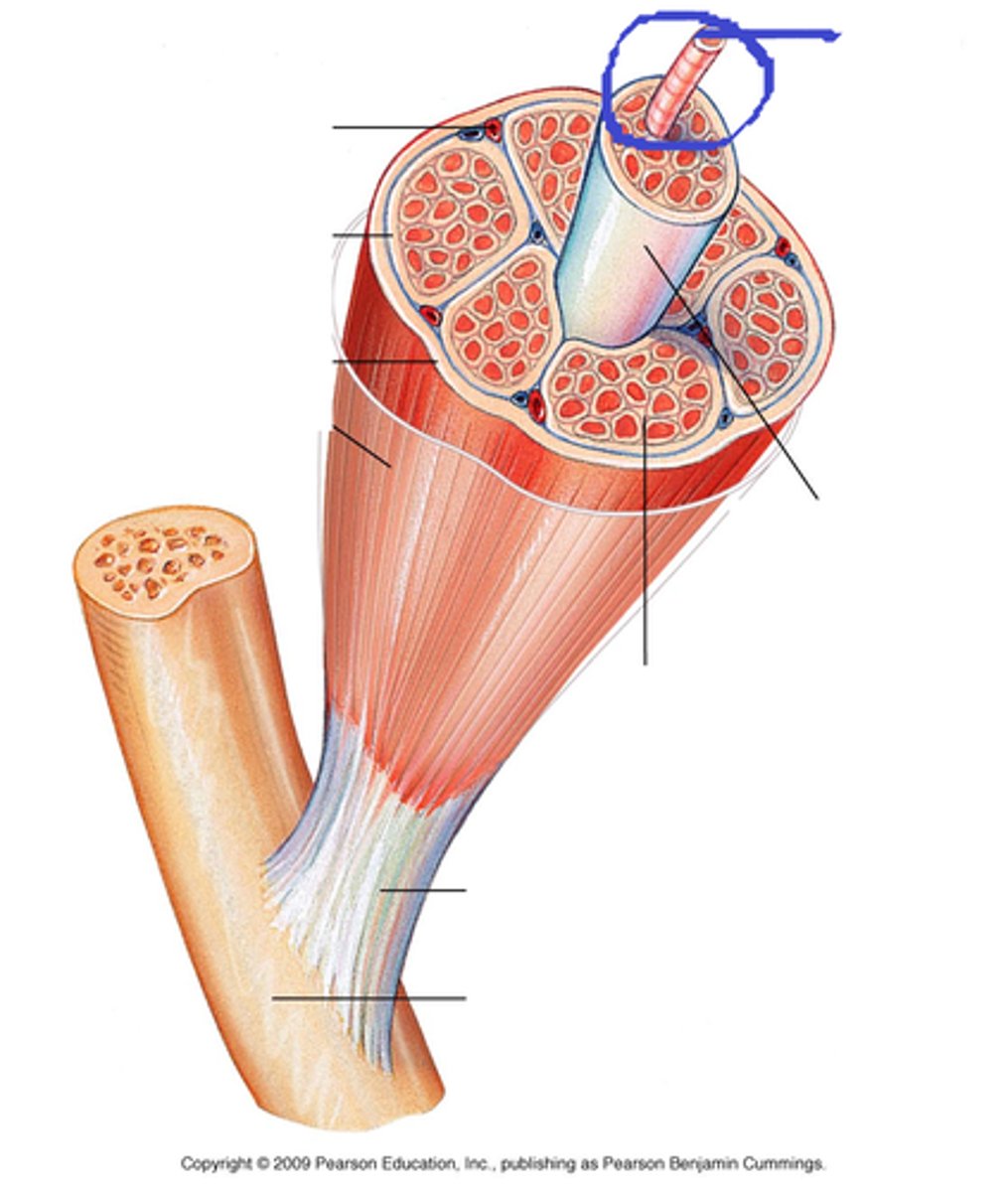
fiber
a muscle cell
fixator
muscle within a group of muscles that stabilizes, or braces the joint so the motion is steadied; ie. The deltoid muscle fixes the shoulder so the motion of flexing the arm at the elbow can be accomplished.
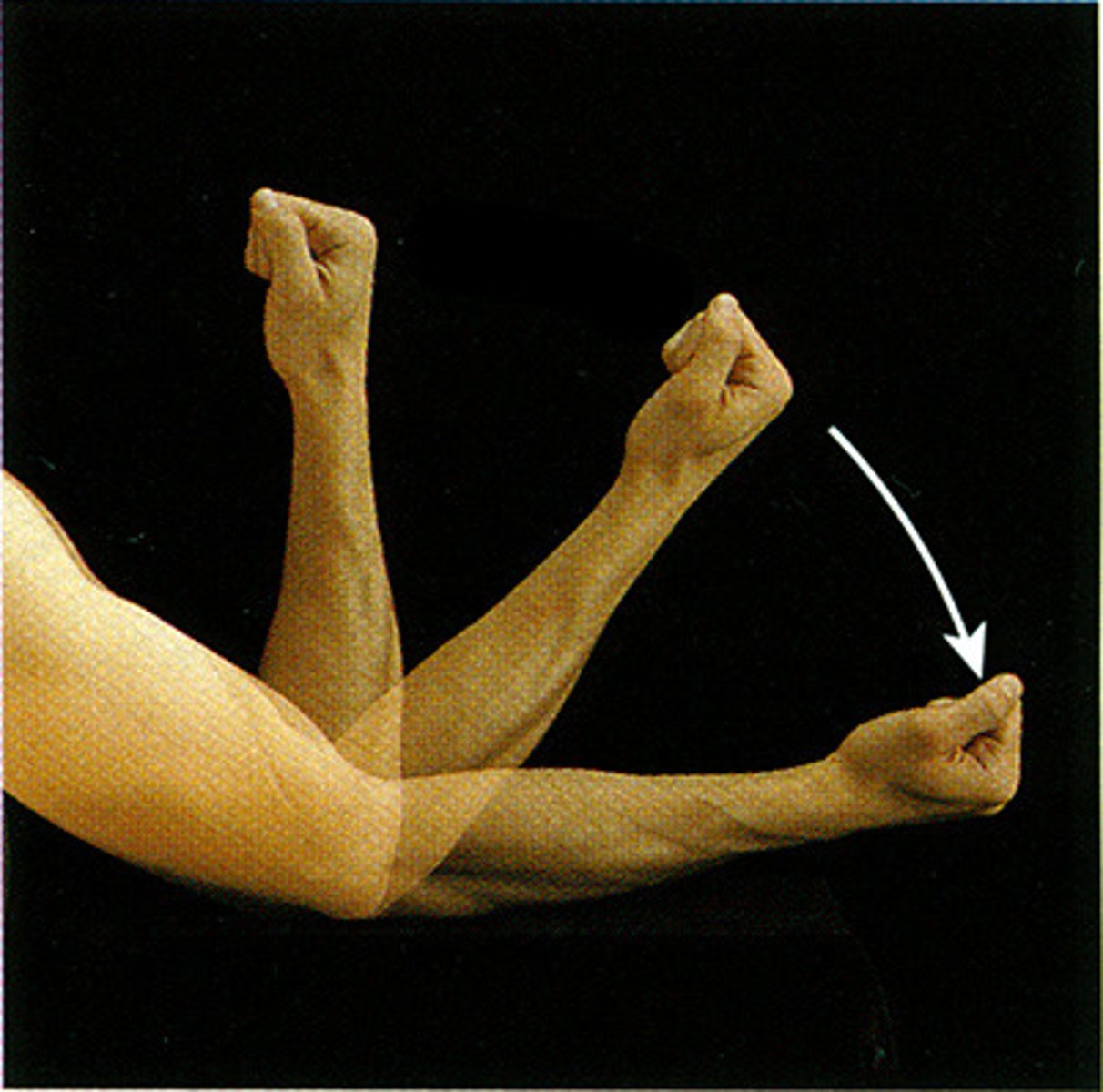
flexion
decreasing the angle between two bones by bending a limb at a joint
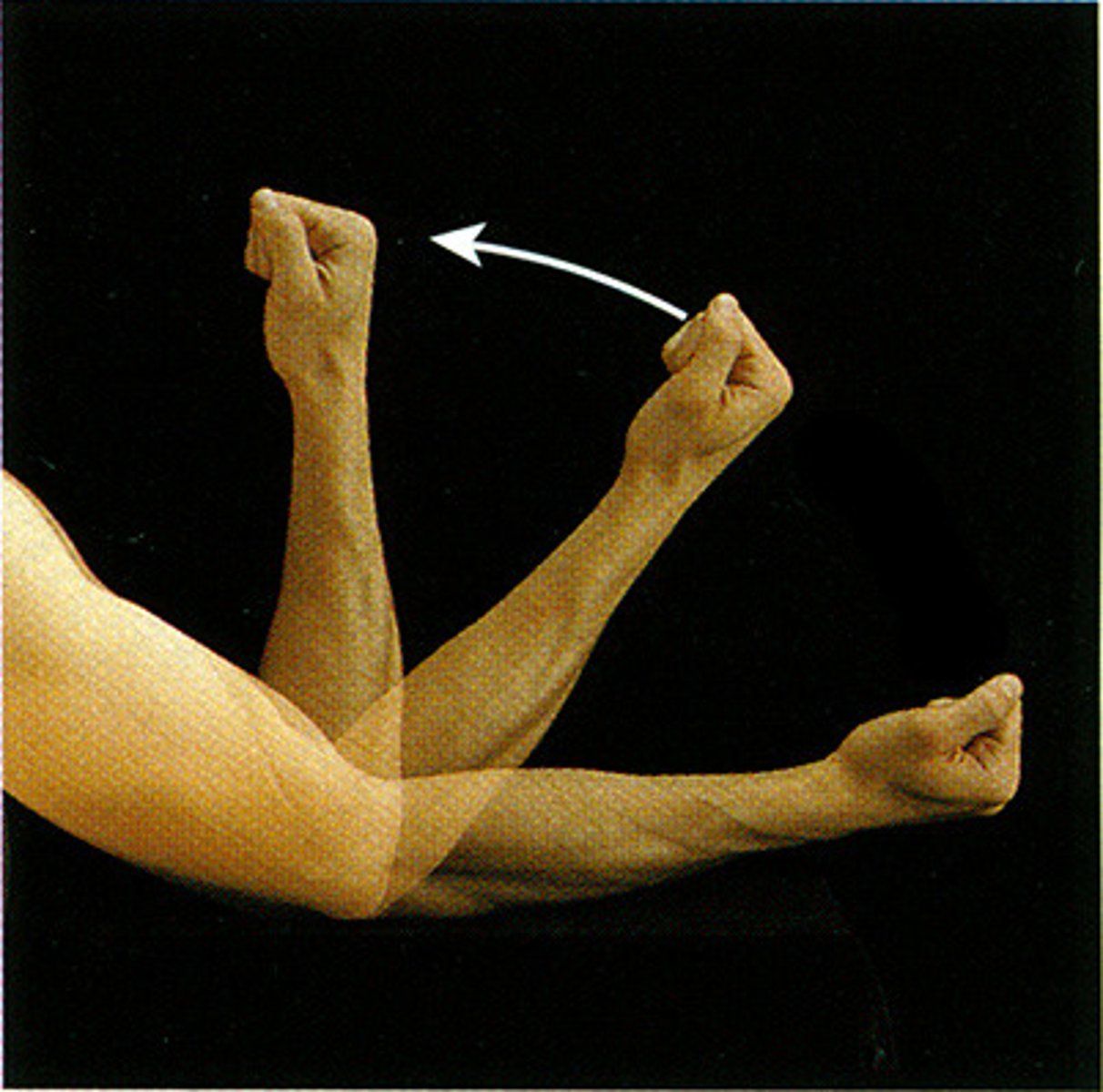
hyperextension
the extreme or overextension of a limb or body part beyond its normal limit
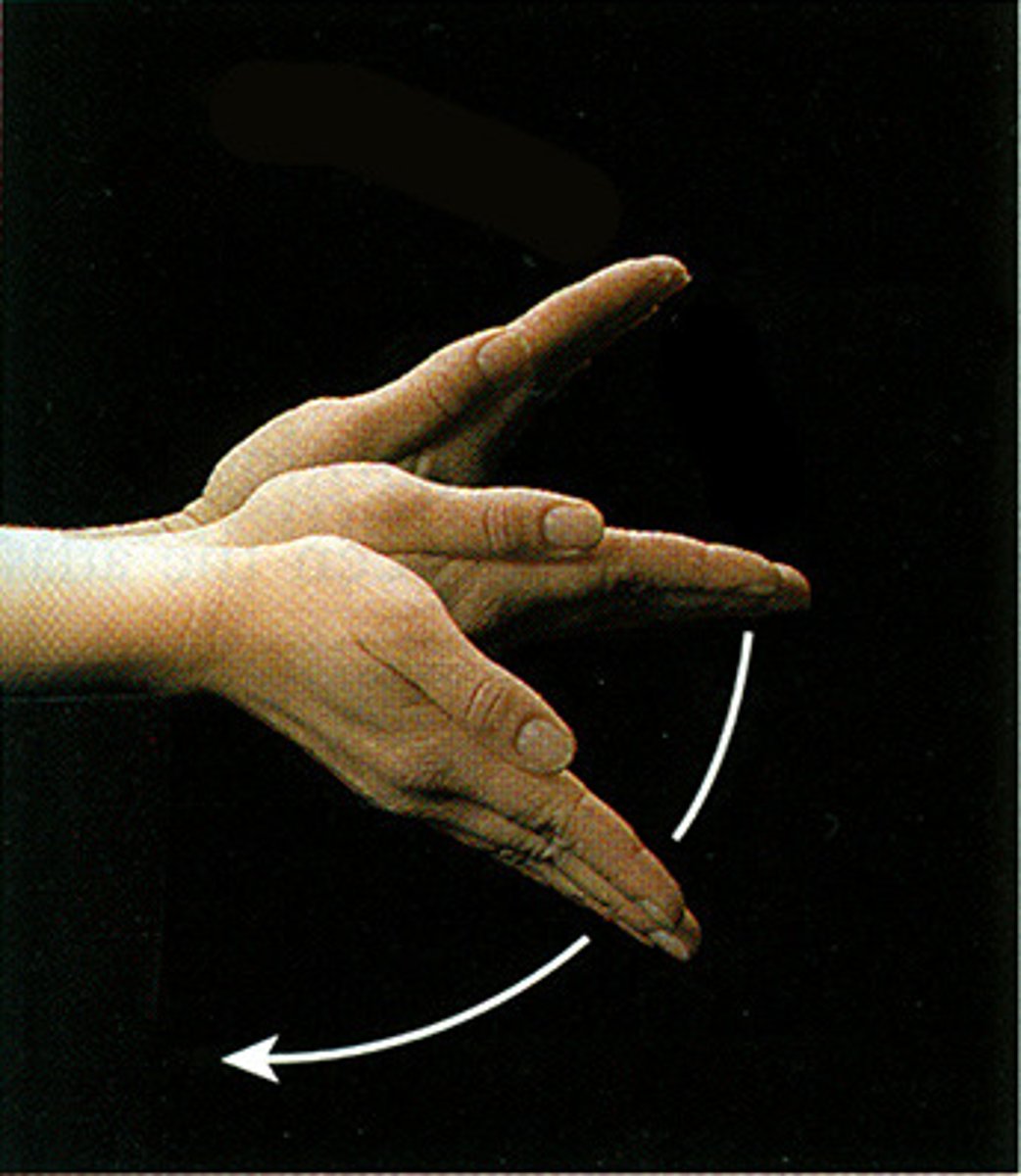
inversion
foot turned inward so you can see the inside / arch - causes a bowl-legged walking stance
lactic acid
product of fermentation - cause of soreness and muscle fatigue

opposition
Movement of the thumb to touch the fingertips
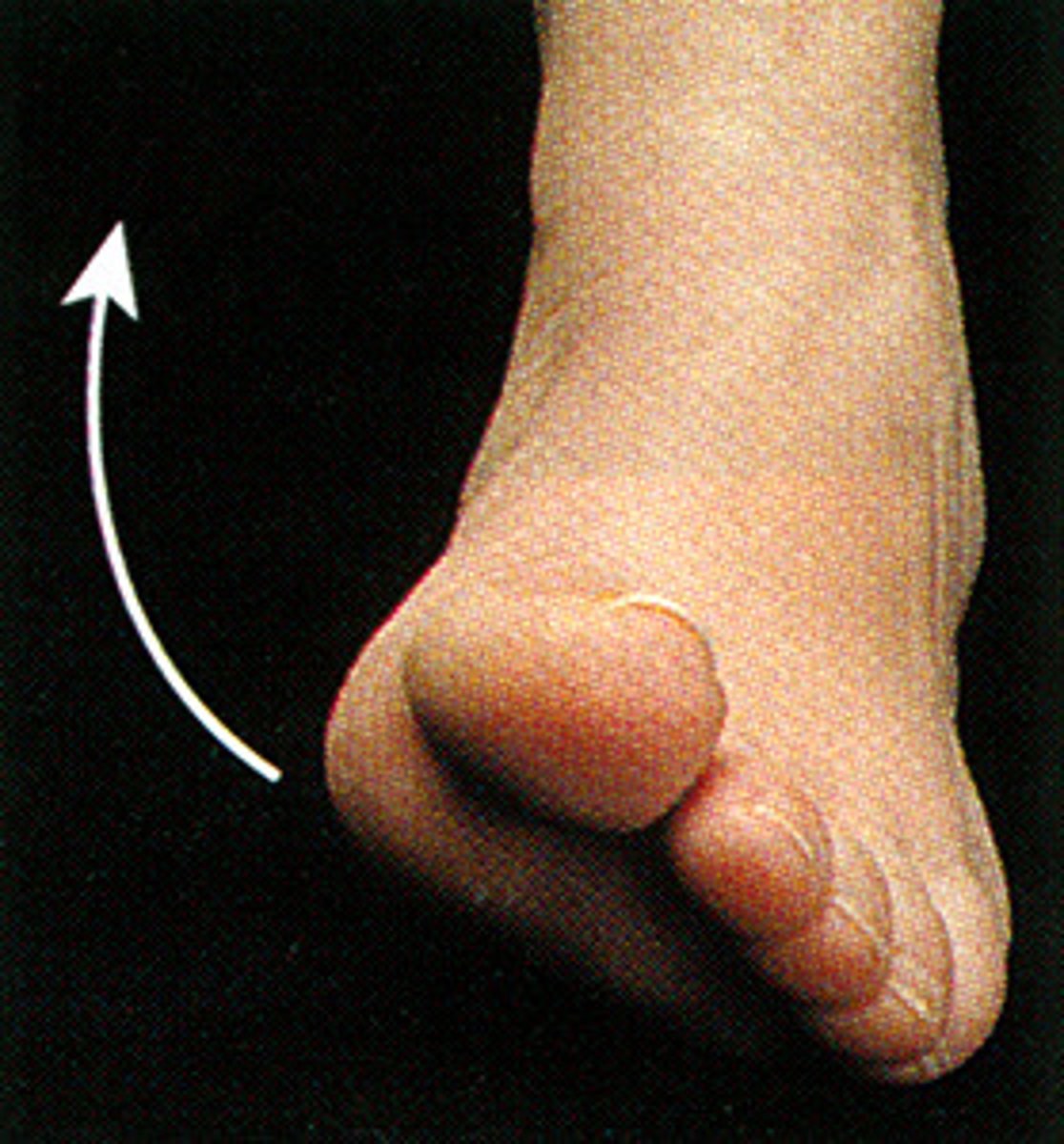
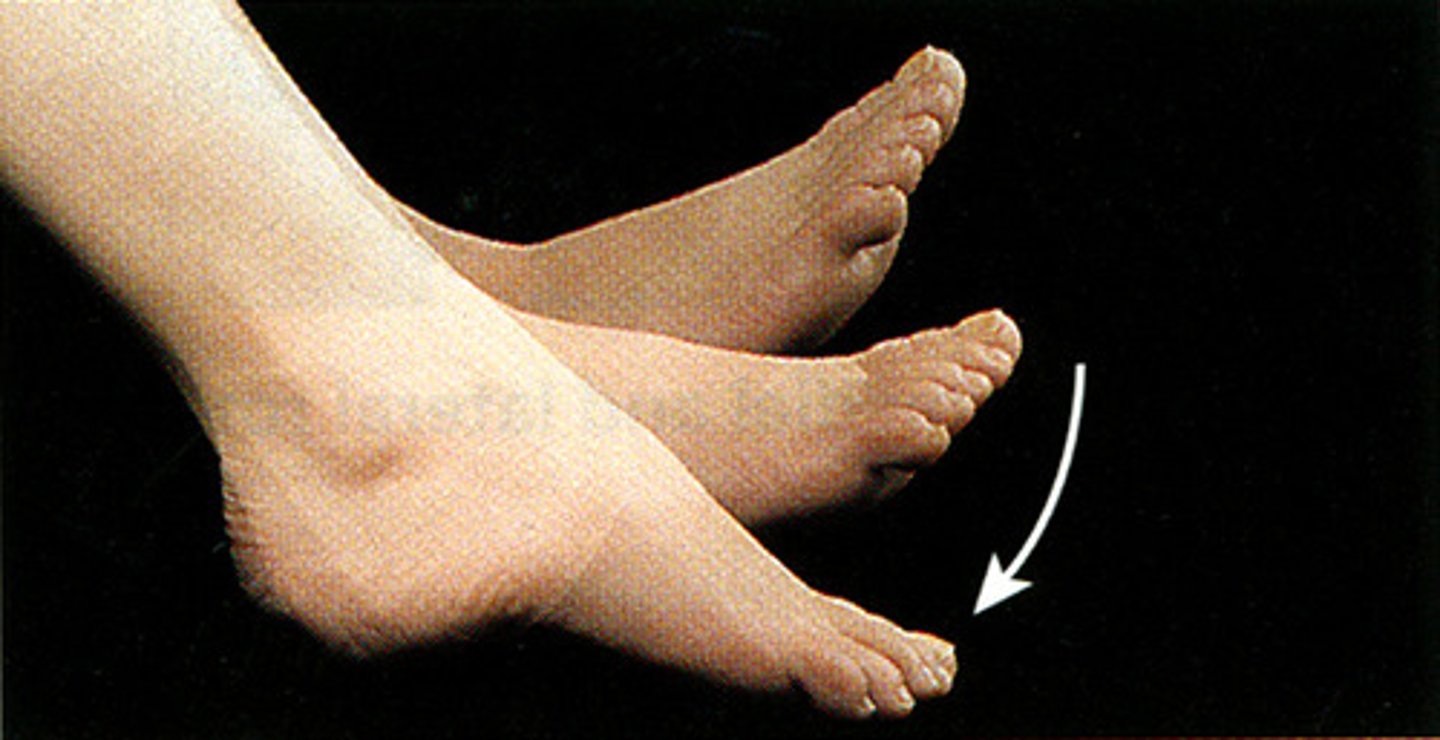
plantarflexion
to point the toes down
prime mover
muscle within a group of muscles that accomplishes the primary movement; ie. When bending the elbow, the biceps brachii accomplishes most of the arm's movement.
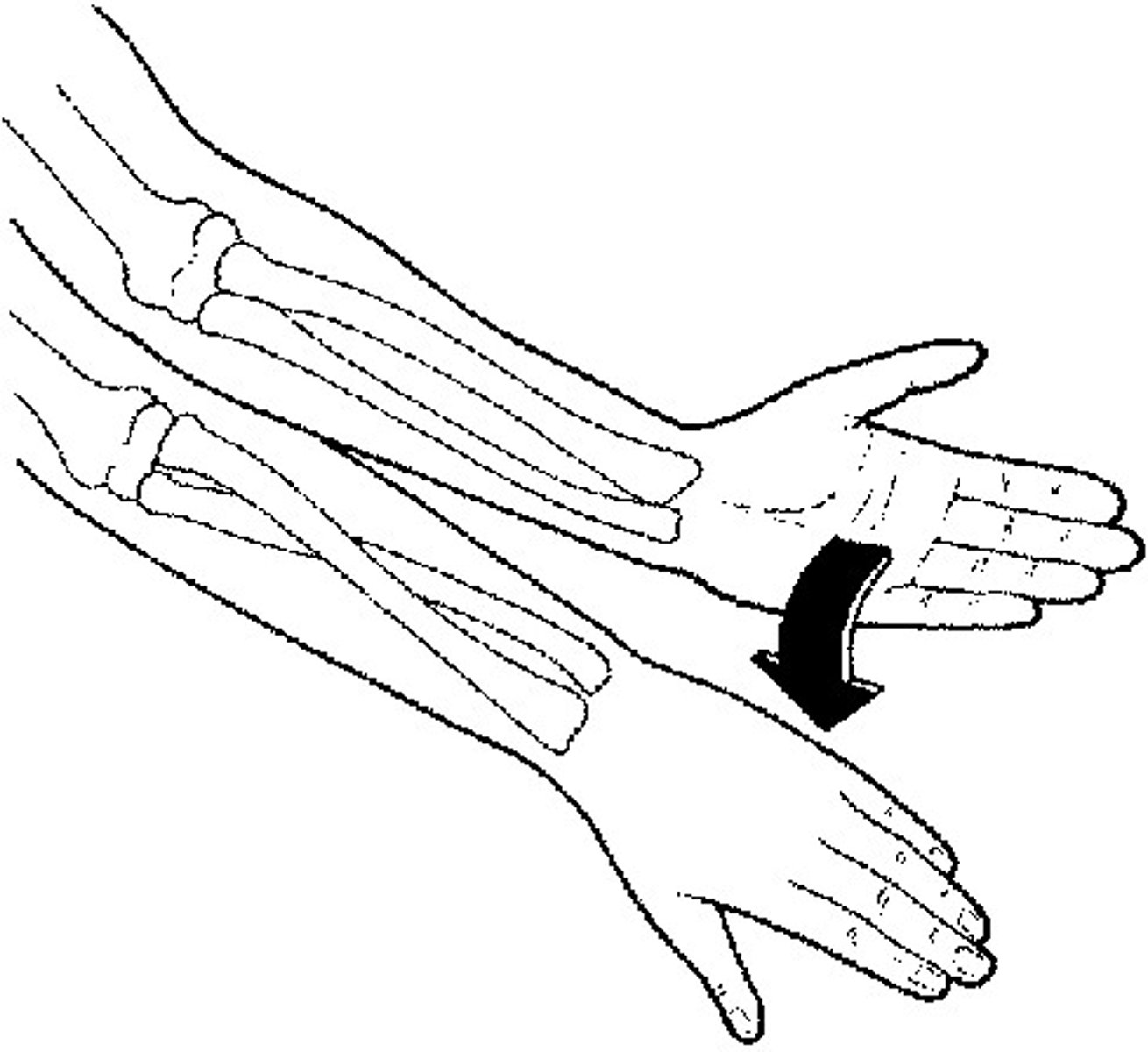
pronation
movement that turns the palm down
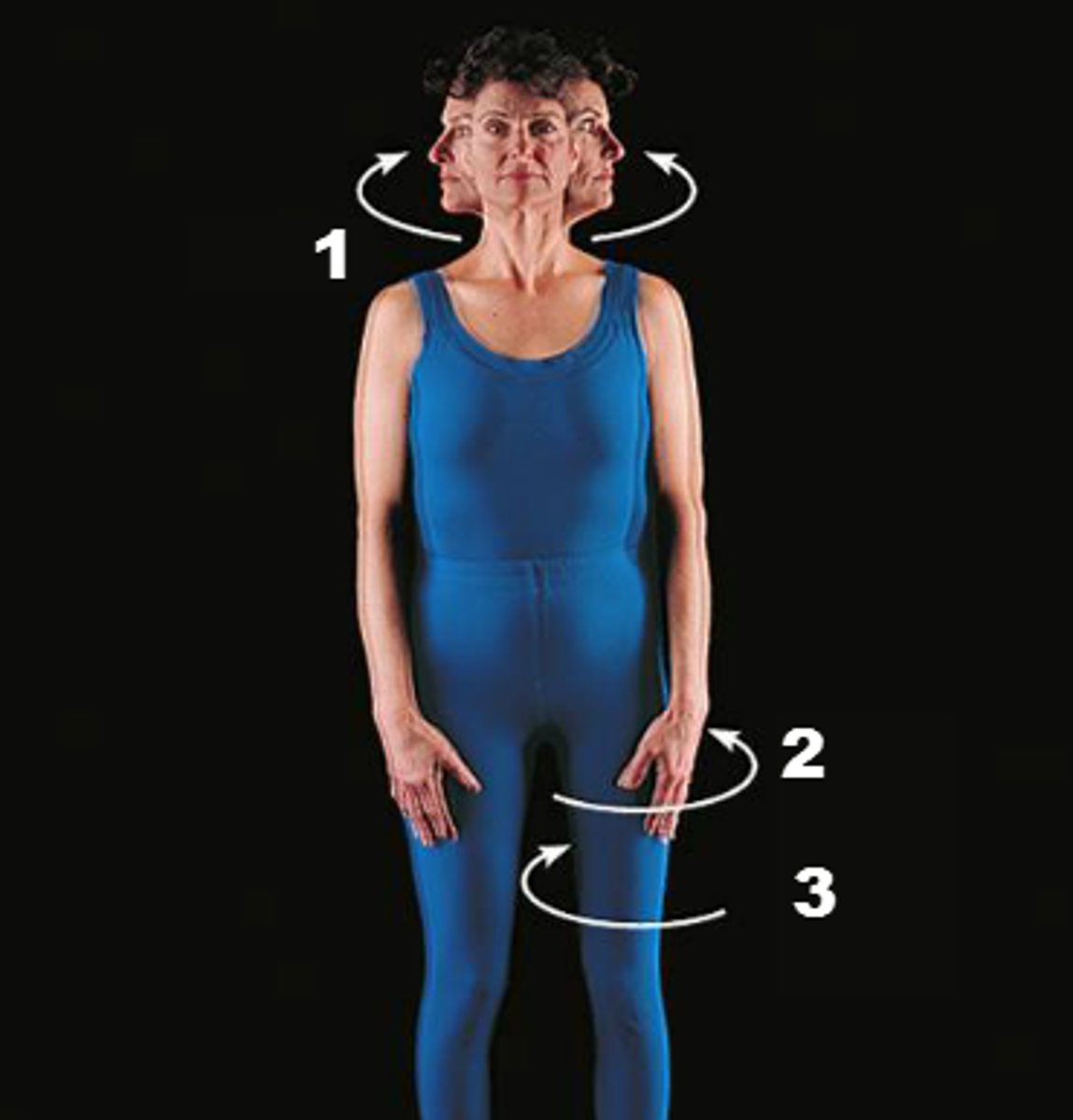
rotation
circular movement around an axis
supination
movement that turns the palm up
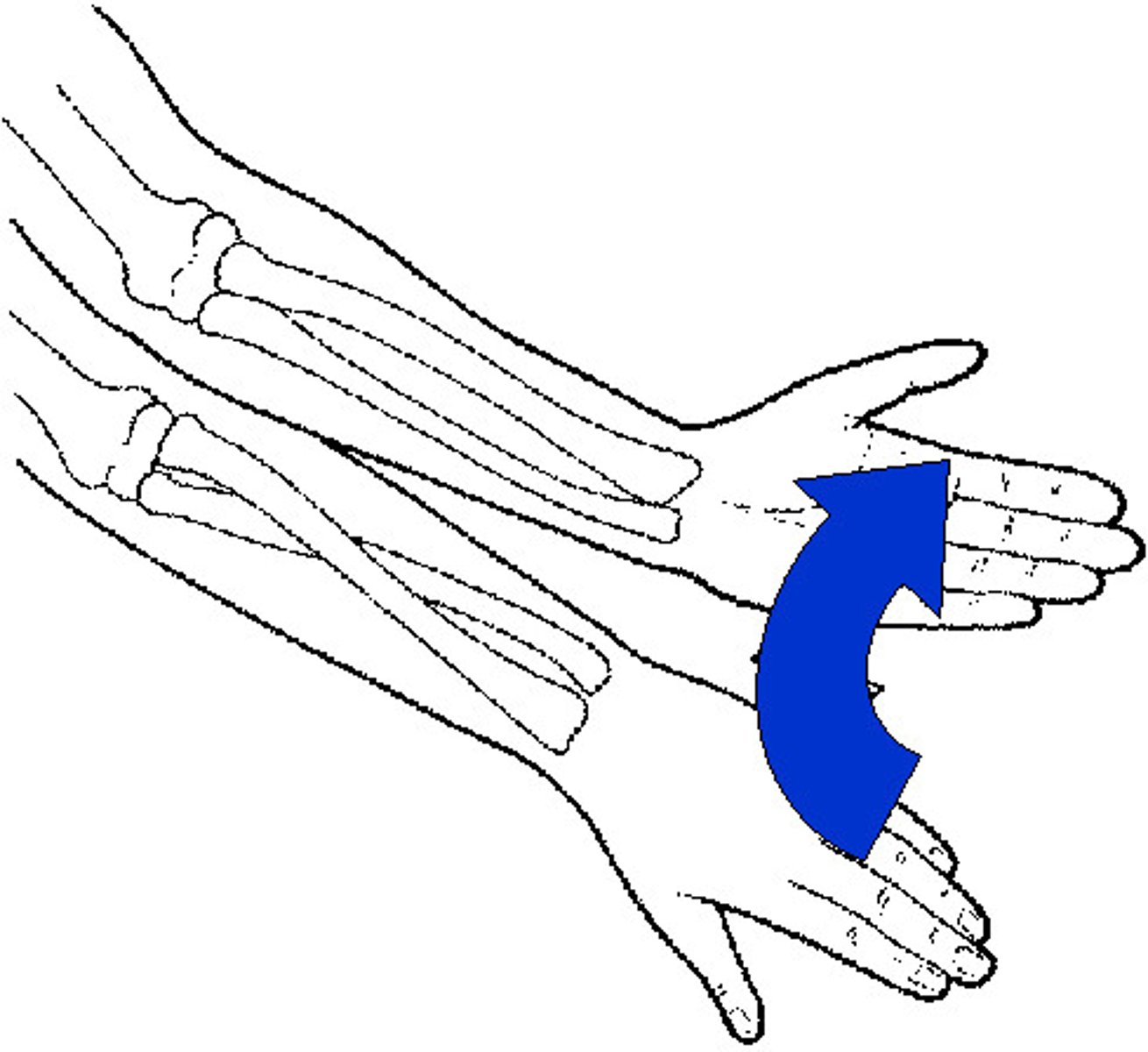
synergist
a muscle that works with and assists the action of a prime mover; ie. The brachialis is the synergist of the biceps brachii.

skeletal physiology
functions of the skeletal system include: support, mineral storage; hematopoiesis; protection; some movement due to muscle attachment sites
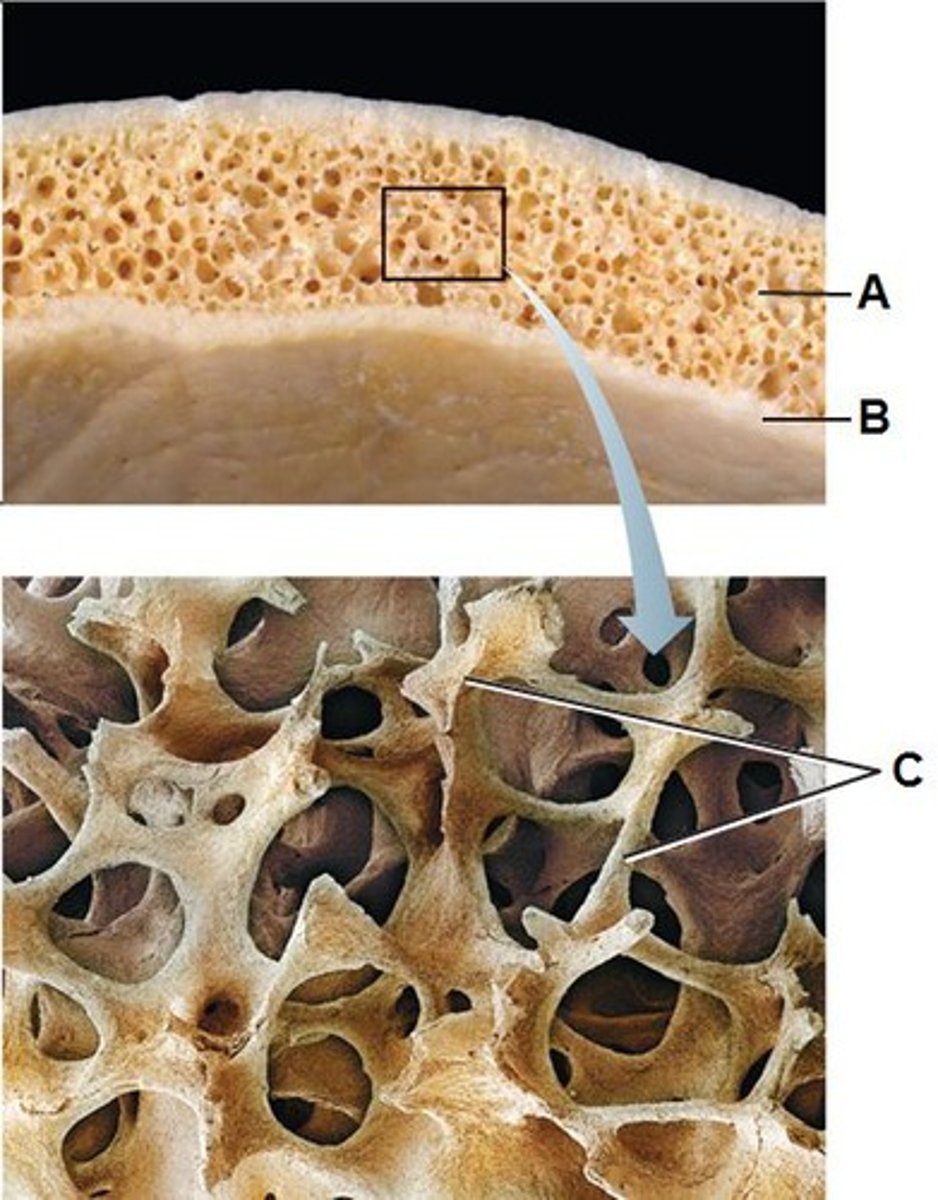
compact bone
hard, dense osseous tissue that looks smooth & homogeneous
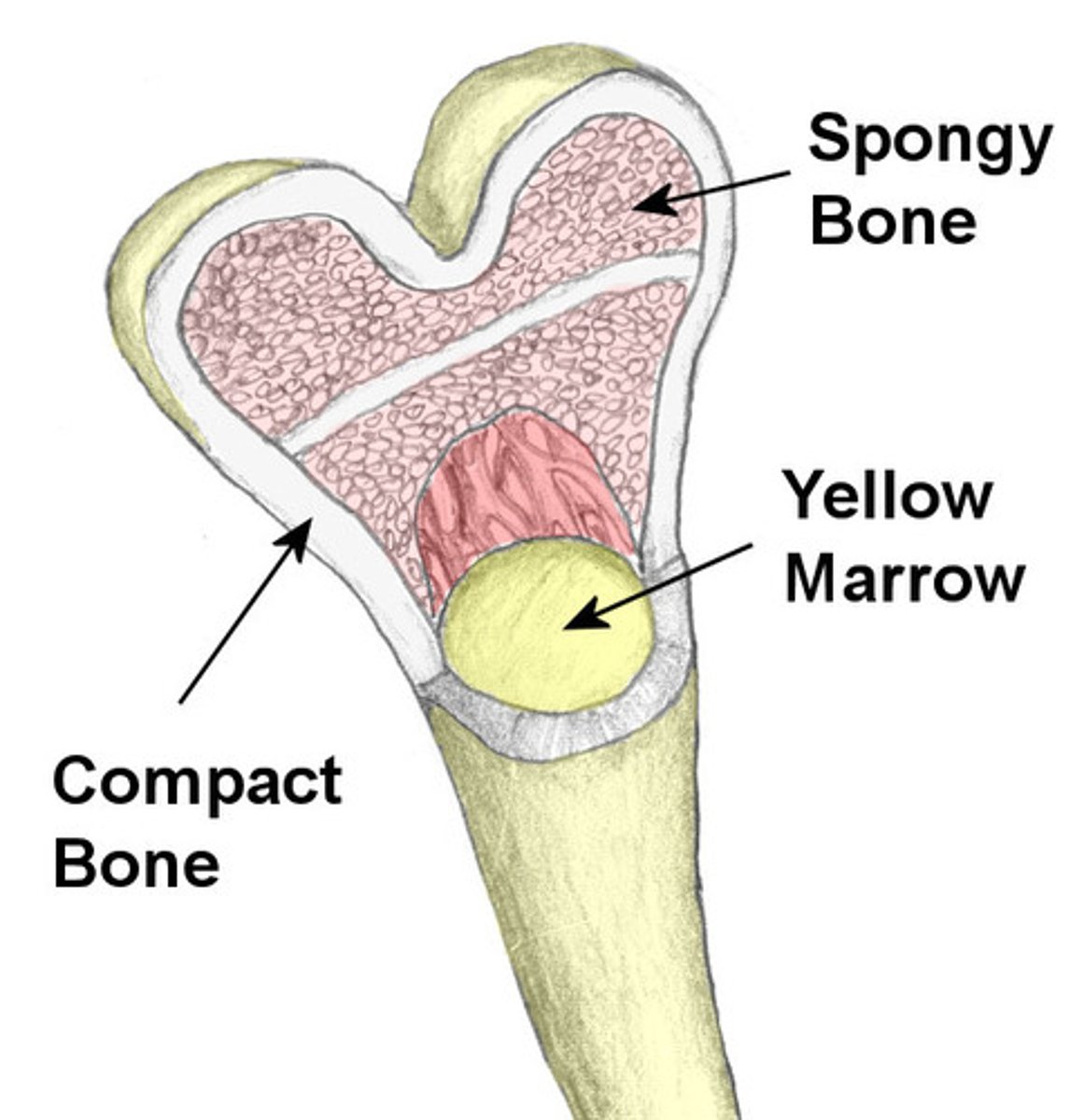
spongy bone
less dense osseous tissue composed of small needlelike pieces of bone and lots of open space